Aging and scaling of aftershocks
|
|
|
- Collin Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aging and scaling of aftershocks Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University, Chiba , Japan A part of the seismic time series, in hich the Omori la for temporal pattern of aftershocks holds, is refereed to as the Omori regime. Here the properties of correlation beteen earthquake events both inside and outside of the Omori regime are studied by analysis of the data taken in southern California. It is found that inside of the Omori regime correlation exhibits the aging phenomenon, in marked contrast to the fact that no aging is observed outside of the Omori regime. The scaling nature of aging is also discussed and the form of the function responsible for it is presented. The results indicate that complex fault-fault interactions may be governed by glassy dynamics. PACS number(s): f, Da, b 1
2 A large shallo earthquake tends to reorganize the stress distribution in the relevant area that leads to the sarm of aftershocks. A complex energy landscape ith a number of local minima is created, the fault-fault interactions may be long-range and random, and shortness of the event time intervals implies the quenched disorder. The (modified form of) Omori la [1,2] states that the number of aftershocks, dn(), t occurring beteen the short time interval t ~ t + dt, here t stands for time elapsed after the mainshock, obeys dn() t 1 ~, (1) dt ( c+ t ) p here c is a positive constant and the exponent, p, empirically ranges from about 0.8 to 1.5. The Omori regime, in hich this la holds, plays a distinguished role in the seismic time series because of the slo poer-la decay of the rate of frequency, dn()/ t dt, and nonstationarity. In this Letter, e report the discovery of the aging phenomenon and the scaling la for aftershocks. By contrast, no aging is observed outside the Omori regime. These results and observations indicate that the complex fault-fault interactions for aftershocks may be governed by glassy dynamics [3,4]. Our idea is as follos. We propose to employ as the basic physical random variable the time of the nth aftershock ith arbitrary magnitude, t n, folloing the mainshock at t 0. Then, e define the correlation function for the aftershock events as 2
3 Cn ( + n, n) = < tn+ n tn > < tn n t + >< n >, (2) 2 2 σ σ n+ n n here the averages and the variance are given by < t > = ( 1 / N) t +, N 1 < t t > = ( 1 / N) t t m m' k = 0 m+ k m' + k N 1 m m k k = 0, and σ 2 m =< t 2 m > < t 2 m >, respectively. It clearly satisfies the initial condition: Cn (, n)= 1. If the series { t m } is stationary, then the correlation function in Eq. (2) becomes independent of the aiting time, n, hereas nonstationarity is characterized by the n dependence of the correlation function. We have analyzed the seismic data provided by the Southern California Earthquake Data Center (available at Among extensive data analyses, e here present to typical examples. Their mainshocks are M7.3 at o o 11:57:34.1 on June 28, 1992 ( 'N latitude, 'W longitude, and 0.97 km o in depth) and M7.1 at 9:46:44.13 on October 16, 1999 ( 'N latitude, o 'W longitude, and 0.02 km in depth). According to the data beteen 1984 and 2002, the maximum depth is km. Therefore, these mainshocks are considered to be very shallo, having in fact been folloed by the sarms of aftershocks. For these mainshocks, e have identified the corresponding Omori regimes by examining the best fits of the (modified form of) Omori la in Eq. (1) to the data based on the method of least squares. (Hoever, it does not seem to be necessary to present such identifications here.) An important point is that e do not put restrictions on the area for the aftershocks but consider hole of the relevant area, according to the nonreductionistic philosophy for complexity of the earthquake phenomenon. Recently, e have studied 3
4 the statistical properties of the three-dimensional distance beteen to successive earthquakes [5] and the netork structure [6]. We have discovered that the distance distribution obeys Tsallis nonextensive statistics [7,8] and the earthquakes yields an evolving scale-free netork [9,10]. These results highlight the complex-system aspect of the earthquake phenomenon. In Figs. 1 and 2, e present the plots of the correlation functions ith respect to the event number, n, for various values of the aiting time, n, inside of the Omori regimes. The clear aging phenomenon is appreciated. On the other hand, the correlation functions outside of the Omori regime are plotted in Fig. 3. Almost no aging is observed there. This shos a distinguished nonstationary feature of the Omori regimes. A point of interest regarding aging depicted in Figs. 1 and 2 is that it is possible to realize the data collapses by simply rescaling n by a certain function, f ( n ). By this manipulation, Figs. 1 and 2 are transformed to Figs. 4 and 5, respectively. The value of the function, f ( n ), for each n is determined in such a ay that the discrepancies beteen the correlation functions measured by the l 1 norm distance becomes minimum. Also, f ( 0) = 1 should hold. The corresponding values of f ( n ) obtained by this procedure are shon as the dots in Fig. 6 and 7. It turns out that they are ell fitted by a to-parameter function γ f ( n )= an + 1, (3) ith hich no the scaling la 4
5 Cn ( + n, n) = Cn ( / f ( n )) (4) may be established. In conclusion, e have discovered the aging phenomenon and the scaling la of aftershocks inside of the Omori regime through analysis of the seismic data taken in southern California. Quenched disorder, slo relaxation (the poer-la nature of the Omori la), the aging phenomenon, and the scaling la are all characteristics in physics of glasses. The present results and these observations indicate that complex fault-fault interactions leading to aftershocks may be governed by glassy dynamics. This opens a ne possibility of approaching the yet unclear mechanism of aftershocks by the use of available physical models such as spin glasses. [1] F. Omori, J. Coll. Sci. Imper. Univ. Tokyo 7, 111 (1894). [2] T. Utsu, Geophys. Mag. 30, 521 (1961). [3] Spin Glasses and Random Fields, edited by A. P. Young (World Scientific, Singapore, 1998). [4] L. F. Cugliandolo, Les Houches lectures, cond-mat/ [5] S. Abe and N. Suzuki, J. Geophys. Res. 108 (B2), 2113 (2003). [6] S. Abe and N. Suzuki, e-print cond-mat/ [7] C. Tsallis, J. Stat. Phys. 52, 479 (1988). 5
6 [8] Nonextensive Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, edited by S. Abe and Y. Okamoto (Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, 2001). [9] A.-L. Barabási and R. Albert, Science 286, 509 (1999). [10] S. N. Dorogovtsev and J. F. F. Mendes, Evolution of Netorks (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2003). Figure Captions Fig. 1 Plots of the correlation functions ith respect to the event number, n, inside of the Omori regime of the earthquake M7.3 in 1992, in the dimensionless units. The values of the aiting time are, n = 0, 600, 1200, and N = The aging phenomenon is clearly appreciated. Fig. 2 Plots of the correlation functions ith respect to the event number, n, inside of the Omori regime of the earthquake M7.1 in 1999, in the dimensionless units. The values of the aiting time are, n = 0, 400, 800, and N = The aging phenomenon is clearly appreciated. 6
7 Fig. 3 Plots of the correlation functions ith respect to the event number, n, outside of the Omori regime of the earthquake M7.1 in 1999, in the dimensionless units. The values of the aiting time are, n = 0, 400, 800, and N = No aging phenomenon is recognized. Fig. 4 The data collapse corresponding to Fig. 1 by rescaling of time by the factor f( n ). The associated values of f( n ) are given in Fig. 6. All quantities are dimensionless. Fig. 5 The data collapse corresponding to Fig. 2 by rescaling of time by the factor f( n ). The associated values of f( n ) are given in Fig. 7. All quantities are dimensionless. Fig. 6 The values of f( n ) fitted by the function in Eq. (3) ith a = and γ = 162., corresponding to Fig. 4. Here, more values of n are examined than in Fig. 4. All quantities are dimensionless. Fig. 7 The values of f( n ) fitted by the function in Eq. (3) ith a = and γ = 100., corresponding to Fig. 5. Here, more values of n are examined than in Fig. 5. All quantities are dimensionless. 7
8 This figure "aging-figure_1.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
9 This figure "aging-figure_2.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
10 This figure "aging-figure_3.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
11 This figure "aging-figure_4.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
12 This figure "aging-figure_5.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
13 This figure "aging-figure_6.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
14 This figure "aging-figure_7.jpg" is available in "jpg" format from:
Small-world structure of earthquake network
 Small-world structure of earthquake network Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
Small-world structure of earthquake network Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
Scale-free network of earthquakes
 Scale-free network of earthquakes Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University, Chiba
Scale-free network of earthquakes Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University, Chiba
Gutenberg-Richter Law for Internetquakes
 Gutenberg-Richter Law for Internetquakes Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
Gutenberg-Richter Law for Internetquakes Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
Finite data-size scaling of clustering in earthquake networks
 Finite data-size scaling of clustering in earthquake networks Sumiyoshi Abe a,b, Denisse Pastén c and Norikazu Suzuki d a Department of Physical Engineering, Mie University, Mie 514-8507, Japan b Institut
Finite data-size scaling of clustering in earthquake networks Sumiyoshi Abe a,b, Denisse Pastén c and Norikazu Suzuki d a Department of Physical Engineering, Mie University, Mie 514-8507, Japan b Institut
Stability of Tsallis entropy and instabilities of Rényi and normalized Tsallis entropies: A basis for q-exponential distributions
 PHYSICAL REVIE E 66, 4634 22 Stability of Tsallis entropy and instabilities of Rényi and normalized Tsallis entropies: A basis for -exponential distributions Sumiyoshi Abe Institute of Physics, University
PHYSICAL REVIE E 66, 4634 22 Stability of Tsallis entropy and instabilities of Rényi and normalized Tsallis entropies: A basis for -exponential distributions Sumiyoshi Abe Institute of Physics, University
Interpretation of the Omori law
 Interpretation of the Omori law Anatol V. Guglielmi Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth, Russian Academy of Sciences, ul. B. Gruzinskaya 10, Moscow, 13995 Russia e-mail: guglielmi@mail.ru This paper
Interpretation of the Omori law Anatol V. Guglielmi Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth, Russian Academy of Sciences, ul. B. Gruzinskaya 10, Moscow, 13995 Russia e-mail: guglielmi@mail.ru This paper
Subdiffusion of volcanic earthquakes
 Subdiffusion of volcanic earthquakes Sumiyoshi Abe,2,3 and Norikazu Suzuki 4 Physics Division, Faculty of Information Science and Engineering, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 3602, China 2 Department of Physical
Subdiffusion of volcanic earthquakes Sumiyoshi Abe,2,3 and Norikazu Suzuki 4 Physics Division, Faculty of Information Science and Engineering, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 3602, China 2 Department of Physical
Anomalous diffusion of volcanic earthquakes
 Anomalous diffusion of volcanic earthquakes SUMIYOSHI ABE 1,2 and NORIKAZU SUZUKI 3 1 Department of Physical Engineering, Mie University, Mie 514-8507, Japan 2 Institute of Physics, Kazan Federal University,
Anomalous diffusion of volcanic earthquakes SUMIYOSHI ABE 1,2 and NORIKAZU SUZUKI 3 1 Department of Physical Engineering, Mie University, Mie 514-8507, Japan 2 Institute of Physics, Kazan Federal University,
Distribution of volcanic earthquake recurrence intervals
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005942, 2009 Distribution of volcanic earthquake recurrence intervals M. Bottiglieri, 1 C. Godano, 1 and L. D Auria 2 Received 21 July 2008;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005942, 2009 Distribution of volcanic earthquake recurrence intervals M. Bottiglieri, 1 C. Godano, 1 and L. D Auria 2 Received 21 July 2008;
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Mar 2008](/thumbs/86/93817801.jpg) CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
CD2dBS-v2 Convergence dynamics of 2-dimensional isotropic and anisotropic Bak-Sneppen models Burhan Bakar and Ugur Tirnakli Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ege University, 35100 Izmir, Turkey
Possible Cosmic Influences on the 1966 Tashkent Earthquake and its Largest Aftershocks
 Geophys. J. R. mtr. Sac. (1974) 38, 423-429. Possible Cosmic Influences on the 1966 Tashkent Earthquake and its Largest Aftershocks G. P. Tamrazyan (Received 1971 August 13)* Summary I present evidence
Geophys. J. R. mtr. Sac. (1974) 38, 423-429. Possible Cosmic Influences on the 1966 Tashkent Earthquake and its Largest Aftershocks G. P. Tamrazyan (Received 1971 August 13)* Summary I present evidence
arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003 arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003](/thumbs/90/101580441.jpg) Is Earthquake Triggering Driven by Small Earthquakes? arxiv:physics/0210056v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003 Agnès Helmstetter Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, Observatoire de Grenoble,
Is Earthquake Triggering Driven by Small Earthquakes? arxiv:physics/0210056v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003 Agnès Helmstetter Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, Observatoire de Grenoble,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Jan 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Jan 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Jan 2004](/thumbs/73/68423743.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0401382v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Jan 2004 Non-Poisson distribution of the time distances between two consecutive clusters of earthquakes Luigi Palatella a, Paolo Allegrini b, Paolo Grigolini
arxiv:cond-mat/0401382v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 21 Jan 2004 Non-Poisson distribution of the time distances between two consecutive clusters of earthquakes Luigi Palatella a, Paolo Allegrini b, Paolo Grigolini
The Role of Asperities in Aftershocks
 The Role of Asperities in Aftershocks James B. Silva Boston University April 7, 2016 Collaborators: William Klein, Harvey Gould Kang Liu, Nick Lubbers, Rashi Verma, Tyler Xuan Gu OUTLINE Introduction The
The Role of Asperities in Aftershocks James B. Silva Boston University April 7, 2016 Collaborators: William Klein, Harvey Gould Kang Liu, Nick Lubbers, Rashi Verma, Tyler Xuan Gu OUTLINE Introduction The
Additional information for the paper:
 Additional information for the paper: Similarity of fluctuations in correlated systems: The case of seismicity by P. A. Varotsos,2*, N. V. Sarlis, H. K. Tanaka 3, E. S. Skordas 2 Solid State Section, Physics
Additional information for the paper: Similarity of fluctuations in correlated systems: The case of seismicity by P. A. Varotsos,2*, N. V. Sarlis, H. K. Tanaka 3, E. S. Skordas 2 Solid State Section, Physics
Group-invariant solutions of nonlinear elastodynamic problems of plates and shells *
 Group-invariant solutions of nonlinear elastodynamic problems of plates and shells * V. A. Dzhupanov, V. M. Vassilev, P. A. Dzhondzhorov Institute of mechanics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Acad. G.
Group-invariant solutions of nonlinear elastodynamic problems of plates and shells * V. A. Dzhupanov, V. M. Vassilev, P. A. Dzhondzhorov Institute of mechanics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Acad. G.
Fundamentals of DC Testing
 Fundamentals of DC Testing Aether Lee erigy Japan Abstract n the beginning of this lecture, Ohm s la, hich is the most important electric la regarding DC testing, ill be revieed. Then, in the second section,
Fundamentals of DC Testing Aether Lee erigy Japan Abstract n the beginning of this lecture, Ohm s la, hich is the most important electric la regarding DC testing, ill be revieed. Then, in the second section,
Weight-driven growing networks
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 71, 026103 2005 Weight-driven groing netorks T. Antal* and P. L. Krapivsky Center for Polymer Studies and Department of Physics, Boston University, Boston, Massachusetts 02215, USA Received
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 71, 026103 2005 Weight-driven groing netorks T. Antal* and P. L. Krapivsky Center for Polymer Studies and Department of Physics, Boston University, Boston, Massachusetts 02215, USA Received
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 20 Feb 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 20 Feb 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 20 Feb 2004](/thumbs/92/110892381.jpg) Very Long Time Magnetization Decays in Spin Glasses G. G. Kenning and G. F. Rodriguez Department of Physics, University of California Riverside, California 92521-0101 arxiv:cond-mat/0402509v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn]
Very Long Time Magnetization Decays in Spin Glasses G. G. Kenning and G. F. Rodriguez Department of Physics, University of California Riverside, California 92521-0101 arxiv:cond-mat/0402509v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn]
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Note. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Note File Name: Peer Revie File Description: Supplementary Fig.1. Complete set of ACFs extracted by FLCS analysis.
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Note File Name: Peer Revie File Description: Supplementary Fig.1. Complete set of ACFs extracted by FLCS analysis.
Language Recognition Power of Watson-Crick Automata
 01 Third International Conference on Netorking and Computing Language Recognition Poer of Watson-Crick Automata - Multiheads and Sensing - Kunio Aizaa and Masayuki Aoyama Dept. of Mathematics and Computer
01 Third International Conference on Netorking and Computing Language Recognition Poer of Watson-Crick Automata - Multiheads and Sensing - Kunio Aizaa and Masayuki Aoyama Dept. of Mathematics and Computer
Adaptive Noise Cancellation
 Adaptive Noise Cancellation P. Comon and V. Zarzoso January 5, 2010 1 Introduction In numerous application areas, including biomedical engineering, radar, sonar and digital communications, the goal is
Adaptive Noise Cancellation P. Comon and V. Zarzoso January 5, 2010 1 Introduction In numerous application areas, including biomedical engineering, radar, sonar and digital communications, the goal is
Mechanical origin of aftershocks: Supplementary Information
 Mechanical origin of aftershocks: Supplementary Information E. Lippiello Department of Mathematics and Physics, Second University of Naples, Via Vivaldi 43, 81100 Caserta, Italy & Kavli Institute for Theoretical
Mechanical origin of aftershocks: Supplementary Information E. Lippiello Department of Mathematics and Physics, Second University of Naples, Via Vivaldi 43, 81100 Caserta, Italy & Kavli Institute for Theoretical
arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 15 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 15 Dec 2009 arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 15 Dec 2009](/thumbs/96/128729428.jpg) Power laws of the in-degree and out-degree distributions of complex networks arxiv:0912.2793v1 [physics.soc-ph] 15 Dec 2009 Shinji Tanimoto Department of Mathematics, Kochi Joshi University, Kochi 780-8515,
Power laws of the in-degree and out-degree distributions of complex networks arxiv:0912.2793v1 [physics.soc-ph] 15 Dec 2009 Shinji Tanimoto Department of Mathematics, Kochi Joshi University, Kochi 780-8515,
The 150th Anniversary of Fusakichi Omori
 arxiv 2018 The 150th Anniversary of Fusakichi Omori Anatol V. Guglielmi, Alexey D. Zavyalov Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth, Russian Academy of Sciences, ul. B. Gruzinskaya 10, Moscow, 123995
arxiv 2018 The 150th Anniversary of Fusakichi Omori Anatol V. Guglielmi, Alexey D. Zavyalov Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth, Russian Academy of Sciences, ul. B. Gruzinskaya 10, Moscow, 123995
arxiv:physics/ v1 6 Aug 2006
 The application of the modified form of Båth s law to the North Anatolian Fault Zone arxiv:physics/0608064 v1 6 Aug 2006 1. INTRODUCTION S E Yalcin, M L Kurnaz Department of Physics, Bogazici University,
The application of the modified form of Båth s law to the North Anatolian Fault Zone arxiv:physics/0608064 v1 6 Aug 2006 1. INTRODUCTION S E Yalcin, M L Kurnaz Department of Physics, Bogazici University,
Toward automatic aftershock forecasting in Japan
 Toward automatic aftershock forecasting in Japan T. Omi (The Univ. of Tokyo) Y. Ogata (ISM) K. Shiomi (NIED) B. Enescu (Tsukuba Univ.) K. Sawazaki (NIED) K. Aihara (The Univ. of Tokyo) @Statsei9 Forecasting
Toward automatic aftershock forecasting in Japan T. Omi (The Univ. of Tokyo) Y. Ogata (ISM) K. Shiomi (NIED) B. Enescu (Tsukuba Univ.) K. Sawazaki (NIED) K. Aihara (The Univ. of Tokyo) @Statsei9 Forecasting
Ergodicity,non-ergodic processes and aging processes
 Ergodicity,non-ergodic processes and aging processes By Amir Golan Outline: A. Ensemble and time averages - Definition of ergodicity B. A short overvie of aging phenomena C. Examples: 1. Simple-glass and
Ergodicity,non-ergodic processes and aging processes By Amir Golan Outline: A. Ensemble and time averages - Definition of ergodicity B. A short overvie of aging phenomena C. Examples: 1. Simple-glass and
Effects of data windows on the methods of surrogate data
 Effects of data windows on the methods of surrogate data Tomoya Suzuki, 1 Tohru Ikeguchi, and Masuo Suzuki 1 1 Graduate School of Science, Tokyo University of Science, 1-3 Kagurazaka, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo
Effects of data windows on the methods of surrogate data Tomoya Suzuki, 1 Tohru Ikeguchi, and Masuo Suzuki 1 1 Graduate School of Science, Tokyo University of Science, 1-3 Kagurazaka, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo
Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Page 1 of 5 Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An aftershock is a smaller earthquake that occurs after a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock. If an aftershock is
Page 1 of 5 Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An aftershock is a smaller earthquake that occurs after a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock. If an aftershock is
log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =
![log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) = log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =](/thumbs/92/109466632.jpg) Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL MODELLING LECTURES 6-7: MODELLING WEALTH DISTRIBUTION
 January 004 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL MODELLING LECTURES 6-7: MODELLING WEALTH DISTRIBUTION Project in Geometry and Physics, Department of Mathematics University of California/San Diego, La Jolla, CA
January 004 INTRODUCTION TO MATHEMATICAL MODELLING LECTURES 6-7: MODELLING WEALTH DISTRIBUTION Project in Geometry and Physics, Department of Mathematics University of California/San Diego, La Jolla, CA
Fluctuations in the aging dynamics of structural glasses
 Fluctuations in the aging dynamics of structural glasses Horacio E. Castillo Collaborator: Azita Parsaeian Collaborators in earlier work: Claudio Chamon Leticia F. Cugliandolo José L. Iguain Malcolm P.
Fluctuations in the aging dynamics of structural glasses Horacio E. Castillo Collaborator: Azita Parsaeian Collaborators in earlier work: Claudio Chamon Leticia F. Cugliandolo José L. Iguain Malcolm P.
The dune size distribution and scaling relations of barchan dune fields
 Granular Matter (29) :7 DOI.7/s35-8-2-4 The dune size distribution and scaling relations of barchan dune fields Orencio Durán Veit Schämmle Pedro G. Lind Hans J. Herrmann Received: 9 May 28 / Published
Granular Matter (29) :7 DOI.7/s35-8-2-4 The dune size distribution and scaling relations of barchan dune fields Orencio Durán Veit Schämmle Pedro G. Lind Hans J. Herrmann Received: 9 May 28 / Published
The Centenary of the Omori Formula for a Decay Law of Aftershock Activity
 The Centenary of the Omori Formula for a Decay Law of Aftershock Activity Author; Tokuji Utsu, Yosihiko Ogata, and Ritsuko S. Matsu'ura Presentater; Okuda Takashi 8. p Values from Superposed Sequences
The Centenary of the Omori Formula for a Decay Law of Aftershock Activity Author; Tokuji Utsu, Yosihiko Ogata, and Ritsuko S. Matsu'ura Presentater; Okuda Takashi 8. p Values from Superposed Sequences
be a deterministic function that satisfies x( t) dt. Then its Fourier
 Lecture Fourier ransforms and Applications Definition Let ( t) ; t (, ) be a deterministic function that satisfies ( t) dt hen its Fourier it ransform is defined as X ( ) ( t) e dt ( )( ) heorem he inverse
Lecture Fourier ransforms and Applications Definition Let ( t) ; t (, ) be a deterministic function that satisfies ( t) dt hen its Fourier it ransform is defined as X ( ) ( t) e dt ( )( ) heorem he inverse
Enhancing Generalization Capability of SVM Classifiers with Feature Weight Adjustment
 Enhancing Generalization Capability of SVM Classifiers ith Feature Weight Adjustment Xizhao Wang and Qiang He College of Mathematics and Computer Science, Hebei University, Baoding 07002, Hebei, China
Enhancing Generalization Capability of SVM Classifiers ith Feature Weight Adjustment Xizhao Wang and Qiang He College of Mathematics and Computer Science, Hebei University, Baoding 07002, Hebei, China
Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 2004 and 2005
 P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Aug 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Aug 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Aug 2004](/thumbs/74/69831888.jpg) Conservation laws for the voter model in complex networks arxiv:cond-mat/0408101v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Aug 2004 Krzysztof Suchecki, 1,2 Víctor M. Eguíluz, 1 and Maxi San Miguel 1 1 Instituto Mediterráneo
Conservation laws for the voter model in complex networks arxiv:cond-mat/0408101v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Aug 2004 Krzysztof Suchecki, 1,2 Víctor M. Eguíluz, 1 and Maxi San Miguel 1 1 Instituto Mediterráneo
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 1998](/thumbs/80/81746456.jpg) Nonequilibrium Phase Transition in the Kinetic Ising model: Dynamical symmetry breaking by randomly varying magnetic field arxiv:cond-mat/979v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 998 Muktish Acharyya Institute
Nonequilibrium Phase Transition in the Kinetic Ising model: Dynamical symmetry breaking by randomly varying magnetic field arxiv:cond-mat/979v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 2 Apr 998 Muktish Acharyya Institute
Theory of earthquake recurrence times
 Theory of earthquake recurrence times Alex SAICHEV1,2 and Didier SORNETTE1,3 1ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2Mathematical Department, Nizhny Novgorod State University, Russia. 3Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
Theory of earthquake recurrence times Alex SAICHEV1,2 and Didier SORNETTE1,3 1ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2Mathematical Department, Nizhny Novgorod State University, Russia. 3Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
From time series to superstatistics
 From time series to superstatistics Christian Beck School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London, Mile End Road, London E 4NS, United Kingdom Ezechiel G. D. Cohen The Rockefeller University,
From time series to superstatistics Christian Beck School of Mathematical Sciences, Queen Mary, University of London, Mile End Road, London E 4NS, United Kingdom Ezechiel G. D. Cohen The Rockefeller University,
MEASUREMENTS OF TIME-SPACE DISTRIBUTION OF CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER TO AIR USING A THIN CONDUCTIVE-FILM
 MEASUREMENTS OF TIME-SPACE DISTRIBUTION OF CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER TO AIR USING A THIN CONDUCTIVE-FILM Hajime Nakamura Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Defense Academy 1-10-0 Hashirimizu,
MEASUREMENTS OF TIME-SPACE DISTRIBUTION OF CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER TO AIR USING A THIN CONDUCTIVE-FILM Hajime Nakamura Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Defense Academy 1-10-0 Hashirimizu,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v4 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 23 May 2001
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v4 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 23 May 2001 arxiv:cond-mat/ v4 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 23 May 2001](/thumbs/94/121796770.jpg) Phase Diagram of the three-dimensional Gaussian andom Field Ising Model: A Monte Carlo enormalization Group Study arxiv:cond-mat/488v4 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 3 May M. Itakura JS Domestic esearch Fellow, Center
Phase Diagram of the three-dimensional Gaussian andom Field Ising Model: A Monte Carlo enormalization Group Study arxiv:cond-mat/488v4 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 3 May M. Itakura JS Domestic esearch Fellow, Center
CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION. From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum
 CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 19 CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION 3.0. Introduction
CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION From Exploratory Factor Analysis Ledyard R Tucker and Robert C. MacCallum 1997 19 CHAPTER 3 THE COMMON FACTOR MODEL IN THE POPULATION 3.0. Introduction
Spatial and Temporal Behaviors in a Modified Evolution Model Based on Small World Network
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 42 (2004) pp. 242 246 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 42, No. 2, August 15, 2004 Spatial and Temporal Behaviors in a Modified Evolution Model Based on Small
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 42 (2004) pp. 242 246 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 42, No. 2, August 15, 2004 Spatial and Temporal Behaviors in a Modified Evolution Model Based on Small
SCALING DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LARGE INTERPLATE AND INTRAPLATE EARTHQUAKES
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 65-70, February 1986 SCALING DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LARGE INTERPLATE AND INTRAPLATE EARTHQUAKES BY C. H. SCHOLZ, C. A. AVILES*, AND S.
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 65-70, February 1986 SCALING DIFFERENCES BETWEEN LARGE INTERPLATE AND INTRAPLATE EARTHQUAKES BY C. H. SCHOLZ, C. A. AVILES*, AND S.
Anomalous early aftershock decay rate of the 2004 Mw6.0 Parkfield, California, earthquake
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33,, doi:10.1029/2006gl026744, 2006 Anomalous early aftershock decay rate of the 2004 Mw6.0 Parkfield, California, earthquake Zhigang Peng, 1,2 John E. Vidale, 1 and
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33,, doi:10.1029/2006gl026744, 2006 Anomalous early aftershock decay rate of the 2004 Mw6.0 Parkfield, California, earthquake Zhigang Peng, 1,2 John E. Vidale, 1 and
A ROBUST BEAMFORMER BASED ON WEIGHTED SPARSE CONSTRAINT
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 16, 53 60, 2010 A ROBUST BEAMFORMER BASED ON WEIGHTED SPARSE CONSTRAINT Y. P. Liu and Q. Wan School of Electronic Engineering University of Electronic
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 16, 53 60, 2010 A ROBUST BEAMFORMER BASED ON WEIGHTED SPARSE CONSTRAINT Y. P. Liu and Q. Wan School of Electronic Engineering University of Electronic
On Lithium Wall and Performance of Magnetic Fusion Device
 On Lithium Wall and Performance of Magnetic Fusion Device S. I. Krasheninnikov 1, L. E. Zakharov 2, and G. V. Pereverzev 3 1 University California San Diego, La Jolla, USA 2 Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory,
On Lithium Wall and Performance of Magnetic Fusion Device S. I. Krasheninnikov 1, L. E. Zakharov 2, and G. V. Pereverzev 3 1 University California San Diego, La Jolla, USA 2 Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory,
Exploring aftershock properties with depth
 Exploring aftershock properties with depth Peter Shebalin 1,2, Clément Narteau 2, Matthias Holschneider 3 1 International Institute of Earthquake Prediction Theory and Mathematical Geophysics, Moscow,
Exploring aftershock properties with depth Peter Shebalin 1,2, Clément Narteau 2, Matthias Holschneider 3 1 International Institute of Earthquake Prediction Theory and Mathematical Geophysics, Moscow,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Jan 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Jan 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Jan 2007](/thumbs/91/105034253.jpg) BURST STATISTICS AS A CRITERION FOR IMMINENT FAILURE arxiv:cond-mat/0701268v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Jan 2007 Srutarshi Pradhan 1, Alex Hansen 2 and Per C. Hemmer 3 Department of Physics, Norwegian University
BURST STATISTICS AS A CRITERION FOR IMMINENT FAILURE arxiv:cond-mat/0701268v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Jan 2007 Srutarshi Pradhan 1, Alex Hansen 2 and Per C. Hemmer 3 Department of Physics, Norwegian University
Implementation of a new memristor-based multiscroll hyperchaotic system
 Pramana J. Phys. (7) 88: 3 DOI.7/s3-6-3-3 c Indian Academy of Sciences Implementation of a ne memristor-based multiscroll hyperchaotic system CHUNHUA WANG, HU XIA and LING ZHOU College of Computer Science
Pramana J. Phys. (7) 88: 3 DOI.7/s3-6-3-3 c Indian Academy of Sciences Implementation of a ne memristor-based multiscroll hyperchaotic system CHUNHUA WANG, HU XIA and LING ZHOU College of Computer Science
Impact of earthquake rupture extensions on parameter estimations of point-process models
 1 INTRODUCTION 1 Impact of earthquake rupture extensions on parameter estimations of point-process models S. Hainzl 1, A. Christophersen 2, and B. Enescu 1 1 GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Germany; 2 Swiss
1 INTRODUCTION 1 Impact of earthquake rupture extensions on parameter estimations of point-process models S. Hainzl 1, A. Christophersen 2, and B. Enescu 1 1 GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Germany; 2 Swiss
Gutenberg-Richter Relationship: Magnitude vs. frequency of occurrence
 Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
Generalized Entropy Composition with Different q Indices: A Trial
 arxiv:cond-mat/000458v Apr 2000 Generalized Entropy Composition with Different q Indices: A Trial in International Workshop on Classical and Quantum Complexity and Nonextensive Thermodynamics (Denton-Texas,
arxiv:cond-mat/000458v Apr 2000 Generalized Entropy Composition with Different q Indices: A Trial in International Workshop on Classical and Quantum Complexity and Nonextensive Thermodynamics (Denton-Texas,
Heat Transfer Analysis of a Space Radiating Fin with Variable Thermal Conductivity
 Heat Transfer Analysis of a Space Radiating Fin ith Variale Thermal Conductivity Farzad Bazdidi-Tehrani, azdid@iust.ac.ir Department of Mechanical ngineering, Iran University of Science and Technology,
Heat Transfer Analysis of a Space Radiating Fin ith Variale Thermal Conductivity Farzad Bazdidi-Tehrani, azdid@iust.ac.ir Department of Mechanical ngineering, Iran University of Science and Technology,
Some Classes of Invertible Matrices in GF(2)
 Some Classes of Invertible Matrices in GF() James S. Plank Adam L. Buchsbaum Technical Report UT-CS-07-599 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee August 16, 007
Some Classes of Invertible Matrices in GF() James S. Plank Adam L. Buchsbaum Technical Report UT-CS-07-599 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee August 16, 007
CHARACTERIZATION OF ULTRASONIC IMMERSION TRANSDUCERS
 CHARACTERIZATION OF ULTRASONIC IMMERSION TRANSDUCERS INTRODUCTION David D. Bennink, Center for NDE Anna L. Pate, Engineering Science and Mechanics Ioa State University Ames, Ioa 50011 In any ultrasonic
CHARACTERIZATION OF ULTRASONIC IMMERSION TRANSDUCERS INTRODUCTION David D. Bennink, Center for NDE Anna L. Pate, Engineering Science and Mechanics Ioa State University Ames, Ioa 50011 In any ultrasonic
PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions
 . Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
. Onur 13.03.2008 PET467E-Analysis of Well Pressure Tests 2008 Spring/İTÜ HW No. 5 Solutions Due date: 21.03.2008 Subject: Analysis of an dradon test ith ellbore storage and skin effects by using typecurve
Self-organized Criticality in a Modified Evolution Model on Generalized Barabási Albert Scale-Free Networks
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 47 (2007) pp. 512 516 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 47, No. 3, March 15, 2007 Self-organized Criticality in a Modified Evolution Model on Generalized Barabási
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 47 (2007) pp. 512 516 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 47, No. 3, March 15, 2007 Self-organized Criticality in a Modified Evolution Model on Generalized Barabási
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Minimize Cost of Materials
 Question 1: Ho do you find the optimal dimensions of a product? The size and shape of a product influences its functionality as ell as the cost to construct the product. If the dimensions of a product
Question 1: Ho do you find the optimal dimensions of a product? The size and shape of a product influences its functionality as ell as the cost to construct the product. If the dimensions of a product
N-bit Parity Neural Networks with minimum number of threshold neurons
 Open Eng. 2016; 6:309 313 Research Article Open Access Marat Z. Arslanov*, Zhazira E. Amirgalieva, and Chingiz A. Kenshimov N-bit Parity Neural Netorks ith minimum number of threshold neurons DOI 10.1515/eng-2016-0037
Open Eng. 2016; 6:309 313 Research Article Open Access Marat Z. Arslanov*, Zhazira E. Amirgalieva, and Chingiz A. Kenshimov N-bit Parity Neural Netorks ith minimum number of threshold neurons DOI 10.1515/eng-2016-0037
arxiv: v3 [physics.bio-ph] 2 May 2018
![arxiv: v3 [physics.bio-ph] 2 May 2018 arxiv: v3 [physics.bio-ph] 2 May 2018](/thumbs/78/77530851.jpg) Poer la rheology of generalised Maxell and Kelvin-Voigt models arxiv:56.927v3 [physics.bio-ph] 2 May 28, 2, P. Patrício ISEL - Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Instituto Politécnico de Lisboa,
Poer la rheology of generalised Maxell and Kelvin-Voigt models arxiv:56.927v3 [physics.bio-ph] 2 May 28, 2, P. Patrício ISEL - Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Instituto Politécnico de Lisboa,
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
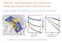 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Aspects of risk assessment in power-law distributed natural hazards
 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (2004) 4: 309 313 SRef-ID: 1684-9981/nhess/2004-4-309 European Geosciences Union 2004 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Aspects of risk assessment in power-law
Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences (2004) 4: 309 313 SRef-ID: 1684-9981/nhess/2004-4-309 European Geosciences Union 2004 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Aspects of risk assessment in power-law
Accurate and Estimation Methods for Frequency Response Calculations of Hydroelectric Power Plant
 Accurate and Estimation Methods for Frequency Response Calculations of Hydroelectric Poer Plant SHAHRAM JAI, ABOLFAZL SALAMI epartment of Electrical Engineering Iran University of Science and Technology
Accurate and Estimation Methods for Frequency Response Calculations of Hydroelectric Poer Plant SHAHRAM JAI, ABOLFAZL SALAMI epartment of Electrical Engineering Iran University of Science and Technology
Metastability in the Hamiltonian Mean Field model and Kuramoto model
 Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on News, Expectations and Trends in Statistical Physics (NEXT-ΣΦ 2005) 13-18 August 2005, Kolymbari, Crete, Greece Metastability in the Hamiltonian Mean
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on News, Expectations and Trends in Statistical Physics (NEXT-ΣΦ 2005) 13-18 August 2005, Kolymbari, Crete, Greece Metastability in the Hamiltonian Mean
Energy-Decreasing Dynamics in Mean-Field Spin Models
 arxiv:cond-mat/0210545 v1 24 Oct 2002 Energy-Decreasing Dynamics in Mean-Field Spin Models L. Bussolari, P. Contucci, M. Degli Esposti, C. Giardinà Dipartimento di Matematica dell Università di Bologna,
arxiv:cond-mat/0210545 v1 24 Oct 2002 Energy-Decreasing Dynamics in Mean-Field Spin Models L. Bussolari, P. Contucci, M. Degli Esposti, C. Giardinà Dipartimento di Matematica dell Università di Bologna,
An Improved Driving Scheme in an Electrophoretic Display
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 3 No. 4, April, 2013 An Improved Driving Scheme in an Electrophoretic Display Pengfei Bai 1, Zichuan Yi 1, Guofu Zhou 1,2 1 Electronic Paper Displays
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 3 No. 4, April, 2013 An Improved Driving Scheme in an Electrophoretic Display Pengfei Bai 1, Zichuan Yi 1, Guofu Zhou 1,2 1 Electronic Paper Displays
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
 PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 76 4 MARCH 1996 NUMBER 10 Finite-Size Scaling and Universality above the Upper Critical Dimensionality Erik Luijten* and Henk W. J. Blöte Faculty of Applied Physics, Delft
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 76 4 MARCH 1996 NUMBER 10 Finite-Size Scaling and Universality above the Upper Critical Dimensionality Erik Luijten* and Henk W. J. Blöte Faculty of Applied Physics, Delft
Earthquake Clustering and Declustering
 Earthquake Clustering and Declustering Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley joint with (separately) Peter Shearer, SIO/IGPP, UCSD Brad Luen 4 October 2011 Institut de Physique du Globe
Earthquake Clustering and Declustering Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley joint with (separately) Peter Shearer, SIO/IGPP, UCSD Brad Luen 4 October 2011 Institut de Physique du Globe
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences
 Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 7 (0) 09 8 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Asian Earth Sciences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jseaes Maximum magnitudes in aftershock
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 7 (0) 09 8 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Asian Earth Sciences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jseaes Maximum magnitudes in aftershock
Drift & Anisotropy Parameters in Sporadic-E & Normal-E Layers"
 ndian Journal of Radio Space Physics Vol. 5, December 1976, pp. 272-276 Drift & Anisotropy Parameters in Sporadic-E & Normal-E Layers" S P MANOHAR RAO & B RAMACHANDRA RAO Department of Physics, An dhra
ndian Journal of Radio Space Physics Vol. 5, December 1976, pp. 272-276 Drift & Anisotropy Parameters in Sporadic-E & Normal-E Layers" S P MANOHAR RAO & B RAMACHANDRA RAO Department of Physics, An dhra
Variable Viscosity Effect on Heat Transfer over a. Continuous Moving Surface with Variable Internal. Heat Generation in Micropolar Fluids
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 128, 6365-6379 Variable Viscosity Effect on Heat Transfer over a Continuous Moving Surface ith Variable Internal Heat Generation in Micropolar Fluids M.
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 128, 6365-6379 Variable Viscosity Effect on Heat Transfer over a Continuous Moving Surface ith Variable Internal Heat Generation in Micropolar Fluids M.
Because of its reputation of validity over a wide range of
 The magnitude distribution of declustered earthquakes in Southern California Leon Knopoff* Department of Physics and Astronomy and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
The magnitude distribution of declustered earthquakes in Southern California Leon Knopoff* Department of Physics and Astronomy and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
Nonuniqueness of canonical ensemble theory. arising from microcanonical basis
 onuniueness of canonical enseble theory arising fro icrocanonical basis arxiv:uant-ph/99097 v2 25 Oct 2000 Suiyoshi Abe and A. K. Rajagopal 2 College of Science and Technology, ihon University, Funabashi,
onuniueness of canonical enseble theory arising fro icrocanonical basis arxiv:uant-ph/99097 v2 25 Oct 2000 Suiyoshi Abe and A. K. Rajagopal 2 College of Science and Technology, ihon University, Funabashi,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 17 Jan 2003
 Local Distributions and Rate Fluctuations in a Unified Scaling Law for Earthquakes Álvaro Corral Departament de Física, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Edifici Cc, E-08193 Bellaterra, arxiv:cond-mat/0301321v1
Local Distributions and Rate Fluctuations in a Unified Scaling Law for Earthquakes Álvaro Corral Departament de Física, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Edifici Cc, E-08193 Bellaterra, arxiv:cond-mat/0301321v1
arxiv: v3 [physics.soc-ph] 9 May 2014
![arxiv: v3 [physics.soc-ph] 9 May 2014 arxiv: v3 [physics.soc-ph] 9 May 2014](/thumbs/92/109706774.jpg) arxiv:1309.5680v3 [physics.soc-ph] 9 May 2014 Modeling nonuniversal citation distributions: the role of scientific journals Zheng Yao 1, Xiao-Long Peng 1, Li-Jie Zhang 3,2 and Xin-Jian Xu 1,2 1 Department
arxiv:1309.5680v3 [physics.soc-ph] 9 May 2014 Modeling nonuniversal citation distributions: the role of scientific journals Zheng Yao 1, Xiao-Long Peng 1, Li-Jie Zhang 3,2 and Xin-Jian Xu 1,2 1 Department
Giant Enhancement of Quantum Decoherence by Frustrated Environments
 ISSN 0021-3640, JETP Letters, 2006, Vol. 84, No. 2, pp. 99 103. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 2006.. Giant Enhancement of Quantum Decoherence by Frustrated Environments S. Yuan a, M. I. Katsnelson b, and
ISSN 0021-3640, JETP Letters, 2006, Vol. 84, No. 2, pp. 99 103. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 2006.. Giant Enhancement of Quantum Decoherence by Frustrated Environments S. Yuan a, M. I. Katsnelson b, and
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999](/thumbs/95/123482736.jpg) BARI-TH 347/99 arxiv:cond-mat/9907149v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999 PHASE ORDERING IN CHAOTIC MAP LATTICES WITH CONSERVED DYNAMICS Leonardo Angelini, Mario Pellicoro, and Sebastiano Stramaglia Dipartimento
BARI-TH 347/99 arxiv:cond-mat/9907149v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Sep 1999 PHASE ORDERING IN CHAOTIC MAP LATTICES WITH CONSERVED DYNAMICS Leonardo Angelini, Mario Pellicoro, and Sebastiano Stramaglia Dipartimento
= Prob( gene i is selected in a typical lab) (1)
 Supplementary Document This supplementary document is for: Reproducibility Probability Score: Incorporating Measurement Variability across Laboratories for Gene Selection (006). Lin G, He X, Ji H, Shi
Supplementary Document This supplementary document is for: Reproducibility Probability Score: Incorporating Measurement Variability across Laboratories for Gene Selection (006). Lin G, He X, Ji H, Shi
Property of Tsallis entropy and principle of entropy increase
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 691 696 Property of Tsallis entropy and principle of entropy increase Du Jiulin Department of Physics, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China Abstract.
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 691 696 Property of Tsallis entropy and principle of entropy increase Du Jiulin Department of Physics, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China Abstract.
Max-Margin Ratio Machine
 JMLR: Workshop and Conference Proceedings 25:1 13, 2012 Asian Conference on Machine Learning Max-Margin Ratio Machine Suicheng Gu and Yuhong Guo Department of Computer and Information Sciences Temple University,
JMLR: Workshop and Conference Proceedings 25:1 13, 2012 Asian Conference on Machine Learning Max-Margin Ratio Machine Suicheng Gu and Yuhong Guo Department of Computer and Information Sciences Temple University,
A New Method for Calculating Oil-Water Relative Permeabilities with Consideration of Capillary Pressure
 A Ne Method for Calculating Oil-Water Relative Permeabilities ith Consideration of Capillary Pressure K. Li, P. Shen, & T. Qing Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development (RIPED), P.O.B.
A Ne Method for Calculating Oil-Water Relative Permeabilities ith Consideration of Capillary Pressure K. Li, P. Shen, & T. Qing Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development (RIPED), P.O.B.
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 10 Aug 2002
 Model-free derivations of the Tsallis factor: constant heat capacity derivation arxiv:cond-mat/0208205 v1 10 Aug 2002 Abstract Wada Tatsuaki Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Ibaraki
Model-free derivations of the Tsallis factor: constant heat capacity derivation arxiv:cond-mat/0208205 v1 10 Aug 2002 Abstract Wada Tatsuaki Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Ibaraki
Statistical similarity between high energy charged particle fluxes in near-earth space and earthquakes
 Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss., 2, 3183 3192, 14 www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci-discuss.net/2/3183/14/ doi:.194/nhessd-2-3183-14 Author(s) 14. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss., 2, 3183 3192, 14 www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci-discuss.net/2/3183/14/ doi:.194/nhessd-2-3183-14 Author(s) 14. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth
Testing for Poisson Behavior
 Testing for Poisson Behavior Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley joint with Brad Luen 17 April 2012 Seismological Society of America Annual Meeting San Diego, CA Quake Physics versus
Testing for Poisson Behavior Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley joint with Brad Luen 17 April 2012 Seismological Society of America Annual Meeting San Diego, CA Quake Physics versus
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR
 A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
Scaling and memory in recurrence intervals of Internet traffic
 Published in "Europhysics Letters 87: 68001, 2009" which should be cited to refer to this work. Scaling and memory in recurrence intervals of Internet traffic Shi-Min Cai 1,2, Zhong-Qian Fu 1,TaoZhou 2,3(a),JunGu
Published in "Europhysics Letters 87: 68001, 2009" which should be cited to refer to this work. Scaling and memory in recurrence intervals of Internet traffic Shi-Min Cai 1,2, Zhong-Qian Fu 1,TaoZhou 2,3(a),JunGu
Are Declustered Earthquake Catalogs Poisson?
 Are Declustered Earthquake Catalogs Poisson? Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley Brad Luen Department of Mathematics, Reed College 14 October 2010 Department of Statistics, Penn State
Are Declustered Earthquake Catalogs Poisson? Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley Brad Luen Department of Mathematics, Reed College 14 October 2010 Department of Statistics, Penn State
ISSN Article. Tsallis Entropy, Escort Probability and the Incomplete Information Theory
 Entropy 2010, 12, 2497-2503; doi:10.3390/e12122497 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Tsallis Entropy, Escort Probability and the Incomplete Information Theory Amir
Entropy 2010, 12, 2497-2503; doi:10.3390/e12122497 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Tsallis Entropy, Escort Probability and the Incomplete Information Theory Amir
ON FRACTIONAL RELAXATION
 Fractals, Vol. 11, Supplementary Issue (February 2003) 251 257 c World Scientific Publishing Company ON FRACTIONAL RELAXATION R. HILFER ICA-1, Universität Stuttgart Pfaffenwaldring 27, 70569 Stuttgart,
Fractals, Vol. 11, Supplementary Issue (February 2003) 251 257 c World Scientific Publishing Company ON FRACTIONAL RELAXATION R. HILFER ICA-1, Universität Stuttgart Pfaffenwaldring 27, 70569 Stuttgart,
An Analog Analogue of a Digital Quantum Computation
 An Analog Analogue of a Digital Quantum Computation arxiv:quant-ph/9612026v1 6 Dec 1996 Edard Farhi Center for Theoretical Physics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 Sam Gutmann
An Analog Analogue of a Digital Quantum Computation arxiv:quant-ph/9612026v1 6 Dec 1996 Edard Farhi Center for Theoretical Physics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 Sam Gutmann
Criteria for the determination of a basic Clark s flow time distribution function in network planning
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:4 No:0 60 Criteria for the determination of a basic Clark s flo time distribution function in netork planning Dusko Letić, Branko Davidović,
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:4 No:0 60 Criteria for the determination of a basic Clark s flo time distribution function in netork planning Dusko Letić, Branko Davidović,
arxiv: v1 [physics.geo-ph] 6 Jun 2016
![arxiv: v1 [physics.geo-ph] 6 Jun 2016 arxiv: v1 [physics.geo-ph] 6 Jun 2016](/thumbs/94/120550572.jpg) epl draft Extensive Characterization of Seismic Laws in Acoustic Emissions of Crumpled Plastic Sheets arxiv:1.17v1 [physics.geo-ph] Jun 1 Leandro S. Costa 1, Ervin K. Lenzi, Renio S. Mendes 1 and Haroldo
epl draft Extensive Characterization of Seismic Laws in Acoustic Emissions of Crumpled Plastic Sheets arxiv:1.17v1 [physics.geo-ph] Jun 1 Leandro S. Costa 1, Ervin K. Lenzi, Renio S. Mendes 1 and Haroldo
Towards a Theory of Societal Co-Evolution: Individualism versus Collectivism
 Toards a Theory of Societal Co-Evolution: Individualism versus Collectivism Kartik Ahuja, Simpson Zhang and Mihaela van der Schaar Department of Electrical Engineering, Department of Economics, UCLA Theorem
Toards a Theory of Societal Co-Evolution: Individualism versus Collectivism Kartik Ahuja, Simpson Zhang and Mihaela van der Schaar Department of Electrical Engineering, Department of Economics, UCLA Theorem
CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION
 CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION Jericho L. P. Reyes, Chih-Ying Chen, Keen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program,
CALCULATION OF STEAM AND WATER RELATIVE PERMEABILITIES USING FIELD PRODUCTION DATA, WITH LABORATORY VERIFICATION Jericho L. P. Reyes, Chih-Ying Chen, Keen Li and Roland N. Horne Stanford Geothermal Program,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 8 Jan 2004
 Multifractality and nonextensivity at the edge of chaos of unimodal maps E. Mayoral and A. Robledo arxiv:cond-mat/0401128 v1 8 Jan 2004 Instituto de Física, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apartado
Multifractality and nonextensivity at the edge of chaos of unimodal maps E. Mayoral and A. Robledo arxiv:cond-mat/0401128 v1 8 Jan 2004 Instituto de Física, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apartado
