Exploring aftershock properties with depth
|
|
|
- Jonah Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exploring aftershock properties with depth Peter Shebalin 1,2, Clément Narteau 2, Matthias Holschneider 3 1 International Institute of Earthquake Prediction Theory and Mathematical Geophysics, Moscow, Russia shebalin@mitp.ru 2 Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, France narteau@ipgp.fr 3 Institutes of Applied and Industrial Mathematics, Universität Potsdam, Germany matthias.holschneider@googl .com
2 Strong dependence of c-value on depth (to avoid focal mechanism effect we consider vertical strike-slip faults in California) 1/(t+c) 1/(t+c) p min 1.0 c (day) p sec
3 Main shock depths / aftershock depths: no big difference 20 Mainsocks depth, km 20 Aftershocks depth, km
4 Les zones 20-km large le long les failles verticales strike-slip en Californie l
5 c-value-depth in different segments (a) (b) (c) (d) Northern San Andreas Calaveras Bartlett Spring Hayward l (e) (f) (g) (h) Maacama San Andreas Creeping Section Southern San Andreas Elsinore (i) (j) (k) (l) San Jacinto Imperial Landers Laguna Salada
6 How to avoid the possible effect of non-complete catalog? We use the same rules as in [Narteau et al., 2009] 1) We consider the interval from 10 seconds to 24 hours 2) Limited main shock range: from 2.8 to 4.0 3) Limited aftershock magnitude range: from 1.8 to 2.8 l 4) Simple rule to select aftershocks: hypocentral distance <4km from mainshock (results do not depend much on this choice) 5) Secondary aftershock sequences (after large aftershocks) are disregarded 6) Séquences containing events with magnitude larger than mainshockqui are disregarded. Deselection according 5 and 6 <3% of events We construct stacks of events according the mainshock depths (2 km sliding window). Minimum number of events in a stack - 50
7 Bayesian analysis: difference is statistically significant h=5-7 km l h=10-12 km
8 The delay of the power-law decay (c-value) depends on stress. Our basic hypothesis band Limited Power Law (LPL) model. (Narteau et al., JGR, 2002) c t b 1/λ b Aftershock The distribution temporal of stresses distribution in and is near a the main superposition shock fault is highly of a large heterogeneous. number of exponents. We assume uniform distribution limited by some value σ b. The distribution of stresses in and near the main shock We suppose fault is the highly aftershock heterogeneous. rate at stress Short σ is equal: exponents occur λ=λ high o exp(σ/σ stress 0 sub-areas, -1) (1) long exponents in low stress sub-areas. Each asperity produces only one earthquake, accordingly the number of aftershocks at stress σ is δn(t, σ)/δt=-λ(σ) Ν(t,σ) (2) Faster So at each than specific power-law stress decay the at decay the end is exponential of the sequence is caused by a deficit of long exponents. Integrating exponential One of possible N(t,σ) interpretations obtained from is eq. (1) over all σ, we have the total rate of aftershocks: Λ(t)=A(γ(p,λ In this talk we consider b t) - γ(p,λ aftershock a t))/t sequences p (3) Where γ(p,x) incomplete Gamma function; over short times. It is natural to use differential stress σ=σ 1 -σ 3
9 LPL vs Omori-Utsu LPL! Λ! =!!!!!!!!!!"!=!!!,!!!!!!,!!!,!!!!!!!! =!!!!!!!!!!,!! =!(!! ),!!! =!(!! )!!!!!!,! =!!!!!!!!"!"!Incomplete!Gamma!function!! Omori-Utsu Λ! =! (! +!)!! p = 1!!!!!!!!! = 0!!!!!c! 1/!!! c(p=1) estimated in (t s,t e ) è <log t> - (log t e log t s )/2
10 Geometric mean instead of the c-value c(p=1) è <log t> - (log t e log t s )/2 <log10(t)> 0.5log10(tstop/tstart) <log10(t)> 0.5log10(tstop/tstart) <log10(t)>=0.371log10(c) c(p=1), days
11 c(p=1) è <log t> - (log t e log t s )/2 (a) (b) (c) (d) Northern San Andreas Calaveras Bartlett Spring Hayward Northern San Andreas Calaveras Bartlett Spring Hayward
12 c(p=1) è <log t> - (log t e log t s )/2 (e) (f) (g) (h) Maacama San Andreas Creeping Section Southern San Andreas Elsinore Maacama San Andreas Creeping Section Southern San Andreas Elsinore
13 c(p=1) è <log t> - (log t e log t s )/2 (i) (j) (k) (l) San Jacinto Imperial Landers Laguna Salada San Jacinto Imperial Landers Laguna Salada
14 Effect of magnitudes? (c-value may depend both on main shock and aftershock magnitudes) Stacks according to the main shock magnitude Stacks according to the aftershock magnitude Average magnitudes main shocks aftershocks No effect!!! Magnitudes slightly decrease at 5-15 km C-value should not decrease, but it does
15 Interpretation (depths 5 to 15 km) τ > τ r =µσ n + τ 0 (1) For strike-slip faults σ 2 is vertical; we assume [Sibson, 1974] σ 2 =(σ 1 +σ 3 )/2, τ 0 =0, and find minimal value of R=σ 1 /σ 3, required to initiate sliding: then the sliding initiation criterion is: R =[(1+µ 2 ) 1/2 -µ] -2 (2) (σ 1 -σ 3 ) > 2(R -1)/(R +1) ρgh (1-γ) (3) ρgh (1-γ) = ρgh P overburden pressure
16 Interpretation (depths 5 to 15 km) (3) gives an upper limit σ b of the distribution of σ=σ 1 -σ 3 in the aftershock zone (LPL model): σ b =2(R -1)/(R +1) ρgh (1-γ), R =[(1+µ 2 ) 1/2 -µ] -2 From c(p=1) 1/λ b and λ b =λ 0 exp(σ b /σ 0-1), assuming µ and γ not depending of h, and considering gradient of log(c), we obtain: -d log(c)/d h = const 1 + const 2 (R -1)/(R +1) h The gradient of log(c), up to a constant, gives an estimate of µ. One landmark is sufficient to know the constant.
17 Estimating µ from gradient of log(c)
18 Problem of interpretation: positive gradient of log(c) for depths 0 5 km Zone of stable friction (0-5 km) velocity strengthening??? [Scholz, 1998] Number of earthquakes τ = [µ 0 +a log(v/v 0 )+b log(v 0 θ/l)] σ at steady state: τ = [µ 0 +(a-b) log(v/v 0 )] σ From: C.Scholz. Earthquakes and friction laws. Nature. 391, 38-42, 1998.
19 Problem of interpretation: positive gradient of log(c) for depths 0 5 km Role of fluids? Geysers Salton Sea (a) (b) (c) 1 Geysers Salton Sea Geothermal Field 1 Mammoth lakes Mammoth Lakes 1e Mainsocks depth, km 1e Drop of the normal stress (injections of fluides and vapor).
20 Conclusions The delay of the power-law decay of aftershock sequences is not zero This delay is connected to stress field: generally smaller delay (smaller c-value of Omori-Utsu law) corresponds to larger share stresses l Calibration of the c-value stress relation needs more detailed modeling C-value estimates may be replaced by geometric average of elapse times, normalized by time window
Supporting Information for Break of slope in earthquake-size distribution reveals creep rate along the San Andreas fault system
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Break of slope in earthquake-size distribution reveals creep rate along the San Andreas fault system Inessa Vorobieva, 1,2 Peter Shebalin, 1,2 Clément
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Break of slope in earthquake-size distribution reveals creep rate along the San Andreas fault system Inessa Vorobieva, 1,2 Peter Shebalin, 1,2 Clément
Short-Term Earthquake Forecasting Using Early Aftershock Statistics
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 101, No. 1, pp. 297 312, February 2011, doi: 10.1785/0120100119 Short-Term Earthquake Forecasting Using Early Aftershock Statistics by Peter Shebalin,
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 101, No. 1, pp. 297 312, February 2011, doi: 10.1785/0120100119 Short-Term Earthquake Forecasting Using Early Aftershock Statistics by Peter Shebalin,
Limitations of Earthquake Triggering Models*
 Limitations of Earthquake Triggering Models* Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 16, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute * in Southern California Why do earthquakes cluster in time and space?
Limitations of Earthquake Triggering Models* Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 16, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute * in Southern California Why do earthquakes cluster in time and space?
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
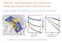 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Earthquake Stress Drops in Southern California
 Earthquake Stress Drops in Southern California Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 11, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions, slip history,
Earthquake Stress Drops in Southern California Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 11, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions, slip history,
ETH Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich
 Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich Earthquake Statistics using ZMAP Recent Results Danijel Schorlemmer, Stefan Wiemer Zürich, Swiss Seismological Service, Switzerland Contributions by: Matt Gerstenberger
Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich Earthquake Statistics using ZMAP Recent Results Danijel Schorlemmer, Stefan Wiemer Zürich, Swiss Seismological Service, Switzerland Contributions by: Matt Gerstenberger
Geo736: Seismicity and California s Active Faults Introduction
 Geo736: Seismicity and California s Active Faults Course Notes: S. G. Wesnousky Spring 2018 Introduction California sits on the boundary of the Pacific - North American plate boundary (Figure 1). Relative
Geo736: Seismicity and California s Active Faults Course Notes: S. G. Wesnousky Spring 2018 Introduction California sits on the boundary of the Pacific - North American plate boundary (Figure 1). Relative
to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San
 Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
friction friction a-b slow fast increases during sliding
 µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller
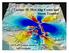 Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes
 Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from fault roughness and b-value analysis in stick-slip experiments
 What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from fault roughness and b-value analysis in stick-slip experiments T. H. W. Goebel 1, G. Kwiatek 2, T. W. Becker 3, G. Dresen 2, E.E. Brodsky 1 1 UC Santa
What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from fault roughness and b-value analysis in stick-slip experiments T. H. W. Goebel 1, G. Kwiatek 2, T. W. Becker 3, G. Dresen 2, E.E. Brodsky 1 1 UC Santa
Spatiotemporal Analyses of Earthquake Productivity and Size Distribution: Observations and Simulations
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 93, No. 5, pp. 2069 2081, October 2003 Spatiotemporal Analyses of Earthquake Productivity and Size Distribution: Observations and Simulations by A.
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 93, No. 5, pp. 2069 2081, October 2003 Spatiotemporal Analyses of Earthquake Productivity and Size Distribution: Observations and Simulations by A.
Stress modulation on the San Andreas fault by interseismic fault system interactions Jack Loveless and Brendan Meade, Geology, 2011
 Stress modulation on the San Andreas fault by interseismic fault system interactions Jack Loveless and Brendan Meade, Geology, 2011 A three step process: 1 - Assimilate plate boundary wide GPS data into
Stress modulation on the San Andreas fault by interseismic fault system interactions Jack Loveless and Brendan Meade, Geology, 2011 A three step process: 1 - Assimilate plate boundary wide GPS data into
Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us?
 Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us? Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego October 27, 2014 SCEC Community Stress Model Workshop Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions,
Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us? Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego October 27, 2014 SCEC Community Stress Model Workshop Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions,
Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003239, 2004 Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California Jeanne L. Hardebeck and Andrew J. Michael U.S.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003239, 2004 Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California Jeanne L. Hardebeck and Andrew J. Michael U.S.
Ninth Workshop on Non-linear Dynamics and Earthquake Predictions
 186418 Ninth Workshop on Nonlinear Dynamics and Earthquake Predictions 1 13 October 2007 A limited powerlaw for the aftershock decay rate Clement Narteau Equipe de Geomorphologie Laboratoire de Dynamique
186418 Ninth Workshop on Nonlinear Dynamics and Earthquake Predictions 1 13 October 2007 A limited powerlaw for the aftershock decay rate Clement Narteau Equipe de Geomorphologie Laboratoire de Dynamique
CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY. Earth Formation Plate Tectonics Sources of Earthquakes...
 CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY Earth Formation... 1-2 Plate Tectonics... 1-2 Sources of Earthquakes... 1-3 Earth Faults... 1-4 Fault Creep... 1-5 California Faults... 1-6 Earthquake
CHAPTER 1 BASIC SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE TERMINOLGY Earth Formation... 1-2 Plate Tectonics... 1-2 Sources of Earthquakes... 1-3 Earth Faults... 1-4 Fault Creep... 1-5 California Faults... 1-6 Earthquake
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
ALM: An Asperity-based Likelihood Model for California
 ALM: An Asperity-based Likelihood Model for California Stefan Wiemer and Danijel Schorlemmer Stefan Wiemer and Danijel Schorlemmer 1 ETH Zürich, Switzerland INTRODUCTION In most earthquake hazard models,
ALM: An Asperity-based Likelihood Model for California Stefan Wiemer and Danijel Schorlemmer Stefan Wiemer and Danijel Schorlemmer 1 ETH Zürich, Switzerland INTRODUCTION In most earthquake hazard models,
Short-Term Properties of Earthquake Catalogs and Models of Earthquake Source
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 4, pp. 1207 1228, August 2004 Short-Term Properties of Earthquake Catalogs and Models of Earthquake Source by Yan Y. Kagan Abstract I review
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 4, pp. 1207 1228, August 2004 Short-Term Properties of Earthquake Catalogs and Models of Earthquake Source by Yan Y. Kagan Abstract I review
State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault
 ELEVEN State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault Hirao Kanamori and Harold Magistrale NTRODUCTON Data from the Southern California Seismic Network have been extensively used to map spatial
ELEVEN State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault Hirao Kanamori and Harold Magistrale NTRODUCTON Data from the Southern California Seismic Network have been extensively used to map spatial
Foreshock Characteristics in Taiwan: Potential Earthquake Warning
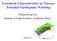 Foreshock Characteristics in Taiwan: Potential Earthquake Warning Cheng-Horng Lin Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica 2010/9/14 Outline Foreshocks and potential applications Previous foreshock
Foreshock Characteristics in Taiwan: Potential Earthquake Warning Cheng-Horng Lin Institute of Earth Sciences, Academia Sinica 2010/9/14 Outline Foreshocks and potential applications Previous foreshock
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group Plan for the San Andreas Fault System
 Introduction Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group Plan for the San Andreas Fault System This document puts forward a draft implementation plan for the San Andreas Fault component of the Plate Boundary
Introduction Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group Plan for the San Andreas Fault System This document puts forward a draft implementation plan for the San Andreas Fault component of the Plate Boundary
Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding
 Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area. Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC
 Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
The Role of Asperities in Aftershocks
 The Role of Asperities in Aftershocks James B. Silva Boston University April 7, 2016 Collaborators: William Klein, Harvey Gould Kang Liu, Nick Lubbers, Rashi Verma, Tyler Xuan Gu OUTLINE Introduction The
The Role of Asperities in Aftershocks James B. Silva Boston University April 7, 2016 Collaborators: William Klein, Harvey Gould Kang Liu, Nick Lubbers, Rashi Verma, Tyler Xuan Gu OUTLINE Introduction The
Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 85, No. 5, pp. 1513-1517, October 1995 Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications by
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 85, No. 5, pp. 1513-1517, October 1995 Rotation of the Principal Stress Directions Due to Earthquake Faulting and Its Seismological Implications by
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities
 Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Anomalous early aftershock decay rate of the 2004 Mw6.0 Parkfield, California, earthquake
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33,, doi:10.1029/2006gl026744, 2006 Anomalous early aftershock decay rate of the 2004 Mw6.0 Parkfield, California, earthquake Zhigang Peng, 1,2 John E. Vidale, 1 and
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33,, doi:10.1029/2006gl026744, 2006 Anomalous early aftershock decay rate of the 2004 Mw6.0 Parkfield, California, earthquake Zhigang Peng, 1,2 John E. Vidale, 1 and
Interactions and triggering in a 3-D rate-and-state asperity model
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 5 45, doi:1.1/jgrb.5187, 13 Interactions and triggering in a 3-D rate-and-state asperity model P. Dublanchet, 1 P. Bernard, 1 and P. Favreau 1 Received
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 5 45, doi:1.1/jgrb.5187, 13 Interactions and triggering in a 3-D rate-and-state asperity model P. Dublanchet, 1 P. Bernard, 1 and P. Favreau 1 Received
Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system
 Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system Slow slip in Upper Crust Aseismic creep, afterslip and spontaneous slow slip events on some faults in upper 15 km Mostly aseismic but accompanied by
Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system Slow slip in Upper Crust Aseismic creep, afterslip and spontaneous slow slip events on some faults in upper 15 km Mostly aseismic but accompanied by
Observational analysis of correlations between aftershock productivities and regional conditions in the context of a damage rheology model
 Geophys. J. Int. (2009) 177, 481 490 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04145.x FAST TRACK PAPER Observational analysis of correlations between aftershock productivities and regional conditions in the context
Geophys. J. Int. (2009) 177, 481 490 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2009.04145.x FAST TRACK PAPER Observational analysis of correlations between aftershock productivities and regional conditions in the context
Zhigang Peng. Curriculum Vitae. School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Phone: Georgia Institute of Technology Fax:
 Zhigang Peng Curriculum Vitae School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Phone: 404-894-0231 Georgia Institute of Technology Fax: 404-894-5638 Office: ES&T Building, Rm. 2256 Email: zhigang.peng@eas.gatech.edu
Zhigang Peng Curriculum Vitae School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Phone: 404-894-0231 Georgia Institute of Technology Fax: 404-894-5638 Office: ES&T Building, Rm. 2256 Email: zhigang.peng@eas.gatech.edu
Mechanical origin of aftershocks: Supplementary Information
 Mechanical origin of aftershocks: Supplementary Information E. Lippiello Department of Mathematics and Physics, Second University of Naples, Via Vivaldi 43, 81100 Caserta, Italy & Kavli Institute for Theoretical
Mechanical origin of aftershocks: Supplementary Information E. Lippiello Department of Mathematics and Physics, Second University of Naples, Via Vivaldi 43, 81100 Caserta, Italy & Kavli Institute for Theoretical
Automatic Moment Tensor Analyses, In-Situ Stress Estimation and Temporal Stress Changes at The Geysers EGS Demonstration Project
 PROCEEDINGS, 42nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 13-15, 2017 SGP-TR-212 Automatic Moment Tensor Analyses, In-Situ Stress Estimation and
PROCEEDINGS, 42nd Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, February 13-15, 2017 SGP-TR-212 Automatic Moment Tensor Analyses, In-Situ Stress Estimation and
Comprehensive analysis of earthquake source spectra and swarms in the Salton Trough, California
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008263, 2011 Comprehensive analysis of earthquake source spectra and swarms in the Salton Trough, California X. Chen 1 and P. M. Shearer 1
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008263, 2011 Comprehensive analysis of earthquake source spectra and swarms in the Salton Trough, California X. Chen 1 and P. M. Shearer 1
High-resolution image of Calaveras Fault seismicity
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B9, 2186, doi:10.1029/2001jb000633, 2002 High-resolution image of Calaveras Fault seismicity David P. Schaff, 1 Götz H. R. Bokelmann, and Gregory C. Beroza
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B9, 2186, doi:10.1029/2001jb000633, 2002 High-resolution image of Calaveras Fault seismicity David P. Schaff, 1 Götz H. R. Bokelmann, and Gregory C. Beroza
Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 2004 and 2005
 P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
P-168 Seismic Characteristics and Energy Release of Aftershock Sequences of Two Giant Sumatran Earthquakes of 004 and 005 R. K. Jaiswal*, Harish Naswa and Anoop Singh Oil and Natural Gas Corporation, Vadodara
arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003 arxiv:physics/ v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003](/thumbs/90/101580441.jpg) Is Earthquake Triggering Driven by Small Earthquakes? arxiv:physics/0210056v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003 Agnès Helmstetter Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, Observatoire de Grenoble,
Is Earthquake Triggering Driven by Small Earthquakes? arxiv:physics/0210056v2 [physics.geo-ph] 18 Aug 2003 Agnès Helmstetter Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, Observatoire de Grenoble,
Normal stress causes normal strain σ 22
 Normal stress causes normal strain blue box = before yellow box = after x 2 = Eɛ 22 ɛ 22 = E x 3 x 1 force is acting on the x2 face force is acting in the x2 direction Why do I draw this with equal stresses
Normal stress causes normal strain blue box = before yellow box = after x 2 = Eɛ 22 ɛ 22 = E x 3 x 1 force is acting on the x2 face force is acting in the x2 direction Why do I draw this with equal stresses
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Nontrivial Decay of Aftershock Density With Distance in Southern California. Javad Moradpour Taleshi A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Nontrivial Decay of Aftershock Density With Distance in Southern California by Javad Moradpour Taleshi A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Nontrivial Decay of Aftershock Density With Distance in Southern California by Javad Moradpour Taleshi A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Y. Y. Kagan and L. Knopoff Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90024, USA
 Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1987) 88, 723-731 Random stress and earthquake statistics: time dependence Y. Y. Kagan and L. Knopoff Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1987) 88, 723-731 Random stress and earthquake statistics: time dependence Y. Y. Kagan and L. Knopoff Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress?
 When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
Toward automatic aftershock forecasting in Japan
 Toward automatic aftershock forecasting in Japan T. Omi (The Univ. of Tokyo) Y. Ogata (ISM) K. Shiomi (NIED) B. Enescu (Tsukuba Univ.) K. Sawazaki (NIED) K. Aihara (The Univ. of Tokyo) @Statsei9 Forecasting
Toward automatic aftershock forecasting in Japan T. Omi (The Univ. of Tokyo) Y. Ogata (ISM) K. Shiomi (NIED) B. Enescu (Tsukuba Univ.) K. Sawazaki (NIED) K. Aihara (The Univ. of Tokyo) @Statsei9 Forecasting
High-resolution Time-independent Grid-based Forecast for M >= 5 Earthquakes in California
 High-resolution Time-independent Grid-based Forecast for M >= 5 Earthquakes in California A. Helmstetter, Yan Kagan, David Jackson To cite this version: A. Helmstetter, Yan Kagan, David Jackson. High-resolution
High-resolution Time-independent Grid-based Forecast for M >= 5 Earthquakes in California A. Helmstetter, Yan Kagan, David Jackson To cite this version: A. Helmstetter, Yan Kagan, David Jackson. High-resolution
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA
 Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Jack Loveless Department of Geosciences Smith College
 Geodetic constraints on fault interactions and stressing rates in southern California Jack Loveless Department of Geosciences Smith College jloveless@smith.edu Brendan Meade Department of Earth & Planetary
Geodetic constraints on fault interactions and stressing rates in southern California Jack Loveless Department of Geosciences Smith College jloveless@smith.edu Brendan Meade Department of Earth & Planetary
Gutenberg-Richter Relationship: Magnitude vs. frequency of occurrence
 Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
The largest aftershock: How strong, how far away, how delayed?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2011gl050604, 2012 The largest aftershock: How strong, how far away, how delayed? M. Tahir, 1 J.-R. Grasso, 1 and D. Amorèse 2 Received 15 December 2011;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2011gl050604, 2012 The largest aftershock: How strong, how far away, how delayed? M. Tahir, 1 J.-R. Grasso, 1 and D. Amorèse 2 Received 15 December 2011;
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (21) 183, 433 45 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.21.4745.x Quantifying focal mechanism heterogeneity for fault zones in central and southern California Iain W.
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (21) 183, 433 45 doi: 1.1111/j.1365-246X.21.4745.x Quantifying focal mechanism heterogeneity for fault zones in central and southern California Iain W.
Theory of earthquake recurrence times
 Theory of earthquake recurrence times Alex SAICHEV1,2 and Didier SORNETTE1,3 1ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2Mathematical Department, Nizhny Novgorod State University, Russia. 3Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
Theory of earthquake recurrence times Alex SAICHEV1,2 and Didier SORNETTE1,3 1ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2Mathematical Department, Nizhny Novgorod State University, Russia. 3Institute of Geophysics and Planetary
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures
 Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Slip on faults in the Imperial Valley triggered by the 4 April 2010 Mw 7.2 El Mayor Cucapah earthquake revealed by InSAR
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045235, 2011 Slip on faults in the Imperial Valley triggered by the 4 April 2010 Mw 7.2 El Mayor Cucapah earthquake revealed by InSAR Meng Wei,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045235, 2011 Slip on faults in the Imperial Valley triggered by the 4 April 2010 Mw 7.2 El Mayor Cucapah earthquake revealed by InSAR Meng Wei,
Rate and State Friction and the Modeling of Aseismic Slip
 Rate and State Friction and the Modeling of Aseismic Slip Hugo Perfettini 1,2 1 : Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) 2 : Institut des Sciences de la Terre (ISTerre) Characteristics of Afterslip
Rate and State Friction and the Modeling of Aseismic Slip Hugo Perfettini 1,2 1 : Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) 2 : Institut des Sciences de la Terre (ISTerre) Characteristics of Afterslip
Aftershock Sequences Modeled with 3-D Stress Heterogeneity and Rate-State Seismicity Equations: Implications for Crustal Stress Estimation
 Pure Appl. Geophys. 167 (2010), 1067 1085 Ó 2010 The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com DOI 10.1007/s00024-010-0093-1 Pure and Applied Geophysics Aftershock Sequences
Pure Appl. Geophys. 167 (2010), 1067 1085 Ó 2010 The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com DOI 10.1007/s00024-010-0093-1 Pure and Applied Geophysics Aftershock Sequences
13w2171: Statistics and Triggering of Earthquakes Aug 30 - Sep 1, 2013 MEALS
 13w2171: Statistics and Triggering of Earthquakes Aug 30 - Sep 1, 2013 MEALS Coffee Breaks: As per daily schedule, in the foyer of the TransCanada Pipeline Pavilion (TCPL) (included in workshop) **For
13w2171: Statistics and Triggering of Earthquakes Aug 30 - Sep 1, 2013 MEALS Coffee Breaks: As per daily schedule, in the foyer of the TransCanada Pipeline Pavilion (TCPL) (included in workshop) **For
Rheology III. Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep
 Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
The Centenary of the Omori Formula for a Decay Law of Aftershock Activity
 The Centenary of the Omori Formula for a Decay Law of Aftershock Activity Author; Tokuji Utsu, Yosihiko Ogata, and Ritsuko S. Matsu'ura Presentater; Okuda Takashi 8. p Values from Superposed Sequences
The Centenary of the Omori Formula for a Decay Law of Aftershock Activity Author; Tokuji Utsu, Yosihiko Ogata, and Ritsuko S. Matsu'ura Presentater; Okuda Takashi 8. p Values from Superposed Sequences
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard. Earthquake Environment
 Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Bayesian analysis of the modified Omori law
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL., XXXX, DOI:10.1029/2002JB001868, 1 Bayesian analysis of the modified Omori law M. Holschneider 2 3 Institute of Dynamics of Complex Systems (DYCOS) Universität Potsdam,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL., XXXX, DOI:10.1029/2002JB001868, 1 Bayesian analysis of the modified Omori law M. Holschneider 2 3 Institute of Dynamics of Complex Systems (DYCOS) Universität Potsdam,
Earthquake Clustering and Declustering
 Earthquake Clustering and Declustering Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley joint with (separately) Peter Shearer, SIO/IGPP, UCSD Brad Luen 4 October 2011 Institut de Physique du Globe
Earthquake Clustering and Declustering Philip B. Stark Department of Statistics, UC Berkeley joint with (separately) Peter Shearer, SIO/IGPP, UCSD Brad Luen 4 October 2011 Institut de Physique du Globe
Aging and scaling of aftershocks
 Aging and scaling of aftershocks Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University, Chiba
Aging and scaling of aftershocks Sumiyoshi Abe 1 and Norikazu Suzuki 2 1 Institute of Physics, University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8571, Japan 2 College of Science and Technology, Nihon University, Chiba
Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Page 1 of 5 Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An aftershock is a smaller earthquake that occurs after a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock. If an aftershock is
Page 1 of 5 Aftershock From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An aftershock is a smaller earthquake that occurs after a previous large earthquake, in the same area of the main shock. If an aftershock is
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
In geophysics there is increasing interest in modeling spatially nonuniform stress,
 Chapter 1. Introduction I-1 In geophysics there is increasing interest in modeling spatially nonuniform stress, i.e., spatially heterogeneous stress, on 2D planar faults as a means of explaining a variety
Chapter 1. Introduction I-1 In geophysics there is increasing interest in modeling spatially nonuniform stress, i.e., spatially heterogeneous stress, on 2D planar faults as a means of explaining a variety
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Abstract
 Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Acoustic emissions document stress changes over many seismic cycles in stick-slip experiments
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 2049 2054, doi:10.1002/grl.50507, 2013 Acoustic emissions document stress changes over many seismic cycles in stick-slip experiments T. H. W. Goebel, 1 D. Schorlemmer,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 2049 2054, doi:10.1002/grl.50507, 2013 Acoustic emissions document stress changes over many seismic cycles in stick-slip experiments T. H. W. Goebel, 1 D. Schorlemmer,
6 Source Characterization
 6 Source Characterization Source characterization describes the rate at which earthquakes of a given magnitude, and dimensions (length and width) occur at a given location. For each seismic source, the
6 Source Characterization Source characterization describes the rate at which earthquakes of a given magnitude, and dimensions (length and width) occur at a given location. For each seismic source, the
Fault Processes on the Anza section of the San Jacinto Fault
 Fault Processes on the nza section of the San Jacinto Fault J. Steidl (USB), M. Gladwin, R. Gwyther (SIRO ust.), F. Vernon (USD) SUMMRY We propose to instrument the nza slip gap and transition areas of
Fault Processes on the nza section of the San Jacinto Fault J. Steidl (USB), M. Gladwin, R. Gwyther (SIRO ust.), F. Vernon (USD) SUMMRY We propose to instrument the nza slip gap and transition areas of
arxiv:physics/ v1 6 Aug 2006
 The application of the modified form of Båth s law to the North Anatolian Fault Zone arxiv:physics/0608064 v1 6 Aug 2006 1. INTRODUCTION S E Yalcin, M L Kurnaz Department of Physics, Bogazici University,
The application of the modified form of Båth s law to the North Anatolian Fault Zone arxiv:physics/0608064 v1 6 Aug 2006 1. INTRODUCTION S E Yalcin, M L Kurnaz Department of Physics, Bogazici University,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1158 Characteristic Slip for 5 great earthquakes along the Fuyun fault in China. Klinger 1 Y., Etchebes 1 M., Tapponnier 2 P., and Narteau 1 C. 1 Institut de
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1158 Characteristic Slip for 5 great earthquakes along the Fuyun fault in China. Klinger 1 Y., Etchebes 1 M., Tapponnier 2 P., and Narteau 1 C. 1 Institut de
Integrating NASA Space Geodetic Observations with Numerical Simulations of a Changing Earth
 Integrating NASA Space Geodetic Observations with Numerical Simulations of a Changing Earth John B. Rundle (1), Louise H. Kellogg (2), Kristy F. Tiampo (3), William Klein (4) and Paul B. Rundle (5) (1)
Integrating NASA Space Geodetic Observations with Numerical Simulations of a Changing Earth John B. Rundle (1), Louise H. Kellogg (2), Kristy F. Tiampo (3), William Klein (4) and Paul B. Rundle (5) (1)
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
Elastic rebound theory
 Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source
 Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Special Publication 36 Empirical Green s Function Analysis of the Wells, Nevada, Earthquake Source by Mendoza, C. 1 and Hartzell S. 2 1 Centro de Geociencias, Universidad
Secondary Aftershocks and Their Importance for Aftershock Forecasting
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 93, No. 4, pp. 1433 1448, August 23 Secondary Aftershocks and Their Importance for Aftershock Forecasting by Karen R. Felzer, Rachel E. Abercrombie,
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 93, No. 4, pp. 1433 1448, August 23 Secondary Aftershocks and Their Importance for Aftershock Forecasting by Karen R. Felzer, Rachel E. Abercrombie,
Evolution of stress in Southern California for the past 200 years from coseismic, postseismic and interseismic stress changes
 Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 169, 1164 1179 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03391.x Evolution of stress in Southern California for the past 200 years from coseismic, postseismic and interseismic stress changes
Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 169, 1164 1179 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03391.x Evolution of stress in Southern California for the past 200 years from coseismic, postseismic and interseismic stress changes
Yusuke Mukuhira. Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics
 Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics Yusuke Mukuhira Postdoctoral Fellow (JSPS research fellow) Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
Integration of Induced Seismicity and Geomechanics For Better Understanding of Reservoir Physics Yusuke Mukuhira Postdoctoral Fellow (JSPS research fellow) Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary
2 June 15. Summer Session Horst Rademacher. Lect 3: California EQ. and Faults.
 2 June 15 2 Summer Session 2015 Horst Rademacher HH Lect 3: California EQ and Faults http://seismo.berkeley.edu/summersession/eps20/ Class Organization Website: You need to sign up for class announcements!
2 June 15 2 Summer Session 2015 Horst Rademacher HH Lect 3: California EQ and Faults http://seismo.berkeley.edu/summersession/eps20/ Class Organization Website: You need to sign up for class announcements!
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR
 A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
On rate-state and Coulomb failure models
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B4, PAGES 7857 7871, APRIL 10, 2000 On rate-state and Coulomb failure models J. Gomberg U.S. Geological Survey, Center for Earthquake Research and Information,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B4, PAGES 7857 7871, APRIL 10, 2000 On rate-state and Coulomb failure models J. Gomberg U.S. Geological Survey, Center for Earthquake Research and Information,
Regional Geodesy. Shimon Wdowinski. MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region. University of Miami
 MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications for aftershock rates
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
JCR (2 ), JGR- (1 ) (4 ) 11, EPSL GRL BSSA
 Dun Wang ( ) In collaboration with: Hitoshi Kawakatsu, Jim Mori, Kazuki Koketsu, Takuto Maeda, Hiroshi Tsuroka, Jiancang Zhunag, Lihua Fang, and Qiang Yao School of Geosciences, China University of Geosciences
Dun Wang ( ) In collaboration with: Hitoshi Kawakatsu, Jim Mori, Kazuki Koketsu, Takuto Maeda, Hiroshi Tsuroka, Jiancang Zhunag, Lihua Fang, and Qiang Yao School of Geosciences, China University of Geosciences
Long-range triggered earthquakes that continue after the wave train passes
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L15313, doi:10.1029/2006gl026605, 2006 Long-range triggered earthquakes that continue after the wave train passes Emily E. Brodsky 1 Received
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L15313, doi:10.1029/2006gl026605, 2006 Long-range triggered earthquakes that continue after the wave train passes Emily E. Brodsky 1 Received
What We Know (and don t know)
 What We Know (and don t know) about the M5.1 La Habra Earthquake Dr. Robert Graves U.S. Geological Survey In collaboration with: Dr. Egill Hauksson and Dr. Thomas Göbel Caltech Dr. Elizabeth Cochran U.S.
What We Know (and don t know) about the M5.1 La Habra Earthquake Dr. Robert Graves U.S. Geological Survey In collaboration with: Dr. Egill Hauksson and Dr. Thomas Göbel Caltech Dr. Elizabeth Cochran U.S.
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Separating Tectonic, Magmatic, Hydrological, and Landslide Signals in GPS Measurements near Lake Tahoe, Nevada-California
 Separating Tectonic, Magmatic, Hydrological, and Landslide Signals in GPS Measurements near Lake Tahoe, Nevada-California Geoffrey Blewitt, Corné Kreemer, William C. Hammond, & Hans-Peter Plag NV Geodetic
Separating Tectonic, Magmatic, Hydrological, and Landslide Signals in GPS Measurements near Lake Tahoe, Nevada-California Geoffrey Blewitt, Corné Kreemer, William C. Hammond, & Hans-Peter Plag NV Geodetic
Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere. Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University
 3D Viscoelastic Earthquake Cycle Models Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University In collaboration with:
3D Viscoelastic Earthquake Cycle Models Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University In collaboration with:
CHARACTERIZING EARTHQUAKE SLIP MODELS FOR THE PREDICTION OF STRONG GROUND MOTION
 CHARACTERIZING EARTHQUAKE SLIP MODELS FOR THE PREDICTION OF STRONG GROUND MOTION P G SOMERVILLE 1, K IRIKURA, N ABRAHAMSON 3, S SAWADA 4, T KAGAWA 5 And Y TATSUMI 6 SUMMARY Over the past fifteen years,
CHARACTERIZING EARTHQUAKE SLIP MODELS FOR THE PREDICTION OF STRONG GROUND MOTION P G SOMERVILLE 1, K IRIKURA, N ABRAHAMSON 3, S SAWADA 4, T KAGAWA 5 And Y TATSUMI 6 SUMMARY Over the past fifteen years,
log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =
![log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) = log (N) 2.9<M< <M< <M< <M<4.9 tot in bin [N] = Mid Point M log (N) =](/thumbs/92/109466632.jpg) Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
Solution Set for Assignment Exercise : Gutenberg-Richter relationship: log() = a + b. M A) For a time period between January, 90 to December 3, 998 tot in bin [] = 450 6 57 22 7 5 Mid Point M 3.5 3.65
Variations in Tremor Activity and Implications for Lower Crustal Deformation Along the Central San Andreas Fault
 Variations in Tremor Activity and Implications for Lower Crustal Deformation Along the Central San Andreas Fault David R. Shelly USGS, Menlo Park Shelly and Hardebeck, GRL, 2010 Collaborators: Jeanne Hardebeck
Variations in Tremor Activity and Implications for Lower Crustal Deformation Along the Central San Andreas Fault David R. Shelly USGS, Menlo Park Shelly and Hardebeck, GRL, 2010 Collaborators: Jeanne Hardebeck
Earthquake Tectonics and Hazards on the Continents June Recognizing and characterizing strike-slip faults and earthquakes in USA
 2464-4 Earthquake Tectonics and Hazards on the Continents 17-28 June 2013 Recognizing and characterizing strike-slip faults and earthquakes in USA S. G. Wesnousky Univ. of Nevada USA Strike-slip Faults
2464-4 Earthquake Tectonics and Hazards on the Continents 17-28 June 2013 Recognizing and characterizing strike-slip faults and earthquakes in USA S. G. Wesnousky Univ. of Nevada USA Strike-slip Faults
San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model
 San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model Steven N. Ward Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA,
San Francisco Bay Area Earthquake Simulations: A step toward a Standard Physical Earthquake Model Steven N. Ward Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 102, NO. Bll, PAGES 24,411-24,435, NOVEMBER 10, 1997
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 102, NO. Bll, PAGES 24,411-24,435, NOVEMBER 10, 1997 Stress evolution in southern California and triggering of moderate-, small-, and micro-size earthquakes Jishu
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 102, NO. Bll, PAGES 24,411-24,435, NOVEMBER 10, 1997 Stress evolution in southern California and triggering of moderate-, small-, and micro-size earthquakes Jishu
