Fermentis Active Dry Yeast B R E W E R Y R E S O U R C E R O A D S H O W / 1 6 TH F E B. 2017
|
|
|
- Peregrine Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fermentis Active Dry Yeast B R E W E R Y R E S O U R C E R O A D S H O W / 1 6 TH F E B. 2017
2 PLAN 1.Lesaffre/ Fermentis 2.What is active dry yeast? 3.How to use dry yeast? 4.Fermentation kinetics 5.Characteristics at the end of fermentation 6.Aromatic profile
3 PLAN 1.Lesaffre/ Fermentis 2.What is active dry yeast? 3.How to use dry yeast? 4.Fermentation kinetics 5.Characteristics at the end of fermentation 6.Aromatic profile
4 1. LESAFFRE / FERMENTI S M O R E T H A N 160 Y E A R S OF H I S T O R Y 1853: Louis Lesaffre & Louis Bonduelle grain alcohol and gin plant in Marquette-lez-Lille (North of France). 1863: They purchase a mill in Marcqen-Barœul, converted into a grain alcohol distillery (Our SIL plant today) 39-45: the distill plant is destroyed. After the 2nd world war new plant of yeast New development
5 1. LESAFFRE / FERMENTI S F E R M E N T I S, PA R T O F L E S A F F R E
6 1. LESAFFRE / FERMENTI S V I E W OF O U R P R O D U C T I O N P L A N T I N G E N T ( B E L G I U M )
7 1. LESAFFRE / FERMENTI S F E R M E N T I S I N F E W W O R D S Fermentis is the business unit of Lesaffre in charge of the development and sales of innovative products and services for beer, wine, spirits and potable ethanol. Our mission: Create & deliver innovative and dependable ferments and derivatives offering sustainable technical solutions.
8 PLAN 1.Lesaffre/ Fermentis 2.What is active dry yeast? 3.How to use dry yeast? 4.Fermentation kinetics 5.Characteristics at the end of fermentation 6.Aromatic profile
9 2. WHAT IS ACTIVE DRY YEAST? YEAST, A L I V I N G T R E A S U R E! Yeast is a fragile, living organism: we do not manufacture yeast. We grow it. This microscopic fungus is no larger than 6 to 8 thousandths of a millimeter in size, yet has exceptional fermentation characteristics. The most well-known yeast is Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In the presence of air and nutrients introduced into the fermenter, yeast multiplies (yeast propagation). In the absence of air, it produces alcohol, gas and aromas. Yeast can be used for a variety of purposes: Producing fermented drinks Making bread dough rise Improving the well-being of people, animals and plants Producing bioethanol and new green chemistry products Yeast cell in division, as seen under a microscope Diagram of a yeast cell
10 Dry yeast production: Global view of the process Tube Carlsberg x100 grammes Pre-fermentation x100 kg First gen. x1 tonne 2 nd Gen. x10 tonnes Fermentis 2017 All rights reserved
11 2. WHAT IS ACTIVE DRY YEAST? A C T I V E D R Y YEAST P R O D U C T I O N After drying: Active dry yeast present themselves as small particles. They are vacuum-packed to preserve them from oxygen and moisture. Productions are released based on specific & strict quality tests (purity, composition, ageing, properties). They have a 3 years shelf life from production date.
12 Gx WHAT IS ACTIVE DRY YEAST? O B S E R VAT I O N O F T H E YEAST C E L L Before drying After drying 25-30% dry matter Smooth surface 94-96,5% dry matter Uneven surface
13 PLAN 1.Lesaffre/ Fermentis 2.What is active dry yeast? 3.How to use dry yeast? 4.Fermentation kinetics 5.Characteristics at the end of fermentation 6.Aromatic profile
14 3. HOW TO USE DRY YEAST? Malt R A W M AT E R I A L S Hops Boiling Yeast Fermentation & maturation Lager yeasts Objective of population : > 7 6 cells / ml Pitching rate: g/hl Ale yeasts Objective of population : >3 6 cells / ml Pitching rate: 50 80g/hl S a f L a g e r S - 2 3, S e t W / 7 0 S a f A l e S - 0 4, K - 9 7, U S - 0 5, W B - 0 6, S - 3 3, T - 5 8, B E
15 3. HOW TO USE DRY YEAST? R E H Y D R AT I O N B E F O R E P I T C H I N G Temperature of rehydration Ale C Lager C Sprinkle the yeast on liquid surface Gently stir Wait 30mn Pitch into the fermentation vessel 15
16 3. HOW TO USE DRY YEAST? T I M E B E F O R E P I T C H I N G Temperature after rehydration and before pitching Maximum waiting time 4 C 18 h 20 C 6 h 25 C 4 h Valid for any type of dry yeast rehydrated 16
17 3. HOW TO USE DRY YEAST? D I R E C T P I T C H I N G 1/ Fill the tank with wort at C (depending on strain) 2/ Pitch the yeast straight into the wort 3/ Complete the tank with wort at fermentation temperature 17
18 3. HOW TO USE DRY YEAST? A N A D A P T E D O F F E R F O R E A C H S C A L E Home brewer Craft brewer Industrial brewer Sachets of 11,5g Sachets of 500g Boxes of 10kg 18
19 3. HOW TO USE DRY YEAST? B E N E F I T S F O R T H E B R E W E R E A S Y T O S O U R C E Low weight & volume Often sent with malt, hops, and brewing ingredients No need for refrigerated transport Short lead-time, no delay in receiving yeast E A S Y T O S T O R E No loss in viability with a storage at low temperature (<10 C, fridge or maturation room) 3 years shelf life Opportunity for a security stock, independence EASY TO USE No need for lab equipment Easier planning: ready to pitch within 30 minutes Flexibility: immediate switch from one strain to another Wide range available for all types of beers RELIABLE, CONSISTENT Accurate conversion of dry matter weight into yeast cell count Guaranteed microbial quality Avoid failed propagation Fast fermentation start Better consistency than fresh yeast 19
20 3. HOW TO USE DRY YEAST? C O S T S AV O I D E D W I T H D R Y YEAST Y E A S T B A N K M A N A G E M E N T P R O P A G A T I O N L A B O R A T O R Y P R O P A G A T I O N C O S T S Consommables (air stérile, vapeur, refroidissement, electricité, CIP additionnel ) Labour Maintenance Quality control Production materials F A I L E D F E R M E N T A T I O N / P R O P A G A T I O N 20
21 PLAN 1.Lesaffre/ Fermentis 2.What is active dry yeast? 3.How to use dry yeast? 4.Fermentation kinetics 5.Characteristics at the end of fermentation 6.Aromatic profile
22 4. FERMENTA TION KINETICS P R O T O C O L EBC tubes Initial gravity: 18 P Temperature: 20 C for Ales 12 C for Lagers for 48h, then 14 C
23 % assimilated sugars 4. FERMENTA TION KINETICS V E R Y D I F F E R E N T K I N E T I C S OF F E R M E N TAT I O N 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Time (Days) S23 18 S W34/70 18 S04 18 US05 18 K97 18 T58 18 S33 18 WB06 Lager Ale
24 PLAN 1.Lesaffre/ Fermentis 2.What is active dry yeast? 3.How to use dry yeast? 4.Fermentation kinetics 5.Characteristics at the end of fermentation 6.Aromatic profile
25 5. CHARACTERIS TICS AT THE END OF FERMENTATIO N E N D O F F E R M E N TAT I O N R E S I D U A L S U G A R S ( M A L T O T R I O S E ) Apparent fermentation degree and attenuation Residual maltotriose Function of the yeast strain Function of the initial gravity F I N A L E T H A N O L What is the maximum level of ethanol produced? Function of the yeast strain Function of the initial gravity F L O C U L AT I O N - S E D I M E N TAT I O N
26 5. CHARACTERIS TICS AT THE END OF FERMENTATIO N D I F F E R E N T S U G A R S Maltotriose Glucose Maltose Melibiose
27 SafLager SafAle 5. CHARACTERIS TICS AT THE END OF FERMENTATIO N S U G A R S C O N S U M P T I O N WB-06 BE-256 K-97 US-05 S-04 T-58 S-33 W-34/70 S-189 S Residual Maltotriose (g/l)
28 W34/70 S23 S189 K97 US05 S04 WB06 S33 T58 Abbaye 5. CHARACTERIS TICS AT THE END OF FERMENTATIO N A P PA R E N T AT T E N U AT I O N 90% Attenuation (%) 85% 80% 75% 70% 65% 60% Saflager Safale Safbrew
29 W34/70 S23 S189 K97 US05 S04 WB06 S33 T58 B E Abbaye 5. CHARACTERIS TICS AT THE END OF FERMENTATIO N A L C O H O L T O L E R A N C E Maximum Alcohol achieved in the trials (EBC Tubes) Saflager Safale Safbrew
30 5. CHARACTERIS TICS AT THE END OF FERMENTATIO N F I N A L E T H A N O L C O N T E N T D E P E N D S O N : T H E I N I T I A L G R AV I T Y H Y D R O LY S I S ( Q U A L I T Y O F T H E M A LT, D I A G R A M O F M A S H I N G, E N Z Y M AT I C A C T I V I T Y ) T H E Y E A S T ( S T R A I N, N U T R I T I O N ) O T H E R F A C T O R S ( C O N TA M I N AT I O N S, E T C. )
31 5. CHARACTERIS TICS AT THE END OF FERMENTATIO N S E D I M E N TAT I O N SPEED K-97 WB-06 T-58 S-33 S-23 S-189 W-34/70 US-05 BE-256 S-04
32 PLAN 1.Lesaffre/ Fermentis 2.What is active dry yeast? 3.How to use dry yeast? 4.Fermentation kinetics 5.Characteristics at the end of fermentation 6.Aromatic profile
33 6. AROMATIC PROFILE E X T R A C T I O N & D E T E C T I O N O F V O L AT I L E S C O M P O U N D S Separation of volatile compounds by gaz chromatography Simultaneous detection of volatile compounds by mass spectrometry and by human nose 33
34 W34/70 S23 S189 K97 US05 S04 WB06 S33 T58 W34/70 S23 S189 K97 US05 S04 WB06 S33 T58 6. AROMATIC PROFILE V O L AT I L E M O L E C U L E S Total Esters (ppm) = Ethylacetate + Isoamylacetate Total Higher Alcohols (ppm) = Propanol + Isobutanol + Isoamylalcohol Saflager Safale Safbrew Saflager Safale Safbrew Acetaldehydes (ppm) W34/70 S23 S189 K97 US05 S04 WB06 S33 T58 Saflager Safale Safbrew
35 CONCLUSI ON YEAST IS A KEY MICROORGANISM FOR FERMENTED BEVERAGES DIVERSITY, WATER, MALT, HOP, YEAST AND BREWER ARE UNIQUE, Experiment!
36 To know more about our products and services: fermentis.com Thanks for your attention! Fermentis.c om
Chemical Processes Part 1: Intro and Chemistry Basics
 Chemical Processes Part 1: Intro and Chemistry Basics How are chemistry and chemical engineering different? Chemists Small batches Determine reactions to make new compounds in test tubes Prepare and conduct
Chemical Processes Part 1: Intro and Chemistry Basics How are chemistry and chemical engineering different? Chemists Small batches Determine reactions to make new compounds in test tubes Prepare and conduct
Fast and effective. quality monitoring for breweries. Thermo Scientific Gallery Plus Beermaster
 Thermo Scientific Gallery Plus Beermaster Fast and effective quality monitoring for breweries Colorimetric beer, wort and malt analysis Automated bitterness analysis Thermo Scientific Gallery Plus Beermaster
Thermo Scientific Gallery Plus Beermaster Fast and effective quality monitoring for breweries Colorimetric beer, wort and malt analysis Automated bitterness analysis Thermo Scientific Gallery Plus Beermaster
1 What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen. oxygen only. steam. yeast
 What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen oxygen only steam yeast 2 Which term describes the formation of ethanol from glucose? cracking distillation polymerisation 3 Which
What is used in the production of ethanol from ethene? hydrogen and oxygen oxygen only steam yeast 2 Which term describes the formation of ethanol from glucose? cracking distillation polymerisation 3 Which
Some Families of Organic Compounds HL
 Name: Organic Chemistry 22. Some Families of Organic Compounds Objectives -define tetrahedral carbon -explain what is meant by the term alcohol -describe the alcohols as a homologous series of organic
Name: Organic Chemistry 22. Some Families of Organic Compounds Objectives -define tetrahedral carbon -explain what is meant by the term alcohol -describe the alcohols as a homologous series of organic
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) TOPIC 1: EXPERIMENTAL CHEMISTRY 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) TOPIC 1: EXPERIMENTAL CHEMISTRY
 5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) TOPIC 1: EXPERIMENTAL CHEMISTRY 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) TOPIC 1: EXPERIMENTAL CHEMISTRY SUB-TOPIC 1.2 METHODS OF PURIFICATION AND ANALYSIS LEARNING
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) TOPIC 1: EXPERIMENTAL CHEMISTRY 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) TOPIC 1: EXPERIMENTAL CHEMISTRY SUB-TOPIC 1.2 METHODS OF PURIFICATION AND ANALYSIS LEARNING
Lecture 29.Manufacture of Ethanol from Molasses
 Lecture 29.Manufacture of Ethanol from Molasses 29.1 Introduction Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, clear, colourless liquid. Ethanol is a good solvent. It is also used as a germicide, beverage, antifreeze,
Lecture 29.Manufacture of Ethanol from Molasses 29.1 Introduction Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, clear, colourless liquid. Ethanol is a good solvent. It is also used as a germicide, beverage, antifreeze,
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based
 Distillation Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in their volatilities in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process,
Distillation Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in their volatilities in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process,
Chapter 10 Organic Reactions
 Chapter 0 Organic Reactions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 85 marks Comments: Page of 32 This question is about organic compounds. (a) Ethanol burns in air. Use the correct answer from the
Chapter 0 Organic Reactions Name: Class: Date: Time: 85 minutes Marks: 85 marks Comments: Page of 32 This question is about organic compounds. (a) Ethanol burns in air. Use the correct answer from the
Part 4- Biology Paper 1 Bioenergetics Application Questions
 Part 4- Biology Paper 1 Bioenergetics Application Questions AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.4 Bioenergetics Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what happens in photosynthesis, including using
Part 4- Biology Paper 1 Bioenergetics Application Questions AQA Biology (8461) from 2016 Topic B4.4 Bioenergetics Topic Student Checklist R A G Describe what happens in photosynthesis, including using
SEC. Interpretation Guide. Select E. coli Count Plate
 Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm Select E. coli Count Plate is a sample-ready-culture medium system which contains selective agents, nutrients, a cold-water-soluble gelling agent, and an indicator
Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm Select E. coli Count Plate is a sample-ready-culture medium system which contains selective agents, nutrients, a cold-water-soluble gelling agent, and an indicator
LGC Standards Proficiency Testing Technical Changes January Start Schemes 2016
 FOOD and FEED PT Schemes AFPS (Animal Feeds) Scheme 2016 Two new microbiological samples for 2016: Sample 11 for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria species Sample 12 for the detection
FOOD and FEED PT Schemes AFPS (Animal Feeds) Scheme 2016 Two new microbiological samples for 2016: Sample 11 for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria species Sample 12 for the detection
DAPS. Scheme Description. Alcoholic Drinks Proficiency Testing Scheme
 DAPS Alcoholic Drinks Proficiency Testing Scheme Scheme Description LGC Standards Proficiency Testing 1 Chamberhall Business Park Chamberhall Green Bury, BL9 0AP UK. Telephone: +44 (0) 161 762 2500 Fax:
DAPS Alcoholic Drinks Proficiency Testing Scheme Scheme Description LGC Standards Proficiency Testing 1 Chamberhall Business Park Chamberhall Green Bury, BL9 0AP UK. Telephone: +44 (0) 161 762 2500 Fax:
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 4: Cellular Physiology
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 4: Cellular Physiology NC Essential Standard: 1.2.1 Explain how homeostasis is maintained in a cell and within an organism in various environments
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 4: Cellular Physiology NC Essential Standard: 1.2.1 Explain how homeostasis is maintained in a cell and within an organism in various environments
5A Order Among Cells. 5B Cellular Respiration
 Life Science Chapter 5 Activities of Cells 5A Order Among Cells unicellular the cells survive by themselves (example paramecium) Multicellular organisms divide the functions they need to perform among
Life Science Chapter 5 Activities of Cells 5A Order Among Cells unicellular the cells survive by themselves (example paramecium) Multicellular organisms divide the functions they need to perform among
Chemical Analysis. Low Level Oxygenates Analyzer. Trace Analysis of Oxygenates in Hydrocarbon Matrices. Gas Chromatography.
 Chemical Analysis Low Level Oxygenates Analyzer Trace Analysis of Oxygenates in Hydrocarbon Matrices think forward Gas Chromatography The determination of sub to high ppm levels of ethers, alcohols, aldehydes
Chemical Analysis Low Level Oxygenates Analyzer Trace Analysis of Oxygenates in Hydrocarbon Matrices think forward Gas Chromatography The determination of sub to high ppm levels of ethers, alcohols, aldehydes
Chapter 3: Chemical Reactions and the Earth s Composition
 Chapter 3: Chemical Reactions and the Earth s Composition Problems: 3.1-3.3, 3.5, 3.11-3.86, 3.95-3.115, 3.119-3.120, 3.122, 3.125-3.128, 3.132, 3.134, 3.136-3.138-3.141 3.2 The Mole Stoichiometry (STOY-key-OM-e-tree):
Chapter 3: Chemical Reactions and the Earth s Composition Problems: 3.1-3.3, 3.5, 3.11-3.86, 3.95-3.115, 3.119-3.120, 3.122, 3.125-3.128, 3.132, 3.134, 3.136-3.138-3.141 3.2 The Mole Stoichiometry (STOY-key-OM-e-tree):
Which farm is likely to have been using too much fertiliser on its land? farm C. farm B
 1 What is produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast? lactic acid carbon dioxide 2 What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants? carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen glucose + carbon
1 What is produced by anaerobic respiration in yeast? lactic acid carbon dioxide 2 What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants? carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen glucose + carbon
Bindzil for the beverage industry. Colloidal silica dispersions uses and benefits
 Bindzil for the beverage industry Colloidal silica dispersions uses and benefits Colloidal silica dispersions for beverage clarification Colloidal silica is used as a flocculation agent for wine and fruit
Bindzil for the beverage industry Colloidal silica dispersions uses and benefits Colloidal silica dispersions for beverage clarification Colloidal silica is used as a flocculation agent for wine and fruit
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.28-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE GB PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.28-2016
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.28-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE GB PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.28-2016
Recipe detail information
 Magic Bonito Yield 1 batches Ingredients (1 batches) Amount Measure Name Price Bahan (Ingredients); IDR 0.00 * 350.00 g High Protein Flour IDR 0.00 * g 150.00 g Medium Protein Flour IDR 0.00 * g 100.00
Magic Bonito Yield 1 batches Ingredients (1 batches) Amount Measure Name Price Bahan (Ingredients); IDR 0.00 * 350.00 g High Protein Flour IDR 0.00 * g 150.00 g Medium Protein Flour IDR 0.00 * g 100.00
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
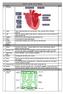 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
MISSION STATEMENT. The PNRI contributes to the improvement of the quality of Filipino life through the
 Our Organization Our Organization MISSION STATEMENT The PNRI contributes to the improvement of the quality of Filipino life through the highest standards of nuclear research and development, specialized
Our Organization Our Organization MISSION STATEMENT The PNRI contributes to the improvement of the quality of Filipino life through the highest standards of nuclear research and development, specialized
Laboratory Techniques for Small Distilleries
 2009 TTB Expo Presentation Laboratory Techniques for Small Distilleries Presented by Norma R. Hill Scientific Services Division Overview Basic Assumptions: Target audience Basic terminology Analytical
2009 TTB Expo Presentation Laboratory Techniques for Small Distilleries Presented by Norma R. Hill Scientific Services Division Overview Basic Assumptions: Target audience Basic terminology Analytical
Principles of Thin Layer Chromatography
 REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #113 Principles of Thin Layer Chromatography Experiment Objective: The objective of this experiment is to gain an understanding of the theory and methods of thin layer chromatography.
REVISED & UPDATED Edvo-Kit #113 Principles of Thin Layer Chromatography Experiment Objective: The objective of this experiment is to gain an understanding of the theory and methods of thin layer chromatography.
Science at the University of Auckland. Presented by igem
 Science at the University of Auckland Presented by igem Who are we? First of all Collecting Samples Why collect samples? Any ideas? To learn more about what you are studying To diagnose illnesses To collect
Science at the University of Auckland Presented by igem Who are we? First of all Collecting Samples Why collect samples? Any ideas? To learn more about what you are studying To diagnose illnesses To collect
Anethole. Gas chromatograhpy determination of trans-anethole in Spirit srinks of viti-vinicultural origin
 OIVMABS15 Anethole. Gas chromatograhpy determination of transanethole in Type II method SCOPE This method is suitable for the determination of transanethole in aniseedflavoured spirit drinks using capillary
OIVMABS15 Anethole. Gas chromatograhpy determination of transanethole in Type II method SCOPE This method is suitable for the determination of transanethole in aniseedflavoured spirit drinks using capillary
Fractional Distillation of Biosynthesized Ethanol (#2)
 Fractional Distillation of Biosynthesized Ethanol (#2) Reference Williamson, K.L.; Minard, R.; Masters, K.M. Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments, 5 th Ed. ougton Mifflin Co.: Boston, 2007, p
Fractional Distillation of Biosynthesized Ethanol (#2) Reference Williamson, K.L.; Minard, R.; Masters, K.M. Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments, 5 th Ed. ougton Mifflin Co.: Boston, 2007, p
ATP, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
 ATP, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Energy for Cells Free Energy: the energy available to do work Types of Reactions Endergonic Reactions: require an input of energy Exergonic Reactions: release
ATP, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Energy for Cells Free Energy: the energy available to do work Types of Reactions Endergonic Reactions: require an input of energy Exergonic Reactions: release
Preparation of an Ester Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin)
 Preparation of an Ester Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) BJECTIVE: To become familiar with the techniques and principle of esterification. DISCUSSIN: Aspirin is a drug widely used as an antipyretic agent
Preparation of an Ester Acetylsalicylic Acid (Aspirin) BJECTIVE: To become familiar with the techniques and principle of esterification. DISCUSSIN: Aspirin is a drug widely used as an antipyretic agent
A- Determination Of Boiling point B- Distillation
 EXP. NO. 2 A- Determination Of Boiling point B- Distillation The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. The normal boiling
EXP. NO. 2 A- Determination Of Boiling point B- Distillation The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. The normal boiling
Interpretation Guide. Aerobic Count Plate
 Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm is a ready-made culture medium system that contains modified Standard Methods nutrients, a cold-water-soluble gelling agent and an indicator that facilitates colony
Interpretation Guide The 3M Petrifilm is a ready-made culture medium system that contains modified Standard Methods nutrients, a cold-water-soluble gelling agent and an indicator that facilitates colony
Chapter 4: Energy From the sun to you in two easy steps
 Chapter 4: Energy From the sun to you in two easy steps Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Understand and be able to explain the following: How energy flows from
Chapter 4: Energy From the sun to you in two easy steps Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Understand and be able to explain the following: How energy flows from
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy. Name: Teacher: Hour:
 Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy Name: Teacher: Hour: 1 Unit: Cell Processes and Energy Unit Completion Date: Vocabulary and Big Ideas Photosynthesis photosynthesis autotroph heterotroph chlorophyll
Chapter 3 Cell Processes and Energy Name: Teacher: Hour: 1 Unit: Cell Processes and Energy Unit Completion Date: Vocabulary and Big Ideas Photosynthesis photosynthesis autotroph heterotroph chlorophyll
Measure, what is measurable, and make measurable that which is not. Galileo Galilei ( ) Portfolio
 Measure, what is measurable, and make measurable that which is not. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Portfolio 1 Polarimetry High-precision, reliable polarimeters for concentration measurements of optically
Measure, what is measurable, and make measurable that which is not. Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Portfolio 1 Polarimetry High-precision, reliable polarimeters for concentration measurements of optically
Organic Chemistry. Alkanes are hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds.
 Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
Organic Chemistry Organic compounds: The branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon compounds is called organic chemistry. Catenation: The carbon atom has a property to undergo self linking
Best-in-class API / HPAPI / Small Molecules Custom Manufacturing
 Best-in-class API / HPAPI / Small Molecules Custom Manufacturing Six production locations countless options. USA: TIPPECANOE World s largest HPAPI capacity Four cgmp plants and pilot plant, 140 vessels,
Best-in-class API / HPAPI / Small Molecules Custom Manufacturing Six production locations countless options. USA: TIPPECANOE World s largest HPAPI capacity Four cgmp plants and pilot plant, 140 vessels,
AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri. Chapter 4 Stoichiometry and MB with Reactions
 AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri Chapter 4 Stoichiometry and MB with Reactions Stoichiometry Stoichiometry provides a quantitative means of relating the amount of
AE 205 Materials and Energy Balances Asst. Prof. Dr. Tippabust Eksangsri Chapter 4 Stoichiometry and MB with Reactions Stoichiometry Stoichiometry provides a quantitative means of relating the amount of
Designed polymers for purification of flavor oils
 Designed polymers for purification of flavor oils IFEAT Conference 2014 Rome, September 23, 2014 Ecevit Yilmaz, PhD Global Product Manager Industrial Resins MIP Technologies AB a subsidiary of Biotage
Designed polymers for purification of flavor oils IFEAT Conference 2014 Rome, September 23, 2014 Ecevit Yilmaz, PhD Global Product Manager Industrial Resins MIP Technologies AB a subsidiary of Biotage
STATE OF COLORADO DESIGN CRITERIA FOR POTABLE WATER SYSTEMS WATER QUALITY CONTROL DIVISION. Price: $5.00. Revised March 31, 1997
 STATE OF COLORADO DESIGN CRITERIA FOR POTABLE WATER SYSTEMS WATER QUALITY CONTROL DIVISION Revised March 31, 1997 Price: $5.00 a. an arrangement where the water pipe to be injected with chlorine enters
STATE OF COLORADO DESIGN CRITERIA FOR POTABLE WATER SYSTEMS WATER QUALITY CONTROL DIVISION Revised March 31, 1997 Price: $5.00 a. an arrangement where the water pipe to be injected with chlorine enters
Adding these quantities together gives the total kilogram moles.
 Adding these quantities together gives the total kilogram moles. Example 14 In normal living cells, the nitrogen requirement for the cells is provided from protein metabolism (i.e., consumption of the
Adding these quantities together gives the total kilogram moles. Example 14 In normal living cells, the nitrogen requirement for the cells is provided from protein metabolism (i.e., consumption of the
Annex 2. Healthy Living Guarantee Mark. Food criteria
 Annex 2 Healthy Living Guarantee Mark Food criteria Croatian Institute of Public Health Zagreb, July 2016 2 General criteria for all foodstuffs 1 The basis for setting criteria for more appropriate selection
Annex 2 Healthy Living Guarantee Mark Food criteria Croatian Institute of Public Health Zagreb, July 2016 2 General criteria for all foodstuffs 1 The basis for setting criteria for more appropriate selection
Distillation. Boiling
 Distillation The most important technique for separating and purifying organic liquids is distillation 21. A gross oversimplification of the technique is this: the impure liquid in one vessel is vaporized,
Distillation The most important technique for separating and purifying organic liquids is distillation 21. A gross oversimplification of the technique is this: the impure liquid in one vessel is vaporized,
GLUTEN RAPID KIT. Product: GLTN Lateral Flow Devices for Qualitative Analysis of Gluten Proteins. Storage at 4-8 C (35-45 F)
 GLUTEN RAPID KIT Lateral Flow Devices for Qualitative Analysis of Gluten Proteins Product: GLTN-1005 Storage at 4-8 C (35-45 F) UPDATED FEBRUARY 2013 Gluten Rapid LFD Analysis Note: This kit format has
GLUTEN RAPID KIT Lateral Flow Devices for Qualitative Analysis of Gluten Proteins Product: GLTN-1005 Storage at 4-8 C (35-45 F) UPDATED FEBRUARY 2013 Gluten Rapid LFD Analysis Note: This kit format has
HPLC Columns. STANDARD Pullulan P-82 MANUAL. Shodex HPLC Columns Europe, Middle East, Africa, Russia
 HPLC Columns MANUAL STANDARD Pullulan P-82 Shodex HPLC Columns Europe, Middle East, Africa, Russia For technical support please use contact details shown below: SHOWA DENKO EUROPE GmbH Shodex Business
HPLC Columns MANUAL STANDARD Pullulan P-82 Shodex HPLC Columns Europe, Middle East, Africa, Russia For technical support please use contact details shown below: SHOWA DENKO EUROPE GmbH Shodex Business
Determination of Reducing Sugar Content: Clinitest, Benedict s Solution and the Rebelein Titration
 Determination of Reducing Sugar Content: Clinitest, Benedict s Solution and the Rebelein Titration Chemical Concepts and Techniques: The most important sugars present in wine and fruit juice are the hexoses
Determination of Reducing Sugar Content: Clinitest, Benedict s Solution and the Rebelein Titration Chemical Concepts and Techniques: The most important sugars present in wine and fruit juice are the hexoses
The Extraction of Lactic acid from Maize (Zea may)
 International Journal of Material Science Innovations (IJMSI) 2(3): 47-51, 2014 ISSN 2289-4063 Academic Research Online Publisher Research Article The Extraction of Lactic acid from Maize (Zea may) Mahmud
International Journal of Material Science Innovations (IJMSI) 2(3): 47-51, 2014 ISSN 2289-4063 Academic Research Online Publisher Research Article The Extraction of Lactic acid from Maize (Zea may) Mahmud
Aspirin Lab By Maya Parks Partner: Ben Seufert 6/5/15, 6/8/15
 Aspirin Lab By Maya Parks Partner: Ben Seufert 6/5/15, 6/8/15 Abstract: This lab was performed to synthesize acetyl salicylic acid or aspirin from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. We had learned in class
Aspirin Lab By Maya Parks Partner: Ben Seufert 6/5/15, 6/8/15 Abstract: This lab was performed to synthesize acetyl salicylic acid or aspirin from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. We had learned in class
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
Biofuels Series. Application Note 301LS RAPID MEASUREMENT OF XYLOSE AND GLUCOSE MONITORING CORN STOVER FERMENTATION IN BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION
 Biofuels Series RAPID MEASUREMENT OF XYLOSE AND GLUCOSE MONITORING CORN STOVER FERMENTATION IN BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION Application Note 31LS Rapid Measurement of Xylose and Glucose Monitoring Corn Stover
Biofuels Series RAPID MEASUREMENT OF XYLOSE AND GLUCOSE MONITORING CORN STOVER FERMENTATION IN BIOETHANOL PRODUCTION Application Note 31LS Rapid Measurement of Xylose and Glucose Monitoring Corn Stover
Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide
 Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide A. Introduction 1. All living things need energy for metabolism. a. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis; break down glucose during cellular
Ch. 9 - Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Study Guide A. Introduction 1. All living things need energy for metabolism. a. Plants produce glucose through photosynthesis; break down glucose during cellular
Applications of genome alignment
 Applications of genome alignment Comparing different genome assemblies Locating genome duplications and conserved segments Gene finding through comparative genomics Analyzing pathogenic bacteria against
Applications of genome alignment Comparing different genome assemblies Locating genome duplications and conserved segments Gene finding through comparative genomics Analyzing pathogenic bacteria against
DETERMINATION OF ACETIC ACID IN VINEGAR
 DETERMINATION OF ACETIC ACID IN VINEGAR 1 INTRODUCTION Juices from plants and fruits contain sugar. When these juices are fermented, the sugar molecules are converted into ethyl alcohol molecules (C 2
DETERMINATION OF ACETIC ACID IN VINEGAR 1 INTRODUCTION Juices from plants and fruits contain sugar. When these juices are fermented, the sugar molecules are converted into ethyl alcohol molecules (C 2
Concentrations. 3. A total of 60 g of sodium chloride (NaCl) are dissolved in 240 g water. Give the NaCl concentration in mass percent.
 Concentrations Most chemical reactions take place in solutions. We therefore have no pure substances but certain amounts of them in a certain amount of a solvent. Thus, the important thing is the ratio
Concentrations Most chemical reactions take place in solutions. We therefore have no pure substances but certain amounts of them in a certain amount of a solvent. Thus, the important thing is the ratio
A b o u t u s. i n e s s o f o u r s ta f f.
 A b o u t u s I n t h e s u m m e r o f 1 9 9 7 w e f o u n d o u r f i r s t s u m m e r t r u f f l e s i n t h e s h a d y f o r e s t s o f T r a n s y lva n i a, a m o m e n t t h at c a p t u r e
A b o u t u s I n t h e s u m m e r o f 1 9 9 7 w e f o u n d o u r f i r s t s u m m e r t r u f f l e s i n t h e s h a d y f o r e s t s o f T r a n s y lva n i a, a m o m e n t t h at c a p t u r e
ATP: Energy for Life ATP. Chapter 6. What Is ATP? What Does ATP Do for You? Photosynthesis. Cell Respiration. Chemical Structure of ATP
 Chapter 6 Photosynthesis : Energy for Life Cell Respiration What Is? Energy used by all Cells Chemical Structure of Adenine Base Adenosine Triphosphate Organic molecule containing highenergy Phosphate
Chapter 6 Photosynthesis : Energy for Life Cell Respiration What Is? Energy used by all Cells Chemical Structure of Adenine Base Adenosine Triphosphate Organic molecule containing highenergy Phosphate
Stable isotope analytical methods
 Stable isotope analytical methods Powerful to ensure food and beverage authenticity. Based on the principle that C, H, O, N of organic matter exist in their naturally occurring isotopic forms - 13 C/ 12
Stable isotope analytical methods Powerful to ensure food and beverage authenticity. Based on the principle that C, H, O, N of organic matter exist in their naturally occurring isotopic forms - 13 C/ 12
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace the laboratory manual. Fractional Distillation notes
 Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace the laboratory manual. Fractional Distillation notes History and Application: Fractional distillation is one of the most widely used separation
Reminder: These notes are meant to supplement, not replace the laboratory manual. Fractional Distillation notes History and Application: Fractional distillation is one of the most widely used separation
European Brewery Convention
 1 European Brewery Convention PRESS REPORT Determination of Alcohol in Low Alcohol and Non Alcohol Beers by Gas Chromatography-FID, Near Infra Red Spectroscopy and Catalytic Combustion methods Submitted
1 European Brewery Convention PRESS REPORT Determination of Alcohol in Low Alcohol and Non Alcohol Beers by Gas Chromatography-FID, Near Infra Red Spectroscopy and Catalytic Combustion methods Submitted
12BL Experiment 7: Vanillin Reduction
 12BL Experiment 7: Vanillin Reduction Safety: Proper lab goggles/glasses must be worn (even over prescription glasses). WEAR GLOVES and please handle the following chemicals with care: Hydrochloric acid
12BL Experiment 7: Vanillin Reduction Safety: Proper lab goggles/glasses must be worn (even over prescription glasses). WEAR GLOVES and please handle the following chemicals with care: Hydrochloric acid
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis a set of chemical reactions that converts carbon dioxide and water to food for plants, cyanobacteria and plant like protists Carbon Dioxide + Water
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis a set of chemical reactions that converts carbon dioxide and water to food for plants, cyanobacteria and plant like protists Carbon Dioxide + Water
Blood Alcohol Determination using Static Headspace Analysis with Optimized Sample Throughput
 JSB is an authorised partner of Blood Alcohol Determination using Static Headspace Analysis with Optimized Sample Throughput Application Note - Environmental #129 Author Anne Jurek Applications Chemist
JSB is an authorised partner of Blood Alcohol Determination using Static Headspace Analysis with Optimized Sample Throughput Application Note - Environmental #129 Author Anne Jurek Applications Chemist
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Key Concepts How does a cell obtain energy? How do some cells make food molecules? Cells and Energy What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
Cell Structure and Function Key Concepts How does a cell obtain energy? How do some cells make food molecules? Cells and Energy What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Keywords
 Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
Semester 1: Unit 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Semester 1: Unit 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Obtaining and Using Energy What do you know? What is energy? What do you need energy for? How does your body use/store energy? Energy is the ability to do
Semester 1: Unit 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Obtaining and Using Energy What do you know? What is energy? What do you need energy for? How does your body use/store energy? Energy is the ability to do
Distillation of Liquids: Separation of 2-Propanol from Water by Fractional Distillation
 Distillation of Liquids: Separation of 2-Propanol from Water by Fractional Distillation Introduction: Distillation is the process of vaporizing a liquid, condensing the vapor, and collecting the condensate
Distillation of Liquids: Separation of 2-Propanol from Water by Fractional Distillation Introduction: Distillation is the process of vaporizing a liquid, condensing the vapor, and collecting the condensate
Intermediates. THF Solutions. Expanded Tetrahydrofuran Offer for Pharma Customers in Europe
 Intermediates THF Solutions Expanded Tetrahydrofuran Offer for Pharma Customers in Europe BASF We create chemistry About BASF At BASF, we create chemistry and have been doing so for 150 years. Our portfolio
Intermediates THF Solutions Expanded Tetrahydrofuran Offer for Pharma Customers in Europe BASF We create chemistry About BASF At BASF, we create chemistry and have been doing so for 150 years. Our portfolio
Floating Disks: An Investigation of Photosynthesis Student Materials. Introduction Lab Protocol Data Collection Worksheet...
 Student Materials Introduction... 2 Lab Protocol... 3 Data Collection Worksheet... 5 Pre-Lab Questions... 6 Post-Lab Questions and Analysis... 7 Students You should read the Introduction and Lab Protocol
Student Materials Introduction... 2 Lab Protocol... 3 Data Collection Worksheet... 5 Pre-Lab Questions... 6 Post-Lab Questions and Analysis... 7 Students You should read the Introduction and Lab Protocol
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4923060500* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2014
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4923060500* CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/61 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical October/November 2014
Science Paper 1. Stage minutes. Page Mark Total. Name.. Additional materials: Ruler
 1 45 minutes Science Paper 1 Stage 9 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on the question paper. You should show all your working
1 45 minutes Science Paper 1 Stage 9 Name.. Additional materials: Ruler READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST Answer all questions in the spaces provided on the question paper. You should show all your working
Applying the Technology of the TurboMatrix 650 ATD to the Analysis of Liquid Accelerants in Arson Investigation
 Applying the Technology of the TurboMatrix 650 ATD to the Analysis of Liquid Accelerants in Arson Investigation Introduction Fire investigation involves many different types of analyses from crime scene
Applying the Technology of the TurboMatrix 650 ATD to the Analysis of Liquid Accelerants in Arson Investigation Introduction Fire investigation involves many different types of analyses from crime scene
Which particle diagram represents molecules of only one compound in the gaseous phase?
 Name: 1) Which species represents a chemical compound? 9114-1 - Page 1 NaHCO3 NH4 + Na N2 2) 3) 4) Which substance represents a compound? Co(s) O2(g) CO(g) C(s) Which terms are used to identify pure substances?
Name: 1) Which species represents a chemical compound? 9114-1 - Page 1 NaHCO3 NH4 + Na N2 2) 3) 4) Which substance represents a compound? Co(s) O2(g) CO(g) C(s) Which terms are used to identify pure substances?
GCSE Chemistry. Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know. Name: Science Group: Teacher:
 GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
GCSE Chemistry Module C7 Further Chemistry: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: R.A.G. each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this A = Amber: I partly
The Effect of Temperature on the Growth Rate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
 The Effect of Temperature on the Growth Rate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Tim Cheung, Jessica Ko, Jae Lee, and Manpreet Takhi Abstract: We conducted our experiment to determine whether increasing incubation
The Effect of Temperature on the Growth Rate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Tim Cheung, Jessica Ko, Jae Lee, and Manpreet Takhi Abstract: We conducted our experiment to determine whether increasing incubation
Ch. 4 Cells and Energy. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Ch. 4 Cells and Energy Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 1 2 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP Living organisms need energy Most comes indirectly from sun! Some change sunlight into organic compounds Others
Ch. 4 Cells and Energy Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration 1 2 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP Living organisms need energy Most comes indirectly from sun! Some change sunlight into organic compounds Others
Cellular Respiration. Anaerobic vs Aerobic
 Cellular Respiration Anaerobic vs Aerobic What is Cellular Respiration? Process where organisms use GLUCOSE (sugar) to create ENERGY! The energy that is released from chemical bonds during Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration Anaerobic vs Aerobic What is Cellular Respiration? Process where organisms use GLUCOSE (sugar) to create ENERGY! The energy that is released from chemical bonds during Cellular Respiration
Lab #11: Investigating Intermolecular Forces (mini-lab)
 (mini-lab) Part One: The Penny Drop Activity What effects do intermolecular forces have on surface tension? Name Materials: Pennies Water Rubbing Alcohol (ethyl or isopropyl will work fine) Dec. 14, 2016
(mini-lab) Part One: The Penny Drop Activity What effects do intermolecular forces have on surface tension? Name Materials: Pennies Water Rubbing Alcohol (ethyl or isopropyl will work fine) Dec. 14, 2016
Chem 102b Experiment 14: Part II Revised Preparation of Esters
 http://www.chem.arizona.edu/courseweb/981/chem102b1/fisher_esterification.html Purpose of the Experiment: Chem 102b Experiment 14: Part II Revised Preparation of Esters Students will be given alcohols
http://www.chem.arizona.edu/courseweb/981/chem102b1/fisher_esterification.html Purpose of the Experiment: Chem 102b Experiment 14: Part II Revised Preparation of Esters Students will be given alcohols
Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Answer Acceptable answers Mark
 1(a)(i) C 4H 8O 2 capital letters; numbers must be subscripts ignore structural formulae such as CH 3COOCH 2CH 3 i.e. must have just C 4, H 8 and O 2 in any order. Answer 1(a)(ii) ethanol + ethanoic acid
1(a)(i) C 4H 8O 2 capital letters; numbers must be subscripts ignore structural formulae such as CH 3COOCH 2CH 3 i.e. must have just C 4, H 8 and O 2 in any order. Answer 1(a)(ii) ethanol + ethanoic acid
# 5 Determination of Boiling Points
 # 5 Determination of Boiling Points Purpose: The object of this experiment is to identify a liquid from its boiling point. Introduction The boiling point of a compound is the temperature at which it changes
# 5 Determination of Boiling Points Purpose: The object of this experiment is to identify a liquid from its boiling point. Introduction The boiling point of a compound is the temperature at which it changes
Overview of Photosynthesis
 Overview of Photosynthesis Most autotrophs (organisms that create their own food), make organic compounds (sugars/glucose) using a process called photosynthesis. This process occurs only in plants. Overview
Overview of Photosynthesis Most autotrophs (organisms that create their own food), make organic compounds (sugars/glucose) using a process called photosynthesis. This process occurs only in plants. Overview
Unit I Unit Operations
 Unit I Unit Operations Introduction to process & Instrumentation for Chemical Chemical Process Control and Instrumentation Automatic and Instrument control chemical processes are common and essential.
Unit I Unit Operations Introduction to process & Instrumentation for Chemical Chemical Process Control and Instrumentation Automatic and Instrument control chemical processes are common and essential.
The Craft Beverage Laboratory Craft Beverage Regional Exchange Group
 The Craft Beverage Laboratory Craft Beverage Regional Exchange Group Richard Gualandi 05.28.2013 www.ncbionetwork.org The Craft Beverage Laboratory Laboratory Safety Determining your Needs Planning your
The Craft Beverage Laboratory Craft Beverage Regional Exchange Group Richard Gualandi 05.28.2013 www.ncbionetwork.org The Craft Beverage Laboratory Laboratory Safety Determining your Needs Planning your
Prelab Reading Assignment: Laboratory Techniques in Organic Chemistry, 4 th Ed. Chapter 19
 CHEM 213 Technique Experiments Experiment 5: Column Chromatography Number of labs - one Reactions performed None Chemicals used: Fluorene-fluorenone mixture, hexanes, methylene chloride, silica gel Supplies
CHEM 213 Technique Experiments Experiment 5: Column Chromatography Number of labs - one Reactions performed None Chemicals used: Fluorene-fluorenone mixture, hexanes, methylene chloride, silica gel Supplies
RAPID KJELDAHL BENCHNOTES
 RAPID KJELDAHL BENCHNOTES Methodology for the Determination of Alcohol in a Mixture by Direct Distillation with the RapidStill II Principle: This method covers the determination of percent alcohol in distilled
RAPID KJELDAHL BENCHNOTES Methodology for the Determination of Alcohol in a Mixture by Direct Distillation with the RapidStill II Principle: This method covers the determination of percent alcohol in distilled
Masters for transparencies. 5.1 Matter and materials
 Masters for transparencies 5.1 Matter and materials KNOWLEDGE AREA: MATTER AND MATERIALS Matter and materials Macroscopic properties of matter Matter is composed of particles. States of matter and the
Masters for transparencies 5.1 Matter and materials KNOWLEDGE AREA: MATTER AND MATERIALS Matter and materials Macroscopic properties of matter Matter is composed of particles. States of matter and the
APPLICATION OF MASS SPECTROMETRY IN BREWING SCIENCE
 APPLICATION OF MASS SPECTROMETRY IN BREWING SCIENCE IZTOK JOŽE KOŠIR, MATJAŽ DEŽELAK, MIHA OCVIRK INŠTITUT ZA HMELJARSTVO IN PIVOVARSTVO SLOVENIJE MassTwin 2018, April 2018 OUTLINE Introduction Beer Beer
APPLICATION OF MASS SPECTROMETRY IN BREWING SCIENCE IZTOK JOŽE KOŠIR, MATJAŽ DEŽELAK, MIHA OCVIRK INŠTITUT ZA HMELJARSTVO IN PIVOVARSTVO SLOVENIJE MassTwin 2018, April 2018 OUTLINE Introduction Beer Beer
Preparing the sample for determination of Viability
 Preparing the sample for determination of Viability I. For preparing one sample for analysis you will need: - 1 pcs CELLCHIP - 1 piece of colored Eppendorf with SOFIA GREEN lyophilized dye - 1 piece of
Preparing the sample for determination of Viability I. For preparing one sample for analysis you will need: - 1 pcs CELLCHIP - 1 piece of colored Eppendorf with SOFIA GREEN lyophilized dye - 1 piece of
Honors Chemistry Chapter 2 Problem Handout Solve the following on separate sheets of paper. Where appropriate, show all work. 1. Convert each of the
 Honors Chemistry Chapter 2 Problem Handout Solve the following on separate sheets of paper. Where appropriate, show all work. 1. Convert each of the following quantities to the required unit. a. 12.75
Honors Chemistry Chapter 2 Problem Handout Solve the following on separate sheets of paper. Where appropriate, show all work. 1. Convert each of the following quantities to the required unit. a. 12.75
THE FUTURE OF ISS UTILIZATION: AN INDUSTRY PERSPECTIVE
 LEIDEN, NETHERLANDS - DECEMBER 2015 THE FUTURE OF ISS UTILIZATION: AN INDUSTRY PERSPECTIVE #FUTUREISS M R. H A M I S H T O R R I E, D I R E C T O R O F C O R P O R A T E S O C I A L R E S P O N S I B I
LEIDEN, NETHERLANDS - DECEMBER 2015 THE FUTURE OF ISS UTILIZATION: AN INDUSTRY PERSPECTIVE #FUTUREISS M R. H A M I S H T O R R I E, D I R E C T O R O F C O R P O R A T E S O C I A L R E S P O N S I B I
Speed and flexibility
 Speed and flexibility Automate your environmental, water, detergent, food and beverage analysis Thermo Scientific Gallery and Gallery Plus discrete industrial analyzers Improve productivity, reproducible
Speed and flexibility Automate your environmental, water, detergent, food and beverage analysis Thermo Scientific Gallery and Gallery Plus discrete industrial analyzers Improve productivity, reproducible
Ev e ry living c e l l needs a source of
 12 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Ev e ry living c e l l needs a source of energy. Without energy, metabolism all of the chemical reactions that occur within cells will not occur. In this activity,
12 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Ev e ry living c e l l needs a source of energy. Without energy, metabolism all of the chemical reactions that occur within cells will not occur. In this activity,
Lesson Overview. Energy and Life. Energy of Life 2.1
 Energy of Life 2.1 Learning Goals for 2.1 1.Trace the flow of energy from the sun through a living system. 2.Explain the process of photosynthesis 3.Give examples of producers and consumers. 4.Explain
Energy of Life 2.1 Learning Goals for 2.1 1.Trace the flow of energy from the sun through a living system. 2.Explain the process of photosynthesis 3.Give examples of producers and consumers. 4.Explain
Biofuel Enzyme LAB. Name
 Biofuel Enzyme LAB Name Background Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions. Since they do not chemically react with the substrate, they can work again and again to help convert
Biofuel Enzyme LAB Name Background Enzymes are proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions. Since they do not chemically react with the substrate, they can work again and again to help convert
Preservation Effect of Antimold-Mild and Negamold for Chiffon Cake
 Oct, 12, 2017 ~Freund s Food Preservation Agents~ Preservation Effect of Antimold-Mild and Negamold for Chiffon Cake Freund Corporation 1. Introduction Chiffon cake has one of the shortest expiration dates
Oct, 12, 2017 ~Freund s Food Preservation Agents~ Preservation Effect of Antimold-Mild and Negamold for Chiffon Cake Freund Corporation 1. Introduction Chiffon cake has one of the shortest expiration dates
RESOLUTION OIV-OENO CONSIDERING the work of the Specifications of Oenological Products Expert Group,
 RESOLUTION OIV-OENO 578-2017 MONOGRAPH ON SELECTIVE PLANT FIBRES THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY, In view of article 2, paragraph 2 iv of the Agreement of 3 April 2001 establishing the International Organisation
RESOLUTION OIV-OENO 578-2017 MONOGRAPH ON SELECTIVE PLANT FIBRES THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY, In view of article 2, paragraph 2 iv of the Agreement of 3 April 2001 establishing the International Organisation
Lab 3 Guide: Gas Chromatography (GC) (Sept 8-14)
 Lab 3 Guide: Gas Chromatography (GC) (Sept 8-14) How GC works The Basic Idea Gas chromatography (GC) is mainly used for the qualitative analysis of samples: it answers the question What chemicals are present
Lab 3 Guide: Gas Chromatography (GC) (Sept 8-14) How GC works The Basic Idea Gas chromatography (GC) is mainly used for the qualitative analysis of samples: it answers the question What chemicals are present
PHOTOSYNTHESIS STARTS WITH
 Name Date Period PHOTOSYNTHESIS STARTS WITH 1. Molecules that collect light energy are called _P. 2. Chlorophyll a and b absorb _B -_V and _R wavelengths of light best. 3. _C is the main light absorbing
Name Date Period PHOTOSYNTHESIS STARTS WITH 1. Molecules that collect light energy are called _P. 2. Chlorophyll a and b absorb _B -_V and _R wavelengths of light best. 3. _C is the main light absorbing
Chemistry Project. Measuring the Amount of Acetic Acid In Vinegar by Titration with an Indicator Solution
 Chemistry Project easuring the Amount of Acetic Acid In inegar by Titration with an Indicator Solution Index 1 Certificate 2 Acknowledgement Aim 4 Objective 5 Introduction 6 aterials and Equipment 7 Theory
Chemistry Project easuring the Amount of Acetic Acid In inegar by Titration with an Indicator Solution Index 1 Certificate 2 Acknowledgement Aim 4 Objective 5 Introduction 6 aterials and Equipment 7 Theory
MIXTURES, COMPOUNDS, & SOLUTIONS
 MIXTURES, COMPOUNDS, & SOLUTIONS As with elements, few compounds are found pure in nature and usually found as mixtures with other compounds. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are
MIXTURES, COMPOUNDS, & SOLUTIONS As with elements, few compounds are found pure in nature and usually found as mixtures with other compounds. A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2
 1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
