Science at the University of Auckland. Presented by igem
|
|
|
- Thomasine Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science at the University of Auckland Presented by igem
2 Who are we?
3 First of all Collecting Samples
4 Why collect samples? Any ideas? To learn more about what you are studying To diagnose illnesses To collect data To discover new organisms To discover new medicines
5 How do you do it? With specific tools Swabs Petri dish Agar Sterile conditions? Any ideas? Depends on what you are sampling Exanple: Hand Wash 1. Take a small amount of water in one palm and use two fingers to rub the water around your palm. 2. Pour water into agar plate and spread around the plate with a cotton bud. (Be careful not to break the agar)
6 Break into Groups!! 5 groups
7 What do you want to do? 1. Go outside and find some water or soil OR 2. Use some water and do a hand wash
8 5 Minutes to Collect your Microbial Sample!
9 Microbiology
10 What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the study of Microbes.
11 Why is Microbiology Important? Any Ideas?
12 Before that... What is a Microbe? A microbe is an organism that is either very difficult or impossible to see with the naked eye. You need a Microscope! They can be both Eukaryotes ( organisms with organelles) or Prokaryotes (single-celled organisms with no organelles ie. Bacteria or Archaea) Microbes are not all harmful!! The majority of microbes are actually harmless. idth=635&name=microbes-small.jpg
13 Why is Microbiology Important? Any new ideas? The discovery, diagnosis and study of diseases The discovery of new medicines Helps us to solve environmental issues Helps us understand how our own bodies work. The Human Gut Microbiome! Cheese, Bread and Beer!
14 Where do you find them? Any Ideas? Everything is everywhere but the environment selects!
15 Some Famous Microbes
16 Saccharomyces cerevisiae ked%20items.jpg Is a Yeast, which means it is a Eukaryote Is found naturally in the skins of fruit Its most famous function is the production of Ethanol from Glucose Is used in the food industry for many things Bread Cheese Yogurt Wine Beer Spirits Vegemite
17 Penicillium ssp. Is a Fungi, which means it is a Eukaryote Can naturally be found in soil The most famous function is the production of the antibiotic Penicillin from which most of today's antibiotics are derived Various species within the Penicillium genus are used for different products Antibiotics Cheeses (Camembert, Brie, Danish Blue Cheese and Gorgonzola Many are also plant pathogens
18 Escherichia coli Is a Bacteria which means it is a prokaryote Is a gut microbe that can only survive outside of the body for a short time E.coli can live off of many different food sources and can produce many different bi-products Due to its small genome and the amount of research done on E.coli it is often used as a model organism in labs, is genetically modified to produce different compounds and is also a coliform used as an indicator organism to test for pathogens. c/ecoli_2.jpg
19 What kinds of Microbes do you think are interesting? Find an interesting microbe to share with us next time!
20 What do you think so far about Microbiology? What do you think about doing science at University? Ask us about studying at the University of Auckland
21 Question Time
22 Things to remember for next time. Remember to find a microbe that you think is interesting to share with us next time! Think about any questions you might have for us. Ask us anything!
23 See you next time!
Introduction To Microbiology CLS 311
 Introduction To Microbiology CLS 311 What is microbiology? It is a branch of biology that studies microorganisms and their effects on humans Microorganisms a collection of organisms that share the characteristic
Introduction To Microbiology CLS 311 What is microbiology? It is a branch of biology that studies microorganisms and their effects on humans Microorganisms a collection of organisms that share the characteristic
Connexions module: m Prokaryotic Cells. OpenStax College. Abstract. By the end of this section, you will be able to:
 Connexions module: m44406 1 Prokaryotic Cells OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Connexions module: m44406 1 Prokaryotic Cells OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Introduction to Microbiology. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Unit3L.3: Micro-organisms
 Unit3L.3: Bacteria Viruses Fungi Science skills: Classification Observing Predicting Comparing 37 3.8.1 Life Science Bacteria Why should I keep myself clean? Germs! Germs! Germs! Germs can be too tiny
Unit3L.3: Bacteria Viruses Fungi Science skills: Classification Observing Predicting Comparing 37 3.8.1 Life Science Bacteria Why should I keep myself clean? Germs! Germs! Germs! Germs can be too tiny
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Key Concepts How does a cell obtain energy? How do some cells make food molecules? Cells and Energy What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
Cell Structure and Function Key Concepts How does a cell obtain energy? How do some cells make food molecules? Cells and Energy What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1
 OBJECTIVE: INTRODUCE BIOLOGY AND REVIEW SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1 ON THE WHITEBOARDS! Brainstorm about what you remember about cells What you know about them (choose a colour) What you sort of remember
OBJECTIVE: INTRODUCE BIOLOGY AND REVIEW SOME PAST KNOWLEDGE. Lesson 1 ON THE WHITEBOARDS! Brainstorm about what you remember about cells What you know about them (choose a colour) What you sort of remember
2 Domains and Kingdoms
 CHAPTER 11 2 s and Kingdoms SECTION Classification 7.1.a, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Which domains are
CHAPTER 11 2 s and Kingdoms SECTION Classification 7.1.a, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Which domains are
Classification. Classifying Organisms. * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics
 Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Classification Classifying Organisms * Organisms are divided into 3 domains and 6 kingdoms based on the following characteristics Cell Type: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic - No nucleus Eukaryotic
Microbiology 101 Introduction to Microbes Activity A: Adopt a Microbe
 Microbiology 101 Introduction to Microbes Activity A: Adopt a Microbe Microbe Basics A microorganism, or microbe, is a microscopic organism (also known as something that you need a microscope to see) that
Microbiology 101 Introduction to Microbes Activity A: Adopt a Microbe Microbe Basics A microorganism, or microbe, is a microscopic organism (also known as something that you need a microscope to see) that
MICROBIOLOGY MIMM211 (Biology of Microorganisms) Lecture 1. MICROBIOLOGY MIMM211 (Biology of Microorganisms) Course coordinator
 MICROBIOLOGY MIMM211 Lecture 1 Dr. Benoit Cousineau Department of Microbiology & Immunology McGill University MICROBIOLOGY MIMM211 Course coordinator Dr. Benoit Cousineau Address: Lyman Duff Medical Building,
MICROBIOLOGY MIMM211 Lecture 1 Dr. Benoit Cousineau Department of Microbiology & Immunology McGill University MICROBIOLOGY MIMM211 Course coordinator Dr. Benoit Cousineau Address: Lyman Duff Medical Building,
Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you
 45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
Name Block Chapter 6, Section 3, Bacteria, pages Information taken from Prentice Hall Science Explorer, Life Science, 2004
 SOL LS.4 The student will investigate and understand how organisms can be classified. Key concepts include a) The distinguishing characteristics of domains of organisms b) The distinguishing characteristics
SOL LS.4 The student will investigate and understand how organisms can be classified. Key concepts include a) The distinguishing characteristics of domains of organisms b) The distinguishing characteristics
Warm Up. What are some examples of living things? Describe the characteristics of living things
 Warm Up What are some examples of living things? Describe the characteristics of living things Objectives Identify the levels of biological organization and explain their relationships Describe cell structure
Warm Up What are some examples of living things? Describe the characteristics of living things Objectives Identify the levels of biological organization and explain their relationships Describe cell structure
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY
 INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology
 Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
Name Lab 1: Using the Microscope & Cell Biology The anatomy of the compound microscope Review or learn the following parts of the compound microscope and their functions. Eyepieces Objectives Arm Stage
Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Bellringer. Objectives. Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Vocabulary. Objectives, continued
 Bellringer Why do you think cells weren t discovered until 1665? What invention do you think made their discovery possible? Do you think people can ever see cells with the naked eye? Explain your answer.
Bellringer Why do you think cells weren t discovered until 1665? What invention do you think made their discovery possible? Do you think people can ever see cells with the naked eye? Explain your answer.
Biology I: Macaw Book Unit IV: Microbiology
 Biology I: Macaw Book Unit IV: Microbiology Chapter 21 Fungus Fungus Lab Name: Date: Hour: Fungus Lab Pre-Lab Discussion Fungi are heterotrophic eukaryotes with cell walls that contain chitin. Most people
Biology I: Macaw Book Unit IV: Microbiology Chapter 21 Fungus Fungus Lab Name: Date: Hour: Fungus Lab Pre-Lab Discussion Fungi are heterotrophic eukaryotes with cell walls that contain chitin. Most people
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE
 19 January, 2018 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE Document Filetype: PDF 222.61 KB 0 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE How to Tell the Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
19 January, 2018 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE Document Filetype: PDF 222.61 KB 0 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE How to Tell the Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
pglo/amp R Bacterial Transformation Lab
 pglo/amp R Bacterial Transformation Lab Name: Date: Purpose: To gain an understanding of the techniques of culturing E. coli bacteria and transforming E. coli bacteria using genetic engineering. Introduction:
pglo/amp R Bacterial Transformation Lab Name: Date: Purpose: To gain an understanding of the techniques of culturing E. coli bacteria and transforming E. coli bacteria using genetic engineering. Introduction:
Microbe Mission C Test
 Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Molecular and cellular biology is about studying cell structure and function
 Chapter 1 Exploring the World of the Cell In This Chapter Discovering the microscopic world Getting matter and energy Reading the genetic code Molecular and cellular biology is about studying cell structure
Chapter 1 Exploring the World of the Cell In This Chapter Discovering the microscopic world Getting matter and energy Reading the genetic code Molecular and cellular biology is about studying cell structure
Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques
 Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques OBJECTIVES 1. Perform a streak-plate to separate the cells of a mixed culture so that discrete colonies can be isolated. 2. Perform a pour-plate (loop) dilution
Lab Exercise 5: Pure culture techniques OBJECTIVES 1. Perform a streak-plate to separate the cells of a mixed culture so that discrete colonies can be isolated. 2. Perform a pour-plate (loop) dilution
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION
 ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION Eric Pomper Microbiology 9 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Grade 9 Introduction Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast) were grown together
ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION Eric Pomper Microbiology 9 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Grade 9 Introduction Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast) were grown together
What s In a Name? (Lexile 840L)
 6.12: lassification of Organisms What s In a Name? (Lexile 840L) 1 Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet. These
6.12: lassification of Organisms What s In a Name? (Lexile 840L) 1 Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet. These
A. Changes in the New Biology Curriculum
 A. Changes in the New Biology Curriculum The changes made in the Biology curriculum for 2003 and afterwards are summarized in the table below. They include additions, deletions or rewriting of topics in
A. Changes in the New Biology Curriculum The changes made in the Biology curriculum for 2003 and afterwards are summarized in the table below. They include additions, deletions or rewriting of topics in
What are Cells? How is this bacterium similar to a human? organism: a living thing. The cell is the basic unit of life.
 Have you ever wondered how people are similar to bacteria? It may seem like a silly question. After all, humans and bacteria are very different in size and complexity. Yet scientists have learned that
Have you ever wondered how people are similar to bacteria? It may seem like a silly question. After all, humans and bacteria are very different in size and complexity. Yet scientists have learned that
Reading Science! Name: Date: What s In A Name? Lexile 870L
 6.12: lassification of Organisms Name: ate: 1 2 3 What s In Name? Lexile 870L Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as
6.12: lassification of Organisms Name: ate: 1 2 3 What s In Name? Lexile 870L Shakespeare famously wrote in Romeo and Juliet, What s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as
Vocabulary: Fill in the definition for each word. Use your book and/or class notes. You can put the words in your own words. Animalia: Archaea:
 Name: _ Due Date: _ Per: _ Unit 4.2 Study Guide Directions: Complete all sections to the best of your ability. On the day of the Quiz (the due date for this assignment) turn this in with all of your Unit
Name: _ Due Date: _ Per: _ Unit 4.2 Study Guide Directions: Complete all sections to the best of your ability. On the day of the Quiz (the due date for this assignment) turn this in with all of your Unit
NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3)
 NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3) How are Bacteria Different from Viruses? Bacteria are different from viruses in that they: -are much bigger -have a different structure (made of cells) therefore are considered LIVING
NOTES: 20.2 (& 20.3) How are Bacteria Different from Viruses? Bacteria are different from viruses in that they: -are much bigger -have a different structure (made of cells) therefore are considered LIVING
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 3. Names: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are you supposed to be learning in this activity? 2. Why do you think learning this
3. Names: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are you supposed to be learning in this activity? 2. Why do you think learning this
KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS. 2. Most infectious diseases are caused by microbes.
 Who s Who? 44 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW I N V E S T I O N I G AT SUMMARY Cards with images of the major groups of disease-causing microbes (s, bacteria, and es) are presented. Students
Who s Who? 44 40- to 1 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW I N V E S T I O N I G AT SUMMARY Cards with images of the major groups of disease-causing microbes (s, bacteria, and es) are presented. Students
Overview of Photosynthesis
 Overview of Photosynthesis Most autotrophs (organisms that create their own food), make organic compounds (sugars/glucose) using a process called photosynthesis. This process occurs only in plants. Overview
Overview of Photosynthesis Most autotrophs (organisms that create their own food), make organic compounds (sugars/glucose) using a process called photosynthesis. This process occurs only in plants. Overview
Fungi with a Fun Guy: Feasts, Famines and the Fungus among Us Lauren Jackson v1.0
 Fungi with a Fun Guy: Feasts, Famines and the Fungus among Us Lauren Jackson 2016-05-21 v1.0 Session Goals: 1. Investigate how fungi impact our food system a. Visualize fungal structures used to decay
Fungi with a Fun Guy: Feasts, Famines and the Fungus among Us Lauren Jackson 2016-05-21 v1.0 Session Goals: 1. Investigate how fungi impact our food system a. Visualize fungal structures used to decay
Biology 160 Cell Lab. Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm. Student Learning Outcomes:
 Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
DO NOW (On notecard):
 Learner Profile: Communicators Monday, September 28 AGENDA 15 min Enter the classroom silently and find your seat. 1. Take out pencils, HAWK card, agenda, and classification notes 2. Everything else gets
Learner Profile: Communicators Monday, September 28 AGENDA 15 min Enter the classroom silently and find your seat. 1. Take out pencils, HAWK card, agenda, and classification notes 2. Everything else gets
Unit Two: Biodiversity. Chapter 4
 Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Unit Two: Biodiversity Chapter 4 A. Classifying Living Things (Ch.4 - page 100) Scientific knowledge is constantly evolving ( changing ): new evidence is discovered laws and theories are tested and possibly
Have cell walls Made of
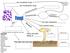 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th edition by Nester Anderson and Roberts Solution Manual. plants could use. microorganisms.
 Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th edition by Nester Anderson and Roberts Solution Manual Chapter # and Question Answer Question type Chapter 1 How did Louis Pasteur help Pasteur demonstrated that swan
Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th edition by Nester Anderson and Roberts Solution Manual Chapter # and Question Answer Question type Chapter 1 How did Louis Pasteur help Pasteur demonstrated that swan
INTRODUCTION prokaryotic eukaryotic pigments
 INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
INTRODUCTION This exercise is intended for you to get familiar and comfortable with using a microscope as well as identifying common microbial groups. Thus, we will observe representatives of all microbes
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology
 Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Microorganisms that prepares their food from water and carbon dioxide
Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Microorganisms that prepares their food from water and carbon dioxide
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules
 Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules. Early History of Microbiology: Fig. 1.4
 Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Biological Kingdoms. An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things
 Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
Biological Kingdoms An introduction to the six kingdoms of living things 3 Domains Archaea 6 Kingdoms Archaebacteria Bacteria Eubacteria Eukaryota Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Domain Eukaryota Kingdom
KNOW the MICROBES. What are microbes? What are the different types? Who saw them first? How small are they? How do they look?
 KNOW the MICROBES What are microbes? What are the different types? Who saw them first? How small are they? How do they look? - PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North
KNOW the MICROBES What are microbes? What are the different types? Who saw them first? How small are they? How do they look? - PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr
 Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Solution Manual for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition by Eugene Nester, Denise Anderson and C. Evans Roberts
 Solution Manual for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition by Eugene Nester, Denise Anderson and C. Evans Roberts Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/solution-manualfor-microbiology-a-human-perspective-7th-edition-by-nester-andersonroberts/
Solution Manual for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition by Eugene Nester, Denise Anderson and C. Evans Roberts Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/solution-manualfor-microbiology-a-human-perspective-7th-edition-by-nester-andersonroberts/
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort
 Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
Characteristics of Living Things Card Sort All of these terms are characteristics of organisms that allow scientists to classify (organize) them into groups. Chapter 9 in your text covers the characteristics
2 Domains and Kingdoms
 CHAPTER 9 2 Domains and Kingdoms SECTION Classification BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are prokaryotes classified? How are eukaryotes classified?
CHAPTER 9 2 Domains and Kingdoms SECTION Classification BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How are prokaryotes classified? How are eukaryotes classified?
Lesson 2 The Cell. Student Labs and Activities. Launch Lab 25
 Lesson 2 The Cell Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 Language Arts Support 32 School to Home 34
Lesson 2 The Cell Student Labs and Activities Page Launch Lab 25 Content Vocabulary 26 Lesson Outline 27 MiniLab 29 Content Practice A 30 Content Practice B 31 Language Arts Support 32 School to Home 34
Full file at
 Chapter # and Question type Short answer #1. Question How did Louis Pasteur help disprove spontaneous generation? Answer Pasteur demonstrated that swan necked flasks containing sterile growth medium would
Chapter # and Question type Short answer #1. Question How did Louis Pasteur help disprove spontaneous generation? Answer Pasteur demonstrated that swan necked flasks containing sterile growth medium would
The Characteristics of Cells
 1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms. What You Will Learn The cell theory explains why cells are important for living things. All cells have a cell
1 The Characteristics of Cells Key Concept Cells function similarly in all living organisms. What You Will Learn The cell theory explains why cells are important for living things. All cells have a cell
3 The Organization of Living Things
 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
CHAPTER 1 SECTION Cells: The Basic Units of Life 3 The Organization of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the advantages of
Purpose (1 point) Investigate differences to cell size and shape across various kingdoms
 Living Cells Lab 61 points total As will be seen through this lab, there is no such thing as a typical cell. Though both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are often shown as general cells (p. 206), rarely
Living Cells Lab 61 points total As will be seen through this lab, there is no such thing as a typical cell. Though both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are often shown as general cells (p. 206), rarely
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Bacteria (pages 48 57)
 Bacteria (pages 48 57) The Bacterial Cell (pages 48 50) Key Concept: Bacteria are prokaryotes. The genetic material in their cells is not contained in a nucleus. Bacteria are single-celled organisms that
Bacteria (pages 48 57) The Bacterial Cell (pages 48 50) Key Concept: Bacteria are prokaryotes. The genetic material in their cells is not contained in a nucleus. Bacteria are single-celled organisms that
Living Things are Highly Organized. Levels of Organization
 Living Things are Highly Organized Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things 1.Made Up of Cells 2. Reproduction 3. Contains DNA; Living things are based on a universal genetic code. 4. Growth
Living Things are Highly Organized Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things 1.Made Up of Cells 2. Reproduction 3. Contains DNA; Living things are based on a universal genetic code. 4. Growth
Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang
 Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang Research Silver is considered to be a very toxic and lethal element to many microbes and bacteria. In the last decade, scientist believed that the
Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang Research Silver is considered to be a very toxic and lethal element to many microbes and bacteria. In the last decade, scientist believed that the
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis a set of chemical reactions that converts carbon dioxide and water to food for plants, cyanobacteria and plant like protists Carbon Dioxide + Water
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis a set of chemical reactions that converts carbon dioxide and water to food for plants, cyanobacteria and plant like protists Carbon Dioxide + Water
Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: FUNGI
 Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: FUNGI Fungi are eukaryotic heterotrophs that have cell walls. They are part of the nature s recycling system. They break down organic compounds. Fungi are used in wine, beer, cheese,
Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: FUNGI Fungi are eukaryotic heterotrophs that have cell walls. They are part of the nature s recycling system. They break down organic compounds. Fungi are used in wine, beer, cheese,
chapter one: the history of microbiology
 chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
Adding the class. Prerequisites. Welcome to Bio 139 General Microbiology. Syllabus. Amy Rogers, M.D., Ph.D.
 Adding the class Welcome to Bio 139 General Microbiology Amy Rogers, M.D., Ph.D. Lectures MW 12:00-1:15 PM (section 8) Labs: MW 1:30-2:45 PM or MW 3:00 PM-4:15 PM I anticipate a large number of students
Adding the class Welcome to Bio 139 General Microbiology Amy Rogers, M.D., Ph.D. Lectures MW 12:00-1:15 PM (section 8) Labs: MW 1:30-2:45 PM or MW 3:00 PM-4:15 PM I anticipate a large number of students
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION
 CELL THEORY & FUNCTION DISCOVERY OF THE CELL Can t see cells, so who knew they existed? Discovered after the microscope was invented. Mid 1600s when scientists began using microscopes Robert Hooke
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION DISCOVERY OF THE CELL Can t see cells, so who knew they existed? Discovered after the microscope was invented. Mid 1600s when scientists began using microscopes Robert Hooke
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date:
 Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: / 90 Name: Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your grammar/writing
Some history. Now, we know that Robert Hooke was not looking at living cells, but the remains of dead cell walls.
 The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
INTRODUCTION bioactive compounds Pigmentation chromobacteria water soluble water insoluble
 INTRODUCTION So far we have witnessed several useful applications of microbes including applications in food and the bioremediation of the environment. Besides consuming the desired substrate (oil) and
INTRODUCTION So far we have witnessed several useful applications of microbes including applications in food and the bioremediation of the environment. Besides consuming the desired substrate (oil) and
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan
 no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
Ev e ry living c e l l needs a source of
 12 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Ev e ry living c e l l needs a source of energy. Without energy, metabolism all of the chemical reactions that occur within cells will not occur. In this activity,
12 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Ev e ry living c e l l needs a source of energy. Without energy, metabolism all of the chemical reactions that occur within cells will not occur. In this activity,
Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review
 Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review Complete the following short answer questions. 1. Define microbiology. The study of microorganisms. 2. What are the six major groups of organisms
Name: Block: Date: Microbiology Chapters 1 and 2 Review Complete the following short answer questions. 1. Define microbiology. The study of microorganisms. 2. What are the six major groups of organisms
FUNGUS AMONG US THE NANOPARTICLE PRODUCERS
 FUNGUS AMONG US THE NANOPARTICLE PRODUCERS Recent discoveries continue to highlight the many uses of that wonderful kingdom of life, fungus. Penicillin, a group of antibiotics that changed medicine forever,
FUNGUS AMONG US THE NANOPARTICLE PRODUCERS Recent discoveries continue to highlight the many uses of that wonderful kingdom of life, fungus. Penicillin, a group of antibiotics that changed medicine forever,
Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes
 Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes OBJECTIVES 1. To observe representatives of major types of microbes. 2. To cultivate select representatives of major types of microbes. 3. Understand key
Lab Exercise: Diversity of Eukaryotic Microbes OBJECTIVES 1. To observe representatives of major types of microbes. 2. To cultivate select representatives of major types of microbes. 3. Understand key
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Day 1. What You ll Learn. 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells.
 What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
What You ll Learn Day 1 1. Organisms are living things. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 3. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic A cell is the basic unit and structure
CELL THEORY & FUNCTION
 UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
UNIT 1- THE CELL CELL THEORY & FUNCTION A Word From Bill Record your observations about the picture to the right. What do you think you are you looking at? Describe the structure with as much detail
Investigating Cells Lab. 1. What major differences do you expect to see between bacterial cells and plant/animal
 Investigating Cells Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Questions: o How do you use a microscope? o What do bacterial cells look like? o Are there any visible differences between plant cells and animal cells? o What
Investigating Cells Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Questions: o How do you use a microscope? o What do bacterial cells look like? o Are there any visible differences between plant cells and animal cells? o What
Microbe Mission B Test
 Microbe Mission B Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Part 1: Microscopes Names the following structures
Microbe Mission B Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Part 1: Microscopes Names the following structures
The Science of Life. Introduction to Biology
 The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
The Diversity of Life Lesson 1 What is Life?
 Chapter 1 The Diversity of Life Lesson 1 What is Life? Objectives List the characteristics all living things share. Explain where living things come from. Identify what all living things need to survive.
Chapter 1 The Diversity of Life Lesson 1 What is Life? Objectives List the characteristics all living things share. Explain where living things come from. Identify what all living things need to survive.
Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 5 Cell Structure and Function Can you name something that you know exists even though you can t see it with your eyes? A drop of pond water has tiny swimming organisms and small bits of plant material,
Chapter 5 Cell Structure and Function Can you name something that you know exists even though you can t see it with your eyes? A drop of pond water has tiny swimming organisms and small bits of plant material,
INTRODUCTION TO CELLS. Name: Block:
 INTRODUCTION TO CELLS Name: Block: 1 2 The Human Cheek Cell Write a short description of each of the following: --cell membrane --cytoplasm --nucleus --organelle Procedure: 1.Gently scrape the inside of
INTRODUCTION TO CELLS Name: Block: 1 2 The Human Cheek Cell Write a short description of each of the following: --cell membrane --cytoplasm --nucleus --organelle Procedure: 1.Gently scrape the inside of
Biology Assessment. Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes Bacteria
 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
STAAR Biology Assessment
 STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
Viruses p.122. Viruses are very small structures which can make other organisms sick.
 Viruses p.122 Viruses are very small structures which can make other organisms sick. Illness is caused when the viruses invade an organisms cells and use that cell s resources to make more viruses. Viruses
Viruses p.122 Viruses are very small structures which can make other organisms sick. Illness is caused when the viruses invade an organisms cells and use that cell s resources to make more viruses. Viruses
Scientific names allow scientists to talk about particular species without confusion
 Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Chapter 01: Scope of Microbiology VanMeter: Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional, 2nd Edition
 Chapter 01: Scope of Microbiology VanMeter: Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional, 2nd Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In the sixteenth century a father-and-son team, by the name of, produced a compound
Chapter 01: Scope of Microbiology VanMeter: Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional, 2nd Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. In the sixteenth century a father-and-son team, by the name of, produced a compound
Origins - Three Domain Classification PROKARYOTES
 Bacteria Origins - Three Domain Classification EU PROKARYOTES I. Origins of Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria A. Prokaryotes = 1. Kingdom Eubacteria 2. Kingdom Archaebacteria 3. Prokaryote
Bacteria Origins - Three Domain Classification EU PROKARYOTES I. Origins of Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria A. Prokaryotes = 1. Kingdom Eubacteria 2. Kingdom Archaebacteria 3. Prokaryote
UNITY AND DIVERSITY. Why do we classify things? Organizing the world of organsims. The Tree of Life
 Classification Why do we classify things? Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. There are millions of organisms on earth! Organisms are classified
Classification Why do we classify things? Classification provides scientists and students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. There are millions of organisms on earth! Organisms are classified
Science activities: Fourth Grade
 activities: Fourth Grade UNIT CONTENT STANDARD ACTIVITY NAME DESCRIPTION WEEK #1 9/13-9/17 WEEK #2 9/27-10/1 Investigation & experimentatio n 6.c: Formulate and justify predictions based on causeand-effect
activities: Fourth Grade UNIT CONTENT STANDARD ACTIVITY NAME DESCRIPTION WEEK #1 9/13-9/17 WEEK #2 9/27-10/1 Investigation & experimentatio n 6.c: Formulate and justify predictions based on causeand-effect
Name: /92 Grade: Microbe Mission regionals test Part A: Microscopy Label all parts. (1 pt each)
 Name: /92 Grade: Microbe Mission regionals test Part A: Microscopy Label all parts. (1 pt each) 15. You are looking at a sample of euglena through a microscope with the x10 objective lens. One specimen
Name: /92 Grade: Microbe Mission regionals test Part A: Microscopy Label all parts. (1 pt each) 15. You are looking at a sample of euglena through a microscope with the x10 objective lens. One specimen
In Cellular Respiration, are removed from sugar and transferred to
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lec. 5, Part A (Guided Notes) Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration Energy is needed by cells to do work Chemical energy, a form of potential energy, is stored in bonds of food molecules (such
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lec. 5, Part A (Guided Notes) Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration Energy is needed by cells to do work Chemical energy, a form of potential energy, is stored in bonds of food molecules (such
Electron micrograph of the bacteria Escherichia coli AKA..E. coli
 Domain The Domain Bacteria, has a wide variety of single celled organisms. They are often called prokaryotes because they have no nuclei. The term prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό- (pro-) "before" +
Domain The Domain Bacteria, has a wide variety of single celled organisms. They are often called prokaryotes because they have no nuclei. The term prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό- (pro-) "before" +
