Errata and additional material for Infinite-Dimensional Dynamical Systems
|
|
|
- Jessica Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Errata and additional material for Infinite-Dimensional Dynamical Systems Many thanks to all who have sent me errata, including: Marco Cabral, Carmen Chicone, Marcus Garvie, Grzegorz Lukaszewicz, Edgardo Moyano, & Vittorino Pata Errata in the book p 25, l 13 dx is missing from two integrals p 43, equation (2.3) should read T (0) = id. p 45, l 9 p 46, l5- delete a before locally change x(t) to x(s) p 52, l 13 RHS should be 0 p 75, l 7- closed ball required (should be B(0, 1)) p 77, l 8- p 80, l 3- p 103, l 9 Should be inf q(x) and sup w(x), not vice versa Should be x n x and A x n ȳ Should be e j p 105, l 5- It is not true that the Alaoglu weak-* compactness theorem is valid in any Banach space, as the following example shows (thanks to Vittorino Pata for this example): take X = l, and consider the sequence of functionals L n : X R defined by L n (x) = x n when x = (x 1, x 2, x 3,...). The L n is clearly a bounded sequence in (l ), but does not have a weakly- * convergent subsequence. However, Corollary 4.19 (Reflexive weak compactness) does hold as stated, i.e. is true for any reflexive (not necessarily separable) Banach space - this is where Yosida (1980) provides a proof. 1
2 p 109, equation (5.1) and (5.3) on page 110 be partial derivatives ( / x j ). all derivatives (d/dx j ) should p 112, Definition should say that the derivatives of φ n should converge uniformly to the corresponding derivatives of φ p 115, l 5 should be Theorem 5.4 p 125, l 1 should be a function u H k (R m +) p 132, l 8- the integral is between 1 and 1 p 160, l 6- shoudl be u instead of u(t) p 161, l 4- (5.14) (not (5.13)) p 176, l 4- The use of λ in Proposition 6.15 is required since we cannot prove immediately H 2 regularity on the whole of D +, but only on λd + for some 0 < λ < 1. p 190, l 8- p 196, l 14 should be du h /dt du/dt change ψ to ψ(t) p 203ff Section 7.4.3: in fact it is possible to make estimates on u n u m, following the calculations in section 7.4.2, and show directly that {u n } is a Cauchy sequence in L 2 (0, T ; V ) and L (0, T ; H), removing the need to extract subsequences. However, the presentation as it stands closely parallels the treatment in subsequent chapters when the subsequence method is necessary. p 204, l 12 weak-* convergence of P n f to f in L 2 (0, T ; V ) follows using a much simpler argument. In fact, a straightforward application of Lebesgue s dominated convergence theorem (theorem 1.7 (iii)) shows that P n f converges strongly to f in L 2 (0, T ; V ). p 205, l 9- change to suppose that x n is given by the constant sequence 2
3 p 207, l 8 should be t [0, T ] p 229, equation (8.30) the expression [1 + u H 1 + v H 1] should be raised to the power of γ rather than 1 : the last line of the inequality in the proof 2 should end (1 + u 2γ L + v 2qγ L 2qγ) 2γ rather than what is written. p231, Exercise 8.1 You need to assume that X and Y are continuously embedded in some other Banach space Z. [If X Y is dense in both X and Y then we have true equality (X Y ) = X + Y ; otherwise one should say that elements of (X Y ) can be formed by adding the restrictions to X Y of elements of X and Y.] p 235, l 2- change to neglecting all the nonlinear terms in (9.1) and taking f to be time-independent p 248 we in fact need to take w C 1 (0, T ; C 1 (Ω)) in the argument showing the convergence of B(u n, u n ) to B(u, u), and then use the density of C 1 (0, T ; C 1 (Ω)) in L q (0, T ; V ). In fact it is better to take w = N j=1 c j(t)w j, with c j (t) continuous: for such w it is easy to show that T 0 P n B(u n, u n ), w dt T 0 B(u, u), w dt, and then since such w are dense in L p (0, T ; V ) we obtain convergence of P n B(u n, u n ) to B(u, u) in one step. p 274, Proposition equilibrium point. p 275, Theorem second sentence should end then ω(u 0 ) is a single Equation (10.20) should read A = A W s (E) = A z E W s (z). p 276, l 1 change double equality to the two equalities p 276, l 9- change u 0 A to v 0 A 3
4 p 277 the example is wrong (thanks to Prof. Grzegorz Lukaszewicz of Warsaw University for pointing this out). The calculations given are in fact for dx/dt = zy dy/dt = zx dz/dt = µz z. However, there are some subtleties here. In fact for this example every point has a compact ω limit set, even though the attractor z 0 is not compact, and this is why Proposition and its corollary still apply: that problems can arise otherwise is shown in the simpler system ż = z 2 with ẋ = zx which has solution x(t) = x 0 (1 + z 0 t) and z(t) = z 0 /(1 + z 0 t): although on z 0 all points are stationary, the x component of every solution has constant speed x 0 z 0. An example that does away with the need for such subtleties since it does in fact have a compact global attractor is or in polar coordinates dx/dt = (1 (x 2 + y 2 ))x yz dy/dt = (1 (x 2 + y 2 ))y + xz dz/dt = µz z, dr/dt = r(1 r 2 ) dθ/dt = z dz/dt = µz z. p 287, l 7- (8.27) (not (8.26)); also in l 1-, should be 2l + 1 not l + 1 p 288, l 2- * missing above the arrow (it s weak-* convergence) p 294, equation (11.17) the central term in the equality should be Ω f(u)u t dx. p 354, l 6 of Notes the reference for fractal dimension is to Clark Robinson s 1995 book Dynamical Systems. p 354, l -6 instead of the paper by Blinchevskaya & Ilyashenko (which still has not appeared), see instead: Chepyzhov & Ilyin: A note on the fractal dimension of attractors of dissipative dynamical systems. Nonlinear Anal. 44 (2001), no. 6, Ser. A: Theory Methods,
5 p 381, equation (14.34) the term in k should be k 1/2. p 390, Definition 15.2 (Strong Squeezing Property) the strictly positive constant k that occurs in (15.9) depends only on the projection P (i.e. only on n). p 391, l 4ff and the two displayed equations should read Qu Qv e kt Qu t Qv t Qu Qv 2R H e kt, the conclusion being that Qu = Qv. The result then follows as before. p 391, Definition 15.4 (i), B(0, ρ) P H should be replaced by P H \ [B(0, ρ) P H], the idea being that the portion of the flat space P H outside the absorbing ball B(0, ρ) is invariant. p 394, l2 we need t t 0 (Y ). It would be possible to consider B(0, u 0 ) instead of a general bounded set Y, and thus obtain more clearly dist(s(t)u 0, M) C( u 0 )e kt. [A more careful proof of exponential convergence can be used to show that in fact dist(s(t)u 0, M) C dist(u 0, M)e kt, see, for example, Chow et al. (1992).] p 418, l5 while checking that ϕ satisfies the uniqueness property, the lefthand side should be ϕ(t; ϕ(s; x)). Solutions to Exercises Some numbering problems for Chapter 3: Solution 3.8 is for Exercise 3.7; Solution 3.9 for Exercise 3.8; and Solution 3.7 is for Exercise
6 The solution for Exercise 8.1 is incorrect, since the application of the Hahn- Banach Theorem does not give a linear functional on X, since it extends a linear functional on Z = X Y which is continuous with respect to the norm of Z, but not that of X. Thanks to Vittorino Pata for a helpful correspondence to clear this up. We need to assume in addition that X and Y are continuously embedded in some other Banach space Z. Now take f (X Y ). Now consider the subspace D of X Y consisting of vectors of the form (w, w) with w X Y. Define a bounded linear functional h on D by h(w, w) = f(w). Now use the Hahn-Banach theorem to extend h to a linear functional g on X Y, and set f 1 (w) = g(w, 0) and f 2 (w) = g(0, w). Then f 1 X and f 2 Y, and g = f 1 +f 2. Then for w X Y, f = f 1 +f 2. Clearly if X Y is dense in X and Y then f 1 and f 2 are uniquely defined by their restrictions to X Y, and so the equality (X Y ) = X + Y is meaningful. Otherwise, as noted above, we in fact have f = f 1 X Y +f 2 X Y, where f 1 X and f 2 Y. Additional material There is a very elegant formulation of an existence result for global attractors (cf. theorem 10.5) that is due to Crauel (2001) in the case of random attractors. Theorem 1. There exists a global attractor A iff there exists a compact attracting set K, and then A = ω(k). 6
7 Note that the condition of a compact attracting set is much weaker than the existence of a compact absorbing set. The proof requires the following simple lemma: Lemma 2. If K is a compact set and x n is a sequence such that dist(x n, K) 0 then {x n } has a convergent subsequence whose limit lies in K. As a first step to proving this new theorem first we reprove proposition 10.3 under the weaker condition here. Proposition 3. If there exists a compact attracting set K then the ω-limit set ω(x) of any bounded set X is a non-empty, invariant, closed subset of K. Furthermore ω(x) attracts X. Proof. To see that ω(x) is non-empty choose some point x X. Then since K is attracting dist(s(n)x, K) 0. It follows that for some sequence n j 0 S(n j )x x K. As the intersection of a decreasing sequence of closed sets ω(x) is clearly closed. To show that ω(x) K suppose that t n, x n X and Then since K is attracting S(t n )x n y. dist(s(t n )x n, K) 0, implying that a subsequence of S(t n )x n converges to a point in K. Since the sequence itself converges it follows that y K. So ω(x) is compact. Now suppose that ω(x) does not attract X. Then there exists a δ > 0 and a sequence of t n such that dist(s(t n )X, ω(x)) > δ, 7
8 and hence x n X such that dist(s(t n )x n, ω(x)) > δ. (1) However, the argument above shows that a subsequence of {S(t n )x n } converges to some point z. By (1) we should have dist(z, ω(x)) δ, while by definition z ω(x). So ω(x) attracts X. Now observe that and that since ω(x) is invariant A B = ω(a) ω(b), (2) ω[ω(x)] = t 0 S(s)ω(X) = ω(x). (3) s t Proof. (Proof of theorem 1). It follows from the previous proposition that ω(k) is non-empty, compact, invariant, and attracts K. So all we have to prove is that ω(k) attracts X. Since ω(x) attracts X it suffices to show that ω(x) ω(k). But this follows immediately from (2) and (3). 8
Functional Analysis HW #1
 Functional Analysis HW #1 Sangchul Lee October 9, 2015 1 Solutions Solution of #1.1. Suppose that X
Functional Analysis HW #1 Sangchul Lee October 9, 2015 1 Solutions Solution of #1.1. Suppose that X
Errata Applied Analysis
 Errata Applied Analysis p. 9: line 2 from the bottom: 2 instead of 2. p. 10: Last sentence should read: The lim sup of a sequence whose terms are bounded from above is finite or, and the lim inf of a sequence
Errata Applied Analysis p. 9: line 2 from the bottom: 2 instead of 2. p. 10: Last sentence should read: The lim sup of a sequence whose terms are bounded from above is finite or, and the lim inf of a sequence
SYNCHRONIZATION OF NONAUTONOMOUS DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 003003, No. 39, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp SYNCHRONIZATION OF
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 003003, No. 39, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp SYNCHRONIZATION OF
Overview of normed linear spaces
 20 Chapter 2 Overview of normed linear spaces Starting from this chapter, we begin examining linear spaces with at least one extra structure (topology or geometry). We assume linearity; this is a natural
20 Chapter 2 Overview of normed linear spaces Starting from this chapter, we begin examining linear spaces with at least one extra structure (topology or geometry). We assume linearity; this is a natural
PROBLEMS. (b) (Polarization Identity) Show that in any inner product space
 1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
1 Professor Carl Cowen Math 54600 Fall 09 PROBLEMS 1. (Geometry in Inner Product Spaces) (a) (Parallelogram Law) Show that in any inner product space x + y 2 + x y 2 = 2( x 2 + y 2 ). (b) (Polarization
MATH 4200 HW: PROBLEM SET FOUR: METRIC SPACES
 MATH 4200 HW: PROBLEM SET FOUR: METRIC SPACES PETE L. CLARK 4. Metric Spaces (no more lulz) Directions: This week, please solve any seven problems. Next week, please solve seven more. Starred parts of
MATH 4200 HW: PROBLEM SET FOUR: METRIC SPACES PETE L. CLARK 4. Metric Spaces (no more lulz) Directions: This week, please solve any seven problems. Next week, please solve seven more. Starred parts of
Applied Analysis (APPM 5440): Final exam 1:30pm 4:00pm, Dec. 14, Closed books.
 Applied Analysis APPM 44: Final exam 1:3pm 4:pm, Dec. 14, 29. Closed books. Problem 1: 2p Set I = [, 1]. Prove that there is a continuous function u on I such that 1 ux 1 x sin ut 2 dt = cosx, x I. Define
Applied Analysis APPM 44: Final exam 1:3pm 4:pm, Dec. 14, 29. Closed books. Problem 1: 2p Set I = [, 1]. Prove that there is a continuous function u on I such that 1 ux 1 x sin ut 2 dt = cosx, x I. Define
3 (Due ). Let A X consist of points (x, y) such that either x or y is a rational number. Is A measurable? What is its Lebesgue measure?
 MA 645-4A (Real Analysis), Dr. Chernov Homework assignment 1 (Due ). Show that the open disk x 2 + y 2 < 1 is a countable union of planar elementary sets. Show that the closed disk x 2 + y 2 1 is a countable
MA 645-4A (Real Analysis), Dr. Chernov Homework assignment 1 (Due ). Show that the open disk x 2 + y 2 < 1 is a countable union of planar elementary sets. Show that the closed disk x 2 + y 2 1 is a countable
Attractors and Finite-Dimensional Behaviour in the Navier-Stokes Equations
 Attractors and Finite-Dimensional Behaviour in the Navier-Stokes Equations Instructional Conference Mathematical Analysis of Hydrodynamics ICMS Edinburgh June 2003 James C. Robinson (Royal Society University
Attractors and Finite-Dimensional Behaviour in the Navier-Stokes Equations Instructional Conference Mathematical Analysis of Hydrodynamics ICMS Edinburgh June 2003 James C. Robinson (Royal Society University
Recall that if X is a compact metric space, C(X), the space of continuous (real-valued) functions on X, is a Banach space with the norm
 Chapter 13 Radon Measures Recall that if X is a compact metric space, C(X), the space of continuous (real-valued) functions on X, is a Banach space with the norm (13.1) f = sup x X f(x). We want to identify
Chapter 13 Radon Measures Recall that if X is a compact metric space, C(X), the space of continuous (real-valued) functions on X, is a Banach space with the norm (13.1) f = sup x X f(x). We want to identify
Takens embedding theorem for infinite-dimensional dynamical systems
 Takens embedding theorem for infinite-dimensional dynamical systems James C. Robinson Mathematics Institute, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV4 7AL, U.K. E-mail: jcr@maths.warwick.ac.uk Abstract. Takens
Takens embedding theorem for infinite-dimensional dynamical systems James C. Robinson Mathematics Institute, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV4 7AL, U.K. E-mail: jcr@maths.warwick.ac.uk Abstract. Takens
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES. Contents. 1. Sets Functions Countability Axiom of choice Equivalence relations 9
 MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
MAT 570 REAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES PROFESSOR: JOHN QUIGG SEMESTER: FALL 204 Contents. Sets 2 2. Functions 5 3. Countability 7 4. Axiom of choice 8 5. Equivalence relations 9 6. Real numbers 9 7. Extended
Chapter 4 Optimal Control Problems in Infinite Dimensional Function Space
 Chapter 4 Optimal Control Problems in Infinite Dimensional Function Space 4.1 Introduction In this chapter, we will consider optimal control problems in function space where we will restrict ourselves
Chapter 4 Optimal Control Problems in Infinite Dimensional Function Space 4.1 Introduction In this chapter, we will consider optimal control problems in function space where we will restrict ourselves
AN EFFECTIVE METRIC ON C(H, K) WITH NORMAL STRUCTURE. Mona Nabiei (Received 23 June, 2015)
 NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 46 (2016), 53-64 AN EFFECTIVE METRIC ON C(H, K) WITH NORMAL STRUCTURE Mona Nabiei (Received 23 June, 2015) Abstract. This study first defines a new metric with
NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 46 (2016), 53-64 AN EFFECTIVE METRIC ON C(H, K) WITH NORMAL STRUCTURE Mona Nabiei (Received 23 June, 2015) Abstract. This study first defines a new metric with
The weak topology of locally convex spaces and the weak-* topology of their duals
 The weak topology of locally convex spaces and the weak-* topology of their duals Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto April 3, 2014 1 Introduction These notes
The weak topology of locally convex spaces and the weak-* topology of their duals Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto April 3, 2014 1 Introduction These notes
Applied Math Qualifying Exam 11 October Instructions: Work 2 out of 3 problems in each of the 3 parts for a total of 6 problems.
 Printed Name: Signature: Applied Math Qualifying Exam 11 October 2014 Instructions: Work 2 out of 3 problems in each of the 3 parts for a total of 6 problems. 2 Part 1 (1) Let Ω be an open subset of R
Printed Name: Signature: Applied Math Qualifying Exam 11 October 2014 Instructions: Work 2 out of 3 problems in each of the 3 parts for a total of 6 problems. 2 Part 1 (1) Let Ω be an open subset of R
Weak Convergence Methods for Energy Minimization
 Weak Convergence Methods for Energy Minimization Bo Li Department of Mathematics University of California, San Diego E-mail: bli@math.ucsd.edu June 3, 2007 Introduction This compact set of notes present
Weak Convergence Methods for Energy Minimization Bo Li Department of Mathematics University of California, San Diego E-mail: bli@math.ucsd.edu June 3, 2007 Introduction This compact set of notes present
WELL-POSEDNESS FOR HYPERBOLIC PROBLEMS (0.2)
 WELL-POSEDNESS FOR HYPERBOLIC PROBLEMS We will use the familiar Hilbert spaces H = L 2 (Ω) and V = H 1 (Ω). We consider the Cauchy problem (.1) c u = ( 2 t c )u = f L 2 ((, T ) Ω) on [, T ] Ω u() = u H
WELL-POSEDNESS FOR HYPERBOLIC PROBLEMS We will use the familiar Hilbert spaces H = L 2 (Ω) and V = H 1 (Ω). We consider the Cauchy problem (.1) c u = ( 2 t c )u = f L 2 ((, T ) Ω) on [, T ] Ω u() = u H
(x k ) sequence in F, lim x k = x x F. If F : R n R is a function, level sets and sublevel sets of F are any sets of the form (respectively);
 STABILITY OF EQUILIBRIA AND LIAPUNOV FUNCTIONS. By topological properties in general we mean qualitative geometric properties (of subsets of R n or of functions in R n ), that is, those that don t depend
STABILITY OF EQUILIBRIA AND LIAPUNOV FUNCTIONS. By topological properties in general we mean qualitative geometric properties (of subsets of R n or of functions in R n ), that is, those that don t depend
16 1 Basic Facts from Functional Analysis and Banach Lattices
 16 1 Basic Facts from Functional Analysis and Banach Lattices 1.2.3 Banach Steinhaus Theorem Another fundamental theorem of functional analysis is the Banach Steinhaus theorem, or the Uniform Boundedness
16 1 Basic Facts from Functional Analysis and Banach Lattices 1.2.3 Banach Steinhaus Theorem Another fundamental theorem of functional analysis is the Banach Steinhaus theorem, or the Uniform Boundedness
Notes on Integrable Functions and the Riesz Representation Theorem Math 8445, Winter 06, Professor J. Segert. f(x) = f + (x) + f (x).
 References: Notes on Integrable Functions and the Riesz Representation Theorem Math 8445, Winter 06, Professor J. Segert Evans, Partial Differential Equations, Appendix 3 Reed and Simon, Functional Analysis,
References: Notes on Integrable Functions and the Riesz Representation Theorem Math 8445, Winter 06, Professor J. Segert Evans, Partial Differential Equations, Appendix 3 Reed and Simon, Functional Analysis,
SPACES ENDOWED WITH A GRAPH AND APPLICATIONS. Mina Dinarvand. 1. Introduction
 MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69, 1 (2017), 23 38 March 2017 research paper originalni nauqni rad FIXED POINT RESULTS FOR (ϕ, ψ)-contractions IN METRIC SPACES ENDOWED WITH A GRAPH AND APPLICATIONS
MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69, 1 (2017), 23 38 March 2017 research paper originalni nauqni rad FIXED POINT RESULTS FOR (ϕ, ψ)-contractions IN METRIC SPACES ENDOWED WITH A GRAPH AND APPLICATIONS
2 (Bonus). Let A X consist of points (x, y) such that either x or y is a rational number. Is A measurable? What is its Lebesgue measure?
 MA 645-4A (Real Analysis), Dr. Chernov Homework assignment 1 (Due 9/5). Prove that every countable set A is measurable and µ(a) = 0. 2 (Bonus). Let A consist of points (x, y) such that either x or y is
MA 645-4A (Real Analysis), Dr. Chernov Homework assignment 1 (Due 9/5). Prove that every countable set A is measurable and µ(a) = 0. 2 (Bonus). Let A consist of points (x, y) such that either x or y is
A CONCISE PROOF OF THE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF INERTIAL MANIFOLDS
 This paper has appeared in Physics Letters A 200 (1995) 415 417 A CONCISE PROOF OF THE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF INERTIAL MANIFOLDS James C. Robinson Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics,
This paper has appeared in Physics Letters A 200 (1995) 415 417 A CONCISE PROOF OF THE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTION OF INERTIAL MANIFOLDS James C. Robinson Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics,
Weak Topologies, Reflexivity, Adjoint operators
 Chapter 2 Weak Topologies, Reflexivity, Adjoint operators 2.1 Topological vector spaces and locally convex spaces Definition 2.1.1. [Topological Vector Spaces and Locally convex Spaces] Let E be a vector
Chapter 2 Weak Topologies, Reflexivity, Adjoint operators 2.1 Topological vector spaces and locally convex spaces Definition 2.1.1. [Topological Vector Spaces and Locally convex Spaces] Let E be a vector
Notes for Functional Analysis
 Notes for Functional Analysis Wang Zuoqin (typed by Xiyu Zhai) November 6, 2015 1 Lecture 18 1.1 The convex hull Let X be any vector space, and E X a subset. Definition 1.1. The convex hull of E is the
Notes for Functional Analysis Wang Zuoqin (typed by Xiyu Zhai) November 6, 2015 1 Lecture 18 1.1 The convex hull Let X be any vector space, and E X a subset. Definition 1.1. The convex hull of E is the
Continuous Functions on Metric Spaces
 Continuous Functions on Metric Spaces Math 201A, Fall 2016 1 Continuous functions Definition 1. Let (X, d X ) and (Y, d Y ) be metric spaces. A function f : X Y is continuous at a X if for every ɛ > 0
Continuous Functions on Metric Spaces Math 201A, Fall 2016 1 Continuous functions Definition 1. Let (X, d X ) and (Y, d Y ) be metric spaces. A function f : X Y is continuous at a X if for every ɛ > 0
A Note on Some Properties of Local Random Attractors
 Northeast. Math. J. 24(2)(2008), 163 172 A Note on Some Properties of Local Random Attractors LIU Zhen-xin ( ) (School of Mathematics, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012) SU Meng-long ( ) (Mathematics
Northeast. Math. J. 24(2)(2008), 163 172 A Note on Some Properties of Local Random Attractors LIU Zhen-xin ( ) (School of Mathematics, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012) SU Meng-long ( ) (Mathematics
MAT 578 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 MAT 578 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS EXERCISES JOHN QUIGG Exercise 1. Prove that if A is bounded in a topological vector space, then for every neighborhood V of 0 there exists c > 0 such that tv A for all t > c.
MAT 578 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS EXERCISES JOHN QUIGG Exercise 1. Prove that if A is bounded in a topological vector space, then for every neighborhood V of 0 there exists c > 0 such that tv A for all t > c.
THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 515
 THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 515 Proposition 1 (=comment on page 17). If A is an algebra, then any finite union or finite intersection of sets in A is also in A. Proposition 2 (=Proposition 1.1). For every
THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 515 Proposition 1 (=comment on page 17). If A is an algebra, then any finite union or finite intersection of sets in A is also in A. Proposition 2 (=Proposition 1.1). For every
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Lecture - 01
 Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Lecture - 01 Alexandre Nolasco de Carvalho August 08, 2017 Presentation Course contents Aims and purpose of the course Bibliography Motivation To explain what is a dynamical
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Lecture - 01 Alexandre Nolasco de Carvalho August 08, 2017 Presentation Course contents Aims and purpose of the course Bibliography Motivation To explain what is a dynamical
Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces
 Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces In this chapter, we consider continuity properties of real-valued convex functions defined on open convex sets in normed spaces. Recall that every infinitedimensional
Continuity of convex functions in normed spaces In this chapter, we consider continuity properties of real-valued convex functions defined on open convex sets in normed spaces. Recall that every infinitedimensional
HI CAMBRIDGE n S P UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Infinite-Dimensional Dynamical Systems An Introduction to Dissipative Parabolic PDEs and the Theory of Global Attractors JAMES C. ROBINSON University of Warwick HI CAMBRIDGE n S P UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface
Infinite-Dimensional Dynamical Systems An Introduction to Dissipative Parabolic PDEs and the Theory of Global Attractors JAMES C. ROBINSON University of Warwick HI CAMBRIDGE n S P UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface
l(y j ) = 0 for all y j (1)
 Problem 1. The closed linear span of a subset {y j } of a normed vector space is defined as the intersection of all closed subspaces containing all y j and thus the smallest such subspace. 1 Show that
Problem 1. The closed linear span of a subset {y j } of a normed vector space is defined as the intersection of all closed subspaces containing all y j and thus the smallest such subspace. 1 Show that
E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem
 E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem 359 E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem If X is a normed space, then the closed unit ball in X or X is compact if and only if X is finite-dimensional (Problem A.25). Even so, Alaoglu s Theorem
E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem 359 E.7 Alaoglu s Theorem If X is a normed space, then the closed unit ball in X or X is compact if and only if X is finite-dimensional (Problem A.25). Even so, Alaoglu s Theorem
A NOTE ON LINEAR FUNCTIONAL NORMS
 A NOTE ON LINEAR FUNCTIONAL NORMS YIFEI PAN AND MEI WANG Abstract. For a vector u in a normed linear space, Hahn-Banach Theorem provides the existence of a linear functional f, f(u) = u such that f = 1.
A NOTE ON LINEAR FUNCTIONAL NORMS YIFEI PAN AND MEI WANG Abstract. For a vector u in a normed linear space, Hahn-Banach Theorem provides the existence of a linear functional f, f(u) = u such that f = 1.
Determining Asymptotic Behaviour from the Dynamics on Attracting Sets
 Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations 11 (1999) 319 331 Determining Asymptotic Behaviour from the Dynamics on Attracting Sets Jose A. Langa 1 & James C. Robinson 2 Proposed running head: Determining
Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations 11 (1999) 319 331 Determining Asymptotic Behaviour from the Dynamics on Attracting Sets Jose A. Langa 1 & James C. Robinson 2 Proposed running head: Determining
Functional Analysis. Martin Brokate. 1 Normed Spaces 2. 2 Hilbert Spaces The Principle of Uniform Boundedness 32
 Functional Analysis Martin Brokate Contents 1 Normed Spaces 2 2 Hilbert Spaces 2 3 The Principle of Uniform Boundedness 32 4 Extension, Reflexivity, Separation 37 5 Compact subsets of C and L p 46 6 Weak
Functional Analysis Martin Brokate Contents 1 Normed Spaces 2 2 Hilbert Spaces 2 3 The Principle of Uniform Boundedness 32 4 Extension, Reflexivity, Separation 37 5 Compact subsets of C and L p 46 6 Weak
Nonlinear Systems and Control Lecture # 12 Converse Lyapunov Functions & Time Varying Systems. p. 1/1
 Nonlinear Systems and Control Lecture # 12 Converse Lyapunov Functions & Time Varying Systems p. 1/1 p. 2/1 Converse Lyapunov Theorem Exponential Stability Let x = 0 be an exponentially stable equilibrium
Nonlinear Systems and Control Lecture # 12 Converse Lyapunov Functions & Time Varying Systems p. 1/1 p. 2/1 Converse Lyapunov Theorem Exponential Stability Let x = 0 be an exponentially stable equilibrium
Spectral theory for compact operators on Banach spaces
 68 Chapter 9 Spectral theory for compact operators on Banach spaces Recall that a subset S of a metric space X is precompact if its closure is compact, or equivalently every sequence contains a Cauchy
68 Chapter 9 Spectral theory for compact operators on Banach spaces Recall that a subset S of a metric space X is precompact if its closure is compact, or equivalently every sequence contains a Cauchy
ON THE HYPERBOLIC RELAXATION OF THE CAHN-HILLIARD EQUATION IN 3-D: APPROXIMATION AND LONG TIME BEHAVIOUR
 ON THE HYPERBOLIC RELAXATION OF THE CAHN-HILLIARD EQUATION IN 3-D: APPROXIMATION AND LONG TIME BEHAVIOUR ANTONIO SEGATTI Abstract. In this paper we consider the hyperbolic relaxation of the Cahn-Hilliard
ON THE HYPERBOLIC RELAXATION OF THE CAHN-HILLIARD EQUATION IN 3-D: APPROXIMATION AND LONG TIME BEHAVIOUR ANTONIO SEGATTI Abstract. In this paper we consider the hyperbolic relaxation of the Cahn-Hilliard
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Ninth Class
 Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Ninth Class Alexandre Nolasco de Carvalho September 21, 2017 Lemma Let {T (t) : t 0} be a dynamically gradient semigroup in a metric space X, with a global attractor A and a
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Ninth Class Alexandre Nolasco de Carvalho September 21, 2017 Lemma Let {T (t) : t 0} be a dynamically gradient semigroup in a metric space X, with a global attractor A and a
7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces
 7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces 7.1 Completeness Let (X, d) be a metric space. Definition 7.1. A sequence (x n ) n N in X is a Cauchy sequence if for any ɛ > 0, there is N N such that n, m
7 Complete metric spaces and function spaces 7.1 Completeness Let (X, d) be a metric space. Definition 7.1. A sequence (x n ) n N in X is a Cauchy sequence if for any ɛ > 0, there is N N such that n, m
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Functional analysis can be seen as a natural extension of the real analysis to more general spaces. As an example we can think at the Heine - Borel theorem (closed and bounded is
Chapter 1 Introduction Functional analysis can be seen as a natural extension of the real analysis to more general spaces. As an example we can think at the Heine - Borel theorem (closed and bounded is
1.2 Fundamental Theorems of Functional Analysis
 1.2 Fundamental Theorems of Functional Analysis 15 Indeed, h = ω ψ ωdx is continuous compactly supported with R hdx = 0 R and thus it has a unique compactly supported primitive. Hence fφ dx = f(ω ψ ωdy)dx
1.2 Fundamental Theorems of Functional Analysis 15 Indeed, h = ω ψ ωdx is continuous compactly supported with R hdx = 0 R and thus it has a unique compactly supported primitive. Hence fφ dx = f(ω ψ ωdy)dx
NOTES AND ERRATA FOR RECURRENCE AND TOPOLOGY. (τ + arg z) + 1
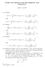 NOTES AND ERRATA FOR RECURRENCE AND TOPOLOGY JOHN M. ALONGI p.11 Replace ρ(t, z) = ρ(t, z) = p.11 Replace sin 2 z e τ ] 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 1 + z (e τ dτ. sin 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 z 2 z e τ ] 2 1 + z (e τ dτ.
NOTES AND ERRATA FOR RECURRENCE AND TOPOLOGY JOHN M. ALONGI p.11 Replace ρ(t, z) = ρ(t, z) = p.11 Replace sin 2 z e τ ] 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 1 + z (e τ dτ. sin 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 z 2 z e τ ] 2 1 + z (e τ dτ.
Analysis Preliminary Exam Workshop: Hilbert Spaces
 Analysis Preliminary Exam Workshop: Hilbert Spaces 1. Hilbert spaces A Hilbert space H is a complete real or complex inner product space. Consider complex Hilbert spaces for definiteness. If (, ) : H H
Analysis Preliminary Exam Workshop: Hilbert Spaces 1. Hilbert spaces A Hilbert space H is a complete real or complex inner product space. Consider complex Hilbert spaces for definiteness. If (, ) : H H
Asymptotic behavior of Ginzburg-Landau equations of superfluidity
 Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-9015, Vol. 3 (2009) 200 (12pp) DOI: 10.1685/CSC09200 Asymptotic behavior of Ginzburg-Landau equations of superfluidity Alessia Berti 1, Valeria Berti 2, Ivana
Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-9015, Vol. 3 (2009) 200 (12pp) DOI: 10.1685/CSC09200 Asymptotic behavior of Ginzburg-Landau equations of superfluidity Alessia Berti 1, Valeria Berti 2, Ivana
Metric Space Topology (Spring 2016) Selected Homework Solutions. HW1 Q1.2. Suppose that d is a metric on a set X. Prove that the inequality d(x, y)
 Metric Space Topology (Spring 2016) Selected Homework Solutions HW1 Q1.2. Suppose that d is a metric on a set X. Prove that the inequality d(x, y) d(z, w) d(x, z) + d(y, w) holds for all w, x, y, z X.
Metric Space Topology (Spring 2016) Selected Homework Solutions HW1 Q1.2. Suppose that d is a metric on a set X. Prove that the inequality d(x, y) d(z, w) d(x, z) + d(y, w) holds for all w, x, y, z X.
Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015)
 Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015) 1. Let X be a set (with no particular algebraic structure). A function d : X X R is called a metric on X (and then X is called a metric space) when d satisfies
Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015) 1. Let X be a set (with no particular algebraic structure). A function d : X X R is called a metric on X (and then X is called a metric space) when d satisfies
2.2 Annihilators, complemented subspaces
 34CHAPTER 2. WEAK TOPOLOGIES, REFLEXIVITY, ADJOINT OPERATORS 2.2 Annihilators, complemented subspaces Definition 2.2.1. [Annihilators, Pre-Annihilators] Assume X is a Banach space. Let M X and N X. We
34CHAPTER 2. WEAK TOPOLOGIES, REFLEXIVITY, ADJOINT OPERATORS 2.2 Annihilators, complemented subspaces Definition 2.2.1. [Annihilators, Pre-Annihilators] Assume X is a Banach space. Let M X and N X. We
The Dirichlet s P rinciple. In this lecture we discuss an alternative formulation of the Dirichlet problem for the Laplace equation:
 Oct. 1 The Dirichlet s P rinciple In this lecture we discuss an alternative formulation of the Dirichlet problem for the Laplace equation: 1. Dirichlet s Principle. u = in, u = g on. ( 1 ) If we multiply
Oct. 1 The Dirichlet s P rinciple In this lecture we discuss an alternative formulation of the Dirichlet problem for the Laplace equation: 1. Dirichlet s Principle. u = in, u = g on. ( 1 ) If we multiply
An introduction to some aspects of functional analysis
 An introduction to some aspects of functional analysis Stephen Semmes Rice University Abstract These informal notes deal with some very basic objects in functional analysis, including norms and seminorms
An introduction to some aspects of functional analysis Stephen Semmes Rice University Abstract These informal notes deal with some very basic objects in functional analysis, including norms and seminorms
MATH MEASURE THEORY AND FOURIER ANALYSIS. Contents
 MATH 3969 - MEASURE THEORY AND FOURIER ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOCH Contents 1. Measure Theory 2 1.1. Properties of Measures 3 1.2. Constructing σ-algebras and measures 3 1.3. Properties of the Lebesgue measure
MATH 3969 - MEASURE THEORY AND FOURIER ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOCH Contents 1. Measure Theory 2 1.1. Properties of Measures 3 1.2. Constructing σ-algebras and measures 3 1.3. Properties of the Lebesgue measure
Topology. Xiaolong Han. Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA address:
 Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
Topology Xiaolong Han Department of Mathematics, California State University, Northridge, CA 91330, USA E-mail address: Xiaolong.Han@csun.edu Remark. You are entitled to a reward of 1 point toward a homework
Introduction to Functional Analysis
 Introduction to Functional Analysis Carnegie Mellon University, 21-640, Spring 2014 Acknowledgements These notes are based on the lecture course given by Irene Fonseca but may differ from the exact lecture
Introduction to Functional Analysis Carnegie Mellon University, 21-640, Spring 2014 Acknowledgements These notes are based on the lecture course given by Irene Fonseca but may differ from the exact lecture
Functional Analysis HW #3
 Functional Analysis HW #3 Sangchul Lee October 26, 2015 1 Solutions Exercise 2.1. Let D = { f C([0, 1]) : f C([0, 1])} and define f d = f + f. Show that D is a Banach algebra and that the Gelfand transform
Functional Analysis HW #3 Sangchul Lee October 26, 2015 1 Solutions Exercise 2.1. Let D = { f C([0, 1]) : f C([0, 1])} and define f d = f + f. Show that D is a Banach algebra and that the Gelfand transform
Banach Spaces V: A Closer Look at the w- and the w -Topologies
 BS V c Gabriel Nagy Banach Spaces V: A Closer Look at the w- and the w -Topologies Notes from the Functional Analysis Course (Fall 07 - Spring 08) In this section we discuss two important, but highly non-trivial,
BS V c Gabriel Nagy Banach Spaces V: A Closer Look at the w- and the w -Topologies Notes from the Functional Analysis Course (Fall 07 - Spring 08) In this section we discuss two important, but highly non-trivial,
Algebraic Topology European Mathematical Society Zürich 2008 Tammo tom Dieck Georg-August-Universität
 1 Algebraic Topology European Mathematical Society Zürich 2008 Tammo tom Dieck Georg-August-Universität Corrections for the first printing Page 7 +6: j is already assumed to be an inclusion. But the assertion
1 Algebraic Topology European Mathematical Society Zürich 2008 Tammo tom Dieck Georg-August-Universität Corrections for the first printing Page 7 +6: j is already assumed to be an inclusion. But the assertion
A Concise Course on Stochastic Partial Differential Equations
 A Concise Course on Stochastic Partial Differential Equations Michael Röckner Reference: C. Prevot, M. Röckner: Springer LN in Math. 1905, Berlin (2007) And see the references therein for the original
A Concise Course on Stochastic Partial Differential Equations Michael Röckner Reference: C. Prevot, M. Röckner: Springer LN in Math. 1905, Berlin (2007) And see the references therein for the original
1 The Local-to-Global Lemma
 Point-Set Topology Connectedness: Lecture 2 1 The Local-to-Global Lemma In the world of advanced mathematics, we are often interested in comparing the local properties of a space to its global properties.
Point-Set Topology Connectedness: Lecture 2 1 The Local-to-Global Lemma In the world of advanced mathematics, we are often interested in comparing the local properties of a space to its global properties.
The goal of this chapter is to study linear systems of ordinary differential equations: dt,..., dx ) T
 1 1 Linear Systems The goal of this chapter is to study linear systems of ordinary differential equations: ẋ = Ax, x(0) = x 0, (1) where x R n, A is an n n matrix and ẋ = dx ( dt = dx1 dt,..., dx ) T n.
1 1 Linear Systems The goal of this chapter is to study linear systems of ordinary differential equations: ẋ = Ax, x(0) = x 0, (1) where x R n, A is an n n matrix and ẋ = dx ( dt = dx1 dt,..., dx ) T n.
4 Countability axioms
 4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
4 COUNTABILITY AXIOMS 4 Countability axioms Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space X is said to be first countable if for any x X, there is a countable basis for the neighborhoods of x. X is said
Contents: 1. Minimization. 2. The theorem of Lions-Stampacchia for variational inequalities. 3. Γ -Convergence. 4. Duality mapping.
 Minimization Contents: 1. Minimization. 2. The theorem of Lions-Stampacchia for variational inequalities. 3. Γ -Convergence. 4. Duality mapping. 1 Minimization A Topological Result. Let S be a topological
Minimization Contents: 1. Minimization. 2. The theorem of Lions-Stampacchia for variational inequalities. 3. Γ -Convergence. 4. Duality mapping. 1 Minimization A Topological Result. Let S be a topological
Analysis Qualifying Exam
 Analysis Qualifying Exam Spring 2017 Problem 1: Let f be differentiable on R. Suppose that there exists M > 0 such that f(k) M for each integer k, and f (x) M for all x R. Show that f is bounded, i.e.,
Analysis Qualifying Exam Spring 2017 Problem 1: Let f be differentiable on R. Suppose that there exists M > 0 such that f(k) M for each integer k, and f (x) M for all x R. Show that f is bounded, i.e.,
Chapter 14. Duality for Normed Linear Spaces
 14.1. Linear Functionals, Bounded Linear Functionals, and Weak Topologies 1 Chapter 14. Duality for Normed Linear Spaces Note. In Section 8.1, we defined a linear functional on a normed linear space, a
14.1. Linear Functionals, Bounded Linear Functionals, and Weak Topologies 1 Chapter 14. Duality for Normed Linear Spaces Note. In Section 8.1, we defined a linear functional on a normed linear space, a
2 Statement of the problem and assumptions
 Mathematical Notes, 25, vol. 78, no. 4, pp. 466 48. Existence Theorem for Optimal Control Problems on an Infinite Time Interval A.V. Dmitruk and N.V. Kuz kina We consider an optimal control problem on
Mathematical Notes, 25, vol. 78, no. 4, pp. 466 48. Existence Theorem for Optimal Control Problems on an Infinite Time Interval A.V. Dmitruk and N.V. Kuz kina We consider an optimal control problem on
Nonlinear Systems Theory
 Nonlinear Systems Theory Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 2: Nonlinear Systems Theory Overview Our next goal is to extend LMI s and optimization to nonlinear systems analysis. Today we
Nonlinear Systems Theory Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 2: Nonlinear Systems Theory Overview Our next goal is to extend LMI s and optimization to nonlinear systems analysis. Today we
ATTRACTORS FOR THE STOCHASTIC 3D NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS
 Stochastics and Dynamics c World Scientific Publishing Company ATTRACTORS FOR THE STOCHASTIC 3D NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS PEDRO MARÍN-RUBIO Dpto. Ecuaciones Diferenciales y Análisis Numérico Universidad
Stochastics and Dynamics c World Scientific Publishing Company ATTRACTORS FOR THE STOCHASTIC 3D NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS PEDRO MARÍN-RUBIO Dpto. Ecuaciones Diferenciales y Análisis Numérico Universidad
LMI Methods in Optimal and Robust Control
 LMI Methods in Optimal and Robust Control Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 15: Nonlinear Systems and Lyapunov Functions Overview Our next goal is to extend LMI s and optimization to nonlinear
LMI Methods in Optimal and Robust Control Matthew M. Peet Arizona State University Lecture 15: Nonlinear Systems and Lyapunov Functions Overview Our next goal is to extend LMI s and optimization to nonlinear
Topological vectorspaces
 (July 25, 2011) Topological vectorspaces Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ Natural non-fréchet spaces Topological vector spaces Quotients and linear maps More topological
(July 25, 2011) Topological vectorspaces Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ Natural non-fréchet spaces Topological vector spaces Quotients and linear maps More topological
1.A Topological spaces The initial topology is called topology generated by (f i ) i I.
 kechris.tex December 12, 2012 Classical descriptive set theory Notes from [Ke]. 1 1 Polish spaces 1.1 Topological and metric spaces 1.A Topological spaces The initial topology is called topology generated
kechris.tex December 12, 2012 Classical descriptive set theory Notes from [Ke]. 1 1 Polish spaces 1.1 Topological and metric spaces 1.A Topological spaces The initial topology is called topology generated
Minimal periods of semilinear evolution equations with Lipschitz nonlinearity
 Minimal periods of semilinear evolution equations with Lipschitz nonlinearity James C. Robinson a Alejandro Vidal-López b a Mathematics Institute, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV4 7AL, U.K. b Departamento
Minimal periods of semilinear evolution equations with Lipschitz nonlinearity James C. Robinson a Alejandro Vidal-López b a Mathematics Institute, University of Warwick, Coventry, CV4 7AL, U.K. b Departamento
Commutative Banach algebras 79
 8. Commutative Banach algebras In this chapter, we analyze commutative Banach algebras in greater detail. So we always assume that xy = yx for all x, y A here. Definition 8.1. Let A be a (commutative)
8. Commutative Banach algebras In this chapter, we analyze commutative Banach algebras in greater detail. So we always assume that xy = yx for all x, y A here. Definition 8.1. Let A be a (commutative)
Compact operators on Banach spaces
 Compact operators on Banach spaces Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto November 12, 2017 1 Introduction In this note I prove several things about compact
Compact operators on Banach spaces Jordan Bell jordan.bell@gmail.com Department of Mathematics, University of Toronto November 12, 2017 1 Introduction In this note I prove several things about compact
A note on some approximation theorems in measure theory
 A note on some approximation theorems in measure theory S. Kesavan and M. T. Nair Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, Chennai - 600 06 email: kesh@iitm.ac.in and mtnair@iitm.ac.in
A note on some approximation theorems in measure theory S. Kesavan and M. T. Nair Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, Chennai - 600 06 email: kesh@iitm.ac.in and mtnair@iitm.ac.in
2. Metric Spaces. 2.1 Definitions etc.
 2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
2. Metric Spaces 2.1 Definitions etc. The procedure in Section for regarding R as a topological space may be generalized to many other sets in which there is some kind of distance (formally, sets with
Problem Set 6: Solutions Math 201A: Fall a n x n,
 Problem Set 6: Solutions Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. Is (x n ) n=0 a Schauder basis of C([0, 1])? No. If f(x) = a n x n, n=0 where the series converges uniformly on [0, 1], then f has a power series
Problem Set 6: Solutions Math 201A: Fall 2016 Problem 1. Is (x n ) n=0 a Schauder basis of C([0, 1])? No. If f(x) = a n x n, n=0 where the series converges uniformly on [0, 1], then f has a power series
A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO BANACH LATTICES AND
 CHAPTER A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO BANACH LATTICES AND POSITIVE OPERATORS In tis capter we give a brief introduction to Banac lattices and positive operators. Most results of tis capter can be found, e.g.,
CHAPTER A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO BANACH LATTICES AND POSITIVE OPERATORS In tis capter we give a brief introduction to Banac lattices and positive operators. Most results of tis capter can be found, e.g.,
Lipschitz p-convex and q-concave maps
 Lipschitz p-convex and q-concave maps J. Alejandro Chávez-Domínguez Instituto de Ciencias Matemáticas, CSIC-UAM-UCM-UC3M, Madrid and Department of Mathematics, University of Texas at Austin Conference
Lipschitz p-convex and q-concave maps J. Alejandro Chávez-Domínguez Instituto de Ciencias Matemáticas, CSIC-UAM-UCM-UC3M, Madrid and Department of Mathematics, University of Texas at Austin Conference
MH 7500 THEOREMS. (iii) A = A; (iv) A B = A B. Theorem 5. If {A α : α Λ} is any collection of subsets of a space X, then
 MH 7500 THEOREMS Definition. A topological space is an ordered pair (X, T ), where X is a set and T is a collection of subsets of X such that (i) T and X T ; (ii) U V T whenever U, V T ; (iii) U T whenever
MH 7500 THEOREMS Definition. A topological space is an ordered pair (X, T ), where X is a set and T is a collection of subsets of X such that (i) T and X T ; (ii) U V T whenever U, V T ; (iii) U T whenever
FIXED POINT OF CONTRACTION AND EXPONENTIAL ATTRACTORS. Y. Takei and A. Yagi 1. Received February 22, 2006; revised April 6, 2006
 Scientiae Mathematicae Japonicae Online, e-2006, 543 550 543 FIXED POINT OF CONTRACTION AND EXPONENTIAL ATTRACTORS Y. Takei and A. Yagi 1 Received February 22, 2006; revised April 6, 2006 Abstract. The
Scientiae Mathematicae Japonicae Online, e-2006, 543 550 543 FIXED POINT OF CONTRACTION AND EXPONENTIAL ATTRACTORS Y. Takei and A. Yagi 1 Received February 22, 2006; revised April 6, 2006 Abstract. The
Functional Analysis I
 Functional Analysis I Course Notes by Stefan Richter Transcribed and Annotated by Gregory Zitelli Polar Decomposition Definition. An operator W B(H) is called a partial isometry if W x = X for all x (ker
Functional Analysis I Course Notes by Stefan Richter Transcribed and Annotated by Gregory Zitelli Polar Decomposition Definition. An operator W B(H) is called a partial isometry if W x = X for all x (ker
Real Analysis Notes. Thomas Goller
 Real Analysis Notes Thomas Goller September 4, 2011 Contents 1 Abstract Measure Spaces 2 1.1 Basic Definitions........................... 2 1.2 Measurable Functions........................ 2 1.3 Integration..............................
Real Analysis Notes Thomas Goller September 4, 2011 Contents 1 Abstract Measure Spaces 2 1.1 Basic Definitions........................... 2 1.2 Measurable Functions........................ 2 1.3 Integration..............................
Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7
 Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, February 5th, 2016 Please do Exercises 3, 6, 14, 16*, 17, 18, 21*, 23*, 24, 27*. Exercises marked
Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, February 5th, 2016 Please do Exercises 3, 6, 14, 16*, 17, 18, 21*, 23*, 24, 27*. Exercises marked
Asymptotic Stability by Linearization
 Dynamical Systems Prof. J. Rauch Asymptotic Stability by Linearization Summary. Sufficient and nearly sharp sufficient conditions for asymptotic stability of equiiibria of differential equations, fixed
Dynamical Systems Prof. J. Rauch Asymptotic Stability by Linearization Summary. Sufficient and nearly sharp sufficient conditions for asymptotic stability of equiiibria of differential equations, fixed
Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015)
 Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015) 1. Let X be a set (with no particular algebraic structure). A function d : X X R is called a metric on X (and then X is called a metric space) when d satisfies
Your first day at work MATH 806 (Fall 2015) 1. Let X be a set (with no particular algebraic structure). A function d : X X R is called a metric on X (and then X is called a metric space) when d satisfies
Filters in Analysis and Topology
 Filters in Analysis and Topology David MacIver July 1, 2004 Abstract The study of filters is a very natural way to talk about convergence in an arbitrary topological space, and carries over nicely into
Filters in Analysis and Topology David MacIver July 1, 2004 Abstract The study of filters is a very natural way to talk about convergence in an arbitrary topological space, and carries over nicely into
In essence, Dynamical Systems is a science which studies differential equations. A differential equation here is the equation
 Lecture I In essence, Dynamical Systems is a science which studies differential equations. A differential equation here is the equation ẋ(t) = f(x(t), t) where f is a given function, and x(t) is an unknown
Lecture I In essence, Dynamical Systems is a science which studies differential equations. A differential equation here is the equation ẋ(t) = f(x(t), t) where f is a given function, and x(t) is an unknown
Corollary A linear operator A is the generator of a C 0 (G(t)) t 0 satisfying G(t) e ωt if and only if (i) A is closed and D(A) = X;
 2.2 Rudiments 71 Corollary 2.12. A linear operator A is the generator of a C 0 (G(t)) t 0 satisfying G(t) e ωt if and only if (i) A is closed and D(A) = X; (ii) ρ(a) (ω, ) and for such λ semigroup R(λ,
2.2 Rudiments 71 Corollary 2.12. A linear operator A is the generator of a C 0 (G(t)) t 0 satisfying G(t) e ωt if and only if (i) A is closed and D(A) = X; (ii) ρ(a) (ω, ) and for such λ semigroup R(λ,
8 Change of variables
 Tel Aviv University, 2013/14 Analysis-III,IV 111 8 Change of variables 8a What is the problem................ 111 8b Examples and exercises............... 113 8c Differentiating set functions............
Tel Aviv University, 2013/14 Analysis-III,IV 111 8 Change of variables 8a What is the problem................ 111 8b Examples and exercises............... 113 8c Differentiating set functions............
Math 209B Homework 2
 Math 29B Homework 2 Edward Burkard Note: All vector spaces are over the field F = R or C 4.6. Two Compactness Theorems. 4. Point Set Topology Exercise 6 The product of countably many sequentally compact
Math 29B Homework 2 Edward Burkard Note: All vector spaces are over the field F = R or C 4.6. Two Compactness Theorems. 4. Point Set Topology Exercise 6 The product of countably many sequentally compact
1 Topology Definition of a topology Basis (Base) of a topology The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3
 Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
Index Page 1 Topology 2 1.1 Definition of a topology 2 1.2 Basis (Base) of a topology 2 1.3 The subspace topology & the product topology on X Y 3 1.4 Basic topology concepts: limit points, closed sets,
arxiv: v3 [math.ds] 9 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v3 [math.ds] 9 Nov 2012 arxiv: v3 [math.ds] 9 Nov 2012](/thumbs/92/108796755.jpg) Positive expansive flows Alfonso Artigue November 13, 2018 arxiv:1210.3202v3 [math.ds] 9 Nov 2012 Abstract We show that every positive expansive flow on a compact metric space consists of a finite number
Positive expansive flows Alfonso Artigue November 13, 2018 arxiv:1210.3202v3 [math.ds] 9 Nov 2012 Abstract We show that every positive expansive flow on a compact metric space consists of a finite number
THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 516
 THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 516 Results labeled Theorem Ea.b.c (or Proposition Ea.b.c, etc.) refer to Theorem c from section a.b of Evans book (Partial Differential Equations). Proposition 1 (=Proposition
THEOREMS, ETC., FOR MATH 516 Results labeled Theorem Ea.b.c (or Proposition Ea.b.c, etc.) refer to Theorem c from section a.b of Evans book (Partial Differential Equations). Proposition 1 (=Proposition
Functional Analysis. Franck Sueur Metric spaces Definitions Completeness Compactness Separability...
 Functional Analysis Franck Sueur 2018-2019 Contents 1 Metric spaces 1 1.1 Definitions........................................ 1 1.2 Completeness...................................... 3 1.3 Compactness......................................
Functional Analysis Franck Sueur 2018-2019 Contents 1 Metric spaces 1 1.1 Definitions........................................ 1 1.2 Completeness...................................... 3 1.3 Compactness......................................
Finite-dimensional spaces. C n is the space of n-tuples x = (x 1,..., x n ) of complex numbers. It is a Hilbert space with the inner product
 Chapter 4 Hilbert Spaces 4.1 Inner Product Spaces Inner Product Space. A complex vector space E is called an inner product space (or a pre-hilbert space, or a unitary space) if there is a mapping (, )
Chapter 4 Hilbert Spaces 4.1 Inner Product Spaces Inner Product Space. A complex vector space E is called an inner product space (or a pre-hilbert space, or a unitary space) if there is a mapping (, )
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS-NORMED SPACE
 MAT641- MSC Mathematics, MNIT Jaipur FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS-NORMED SPACE DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR 1. Normed space Norm generalizes the concept of length in an arbitrary
MAT641- MSC Mathematics, MNIT Jaipur FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS-NORMED SPACE DR. RITU AGARWAL MALAVIYA NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY JAIPUR 1. Normed space Norm generalizes the concept of length in an arbitrary
Phase-field systems with nonlinear coupling and dynamic boundary conditions
 1 / 46 Phase-field systems with nonlinear coupling and dynamic boundary conditions Cecilia Cavaterra Dipartimento di Matematica F. Enriques Università degli Studi di Milano cecilia.cavaterra@unimi.it VIII
1 / 46 Phase-field systems with nonlinear coupling and dynamic boundary conditions Cecilia Cavaterra Dipartimento di Matematica F. Enriques Università degli Studi di Milano cecilia.cavaterra@unimi.it VIII
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: WEAK AND WEAK* CONVERGENCE
 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: WEAK AND WEAK* CONVERGENCE CHRISTOPHER HEIL 1. Weak and Weak* Convergence of Vectors Definition 1.1. Let X be a normed linear space, and let x n, x X. a. We say that
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS LECTURE NOTES: WEAK AND WEAK* CONVERGENCE CHRISTOPHER HEIL 1. Weak and Weak* Convergence of Vectors Definition 1.1. Let X be a normed linear space, and let x n, x X. a. We say that
