Why are earthquake slip zones so narrow?
|
|
|
- Amberlynn Hamilton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Why are earthquake slip zones so narrow? John W. Rudnicki Northwestern University Evanston, IL (with Jim Rice, Harvard University) October 9, 9 University o Minnesota. Geomechanics Seminar
2 F. Chester, J. Evans and R. Biegel, J. Geoph. Res., 98 (B1), (1993) 3-1 m (Damage highly cracked rock. Zone with macro aults or ractures extends ~ 1x urther.) 1-1 m (Sometimes described as oliated gouge, or or some aults, simply as gouge.) 1s-1s mm (But principal ailure surace is much thinner, typically < 1-5 mm!)
3 J.Geophys. Res. (1993)
4 Chester, F. M., and J. S. Chester, Ultracataclasite structure and riction processes o the Punchbowl ault, San Andreas system, Caliornia, Tectonophysics, 95 (1-): 199-1,1998 Prominent slip surace (pss) is located in the center o the layer and identiied by the black arrows. (Exhumed rom -4 km depth. Total slip 44 km. Several km o slip in earthquakes on pss.)
5 From J. S. Chester and D. L. Goldsby, SCEC Ann. Rpt., 3 (also, Chester et al., EOS, Trans AGU, 3) Punchbowl Fault prominent slip surace mm-thick layer; crystal-lattice preerred orientation (evidence: uniorm bireringence, bright layer); contains distinct microscopic slip suraces, 1 3 μm thick.
6 Q: Could coupling o luid and thermal diusion with slip be a actor in setting the width o the slip zone?
7 Stability o spatially uniorm, adiabatic, undrained, shear: y γ h / σ= n τ constant h/ h/ x σ n
8 Governing equations or shearing velocity V(y, t), shear stress τ(y, t), pore pressure p(y, t), and temperature T(y, t): Equation o Motion τ y = (inertia irrelevant), σ = const. Energy Balance V o T q h T τ = ρ c +, qh = K y t y y Fluid Mass Conservation m q ρ k p =, q = t y η y Even i y directions accelerations are large say, 1 1 g, stress change is small over narrow region near ault where luid and diusion processes are important. n Heat generated due to inelastic shear (neglect elastic) Neglects small terms due to work o normal stress and pore pressure and energy transer due to low o luid [Small work terms, σ h pq / ρ, and energy outlow eq.] Heat lux, Fourier s law n Fluid mass change (per unit reerence volume) Darcy s law
9 Dependence o Fluid Mass (per unit reerence volume) m= ρ n ( n = pore volume per unit reerence volume, ρ = luid mass density) el pl m ρ n n = n + ρ + t t t t should be measured or calculated or el one dimensional strain. 1 n p T = β +Λ n n n t t t ( β, Λ are compressb i ility and thermal expansivity o pore volume) 1 ρ n n ( β, Λ are compressibility and thermal expansivity o pore 1 ρ ρ p T = β Λ t t t m p T n = β Λ + t t t t ( n) n ( n) β n β + β pl is an elastic storage coeicient luid) Λ ( λ λ )/ β + β ratio o pore pressure change to temperature change during undrained, elastic deormation
10 Governing Equations τ =, τ = τ( t) y τ ρ α y t y α = K ρ c th V T T = c th / is thermal diusivity 1 Λ + = α hy t t β t y pl p T n p ( ) α = k / η n β β is hydraulic diusivity hy + n
11 Constitutive Relation: Friction Eective normal compressive stress τ = ( σ p) = ( V / y), (...) > In calculations, use ( ) ( ) ( γ) = γ + aln γ / γ where a n.15 is typical o experimental observations About.6 but can be substantially reduced at high slip rates by lash heating o asperities, gel ormation, melting. Simple rate-strengthening riction model; approximately valid only in stable regions in which rupture cannot nucleate, but may propagate through (or in unstable regions that have shear-heated to a rictionally stable T range). (Fuller rate-state description, with localization limiter, must be used in regions o unstable, rate-weakening, riction.)
12 Sliding velocity Fuller rate/state description. Vθ (, ) V 1 V Sliding distance Canonical experiment: aln( V/ V1) bln( V/ V1) ( ss V ) 1 d c ( ss V ) Sliding distance ( ) ( ) ( V) = V + aln V / V + bln( θ / θ ) dθ θv = g( θ, V) = 1 slowness or aging law dt d Ruina (1983), Dieterich c
13 Constitutive Relation: Dilatancy 1 ( ) pl pl n = n ( γ) = C + εln 1 + γ / C 1 where C and C are constants ε γ ε γ = t C + γ t γ t pl n Form introduced by Segall and Rice (1995) but neglects state dependence included by them. Inerred rom experiments by Marone et al. (199) and Byerlee and Lockner (1994). Fit with experiments implies ε 1 4 Note that dilatancy reaches a constant value or ixed strain-rate. Should also include a critical state type term that depends on eective stress. In linearized analysis this term only modiies a poroelastic constant.
14 Spatially uniorm solution (Lachenbruch, 198): V( y, t) = V ( y) = γ y ( γ = uniorm shearing rate), pyt (, ) = p( t), τ( yt, ) = τ ( t) = ( γ )[ σ p( t)], o n σ p () t = [ σ p ()]exp( H γ t) [ call this σ ()] t H n n o 1 where o o is a characteristic strain or decay o strength o H = ( γ ) Λ/ ρ c ( γ ) / [1.7(1 + β / β )], o o n T( y, t) = T ( t), ρ cdt ( t)/ dt = ( γ ) σ ( t) γ o o Is this solution stable (I.e., to spatial non-uniormities)? ANS: NO! For constant riction actor, deormation would localize to a plane. What are the eects o rate-strengthening riction and dilatancy? o
15 Linearized perturbation about time-dependent spatially uniorm solution: (irst neglect dilatancy) V( y, t) = γ y+ V ( y, t), p( y, t) = p ( t) + p ( y, t), o 1 1 T( yt, ) = T( t) + T( yt, ), = ( γ ) + ( γ ) V( yt, )/ y 1 o o 1 Linearized Equations: V1 ( γo) p1+ ( γo) σ( t) = y y V1 V1 o T1 T 1 ( γo) σ( t) ( γo) p1γo + ( γo) σ( t) γo = ρ c αth, y y t y p T p t t y Λ = αhy Boundary conditions: No heat (adiabatic) or mass (undrained low): T / y =, p / y = at y = ± h/ 1 1 Nature o solution with spatial dependence exp(πiy/λ): σ (t) V 1 (y,t) y σ (t) exp( Hγ o t) V 1 (y,t) y, p 1 (y,t), T 1 (y,t) exp(st)exp(πiy / λ) exp[(s+ Hγ o )t]exp(πiy / λ)
16 s = s(λ) satisies: 1 Instability condition : (s) ( ) ( ) ( ) 4πα 4 ch παhy γ γ zh γ = s s where z = = = λ λ γ γ a V y R > λ > λ = π cr α ( αth + αhy ) th + α hy ( z+ ) H γ αα th hy V Near λ = λcr, Im( s) zh, oscillatory h (implies unloading i perturbations become large enough but not included here.) Typically o order -6, in results o low shear-rate experiments.
17 Parameter Values γ α th = = = o 1 / s, ρ c.7 MPa/ K.65 mm / s (range.5 to.7 mm / s) λ = β η = 3 o 4 1 / K,.7 / GPa, 1 Pa-s λ λ Λ + β β o n 1.6 / (1 n / ) MPa/ K ( γ ) =.6,.4,. z = 4, 7, 13 appropriate or water at 8 km depth assuming hydrostatic conditions (1 MPa/km) and a typical thermal gradient ( 5 K/km Low end hydromechanical parameters : n =.4, β / β = 1 α hy H =.35 n = Λ = 1.8 mm /s,.8 MPa/C, ( γ ) based on laboratory measurments o ault gouge material (Wibberley [] and Wibberley and Shimamoto [3] and Lockner et al. [] High end hydromechanical parameters: n =.6, β / β = 4 α hy 4.8 mm /s,.3 MPa/C, H =.1 ( γ ) n = Λ = modiied to estimate eects o increased damaged caused by elevated stresses near the edge o the propagating rupture.
18 Numerical Values o Critical Wavelength ( γ ) =.6,.4,. Low end Parameters λ cr.36 mm,.534(.441) mm, 1.3(.63) mm High end Parameters λ cr = =.849 mm, 1.58(1.4) mm,.43(1.47) mm Highest value typical or rock, but riction at rapid rates o shearing could be reduced by lash heating at asperities, gel ormation, etc. Possible " sel - consistent" estimate o shear layer thickness h at large shear: γ = V / h, V = 1 m/s, h λ α + α th hy h 4π ( z+ ) HV Low end Parameters h = 1.9 μm, 6.5(19.4) μm, 16(38.9) μm High end Parameters h = 7 μm, 158(18) μm, 59(16) μm cr would not expect to see layer thicknesses larger than the critical wavelength since these would localize. order 1 to several 1 μm
19 1 Critical Wavelength, λ crit (mm) Homogeneous shear possible at small h ( λ crit > h ) h = λ crit High End, =. High End, =.6 Low End, =.6 Low End, =. 1E-3 1E Layer width, h (mm)
20 Linearized perturbation about time-dependent spatially uniorm solution: (now neglect rate-strengthening) V( y, t) = γ y+ V ( y, t), p( y, t) = p ( t) + p ( y, t), o 1 1 T( yt, ) = T( t) + T( yt, ), = ( γ ) + ( γ ) V( yt, )/ y 1 o o 1 Linearized Equations: y ( p ) 1 = o T1 T 1 σ() t γ1 p1 = ρ c αth, t y p T ε γ p t t t y Λ + = αhy βγ Boundary conditions: No heat (adiabatic) or mass (undrained low): T / y =, p / y = at y = ± h/ 1 1 Nature o solution with spatial dependence exp(πiy/λ): γ, p ( y, t), T( y, t) exp( st)exp( πiy/ λ) 1 1 1
21 Resulting Equations p () t = 1 Λ T() t + ( εβ / γ ) γ () t = ( εβ / γ ) C 1 1 d γ 1 γ () tˆ B 1 { exp( tˆ) Θ } = CBΘ dtˆ 1 1 No perturbation in pore pressure! C = Λ ( γ / εβ ) T() + γ () 1 1 a constant o the order o the magnitude o initial perturbations where tˆ = H γ t ( p ) B = σ β / ε - Θ = n BH γλ / 4πα Solution: th tˆ 1 γ ( tˆ) = exp B 1 ( 1 exp( tˆ) tˆ/ Θ γ () + BCΘ exp B 1 ( 1 exp( ξ) ξ / Θ) dξ tˆ 1 γ () t = γ ( r) dr 1 1 H I Θ > 1, coeicient is positive at small times, tˆ, implying rapid growth, but becomes negative as tˆ, implying exponential decay.
22 1 6 B = 4, Θ = e B = 13, Θ = sqrt (e) All results or C = γ 1 (Hγ t)/γ 1 () unperturbed solution Approximate result is the maximum strain-rate multiplied by the time at which it occurs t ˆ = ln Θ Hγ t Hγ 1 ( t )/γ 1 () accumulated strain approximation B = 4, Θ = e =.716 Hγ 1 ( t )/γ 1 () 1 1 accumulated strain approximation B = 13, Θ = sqrt(e) = Hγ t Hγ t
23 16 Θ crit 1 8 Threshold 1 4 Threshold B
24 Θ>Θ crit or instability 3 4 (based on an accumulated strain o 1 or 1 ) λ > λ = π crit 4 3 For B = 4, Θ =.5 (.15) or an accumulated strain 1 (1 ) crit Using this and low end parameters λ crit =.3, Θ α crit th BH γ.368,.5 mm or ( γ ) =.6,.4,. For B = 13, Θ = 1.6 or an accumulated strain 1 crit Using this and high end parameters λ crit =.11,..58,.365 mm or ( γ ) =.6,.4,. (About 4 to 1 smaller than or rate-strengthening) For "sel - consistent" estimate o layer thickness: γ = V / h, V = 1 m/s and setting λ = h low end parameters: 9., 13.5, 7.1 μm high end parameters: 4.41, 6.66, 13.3 μm crit 4
25 1 Critical Wavelength, λ crit (mm) Homogeneous shear possible at small h ( λ crit > h ) h = λ crit Viscous, High Viscous, Low Dilatant, High Dilatant, Low 1E-3 1E Layer width, h (mm)
26 γ (t) / γ γ (t) / γ No dilatancy n = 13 n = s = γ t n = s = γ t γ (t) / γ t γ (t) / γ t No dilatancy n = 13 n = s = γ t s = γ t Combined eects o rate-strengthening and dilatancy. High end parameters with B = 13, h = 1mm. Let column is strain-rate; right is strain No dilatancy Wavelength just less than critical (n = 13) based on rate-strengthening only. Wavelength just greater than critical (n = 1) based on rate-strengthening only. Is stabilized by addition o dilatancy. γ (t) / γ n = 11 γ (t) / γ t For a slightly larger wavelength (n = 11), strain-rate appears to be going to zero, but strains are becoming large ~ s = γ t s = γ t I wavelength is increased urther (n = 1) strains 1 6
27 Implications: Even with velocity strengthening and dilatancy must expect large shear strain to be conined to a thin zone, less than diusion penetration distances o heat and luid in moderate and larger events. Justiies use o model based on slip on a plane. Observed 1-5 mm deormed zone thickness in gouge may be a precursor thickness (i.e., λcr based on an initial, broad h) not the thickness o the large shear zone.
28 Limitations (in process o overcoming!?): Linearized perturbation analysis (mainly o two eects separately) Need ull nonlinear numerical analysis (Victor Tsai did some preliminary calculations) More elaborate description o dilatancy. Include variation o luid properties with pressure and temperature changes.
29 Thanks! Questions?
Shear localization due to thermal pressurization of pore fluids in rapidly sheared granular media
 BIOT-5 Conference, Vienna, 10-12 July 2013, Symposium MS02, Mechanics of fluid-infiltrated earth materials - in memory of Terzaghi and Biot Session MS02-2, Localization and failure, presentation MS02-2.1,
BIOT-5 Conference, Vienna, 10-12 July 2013, Symposium MS02, Mechanics of fluid-infiltrated earth materials - in memory of Terzaghi and Biot Session MS02-2, Localization and failure, presentation MS02-2.1,
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture Propagation: Evidence from Geological and Seismological Observations
 Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 9, 21 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Rate and State Friction Velocity step test to measure RSF parameters SHS test to measure RSF parameters
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 9, 21 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Rate and State Friction Velocity step test to measure RSF parameters SHS test to measure RSF parameters
Shear localization due to thermal pressurization of pore fluids in rapidly sheared granular media
 Symposium on the Application of Mechanics to Geophysics Scripps Institute of Oceanography, University of California at San Diego 17 and 18 January 2015 Shear localization due to thermal pressurization
Symposium on the Application of Mechanics to Geophysics Scripps Institute of Oceanography, University of California at San Diego 17 and 18 January 2015 Shear localization due to thermal pressurization
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area. Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC
 Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors
 Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge, 1. Linearized stability analysis
 JOURNAL OF GOPHYSICAL RSARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:0.029/, Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge,. Linearized stability analysis James R. Rice,,2, John W. Rudnicki 3,4,
JOURNAL OF GOPHYSICAL RSARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:0.029/, Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge,. Linearized stability analysis James R. Rice,,2, John W. Rudnicki 3,4,
Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge: 1. Linearized Stability Analysis
 Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge:. Linearized Stability Analysis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Stability and Localization of Rapid Shear in Fluid-Saturated Fault Gouge:. Linearized Stability Analysis The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta. California Institute of Technology
 Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985 #1586}
 12.524, 2005 09 28 LE04: Friction and Constitutive Laws 1 Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985
12.524, 2005 09 28 LE04: Friction and Constitutive Laws 1 Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing
 A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
Shear heating of a fluid-saturated slip-weakening dilatant fault zone 1. Limiting regimes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2121, doi:10.1029/2001jb001653, 2003 Shear heating of a fluid-saturated slip-weakening dilatant fault zone 1. Limiting regimes Dmitry I. Garagash Department
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2121, doi:10.1029/2001jb001653, 2003 Shear heating of a fluid-saturated slip-weakening dilatant fault zone 1. Limiting regimes Dmitry I. Garagash Department
Localization in Undrained Deformation
 Localization in Undrained Deformation J. W. Rudnicki Dept. of Civil and Env. Engn. and Dept. of Mech. Engn. Northwestern University Evanston, IL 621-319 John.Rudnicki@gmail.com Fourth Biot Conference on
Localization in Undrained Deformation J. W. Rudnicki Dept. of Civil and Env. Engn. and Dept. of Mech. Engn. Northwestern University Evanston, IL 621-319 John.Rudnicki@gmail.com Fourth Biot Conference on
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Multiphysicscouplings and stability in geomechanics
 ALERT Geomaterials 25 th ALERT Workshop, Aussois, France 29 Sept.-1 Oct. 214 Multiphysicscouplings and stability in geomechanics Jean Sulem, Ioannis Stefanou Laboratoire Navier, Ecole des Ponts ParisTech,
ALERT Geomaterials 25 th ALERT Workshop, Aussois, France 29 Sept.-1 Oct. 214 Multiphysicscouplings and stability in geomechanics Jean Sulem, Ioannis Stefanou Laboratoire Navier, Ecole des Ponts ParisTech,
39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow
 39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow Gradually varied unsteady low occurs when the low variables such as the low depth and velocity do not change rapidly in time and space. Such lows are very common in
39.1 Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow Gradually varied unsteady low occurs when the low variables such as the low depth and velocity do not change rapidly in time and space. Such lows are very common in
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE. Kyle Withers Qian Yao
 FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
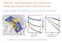 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Dynamic weakening and the depth dependence of earthquake fauling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, 1 2 Dynamic weakening and the depth dependence of earthquake fauling Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt 2 N. Brantut, Rock and Ice Physics Laboratory,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, 1 2 Dynamic weakening and the depth dependence of earthquake fauling Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt 2 N. Brantut, Rock and Ice Physics Laboratory,
The depth-dependence of dynamic weakening
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.19/, The depth-dependence of dynamic weakening Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt Abstract. Earthquake propagation along faults is controlled by both
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.19/, The depth-dependence of dynamic weakening Nicolas Brantut 1, John D. Platt Abstract. Earthquake propagation along faults is controlled by both
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008556, 2011 Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008556, 2011 Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
Shear heating of a fluid-saturated slip-weakening dilatant fault zone: 2. Quasi-drained regime
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B10, 2472, doi:10.1029/2002jb002218, 2003 Shear heating of a fluid-saturated slip-weakening dilatant fault zone: 2. Quasi-drained regime Dmitry I. Garagash
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B10, 2472, doi:10.1029/2002jb002218, 2003 Shear heating of a fluid-saturated slip-weakening dilatant fault zone: 2. Quasi-drained regime Dmitry I. Garagash
Friction. Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces.
 Friction Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces. We first describe the results of laboratory friction experiments, and then discuss the implications of the friction constitutive
Friction Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces. We first describe the results of laboratory friction experiments, and then discuss the implications of the friction constitutive
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF NANOFLUIDS. Convective heat transfer analysis of nanofluid flowing inside a
 Chapter 4 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF NANOFLUIDS Convective heat transer analysis o nanoluid lowing inside a straight tube o circular cross-section under laminar and turbulent conditions
Chapter 4 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS OF NANOFLUIDS Convective heat transer analysis o nanoluid lowing inside a straight tube o circular cross-section under laminar and turbulent conditions
How pore fluid pressurization influences crack tip processes during dynamic rupture
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, How pore fluid pressurization influences crack tip processes during dynamic rupture Nicolas Brantut,,2,3 and James R. Rice 3 We calculate temperature
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.29/, How pore fluid pressurization influences crack tip processes during dynamic rupture Nicolas Brantut,,2,3 and James R. Rice 3 We calculate temperature
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation. Luis A. Dalguer
 Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Frictional rheologies have a wide range of applications in engineering
 A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes
 Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation
 Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
Earthquake and Volcano Deformation Paul Segall Stanford University Draft Copy September, 2005 Last Updated Sept, 2008 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: To be published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, c
An Integrated Discrete Fracture Model for Description of Dynamic Behavior in Fractured Reservoirs
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanord University, Stanord, Caliornia, February 24-26, 2014 SGP-TR-202 An Integrated Discrete Fracture Model or Description o Dynamic
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanord University, Stanord, Caliornia, February 24-26, 2014 SGP-TR-202 An Integrated Discrete Fracture Model or Description o Dynamic
FLUID MECHANICS. Lecture 7 Exact solutions
 FLID MECHANICS Lecture 7 Eact solutions 1 Scope o Lecture To present solutions or a ew representative laminar boundary layers where the boundary conditions enable eact analytical solutions to be obtained.
FLID MECHANICS Lecture 7 Eact solutions 1 Scope o Lecture To present solutions or a ew representative laminar boundary layers where the boundary conditions enable eact analytical solutions to be obtained.
Earthquake Slip Between Dissimilar Poroelastic Materials
 Earthquake Slip Between Dissimilar Poroelastic Materials The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Dunham, Eric
Earthquake Slip Between Dissimilar Poroelastic Materials The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Dunham, Eric
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998. 26:643 96 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING Chris Marone Department
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998. 26:643 96 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING Chris Marone Department
Earthquake nucleation. Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab
 Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
1.0. Shear Strength ( τ τ c )/ τ Fault Slip (w/d c ) Peak Strength (τp τ c)/ τ 0 1.2
 Evolution of contacting rock surfaces and a slip- and time-dependent fault constitutive law Hideo Aochi and Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Department of Earth and Planetary Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Evolution of contacting rock surfaces and a slip- and time-dependent fault constitutive law Hideo Aochi and Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Department of Earth and Planetary Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 16, 9 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Energy Balance of dynamic rupture Crack tip stress field Frictional Rupture Fronts Meet in the lab (522
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 16, 9 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Energy Balance of dynamic rupture Crack tip stress field Frictional Rupture Fronts Meet in the lab (522
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations Eric G. Daub and Jean M. Carlson Department of Physics, University
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations Eric G. Daub and Jean M. Carlson Department of Physics, University
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
friction friction a-b slow fast increases during sliding
 µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
THE NEAR-WELLBORE PRESSURE CALCULATION MODEL INCORPORATING THERMOCHEMICAL EFFECT
 HERMAL CIENCE: Year 2018, Vol. 22, No. 1B, pp. 623-630 623 HE NEAR-WELLBORE PREURE CALCULAION MODEL INCORPORAING HERMOCHEMICAL EFFEC by Zhiqiang ANG, Qian LI *, and Hu YIN Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering
HERMAL CIENCE: Year 2018, Vol. 22, No. 1B, pp. 623-630 623 HE NEAR-WELLBORE PREURE CALCULAION MODEL INCORPORAING HERMOCHEMICAL EFFEC by Zhiqiang ANG, Qian LI *, and Hu YIN Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering
Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity
 Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity 13th February 2011 1 Introduction Much as mass(material) is transported within luids (gases and liquids), linear momentum is also associated with transport,
Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity 13th February 2011 1 Introduction Much as mass(material) is transported within luids (gases and liquids), linear momentum is also associated with transport,
Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
1/22/2015. High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics
 High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA
 3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault model
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21306, doi:10.1029/2008gl035614, 2008 Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21306, doi:10.1029/2008gl035614, 2008 Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault
On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent faults
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Strain localization driven by thermal decomposition during seismic shear
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 12, DOI:1.12/214JB11493, 215 Strain localization driven by thermal decomposition during seismic shear John D. Platt 1,2, Nicolas Brantut 3, and James R. Rice 1,4 Abstract.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 12, DOI:1.12/214JB11493, 215 Strain localization driven by thermal decomposition during seismic shear John D. Platt 1,2, Nicolas Brantut 3, and James R. Rice 1,4 Abstract.
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Off-Fault Plasticity and Earthquake Rupture Dynamics: 2. Effects of Fluid Saturation
 Off-Fault Plasticity and Earthquake Rupture Dynamics: 2. Effects of Fluid Saturation The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Off-Fault Plasticity and Earthquake Rupture Dynamics: 2. Effects of Fluid Saturation The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Natural convection in a vertical strip immersed in a porous medium
 European Journal o Mechanics B/Fluids 22 (2003) 545 553 Natural convection in a vertical strip immersed in a porous medium L. Martínez-Suástegui a,c.treviño b,,f.méndez a a Facultad de Ingeniería, UNAM,
European Journal o Mechanics B/Fluids 22 (2003) 545 553 Natural convection in a vertical strip immersed in a porous medium L. Martínez-Suástegui a,c.treviño b,,f.méndez a a Facultad de Ingeniería, UNAM,
Going beyond failure in mechanics From bifurcation theory to strain localization and earthquake control
 Séminaire de Calcul Scientifique du CERMICS Going beyond failure in mechanics From bifurcation theory to strain localization and earthquake control Ioannis Stefanou (Navier, ENPC) 19 avril 2018 Going beyond
Séminaire de Calcul Scientifique du CERMICS Going beyond failure in mechanics From bifurcation theory to strain localization and earthquake control Ioannis Stefanou (Navier, ENPC) 19 avril 2018 Going beyond
The influence of hydraulic fracturing on microseismic propagation
 The inluence o hydraulic racturing on microseismic propagation Xiaolin Zhang 1, Feng Zhang 1, Xiang-Yang Li 1, 1 CPC Geophysical Key Lab, China University o Petroleum, Changping, Beijing, China, 1049 Email:
The inluence o hydraulic racturing on microseismic propagation Xiaolin Zhang 1, Feng Zhang 1, Xiang-Yang Li 1, 1 CPC Geophysical Key Lab, China University o Petroleum, Changping, Beijing, China, 1049 Email:
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law
 Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
On rate-state and Coulomb failure models
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B4, PAGES 7857 7871, APRIL 10, 2000 On rate-state and Coulomb failure models J. Gomberg U.S. Geological Survey, Center for Earthquake Research and Information,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B4, PAGES 7857 7871, APRIL 10, 2000 On rate-state and Coulomb failure models J. Gomberg U.S. Geological Survey, Center for Earthquake Research and Information,
Earthquake ruptures with thermal weakening and the operation of major faults at low overall stress levels
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006143, 2009 Earthquake ruptures with thermal weakening and the operation of major faults at low overall stress
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006143, 2009 Earthquake ruptures with thermal weakening and the operation of major faults at low overall stress
Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes
 Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
The role of thermal pressurization and dilatancy in controlling the rate of fault slip
 The role of thermal pressurization and dilatancy in controlling the rate of fault slip Paul Segall Geophysics Department Stanford University Stanford, CA, 9435 Email: segall@stanford.edu Andrew M. Bradley
The role of thermal pressurization and dilatancy in controlling the rate of fault slip Paul Segall Geophysics Department Stanford University Stanford, CA, 9435 Email: segall@stanford.edu Andrew M. Bradley
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle. Read KK&V chapter 2.10
 Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
HYDROMAGNETIC DIVERGENT CHANNEL FLOW OF A VISCO- ELASTIC ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTING FLUID
 Rita Choudhury et al. / International Journal o Engineering Science and Technology (IJEST) HYDROAGNETIC DIVERGENT CHANNEL FLOW OF A VISCO- ELASTIC ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTING FLUID RITA CHOUDHURY Department
Rita Choudhury et al. / International Journal o Engineering Science and Technology (IJEST) HYDROAGNETIC DIVERGENT CHANNEL FLOW OF A VISCO- ELASTIC ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTING FLUID RITA CHOUDHURY Department
A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR
 A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR Chris Marone, Brett Carperter, Derek Elsworth, Igor Faoro, Matt Ikari, Matt Knuth, André Niemeijer, Demian Saffer, and
A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR Chris Marone, Brett Carperter, Derek Elsworth, Igor Faoro, Matt Ikari, Matt Knuth, André Niemeijer, Demian Saffer, and
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress?
 When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
Using transient stresses to monitor poroelastic and stress conditions in CO 2 reservoirs
 Using transient stresses to monitor poroelastic and stress conditions in CO 2 reservoirs Andrew A. Delorey and Paul A. Johnson July 6, 2016 1 Stress, Pore Pressure, and Poroelastic Behavior Induced seismicity
Using transient stresses to monitor poroelastic and stress conditions in CO 2 reservoirs Andrew A. Delorey and Paul A. Johnson July 6, 2016 1 Stress, Pore Pressure, and Poroelastic Behavior Induced seismicity
PARCYCLIC: FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE LIQUEFACTION RESPONSE ON PARALLEL COMPUTERS
 13 th World Conerence on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 361 PARCYCLIC: FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE LIQUEFACTION RESPONSE ON PARALLEL COMPUTERS Jun PENG
13 th World Conerence on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 361 PARCYCLIC: FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE LIQUEFACTION RESPONSE ON PARALLEL COMPUTERS Jun PENG
Heating and weakening of faults during earthquake slip
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:1.129/25jb46, 26 Heating and weakening of faults during earthquake slip James R. Rice 1 Received 21 August 25; accepted 23 January 26; published 24 May 26.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:1.129/25jb46, 26 Heating and weakening of faults during earthquake slip James R. Rice 1 Received 21 August 25; accepted 23 January 26; published 24 May 26.
Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications for aftershock rates
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Shear-induced dilatancy of fluid-saturated faults: Experiment and theory
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006273, 2009 Shear-induced dilatancy of fluid-saturated faults: Experiment and theory Jon Samuelson, 1 Derek Elsworth,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006273, 2009 Shear-induced dilatancy of fluid-saturated faults: Experiment and theory Jon Samuelson, 1 Derek Elsworth,
THE MODEL OF DRYING SESSILE DROP OF COLLOIDAL SOLUTION
 THE MODEL OF DRYING SESSILE DROP OF COLLOIDAL SOLUTION I.V.Vodolazskaya, Yu.Yu.Tarasevic Astrakan State University, a Tatiscev St., Astrakan, 41456, Russia e-mail: tarasevic@aspu.ru e ave proposed and
THE MODEL OF DRYING SESSILE DROP OF COLLOIDAL SOLUTION I.V.Vodolazskaya, Yu.Yu.Tarasevic Astrakan State University, a Tatiscev St., Astrakan, 41456, Russia e-mail: tarasevic@aspu.ru e ave proposed and
Non-newtonian Rabinowitsch Fluid Effects on the Lubrication Performances of Sine Film Thrust Bearings
 International Journal o Mechanical Engineering and Applications 7; 5(): 6-67 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmea doi:.648/j.ijmea.75.4 ISSN: -X (Print); ISSN: -48 (Online) Non-newtonian Rabinowitsch
International Journal o Mechanical Engineering and Applications 7; 5(): 6-67 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmea doi:.648/j.ijmea.75.4 ISSN: -X (Print); ISSN: -48 (Online) Non-newtonian Rabinowitsch
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation
 Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
OE4625 Dredge Pumps and Slurry Transport. Vaclav Matousek October 13, 2004
 OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 1 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie Transport OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie
OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 1 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie Transport OE465 Vaclav Matousek October 13, 004 Dredge Vermelding Pumps onderdeel and Slurry organisatie
A viscoelastic damage rheology and rate- and state-dependent friction
 Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 161, 179 190 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02583.x A viscoelastic damage rheology and rate- and state-dependent friction Vladimir Lyakhovsky, 1 Yehuda Ben-Zion 2 and Amotz Agnon
Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 161, 179 190 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02583.x A viscoelastic damage rheology and rate- and state-dependent friction Vladimir Lyakhovsky, 1 Yehuda Ben-Zion 2 and Amotz Agnon
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Peer Reviewed Title: Fracture permeability and seismic wave scattering--poroelastic linear-slip interface model for heterogeneous fractures Author: Nakagawa, S. Publication
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Peer Reviewed Title: Fracture permeability and seismic wave scattering--poroelastic linear-slip interface model for heterogeneous fractures Author: Nakagawa, S. Publication
Effect of varying normal stress on stability and dynamic motion of a spring-slider system with rate- and state-dependent friction
 Earthq Sci (2014) 27(6):577 587 DOI 10.1007/s11589-014-0098-4 RESEARCH PAPER Effect of varying normal stress on stability and dynamic motion of a spring-slider system with rate- and state-dependent friction
Earthq Sci (2014) 27(6):577 587 DOI 10.1007/s11589-014-0098-4 RESEARCH PAPER Effect of varying normal stress on stability and dynamic motion of a spring-slider system with rate- and state-dependent friction
Analysis of Non-Thermal Equilibrium in Porous Media
 Analysis o Non-Thermal Equilibrium in Porous Media A. Nouri-Borujerdi, M. Nazari 1 School o Mechanical Engineering, Shari University o Technology P.O Box 11365-9567, Tehran, Iran E-mail: anouri@shari.edu
Analysis o Non-Thermal Equilibrium in Porous Media A. Nouri-Borujerdi, M. Nazari 1 School o Mechanical Engineering, Shari University o Technology P.O Box 11365-9567, Tehran, Iran E-mail: anouri@shari.edu
Effect of Thermal Pressurization on Radiation Efficiency
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No. 4, pp. 2293 2304, August 2009, doi: 10.1785/0120080187 Effect of Thermal Pressurization on Radiation Efficiency by Jeen-Hwa Wang Abstract
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No. 4, pp. 2293 2304, August 2009, doi: 10.1785/0120080187 Effect of Thermal Pressurization on Radiation Efficiency by Jeen-Hwa Wang Abstract
Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface
 Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface Laurent BAILLET LGIT (Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique) Grenoble France laurent.baillet@ujf-grenoble.fr http://www-lgit.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr/users/lbaillet/
Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface Laurent BAILLET LGIT (Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique) Grenoble France laurent.baillet@ujf-grenoble.fr http://www-lgit.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr/users/lbaillet/
Comments on Magnetohydrodynamic Unsteady Flow of A Non- Newtonian Fluid Through A Porous Medium
 Comments on Magnetohydrodynamic Unsteady Flow o A Non- Newtonian Fluid Through A Porous Medium Mostaa A.A.Mahmoud Department o Mathematics, Faculty o Science, Benha University (358), Egypt Abstract The
Comments on Magnetohydrodynamic Unsteady Flow o A Non- Newtonian Fluid Through A Porous Medium Mostaa A.A.Mahmoud Department o Mathematics, Faculty o Science, Benha University (358), Egypt Abstract The
The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate and state friction model
 J. Earth Syst. Sci. (018) 17:45 c Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s1040-018-0935- The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate
J. Earth Syst. Sci. (018) 17:45 c Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s1040-018-0935- The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate
NUMERICAL ASSESSMENT OF REINFORCED CONCRETE MEMBERS RETROFITTED WITH FIBER REINFORCED POLYMER FOR RESISTING BLAST LOADING
 NUMERICAL ASSESSMENT OF REINFORCED CONCRETE MEMBERS RETROFITTED WITH FIBER REINFORCED POLYMER FOR RESISTING BLAST LOADING By GRAHAM LONG A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA
NUMERICAL ASSESSMENT OF REINFORCED CONCRETE MEMBERS RETROFITTED WITH FIBER REINFORCED POLYMER FOR RESISTING BLAST LOADING By GRAHAM LONG A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA
Double porosity modeling in elastic wave propagation for reservoir characterization
 Stanord Exploration Project, Report 98, September 2, 1998, pages 1 243 Double porosity modeling in elastic wave propagation or reservoir characterization James G. Berryman 1 and Herbert F. Wang 2 keywords:
Stanord Exploration Project, Report 98, September 2, 1998, pages 1 243 Double porosity modeling in elastic wave propagation or reservoir characterization James G. Berryman 1 and Herbert F. Wang 2 keywords:
Role of in situ stress and fluid compressibility on Slow Slip Events (SSE) & instability triggering (EQ) Derived from a Poro-Plastic Fault Core Model
 Role of in situ stress and fluid compressibility on Slow Slip Events (SSE) & instability triggering (EQ) Derived from a Poro-Plastic Fault Core Model MAURY Vincent*, PIAU Jean-Michel**, FITZENZ Delphine***
Role of in situ stress and fluid compressibility on Slow Slip Events (SSE) & instability triggering (EQ) Derived from a Poro-Plastic Fault Core Model MAURY Vincent*, PIAU Jean-Michel**, FITZENZ Delphine***
Hitoshi Hirose (1), and Kazuro Hirahara (2) Abstract. Introduction
 Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Microscopic elasticity and rate and state friction evolution laws
 Article Volume 13, umber 12 6 December 2012 Q12002, doi:10.1029/2012gc004393 ISS: 1525-2027 Microscopic elasticity and rate and state friction evolution laws orman H. Sleep Department of, Stanford University,
Article Volume 13, umber 12 6 December 2012 Q12002, doi:10.1029/2012gc004393 ISS: 1525-2027 Microscopic elasticity and rate and state friction evolution laws orman H. Sleep Department of, Stanford University,
Thermal and chemical effects in shear and compaction bands
 Thermal and chemical effects in shear and compaction bands Jean Sulem, Ioannis Stefanou To cite this version: Jean Sulem, Ioannis Stefanou. Thermal and chemical effects in shear and compaction bands. Geomechanics
Thermal and chemical effects in shear and compaction bands Jean Sulem, Ioannis Stefanou To cite this version: Jean Sulem, Ioannis Stefanou. Thermal and chemical effects in shear and compaction bands. Geomechanics
MICROMECHANICAL FAILURE ANALYSIS OF UNIDIRECTIONAL FIBER-REINFORCED COMPOSITES UNDER IN-PLANE AND TRANSVERSE SHEAR
 THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS MICROMECHANICAL FAILURE ANALYSIS OF UNIDIRECTIONAL FIBER-REINFORCED COMPOSITES UNDER IN-PLANE AND TRANSVERSE SHEAR Lei Yang*, Ying Yan, Zhiguo
THE 19 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS MICROMECHANICAL FAILURE ANALYSIS OF UNIDIRECTIONAL FIBER-REINFORCED COMPOSITES UNDER IN-PLANE AND TRANSVERSE SHEAR Lei Yang*, Ying Yan, Zhiguo
A study on the Accelerated Life Test Coupled with Computation for Life Prediction of Product According to Wear and Damage
 International Journal o Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering IJMME-IJENS Vol:15 No:03 106 A study on the Accelerated Lie Test Coupled with Computation or Lie Prediction o Product According to Wear and
International Journal o Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering IJMME-IJENS Vol:15 No:03 106 A study on the Accelerated Lie Test Coupled with Computation or Lie Prediction o Product According to Wear and
FATIGUE DURABILITY OF CONCRETE EXTERNALLY STRENGTHENED WITH FRP SHEETS
 FATIGUE DURABILITY OF CONCRETE EXTERNALLY STRENGTHENED WITH FRP SHEETS H. Diab () and Zhishen Wu () () Department o Urban and Civil Engineering, Ibaraki University, Japan Abstract A primary concern o the
FATIGUE DURABILITY OF CONCRETE EXTERNALLY STRENGTHENED WITH FRP SHEETS H. Diab () and Zhishen Wu () () Department o Urban and Civil Engineering, Ibaraki University, Japan Abstract A primary concern o the
PETE 693 WELL STIMULATION, Spring 2014 Instructor: Dr. Dare Awoleke. Midterm, Thursday, 10 th April, 2014 Duration: 8:15 10:45am
 PETE 693 WELL STIMULATION, Spring 2014 Instructor: Dr. Dare Awoleke Midterm, Thursday, 10 th April, 2014 Duration: 8:15 10:45am Instructions Open book. Open notes. Use all you can except your neighbour.
PETE 693 WELL STIMULATION, Spring 2014 Instructor: Dr. Dare Awoleke Midterm, Thursday, 10 th April, 2014 Duration: 8:15 10:45am Instructions Open book. Open notes. Use all you can except your neighbour.
The critical slip distance for seismic and aseismic fault zones of finite width
 The critical slip distance for seismic and aseismic fault zones of finite width Chris Marone 1, Massimo Cocco, Eliza Richardson 1, and Elisa Tinti Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Rome,
The critical slip distance for seismic and aseismic fault zones of finite width Chris Marone 1, Massimo Cocco, Eliza Richardson 1, and Elisa Tinti Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Rome,
