The Corrupting Influence of Variability
|
|
|
- Janel Hopkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Th Corrupting Influnc of Vribility Whn luck is on your sid, you cn do without brins. Giordno Bruno,burnd t th stk in 1600 Th mor you know th luckir you gt. J.R. Ewing of Dlls 1 Prformnc of Sril Lin Msurs: Throughput Invntory (RMI, WIP, FGI) Cycl Tim Ld Tim Customr Srvic Qulity Evlution: Comprison to prfct vlus Rltiv wights consistnt with businss strtgy? Links to Businss Strtgy: Would invntory rduction rsult in significnt cost svings? Would CT (or LT) rduction rsult in significnt comptitiv dvntg? Would TH incrs hlp gnrt significntly mor rvnu? Would improvd customr srvic gnrt businss ovr th long run? 1
2 Influnc of Vribility Vribility Lw: Incrsing vribility lwys dgrds th prformnc of production systm. Exmpls: procss tim vribility pushs bst cs towrd worst cs highr dmnd vribility rquirs mor sfty stock for sm lvl of customr srvic highr cycl tim vribility rquirs longr ld tim quots to ttin sm lvl of on-tim dlivry 3 Vribility Buffring Buffring Lw: Systms with vribility must b buffrd by som combintion of: 1. invntory. cpcity 3. tim. Intrprttion: If you cnnot py to rduc vribility, you will py in trms of high WIP, undr-utilizd cpcity, or rducd customr srvic (i.., lost sls, long ld tims, nd/or lt dlivris). 4
3 Vribility Buffring Exmpls Bllpoint Pns: cn t buffr with tim (who will bckordr chp pn?) cn t buffr with cpcity (too xpnsiv, nd slow) must buffr with invntory Ambulnc Srvic: cn t buffr with invntory (stock of mrgncy srvics?) cn t buffr with tim (violts strtgic objctivs) must buffr with cpcity Orgn Trnsplnts: cn t buffr with WIP (prishbl) cn t buffr with cpcity (thiclly nywy) must buffr with tim 5 Simultion Studis TH Constrind Systm (push) r, c B(1) t (1), c (1) B() t (), c () B(3) t (3), c (3) B(4) t (4), c (4) Infinit rw mtrils WIP Constrind Systm (pull) t (1), c (1) B() t (), c () B(3) t (3), c (3) B(4) t (4), c (4) r = rrivl rt c t ( i) = ffctiv procss tim t sttion i c ( i) = ffctiv CV t sttion i = CV of intrrrivl tims B( i) = buffr siz in front of sttion i 6 3
4 Vribility Rduction in Push Systms Cs t(i), i = 1,, 4 (min) t(3) (min) c(i), i = 1-4 (unitlss) TH (j/min) CT (min) bst cs WIP buffr cpcity buffr rducd vribility Nots: r = 0.8, c = c (i) in ll css. B(i) =, i = 1-4 in ll css. Obsrvtions: TH is st by rls rt in push systm. Incrsing cpcity (r b ) rducs nd for WIP buffring. Rducing procss vribility rducs WIP for sm TH, rducs CT for sm TH, nd rducs CT vribility. WIP (jobs) σ CT (min) Commnts 7 Cs t(i), i = 1,,4 (min) Vribility Rduction in Pull Systms t(3) (min) c(i), i = 1-4 (unitlss) B(3) (jobs) TH (j/min) CT (min) WIP (jobs) σ CT (min) Nots: Sttion 1 pulls in job whnvr it bcoms mpty. B(i) = 0, i = 1,, 4 in ll css, xcpt cs 6, which hs B() = 1. Commnts bst cs plin JIT inv buffr vr rduction inv buffr + vr rduction non-bottlnck buffr 8 4
5 Vribility Rduction in Pull Systms (cont.) Obsrvtions: Cpping WIP without rducing vribility rducs TH. WIP cp limits ffct of procss vribility on WIP/CT. Rducing procss vribility incrss TH, givn sm buffrs. Adding buffr spc t bottlnck incrss TH. Mgnitud of impct of dding buffrs dpnds on vribility. Buffring lss hlpful t non-bottlncks. Rducing procss vribility rducs CT vribility. Conclusion: if you cn t py to rduc vribility now, you will py ltr with lost throughput, wstd cpcity, infltd cycl tims, xcss invntory, long ld tims,or poor customr srvic! 9 Vribility from Btching VUT Eqution: CT dpnds on procss vribility nd flow vribility Btching: ffcts flow vribility ffcts witing invntory Conclusion: btching is n importnt dtrminnt of prformnc 10 5
6 Procss Btch Vrsus Mov Btch Ddictd Assmbly Lin: Wht should th btch siz b? Procss Btch: Rltd to lngth of stup. Th longr th stup th lrgr th lot siz rquird for th sm cpcity. Mov (trnsfr) Btch: Why should it qul procss btch? Th smllr th mov btch, th shortr th cycl tim. Th smllr th mov btch, th mor mtril hndling. Lot Splitting: Mov btch cn b diffrnt from procss btch. 1. Estblish smllst conomicl mov btch.. Group mov btchs of lik fmilis togthr t bottlnck to void stups. 3. Implmnt using bcklog. 11 Procss Btching Effcts Typs of Procss Btching: 1. Sril Btching: procsss with squnc-dpndnt stups btch siz is numbr of jobs btwn stups btching usd to rduc loss of cpcity from stups. Prlll Btching: tru btch oprtions (.g., ht trt) btch siz is numbr of jobs run togthr btching usd to incrs ffctiv rt of procss 1 6
7 Procss Btching Procss Btching Lw: In sttions with btch oprtions or significnt chngovr tims: Th minimum procss btch siz tht yilds stbl systm my b grtr thn on. As procss btch siz bcoms lrg, cycl tim grows proportionlly with btch siz. Cycl tim t th sttion will b minimizd for som procss btch siz, which my b grtr thn on. Bsic Btching Trdoff: WIP vrsus cpcity 13 Sril Btching Prmtrs: k = sril btch siz (10) t = tim to procss singl prt (1) s = tim to prform stup (5) c c = CV for btch (prts + stup) (0.5) r = rrivl rt for prts (0.4) = CV of btch rrivls (1.0) r,c k t s stup t 0 Tim for btch: t = kt + s (t = 15) forming btch quu of btchs 14 7
8 q Procss Btching Effcts (cont.) Arrivl of btchs: r /k (0.4/10 = 0.04) Utiliztion: u = (r /k)(kt + s) = r (t + s/k ) (0.4(5/10 + 1) = 0.6) For stbility: u < 1 implis sr (5.0)(0.4) k > or ( k > = 3.33) 1 tr 1 (1.0 _(0.4) minimum btch siz rquird for stbility of systm Procss Btching Effcts (cont.) CT Avrg quu tim t sttion: c + c u = t = 1 u ( ) ( ) ( )( ) Avrg cycl tim dpnds on mov btch siz: Mov btch = procss btch Mov btch = 1 CT CT split non split = CT + t q = CT = = q 15 = s + kt k + 1 = CTq + s + t = (1.0) = Not: w ssum rrivl CV of btchs is c rgrdlss of btch siz n pproximtion... Not: splitting mov btchs rducs wit for btch tim. 16 8
9 Cycl Tim vs. Btch Siz 5 hr stup Cycl Tim (hrs) Optimum Btch Sizs Btch Siz (jobs/btch) No Lot Splitting Lot Splitting 17 Cycl Tim vs Btch Siz.5 hr stup Optimum Btch Sizs Btch Siz (jobs/btch) 18 9
10 Stup Tim Rduction Whr? Sttions whr cpcity is xpnsiv Excss cpcity my somtims b chpr Stps: 1. Extrnliz portions of stup. Rduc djustmnt tim (guids, clmps, tc.) 3. Tchnologicl dvncmnts (hoists, quick-rls, tc.) Cvt: Don t count on cpcity incrs; mor flxibility will rquir mor stups. 19 Prlll Btching Prmtrs: k = prlll btch siz (10) c c t = tim to procss btch (90) = CV for btch (1.0) r = rrivl rt for prts (0.05) = CV of btch rrivls(1.0) B = mximum btch siz (100) k 1 1 Tim to form btch: W = r r,c k t ((10 1)/)(1/0.005) = 90) Tim to procss btch: t = t (t = 90) forming btch quu of btchs 0 10
11 Prlll Btching (cont.) Arrivl of btchs: r /k (0.05/10 = 0.005) Utiliztion: u = (r /k)(t) ((0.005)(90) = 0.45) For stbility: u < 1 implis k > r t or ( k > (0.05)(90) = 4.5) minimum btch siz rquird for stbility of systm... 1 Prlll Btching (cont.) Avrg wit-for-btch tim: k WT = = = r btch siz ffcts both wit-for-btch tim nd quu tim Avrg quu plus procss tim t sttion: + + CT = ( )( ) + = ( )( ) c / k c u t t = u Totl cycl tim: CT + WT = =
12 Cycl Tim vs. Btch Siz in Prlll Oprtion Totl Cycl Tim quu tim du to utiliztion wit for btch tim N b Optimum Btch Siz B 3 Mov Btching Mov Btching Lw: Cycl tims ovr sgmnt of routing r roughly proportionl to th trnsfr btch sizs usd ovr tht sgmnt, providd thr is no witing for th convync dvic. Insights: Bsic Btching Trdoff: WIP vs. mov frquncy Quuing for convync dvic cn offst CT rduction from rducd mov btch siz Mov btching intimtly rltd to mtril hndling nd lyout dcisions 4 1
13 Mov Btching Problm: Two mchins in sris First mchin rcivs individul prts t rt r with CV of c (1) nd puts out btchs of siz k. First mchin hs mn procss tim of t (1) for on prt with CV of c (1). Scond mchin rcivs btchs of k nd put out individul prts. How dos cycl tim dpnd on th btch siz k? k r,c (1) t (1),c (1) t (),c () singl job btch Sttion 1 Sttion 5 Mov Btching Clcultions Tim t First Sttion: Avrg tim bfor btching is: c (1) + c (1) u(1) t (1) + t(1) 1 u(1) Avrg tim forming th btch is: k 1 1 k 1 = t (1) r u(1) rgulr VUT qution... first prt wits (k-1)(1/r ), lst prt dosn t wit, so vrg is (k-1)(1/r )/ Avrg tim spnt t th first sttion is: c (1) + c (1) u(1) k 1 CT(1) = t (1) + t(1) + t (1) 1 u(1) u(1) k 1 = CT(1, no btching) + t (1) u(1) 6 13
14 Mov Btching Clcultions (cont.) Output of First Sttion: Tim btwn output of individul prts into th btch is t. Tim btwn output of btchs of siz k is kt. Vrinc of introutput tims of prts is c d (1)t, whr c (1) = (1 u(1) ) c (1) + u(1) c (1) d Vrinc of btchs of siz k is kc d (1)t. SCV of btch rrivls to sttion is: kcd (1) t c () = k t cd (1) = k bcus c d (1)=σ d /t by df of CV bcus dprturs r indpndnt, so vrincs dd vrinc dividd by mn squrd... 7 Mov Btching Clcultions (cont.) Tim t Scond Sttion: Tim to procss btch of siz k is kt (). Vrinc of tim to procss btch of siz k is kc ()t (). SCV for btch of siz k is: kc () t () c () = k t () k Mn tim spnt in prtil btch of siz k is: k 1 t () So, vrg tim spnt t th scond sttion is: cd (1) / k + c () / k u() k 1 CT() = kt () + t () + t () 1 u() VUT qution to comput quu tim of btchs... k 1 = CT(, no btching) + t () indpndnt procss tims... first prt dosn t wit, lst prt wits (k-1)t (), so vrg is (k-1)t ()/ 8 14
15 Mov Btching Clcultions (cont.) Totl Cycl Tim: k CT( btching) = CT(no btching) + 1 k () + 1 t 1 t ( ) u() 1 () = CT(no btching ) + k 1 t 1 + ( ) t u() 1 Insight: Cycl tim incrss with k. Infltion trm dos not involv CV s infltion fctor du to mov btching Congstion from btching is mor bd control thn rndomnss. 9 Assmbly Oprtions Assmbly Oprtions Lw: Th prformnc of n ssmbly sttion is dgrdd by incrsing ny of th following: Numbr of componnts bing ssmbld. Vribility of componnt rrivls. Lck of coordintion btwn componnt rrivls. Obsrvtions: This lw cn b viwd s spcil instnc of vribility lw. Numbr of componnts ffctd by product/procss dsign. Arrivl vribility ffctd by procss vribility nd production control. Coordintion ffctd by schduling nd shop floor control
16 Attcking Vribility Objctivs rduc cycl tim incrs throughput improv customr srvic Lvrs rduc vribility dirctly buffr using invntory buffr using cpcity buffr using tim 31 Cycl Tim Dfinition (Sttion Cycl Tim): Th vrg cycl tim t sttion is md up of th following componnts cycl tim = mov tim + quu tim + stup tim + procss tim + wit-to-btch tim + wit-in-btch tim + wit-to-mtch tim dly tims typiclly mk up 90% of CT Dfinition (Lin Cycl Tim): Th vrg cycl tim in lin is qul to th sum of th cycl tims t th individul sttions lss ny tim tht ovrlps two or mor sttions. 3 16
17 Rducing Quu Dly CT q = V U t c + c u 1 u Rduc Vribility filurs stups unvn rrivls, tc. Rduc Utiliztion rrivl rt (yild, rwork, tc.) procss rt (spd, tim, vilbility, tc) 33 Rducing Btching Dly CT btch = dly t sttions + dly btwn sttions Rduc Procss Btching Optimiz btch sizs Rduc stups Sttions whr cpcity is xpnsiv Cpcity vs. WIP/FT trdoff Rduc Mov Btching Mov mor frquntly Lyout to support mtril hndling (.g., clls) 34 17
18 Rducing Mtching Dly CT btch = dly du to lck of synchroniztion Rduc Vribility High utiliztion fbriction lins Usul vribility rduction mthods Improv Coordintion schduling pull mchnisms modulr dsigns Rduc Numbr of Componnts product rdsign kitting 35 Incrsing Throughput TH = P(bottlnck is busy) bottlnck rt Rduc Blocking/Strving buffr with invntory (nr bottlnck) rduc systm dsir to quu CT q = V U t Incrs Cpcity dd quipmnt incrs oprting tim (.g. spll brks) incrs rlibility rduc yild loss/rwork Rduc Vribility Rduc Utiliztion Not: if WIP is limitd, thn systm dgrds vi TH loss rthr thn WIP/CT infltion 36 18
19 Improving Customr Srvic LT = CT + z σ CT Rduc Avrg CT quu tim btch tim mtch tim Rduc CT Visibl to Customr dlyd diffrntition ssmbl to ordr stock componnts Rduc CT Vribility gnrlly sm s mthods for rducing vrg CT: improv rlibility improv mintinbility rduc lbor vribility improv qulity improv schduling tc 37 Cycl Tim nd Ld Tim CT = 10 σ CT = CT = 10 σ CT = Cycl Tim in Dys 38 19
20 Dignostics Using Fctory Physics Sitution: Two mchins in sris; mchin is bottlnck c = 1 Mchin 1: t0 = 19min c = MTTF = 48 hr MTTR = 8 hr Mchin : t = min c = 1 MTTF = 3.3 hr MTTR = 10 min Spc t mchin for 0 jobs of WIP Dsird throughput.4 jobs/hr, not bing mt Dignostic Exmpl (cont.) Proposl: Instll scond mchin t sttion Expnsiv Vry littl spc Anlysis Tools: c + c u CTq 1 u c = u c + (1 u d Anlysis: Ask why fiv tims... Stp 1: At.4 job/hr CT q t first sttion is 645 minuts, vrg WIP is 5.8 jobs. CT q t scond sttion is 89 minuts, vrg WIP is 35.7 jobs. Spc rquirmnts t mchin r violtd! t ) c VUT qution propogtion qution 40 0
21 Dignostic Exmpl (cont.) Stp : Why is CT q t mchin so big? Brk CT q into CT q c + c u 1 u t = Th 3.11 min trm is smll. Th 1. corrction trm is modrt (u 0.944) Th 3.16 corrction is lrg. ( 316. )( 1. )( 311. min) Stp 3: Why is th corrction trm so lrg? Look t componnts of corrction trm. c = 1.04, c = 5.7. Arrivls to mchin r highly vribl. 41 Dignostic Exmpl (cont.) Stp 4: Why is c to mchin so lrg? Rcll tht c to mchin quls c d from mchin 1, nd cd = u c + (1 u ) c = (0.887 )(6.437) + ( )(1.0) = 5.7 c t mchin 1 is lrg. Stp 5: Why is c t mchin 1 lrg? Effctiv CV t mchin 1 is ffctd by filurs, c = c 0 mr + A(1 A) t 0 = = 6.43 Th infltion du to filurs is lrg. Rducing MTTR t mchin 1 would substntilly improv prformnc. 4 1
22 Procot Cs Sitution Problm: Currnt WIP round 1500 pnls Dsird cpcity of 3000 pnls/dy Typicl output of 1150 pnls/dy Outsid vndor bing usd to mk up slck Proposl: Expos is bottlnck, but in cln room Expnsion would b xpnsiv Suggstd ltrntiv is to dd bk ovn for touchups 43 Procot Cs Lyout IN Lodr Cln Cot 1 Cot Unlodr Unlodr Bk Touchup D&I Inspct Dvlop Lodr Mnufcturing Inspct Expos Cln Room OUT 44
23 Procot Cs Cpcity Clcultions Mchin Nm Procss or Lod Tim (min) Std Dv Procss Tim (min) Convyor Trip Tim (min) Numbr of Mchins MTTF MTTR Avil Stup Tim Rt (p/dy) Tim (min) Cl n Cot Cot Expos Dvlop Inspct Bk MI Touchup r b =,879 p/dy T 0 = 54 min = 0.46 dys W 0 = r b T 0 = 1,334 pnls 45 Procot Cs Bnchmrking TH Rsulting from PWC with WIP = 37,400: TH w = r w + W0 1 b 1,500 =,879 = 1,54 1, ,334 1 Highr thn ctul TH Conclusion: ctul systm is significntly wors thn PWC. Qustion: wht to do? 46 3
24 Procot Cs Fctory Physics Anlysis 1) Expos hs highst utiliztion: incrs cpcity vi brk splling ) Expos hs high V cofficint (nd limitd room for WIP): som is du to oprtor vribilty implmnt trining progrm mor is du to rrivl vribility look t cotr lin 3) Cotr lin hs long, infrqunt filurs: mintin fild rdy rplcmnts 47 Procot Cs Outcom TH (pnls/dy) Bst Cs 700 "Good" Rgion 400 Aftr Prcticl Worst Cs "Bd" Rgion 100 Bfor Worst Cs WIP (pnls) 48 4
25 Corrupting Influnc Tkwys Vrinc Cuss Congstion: mny sourcs of vribility plnnd nd unplnnd Vribility nd Utiliztion Intrct: congstion ffcts multiply utiliztion ffcts r highly nonlinr importnc of bottlnck mngmnt 49 Corrupting Influnc Tkwys (cont.) Vribility Propgts: flow vribility is s disruptiv s procss vribility non-bottlncks cn b mjor problms Vribility Must b Buffrd: invntory cpcity tim 50 5
Errata for Second Edition, First Printing
 Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 71: Eqution (.3) should rd B( R) = θ R 1 x= [1 G( x)] pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1
Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 71: Eqution (.3) should rd B( R) = θ R 1 x= [1 G( x)] pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1
Errata for Second Edition, First Printing
 Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1 G( x)] = θp( R) + ( θ R)[1 G( R)] pg 15, problm 6: dmnd of
Errt for Scond Edition, First Printing pg 68, lin 1: z=.67 should b z=.44 pg 1: Eqution (.63) should rd B( R) = x= R = θ ( x R) p( x) R 1 x= [1 G( x)] = θp( R) + ( θ R)[1 G( R)] pg 15, problm 6: dmnd of
Instructions for Section 1
 Instructions for Sction 1 Choos th rspons tht is corrct for th qustion. A corrct nswr scors 1, n incorrct nswr scors 0. Mrks will not b dductd for incorrct nswrs. You should ttmpt vry qustion. No mrks
Instructions for Sction 1 Choos th rspons tht is corrct for th qustion. A corrct nswr scors 1, n incorrct nswr scors 0. Mrks will not b dductd for incorrct nswrs. You should ttmpt vry qustion. No mrks
, between the vertical lines x a and x b. Given a demand curve, having price as a function of quantity, p f (x) at height k is the curve f ( x,
 Clculus for Businss nd Socil Scincs - Prof D Yun Finl Em Rviw vrsion 5/9/7 Chck wbsit for ny postd typos nd updts Pls rport ny typos This rviw sht contins summris of nw topics only (This rviw sht dos hv
Clculus for Businss nd Socil Scincs - Prof D Yun Finl Em Rviw vrsion 5/9/7 Chck wbsit for ny postd typos nd updts Pls rport ny typos This rviw sht contins summris of nw topics only (This rviw sht dos hv
Multi-Section Coupled Line Couplers
 /0/009 MultiSction Coupld Lin Couplrs /8 Multi-Sction Coupld Lin Couplrs W cn dd multipl coupld lins in sris to incrs couplr ndwidth. Figur 7.5 (p. 6) An N-sction coupld lin l W typiclly dsign th couplr
/0/009 MultiSction Coupld Lin Couplrs /8 Multi-Sction Coupld Lin Couplrs W cn dd multipl coupld lins in sris to incrs couplr ndwidth. Figur 7.5 (p. 6) An N-sction coupld lin l W typiclly dsign th couplr
Integration Continued. Integration by Parts Solving Definite Integrals: Area Under a Curve Improper Integrals
 Intgrtion Continud Intgrtion y Prts Solving Dinit Intgrls: Ar Undr Curv Impropr Intgrls Intgrtion y Prts Prticulrly usul whn you r trying to tk th intgrl o som unction tht is th product o n lgric prssion
Intgrtion Continud Intgrtion y Prts Solving Dinit Intgrls: Ar Undr Curv Impropr Intgrls Intgrtion y Prts Prticulrly usul whn you r trying to tk th intgrl o som unction tht is th product o n lgric prssion
Lecture 11 Waves in Periodic Potentials Today: Questions you should be able to address after today s lecture:
 Lctur 11 Wvs in Priodic Potntils Tody: 1. Invrs lttic dfinition in 1D.. rphicl rprsnttion of priodic nd -priodic functions using th -xis nd invrs lttic vctors. 3. Sris solutions to th priodic potntil Hmiltonin
Lctur 11 Wvs in Priodic Potntils Tody: 1. Invrs lttic dfinition in 1D.. rphicl rprsnttion of priodic nd -priodic functions using th -xis nd invrs lttic vctors. 3. Sris solutions to th priodic potntil Hmiltonin
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Problm A town hs st of houss nd st of rods A rod conncts nd only houss A rod conncting houss u nd v hs rpir cost w(u, v) Gol: Rpir nough (nd no mor) rods such tht:
Minimum Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Problm A town hs st of houss nd st of rods A rod conncts nd only houss A rod conncting houss u nd v hs rpir cost w(u, v) Gol: Rpir nough (nd no mor) rods such tht:
TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION
 TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION. Th indfinit intgrl In mny rspcts, th oprtion of intgrtion tht w r studying hr is th invrs oprtion of drivtion. Dfinition.. Th function F is n ntidrivtiv (or primitiv) of th function
TOPIC 5: INTEGRATION. Th indfinit intgrl In mny rspcts, th oprtion of intgrtion tht w r studying hr is th invrs oprtion of drivtion. Dfinition.. Th function F is n ntidrivtiv (or primitiv) of th function
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HAYSTACK OBSERVATORY WESTFORD, MASSACHUSETTS
 VSRT MEMO #05 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HAYSTACK OBSERVATORY WESTFORD, MASSACHUSETTS 01886 Fbrury 3, 009 Tlphon: 781-981-507 Fx: 781-981-0590 To: VSRT Group From: Aln E.E. Rogrs Subjct: Simplifid
VSRT MEMO #05 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY HAYSTACK OBSERVATORY WESTFORD, MASSACHUSETTS 01886 Fbrury 3, 009 Tlphon: 781-981-507 Fx: 781-981-0590 To: VSRT Group From: Aln E.E. Rogrs Subjct: Simplifid
Chapter 16. 1) is a particular point on the graph of the function. 1. y, where x y 1
 Prctic qustions W now tht th prmtr p is dirctl rltd to th mplitud; thrfor, w cn find tht p. cos d [ sin ] sin sin Not: Evn though ou might not now how to find th prmtr in prt, it is lws dvisl to procd
Prctic qustions W now tht th prmtr p is dirctl rltd to th mplitud; thrfor, w cn find tht p. cos d [ sin ] sin sin Not: Evn though ou might not now how to find th prmtr in prt, it is lws dvisl to procd
INTEGRALS. Chapter 7. d dx. 7.1 Overview Let d dx F (x) = f (x). Then, we write f ( x)
 Chptr 7 INTEGRALS 7. Ovrviw 7.. Lt d d F () f (). Thn, w writ f ( ) d F () + C. Ths intgrls r clld indfinit intgrls or gnrl intgrls, C is clld constnt of intgrtion. All ths intgrls diffr y constnt. 7..
Chptr 7 INTEGRALS 7. Ovrviw 7.. Lt d d F () f (). Thn, w writ f ( ) d F () + C. Ths intgrls r clld indfinit intgrls or gnrl intgrls, C is clld constnt of intgrtion. All ths intgrls diffr y constnt. 7..
Ch 1.2: Solutions of Some Differential Equations
 Ch 1.2: Solutions of Som Diffrntil Equtions Rcll th fr fll nd owl/mic diffrntil qutions: v 9.8.2v, p.5 p 45 Ths qutions hv th gnrl form y' = y - b W cn us mthods of clculus to solv diffrntil qutions of
Ch 1.2: Solutions of Som Diffrntil Equtions Rcll th fr fll nd owl/mic diffrntil qutions: v 9.8.2v, p.5 p 45 Ths qutions hv th gnrl form y' = y - b W cn us mthods of clculus to solv diffrntil qutions of
Lecture contents. Bloch theorem k-vector Brillouin zone Almost free-electron model Bands Effective mass Holes. NNSE 508 EM Lecture #9
 Lctur contnts Bloch thorm -vctor Brillouin zon Almost fr-lctron modl Bnds ffctiv mss Hols Trnsltionl symmtry: Bloch thorm On-lctron Schrödingr qution ch stt cn ccommo up to lctrons: If Vr is priodic function:
Lctur contnts Bloch thorm -vctor Brillouin zon Almost fr-lctron modl Bnds ffctiv mss Hols Trnsltionl symmtry: Bloch thorm On-lctron Schrödingr qution ch stt cn ccommo up to lctrons: If Vr is priodic function:
Limits Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule
 Limits Indtrmint Forms nd L Hospitl s Rul I Indtrmint Form o th Tp W hv prviousl studid its with th indtrmint orm s shown in th ollowin mpls: Empl : Empl : tn [Not: W us th ivn it ] Empl : 8 h 8 [Not:
Limits Indtrmint Forms nd L Hospitl s Rul I Indtrmint Form o th Tp W hv prviousl studid its with th indtrmint orm s shown in th ollowin mpls: Empl : Empl : tn [Not: W us th ivn it ] Empl : 8 h 8 [Not:
UNIT # 08 (PART - I)
 . r. d[h d[h.5 7.5 mol L S d[o d[so UNIT # 8 (PRT - I CHEMICL INETICS EXERCISE # 6. d[ x [ x [ x. r [X[C ' [X [[B r '[ [B [C. r [NO [Cl. d[so d[h.5 5 mol L S d[nh d[nh. 5. 6. r [ [B r [x [y r' [x [y r'
. r. d[h d[h.5 7.5 mol L S d[o d[so UNIT # 8 (PRT - I CHEMICL INETICS EXERCISE # 6. d[ x [ x [ x. r [X[C ' [X [[B r '[ [B [C. r [NO [Cl. d[so d[h.5 5 mol L S d[nh d[nh. 5. 6. r [ [B r [x [y r' [x [y r'
CSE 373: AVL trees. Warmup: Warmup. Interlude: Exploring the balance invariant. AVL Trees: Invariants. AVL tree invariants review
 rmup CSE 7: AVL trs rmup: ht is n invrint? Mihl L Friy, Jn 9, 0 ht r th AVL tr invrints, xtly? Disuss with your nighor. AVL Trs: Invrints Intrlu: Exploring th ln invrint Cor i: xtr invrint to BSTs tht
rmup CSE 7: AVL trs rmup: ht is n invrint? Mihl L Friy, Jn 9, 0 ht r th AVL tr invrints, xtly? Disuss with your nighor. AVL Trs: Invrints Intrlu: Exploring th ln invrint Cor i: xtr invrint to BSTs tht
Engineering 323 Beautiful HW #13 Page 1 of 6 Brown Problem 5-12
 Enginring Bautiful HW #1 Pag 1 of 6 5.1 Two componnts of a minicomputr hav th following joint pdf for thir usful liftims X and Y: = x(1+ x and y othrwis a. What is th probability that th liftim X of th
Enginring Bautiful HW #1 Pag 1 of 6 5.1 Two componnts of a minicomputr hav th following joint pdf for thir usful liftims X and Y: = x(1+ x and y othrwis a. What is th probability that th liftim X of th
Oppgavesett kap. 6 (1 av..)
 Oppgvstt kp. 6 (1 v..) hns.brnn@go.uio.no Problm 1 () Wht is homognous nucltion? Why dos Figur 6.2 in th book show tht w won't gt homognous nucltion in th tmosphr? ˆ Homognous nucltion crts cloud droplts
Oppgvstt kp. 6 (1 v..) hns.brnn@go.uio.no Problm 1 () Wht is homognous nucltion? Why dos Figur 6.2 in th book show tht w won't gt homognous nucltion in th tmosphr? ˆ Homognous nucltion crts cloud droplts
This Week. Computer Graphics. Introduction. Introduction. Graphics Maths by Example. Graphics Maths by Example
 This Wk Computr Grphics Vctors nd Oprtions Vctor Arithmtic Gomtric Concpts Points, Lins nd Plns Eploiting Dot Products CSC 470 Computr Grphics 1 CSC 470 Computr Grphics 2 Introduction Introduction Wh do
This Wk Computr Grphics Vctors nd Oprtions Vctor Arithmtic Gomtric Concpts Points, Lins nd Plns Eploiting Dot Products CSC 470 Computr Grphics 1 CSC 470 Computr Grphics 2 Introduction Introduction Wh do
CIVL 8/ D Boundary Value Problems - Rectangular Elements 1/7
 CIVL / -D Boundr Vlu Prolms - Rctngulr Elmnts / RECANGULAR ELEMENS - In som pplictions, it m mor dsirl to us n lmntl rprsnttion of th domin tht hs four sids, ithr rctngulr or qudriltrl in shp. Considr
CIVL / -D Boundr Vlu Prolms - Rctngulr Elmnts / RECANGULAR ELEMENS - In som pplictions, it m mor dsirl to us n lmntl rprsnttion of th domin tht hs four sids, ithr rctngulr or qudriltrl in shp. Considr
Winter 2016 COMP-250: Introduction to Computer Science. Lecture 23, April 5, 2016
 Wintr 2016 COMP-250: Introduction to Computr Scinc Lctur 23, April 5, 2016 Commnt out input siz 2) Writ ny lgorithm tht runs in tim Θ(n 2 log 2 n) in wors cs. Explin why this is its running tim. I don
Wintr 2016 COMP-250: Introduction to Computr Scinc Lctur 23, April 5, 2016 Commnt out input siz 2) Writ ny lgorithm tht runs in tim Θ(n 2 log 2 n) in wors cs. Explin why this is its running tim. I don
Last time: introduced our first computational model the DFA.
 Lctur 7 Homwork #7: 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3 (hnd in c nd d), Misc: Givn: M, NFA Prov: (q,xy) * (p,y) iff (q,x) * (p,) (follow proof don in clss tody) Lst tim: introducd our first computtionl modl th DFA. Tody
Lctur 7 Homwork #7: 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3 (hnd in c nd d), Misc: Givn: M, NFA Prov: (q,xy) * (p,y) iff (q,x) * (p,) (follow proof don in clss tody) Lst tim: introducd our first computtionl modl th DFA. Tody
Theoretical Study on the While Drilling Electromagnetic Signal Transmission of Horizontal Well
 7 nd ntrntionl Confrnc on Softwr, Multimdi nd Communiction Enginring (SMCE 7) SBN: 978--6595-458-5 Thorticl Study on th Whil Drilling Elctromgntic Signl Trnsmission of Horizontl Wll Y-huo FAN,,*, Zi-ping
7 nd ntrntionl Confrnc on Softwr, Multimdi nd Communiction Enginring (SMCE 7) SBN: 978--6595-458-5 Thorticl Study on th Whil Drilling Elctromgntic Signl Trnsmission of Horizontl Wll Y-huo FAN,,*, Zi-ping
Case Study VI Answers PHA 5127 Fall 2006
 Qustion. A ptint is givn 250 mg immit-rls thophyllin tblt (Tblt A). A wk ltr, th sm ptint is givn 250 mg sustin-rls thophyllin tblt (Tblt B). Th tblts follow on-comprtmntl mol n hv first-orr bsorption
Qustion. A ptint is givn 250 mg immit-rls thophyllin tblt (Tblt A). A wk ltr, th sm ptint is givn 250 mg sustin-rls thophyllin tblt (Tblt B). Th tblts follow on-comprtmntl mol n hv first-orr bsorption
Optics and Non-Linear Optics I Non-linear Optics Tutorial Sheet November 2007
 Optics and Non-Linar Optics I - 007 Non-linar Optics Tutorial Sht Novmbr 007 1. An altrnativ xponntial notion somtims usd in NLO is to writ Acos (") # 1 ( Ai" + A * $i" ). By using this notation and substituting
Optics and Non-Linar Optics I - 007 Non-linar Optics Tutorial Sht Novmbr 007 1. An altrnativ xponntial notion somtims usd in NLO is to writ Acos (") # 1 ( Ai" + A * $i" ). By using this notation and substituting
I. The Connection between Spectroscopy and Quantum Mechanics
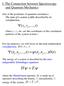 I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
I. Th Connction twn Spctroscopy nd Quntum Mchnics On of th postults of quntum mchnics: Th stt of systm is fully dscrid y its wvfunction, Ψ( r1, r,..., t) whr r 1, r, tc. r th coordints of th constitunt
Mathematics. Mathematics 3. hsn.uk.net. Higher HSN23000
 Highr Mthmtics UNIT Mthmtics HSN000 This documnt ws producd spcilly for th HSN.uk.nt wbsit, nd w rquir tht ny copis or drivtiv works ttribut th work to Highr Still Nots. For mor dtils bout th copyright
Highr Mthmtics UNIT Mthmtics HSN000 This documnt ws producd spcilly for th HSN.uk.nt wbsit, nd w rquir tht ny copis or drivtiv works ttribut th work to Highr Still Nots. For mor dtils bout th copyright
Differential Equations
 UNIT I Diffrntial Equations.0 INTRODUCTION W li in a world of intrrlatd changing ntitis. Th locit of a falling bod changs with distanc, th position of th arth changs with tim, th ara of a circl changs
UNIT I Diffrntial Equations.0 INTRODUCTION W li in a world of intrrlatd changing ntitis. Th locit of a falling bod changs with distanc, th position of th arth changs with tim, th ara of a circl changs
Design/Modeling for Periodic Nano Structures t for EMC/EMI. Outline
 /4/00 Dsign/Modling for Priodic Nno Structurs t for EMC/EMI Ji Chn Dprtmnt of ricl nd Computr Enginring Houston, TX, 7704 Outlin Introduction Composit Mtrils Dsign with Numricl Mixing-Lw FDTD dsign of
/4/00 Dsign/Modling for Priodic Nno Structurs t for EMC/EMI Ji Chn Dprtmnt of ricl nd Computr Enginring Houston, TX, 7704 Outlin Introduction Composit Mtrils Dsign with Numricl Mixing-Lw FDTD dsign of
CSE 373: More on graphs; DFS and BFS. Michael Lee Wednesday, Feb 14, 2018
 CSE 373: Mor on grphs; DFS n BFS Mihl L Wnsy, F 14, 2018 1 Wrmup Wrmup: Disuss with your nighor: Rmin your nighor: wht is simpl grph? Suppos w hv simpl, irt grph with x nos. Wht is th mximum numr of gs
CSE 373: Mor on grphs; DFS n BFS Mihl L Wnsy, F 14, 2018 1 Wrmup Wrmup: Disuss with your nighor: Rmin your nighor: wht is simpl grph? Suppos w hv simpl, irt grph with x nos. Wht is th mximum numr of gs
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr Dtails of th ot St #19 Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1.2, 7.1.3, & 7.2 of Proakis & Manolakis Dfinition of th So Givn signal data points x[n] for n = 0,, -1
EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr Dtails of th ot St #19 Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1.2, 7.1.3, & 7.2 of Proakis & Manolakis Dfinition of th So Givn signal data points x[n] for n = 0,, -1
Floating Point Number System -(1.3)
 Floting Point Numbr Sstm -(.3). Floting Point Numbr Sstm: Comutrs rrsnt rl numbrs in loting oint numbr sstm: F,k,m,M 0. 3... k ;0, 0 i, i,...,k, m M. Nottions: th bs 0, k th numbr o igts in th bs xnsion
Floting Point Numbr Sstm -(.3). Floting Point Numbr Sstm: Comutrs rrsnt rl numbrs in loting oint numbr sstm: F,k,m,M 0. 3... k ;0, 0 i, i,...,k, m M. Nottions: th bs 0, k th numbr o igts in th bs xnsion
HIGHER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Prof Enriqu Mtus Nivs PhD in Mthmtis Edution IGER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS omognous linr qutions with onstnt offiints of ordr two highr Appl rdution mthod to dtrmin solution of th nonhomognous qution
Prof Enriqu Mtus Nivs PhD in Mthmtis Edution IGER ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS omognous linr qutions with onstnt offiints of ordr two highr Appl rdution mthod to dtrmin solution of th nonhomognous qution
Floating Point Number System -(1.3)
 Floting Point Numbr Sstm -(.3). Floting Point Numbr Sstm: Comutrs rrsnt rl numbrs in loting oint numbr sstm: F,k,m,M 0. 3... k ;0, 0 i, i,...,k, m M. Nottions: th bs 0, k th numbr o igits in th bs xnsion
Floting Point Numbr Sstm -(.3). Floting Point Numbr Sstm: Comutrs rrsnt rl numbrs in loting oint numbr sstm: F,k,m,M 0. 3... k ;0, 0 i, i,...,k, m M. Nottions: th bs 0, k th numbr o igits in th bs xnsion
COMP108 Algorithmic Foundations
 Grdy mthods Prudn Wong http://www.s.liv..uk/~pwong/thing/omp108/01617 Coin Chng Prolm Suppos w hv 3 typs of oins 10p 0p 50p Minimum numr of oins to mk 0.8, 1.0, 1.? Grdy mthod Lrning outoms Undrstnd wht
Grdy mthods Prudn Wong http://www.s.liv..uk/~pwong/thing/omp108/01617 Coin Chng Prolm Suppos w hv 3 typs of oins 10p 0p 50p Minimum numr of oins to mk 0.8, 1.0, 1.? Grdy mthod Lrning outoms Undrstnd wht
# 1 ' 10 ' 100. Decimal point = 4 hundred. = 6 tens (or sixty) = 5 ones (or five) = 2 tenths. = 7 hundredths.
 How os it work? Pl vlu o imls rprsnt prts o whol numr or ojt # 0 000 Tns o thousns # 000 # 00 Thousns Hunrs Tns Ons # 0 Diml point st iml pl: ' 0 # 0 on tnth n iml pl: ' 0 # 00 on hunrth r iml pl: ' 0
How os it work? Pl vlu o imls rprsnt prts o whol numr or ojt # 0 000 Tns o thousns # 000 # 00 Thousns Hunrs Tns Ons # 0 Diml point st iml pl: ' 0 # 0 on tnth n iml pl: ' 0 # 00 on hunrth r iml pl: ' 0
CONIC SECTIONS. MODULE-IV Co-ordinate Geometry OBJECTIVES. Conic Sections
 Conic Sctions 16 MODULE-IV Co-ordint CONIC SECTIONS Whil cutting crrot ou might hv noticd diffrnt shps shown th dgs of th cut. Anlticll ou m cut it in thr diffrnt ws, nml (i) (ii) (iii) Cut is prlll to
Conic Sctions 16 MODULE-IV Co-ordint CONIC SECTIONS Whil cutting crrot ou might hv noticd diffrnt shps shown th dgs of th cut. Anlticll ou m cut it in thr diffrnt ws, nml (i) (ii) (iii) Cut is prlll to
( ) Geometric Operations and Morphing. Geometric Transformation. Forward v.s. Inverse Mapping. I (x,y ) Image Processing - Lesson 4 IDC-CG 1
 Img Procssing - Lsson 4 Gomtric Oprtions nd Morphing Gomtric Trnsformtion Oprtions dpnd on Pil s Coordints. Contt fr. Indpndnt of pil vlus. f f (, ) (, ) ( f (, ), f ( ) ) I(, ) I', (,) (, ) I(,) I (,
Img Procssing - Lsson 4 Gomtric Oprtions nd Morphing Gomtric Trnsformtion Oprtions dpnd on Pil s Coordints. Contt fr. Indpndnt of pil vlus. f f (, ) (, ) ( f (, ), f ( ) ) I(, ) I', (,) (, ) I(,) I (,
Weighted Matching and Linear Programming
 Wightd Mtching nd Linr Progrmming Jonthn Turnr Mrch 19, 01 W v sn tht mximum siz mtchings cn b found in gnrl grphs using ugmnting pths. In principl, this sm pproch cn b pplid to mximum wight mtchings.
Wightd Mtching nd Linr Progrmming Jonthn Turnr Mrch 19, 01 W v sn tht mximum siz mtchings cn b found in gnrl grphs using ugmnting pths. In principl, this sm pproch cn b pplid to mximum wight mtchings.
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
CBSE 2015 FOREIGN EXAMINATION
 CBSE 05 FOREIGN EXAMINATION (Sris SSO Cod No 65//F, 65//F, 65//F : Forign Rgion) Not tht ll th sts hv sm qustions Onl thir squnc of pprnc is diffrnt M Mrks : 00 Tim Allowd : Hours SECTION A Q0 Find th
CBSE 05 FOREIGN EXAMINATION (Sris SSO Cod No 65//F, 65//F, 65//F : Forign Rgion) Not tht ll th sts hv sm qustions Onl thir squnc of pprnc is diffrnt M Mrks : 00 Tim Allowd : Hours SECTION A Q0 Find th
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
FSA. CmSc 365 Theory of Computation. Finite State Automata and Regular Expressions (Chapter 2, Section 2.3) ALPHABET operations: U, concatenation, *
 CmSc 365 Thory of Computtion Finit Stt Automt nd Rgulr Exprssions (Chptr 2, Sction 2.3) ALPHABET oprtions: U, conctntion, * otin otin Strings Form Rgulr xprssions dscri Closd undr U, conctntion nd * (if
CmSc 365 Thory of Computtion Finit Stt Automt nd Rgulr Exprssions (Chptr 2, Sction 2.3) ALPHABET oprtions: U, conctntion, * otin otin Strings Form Rgulr xprssions dscri Closd undr U, conctntion nd * (if
ECE 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems. Instructor: Maria K. Michael. Overview. CAD tools for multi-level logic synthesis:
 407 Computr Aidd Dsign for Elctronic Systms Multi-lvl Logic Synthsis Instructor: Maria K. Michal 1 Ovrviw Major Synthsis Phass Logic Synthsis: 2-lvl Multi-lvl FSM CAD tools for multi-lvl logic synthsis:
407 Computr Aidd Dsign for Elctronic Systms Multi-lvl Logic Synthsis Instructor: Maria K. Michal 1 Ovrviw Major Synthsis Phass Logic Synthsis: 2-lvl Multi-lvl FSM CAD tools for multi-lvl logic synthsis:
PHA 5127 Answers Homework 2 Fall 2001
 PH 5127 nswrs Homwork 2 Fall 2001 OK, bfor you rad th answrs, many of you spnt a lot of tim on this homwork. Plas, nxt tim if you hav qustions plas com talk/ask us. Thr is no nd to suffr (wll a littl suffring
PH 5127 nswrs Homwork 2 Fall 2001 OK, bfor you rad th answrs, many of you spnt a lot of tim on this homwork. Plas, nxt tim if you hav qustions plas com talk/ask us. Thr is no nd to suffr (wll a littl suffring
Searching Linked Lists. Perfect Skip List. Building a Skip List. Skip List Analysis (1) Assume the list is sorted, but is stored in a linked list.
 3 3 4 8 6 3 3 4 8 6 3 3 4 8 6 () (d) 3 Sarching Linkd Lists Sarching Linkd Lists Sarching Linkd Lists ssum th list is sortd, but is stord in a linkd list. an w us binary sarch? omparisons? Work? What if
3 3 4 8 6 3 3 4 8 6 3 3 4 8 6 () (d) 3 Sarching Linkd Lists Sarching Linkd Lists Sarching Linkd Lists ssum th list is sortd, but is stord in a linkd list. an w us binary sarch? omparisons? Work? What if
EXST Regression Techniques Page 1
 EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 Signals & Systms Prof. Mark Fowlr ot St #21 D-T Signals: Rlation btwn DFT, DTFT, & CTFT 1/16 W can us th DFT to implmnt numrical FT procssing This nabls us to numrically analyz a signal to find
EECE 301 Signals & Systms Prof. Mark Fowlr ot St #21 D-T Signals: Rlation btwn DFT, DTFT, & CTFT 1/16 W can us th DFT to implmnt numrical FT procssing This nabls us to numrically analyz a signal to find
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALS
 Slid DIGITAL SIGAL PROCESSIG UIT I DISCRETE TIME SIGALS AD SYSTEM Slid Rviw of discrt-tim signals & systms Signal:- A signal is dfind as any physical quantity that varis with tim, spac or any othr indpndnt
Slid DIGITAL SIGAL PROCESSIG UIT I DISCRETE TIME SIGALS AD SYSTEM Slid Rviw of discrt-tim signals & systms Signal:- A signal is dfind as any physical quantity that varis with tim, spac or any othr indpndnt
Basic Polyhedral theory
 Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Chapter 13 Aggregate Supply
 Chaptr 13 Aggrgat Supply 0 1 Larning Objctivs thr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run th short-run tradoff btwn inflation and unmploymnt known as th Phillips
Chaptr 13 Aggrgat Supply 0 1 Larning Objctivs thr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run th short-run tradoff btwn inflation and unmploymnt known as th Phillips
Walk Like a Mathematician Learning Task:
 Gori Dprtmnt of Euction Wlk Lik Mthmticin Lrnin Tsk: Mtrics llow us to prform mny usful mthmticl tsks which orinrily rquir lr numbr of computtions. Som typs of problms which cn b on fficintly with mtrics
Gori Dprtmnt of Euction Wlk Lik Mthmticin Lrnin Tsk: Mtrics llow us to prform mny usful mthmticl tsks which orinrily rquir lr numbr of computtions. Som typs of problms which cn b on fficintly with mtrics
u x v x dx u x v x v x u x dx d u x v x u x v x dx u x v x dx Integration by Parts Formula
 7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
A Simple Code Generator. Code generation Algorithm. Register and Address Descriptors. Example 3/31/2008. Code Generation
 A Simpl Co Gnrtor Co Gnrtion Chptr 8 II Gnrt o for singl si lok How to us rgistrs? In most mhin rhitturs, som or ll of th oprnsmust in rgistrs Rgistrs mk goo tmporris Hol vlus tht r omput in on si lok
A Simpl Co Gnrtor Co Gnrtion Chptr 8 II Gnrt o for singl si lok How to us rgistrs? In most mhin rhitturs, som or ll of th oprnsmust in rgistrs Rgistrs mk goo tmporris Hol vlus tht r omput in on si lok
12/3/12. Outline. Part 10. Graphs. Circuits. Euler paths/circuits. Euler s bridge problem (Bridges of Konigsberg Problem)
 12/3/12 Outlin Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 1 Ciruits Cyl 2 Eulr
12/3/12 Outlin Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 1 Ciruits Cyl 2 Eulr
Chem 104A, Fall 2016, Midterm 1 Key
 hm 104A, ll 2016, Mitrm 1 Ky 1) onstruct microstt tl for p 4 configurtion. Pls numrt th ms n ml for ch lctron in ch microstt in th tl. (Us th formt ml m s. Tht is spin -½ lctron in n s oritl woul writtn
hm 104A, ll 2016, Mitrm 1 Ky 1) onstruct microstt tl for p 4 configurtion. Pls numrt th ms n ml for ch lctron in ch microstt in th tl. (Us th formt ml m s. Tht is spin -½ lctron in n s oritl woul writtn
5/9/13. Part 10. Graphs. Outline. Circuits. Introduction Terminology Implementing Graphs
 Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs 1 Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Outlin Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 2 Ciruits Cyl A spil yl
Prt 10. Grphs CS 200 Algorithms n Dt Struturs 1 Introution Trminology Implmnting Grphs Outlin Grph Trvrsls Topologil Sorting Shortst Pths Spnning Trs Minimum Spnning Trs Ciruits 2 Ciruits Cyl A spil yl
Section 3: Antiderivatives of Formulas
 Chptr Th Intgrl Appli Clculus 96 Sction : Antirivtivs of Formuls Now w cn put th is of rs n ntirivtivs togthr to gt wy of vluting finit intgrls tht is ct n oftn sy. To vlut finit intgrl f(t) t, w cn fin
Chptr Th Intgrl Appli Clculus 96 Sction : Antirivtivs of Formuls Now w cn put th is of rs n ntirivtivs togthr to gt wy of vluting finit intgrls tht is ct n oftn sy. To vlut finit intgrl f(t) t, w cn fin
Coupled Pendulums. Two normal modes.
 Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Data Assimilation 1. Alan O Neill National Centre for Earth Observation UK
 Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
2008 AP Calculus BC Multiple Choice Exam
 008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
Formal Concept Analysis
 Forml Conpt Anlysis Conpt intnts s losd sts Closur Systms nd Implitions 4 Closur Systms 0.06.005 Nxt-Closur ws dvlopd y B. Gntr (984). Lt M = {,..., n}. A M is ltilly smllr thn B M, if B A if th smllst
Forml Conpt Anlysis Conpt intnts s losd sts Closur Systms nd Implitions 4 Closur Systms 0.06.005 Nxt-Closur ws dvlopd y B. Gntr (984). Lt M = {,..., n}. A M is ltilly smllr thn B M, if B A if th smllst
Lecture 6 Thermionic Engines
 Ltur 6 hrmioni ngins Rviw Rihrdson formul hrmioni ngins Shotty brrir nd diod pn juntion nd diod disussion.997 Copyright Gng Chn, MI For.997 Dirt Solr/hrml to ltril nrgy Convrsion WARR M. ROHSOW HA AD MASS
Ltur 6 hrmioni ngins Rviw Rihrdson formul hrmioni ngins Shotty brrir nd diod pn juntion nd diod disussion.997 Copyright Gng Chn, MI For.997 Dirt Solr/hrml to ltril nrgy Convrsion WARR M. ROHSOW HA AD MASS
Homework #3. 1 x. dx. It therefore follows that a sum of the
 Danil Cannon CS 62 / Luan March 5, 2009 Homwork # 1. Th natural logarithm is dfind by ln n = n 1 dx. It thrfor follows that a sum of th 1 x sam addnd ovr th sam intrval should b both asymptotically uppr-
Danil Cannon CS 62 / Luan March 5, 2009 Homwork # 1. Th natural logarithm is dfind by ln n = n 1 dx. It thrfor follows that a sum of th 1 x sam addnd ovr th sam intrval should b both asymptotically uppr-
Miscellaneous open problems in the Regular Boundary Collocation approach
 Miscllnous opn problms in th Rgulr Boundry Colloction pproch A. P. Zilińsi Crcow Univrsity of chnology Institut of Mchin Dsign pz@mch.p.du.pl rfftz / MFS Confrnc ohsiung iwn 5-8 Mrch 0 Bsic formultions
Miscllnous opn problms in th Rgulr Boundry Colloction pproch A. P. Zilińsi Crcow Univrsity of chnology Institut of Mchin Dsign pz@mch.p.du.pl rfftz / MFS Confrnc ohsiung iwn 5-8 Mrch 0 Bsic formultions
Functions and Graphs 1. (a) (b) (c) (f) (e) (d) 2. (a) (b) (c) (d)
 Functions nd Grps. () () (c) - - - O - - - O - - - O - - - - (d) () (f) - - O - 7 6 - - O - -7-6 - - - - - O. () () (c) (d) - - - O - O - O - - O - -. () G() f() + f( ), G(-) f( ) + f(), G() G( ) nd G()
Functions nd Grps. () () (c) - - - O - - - O - - - O - - - - (d) () (f) - - O - 7 6 - - O - -7-6 - - - - - O. () () (c) (d) - - - O - O - O - - O - -. () G() f() + f( ), G(-) f( ) + f(), G() G( ) nd G()
Lecture 37 (Schrödinger Equation) Physics Spring 2018 Douglas Fields
 Lctur 37 (Schrödingr Equation) Physics 6-01 Spring 018 Douglas Filds Rducd Mass OK, so th Bohr modl of th atom givs nrgy lvls: E n 1 k m n 4 But, this has on problm it was dvlopd assuming th acclration
Lctur 37 (Schrödingr Equation) Physics 6-01 Spring 018 Douglas Filds Rducd Mass OK, so th Bohr modl of th atom givs nrgy lvls: E n 1 k m n 4 But, this has on problm it was dvlopd assuming th acclration
Integration by Parts
 Intgration by Parts Intgration by parts is a tchniqu primarily for valuating intgrals whos intgrand is th product of two functions whr substitution dosn t work. For ampl, sin d or d. Th rul is: u ( ) v'(
Intgration by Parts Intgration by parts is a tchniqu primarily for valuating intgrals whos intgrand is th product of two functions whr substitution dosn t work. For ampl, sin d or d. Th rul is: u ( ) v'(
(2) If we multiplied a row of B by λ, then the value is also multiplied by λ(here lambda could be 0). namely
 . DETERMINANT.. Dtrminnt. Introution:I you think row vtor o mtrix s oorint o vtors in sp, thn th gomtri mning o th rnk o th mtrix is th imnsion o th prlllppi spnn y thm. But w r not only r out th imnsion,
. DETERMINANT.. Dtrminnt. Introution:I you think row vtor o mtrix s oorint o vtors in sp, thn th gomtri mning o th rnk o th mtrix is th imnsion o th prlllppi spnn y thm. But w r not only r out th imnsion,
PH427/PH527: Periodic systems Spring Overview of the PH427 website (syllabus, assignments etc.) 2. Coupled oscillations.
 Dy : Mondy 5 inuts. Ovrviw of th PH47 wsit (syllus, ssignnts tc.). Coupld oscilltions W gin with sss coupld y Hook's Lw springs nd find th possil longitudinl) otion of such syst. W ll xtnd this to finit
Dy : Mondy 5 inuts. Ovrviw of th PH47 wsit (syllus, ssignnts tc.). Coupld oscilltions W gin with sss coupld y Hook's Lw springs nd find th possil longitudinl) otion of such syst. W ll xtnd this to finit
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE
 SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
Hospital Readmission Reduction Strategies Using a Penalty-Incentive Model
 Procdings of th 2016 Industrial and Systms Enginring Rsarch Confrnc H. Yang, Z. Kong, and MD Sardr, ds. Hospital Radmission Rduction Stratgis Using a Pnalty-Incntiv Modl Michll M. Alvarado Txas A&M Univrsity
Procdings of th 2016 Industrial and Systms Enginring Rsarch Confrnc H. Yang, Z. Kong, and MD Sardr, ds. Hospital Radmission Rduction Stratgis Using a Pnalty-Incntiv Modl Michll M. Alvarado Txas A&M Univrsity
4037 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Lvl MARK SCHEME for th Octobr/Novmbr 0 sris 40 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 40/ Papr, maimum raw mark 80 This mark schm is publishd as an aid to tachrs and candidats,
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Lvl MARK SCHEME for th Octobr/Novmbr 0 sris 40 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 40/ Papr, maimum raw mark 80 This mark schm is publishd as an aid to tachrs and candidats,
GUC (Dr. Hany Hammad) 9/28/2016
 U (r. Hny Hd) 9/8/06 ctur # 3 ignl flow grphs (cont.): ignl-flow grph rprsnttion of : ssiv sgl-port dvic. owr g qutions rnsducr powr g. Oprtg powr g. vill powr g. ppliction to Ntwork nlyzr lirtion. Nois
U (r. Hny Hd) 9/8/06 ctur # 3 ignl flow grphs (cont.): ignl-flow grph rprsnttion of : ssiv sgl-port dvic. owr g qutions rnsducr powr g. Oprtg powr g. vill powr g. ppliction to Ntwork nlyzr lirtion. Nois
Push trolley capacities from 1 2 through 10 Ton Geared trolley capacities from 1 2 through 100 Ton
 H o i s t n T r o l l y C o m i n t i o n s Push trolly cpcitis from 2 through 0 Ton Gr trolly cpcitis from 2 through 00 Ton CB n CF hn chin hoists cn suspn from ithr PT push trollys or GT gr trollys.
H o i s t n T r o l l y C o m i n t i o n s Push trolly cpcitis from 2 through 0 Ton Gr trolly cpcitis from 2 through 00 Ton CB n CF hn chin hoists cn suspn from ithr PT push trollys or GT gr trollys.
CSE303 - Introduction to the Theory of Computing Sample Solutions for Exercises on Finite Automata
 CSE303 - Introduction to th Thory of Computing Smpl Solutions for Exrciss on Finit Automt Exrcis 2.1.1 A dtrministic finit utomton M ccpts th mpty string (i.., L(M)) if nd only if its initil stt is finl
CSE303 - Introduction to th Thory of Computing Smpl Solutions for Exrciss on Finit Automt Exrcis 2.1.1 A dtrministic finit utomton M ccpts th mpty string (i.., L(M)) if nd only if its initil stt is finl
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Example: Change-Making Problem
 CSC 801- Dsign n Anlysis of Algorithms Ltur 11 Gry Thniqu Exmpl: Chng-Mking Prolm Givn unlimit mounts of oins of nomintions 1 > > m, giv hng for mount n with th lst numr of oins Exmpl: 1 = 25, 2 =10, =
CSC 801- Dsign n Anlysis of Algorithms Ltur 11 Gry Thniqu Exmpl: Chng-Mking Prolm Givn unlimit mounts of oins of nomintions 1 > > m, giv hng for mount n with th lst numr of oins Exmpl: 1 = 25, 2 =10, =
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Computing and Communications -- Network Coding
 89 90 98 00 Computing and Communications -- Ntwork Coding Dr. Zhiyong Chn Institut of Wirlss Communications Tchnology Shanghai Jiao Tong Univrsity China Lctur 5- Nov. 05 0 Classical Information Thory Sourc
89 90 98 00 Computing and Communications -- Ntwork Coding Dr. Zhiyong Chn Institut of Wirlss Communications Tchnology Shanghai Jiao Tong Univrsity China Lctur 5- Nov. 05 0 Classical Information Thory Sourc
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS
 CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT 4 SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS SEMESTER TWO 2014 WEEK 11 WRITTEN EXAMINATION 1 SOLUTIONS
 MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS SEMESTER TWO WEEK WRITTEN EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES QUESTION () Lt p ( z) z z z If z i z ( is
MASTER CLASS PROGRAM UNIT SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS SEMESTER TWO WEEK WRITTEN EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS FOR ERRORS AND UPDATES, PLEASE VISIT WWW.TSFX.COM.AU/MC-UPDATES QUESTION () Lt p ( z) z z z If z i z ( is
Machine Detector Interface Workshop: ILC-SLAC, January 6-8, 2005.
 Intrnational Linar Collidr Machin Dtctor Intrfac Workshop: ILCSLAC, January 68, 2005. Prsntd by Brtt Parkr, BNLSMD Mssag: Tools ar now availabl to optimiz IR layout with compact suprconducting quadrupols
Intrnational Linar Collidr Machin Dtctor Intrfac Workshop: ILCSLAC, January 68, 2005. Prsntd by Brtt Parkr, BNLSMD Mssag: Tools ar now availabl to optimiz IR layout with compact suprconducting quadrupols
Preview. Graph. Graph. Graph. Graph Representation. Graph Representation 12/3/2018. Graph Graph Representation Graph Search Algorithms
 /3/0 Prvw Grph Grph Rprsntton Grph Srch Algorthms Brdth Frst Srch Corrctnss of BFS Dpth Frst Srch Mnmum Spnnng Tr Kruskl s lgorthm Grph Drctd grph (or dgrph) G = (V, E) V: St of vrt (nod) E: St of dgs
/3/0 Prvw Grph Grph Rprsntton Grph Srch Algorthms Brdth Frst Srch Corrctnss of BFS Dpth Frst Srch Mnmum Spnnng Tr Kruskl s lgorthm Grph Drctd grph (or dgrph) G = (V, E) V: St of vrt (nod) E: St of dgs
Mathematics. Complex Number rectangular form. Quadratic equation. Quadratic equation. Complex number Functions: sinusoids. Differentiation Integration
 Mathmatics Compl numbr Functions: sinusoids Sin function, cosin function Diffrntiation Intgration Quadratic quation Quadratic quations: a b c 0 Solution: b b 4ac a Eampl: 1 0 a= b=- c=1 4 1 1or 1 1 Quadratic
Mathmatics Compl numbr Functions: sinusoids Sin function, cosin function Diffrntiation Intgration Quadratic quation Quadratic quations: a b c 0 Solution: b b 4ac a Eampl: 1 0 a= b=- c=1 4 1 1or 1 1 Quadratic
Lecture 4. Conic section
 Lctur 4 Conic sction Conic sctions r locus of points whr distncs from fixd point nd fixd lin r in constnt rtio. Conic sctions in D r curvs which r locus of points whor position vctor r stisfis r r. whr
Lctur 4 Conic sction Conic sctions r locus of points whr distncs from fixd point nd fixd lin r in constnt rtio. Conic sctions in D r curvs which r locus of points whor position vctor r stisfis r r. whr
4.2 Design of Sections for Flexure
 4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY
 MCD CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY NCERT Solvd mpls upto th sction 5 (Introduction) nd 5 (Continuity) : Empl : Chck th continuity of th function f givn by f() = + t = Empl : Emin whthr th function f
MCD CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY NCERT Solvd mpls upto th sction 5 (Introduction) nd 5 (Continuity) : Empl : Chck th continuity of th function f givn by f() = + t = Empl : Emin whthr th function f
On the Role of Fitness, Precision, Generalization and Simplicity in Process Discovery
 On th Rol of Fitnss, Prcision, Gnrliztion n Simplicity in Procss Discovry Joos Buijs Bouwijn vn Dongn Wil vn r Alst http://www.win.tu.nl/coslog/ Avncs in Procss ining ny procss iscovry n conformnc chcking
On th Rol of Fitnss, Prcision, Gnrliztion n Simplicity in Procss Discovry Joos Buijs Bouwijn vn Dongn Wil vn r Alst http://www.win.tu.nl/coslog/ Avncs in Procss ining ny procss iscovry n conformnc chcking
6.1 Integration by Parts and Present Value. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 6.1 Intgration by Parts and Prsnt Valu Copyright Cngag Larning. All rights rsrvd. Warm-Up: Find f () 1. F() = ln(+1). F() = 3 3. F() =. F() = ln ( 1) 5. F() = 6. F() = - Objctivs, Day #1 Studnts will b
6.1 Intgration by Parts and Prsnt Valu Copyright Cngag Larning. All rights rsrvd. Warm-Up: Find f () 1. F() = ln(+1). F() = 3 3. F() =. F() = ln ( 1) 5. F() = 6. F() = - Objctivs, Day #1 Studnts will b
REVISIONS REV DESCRIPTION DATE APPROVED A B C RELEASED AS REVISION A. UPDATE OF REVISION A. UPDATE OF REVISION B.
 SWBS VS SHT RV 499 1 PPLICTION NXT SSY USD ON RF NO. RVISIONS RV DSCRIPTION DT PPROVD B C RLSD S RVISION. UPDT OF RVISION. UPDT OF RVISION B. 10/5/94 4/11/95 D UPDT OF RVISION C. 1/09/06 UPDT OF RVISION
SWBS VS SHT RV 499 1 PPLICTION NXT SSY USD ON RF NO. RVISIONS RV DSCRIPTION DT PPROVD B C RLSD S RVISION. UPDT OF RVISION. UPDT OF RVISION B. 10/5/94 4/11/95 D UPDT OF RVISION C. 1/09/06 UPDT OF RVISION
Chapter 6 Folding. Folding
 Chaptr 6 Folding Wintr 1 Mokhtar Abolaz Folding Th folding transformation is usd to systmatically dtrmin th control circuits in DSP architctur whr multipl algorithm oprations ar tim-multiplxd to a singl
Chaptr 6 Folding Wintr 1 Mokhtar Abolaz Folding Th folding transformation is usd to systmatically dtrmin th control circuits in DSP architctur whr multipl algorithm oprations ar tim-multiplxd to a singl
The Theory of Small Reflections
 Jim Stils Th Univ. of Knss Dt. of EECS 4//9 Th Thory of Smll Rflctions /9 Th Thory of Smll Rflctions Rcll tht w nlyzd qurtr-wv trnsformr usg th multil rflction viw ot. V ( z) = + β ( z + ) V ( z) = = R
Jim Stils Th Univ. of Knss Dt. of EECS 4//9 Th Thory of Smll Rflctions /9 Th Thory of Smll Rflctions Rcll tht w nlyzd qurtr-wv trnsformr usg th multil rflction viw ot. V ( z) = + β ( z + ) V ( z) = = R
Practice Final Exam. 3.) What is the 61st term of the sequence 7, 11, 15, 19,...?
 Discrt mth Prctic Fl Em.) Fd 4 (i ) i=.) Fd i= 6 i.) Wht is th 6st trm th squnc 7,, 5, 9,...? 4.) Wht s th 57th trm, 6,, 4,...? 5.) Wht s th sum th first 60 trms th squnc, 5, 7, 9,...? 6.) Suppos st A
Discrt mth Prctic Fl Em.) Fd 4 (i ) i=.) Fd i= 6 i.) Wht is th 6st trm th squnc 7,, 5, 9,...? 4.) Wht s th 57th trm, 6,, 4,...? 5.) Wht s th sum th first 60 trms th squnc, 5, 7, 9,...? 6.) Suppos st A
Multi-channel Dual Clocks three-dimensional probability Random Multiple Access protocol for Wireless Public Bus Networks based on RTS/CTS mechanism
 MATE Wb of onfrncs 44, 00 ( 06 DO: 0.05/ mtcconf/ 06 4400 Ownd by th uthors, publishd by EDP Scincs, 06 Multi-chnnl Dul locks thr-dimnsionl probbility ndom Multipl Accss protocol for Wirlss Public us Ntworks
MATE Wb of onfrncs 44, 00 ( 06 DO: 0.05/ mtcconf/ 06 4400 Ownd by th uthors, publishd by EDP Scincs, 06 Multi-chnnl Dul locks thr-dimnsionl probbility ndom Multipl Accss protocol for Wirlss Public us Ntworks
a b c cat CAT A B C Aa Bb Cc cat cat Lesson 1 (Part 1) Verbal lesson: Capital Letters Make The Same Sound Lesson 1 (Part 1) continued...
 Progrssiv Printing T.M. CPITLS g 4½+ Th sy, fun (n FR!) wy to tch cpitl lttrs. ook : C o - For Kinrgrtn or First Gr (not for pr-school). - Tchs tht cpitl lttrs mk th sm souns s th littl lttrs. - Tchs th
Progrssiv Printing T.M. CPITLS g 4½+ Th sy, fun (n FR!) wy to tch cpitl lttrs. ook : C o - For Kinrgrtn or First Gr (not for pr-school). - Tchs tht cpitl lttrs mk th sm souns s th littl lttrs. - Tchs th
Random Access Techniques: ALOHA (cont.)
 Random Accss Tchniqus: ALOHA (cont.) 1 Exampl [ Aloha avoiding collision ] A pur ALOHA ntwork transmits a 200-bit fram on a shard channl Of 200 kbps at tim. What is th rquirmnt to mak this fram collision
Random Accss Tchniqus: ALOHA (cont.) 1 Exampl [ Aloha avoiding collision ] A pur ALOHA ntwork transmits a 200-bit fram on a shard channl Of 200 kbps at tim. What is th rquirmnt to mak this fram collision
ELEG 413 Lecture #6. Mark Mirotznik, Ph.D. Professor The University of Delaware
 LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
 Mor Tutorial at www.dumblittldoctor.com Work th problms without a calculator, but us a calculator to chck rsults. And try diffrntiating your answrs in part III as a usful chck. I. Applications of Intgration
Mor Tutorial at www.dumblittldoctor.com Work th problms without a calculator, but us a calculator to chck rsults. And try diffrntiating your answrs in part III as a usful chck. I. Applications of Intgration
Lecture 12 Quantum chromodynamics (QCD) WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Lctur Quntum chromodynmics (QCD) WS/: Introduction to Nuclr nd Prticl Physics QCD Quntum chromodynmics (QCD) is thory of th strong intrction - bsd on color forc, fundmntl forc dscribing th intrctions of
Lctur Quntum chromodynmics (QCD) WS/: Introduction to Nuclr nd Prticl Physics QCD Quntum chromodynmics (QCD) is thory of th strong intrction - bsd on color forc, fundmntl forc dscribing th intrctions of
