Fatigue Life Prediction of Fabric Braided Rubber Hose in Complicated Cyclic Motion
|
|
|
- Nancy Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fatigue Life Prediction of Fabric Braided Rubber Hose in Complicated Cyclic Motion *Jin-Rae Cho 1) and Young-Hyun Kim ) 1) epartment of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Hongik University, Sejong , Korea ) School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan , Korea 1) jrcho@hongik.ac.kr ABSTRACT This paper is concerned with the large deformation and the fatigue life of fabric braided rubber hose in complicated cyclic motion. The fabric braided hose exhibits the complex large deformation while moving along the specific cyclic path so that the fatigue damage is to be accumulated with the number of moving cycles. In order to assess the fatigue life according to the cyclic deformation and the initial mean strain, the modified fatigue model is employed. Two fatigue parameters were determined from the E-N curves that were obtained by the fatigue test using rubber specimens. The fatigue lives are calculated by making use of the rainflow cycle counting method and the Minor cumulative damage law. The numerical experiments are carried out to illustrate the fatigue prediction method, and the large deformation and fatigue life characteristics are parametrically investigated. 1. INTROUCTION Braking hose in the automotive hydraulic braking system plays an important role of delivering the driver s braking force to the brake disc cylinders via internal working oil. Since the traffic accidents caused by the oil leakage may lead to the fatal casualties, the braking hose should be elaborately designed to prevent the microcraking (Kwack and Choi, 9), a main source of oil leakage, during the operation within the whole period of its warranty. The microcraking is mostly attributed to the complicated and large cyclic deformation of hose and to the interference with other adjacent vehicle components. For this reason, the braking hose is in the lamination composition of pure rubber layers and fabric braided layers to effectively prevent the oil leakage and to suppress the excessive large deformation (Entwistle, 1981; Cho et al., 13). The fabric braided layers are composed of periodic warp and fill tows in the complex pattern, so those exhibit the anisotropic behavior even though their base materials are isotropic material (Cho et al., 6; Xu et al., 1; Chuda-Kowalska and Garstecki, 16). Because of the anisotropic behavior of fabric braided layers, the whole braking hose
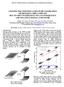
2 exhibits the inherent out-of-plane deformation during the steering and bump/rebound motions of vehicle (Cho et al., 13). And, it becomes one of crucial factors in the design of oil leakage-proof high-durable braking hose, which produces the interferencefree deformed configuration, by utilizing the computer-aided simulation. The hose cyclic path is not unique but manifold depending on the combination of the steering and bump/rebound motions of vehicle (Cho et al., 15). So, a number of major cyclic paths that characterize the hose deformed layout should be identified and numerically interpolated for the numerical simulation. For this reason, the hose deformed configuration for the specific hose cyclic path and the resulting fatigue life have been traditionally evaluated by experiments. However, this approach is highly cost- and time-consuming, and furthermore it leads to the hose layout design of trial and error. To overcome the demerits of experimental approach, the attempts to apply the analytical and computational methods have been attempted by several investigators. As an extension of our previous work (Cho et al., 13; 15) on the braking hose, this paper intends to investigate the characteristics of hose large deformation and fatigue life to the hose cyclic path. Four representative cyclic paths are chosen, and the large deformation and fatigue analyses are carried out for each cyclic path. The homogenization, path interpolation and fatigue evaluation methods are integrated, and the variation of the maximum in-plane and out-of-plane deformations and the critical fatigue life cycles are comparatively investigated to the hose cyclic path.. LARGE EFORMATION OF Fig. 1(a) represents a typical braking hose assembled in the front braking system, where one end is fixed to the main body of vehicle while the other end, called the movable end throughout this manuscript, is attached to the tire assembly using a strut. Hence, the hose movable end is to be moved along with the tire motion, and hence the entire braking hose is forced to be deformed. The vehicle motion could be classified into the horizontal steering mode and the vertical bump/rebound mode. Here, the bump/rebound motion is resulted from the relative vertical movement of tire with respect to the vehicle at quick stop or start, or when the vehicle is running over cleats. (a) (b) Fig.1 (a) Steering and bump/rebound motions of braking hose, (b) nine extreme positions of defining the cyclic paths
3 For a given braking hose, its deformation is not unique but diverse in aspects of the deformed configuration and the deformation magnitude, depending on the moving path of hose movable end. The hose deformation is not only large and complicated but also repetitive, so that the deformed braking hose may contact with other adjacent automotive parts and the hose durability deteriorates in proportional to the repetition number of cyclic deformations. The path of hose movable end is not easy to identify because it is diversely determined according to a combination of the tire steering motion and the bump/rebound motion of vehicle. In fact, its realistic and exact identification would be possible only by either the motion measurement using the vision system or 3- mutibody dynamics (MB) simulation. However, even if possible, such measurement or MB simulation requires the painstaking job for processing the numerous motion data. For this reason, the path is rather simply defined using nine extreme positions shown in Fig. 1(b) that are determined by the tensor product of three positions in the steering mode and three positions in the bump/rebound mode. The neutral position corresponds to the straight driving without bump and rebound, and the left and right positions indicate the maximum steering in the left and right directions. Meanwhile, the bump and rebound indicate the maximum compression and stretching of tire in the vertical direction with respect to the vehicle. Two most representatives are the horizontal path -1-3 and the vertical 4-1-5, where the former corresponds to the leftneutral-right handling in cruising while the latter to the center acceleration and braking, respectively.. FIVE-LAYERE FABRIC BRAIE RUBBER HOSE Fig. (a) shows a five-layered reinforced braking hose composed of three rubber layers and two fabric braided layers. The unfold configuration of braided layer is represented in Fig. (b), where warp and fill tows are woven with the specific helix angle H. Each warp and fill tow are composed of three polyester cords, and the interfaces between warp and fill tows are also assumed to be perfectly bonded. The total number of warp and fill tows within a pitch p is defined by Cr and the diameter of base cord is denoted by denia which is defined by the total weight in gram per 9,m of cord. These material parameters as well as the helix angle are key parameters influencing the anisotropic behavior of braided layer. (a) (b) Fig. Fabric braided rubber hose: (a) layer composition, (b) unfolded fabric braid
4 With the setting of material co-ordinates shown in Fig. (a), two fabric braided layers are modeled as an orthotropic material with the constitutive relation (aniel and Ishai, 1994) given by (1) with six diagonal terms defined by / E E off-diagonal terms are defined by ii 1 jk kj j k and i i3 Gij 3. The other six ij ji E j E ki k jk jk ik ji i j k, k j i kj E E i j () with / E1E E3. Where, subscripts 1, and 3 stand for x, y and z, respectively. Meanwhile, the incompressible hyperelastic behavior of three rubber layers is modeled by a four-term Mooney-Rivlin material model which is expressed by the strain W I, I I defined by energy density functional 1, 3 W I,I,I C I 3 C I 3 C I 3I 3 I (3) In which, I i are the invariants of Green-Lagrange strain tensor and C ij are the material dependent Mooney-Rivlin constants. The incompressibility of rubber is enforced by the last term on the right hand side of Eq. (3). The Mooney-Rivlin constants which were determined by the uniaxial tension test of rubber specimen may be referred to our previous paper (Cho et al., 13). 3. FATIGUE EVALUATION The cyclic motion of braking hose along a specific path produces the complex cyclic variations of strains and stresses, with the presence of mean strain and stress that are resulted from the pre-deformation caused when the braking hose is assembled at the neutral position. When the applied stresses generate predominantly elastic strain amplitudes, the mean stress effect can be taken into consideration by Basquin s mean stress correction method (Basquin, 191; Karolczuk et al., 13) given by N b, where N f is the fatigue life, f the fatigue strength coefficient, and b ar f f the fatigue strength exponent, respectively. Here, denotes the equivalent ar max a
5 fully reversed stress amplitude defined in terms of the maximum stress max and the stress amplitude a. But, when the cyclic response of the material is within the elasticplastic stress-strain range, the mean stress effect on fatigue life is based on the strainlife approach represented by b N N c e p f a f f f (4) where a is the strain amplitude, f the fatigue ductility coefficient, and c the fatigue ductility exponent. The modification of Eq. (4) which is used to predict the fatigue life for zero mean stress was made by several investigators (Smith et al., 197; Ince and Glinka, 11). The current study utilizes the Morrow model given by E f m b N c f f N f (5) E By the way, this correction model is needed to be slightly modified for the current study because the large deformation analysis of braking hose is carried out using the Moonley-Rivlin hyperelastic material model by neglecting the plastic strain. Furthermore, the term f / E is replaced with a material-dependent fatigue parameter K f which can be determined from the N curves shown in Fig. 3(a) in the log-log scale. Then, we have the modified Morrow model given by K N b f m f (6) Since strains and stresses at each material point exhibit the complex time histories composed of a number of harmonic cycles, as illustrated in Fig. 5(b), we employ the Palmgren-Minor cumulative damage law given by Ns i1, i i N n i f i (7) to calculate the total accumulated fatigue damage during a single deformation cycle along the specific cyclic path. Here, N s is the total number of distinct harmonic strain cycles, i the accumulated fatigue damage by the i-th harmonic strain cycle, and n i and N f i the repetition number and the fatigue life of the i-th strain cycle, respectively. N f at each material point within the braking hose along the Then, the fatigue life cycles specific path is calculated by N f 1/. The fatigue life calculation is performed node by node using the signed nodal von Mises strains vm. The repletion numbers n i of each distinct strain cycle are counted by the rainflow cycle counting method.
6 (a) (b) Fig. 3 (a) The N curves of two rubber layers, (b) rainflow cycle counting 4. NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS A five-layered braking hose of the length L of 3 mm and the outer diameter o of 1.5mm is taken for the numerical experiments. The top end is clamped while the bottom end is forced to move along the predefined, where the center co-ordinates and rotations of the cross-section of the bottom end at nine extreme positions are referred to our previous paper (Cho et al., 15) Referring to the previous Fig. (a), the thicknesses of five layers are as follows: 1. 5,. 3 and 1,1mm for the outer, middle and inner rubber layers and.45mm for the outer and inner fabric braided layers. Two fabric braided layers are manufactured with PVA (poly vinyl alcohol) and the helix angles, pitch p and C are as follows: 18. 5mm, 4 and r o for the outer layer and o 14. mm, and for the inner layer. The homogenized orthotropic material properties of the inner and outer fabric braided layers are given in our previous paper (Cho et al., 13). Three rubber layers are manufactured with EPM (ethylene-propylene-dienemonomer), and the fatigue life is evaluated for the outer and inner rubber layers because both layers are weak to fatigue damage and play an important role in preventing the oil leakage. The entire braking hose is uniformly discretized with the total of 33, 8-node hexahedron elements. Basically, the updated Lagrangian formulation is used to compute the increments of strain and stress during the hose large deformation along the cyclic paths, and the invariants of Green-Lagrange strain tensor in Mooney-Rivlin models were evaluated in the sense of total Lagrangian. Two fatigue parameters K and b in the modified Morrow model in Eq. (6) are found to be: 3.73 f and for the inner rubber layer and and for the outer rubber layer, respectively. Fig. 4(a) represents the in-plane and out-of-plane deformed configurations of the braking hose for path 1 when the maximum in-plane deformation reaches the peak value. Those of the remaining three cyclic paths are given in Table 1. It is clearly observed that the maximum values I and O are quite different for different paths. Paths 1 and 3 produce relatively larger in-plane deformations, but conversely, the out- H
7 of-plane deformations at both paths are shown to be insignificant. In case of the out-ofplane deformation, it is shown to be remarkable at paths and 4. The maximum inplane and out-of-plane deformations are largest at path 1 and, respectively, such that is 71.59mm while O is 17.75mm. I (a) (b) Fig. 4 Numerical results of path 1: (a) maximum in- and out-of-plane plane deformations, (b) fatigue life profiles Table 1 Comparison of the hose deformations, the peak equivalent strains and stresses, and the critical fatigue lives to the cyclic path Items Cyclic paths Maximum In-plane deformation (mm) Out-of-plane Peak equivalent strain Peak effective stress (MPa) Critical fatigue life Outer rubber 4,86 1,63 5,735 1,41 (Cycles) Inner rubber 45, ,765 54,48 168,151 Fig. 4(b) represents the fatigue life profiles of the outer and inner rubber layers for path 1. It is observed that the fatigue life of inner rubber layer is much higher than that of the outer rubber layer. This is also observed from Table 1 for the remaining three cyclic paths, which is because the magnitude of bending and torsional strain and stress decreases in inverse proportional to the radius of rubber hose. Meanwhile, it is found that both the peak equivalent strain and stress are remarkable at paths 1 and 3, which is because both paths produce relatively larger deformations. For all the paths, we observed the significantly high strain and stress in the upper one-third region and in the vicinity of lower movable end. The peak equivalent strain.58 was occurred in the vicinity of the upper fixed end at path 1, while the peak effective stress 5.664MPa appeared at the same point but at path 3. We observed that all the cyclic paths show the remarkably lower fatigue lives in the vicinity of upper fixed and lower movable ends because the equivalent strain is relatively larger in these regions. Regarding the hose path, it is found that the critical fatigue life is significantly lower at paths 1 and 3 when
8 compared with paths and 4. As given in Table 1, path 1 shows the lowest critical fatigue life equal to 4,86 in the vicinity of upper fixed end. CONCLUSION In this paper, the large deformation and fatigue life of fabric braided composite rubber hose are investigated to the four representative cyclic paths. It has been observed that the maximum in-plane and out-of plane deformations and the critical fatigue lives are remarkably different for different cyclic paths. These parametric results would be usefully used for the layout and durability design of braking hose. ACKNOWLEGEMENT This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. NRF-14R1A1A558). REFERENCES Basquin, O.H. (191), The exponential law of endurance tests, Proc. Am. Soc. Test. Mater., 1, Cho, J.R., Song, J.I. and Choi, J.H. (6), Prediction of effective mechanical properties of reinforced braid by 3- finite element analysis, Key Eng. Mater., 36-38, Cho, J.R., Jee, Y.B., Kim, W.J., Han, S.R. and Lee, S.B. (13), Homogenization of Braided Fabric Composite for Reliable Large eformation Analysis of Reinforced Rubber Hose, Composites: Part B, 53, Cho, J.R., Yoon, Y.H., Seo, C.W., Kim, Y.G. (15), Fatigue life assessment of fabric braided composite rubber hose in complicated large deformation cyclic motion, Finite Elem. Anal. es., 1, Chuda-Kowalska, M. and Garstecki, A. (16), Experimental study of anisotropic behavior of PU foam in sandwich panels, Steel Comp. Struct., (1), aniel, I.M. and Ishai, O. (1994), Engineering Mechanics of Composite Materials, Oxford University Press, New York. Entwistle, K.M. (1981), The behavior of braided hydraulic hose reinforced with steel wires, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 3, Ince, A. and Glinka, G. (11), A modification of Morrow and Smith-Watson-Topper mean stress correction models, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 34(11), Karolczuk, A., Kowalski, M., Bariski, R. and Zok, F. (13), Fatigue phenomenon in explosively welded steel-titanium clad components subjected to push-pull loading, Int. J. Fatigue, 48, Smith, K.N., Watson, P., Topper, T.H., A stress-strain function for the fatigue of materials, J. Mater., 5, , 197. Xu, L., Kim, S.J. Ong, C.H. and Ha, S.K. (1), Prediction of material properties of biaxial and triaxial braided textile composites, J. Composite Mater., 46(18), 55-7.
Numerical methods of multiaxial fatigue life prediction for elastomers under variable amplitude loadings
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION doi: 10.1111/ffe.12401 Numerical methods of multiaxial fatigue life prediction for elastomers under variable amplitude loadings J. CHUNG and N. H. KIM Department of Mechanical and
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION doi: 10.1111/ffe.12401 Numerical methods of multiaxial fatigue life prediction for elastomers under variable amplitude loadings J. CHUNG and N. H. KIM Department of Mechanical and
Predicting Fatigue Life with ANSYS Workbench
 Predicting Fatigue Life with ANSYS Workbench How To Design Products That Meet Their Intended Design Life Requirements Raymond L. Browell, P. E. Product Manager New Technologies ANSYS, Inc. Al Hancq Development
Predicting Fatigue Life with ANSYS Workbench How To Design Products That Meet Their Intended Design Life Requirements Raymond L. Browell, P. E. Product Manager New Technologies ANSYS, Inc. Al Hancq Development
This guide is made for non-experienced FEA users. It provides basic knowledge needed to start your fatigue calculations quickly.
 Quick Fatigue Analysis Guide This guide is made for non-experienced FEA users. It provides basic knowledge needed to start your fatigue calculations quickly. Experienced FEA analysts can also use this
Quick Fatigue Analysis Guide This guide is made for non-experienced FEA users. It provides basic knowledge needed to start your fatigue calculations quickly. Experienced FEA analysts can also use this
Volume 2 Fatigue Theory Reference Manual
 Volume Fatigue Theory Reference Manual Contents 1 Introduction to fatigue 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1. Description of the applied loading... 1-1.3 Endurance curves... 1-3 1.4 Generalising fatigue data...
Volume Fatigue Theory Reference Manual Contents 1 Introduction to fatigue 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1. Description of the applied loading... 1-1.3 Endurance curves... 1-3 1.4 Generalising fatigue data...
Features and design of elastomer / textile engineered structures. D Boast, C Eng. F Mech E.
 Features and design of elastomer / textile engineered structures D Boast, C Eng. F Mech E. Title of meeting IOM Bla blah Topics Materials: Environmental acids, water, oil, radiation etc. Bonding. Cost.
Features and design of elastomer / textile engineered structures D Boast, C Eng. F Mech E. Title of meeting IOM Bla blah Topics Materials: Environmental acids, water, oil, radiation etc. Bonding. Cost.
A study of forming pressure in the tube-hydroforming process
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 192 19 (2007) 404 409 A study of forming pressure in the tube-hydroforming process Fuh-Kuo Chen, Shao-Jun Wang, Ray-Hau Lin Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 192 19 (2007) 404 409 A study of forming pressure in the tube-hydroforming process Fuh-Kuo Chen, Shao-Jun Wang, Ray-Hau Lin Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Tire Standing Wave Simulation by 3-D Explicit Finite Element Method
 Copyright 2008 ICCES ICCES, vol.7, no.3, pp.123-128 Tire Standing Wave Simulation by 3-D Explicit Finite Element Method Jung-Chul An 1,Jin-RaeCho 1 Summary Tire standing wave is one of the crucial factors
Copyright 2008 ICCES ICCES, vol.7, no.3, pp.123-128 Tire Standing Wave Simulation by 3-D Explicit Finite Element Method Jung-Chul An 1,Jin-RaeCho 1 Summary Tire standing wave is one of the crucial factors
NUMERICAL MODELLING AND EXPERIMENTAL INFLATION VALIDATION OF A BIAS TWO-WHEEL TIRE
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 4 th EURECA 05 Special Issue February (06) 70-8 School of Engineering, Taylor s University NUMERICAL MODELLING AND EXPERIMENTAL INFLATION VALIDATION OF A BIAS
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 4 th EURECA 05 Special Issue February (06) 70-8 School of Engineering, Taylor s University NUMERICAL MODELLING AND EXPERIMENTAL INFLATION VALIDATION OF A BIAS
Analysis Handbook. Metal Fatigue. for Computer-Aided Engineering. Barkey. Yung-Li Lee. Practical Problem-Solving Techniques. Hong-Tae Kang. Mark E.
 Metal Fatigue Analysis Handbook Practical Problem-Solving Techniques for Computer-Aided Engineering Yung-Li Lee Mark E. Barkey Hong-Tae Kang ms- ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD
Metal Fatigue Analysis Handbook Practical Problem-Solving Techniques for Computer-Aided Engineering Yung-Li Lee Mark E. Barkey Hong-Tae Kang ms- ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD
Lecture #8: Ductile Fracture (Theory & Experiments)
 Lecture #8: Ductile Fracture (Theory & Experiments) by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Ductile
Lecture #8: Ductile Fracture (Theory & Experiments) by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing 2015 1 1 1 Ductile
Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model
 Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model J.B. Sang*, L.F. Sun, S.F. Xing,
Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model Mechanical Properties of Polymer Rubber Materials Based on a New Constitutive Model J.B. Sang*, L.F. Sun, S.F. Xing,
Plasticity R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur
 Plasticity R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1. Plasticity:... 3 1.1 Plastic Deformation,
Plasticity R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401 Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 9 Table of Contents 1. Plasticity:... 3 1.1 Plastic Deformation,
* Many components have multiaxial loads, and some of those have multiaxial loading in critical locations
 Why do Multiaxial Fatigue Calculations? * Fatigue analysis is an increasingly important part of the design and development process * Many components have multiaxial loads, and some of those have multiaxial
Why do Multiaxial Fatigue Calculations? * Fatigue analysis is an increasingly important part of the design and development process * Many components have multiaxial loads, and some of those have multiaxial
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec15_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec15_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec15_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
For ASME Committee use only.
 ð15þ KD-232 PROTECTION AGAINST LOCAL FAILURE In addition to demonstrating protection against plastic collapse as defined in KD-231, the local failure criteria below shall be satisfied. KD-232.1 Elastic
ð15þ KD-232 PROTECTION AGAINST LOCAL FAILURE In addition to demonstrating protection against plastic collapse as defined in KD-231, the local failure criteria below shall be satisfied. KD-232.1 Elastic
Fatigue Algorithm Input
 Methods Fatigue Algorithm Input By default, fe-safe analyses stress datasets that contain elastic stresses The calculation of elastic-plastic stress-strains, where necessary, is performed in fe-safe using
Methods Fatigue Algorithm Input By default, fe-safe analyses stress datasets that contain elastic stresses The calculation of elastic-plastic stress-strains, where necessary, is performed in fe-safe using
DETERMINING THE STRESS PATTERN IN THE HH RAILROAD TIES DUE TO DYNAMIC LOADS 1
 PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. CIV. ENG. VOL. 46, NO. 1, PP. 125 148 (2002) DETERMINING THE STRESS PATTERN IN THE HH RAILROAD TIES DUE TO DYNAMIC LOADS 1 Nándor LIEGNER Department of Highway and Railway Engineering
PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. CIV. ENG. VOL. 46, NO. 1, PP. 125 148 (2002) DETERMINING THE STRESS PATTERN IN THE HH RAILROAD TIES DUE TO DYNAMIC LOADS 1 Nándor LIEGNER Department of Highway and Railway Engineering
Comparative Study of Variation of Mooney- Rivlin Hyperelastic Material Models under Uniaxial Tensile Loading
 Comparative Study of Variation of Mooney- Rivlin Hyperelastic Material Models under Uniaxial Tensile Loading A. N. Jadhav 1, Dr. S.R. Bahulikar, N.H. Sapate 3 1 M Tech Design Engg, Mechanical Engineering,
Comparative Study of Variation of Mooney- Rivlin Hyperelastic Material Models under Uniaxial Tensile Loading A. N. Jadhav 1, Dr. S.R. Bahulikar, N.H. Sapate 3 1 M Tech Design Engg, Mechanical Engineering,
Nonlinear bending analysis of laminated composite stiffened plates
 Nonlinear bending analysis of laminated composite stiffened plates * S.N.Patel 1) 1) Dept. of Civi Engineering, BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus, Pilani-333031, (Raj), India 1) shuvendu@pilani.bits-pilani.ac.in
Nonlinear bending analysis of laminated composite stiffened plates * S.N.Patel 1) 1) Dept. of Civi Engineering, BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus, Pilani-333031, (Raj), India 1) shuvendu@pilani.bits-pilani.ac.in
Proceedings of the ASME th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2016 June 19-24, 2016, Busan, South Korea
 Proceedings of the ASME 26 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE26 June 9-24, 26, Busan, South Korea OMAE26-54554 LOCAL STRAIN AND STRESS CALCULATION METHODS OF IRREGULAR
Proceedings of the ASME 26 35th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE26 June 9-24, 26, Busan, South Korea OMAE26-54554 LOCAL STRAIN AND STRESS CALCULATION METHODS OF IRREGULAR
SIMULATION OF MECHANICAL TESTS OF COMPOSITE MATERIAL USING ANISOTROPIC HYPERELASTIC CONSTITUTIVE MODELS
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 18, 2011, No. 1, p. 23 32 23 SIMULATION OF MECHANICAL TESTS OF COMPOSITE MATERIAL USING ANISOTROPIC HYPERELASTIC CONSTITUTIVE MODELS Tomáš Lasota*, JiříBurša* This paper deals
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 18, 2011, No. 1, p. 23 32 23 SIMULATION OF MECHANICAL TESTS OF COMPOSITE MATERIAL USING ANISOTROPIC HYPERELASTIC CONSTITUTIVE MODELS Tomáš Lasota*, JiříBurša* This paper deals
Static and Time Dependent Failure of Fibre Reinforced Elastomeric Components. Salim Mirza Element Materials Technology Hitchin, UK
 Static and Time Dependent Failure of Fibre Reinforced Elastomeric Components Salim Mirza Element Materials Technology Hitchin, UK Introduction Fibre reinforced elastomers are used in many applications,
Static and Time Dependent Failure of Fibre Reinforced Elastomeric Components Salim Mirza Element Materials Technology Hitchin, UK Introduction Fibre reinforced elastomers are used in many applications,
Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture
 Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing
Lecture #7: Basic Notions of Fracture Mechanics Ductile Fracture by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling of Materials in Manufacturing
A Review On Methodology Of Material Characterization And Finite Element Modelling Of Rubber-Like Materials
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 50-301, ISSN (p): 78-8719 PP 06-10 www.iosrjen.org A Review On Methodology Of Material Characterization And Finite Element Modelling Of Rubber-Like Materials
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 50-301, ISSN (p): 78-8719 PP 06-10 www.iosrjen.org A Review On Methodology Of Material Characterization And Finite Element Modelling Of Rubber-Like Materials
Grid supports design for dual-cooled fuel rods
 Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 5 Number 4 011 99 Grid supports design for dual-cooled fuel rods JaeYong Kim, YoungHo Lee, KyungHo Yoon and HyungKyu Kim Innovative Nuclear Fuel Division, Korea Atomic
Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 5 Number 4 011 99 Grid supports design for dual-cooled fuel rods JaeYong Kim, YoungHo Lee, KyungHo Yoon and HyungKyu Kim Innovative Nuclear Fuel Division, Korea Atomic
An alternative design method for the double-layer combined die using autofrettage theory
 https://doi.org/10.5194/ms-8-267-2017 Author(s) 2017. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution.0 License. An alternative design method for the double-layer combined die using autofrettage
https://doi.org/10.5194/ms-8-267-2017 Author(s) 2017. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution.0 License. An alternative design method for the double-layer combined die using autofrettage
EXPERIMENTAL IDENTIFICATION OF HYPERELASTIC MATERIAL PARAMETERS FOR CALCULATIONS BY THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 7, No. EXPERIMENTAL IDENTIFICATION OF HYPERELASTIC MATERIAL PARAMETERS FOR CALCULATIONS BY THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Robert Czabanowski Wroclaw University
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 7, No. EXPERIMENTAL IDENTIFICATION OF HYPERELASTIC MATERIAL PARAMETERS FOR CALCULATIONS BY THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Robert Czabanowski Wroclaw University
Moment redistribution of continuous composite I-girders with high strength steel
 Moment redistribution of continuous composite I-girders with high strength steel * Hyun Sung Joo, 1) Jiho Moon, 2) Ik-Hyun sung, 3) Hak-Eun Lee 4) 1), 2), 4) School of Civil, Environmental and Architectural
Moment redistribution of continuous composite I-girders with high strength steel * Hyun Sung Joo, 1) Jiho Moon, 2) Ik-Hyun sung, 3) Hak-Eun Lee 4) 1), 2), 4) School of Civil, Environmental and Architectural
FATIGUE LIFE EVALUATION OF SUSPENSION KNUCKLE USING MULTIBODY SIMULATION TECHNIQUE
 Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences (JMES) ISSN (Print): 2289-4659; e-issn: 2231-8380; Volume 3, pp. 291-300, December 2012 Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Pekan, Pahang, Malaysia DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15282/jmes.3.2012.5.0027
Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences (JMES) ISSN (Print): 2289-4659; e-issn: 2231-8380; Volume 3, pp. 291-300, December 2012 Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Pekan, Pahang, Malaysia DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15282/jmes.3.2012.5.0027
HERCULES-2 Project. Deliverable: D4.4. TMF model for new cylinder head. <Final> 28 February March 2018
 HERCULES-2 Project Fuel Flexible, Near Zero Emissions, Adaptive Performance Marine Engine Deliverable: D4.4 TMF model for new cylinder head Nature of the Deliverable: Due date of the Deliverable:
HERCULES-2 Project Fuel Flexible, Near Zero Emissions, Adaptive Performance Marine Engine Deliverable: D4.4 TMF model for new cylinder head Nature of the Deliverable: Due date of the Deliverable:
MARKOV CHAIN APPLICATION IN FATIGUE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS FOR DURABILITY ASSESSMENT OF A VEHICLE CRANKSHAFT
 MARKOV CHAIN APPLICATION IN FATIGUE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS FOR DURABILITY ASSESSMENT OF A VEHICLE CRANKSHAFT S. S. K.Singh,2, S. Abdullah 2 and N. A. N.Mohamed 3 Centre of Technology Marine Engineering,
MARKOV CHAIN APPLICATION IN FATIGUE RELIABILITY ANALYSIS FOR DURABILITY ASSESSMENT OF A VEHICLE CRANKSHAFT S. S. K.Singh,2, S. Abdullah 2 and N. A. N.Mohamed 3 Centre of Technology Marine Engineering,
INCREASING RUPTURE PREDICTABILITY FOR ALUMINUM
 1 INCREASING RUPTURE PREDICTABILITY FOR ALUMINUM Influence of anisotropy Daniel Riemensperger, Adam Opel AG Paul Du Bois, PDB 2 www.opel.com CONTENT Introduction/motivation Isotropic & anisotropic material
1 INCREASING RUPTURE PREDICTABILITY FOR ALUMINUM Influence of anisotropy Daniel Riemensperger, Adam Opel AG Paul Du Bois, PDB 2 www.opel.com CONTENT Introduction/motivation Isotropic & anisotropic material
Exercise: concepts from chapter 8
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
University of Sheffield The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire
 The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire Chaoming Yu, I. W. Burgess, Z. Huang, R. J. Plank Department of Civil and Structural Engineering StiFF 05/09/2006 3D composite structures
The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire Chaoming Yu, I. W. Burgess, Z. Huang, R. J. Plank Department of Civil and Structural Engineering StiFF 05/09/2006 3D composite structures
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided
 Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
CHAPTER 7 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DEEP GROOVE BALL BEARING
 113 CHAPTER 7 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DEEP GROOVE BALL BEARING 7. 1 INTRODUCTION Finite element computational methodology for rolling contact analysis of the bearing was proposed and it has several
113 CHAPTER 7 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DEEP GROOVE BALL BEARING 7. 1 INTRODUCTION Finite element computational methodology for rolling contact analysis of the bearing was proposed and it has several
AN ANISOTROPIC PSEUDO-ELASTIC MODEL FOR THE MULLINS EFFECT IN ARTERIAL TISSUE
 XI International Conference on Computational Plasticity. Fundamentals and Applications COMPLAS XI E. Oñate, D.R.J. Owen, D. Peric and B. Suárez (Eds) AN ANISOTROPIC PSEUDO-ELASTIC MODEL FOR THE MULLINS
XI International Conference on Computational Plasticity. Fundamentals and Applications COMPLAS XI E. Oñate, D.R.J. Owen, D. Peric and B. Suárez (Eds) AN ANISOTROPIC PSEUDO-ELASTIC MODEL FOR THE MULLINS
2 Experiment of GFRP bolt
 16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS FATIGUE LIFE EVALUATION OF BOLT MADE OF WOVEN FABRIC FRP Takeshi INOUE*, Hiroaki NAKAI**, Tetsusei KURASHIKI**, Masaru ZAKO**, Yuji KOMETANI*** *Graduate
16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS FATIGUE LIFE EVALUATION OF BOLT MADE OF WOVEN FABRIC FRP Takeshi INOUE*, Hiroaki NAKAI**, Tetsusei KURASHIKI**, Masaru ZAKO**, Yuji KOMETANI*** *Graduate
A Repeated Dynamic Impact Analysis for 7x7 Spacer Grids by using ABAQUS/ Standard and Explicit
 A Repeated Dynamic Impact Analysis for 7x7 Spacer Grids by using ABAQUS/ Standard and Explicit Kim, Jae-Yong, and Yoon, Kyung-Ho* * Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute ABSTRACT Spacer grids(sg) are
A Repeated Dynamic Impact Analysis for 7x7 Spacer Grids by using ABAQUS/ Standard and Explicit Kim, Jae-Yong, and Yoon, Kyung-Ho* * Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute ABSTRACT Spacer grids(sg) are
Life Prediction Under Multiaxial Fatigue
 Lie Prediction Under Multiaxial Fatigue D. Ramesh and M.M. Mayuram Department o Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute o Technology, Madras Chennai-600 036 (India) e-mail: mayuram@iitm.ac.in ABSTRACT
Lie Prediction Under Multiaxial Fatigue D. Ramesh and M.M. Mayuram Department o Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute o Technology, Madras Chennai-600 036 (India) e-mail: mayuram@iitm.ac.in ABSTRACT
Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation on Steel Plate Girders With Deep Section
 6 th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering 11 th International Workshop on Advanced Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology August 1-2, 2015, University of
6 th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering 11 th International Workshop on Advanced Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology August 1-2, 2015, University of
Available online at ScienceDirect. XVII International Colloquium on Mechanical Fatigue of Metals (ICMFM17)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 74 ( 2014 ) 165 169 XVII International Colloquium on Mechanical Fatigue of Metals (ICMFM17) Fatigue of Solder Interconnects
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 74 ( 2014 ) 165 169 XVII International Colloquium on Mechanical Fatigue of Metals (ICMFM17) Fatigue of Solder Interconnects
Lecture #10: Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements
 Lecture #10: 151-0735: Dynamic behavior of materials and structures Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering,
Lecture #10: 151-0735: Dynamic behavior of materials and structures Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering,
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Contact analysis for the modelling of anchors in concrete structures H. Walter*, L. Baillet** & M. Brunet* *Laboratoire de Mecanique des Solides **Laboratoire de Mecanique des Contacts-CNRS UMR 5514 Institut
Contact analysis for the modelling of anchors in concrete structures H. Walter*, L. Baillet** & M. Brunet* *Laboratoire de Mecanique des Solides **Laboratoire de Mecanique des Contacts-CNRS UMR 5514 Institut
A critical analysis of the Mises stress criterion used in frequency domain fatigue life prediction
 Focussed on Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture A critical analysis of the Mises stress criterion used in frequency domain fatigue life prediction Adam Niesłony Opole University of Technology, Poland a.nieslony@po.opole.pl,
Focussed on Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture A critical analysis of the Mises stress criterion used in frequency domain fatigue life prediction Adam Niesłony Opole University of Technology, Poland a.nieslony@po.opole.pl,
A FINITE ELEMENT MODEL TO PREDICT MULTI- AXIAL STRESS-STRAIN RESPONSE OF CERAMIC MATRIX COMPOSITES WITH STRAIN INDUCED DAMAGE
 A FINITE ELEMENT MODEL TO PREDICT MULTI- AXIAL STRESS-STRAIN RESPONSE OF CERAMIC MATRIX COMPOSITES WITH STRAIN INDUCED DAMAGE Daxu Zhang and D. R. Hayhurst School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering,
A FINITE ELEMENT MODEL TO PREDICT MULTI- AXIAL STRESS-STRAIN RESPONSE OF CERAMIC MATRIX COMPOSITES WITH STRAIN INDUCED DAMAGE Daxu Zhang and D. R. Hayhurst School of Mechanical, Aerospace and Civil Engineering,
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus. Case study
 Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
Aim of the study Experimental determination of mechanical parameters Local buckling (wrinkling) Failure maps Optimization of sandwich panels
 METNET Workshop October 11-12, 2009, Poznań, Poland Experimental and numerical analysis of sandwich metal panels Zbigniew Pozorski, Monika Chuda-Kowalska, Robert Studziński, Andrzej Garstecki Poznan University
METNET Workshop October 11-12, 2009, Poznań, Poland Experimental and numerical analysis of sandwich metal panels Zbigniew Pozorski, Monika Chuda-Kowalska, Robert Studziński, Andrzej Garstecki Poznan University
INTRODUCTION TO THE EXPLICIT FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR NONLINEAR TRANSIENT DYNAMICS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE EXPLICIT FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR NONLINEAR TRANSIENT DYNAMICS SHEN R. WU and LEI GU WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION ! PREFACE xv PARTI FUNDAMENTALS 1 1 INTRODUCTION 3
INTRODUCTION TO THE EXPLICIT FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR NONLINEAR TRANSIENT DYNAMICS SHEN R. WU and LEI GU WILEY A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION ! PREFACE xv PARTI FUNDAMENTALS 1 1 INTRODUCTION 3
Finite Element Analysis of Silicone Rubber Spacers Used in Automotive Engine Control Modules
 Finite Element Analysis of Silicone Rubber Spacers Used in Automotive Engine Control Modules Fereydoon Dadkhah Arlene Zahiri Delphi Electronics and Safety Kokomo, IN Abstract Silicone Rubber Spacers in
Finite Element Analysis of Silicone Rubber Spacers Used in Automotive Engine Control Modules Fereydoon Dadkhah Arlene Zahiri Delphi Electronics and Safety Kokomo, IN Abstract Silicone Rubber Spacers in
THE INFLUENCE OF THERMAL ACTIONS AND COMPLEX SUPPORT CONDITIONS ON THE MECHANICAL STATE OF SANDWICH STRUCTURE
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computational Mechanics 013, 1(4), 13-1 THE INFLUENCE OF THERMAL ACTIONS AND COMPLEX SUPPORT CONDITIONS ON THE MECHANICAL STATE OF SANDWICH STRUCTURE Jolanta Błaszczuk
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computational Mechanics 013, 1(4), 13-1 THE INFLUENCE OF THERMAL ACTIONS AND COMPLEX SUPPORT CONDITIONS ON THE MECHANICAL STATE OF SANDWICH STRUCTURE Jolanta Błaszczuk
Manufacturing Remaining Stresses in Truck Frame Rail's Fatigue Life Prediction
 Manuacturing Remaining Stresses in Truck Frame Rail's Fatigue Lie Prediction Claudiomar C. Cunha & Carlos A. N. Dias MSX International & Department o Naval Engineering EPUSP/USP/Brazil Department o Mechanical
Manuacturing Remaining Stresses in Truck Frame Rail's Fatigue Lie Prediction Claudiomar C. Cunha & Carlos A. N. Dias MSX International & Department o Naval Engineering EPUSP/USP/Brazil Department o Mechanical
AN EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF THE FATIGUE DAMAGING EVENTS EXTRACTED USING THE WAVELET BUMP EXTRACTION (WBE) ALGORITHM
 ICEM12-12th International Conference on Experimental Mechanics 29 August - 2 September, 2004 Politecnico di Bari, Italy AN EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF THE FATIGUE DAMAGING EVENTS EXTRACTED USING THE WAVELET
ICEM12-12th International Conference on Experimental Mechanics 29 August - 2 September, 2004 Politecnico di Bari, Italy AN EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF THE FATIGUE DAMAGING EVENTS EXTRACTED USING THE WAVELET
Implementation of fatigue model for unidirectional laminate based on finite element analysis: theory and practice
 Focussed on Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture Implementation of fatigue model for unidirectional laminate based on finite element analysis: theory and practice D. Carrella-Payan, B. Magneville, M. Hack,
Focussed on Multiaxial Fatigue and Fracture Implementation of fatigue model for unidirectional laminate based on finite element analysis: theory and practice D. Carrella-Payan, B. Magneville, M. Hack,
An Analytical Model for Long Tube Hydroforming in a Square Cross-Section Die Considering Anisotropic Effects of the Material
 Journal of Stress Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, Autumn Winter 2016-17 An Analytical Model for Long Tube Hydroforming in a Square Cross-Section Die Considering Anisotropic Effects of the Material H. Haghighat,
Journal of Stress Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, Autumn Winter 2016-17 An Analytical Model for Long Tube Hydroforming in a Square Cross-Section Die Considering Anisotropic Effects of the Material H. Haghighat,
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF COMPOSITE INSERTS FOR A HYBRID ULTRACENTRIFUGE ROTOR
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS OPTIMAL DESIGN OF COMPOSITE INSERTS Hak Gu Lee 1*, Jisang Park 1, Ji Hoon Kim 1 1 Composite Materials Group, KIMS, Changwon, Korea * Corresponding
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS OPTIMAL DESIGN OF COMPOSITE INSERTS Hak Gu Lee 1*, Jisang Park 1, Ji Hoon Kim 1 1 Composite Materials Group, KIMS, Changwon, Korea * Corresponding
Structures and Multiaxial Fatigue Analysis. Timothy Langlais
 Computational Methods for Multiaxial Fatigue 1 Structures and Multiaxial Fatigue Analysis Timothy Langlais University of Minnesota langlais@me.umn.edu Advisers: J. H. Vogel and T. R. Chase http://www.menet.umn.edu/
Computational Methods for Multiaxial Fatigue 1 Structures and Multiaxial Fatigue Analysis Timothy Langlais University of Minnesota langlais@me.umn.edu Advisers: J. H. Vogel and T. R. Chase http://www.menet.umn.edu/
Damage accumulation model for aluminium-closed cell foams subjected to fully reversed cyclic loading
 Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures doi: 10.1111/j.1460-2695.2011.01591.x Damage accumulation model for aluminium-closed cell foams subjected to fully reversed cyclic loading H. PINTO
Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures doi: 10.1111/j.1460-2695.2011.01591.x Damage accumulation model for aluminium-closed cell foams subjected to fully reversed cyclic loading H. PINTO
Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Anisotropic Back-stress Evolution for Orthotropic Fiber-Reinforced Composites
 Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution for Orthotropic Fiber- Reinforced Composites Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution
Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution for Orthotropic Fiber- Reinforced Composites Combined Isotropic-Kinematic Hardening Laws with Antropic Back-stress Evolution
Stress Concentrations, Fatigue, Fracture
 Stress Concentrations, Fatigue, Fracture The fundamental topic in this document is the development of cracks in steel. For structures subjected to cyclic loads, such cracks can develop over time and ultimately
Stress Concentrations, Fatigue, Fracture The fundamental topic in this document is the development of cracks in steel. For structures subjected to cyclic loads, such cracks can develop over time and ultimately
Prediction of Elastic-Plastic Behaviour of Structures at Notches
 Prediction of Elastic-Plastic Behaviour of Structures at Notches TANWEER HUSSAIN*, MUJEEBUDDIN MEMON**, AND ZEESHAN ALI MEMON*** RECEIVED ON 01.05.2012 ACCEPTED ON 21.06.2012 ABSTRACT Under the condition
Prediction of Elastic-Plastic Behaviour of Structures at Notches TANWEER HUSSAIN*, MUJEEBUDDIN MEMON**, AND ZEESHAN ALI MEMON*** RECEIVED ON 01.05.2012 ACCEPTED ON 21.06.2012 ABSTRACT Under the condition
Rigid Flexible Contact Analysis of an Inflated Membrane Balloon with Various Contact Conditions
 roceedings Rigid Flexible Contact Analysis of an Inflated Membrane Balloon with Various Contact Conditions MengXiong Liu and XiDe Li * Department of Engineering Mechanics, Tghua University, Beijing 100084,
roceedings Rigid Flexible Contact Analysis of an Inflated Membrane Balloon with Various Contact Conditions MengXiong Liu and XiDe Li * Department of Engineering Mechanics, Tghua University, Beijing 100084,
Fatigue and Fracture
 Fatigue and Fracture Multiaxial Fatigue Professor Darrell F. Socie Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois 2004-2013 Darrell Socie, All Rights Reserved When is Multiaxial Fatigue Important?
Fatigue and Fracture Multiaxial Fatigue Professor Darrell F. Socie Mechanical Science and Engineering University of Illinois 2004-2013 Darrell Socie, All Rights Reserved When is Multiaxial Fatigue Important?
Critical applied stresses for a crack initiation from a sharp V-notch
 Focussed on: Fracture and Structural Integrity related Issues Critical applied stresses for a crack initiation from a sharp V-notch L. Náhlík, P. Hutař Institute of Physics of Materials, Academy of Sciences
Focussed on: Fracture and Structural Integrity related Issues Critical applied stresses for a crack initiation from a sharp V-notch L. Náhlík, P. Hutař Institute of Physics of Materials, Academy of Sciences
Enhancing Prediction Accuracy In Sift Theory
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS Enhancing Prediction Accuracy In Sift Theory J. Wang 1 *, W. K. Chiu 1 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Fishermans Bend, Australia, Department
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS Enhancing Prediction Accuracy In Sift Theory J. Wang 1 *, W. K. Chiu 1 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Fishermans Bend, Australia, Department
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis
 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Internal shear force V & bending moment M must ensure equilibrium Fig. 3 2 Sign Conventions for Bending and Shear Fig. 3 3
Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 146 (2004) 28 34 Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process Hariharasudhan Palaniswamy, Gracious Ngaile, Taylan Altan ERC
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 146 (2004) 28 34 Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process Hariharasudhan Palaniswamy, Gracious Ngaile, Taylan Altan ERC
Fatigue Damage Development in a Steel Based MMC
 Fatigue Damage Development in a Steel Based MMC V. Tvergaard 1,T.O/ rts Pedersen 1 Abstract: The development of fatigue damage in a toolsteel metal matrix discontinuously reinforced with TiC particulates
Fatigue Damage Development in a Steel Based MMC V. Tvergaard 1,T.O/ rts Pedersen 1 Abstract: The development of fatigue damage in a toolsteel metal matrix discontinuously reinforced with TiC particulates
Testing and Analysis
 Testing and Analysis Testing Elastomers for Hyperelastic Material Models in Finite Element Analysis 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 Biaxial Extension Simple Tension Figure 1, A Typical Final Data Set for Input
Testing and Analysis Testing Elastomers for Hyperelastic Material Models in Finite Element Analysis 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 Biaxial Extension Simple Tension Figure 1, A Typical Final Data Set for Input
Calculating and Displaying Fatigue Results
 Calculating and Displaying Fatigue Results The ANSYS Fatigue Module has a wide range of features for performing calculations and presenting analysis results. By Raymond Browell Product Manager New Technologies
Calculating and Displaying Fatigue Results The ANSYS Fatigue Module has a wide range of features for performing calculations and presenting analysis results. By Raymond Browell Product Manager New Technologies
MULTIAXIAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR FATIGUE CALCULATIONS IN COMPOSITE COMPONENTS
 MULTIAXIAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR FATIGUE CALCULATIONS IN COMPOSITE COMPONENTS Peter Heyes HBM-nCode Abstract Fatigue analysis methods are well-established as part of the product development process for
MULTIAXIAL ASSESSMENT METHOD FOR FATIGUE CALCULATIONS IN COMPOSITE COMPONENTS Peter Heyes HBM-nCode Abstract Fatigue analysis methods are well-established as part of the product development process for
Plane Strain Test for Metal Sheet Characterization
 Plane Strain Test for Metal Sheet Characterization Paulo Flores 1, Felix Bonnet 2 and Anne-Marie Habraken 3 1 DIM, University of Concepción, Edmundo Larenas 270, Concepción, Chile 2 ENS - Cachan, Avenue
Plane Strain Test for Metal Sheet Characterization Paulo Flores 1, Felix Bonnet 2 and Anne-Marie Habraken 3 1 DIM, University of Concepción, Edmundo Larenas 270, Concepción, Chile 2 ENS - Cachan, Avenue
Fatigue-Ratcheting Study of Pressurized Piping System under Seismic Load
 Fatigue-Ratcheting Study of Pressurized Piping System under Seismic Load A. Ravi Kiran, M. K. Agrawal, G. R. Reddy, R. K. Singh, K. K. Vaze, A. K. Ghosh and H. S. Kushwaha Reactor Safety Division, Bhabha
Fatigue-Ratcheting Study of Pressurized Piping System under Seismic Load A. Ravi Kiran, M. K. Agrawal, G. R. Reddy, R. K. Singh, K. K. Vaze, A. K. Ghosh and H. S. Kushwaha Reactor Safety Division, Bhabha
five Mechanics of Materials 1 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture
 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture five mechanics www.carttalk.com of materials Mechanics of Materials 1 Mechanics of Materials MECHANICS MATERIALS
ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture five mechanics www.carttalk.com of materials Mechanics of Materials 1 Mechanics of Materials MECHANICS MATERIALS
A novel approach to predict the growth rate of short cracks under multiaxial loadings
 A novel approach to predict the growth rate of short cracks under multiaxial loadings F. Brugier 1&2, S. Pommier 1, R. de Moura Pinho 2, C. Mary 2 and D. Soria 2 1 LMT-Cachan, ENS Cachan / CNRS / UPMC
A novel approach to predict the growth rate of short cracks under multiaxial loadings F. Brugier 1&2, S. Pommier 1, R. de Moura Pinho 2, C. Mary 2 and D. Soria 2 1 LMT-Cachan, ENS Cachan / CNRS / UPMC
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2195-2204 2195 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS by Ali BELHOCINE * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2015, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 2195-2204 2195 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF A THREE-DIMENSIONAL DISC-PAD MODEL WITH AND WITHOUT THERMAL EFFECTS by Ali BELHOCINE * Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
The Rotating Inhomogeneous Elastic Cylinders of. Variable-Thickness and Density
 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences 23 2008, 237 257 An International Journal c 2008 Dixie W Publishing Corporation, U. S. A. The Rotating Inhomogeneous Elastic Cylinders of Variable-Thickness and
Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences 23 2008, 237 257 An International Journal c 2008 Dixie W Publishing Corporation, U. S. A. The Rotating Inhomogeneous Elastic Cylinders of Variable-Thickness and
THE EFFECT OF GEOMETRY ON FATIGUE LIFE FOR BELLOWS
 Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 343-348 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512003418
Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 343-348 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512003418
Siping Road 1239, , Shanghai, P.R. China
 COMPARISON BETWEEN LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR KINEMATIC HARDENING MODELS TO PREDICT THE MULTIAXIAL BAUSCHINGER EFFECT M.A. Meggiolaro 1), J.T.P. Castro 1), H. Wu 2) 1) Department of Mechanical Engineering,
COMPARISON BETWEEN LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR KINEMATIC HARDENING MODELS TO PREDICT THE MULTIAXIAL BAUSCHINGER EFFECT M.A. Meggiolaro 1), J.T.P. Castro 1), H. Wu 2) 1) Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Load Determination. Fatigue Life Predictions Infinite Life, Stress Life, Strain Life
 Durability Agenda Durability Basics Fatigue, Stress, Strain Load Determination Measurements, Multi-Body Simulation Loads and Damage S-N Curve, Cycle Counting Load Characterization Establishing Durability
Durability Agenda Durability Basics Fatigue, Stress, Strain Load Determination Measurements, Multi-Body Simulation Loads and Damage S-N Curve, Cycle Counting Load Characterization Establishing Durability
Peak Strain and Displacement Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring
 Peak Strain and Displacement Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring AKIRA MITA and SHINPEI TAKAHIRA ABSTRACT Simple and inexpensive passive sensors that can monitor the peak strain or displacement of
Peak Strain and Displacement Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring AKIRA MITA and SHINPEI TAKAHIRA ABSTRACT Simple and inexpensive passive sensors that can monitor the peak strain or displacement of
Chapter 2: Elasticity
 OHP 1 Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 2: lasticity Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng ( 曾文甲 ) Department of Materials ngineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W.F.
OHP 1 Mechanical Properties of Materials Chapter 2: lasticity Prof. Wenjea J. Tseng ( 曾文甲 ) Department of Materials ngineering National Chung Hsing University wenjea@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Reference: W.F.
USING A FATIGUE DATA EDITING APPROACH FOR ANALYSING CYCLE SEQUENCE EFFECTS IN VARIABLE AMPLITUDE ROAD LOADINGS
 047-054 using a fatigue 8/30/06 12:24 PM Page 47 USING A FATIGUE DATA EDITING APPROACH FOR ANALYSING CYCLE SEQUENCE EFFECTS IN VARIABLE AMPLITUDE ROAD LOADINGS S. Abdullah 1 and J.C. Choi 2 1 Department
047-054 using a fatigue 8/30/06 12:24 PM Page 47 USING A FATIGUE DATA EDITING APPROACH FOR ANALYSING CYCLE SEQUENCE EFFECTS IN VARIABLE AMPLITUDE ROAD LOADINGS S. Abdullah 1 and J.C. Choi 2 1 Department
2.1 Strain energy functions for incompressible materials
 Chapter 2 Strain energy functions The aims of constitutive theories are to develop mathematical models for representing the real behavior of matter, to determine the material response and in general, to
Chapter 2 Strain energy functions The aims of constitutive theories are to develop mathematical models for representing the real behavior of matter, to determine the material response and in general, to
Multiaxial Fatigue Life Prediction Methods for Notched Bars of Ti-6Al-4V ABSTRACT
 Multiaxial Fatigue Life Prediction Methods for Notched Bars of Ti-6Al-4V Dr. Alan Kallmeyer 1, Mr. Ahmo Krgo 1, and Dr. Peter Kurath 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, North Dakota State University,
Multiaxial Fatigue Life Prediction Methods for Notched Bars of Ti-6Al-4V Dr. Alan Kallmeyer 1, Mr. Ahmo Krgo 1, and Dr. Peter Kurath 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, North Dakota State University,
Influence of the filament winding process variables on the mechanical behavior of a composite pressure vessel
 Influence of the filament winding process variables on the mechanical behavior of a composite pressure vessel G. Vargas 1 & A. Miravete 2 1 Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Facultad de Ingeniería Mecánica,
Influence of the filament winding process variables on the mechanical behavior of a composite pressure vessel G. Vargas 1 & A. Miravete 2 1 Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Facultad de Ingeniería Mecánica,
Methodology for the evaluation of yield strength and hardening behavior of metallic materials by indentation with spherical tip
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 2003 Methodology for the evaluation of yield strength and hardening behavior of metallic materials by indentation with spherical tip Dejun Ma Department
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 94, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 2003 Methodology for the evaluation of yield strength and hardening behavior of metallic materials by indentation with spherical tip Dejun Ma Department
EDEM DISCRETIZATION (Phase II) Normal Direction Structure Idealization Tangential Direction Pore spring Contact spring SPRING TYPES Inner edge Inner d
 Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo Bulletin of ERS, No. 48 (5) A TWO-PHASE SIMPLIFIED COLLAPSE ANALYSIS OF RC BUILDINGS PHASE : SPRING NETWORK PHASE Shanthanu RAJASEKHARAN, Muneyoshi
Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo Bulletin of ERS, No. 48 (5) A TWO-PHASE SIMPLIFIED COLLAPSE ANALYSIS OF RC BUILDINGS PHASE : SPRING NETWORK PHASE Shanthanu RAJASEKHARAN, Muneyoshi
NEW CONCEPT OF A LOCAL ELASTIC STRESS APPROACH FOR FATIGUE LIFE CALCULATION
 NEW CONCEPT OF A LOCAL ELASTIC STRESS APPROACH FOR FATIGUE LIFE CALCULATION * Milan Ruzicka Jan Papuga Abstract: Principles of different approaches to fatigue life prediction until the crack initiation
NEW CONCEPT OF A LOCAL ELASTIC STRESS APPROACH FOR FATIGUE LIFE CALCULATION * Milan Ruzicka Jan Papuga Abstract: Principles of different approaches to fatigue life prediction until the crack initiation
Mechanical Behavior of Circular Composite Springs with Extended Flat Contact Surfaces
 Mechanical Behavior of Circular Composite Springs with Extended Flat Contact Surfaces Ping-Cheung Tse epartment of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hunghom, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Mechanical Behavior of Circular Composite Springs with Extended Flat Contact Surfaces Ping-Cheung Tse epartment of Mechanical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hunghom, Kowloon, Hong Kong
FEM model of pneumatic spring assembly
 FEM model of pneumatic spring assembly Tien Tran Xuan 1, David Cirkl 2 Department of Applied Mechanics, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University of Liberec, Liberec, Czech Republic 1 Corresponding
FEM model of pneumatic spring assembly Tien Tran Xuan 1, David Cirkl 2 Department of Applied Mechanics, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University of Liberec, Liberec, Czech Republic 1 Corresponding
UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABLE CFRP LAMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF LAY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIAL CURVATURE
 THE 9 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABE CFRP AMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF AY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIA CURVATURE J. Ryu, J-G.
THE 9 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABE CFRP AMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF AY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIA CURVATURE J. Ryu, J-G.
APPLICATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION METHOD DURING CYCLIC LOADING OF CONCRETE BEAM
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21866 Abstract IX th NDT in PROGRESS October 9 11, 2017, Prague, Czech Republic APPLICATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION METHOD DURING CYCLIC LOADING OF CONCRETE
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21866 Abstract IX th NDT in PROGRESS October 9 11, 2017, Prague, Czech Republic APPLICATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION METHOD DURING CYCLIC LOADING OF CONCRETE
Experiments and Numerical Simulations on Stress-State-Dependence of Ductile Damage Criteria
 Experiments and Numerical Simulations on Stress-State-Dependence of Ductile Damage Criteria Michael Brünig, Steffen Gerke and Daniel Brenner Abstract The paper deals with a series of new experiments and
Experiments and Numerical Simulations on Stress-State-Dependence of Ductile Damage Criteria Michael Brünig, Steffen Gerke and Daniel Brenner Abstract The paper deals with a series of new experiments and
Dynamic Analysis of a Reinforced Concrete Structure Using Plasticity and Interface Damage Models
 Dynamic Analysis of a Reinforced Concrete Structure Using Plasticity and Interface Damage Models I. Rhee, K.J. Willam, B.P. Shing, University of Colorado at Boulder ABSTRACT: This paper examines the global
Dynamic Analysis of a Reinforced Concrete Structure Using Plasticity and Interface Damage Models I. Rhee, K.J. Willam, B.P. Shing, University of Colorado at Boulder ABSTRACT: This paper examines the global
Exact and Numerical Solution of Pure Torsional Shaft
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(8): 3043-3052, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Exact and Numerical Solution of Pure Torsional Shaft 1 Irsyadi Yani, 2 M.A Hannan, 1 Hassan Basri, and 2 E. Scavino
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(8): 3043-3052, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Exact and Numerical Solution of Pure Torsional Shaft 1 Irsyadi Yani, 2 M.A Hannan, 1 Hassan Basri, and 2 E. Scavino
Thermal load-induced notch stress intensity factors derived from averaged strain energy density
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Draft ScienceDirect Draft Draft Structural Integrity Procedia 00 (2016) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 21st European Conference on Fracture, ECF21, 20-24
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Draft ScienceDirect Draft Draft Structural Integrity Procedia 00 (2016) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 21st European Conference on Fracture, ECF21, 20-24
The elastic behavior of a rubber-like material for composite glass
 The elastic behavior of a rubber-like material for composite glass Silvia Briccoli Bati 1, Mario Fagone 1, Giovanna Ranocchiai 1 1 Department of Costruzioni, University of Florence, Italy E-mail: silvia.briccolibati@unifi.it
The elastic behavior of a rubber-like material for composite glass Silvia Briccoli Bati 1, Mario Fagone 1, Giovanna Ranocchiai 1 1 Department of Costruzioni, University of Florence, Italy E-mail: silvia.briccolibati@unifi.it
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation.
 UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging
 A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging Y T Im*, S H Kang, and J S Cheon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and
A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging Y T Im*, S H Kang, and J S Cheon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and
