Simulation of the temperature distribution in automotive head lamps
|
|
|
- Ashlynn Morton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simulation of the temperature distribution in automotive head lamps Dr. sc. techn. Christian Mielke, Dr.-Ing. Stepan Senin, Andreas Wenzel, Dr. Carsten Horn, Merkle & Partner, Heidenheim, Germany Johannes Scheuchenpflug, Audi AG, Ingolstadt, Germany Summary: The design of head lamps plays an important part in the development process of modern cars as it contributes significantly to the first impression of a car. However, beyond the design aspect technical requirements have to be fulfilled. These are foremost the lighting properties, the quality of the product and its lifetime. In this respect, the knowledge of the maximum temperature of different components of the head lamp is of great importance during the development process, as the temperature limits of the various materials are not to be exceeded. Therefore, numerical simulation is an important tool for the prediction of temperature distributions in head lamps during the development process. The heat transfer in an automotive head lamp is a complicated process, as different mechanisms have to be taken into account. These are the conduction in the solid parts and the transport due to convection by the air, respectively. Furthermore, heat transport due to thermal radiation plays a dominant role. Together with Audi AG, Merkle & Partner has investigated a method to predict the temperature distribution in a head lamp by means of numerical simulation. Therefore we use Star-CD for the computation of the convective flow field and the software AURA for the calculation of the radiation heat transfer. Both codes are coupled by user-subroutines. Within this presentation we want to briefly describe the methodology of the process. As an example a simplified model of an automotive head lamp is investigated. The influence of the different heat transfer mechanisms is described. Keywords: Head lamps, convection, radiation, conduction, temperature.
2 1 Introduction The look of the head lamps is a distinct design feature in modern cars. Therefore, the design of the head lamps is already investigated in the early development phases of a car. Beyond the design of the head lamps, the technical requirements have also to be fulfilled. These are primarily the lighting characteristics, the lifetime and the quality of the product. Here the information about the temperatures of the different parts is of special interest. The maximum temperature has an important role in the decision which plastic material is used for the different components. For this task numerical simulation is an indispensable tool in support of the development of head lamps, especially for the choice of the materials used. The simulation has to predict the temperature distribution with the necessary accuracy long before a prototype is tested. Nolte [1] has described a method for the simulation of temperature and flow distribution in lighting equipment. This method consists of the coupling of a commercial CFD-Code with a CAL (Computer Aided Lighting)-Program to take account of the radiative heat transport. This method has been extended to the simulation of fogging and de-fogging simulation of vehicle head lamps by Maschkio [2]. A study by Senin [3] describes the coupling of a commercial CFD-Code with an in-house ray tracing program (Forward Ray Tracing). Merkle & Partner has performed numerous investigations on the simulation of the temperature field in head lamps. These investigations resulted in a method to simulation the temperature distribution in head lamps. First we want to describe the model used for the investigation. In the following we briefly want to describe the influence of the different transport mechanisms, e.g. convection and radiation. The model is a simplified head lamp consisting of the relevant parts, for which also experimental investigations exist. 2 Geometrical model A typical head lamp of a modern car has a quite complicated geometry with a lot of different parts inside. For these investigations we used a simplified model of a head lamp, the so called reflector box. This model consists of the important components of a head lamp. The geometry of the reflector box model is shown in Figure 1 below. reflector glass plate housing with insulation cap bulb Figure 1: Geometry of the reflector box model. With this reflector box different physical phenomena of heat transfer can be easily investigated experimentally as well as numerically. Due to the simplicity only the main physical heat transport mechanisms are present. In a realistic head lamp additionally disturbing phenomena would appear, like for example the heat loss in electrical components. Hence with the reflector box model we can investigate isolated phenomena under controlled conditions. Another advantage of the reflector box is its geometrical simplicity, resulting in small mesh sizes and therefore in short computation times. 3 Physical model The heat transfer in a head lamp is a complex process, as all heat transfer mechanisms, e.g. convection and radiation have an important influence on the resulting temperature distribution. The
3 bulb receives surface temperatures in the range of T = 700 K in steady state operation for a given heat loss of Q = 15 W. The resulting heat has to be distributed to the other parts by means of radiation and convection. Since the air volume in car head lamps is constantly reduced, due to more complex parts like adaptive light systems, radiation is going to play an ever increasing role in the overall heat transfer process. For the numerical simulation we want to use as little assumptions as possible. In our process we usually prescribe the resulting heat flux at the surface of the bulb. The distribution of the resulting heat flux between radiation and convection has to be done by the numerical model. The other parameters prescribed in advance are only the material properties. Here also difficulties can appear as especially the radiation properties of the different components of the head lamp are not known in advance. In the following we briefly describe the numerical model and the software used. 4 Numerical model The geometrical complexity of modern head lamps and the requirements to the computation of the radiation exceeds the possibility of most commercially available codes. The numerical model of a typical head lamp consists of roughly to radiation patches. Using commercial software this grid size would result in computation times of several weeks. Hence for the computation of the radiation the code AURA (Audi-Radiation) was developed. This code was developed under the control of Audi AG to solve large radiation problems as they appear in the automotive development. The advantage of AURA is a panel clustering technique where several radiation patches are grouped according to their distance and view field. This technique provides a considerable speedup when compared to other codes. Unfortunately more details cannot be given due to a secrecy agreement. Other examples for the use of AURA are engine cooling and passenger comfort simulations. Using AURA we need about two to three days to solve a typical simulation of an automotive head lamp. Our simplified reflector box model as described above results in smaller mesh sizes for both the radiation and the CFD part. Hence the simulations run faster and we easily can run parameter studies. The heat transfer in a head lamp is dominated by radiation and by convection processes, as already described. The radiation part is computed by AURA and the convective flow field is calculated with Star-CD. To get a correct distribution of the total heat flux in radiation and convection we have to couple both codes. The coupling between Star-CD and AURA is done by user subroutines. AURA delivers surface temperatures to Star-CD, while Star-CD delivers local fluid temperatures and heat transfer coefficients to AURA, respectively. The conduction within the solid materials is done by AURA. Figure 2: Computational domain for the reflector box and cross-section of the computational mesh. Figure 2 shows the numerical model used for our investigations. The AURA model consists of all radiation patches of the reflector box. The CFD-model is a two-fluid-model with one fluid inside the reflector box and an outer fluid surrounding the reflector box to take the external free convection into account. For both fluids the Boussinesq approximation ( = (T)) is assumed. The meshes consist of approximately radiation patches (triangles) in AURA and fluid cells. The fluid mesh is a hybrid mesh. A real head lamp is a complex geometry, with respect to the development times it is impossible to spend a lot of time in creating an optimal mesh with prism layers
4 on all parts. Hence the mesh was obtained using ICEM-CFD Tetra with a conversion of Tetra to Hexa. A prism layer was created only on the glass plate, as this is of special interest. To prepare all the geometry for prism-layers would need too much time. The mesh has an aspect ratio of larger than 0.3 for the tetrahedral elements and a determinant of larger than 0,3 for the hexahedra which is good enough for convergence of the CFD run. The AURA surface grid has an aspect ratio of larger than 0.1. A comparison with a mesh with overall prism layers did not show any significant difference in the resulting temperature distribution but it took much more effort in mesh generation. The simulations were run until a steady state solution was obtained. AURA is a pure unsteady code which was run for a total simulation time of t = 8480 s with a time step of 1 s and an update interval of 10 s with constant boundary conditions. This means that AURA and Star-CD exchange their results every 10 s. As Star-CD was run in steady state mode we took 100 Iterations between each coupling with AURA. Smaller time steps and coupling intervals were also investigated but did not show any difference in the resulting temperature distribution, while much larger intervals will lead to different results. 5 Results 5.1 Experimental study The reflector box was build up as an experimental model at Technical University Illmenau, where the measurements were performed. Unfortunately, no data are available for the temperature distribution inside of the reflector box. By infrared measurement the temperature distribution on the outer side of the glass plate was determined, which is shown in Figure 3. The results show a maximum temperature of T HotSpot = 34.1 C located in the upper region of the glass plate. From this distribution we can assume, that both radiation as well as free convection have an important influence and none of them can be neglected. The slightly asymmetric temperature distribution can be explained by the asymmetric shape of the reflector geometry. T in C T hot spot = 34.1 C Figure 3: Experimental results These experimental results are what we want to hit with our numerical simulation in a robust, safe and accurate method which additionally is fast enough to go ahead with the development process. 5.2 Numerical study To determine the influence of the different heat transfer mechanisms we performed several numerical studies. By evacuating the reflector box we can eliminate the influence of the free convection within the reflector box. The heat transport from the bulb to the glass plate is only performed by radiation.
5 Hence this model results in a pure radiation computation without coupling to Star-CD. However, convective transport to the surroundings is taken into account by lumped heat transfer coefficients. Figure 4: Temperature distribution on the reflector and the outer glass plate (only radiation) In this computation the bulb heats up the cap and the reflector by radiation. The temperate distribution on the reflector is smeared due to the cross conduction, as can be seen in figure 4. Further the reflector radiates towards the glass plate. The hot spot appears in the lower region of the glass plate in the optical axis of the reflector, as one would expect. The maximum temperature on the outer side of the glass plate reaches a value of T = 32 C which is a little bit lower than the measured value of T = 34.1 C. In a second study we investigated the influence of pure convection (heat transport to the environment is modelled by boundary conditions with a prescribed heat transfer resistance). The radiation was turned off. In Figure 5 the velocity and temperature distributions in the symmetry plane are shown. Figure 5: Velocity and temperature distribution in the symmetry plane for the case without radiation. (only convection) The results in this case show clearly that due to convection the temperature level in the upper part of the box rises and hence the temperature on the front plate is considerably higher than measured. This also indicates that a substantial amount of heat has to be transmitted into the environment by radiation in order to achieve the measured temperature level. As neither pure radiation nor pure convection can predict the temperature distribution with the necessary accuracy a coupled simulation was performed, taking into account both effects. The results are shown in the following. The most interesting result is the comparison of the temperature distribution on the outer side of the glass plate. Do the numerical results match the experimental measurements? A comparison is shown in the Figure 6 below.
6 T in C T hot spot = 34,1 C Figure 6: measured and computed temperature distribution on the outer side of the glass plate (coupled simulation). The levels of the colour bands on the right have been adapted to resemble those from the measurement. As we can see from Figure 6, the location of the hot spot as well as the temperature in the hot spot is predicted quit well with a temperature deviation of T = 1K. In the lower part of the glass plate there appears a larger temperature deviation. The reasons for this cannot be clearly explained, as a lot of parameters may be responsible for it. Up to now we don t know if the reflector box is positioned in the experiment exactly horizontally. Especially the boundary conditions in the surrounding of the reflector box are not documented in the experimental study. The surface temperatures in the reflector box are shown in Figure 7. Already in these figures we can see the influence of the convective flow field. The temperature distribution on the reflector surface differs to the almost symmetric distribution shown in Figure 4 for the pure radiation computation. A hot air streak is rising from the bulb leading to a temperature rise in the upper half of the reflector. The footprint of this streak can also be seen on the temperature distribution of the inner surface of the housing. Figure 7: Surface temperature distribution in the reflector box AURA-results (coupled simulation)
7 Figure 8: Temperature distribution in the air inside the reflector box with different scaling (coupled simulation) The temperature distribution in the fluid in Figure 8 shows clearly, that the air is heated up around the bulb and then rises to the top of the housing. Additionally the air is heated at the rear side of the reflector. This side is heated up by conduction from the inner side. At the top of the reflector box the hot air is cooled down by the glass plate and as seen in the velocity distribution in Figure 9 at the glass plate the air flow is directed downward. Hence the hot bulb induces a vortical flow field in the reflector box. Figure 9: Velocity distribution in the reflector box (coupled simulation) According to [3] a discrimination of the effective heat transfer mechanisms (radiation, convection) can be made by plotting the vertical temperature distribution on the front plate. Figure 10 shows such a plot for the current simulation results (radiation, convection and coupled simulation). Herein height and temperature are expressed as dimensionless quantities. The dimensionless height is the ratio of distance from the top of the plate to the plate diameter. The dimensionless temperature is expressed as (T T ) λ A / (P el L S ) This analysis further confirms the assertion that the temperature on the front plate of the reflector box is to a great extent determined by convective heat transfer. However, if the radiation heat transfer was neglected the temperature level would be considerably overestimated. An interesting feature of the plot is the appearance of a second 'shoulder' for the convection simulation at a height of about 0.3. This indicates that there exists a secondary convective roll cell in front of the reflector. This can be seen to a lesser extent in the case of the coupled simulation.
8 Dimensionless temperature (-) Coupled Radiation Convection Dimensionless height (-) Figure 10: Vertical temperature distribution on the front plate (coupled / radiation / convection) 6 Summary Within this article the temperature field in an automotive head lamp was investigated by means of numerical simulation. For the temperature transport all three transport mechanisms are important. The study has shown that the current method is robust enough and delivers the necessary accuracy needed during the development process of a new car. 7 References [1] Nolte, S.: "Eine Methode zur Simulation der Temperatur- und Strömungsverteilung in lichttechnischen Geräten, Cuvillier Verlag, Göttingen, 2007 [2] Maschkio, T.: "CFD-Simulation der Be- und Enttauungsprozesse in Kfz-Scheinwerfern, Dissertation Universität Paderborn, 2007 [3] Senin, S.: "Numerische und experimentelle Untersuchungen zum Wärmetransport in einem Automobilscheinwerfer, Dissertation TU Illmenau, Nomenclature λ A L S P el T T conductivity of the air area of the front plate distance between lamp and front plate electric power of the lamp temperature temperature of the surrounding
Heat Transfer Studies on Structured Metal Sheets
 KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No., pp. 189 196, 2016 Research Article Heat Transfer Studies on Structured Metal Sheets Josef Egert* and Karel Fraňa Department of Power Engineering Equipment, Faculty
KMUTNB Int J Appl Sci Technol, Vol. 9, No., pp. 189 196, 2016 Research Article Heat Transfer Studies on Structured Metal Sheets Josef Egert* and Karel Fraňa Department of Power Engineering Equipment, Faculty
Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) On Ventilation-Cooling Optimization of Electrical Machines
 Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) On Ventilation-Cooling Optimization of Electrical Machines Ryuichi Ujiie, Dr Raphael Arlitt, Hirofumi Etoh Voith Siemens Hydro Power Generation RyuichiUjiie@vs-hydrocom,
Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) On Ventilation-Cooling Optimization of Electrical Machines Ryuichi Ujiie, Dr Raphael Arlitt, Hirofumi Etoh Voith Siemens Hydro Power Generation RyuichiUjiie@vs-hydrocom,
An Evacuated PV/Thermal Hybrid Collector with the Tube/XCPC design
 An Evacuated PV/Thermal Hybrid Collector with the Tube/XCPC design Lun Jiang Chuanjin Lan Yong Sin Kim Yanbao Ma Roland Winston University of California, Merced 4200 N.Lake Rd, Merced CA 95348 ljiang2@ucmerced.edu
An Evacuated PV/Thermal Hybrid Collector with the Tube/XCPC design Lun Jiang Chuanjin Lan Yong Sin Kim Yanbao Ma Roland Winston University of California, Merced 4200 N.Lake Rd, Merced CA 95348 ljiang2@ucmerced.edu
Simulation of a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator
 *Corresponding author: acoliv@fe.up.pt Simulation of a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator... Jorge Facão and Armando C. Oliveira * Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto-New Energy Tec. Unit,
*Corresponding author: acoliv@fe.up.pt Simulation of a linear Fresnel solar collector concentrator... Jorge Facão and Armando C. Oliveira * Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto-New Energy Tec. Unit,
Influence of Heat Transfer Process in Porous Media with Air Cavity- A CFD Analysis
 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference of Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT'17) Toronto, Canada August 21 23, 2017 Paper No. 161 DOI: 10.11159/ffhmt17.161 Influence of Heat Transfer Process
Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference of Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer (FFHMT'17) Toronto, Canada August 21 23, 2017 Paper No. 161 DOI: 10.11159/ffhmt17.161 Influence of Heat Transfer Process
NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION INSIDE OIL-COOLED TRANSFORMER WINDINGS
 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION INSIDE OIL-COOLED TRANSFORMER WINDINGS N. Schmidt 1* and S. Tenbohlen 1 and S. Chen 2 and C. Breuer 3 1 University of Stuttgart,
NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION INSIDE OIL-COOLED TRANSFORMER WINDINGS N. Schmidt 1* and S. Tenbohlen 1 and S. Chen 2 and C. Breuer 3 1 University of Stuttgart,
Essay 4. Numerical Solutions of the Equations of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow
 Essay 4 Numerical Solutions of the Equations of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow 4.1 Introduction In Essay 3, it was shown that heat conduction is governed by a partial differential equation. It will also
Essay 4 Numerical Solutions of the Equations of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow 4.1 Introduction In Essay 3, it was shown that heat conduction is governed by a partial differential equation. It will also
A concept for the integrated 3D flow, heat transfer and structural calculation of compact heat exchangers
 Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 133 A concept for the integrated 3D flow, heat transfer and structural calculation of compact heat exchangers F. Yang, K. Mohrlok, U.
Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 133 A concept for the integrated 3D flow, heat transfer and structural calculation of compact heat exchangers F. Yang, K. Mohrlok, U.
Documentation of the Solutions to the SFPE Heat Transfer Verification Cases
 Documentation of the Solutions to the SFPE Heat Transfer Verification Cases Prepared by a Task Group of the SFPE Standards Making Committee on Predicting the Thermal Performance of Fire Resistive Assemblies
Documentation of the Solutions to the SFPE Heat Transfer Verification Cases Prepared by a Task Group of the SFPE Standards Making Committee on Predicting the Thermal Performance of Fire Resistive Assemblies
Plasma Simulation in STAR-CCM+ -- towards a modern software tool
 Plasma Simulation in STAR-CCM+ -- towards a modern software tool 1 Introduction Electrical arcs and other forms of industrial plasmas have a large number of technical applications, including circuit breakers,
Plasma Simulation in STAR-CCM+ -- towards a modern software tool 1 Introduction Electrical arcs and other forms of industrial plasmas have a large number of technical applications, including circuit breakers,
Department of Energy Science & Engineering, IIT Bombay, Mumbai, India. *Corresponding author: Tel: ,
 ICAER 2011 AN EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL INVESTIGATION OF HEAT LOSSES FROM THE CAVITY RECEIVER USED IN LINEAR FRESNEL REFLECTOR SOLAR THERMAL SYSTEM Sudhansu S. Sahoo* a, Shinu M. Varghese b, Ashwin
ICAER 2011 AN EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL INVESTIGATION OF HEAT LOSSES FROM THE CAVITY RECEIVER USED IN LINEAR FRESNEL REFLECTOR SOLAR THERMAL SYSTEM Sudhansu S. Sahoo* a, Shinu M. Varghese b, Ashwin
Project #1 Internal flow with thermal convection
 Project #1 Internal flow with thermal convection MAE 494/598, Fall 2017, Project 1 (20 points) Hard copy of report is due at the start of class on the due date. The rules on collaboration will be released
Project #1 Internal flow with thermal convection MAE 494/598, Fall 2017, Project 1 (20 points) Hard copy of report is due at the start of class on the due date. The rules on collaboration will be released
ANALYSIS OF CURRENT CLOSE TO THE SURFACE OF NET STRUCTURES Mathias Paschen, University of Rostock, Germany
 ANALYSIS OF CURRENT CLOSE TO THE SURFACE OF NET STRUCTURES Mathias Paschen, University of Rostock, Germany mathias.paschen@uni-rostock.de Abstract The development of the theory of (pelagic) trawls is stagnating
ANALYSIS OF CURRENT CLOSE TO THE SURFACE OF NET STRUCTURES Mathias Paschen, University of Rostock, Germany mathias.paschen@uni-rostock.de Abstract The development of the theory of (pelagic) trawls is stagnating
7/24/2009. CFD study of a passenger car HVAC system. Marcelo Kruger Victor Arume de Souza Regis Ataides Martin Kessler Cesareo de La Rosa Siqueira
 CFD study of a passenger car HVAC system CFD study of a passenger car HVAC system Marcelo Kruger Victor Arume de Souza Regis Ataides Martin Kessler Cesareo de La Rosa Siqueira Gustavo Maia Vinicius Leal
CFD study of a passenger car HVAC system CFD study of a passenger car HVAC system Marcelo Kruger Victor Arume de Souza Regis Ataides Martin Kessler Cesareo de La Rosa Siqueira Gustavo Maia Vinicius Leal
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) FOR THE OPTIMIZATION OF PRODUCTS AND PROCESSES
 THE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF THE CARPATHIAN EURO-REGION SPECIALISTS IN INDUSTRIAL SYSTEMS 7 th EDITION COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) FOR THE OPTIMIZATION OF PRODUCTS AND PROCESSES Franz, Haas DI
THE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE OF THE CARPATHIAN EURO-REGION SPECIALISTS IN INDUSTRIAL SYSTEMS 7 th EDITION COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) FOR THE OPTIMIZATION OF PRODUCTS AND PROCESSES Franz, Haas DI
EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION
 EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION A. K. Kansal, P. Suryanarayana, N. K. Maheshwari Reactor Engineering Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION A. K. Kansal, P. Suryanarayana, N. K. Maheshwari Reactor Engineering Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE AIR FLOW AROUND THE ARRAYS OF SOLAR COLLECTORS
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2011, Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 457-465 457 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE AIR FLOW AROUND THE ARRAYS OF SOLAR COLLECTORS by Vukman V. BAKI] *, Goran S. @IVKOVI], and Milada L. PEZO Laboratory
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 2011, Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 457-465 457 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE AIR FLOW AROUND THE ARRAYS OF SOLAR COLLECTORS by Vukman V. BAKI] *, Goran S. @IVKOVI], and Milada L. PEZO Laboratory
Numerical Investigation of Convective Heat Transfer in Pin Fin Type Heat Sink used for Led Application by using CFD
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 8 July 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Numerical Investigation of Convective Heat Transfer in Pin Fin Type Heat Sink used for Led
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 8 July 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Numerical Investigation of Convective Heat Transfer in Pin Fin Type Heat Sink used for Led
1D and 3D Simulation. C. Hochenauer
 Solar thermal flat-plate l t collectors 1D and 3D Simulation C. Hochenauer Introduction Description of a solar thermal flat-plate collector 1D Simulation - Description of the model - Simulation vs. measurement
Solar thermal flat-plate l t collectors 1D and 3D Simulation C. Hochenauer Introduction Description of a solar thermal flat-plate collector 1D Simulation - Description of the model - Simulation vs. measurement
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 18, NO. 4, OCTOBER
 TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 18, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 1 A New Method for the Calculation of the Hot-Spot Temperature in Power Transformers With ONAN Cooling Zoran Radakovic and Kurt Feser, Fellow,
TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 18, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 1 A New Method for the Calculation of the Hot-Spot Temperature in Power Transformers With ONAN Cooling Zoran Radakovic and Kurt Feser, Fellow,
Heraeus Noblelight is a global
 GROUND ELECTRONICS TRANSPORTATION IR LAMPS DESIGN UNIVERSITY AMBERG-WEIDEN 60 38 IR LAMPS DESIGN ELECTRONICS NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IR HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSES LARISA VON RIEWEL Heraeus Noblelight INTRODUCTION
GROUND ELECTRONICS TRANSPORTATION IR LAMPS DESIGN UNIVERSITY AMBERG-WEIDEN 60 38 IR LAMPS DESIGN ELECTRONICS NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF IR HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSES LARISA VON RIEWEL Heraeus Noblelight INTRODUCTION
THERMAL HYDRAULIC REACTOR CORE CALCULATIONS BASED ON COUPLING THE CFD CODE ANSYS CFX WITH THE 3D NEUTRON KINETIC CORE MODEL DYN3D
 THERMAL HYDRAULIC REACTOR CORE CALCULATIONS BASED ON COUPLING THE CFD CODE ANSYS CFX WITH THE 3D NEUTRON KINETIC CORE MODEL DYN3D A. Grahn, S. Kliem, U. Rohde Forschungszentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Institute
THERMAL HYDRAULIC REACTOR CORE CALCULATIONS BASED ON COUPLING THE CFD CODE ANSYS CFX WITH THE 3D NEUTRON KINETIC CORE MODEL DYN3D A. Grahn, S. Kliem, U. Rohde Forschungszentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Institute
Building heat system sizing
 May 6th, 203 MVK60 Heat and Mass Transfer Project report Building heat system sizing Arnaud BELTOISE Dept. of Energy Sciences, Faculty of Engineering, Lund University, Box 8, 2200 Lund, Sweden . Introduction
May 6th, 203 MVK60 Heat and Mass Transfer Project report Building heat system sizing Arnaud BELTOISE Dept. of Energy Sciences, Faculty of Engineering, Lund University, Box 8, 2200 Lund, Sweden . Introduction
Experimental and Theoretical Evaluation of the Overall Heat Loss Coefficient of a Vacuum Tube Solar Collector
 Experimental and Theoretical Evaluation of the Overall Heat Loss Coefficient of a Vacuum Tube Solar Collector Abdul Waheed Badar *, Reiner Buchholz, and Felix Ziegler Institut für Energietechnik, KT, FG
Experimental and Theoretical Evaluation of the Overall Heat Loss Coefficient of a Vacuum Tube Solar Collector Abdul Waheed Badar *, Reiner Buchholz, and Felix Ziegler Institut für Energietechnik, KT, FG
Investigation of Jet Impingement on Flat Plate Using Triangular and Trapezoid Vortex Generators
 ISSN 2395-1621 Investigation of Jet Impingement on Flat Plate Using Triangular and Trapezoid Vortex Generators #1 Sonali S Nagawade, #2 Prof. S Y Bhosale, #3 Prof. N K Chougule 1 Sonalinagawade1@gmail.com
ISSN 2395-1621 Investigation of Jet Impingement on Flat Plate Using Triangular and Trapezoid Vortex Generators #1 Sonali S Nagawade, #2 Prof. S Y Bhosale, #3 Prof. N K Chougule 1 Sonalinagawade1@gmail.com
Thermo-mechanical Investigation of Ventilated Disc Brake with Finite Element Analysis
 Thermo-mechanical Investigation of Ventilated Disc Brake with Finite Element Analysis Arifin #1, Mohammad Tauviqirrahman #2, Muchammad *3, J. Jamari #, A.P. Bayuseno # # Laboratory for Engineering Design
Thermo-mechanical Investigation of Ventilated Disc Brake with Finite Element Analysis Arifin #1, Mohammad Tauviqirrahman #2, Muchammad *3, J. Jamari #, A.P. Bayuseno # # Laboratory for Engineering Design
Heat Transfer Modeling using ANSYS FLUENT
 Lecture 2 - Conduction Heat Transfer 14.5 Release Heat Transfer Modeling using ANSYS FLUENT 2013 ANSYS, Inc. March 28, 2013 1 Release 14.5 Agenda Introduction Energy equation in solids Equation solved
Lecture 2 - Conduction Heat Transfer 14.5 Release Heat Transfer Modeling using ANSYS FLUENT 2013 ANSYS, Inc. March 28, 2013 1 Release 14.5 Agenda Introduction Energy equation in solids Equation solved
Using Computational Fluid Dynamics And Analysis Of Microchannel Heat Sink
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 4, Issue 12 [Aug. 2015] PP: 67-74 Using Computational Fluid Dynamics And Analysis Of Microchannel Heat Sink M.
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 4, Issue 12 [Aug. 2015] PP: 67-74 Using Computational Fluid Dynamics And Analysis Of Microchannel Heat Sink M.
SUPER-INSULATED LONG-TERM HOT WATER STORAGE
 SUPER-INSULATED LONG-TERM HOT WATER STORAGE Dr. rer. nat. T. Beikircher, Dr.-Ing. F. Buttinger, M. Demharter ZAE Bayern, Dept. 1 Walther Meißner Str. 6, 85748 Garching Phone: +49/89/329442-49 beikircher@muc.zae-bayern.de
SUPER-INSULATED LONG-TERM HOT WATER STORAGE Dr. rer. nat. T. Beikircher, Dr.-Ing. F. Buttinger, M. Demharter ZAE Bayern, Dept. 1 Walther Meißner Str. 6, 85748 Garching Phone: +49/89/329442-49 beikircher@muc.zae-bayern.de
 9 th International Conference on Quantitative InfraRed Thermography July 2-5, 2008, Krakow - Poland Application of infrared thermography for validation of numerical analyses results of a finned cross-flow
9 th International Conference on Quantitative InfraRed Thermography July 2-5, 2008, Krakow - Poland Application of infrared thermography for validation of numerical analyses results of a finned cross-flow
Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector
 Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector INTRODUCTION: Solar heater is one of the simplest and basic technologies in the solar energy field. Collector is the heart of any solar heating system. It absorbs and
Solar Flat Plate Thermal Collector INTRODUCTION: Solar heater is one of the simplest and basic technologies in the solar energy field. Collector is the heart of any solar heating system. It absorbs and
B.V. Gudiksen. 1. Introduction. Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2007 Memorie della
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2007 Memorie della À Ø Ò Ø ËÓÐ Ö ÓÖÓÒ B.V. Gudiksen Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics, University of Oslo, Norway e-mail:boris@astro.uio.no Abstract. The heating mechanism
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2007 Memorie della À Ø Ò Ø ËÓÐ Ö ÓÖÓÒ B.V. Gudiksen Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics, University of Oslo, Norway e-mail:boris@astro.uio.no Abstract. The heating mechanism
Ch. Kasprzyk, TU Dresden
 LES Simulation of Turbulent Flow and Heat Transfer in Cavities of a Heat Sink Ch. Kasprzyk, TU Dresden Th. Frank, F. Menter, ANSYS Germany B. Vogt, Th. Scherer, VOITH Hydro Presentation ACUM 2014, Nürnberg,
LES Simulation of Turbulent Flow and Heat Transfer in Cavities of a Heat Sink Ch. Kasprzyk, TU Dresden Th. Frank, F. Menter, ANSYS Germany B. Vogt, Th. Scherer, VOITH Hydro Presentation ACUM 2014, Nürnberg,
Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System
 Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System Uday M. Jamdade 1, Sandip H. Deshmukh 2, Sanjay S. Deshpande 3 1 Sinhgad college of engineering, pune. 2 Sinhgad college of engineering, Pune 3 Asian academy
Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System Uday M. Jamdade 1, Sandip H. Deshmukh 2, Sanjay S. Deshpande 3 1 Sinhgad college of engineering, pune. 2 Sinhgad college of engineering, Pune 3 Asian academy
Thermal simulation of a complete vehicle using manikin models
 Thermal simulation of a complete vehicle using manikin models Dr. Stefan Paulke, Dr. Daniel Köster, Dr. Regina Hass (P+Z Engineering GmbH) Dr. Viktor Bader, Dr. Stephan Menzel, Andreas Gubalke (Volkswagen
Thermal simulation of a complete vehicle using manikin models Dr. Stefan Paulke, Dr. Daniel Köster, Dr. Regina Hass (P+Z Engineering GmbH) Dr. Viktor Bader, Dr. Stephan Menzel, Andreas Gubalke (Volkswagen
Technical Notes. Introduction. PCB (printed circuit board) Design. Issue 1 January 2010
 Technical Notes Introduction Thermal Management for LEDs Poor thermal management can lead to early LED product failure. This Technical Note discusses thermal management techniques and good system design.
Technical Notes Introduction Thermal Management for LEDs Poor thermal management can lead to early LED product failure. This Technical Note discusses thermal management techniques and good system design.
3D Simulation of the Plunger Cooling during the Hollow Glass Forming Process Model, Validation and Results
 Thomas Bewer, Cham, CH 3D Simulation of the Plunger Cooling during the Hollow Glass Forming Process Model, Validation and Results A steady state model to describe the flow and temperature distribution
Thomas Bewer, Cham, CH 3D Simulation of the Plunger Cooling during the Hollow Glass Forming Process Model, Validation and Results A steady state model to describe the flow and temperature distribution
HEAT LOSS CHARACTERISTICS OF A ROOF INTEGRATED SOLAR MICRO-CONCENTRATING COLLECTOR
 5 th International Conference on Energy Sustainability ASME August 7-10, 2011, Grand Hyatt Washington, Washington DC, USA ESFuelCell2011-54254 HEAT LOSS CHARACTERISTICS OF A ROOF INTEGRATED SOLAR MICRO-CONCENTRATING
5 th International Conference on Energy Sustainability ASME August 7-10, 2011, Grand Hyatt Washington, Washington DC, USA ESFuelCell2011-54254 HEAT LOSS CHARACTERISTICS OF A ROOF INTEGRATED SOLAR MICRO-CONCENTRATING
Analysis of the occurrence of natural convection in a bed of bars in vertical temperature gradient conditions
 archives of thermodynamics Vol. 34(2013), No. 1, 71 83 DOI: 10.2478/aoter-2013-0005 Analysis of the occurrence of natural convection in a bed of bars in vertical temperature gradient conditions RAFAŁ WYCZÓŁKOWSKI
archives of thermodynamics Vol. 34(2013), No. 1, 71 83 DOI: 10.2478/aoter-2013-0005 Analysis of the occurrence of natural convection in a bed of bars in vertical temperature gradient conditions RAFAŁ WYCZÓŁKOWSKI
Revision of GRE/2017/05
 Transmitted by the experts from The International Automotive Lighting and Light Signalling Expert Group (GTB) Informal document GRE-77-12 (77th GRE, 4-7 April 2017 agenda item 5 ) Revision of GRE/2017/05
Transmitted by the experts from The International Automotive Lighting and Light Signalling Expert Group (GTB) Informal document GRE-77-12 (77th GRE, 4-7 April 2017 agenda item 5 ) Revision of GRE/2017/05
A FINITE VOLUME-BASED NETWORK METHOD FOR THE PREDICTION OF HEAT, MASS AND MOMENTUM TRANSFER IN A PEBBLE BED REACTOR
 A FINITE VOLUME-BASED NETWORK METHOD FOR THE PREDICTION OF HEAT, MASS AND MOMENTUM TRANSFER IN A PEBBLE BED REACTOR GP Greyvenstein and HJ van Antwerpen Energy Systems Research North-West University, Private
A FINITE VOLUME-BASED NETWORK METHOD FOR THE PREDICTION OF HEAT, MASS AND MOMENTUM TRANSFER IN A PEBBLE BED REACTOR GP Greyvenstein and HJ van Antwerpen Energy Systems Research North-West University, Private
PH2200 Practice Final Exam Summer 2003
 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
Simulation of Free Convection with Conjugate Heat Transfer
 Simulation of Free Convection with Conjugate Heat Transfer Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari, Kurt Svihla ANSYS, Inc. Abstract This study focuses on free convective and conjugate heat transfer in a naturally ventilated,
Simulation of Free Convection with Conjugate Heat Transfer Hong Xu, Chokri Guetari, Kurt Svihla ANSYS, Inc. Abstract This study focuses on free convective and conjugate heat transfer in a naturally ventilated,
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2017/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2017 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2017/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2017 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
Inverse Heat Flux Evaluation using Conjugate Gradient Methods from Infrared Imaging
 11 th International Conference on Quantitative InfraRed Thermography Inverse Heat Flux Evaluation using Conjugate Gradient Methods from Infrared Imaging by J. Sousa*, L. Villafane*, S. Lavagnoli*, and
11 th International Conference on Quantitative InfraRed Thermography Inverse Heat Flux Evaluation using Conjugate Gradient Methods from Infrared Imaging by J. Sousa*, L. Villafane*, S. Lavagnoli*, and
3.0 FINITE ELEMENT MODEL
 3.0 FINITE ELEMENT MODEL In Chapter 2, the development of the analytical model established the need to quantify the effect of the thermal exchange with the dome in terms of a single parameter, T d. In
3.0 FINITE ELEMENT MODEL In Chapter 2, the development of the analytical model established the need to quantify the effect of the thermal exchange with the dome in terms of a single parameter, T d. In
THERMAL PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF AN INNOVATIVE DOUBLE GLAZING WINDOW
 THERMAL PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF AN INNOVATIVE DOUBLE GLAZING WINDOW Luigi De Giorgi, Carlo Cima, Emilio Cafaro Dipartimento di Energetica, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy Volfango Bertola School
THERMAL PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF AN INNOVATIVE DOUBLE GLAZING WINDOW Luigi De Giorgi, Carlo Cima, Emilio Cafaro Dipartimento di Energetica, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy Volfango Bertola School
Thermal experimental & simulation investigations on new lead frame based LED packages.
 Thermal experimental & simulation investigations on new lead frame based LED packages. B. Pardo, A. Piveteau, J. Routin, S, A. Gasse, T. van Weelden* CEA-Leti, MINATEC Campus, 17 rue des Martyrs, 38054
Thermal experimental & simulation investigations on new lead frame based LED packages. B. Pardo, A. Piveteau, J. Routin, S, A. Gasse, T. van Weelden* CEA-Leti, MINATEC Campus, 17 rue des Martyrs, 38054
Numerical Simulation of the Air Flow and Thermal Comfort in Aircraft Cabins
 Numerical Simulation of the Air Flow and Thermal Comfort in Aircraft Cabins Mikhail Konstantinov, Waldemar Lautenschlager, Andrei Shishkin, Claus Wagner German Aerospace Center, Institute of Aerodynamics
Numerical Simulation of the Air Flow and Thermal Comfort in Aircraft Cabins Mikhail Konstantinov, Waldemar Lautenschlager, Andrei Shishkin, Claus Wagner German Aerospace Center, Institute of Aerodynamics
ELECTRICAL AND THERMAL DESIGN OF UMBILICAL CABLE
 ELECTRICAL AND THERMAL DESIGN OF UMBILICAL CABLE Derek SHACKLETON, Oceaneering Multiflex UK, (Scotland), DShackleton@oceaneering.com Luciana ABIB, Marine Production Systems do Brasil, (Brazil), LAbib@oceaneering.com
ELECTRICAL AND THERMAL DESIGN OF UMBILICAL CABLE Derek SHACKLETON, Oceaneering Multiflex UK, (Scotland), DShackleton@oceaneering.com Luciana ABIB, Marine Production Systems do Brasil, (Brazil), LAbib@oceaneering.com
QUALIFICATION OF A CFD CODE FOR REACTOR APPLICATIONS
 QUALIFICATION OF A CFD CODE FOR REACTOR APPLICATIONS Ulrich BIEDER whole TrioCFD Team DEN-STMF, CEA, UNIVERSITÉ PARIS-SACLAY www.cea.fr SÉMINAIRE ARISTOTE, NOVEMBER 8, 2016 PAGE 1 Outline Obective: analysis
QUALIFICATION OF A CFD CODE FOR REACTOR APPLICATIONS Ulrich BIEDER whole TrioCFD Team DEN-STMF, CEA, UNIVERSITÉ PARIS-SACLAY www.cea.fr SÉMINAIRE ARISTOTE, NOVEMBER 8, 2016 PAGE 1 Outline Obective: analysis
Prediction of Thermal Comfort and Ventilation Efficiency for Small and Large Enclosures by Combined Simulations
 Institute for Thermodynamics and Building Energy Systems, Dresden University of Technology Prediction of Thermal Comfort and Ventilation Efficiency for Small and Large Enclosures by Combined Simulations
Institute for Thermodynamics and Building Energy Systems, Dresden University of Technology Prediction of Thermal Comfort and Ventilation Efficiency for Small and Large Enclosures by Combined Simulations
CFD in Heat Transfer Equipment Professor Bengt Sunden Division of Heat Transfer Department of Energy Sciences Lund University
 CFD in Heat Transfer Equipment Professor Bengt Sunden Division of Heat Transfer Department of Energy Sciences Lund University email: bengt.sunden@energy.lth.se CFD? CFD = Computational Fluid Dynamics;
CFD in Heat Transfer Equipment Professor Bengt Sunden Division of Heat Transfer Department of Energy Sciences Lund University email: bengt.sunden@energy.lth.se CFD? CFD = Computational Fluid Dynamics;
Numerical Simulation of the Air Flow and Thermal Comfort in a Train Cabin
 Paper 328 Numerical Simulation of the Air Flow and Thermal Comfort in a Train Cabin M. Konstantinov 1 and C. Wagner 1,2 1 Institute of Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics University of Technology Ilmenau,
Paper 328 Numerical Simulation of the Air Flow and Thermal Comfort in a Train Cabin M. Konstantinov 1 and C. Wagner 1,2 1 Institute of Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics University of Technology Ilmenau,
A Numerical Study of Convective Heat Transfer in the Compression Chambers of Scroll Compressors
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 A Numerical Study of Convective Heat Transfer in the Compression Chambers of Scroll
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2012 A Numerical Study of Convective Heat Transfer in the Compression Chambers of Scroll
HEAT TRANSFER 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS 5 2 CONDUCTION
 HEAT TRANSFER 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS 5 2 CONDUCTION 11 Fourier s Law of Heat Conduction, General Conduction Equation Based on Cartesian Coordinates, Heat Transfer Through a Wall, Composite Wall
HEAT TRANSFER 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS 5 2 CONDUCTION 11 Fourier s Law of Heat Conduction, General Conduction Equation Based on Cartesian Coordinates, Heat Transfer Through a Wall, Composite Wall
INFLUENCE OF SURFACE EMISSIVITY AND OF LOW EMISSIVITY SHIELDS ON THE THERMAL PROPERTIES OF LOW DENSITY INSULATING MATERIALS
 8th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics HEFAT2011 8 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 11 13 July 2011 Pointe Aux
8th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics HEFAT2011 8 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 11 13 July 2011 Pointe Aux
CHAPTER 6 HEAT DISSIPATION AND TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION OF BRAKE LINER USING STEADY STATE ANALYSIS
 131 CHAPTER 6 HEAT DISSIPATION AND TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION OF BRAKE LINER USING STEADY STATE ANALYSIS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Drum brakes were the first types of brakes used on motor vehicles. Nowadays, over
131 CHAPTER 6 HEAT DISSIPATION AND TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION OF BRAKE LINER USING STEADY STATE ANALYSIS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Drum brakes were the first types of brakes used on motor vehicles. Nowadays, over
Applied CFD Project 1. Christopher Light MAE 598
 Applied CFD Project 1 Christopher Light MAE 598 October 5, 2017 Task 1 The hot water tank shown in Fig 1 is used for analysis of cool water flow with the heat from a hot plate at the bottom. For all tasks,
Applied CFD Project 1 Christopher Light MAE 598 October 5, 2017 Task 1 The hot water tank shown in Fig 1 is used for analysis of cool water flow with the heat from a hot plate at the bottom. For all tasks,
Numerical Analysis of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Ventilated Disc Brake Rotor Using CFD
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 4, Issue 10 [June 2015] PP: 31-38 Numerical Analysis of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Ventilated
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 4, Issue 10 [June 2015] PP: 31-38 Numerical Analysis of Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Ventilated
What can laser light do for (or to) me?
 What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a monolithic exchanger related to high temperature and high pressure operating conditions
 Advanced Computational Methods in Heat Transfer X 25 Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a monolithic exchanger related to high temperature and high pressure operating conditions F. Selimovic & B. Sundén
Advanced Computational Methods in Heat Transfer X 25 Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a monolithic exchanger related to high temperature and high pressure operating conditions F. Selimovic & B. Sundén
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF FLOW FIELD IN WHEELHOUSE OF CARS
 Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol. 5, Num. 2, (2004), pp. 1-8 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF FLOW FIELD IN WHEELHOUSE OF CARS Tamás Régert (1) and Dr. Tamás Lajos (2) (1) Ph.D. student; (2)
Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol. 5, Num. 2, (2004), pp. 1-8 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF FLOW FIELD IN WHEELHOUSE OF CARS Tamás Régert (1) and Dr. Tamás Lajos (2) (1) Ph.D. student; (2)
Theory & Applications of Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD
 جمعية رواد الھندسة والتكنولوجيا Theory & Applications of Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD Prepared and Presented By: Hesham Sami Abdul Munem Mechanical Engineer Pressure Vessels Department ENPPI Contents:
جمعية رواد الھندسة والتكنولوجيا Theory & Applications of Computational Fluid Dynamics CFD Prepared and Presented By: Hesham Sami Abdul Munem Mechanical Engineer Pressure Vessels Department ENPPI Contents:
GRADE 9: Physical processes 4. UNIT 9P.4 6 hours. The electromagnetic spectrum. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 9: Physical processes 4 The electromagnetic spectrum UNIT 9P.4 6 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of seven units on physical processes for Grade 9. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 9: Physical processes 4 The electromagnetic spectrum UNIT 9P.4 6 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of seven units on physical processes for Grade 9. The unit is designed to guide your
Review: Light and Spectra. Absorption and Emission Lines
 1 Review: Light and Spectra Light is a wave It undergoes diffraction and other wave phenomena. But light also is made of particles Energy is carried by photons 1 Wavelength energy of each photon Computer
1 Review: Light and Spectra Light is a wave It undergoes diffraction and other wave phenomena. But light also is made of particles Energy is carried by photons 1 Wavelength energy of each photon Computer
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Conduction is the transfer of heat by the direct contact of particles of matter.
 Matter and Energy Chapter 9 energy flows from a material at a higher temperature to a material at a lower temperature. This process is called heat transfer. How is heat transferred from material to material,
Matter and Energy Chapter 9 energy flows from a material at a higher temperature to a material at a lower temperature. This process is called heat transfer. How is heat transferred from material to material,
Heat Transfer Analysis of Automotive Headlamp Using CFD Methodology
 Heat Transfer Analysis of Automotive Headlamp Using CFD Methodology Manoj Kumar S * N. Suresh Kumar R. Thundil Karuppa Raj Engineer, Dept. of CFD Manager, Dept. of CFD Professor, Dept. of Energy Mechwell
Heat Transfer Analysis of Automotive Headlamp Using CFD Methodology Manoj Kumar S * N. Suresh Kumar R. Thundil Karuppa Raj Engineer, Dept. of CFD Manager, Dept. of CFD Professor, Dept. of Energy Mechwell
Lab 5: Post Processing and Solving Conduction Problems. Objective:
 Lab 5: Post Processing and Solving Conduction Problems Objective: The objective of this lab is to use the tools we have developed in MATLAB and SolidWorks to solve conduction heat transfer problems that
Lab 5: Post Processing and Solving Conduction Problems Objective: The objective of this lab is to use the tools we have developed in MATLAB and SolidWorks to solve conduction heat transfer problems that
Mathematical Modelling of Ceramic Block Heat Transfer Properties
 Proceedings of the 3 RD INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION 18-19 October, 2012, Kaunas, Lithuania Kaunas University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture Studentu st.
Proceedings of the 3 RD INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION 18-19 October, 2012, Kaunas, Lithuania Kaunas University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture Studentu st.
of the heat is dissipated as a result of the flow of electrical current in various conductors. In order to predict temperatures
 Transient Coupled Thermal / Electrical Analysis of a Printed Wiring Board Ben Zandi TES International: (248 362-29 bzandi@tesint.com Jeffrey Lewis TES International Hamish Lewis TES International Abstract
Transient Coupled Thermal / Electrical Analysis of a Printed Wiring Board Ben Zandi TES International: (248 362-29 bzandi@tesint.com Jeffrey Lewis TES International Hamish Lewis TES International Abstract
Summary. The basic principles of the simulation technique SERT
 Determination of the absorption coefficient of structured absorbing systems in a "virtual" reverberation chamber - an application of the sound particle method SERT (Translation of the original publication:
Determination of the absorption coefficient of structured absorbing systems in a "virtual" reverberation chamber - an application of the sound particle method SERT (Translation of the original publication:
Simulation Toolbox. Dielectric and thermal design of power devices
 Simulation Toolbox Dielectric and thermal design of power devices Andreas Blaszczyk, Jörg Ostrowski, Boguslaw Samul, Daniel Szary Demands and trends in power devices are toward compactness and cost efficiency,
Simulation Toolbox Dielectric and thermal design of power devices Andreas Blaszczyk, Jörg Ostrowski, Boguslaw Samul, Daniel Szary Demands and trends in power devices are toward compactness and cost efficiency,
2-D CFD analysis of passenger compartment for thermal comfort and ventilation
 2-D CFD analysis of passenger compartment for thermal comfort and ventilation Ajay Giri 1*, Brajesh Tripathi 2 and H.C. Thakur 3 *1, 3 School of Engineering, Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida, U.P,
2-D CFD analysis of passenger compartment for thermal comfort and ventilation Ajay Giri 1*, Brajesh Tripathi 2 and H.C. Thakur 3 *1, 3 School of Engineering, Gautam Buddha University, Greater Noida, U.P,
CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE
 CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE In this chapter, the governing equations for the proposed numerical model with discretisation methods are presented. Spiral
CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE In this chapter, the governing equations for the proposed numerical model with discretisation methods are presented. Spiral
Comparison of two equations closure turbulence models for the prediction of heat and mass transfer in a mechanically ventilated enclosure
 Proceedings of 4 th ICCHMT May 17-0, 005, Paris-Cachan, FRANCE 381 Comparison of two equations closure turbulence models for the prediction of heat and mass transfer in a mechanically ventilated enclosure
Proceedings of 4 th ICCHMT May 17-0, 005, Paris-Cachan, FRANCE 381 Comparison of two equations closure turbulence models for the prediction of heat and mass transfer in a mechanically ventilated enclosure
This chapter focuses on the study of the numerical approximation of threedimensional
 6 CHAPTER 6: NUMERICAL OPTIMISATION OF CONJUGATE HEAT TRANSFER IN COOLING CHANNELS WITH DIFFERENT CROSS-SECTIONAL SHAPES 3, 4 6.1. INTRODUCTION This chapter focuses on the study of the numerical approximation
6 CHAPTER 6: NUMERICAL OPTIMISATION OF CONJUGATE HEAT TRANSFER IN COOLING CHANNELS WITH DIFFERENT CROSS-SECTIONAL SHAPES 3, 4 6.1. INTRODUCTION This chapter focuses on the study of the numerical approximation
AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF ROAD SURFACE REFLECTION PROPERTIES
 AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF ROAD SURFACE REFLECTION PROPERTIES Corell, D. D 1, Sørensen, K. 2 1 Technical University of Denmark, DTU Fotonik, 4000 Roskilde, DENMARK, 2 Johnsen Consult, 2100 København
AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF ROAD SURFACE REFLECTION PROPERTIES Corell, D. D 1, Sørensen, K. 2 1 Technical University of Denmark, DTU Fotonik, 4000 Roskilde, DENMARK, 2 Johnsen Consult, 2100 København
Simplified Collector Performance Model
 Simplified Collector Performance Model Prediction of the thermal output of various solar collectors: The quantity of thermal energy produced by any solar collector can be described by the energy balance
Simplified Collector Performance Model Prediction of the thermal output of various solar collectors: The quantity of thermal energy produced by any solar collector can be described by the energy balance
Thermal Analysis of Fairchild Dornier 728Jet Wing/Fuselage Interface using MSC.Patran Thermal. Paper number D. Konopka, J. Hyer, A.
 2001-32 Thermal Analysis of Fairchild Dornier 728Jet Wing/Fuselage Interface using MSC.Patran Thermal Paper number 2001-32 D. Konopka, J. Hyer, A. Schönrock Fairchild Dornier GmbH PO Box 1103 82230 Wessling
2001-32 Thermal Analysis of Fairchild Dornier 728Jet Wing/Fuselage Interface using MSC.Patran Thermal Paper number 2001-32 D. Konopka, J. Hyer, A. Schönrock Fairchild Dornier GmbH PO Box 1103 82230 Wessling
Thermal Analysis & Design Improvement of an Internal Air-Cooled Electric Machine Dr. James R. Dorris Application Specialist, CD-adapco
 Thermal Analysis & Design Improvement of an Internal Air-Cooled Electric Machine Dr. James R. Dorris Application Specialist, CD-adapco Thermal Analysis of Electric Machines Motivation Thermal challenges
Thermal Analysis & Design Improvement of an Internal Air-Cooled Electric Machine Dr. James R. Dorris Application Specialist, CD-adapco Thermal Analysis of Electric Machines Motivation Thermal challenges
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature. Topic 6. Transferring Energy. pp WORKBOOK. Name:
 Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 6 Transferring Energy pp. 226-236 WORKBOOK Name: 0 Read pp. 226-227 object or material that can transfer energy to other objects Example: light bulb, the Sun
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 6 Transferring Energy pp. 226-236 WORKBOOK Name: 0 Read pp. 226-227 object or material that can transfer energy to other objects Example: light bulb, the Sun
The energy performance of an airflow window
 The energy performance of an airflow window B.(Bram) Kersten / id.nr. 0667606 University of Technology Eindhoven, department of Architecture Building and Planning, unit Building Physics and Systems. 10-08-2011
The energy performance of an airflow window B.(Bram) Kersten / id.nr. 0667606 University of Technology Eindhoven, department of Architecture Building and Planning, unit Building Physics and Systems. 10-08-2011
Combined Natural Convection and Thermal Radiation in an Inclined Cubical Cavity with a Rectangular Pins Attached to Its Active Wall
 Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences ISSN 2303-4521 Vol.5, No.3, November 2017, pp. 347~354 Available online at:http://pen.ius.edu.ba Combined Natural Convection and Thermal Radiation in an
Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences ISSN 2303-4521 Vol.5, No.3, November 2017, pp. 347~354 Available online at:http://pen.ius.edu.ba Combined Natural Convection and Thermal Radiation in an
Numerical Simulation of Lorentz Force Enhanced Flow Patterns within Glass Melts
 International Scientific Colloquium Modelling for Material Processing Riga, September 16-17, 2010 Numerical Simulation of Lorentz Force Enhanced Flow Patterns within Glass Melts U. Lüdtke, A. Kelm, B.
International Scientific Colloquium Modelling for Material Processing Riga, September 16-17, 2010 Numerical Simulation of Lorentz Force Enhanced Flow Patterns within Glass Melts U. Lüdtke, A. Kelm, B.
FLUID FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER INVESTIGATION OF PERFORATED HEAT SINK UNDER MIXED CONVECTION 1 Mr. Shardul R Kulkarni, 2 Prof.S.Y.
 FLUID FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER INVESTIGATION OF PERFORATED HEAT SINK UNDER MIXED CONVECTION 1 Mr. Shardul R Kulkarni, 2 Prof.S.Y.Bhosale 1 Research scholar, 2 Head of department & Asst professor Department
FLUID FLOW AND HEAT TRANSFER INVESTIGATION OF PERFORATED HEAT SINK UNDER MIXED CONVECTION 1 Mr. Shardul R Kulkarni, 2 Prof.S.Y.Bhosale 1 Research scholar, 2 Head of department & Asst professor Department
A Numerical Investigation of Thermal Conditions and Deformations of the Astronomical Roentgen Telescope
 Spectrum-Roentgen-Gamma International Experiment A Numerical Investigation of Thermal Conditions and Deformations of the Astronomical Roentgen Telescope А. Ryabov, V. Spirin, S. Gulakov, S. Garanin, S.
Spectrum-Roentgen-Gamma International Experiment A Numerical Investigation of Thermal Conditions and Deformations of the Astronomical Roentgen Telescope А. Ryabov, V. Spirin, S. Gulakov, S. Garanin, S.
Transactions on Modelling and Simulation vol 10, 1995 WIT Press, ISSN X
 High temperature heat transfer in glass during cooling - an experimental and computational approach K. Storck, M. Karlsson, B. Augustsson,* D. Loyd Applied Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics, Department
High temperature heat transfer in glass during cooling - an experimental and computational approach K. Storck, M. Karlsson, B. Augustsson,* D. Loyd Applied Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics, Department
Analysis of High Speed Spindle with a Double Helical Cooling Channel R.Sathiya Moorthy, V. Prabhu Raja, R.Lakshmipathi
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012 1 Analysis of High Speed Spindle with a Double Helical Cooling Channel R.Sathiya Moorthy, V. Prabhu Raja, R.Lakshmipathi
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012 1 Analysis of High Speed Spindle with a Double Helical Cooling Channel R.Sathiya Moorthy, V. Prabhu Raja, R.Lakshmipathi
Table of Contents. Foreword... xiii. Preface... xv
 Table of Contents Foreword.... xiii Preface... xv Chapter 1. Fundamental Equations, Dimensionless Numbers... 1 1.1. Fundamental equations... 1 1.1.1. Local equations... 1 1.1.2. Integral conservation equations...
Table of Contents Foreword.... xiii Preface... xv Chapter 1. Fundamental Equations, Dimensionless Numbers... 1 1.1. Fundamental equations... 1 1.1.1. Local equations... 1 1.1.2. Integral conservation equations...
SOP Release. FEV Chassis Reliable Partner in Chassis Development. FEV Chassis Applications and Activities. Concept Layout. Design
 CHASSIS Reliable Partner in Chassis Development FEV Chassis Applications and Activities Founded in 1978, FEV is an internationally recognized leader in the design and development of internal combustion
CHASSIS Reliable Partner in Chassis Development FEV Chassis Applications and Activities Founded in 1978, FEV is an internationally recognized leader in the design and development of internal combustion
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2014/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2014 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
United Nations Economic and Social Council ECE/TRANS/WP.29/GRE/2014/20 Distr.: General 7 August 2014 Original: English Economic Commission for Europe Inland Transport Committee World Forum for Harmonization
There are four phases of matter: Phases of Matter
 HEAT SCIENCE There are four phases of matter: Phases of Matter There are four phases of matter: Phases of Matter Animation States of Matter Solids Solids: Are rigid, crystalline Hold their shape Have little
HEAT SCIENCE There are four phases of matter: Phases of Matter There are four phases of matter: Phases of Matter Animation States of Matter Solids Solids: Are rigid, crystalline Hold their shape Have little
NUMERICAL STUDY OF HEAT TRANSFER IN A FLAT PLAT THERMAL SOLAR COLLECTOR WITH PARTITIONS ATTACHED TO ITS GLAZING. Adel LAARABA.
 NUMERICAL STUDY OF HEAT TRANSFER IN A FLAT PLAT THERMAL SOLAR COLLECTOR WITH PARTITIONS ATTACHED TO ITS GLAZING Adel LAARABA. Department of physics. University of BATNA. (05000) Batna, Algeria Ccorresponding
NUMERICAL STUDY OF HEAT TRANSFER IN A FLAT PLAT THERMAL SOLAR COLLECTOR WITH PARTITIONS ATTACHED TO ITS GLAZING Adel LAARABA. Department of physics. University of BATNA. (05000) Batna, Algeria Ccorresponding
5. AN INTRODUCTION TO BUILDING PHYSICS
 5. AN INTRODUCTION TO BUILDING PHYSICS P. Wouters, S. Martin ABSTRACT This chapter places the System Identification Competition in a broader context of evaluating the thermal performances of building components.
5. AN INTRODUCTION TO BUILDING PHYSICS P. Wouters, S. Martin ABSTRACT This chapter places the System Identification Competition in a broader context of evaluating the thermal performances of building components.
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
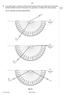 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
APPENDIX 1 DESCRIPTION OF HOT WIRE ANEMOMETER
 146 APPENDIX 1 DESCRIPTION OF HOT WIRE ANEMOMETER Basic Principles of CTA Anemometer The hot-wire anemometer was introduced in its original form in the first half of the 0 th century. A major breakthrough
146 APPENDIX 1 DESCRIPTION OF HOT WIRE ANEMOMETER Basic Principles of CTA Anemometer The hot-wire anemometer was introduced in its original form in the first half of the 0 th century. A major breakthrough
Numerical Study of PCM Melting in Evacuated Solar Collector Storage System
 Numerical Study of PCM Melting in Evacuated Collector Storage System MOHD KHAIRUL ANUAR SHARIF, SOHIF MAT, MOHD AFZANIZAM MOHD ROSLI, KAMARUZZAMAN SOPIAN, MOHD YUSOF SULAIMAN, A. A. Al-abidi. Energy Research
Numerical Study of PCM Melting in Evacuated Collector Storage System MOHD KHAIRUL ANUAR SHARIF, SOHIF MAT, MOHD AFZANIZAM MOHD ROSLI, KAMARUZZAMAN SOPIAN, MOHD YUSOF SULAIMAN, A. A. Al-abidi. Energy Research
PROBLEM Node 5: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
 PROBLEM 4.78 KNOWN: Nodal network and boundary conditions for a water-cooled cold plate. FIND: (a) Steady-state temperature distribution for prescribed conditions, (b) Means by which operation may be extended
PROBLEM 4.78 KNOWN: Nodal network and boundary conditions for a water-cooled cold plate. FIND: (a) Steady-state temperature distribution for prescribed conditions, (b) Means by which operation may be extended
