Interference, vector spaces
|
|
|
- Laurel Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interference, vector spaces Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Quantum Mechanics 1 August 6, 2008 Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 1 / 16
2 Outline 1 The double-slit experiment and its cousins 2 Additions of waves: vector spaces 3 References Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 2 / 16
3 Outline The double-slit experiment and its cousins 1 The double-slit experiment and its cousins 2 Additions of waves: vector spaces 3 References Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 3 / 16
4 The double-slit experiment and its cousins Wave-particle unity Laser Double slit Detector (screen) Use a laser which emits one photon at a time. Use the screen as a detector. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 4 / 16
5 The double-slit experiment and its cousins Wave-particle unity The laser emits one photon at a time. Each photon appears as a single pointlike flash when it arrives at the screen. This is exactly what you expect of a particle. When you plot the positions of many such flashes, then the density of points is governed by the interference fringes. The variation of the intensity through interference is exactly what you expect of a wave. A quantum particle is both a wave and a particle: a wave when it travels through the slit, a particle when seen by the detector. The state of a quantum particle must have a wave description. This is one complex number at each point of space (Schrödinger). The square of the modulus of the wave is proportional to the probability of finding the particle at a point (Born). Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 5 / 16
6 The double-slit experiment and its cousins Which-slit experiment Laser Electron gun Electron detector: coincidence circuit Electrons scatter from photons. Back-to back electrons, if no photon. One of the electrons missing if photon passes through one of the slits. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 6 / 16
7 The double-slit experiment and its cousins Phase coherence Wave function of photon passing through top slit: Ψ 1 (x). Wave function of photon passing through bottom slit: Ψ 2 (x). Full wave function: Ψ(x) = Ψ 1 (x) + Ψ 2 (x). Fixed phase relationship between the two needed for interference, i.e., if Ψ 2 (x) = Ψ 1 (x)a(x)e iφ(x), then Ψ(x) 2 = Ψ 1 (x) 2 { 1 + A(x) 2 + 2A(x)cos φ(x) }. Usual case of interference: φ(x) = k path difference(x). If phase relationship randomized, then interference disappears. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 7 / 16
8 The double-slit experiment and its cousins Quantum cool (Scully and Drühl, 1982) Quantum eraser. 1 What happens if we collect information about which path but never use it? 2 What happens if we collect information about which path but erase the information before looking at it? 3 What happens if we collect information about which path but look at it long after the photons have reached the screen? (Schrödinger, 1935) Schrödinger s cat. Macroscopic quantum states, entanglement. (Bell, 1964) Locality vs reality. Bell s inequalities: quantum entanglement is non-local but cannot be used to send faster-than-light messages. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 8 / 16
9 Outline Additions of waves: vector spaces 1 The double-slit experiment and its cousins 2 Additions of waves: vector spaces 3 References Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 9 / 16
10 Vectors Additions of waves: vector spaces Take vectors such as x = (x 1, x 2, x 3 ) and y = (y 1, y 2, y 3 ). Let a, b, c, etc., be scalars. Then, the following are true 1 A vector multiplied by a scalar is a vector: ax = (ax 1, ax 2, ax 3 ). 2 Two vectors can be added to give a new vector: x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x 2 + y 2, x 3 + y 3 ). Vector addition is commutative: x + y = y + x, and associative: (x + y) + z = x + (y + z). Multiplication by scalars is distributive over vector addition: a(x + y) = ax + ay. Scalar addition is distributive over multiplication by a vector. Scalar multiplication is compatible with multiplication with a vector. 3 There exists a zero vector: 0 such that x + 0 = x for any vector x. There exists a negative of every vector. 4 There is an inner product (dot product): x y = x 1 y 1 + x 2 y 2 + x 3 y 3. The number of linearly independent vectors is the dimension of the space, D. An basis is a choice of D linearly independent vectors, in terms of which one can expand any vector. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 10 / 16
11 Additions of waves: vector spaces Square integrable functions are vectors! Take functions f (x), g(x), etc., such that dx f (x) 2 and dx g(x) 2 exist. Let a, b, c, etc., be constrants. Then, the following are true 1 There is an inner product: dxf (x)g (x). (Prove this) 2 af (x) is square integrable. 3 f (x) + g(x) is square integrable. The sum is clearly commutative and associative. Multiplication by a constant is distributive over the addition of the two functions; scalar addition is distributive over multiplication by a functions; scalar multiplication is compatible with multiplication by a function. 4 There exists a zero function. Every function has a negative. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 11 / 16
12 Additions of waves: vector spaces Coordinates: linear independence and bases Take a collection of vectors {x 1,x 2,x 3,,x N }. such that it is impossible to find any set of N numbers which satisfy the vector equation: a 1 x 1 + a 2 x a N x N = 0. Then, the collection is called linearly independent. The dimension of the vector space is the largest size of a linearly indpendent collection of vectors. Start from any vector x 1. Find a second vector which is linearly independent of this one. If you cannot find one, then the vector space is one-dimensional. If you find one then you have the set {x 1,x 2 }. Find a third vector which is linearly indpendent of these two. If you cannot find one, then the space is 2 dimensional. Otherwise you have the set {x 1,x 2,x 3 }, etc.. Any set of D linearly independent vectors in a vector space of dimension D is called a basis. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 12 / 16
13 Components Additions of waves: vector spaces Given a basis, every vector not in this basis is linearly dependent on the basis vectors. Hence one has an unique decomposition v = v 1 x 1 + v 2 x 2 + v D x D. The numbers v i are the components of the vector in this basis. The basis is orthonormal if x i x j = δ ij. (The Kronecker delta, δ ij, is 1 if i = j and zero otherwise). In an orthonormal basis the components of a vector are obtained by taking a dot product with the basis vectors: v i = v x i. A change from one orthonormal basis to another is performed by taking linear combinations of the components. This linear combination is specified by an orthogonal matrix. In other words: v = Mv, where v is the same as v but in the new basis. Since v v = 1, and the length of the vector is not changed by the choice of basis, one must have M T M = 1 (M T is the transpose of the matrix M). Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 13 / 16
14 Additions of waves: vector spaces The Fourier basis The vector space of square integrable functions is infinite dimensional. The recursive procedure for constructing a linearly independent set does not end in any number of steps. (Prove this). The plane waves, φ k (x) = exp(ikx), provide a basis (almost) on these functions. They are orthogonal under the inner product defined before. However, they are not square integrable. We will assume that this problem can be cured (the cure will come later) and continue. (Cure this) Each square integrable function can be completely specified by its Fourier coefficients: f (k) = f (x) φ k (x), under the inner product defined earlier. The standard representation as an infinite component is the Fourier transform: f (x) f (k). Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 14 / 16
15 Outline References 1 The double-slit experiment and its cousins 2 Additions of waves: vector spaces 3 References Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 15 / 16
16 References References 1 The Feynman Lectures in Physics (Vol 3), by R. P. Feynman et al. The material in this (and the previous) lecture correspond roughly to the first chapter of this book. 2 Quantum Mechanics (Non-relativistic theory), by L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifschitz. The material in this (and the previous) lecture roughly correspond to a few sections of the first chapter of this book. first chapter of this book. 3 Mathematical Methods for Physicists, by G. Arfken. This book contains chapters on matrices and Fourier transforms which will be useful throughout this course. 4 The quantum eraser is discussed in an article in the April 2007 issue of Scientific American. Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Interference, vector spaces QM I 16 / 16
Vector spaces and operators
 Vector spaces and operators Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 22 August, 2013 1 Outline 2 Setting up 3 Exploring 4 Keywords and References Quantum states are vectors We saw that
Vector spaces and operators Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 22 August, 2013 1 Outline 2 Setting up 3 Exploring 4 Keywords and References Quantum states are vectors We saw that
Representations of angular momentum
 Representations of angular momentum Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Quantum Mechanics 1 September 26, 2008 Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Representations of angular momentum QM I 1 / 15 Outline
Representations of angular momentum Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Quantum Mechanics 1 September 26, 2008 Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Representations of angular momentum QM I 1 / 15 Outline
Adding angular momenta
 Adding angular momenta Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 Eleventh Lecture Outline 1 Outline 2 Some definitions 3 The simplest example: summing two momenta 4 Interesting physics: summing
Adding angular momenta Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 Eleventh Lecture Outline 1 Outline 2 Some definitions 3 The simplest example: summing two momenta 4 Interesting physics: summing
3.024 Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Spring 2012 Recitation 1. Office Hours: MWF 9am-10am or by appointment
 Adam Floyd Hannon Office Hours: MWF 9am-10am or by e-mail appointment Topic Outline 1. a. Fourier Transform & b. Fourier Series 2. Linear Algebra Review 3. Eigenvalue/Eigenvector Problems 1. a. Fourier
Adam Floyd Hannon Office Hours: MWF 9am-10am or by e-mail appointment Topic Outline 1. a. Fourier Transform & b. Fourier Series 2. Linear Algebra Review 3. Eigenvalue/Eigenvector Problems 1. a. Fourier
The reality of de Broglie s pilot wave
 The reality of de Broglie s pilot wave António Cardoso Centro de Filosofia das Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Campo Grande, Edifício C4, 1749-016 Lisboa,
The reality of de Broglie s pilot wave António Cardoso Centro de Filosofia das Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, Campo Grande, Edifício C4, 1749-016 Lisboa,
Vectors in Function Spaces
 Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
Jim Lambers MAT 66 Spring Semester 15-16 Lecture 18 Notes These notes correspond to Section 6.3 in the text. Vectors in Function Spaces We begin with some necessary terminology. A vector space V, also
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation
 1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
1 Notes and Directions on Dirac Notation A. M. Steane, Exeter College, Oxford University 1.1 Introduction These pages are intended to help you get a feel for the mathematics behind Quantum Mechanics. The
Review of Quantum Mechanics, cont.
 Review of Quantum Mechanics, cont. 1 Probabilities In analogy to the development of a wave intensity from a wave amplitude, the probability of a particle with a wave packet amplitude, ψ, between x and
Review of Quantum Mechanics, cont. 1 Probabilities In analogy to the development of a wave intensity from a wave amplitude, the probability of a particle with a wave packet amplitude, ψ, between x and
An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually).
 Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
Formalism of Quantum Mechanics Operators Engel 3.2 An operator is a transformation that takes a function as an input and produces another function (usually). Example: In QM, most operators are linear:
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS
 MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
MP463 QUANTUM MECHANICS Introduction Quantum theory of angular momentum Quantum theory of a particle in a central potential - Hydrogen atom - Three-dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator (a model of
Physics 342 Lecture 2. Linear Algebra I. Lecture 2. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 2 Linear Algebra I Lecture 2 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, January 27th, 21 From separation of variables, we move to linear algebra Roughly speaking, this is the study
Physics 342 Lecture 2 Linear Algebra I Lecture 2 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, January 27th, 21 From separation of variables, we move to linear algebra Roughly speaking, this is the study
Erwin Schrödinger and his cat
 Erwin Schrödinger and his cat How to relate discrete energy levels with Hamiltonian described in terms of continгous coordinate x and momentum p? Erwin Schrödinger (887-96) Acoustics: set of frequencies
Erwin Schrödinger and his cat How to relate discrete energy levels with Hamiltonian described in terms of continгous coordinate x and momentum p? Erwin Schrödinger (887-96) Acoustics: set of frequencies
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics
 Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
Review of the Formalism of Quantum Mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics are often stated in textbooks. There are two main properties of physics upon which these postulates are based: 1)the probability
-state problems and an application to the free particle
 -state problems and an application to the free particle Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 3 September, 2013 Outline 1 Outline 2 The Hilbert space 3 A free particle 4 Keywords
-state problems and an application to the free particle Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Quantum Mechanics 1 2013 3 September, 2013 Outline 1 Outline 2 The Hilbert space 3 A free particle 4 Keywords
Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space
 Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
Physics 342 Lecture 16 Linear Algebra in Hilbert Space Lecture 16 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, March 1st, 2010 We have seen the importance of the plane wave solutions to the potentialfree Schrödinger
The Schrodinger Wave Equation (Engel 2.4) In QM, the behavior of a particle is described by its wave function Ψ(x,t) which we get by solving:
 When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
When do we use Quantum Mechanics? (Engel 2.1) Basically, when λ is close in magnitude to the dimensions of the problem, and to the degree that the system has a discrete energy spectrum The Schrodinger
Linear Algebra V = T = ( 4 3 ).
 Linear Algebra Vectors A column vector is a list of numbers stored vertically The dimension of a column vector is the number of values in the vector W is a -dimensional column vector and V is a 5-dimensional
Linear Algebra Vectors A column vector is a list of numbers stored vertically The dimension of a column vector is the number of values in the vector W is a -dimensional column vector and V is a 5-dimensional
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture 2
 Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Short Course in Quantum Information Lecture Formal Structure of Quantum Mechanics Course Info All materials downloadable @ website http://info.phys.unm.edu/~deutschgroup/deutschclasses.html Syllabus Lecture
Lecture 8: Wave-Particle Duality. Lecture 8, p 2
 We choose to examine a phenomenon which is impossible, absolutely impossible, to explain in any classical way, and which has in it the heart of quantum mechanics. In reality, it contains the only mystery.
We choose to examine a phenomenon which is impossible, absolutely impossible, to explain in any classical way, and which has in it the heart of quantum mechanics. In reality, it contains the only mystery.
Physics 342 Lecture 2. Linear Algebra I. Lecture 2. Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I
 Physics 342 Lecture 2 Linear Algebra I Lecture 2 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, January 3th, 28 From separation of variables, we move to linear algebra Roughly speaking, this is the study of
Physics 342 Lecture 2 Linear Algebra I Lecture 2 Physics 342 Quantum Mechanics I Wednesday, January 3th, 28 From separation of variables, we move to linear algebra Roughly speaking, this is the study of
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer. Lecture 5, January 27, 2006
 Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
Chem 3502/4502 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Mechanics) 3 Credits Fall Semester 2006 Christopher J. Cramer Lecture 5, January 27, 2006 Solved Homework (Homework for grading is also due today) We are told
Symmetries for fun and profit
 Symmetries for fun and profit Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Quantum Mechanics 1 August 28, 2008 Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Symmetries for fun and profit QM I 1 / 20 Outline 1 The isotropic
Symmetries for fun and profit Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Quantum Mechanics 1 August 28, 2008 Sourendu Gupta (TIFR Graduate School) Symmetries for fun and profit QM I 1 / 20 Outline 1 The isotropic
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer Choose the better choice of all choices given.
 PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
Page 2. Q1.Electrons and protons in two beams are travelling at the same speed. The beams are diffracted by objects of the same size.
 Q1.Electrons and protons in two beams are travelling at the same speed. The beams are diffracted by objects of the same size. Which correctly compares the de Broglie wavelength λ e of the electrons with
Q1.Electrons and protons in two beams are travelling at the same speed. The beams are diffracted by objects of the same size. Which correctly compares the de Broglie wavelength λ e of the electrons with
INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION
 INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION Keith Hannabuss Balliol College, Oxford Hilary Term 2009 Notation. In these notes we shall often use the physicists bra-ket notation, writing ψ for a vector ψ
INTRODUCTORY NOTES ON QUANTUM COMPUTATION Keith Hannabuss Balliol College, Oxford Hilary Term 2009 Notation. In these notes we shall often use the physicists bra-ket notation, writing ψ for a vector ψ
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer Choose the better choice of all choices given.
 PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
PHYS 280 Practice Final Exam Summer 2016 Name: Multiple Choice Choose the better choice of all choices given. 1. Which of the following isn t a truth about quantum mechanics? A. Physicists are at a consensus
Lecture 13B: Supplementary Notes on Advanced Topics. 1 Inner Products and Outer Products for Single Particle States
 Lecture 13B: Supplementary Notes on Advanced Topics Outer Products, Operators, Density Matrices In order to explore the complexity of many particle systems a different way to represent multiparticle states
Lecture 13B: Supplementary Notes on Advanced Topics Outer Products, Operators, Density Matrices In order to explore the complexity of many particle systems a different way to represent multiparticle states
CHE3935. Lecture 2. Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
 CHE3935 Lecture 2 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics 1 The History Quantum mechanics is strange to us because it deals with phenomena that are, for the most part, unobservable at the macroscopic level i.e.,
CHE3935 Lecture 2 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics 1 The History Quantum mechanics is strange to us because it deals with phenomena that are, for the most part, unobservable at the macroscopic level i.e.,
Outline. Linear Algebra for Computer Vision
 Outline Linear Algebra for Computer Vision Introduction CMSC 88 D Notation and Basics Motivation Linear systems of equations Gauss Elimination, LU decomposition Linear Spaces and Operators Addition, scalar
Outline Linear Algebra for Computer Vision Introduction CMSC 88 D Notation and Basics Motivation Linear systems of equations Gauss Elimination, LU decomposition Linear Spaces and Operators Addition, scalar
PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send to
 Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
Teoretisk Fysik KTH Advanced QM (SI2380), Lecture 2 (Summary of concepts) 1 PLEASE LET ME KNOW IF YOU FIND TYPOS (send email to langmann@kth.se) The laws of QM 1. I now discuss the laws of QM and their
4. Matrix inverses. left and right inverse. linear independence. nonsingular matrices. matrices with linearly independent columns
 L. Vandenberghe ECE133A (Winter 2018) 4. Matrix inverses left and right inverse linear independence nonsingular matrices matrices with linearly independent columns matrices with linearly independent rows
L. Vandenberghe ECE133A (Winter 2018) 4. Matrix inverses left and right inverse linear independence nonsingular matrices matrices with linearly independent columns matrices with linearly independent rows
This is the important completeness relation,
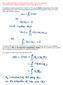 Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Observable quantities are represented by linear, hermitian operators! Compatible observables correspond to commuting operators! In addition to what was written in eqn 2.1.1, the vector corresponding to
Interference Between Distinguishable States. Thomas Alexander Meyer
 Interference Between Distinguishable States Thomas Alexander Meyer Interference effects are known to have a dependence upon indistinguishability of path. For this reason, it is accepted that different
Interference Between Distinguishable States Thomas Alexander Meyer Interference effects are known to have a dependence upon indistinguishability of path. For this reason, it is accepted that different
The following definition is fundamental.
 1. Some Basics from Linear Algebra With these notes, I will try and clarify certain topics that I only quickly mention in class. First and foremost, I will assume that you are familiar with many basic
1. Some Basics from Linear Algebra With these notes, I will try and clarify certain topics that I only quickly mention in class. First and foremost, I will assume that you are familiar with many basic
Lecture 3: Matrix and Matrix Operations
 Lecture 3: Matrix and Matrix Operations Representation, row vector, column vector, element of a matrix. Examples of matrix representations Tables and spreadsheets Scalar-Matrix operation: Scaling a matrix
Lecture 3: Matrix and Matrix Operations Representation, row vector, column vector, element of a matrix. Examples of matrix representations Tables and spreadsheets Scalar-Matrix operation: Scaling a matrix
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Compact Course on Linear Algebra. Wolfram Burgard, Bastian Steder
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Compact Course on Linear Algebra Wolfram Burgard, Bastian Steder Reference Book Thrun, Burgard, and Fox: Probabilistic Robotics Vectors Arrays of numbers Vectors represent
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Compact Course on Linear Algebra Wolfram Burgard, Bastian Steder Reference Book Thrun, Burgard, and Fox: Probabilistic Robotics Vectors Arrays of numbers Vectors represent
Introduction to Quantum Computing
 Introduction to Quantum Computing Part I Emma Strubell http://cs.umaine.edu/~ema/quantum_tutorial.pdf April 12, 2011 Overview Outline What is quantum computing? Background Caveats Fundamental differences
Introduction to Quantum Computing Part I Emma Strubell http://cs.umaine.edu/~ema/quantum_tutorial.pdf April 12, 2011 Overview Outline What is quantum computing? Background Caveats Fundamental differences
The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics and The Limitations of Human Being
 The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics and The Limitations of Human Beings Department of Mathematics 21 February 2011 Supported by NSF Quantum mechanics is very successful in computing quantities than can
The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics and The Limitations of Human Beings Department of Mathematics 21 February 2011 Supported by NSF Quantum mechanics is very successful in computing quantities than can
Quantum Computing Lecture 2. Review of Linear Algebra
 Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Quantum Computing Lecture 2 Review of Linear Algebra Maris Ozols Linear algebra States of a quantum system form a vector space and their transformations are described by linear operators Vector spaces
Lecture 2: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
 CMSC 49: Introduction to Quantum Computation Fall 5, Virginia Commonwealth University Sevag Gharibian Lecture : Introduction to Quantum Mechanics...the paradox is only a conflict between reality and your
CMSC 49: Introduction to Quantum Computation Fall 5, Virginia Commonwealth University Sevag Gharibian Lecture : Introduction to Quantum Mechanics...the paradox is only a conflict between reality and your
On the role of Decoherence in Bohmian Mechanics
 On the role of Decoherence in Bohmian Mechanics Mathematisches Institut LMU München June 8, 2009 My talk is based on my new book on Bohmian mechanics and on a new book coming out next year Sheldon Goldstein,
On the role of Decoherence in Bohmian Mechanics Mathematisches Institut LMU München June 8, 2009 My talk is based on my new book on Bohmian mechanics and on a new book coming out next year Sheldon Goldstein,
Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors,
 chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
chmy564-19 Fri 18jan19 Outline 1. Real and complex p orbitals (and for any l > 0 orbital) 2. Dirac Notation :Symbolic vs shorthand Hilbert Space Vectors, 3. Theorems vs. Postulates Scalar (inner) prod.
Lecture 4: Linear Algebra 1
 Lecture 4: Linear Algebra 1 Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Computational Physics 1 February 12, 2010 c : Sourendu Gupta (TIFR) Lecture 4: Linear Algebra 1 CP 1 1 / 26 Outline 1 Linear problems Motivation
Lecture 4: Linear Algebra 1 Sourendu Gupta TIFR Graduate School Computational Physics 1 February 12, 2010 c : Sourendu Gupta (TIFR) Lecture 4: Linear Algebra 1 CP 1 1 / 26 Outline 1 Linear problems Motivation
Linear Algebra Massoud Malek
 CSUEB Linear Algebra Massoud Malek Inner Product and Normed Space In all that follows, the n n identity matrix is denoted by I n, the n n zero matrix by Z n, and the zero vector by θ n An inner product
CSUEB Linear Algebra Massoud Malek Inner Product and Normed Space In all that follows, the n n identity matrix is denoted by I n, the n n zero matrix by Z n, and the zero vector by θ n An inner product
Experiments testing macroscopic quantum superpositions must be slow
 Experiments testing macroscopic quantum superpositions must be slow spatial (Scientic Reports (2016) - arxiv:1509.02408) Andrea Mari, Giacomo De Palma, Vittorio Giovannetti NEST - Scuola Normale Superiore
Experiments testing macroscopic quantum superpositions must be slow spatial (Scientic Reports (2016) - arxiv:1509.02408) Andrea Mari, Giacomo De Palma, Vittorio Giovannetti NEST - Scuola Normale Superiore
Richard Feynman: Electron waves are probability waves in the ocean of uncertainty.
 Richard Feynman: Electron waves are probability waves in the ocean of uncertainty. Last Time We Solved some of the Problems with Classical Physics Discrete Spectra? Bohr Model but not complete. Blackbody
Richard Feynman: Electron waves are probability waves in the ocean of uncertainty. Last Time We Solved some of the Problems with Classical Physics Discrete Spectra? Bohr Model but not complete. Blackbody
LECTURE 6: LINEAR VECTOR SPACES, BASIS VECTORS AND LINEAR INDEPENDENCE. Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012
 LECTURE 6: LINEAR VECTOR SPACES, BASIS VECTORS AND LINEAR INDEPENDENCE Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012 1 Outline: 6. LINEAR VECTOR SPACES, BASIS VECTORS AND LINEAR INDEPENDENCE 6.1 Linear
LECTURE 6: LINEAR VECTOR SPACES, BASIS VECTORS AND LINEAR INDEPENDENCE Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford MT 2012 1 Outline: 6. LINEAR VECTOR SPACES, BASIS VECTORS AND LINEAR INDEPENDENCE 6.1 Linear
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing. Chapter 1 Mathematical Background
 Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Lecture notes on Quantum Computing Chapter 1 Mathematical Background Vector states of a quantum system with n physical states are represented by unique vectors in C n, the set of n 1 column vectors 1 For
Modified Schrödinger equation, its analysis and experimental verification
 Modified Schrödinger equation, its analysis and experimental verification arxiv:1202.1321v1 [quant-ph] 7 Feb 2012 Isaac Shnaid February 8, 2012 Abstract According to classical non-relativistic Schrödinger
Modified Schrödinger equation, its analysis and experimental verification arxiv:1202.1321v1 [quant-ph] 7 Feb 2012 Isaac Shnaid February 8, 2012 Abstract According to classical non-relativistic Schrödinger
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics
 1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
1 The postulates of quantum mechanics The postulates of quantum mechanics were derived after a long process of trial and error. These postulates provide a connection between the physical world and the
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations
 Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
Continuous quantum states, Particle on a line and Uncertainty relations So far we have considered k-level (discrete) quantum systems. Now we turn our attention to continuous quantum systems, such as a
APPENDIX A. Background Mathematics. A.1 Linear Algebra. Vector algebra. Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components x 1 x 2.
 APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5. De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Many experimental
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5. De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Many experimental
CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I
 1 CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I I. RATIONALIZATION OF THE ELECTRON DIFFRACTION EXPERIMENT We will consider two different rationalizations of the electron double-slit experiment. A. Particle-wave
1 CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I I. RATIONALIZATION OF THE ELECTRON DIFFRACTION EXPERIMENT We will consider two different rationalizations of the electron double-slit experiment. A. Particle-wave
Lecture 9: Macroscopic Quantum Model
 Lecture 9: Macroscopic Quantum Model Outline 1. Development of Quantum Mechanics 2. Schrödinger's Equation Free particle With forces With Electromagnetic force 3. Physical meaning of Wavefunction Probability
Lecture 9: Macroscopic Quantum Model Outline 1. Development of Quantum Mechanics 2. Schrödinger's Equation Free particle With forces With Electromagnetic force 3. Physical meaning of Wavefunction Probability
Introduction. Introductory Remarks
 Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Introductory Remarks This is probably your first real course in quantum mechanics. To be sure, it is understood that you have encountered an introduction to some of the basic concepts, phenomenology, history,
Harmonic Oscillator I
 Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
Physics 34 Lecture 7 Harmonic Oscillator I Lecture 7 Physics 34 Quantum Mechanics I Monday, February th, 008 We can manipulate operators, to a certain extent, as we would algebraic expressions. By considering
LINEAR ALGEBRA: THEORY. Version: August 12,
 LINEAR ALGEBRA: THEORY. Version: August 12, 2000 13 2 Basic concepts We will assume that the following concepts are known: Vector, column vector, row vector, transpose. Recall that x is a column vector,
LINEAR ALGEBRA: THEORY. Version: August 12, 2000 13 2 Basic concepts We will assume that the following concepts are known: Vector, column vector, row vector, transpose. Recall that x is a column vector,
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra)
 AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 2: Orthogonal Vectors and Matrices; Vector Norms Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 11 Outline 1 Orthogonal
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 2: Orthogonal Vectors and Matrices; Vector Norms Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 11 Outline 1 Orthogonal
Beginning Modern Quantum
 Beginning Modern Quantum Born s probability interpretation The indeterminacy ( uncertainty ) principle The Schroedinger equation The Copenhagen interpretation 419 Term Paper Abstract due today Homework
Beginning Modern Quantum Born s probability interpretation The indeterminacy ( uncertainty ) principle The Schroedinger equation The Copenhagen interpretation 419 Term Paper Abstract due today Homework
Decoherence and The Collapse of Quantum Mechanics. A Modern View
 Decoherence and The Collapse of Quantum Mechanics A Modern View It s time to make decoherence mainstream QM is ~90 years old But it is still taught like the 1930s Modern textbooks still ignore measurement
Decoherence and The Collapse of Quantum Mechanics A Modern View It s time to make decoherence mainstream QM is ~90 years old But it is still taught like the 1930s Modern textbooks still ignore measurement
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy. Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case:
 The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
The Schrodinger Equation and Postulates Common operators in QM: Potential Energy Often depends on position operator: Kinetic Energy 1-D case: 3-D case Time Total energy = Hamiltonian To find out about
Modern Physics notes Paul Fendley Lecture 3
 Modern Physics notes Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 3 Electron Wavelength Probability Amplitude Which slit? Photons Born, IV.4 Feynman, 1.6-7, 2.1 Fowler, Rays and Particles The wavelength of
Modern Physics notes Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 3 Electron Wavelength Probability Amplitude Which slit? Photons Born, IV.4 Feynman, 1.6-7, 2.1 Fowler, Rays and Particles The wavelength of
j=1 u 1jv 1j. 1/ 2 Lemma 1. An orthogonal set of vectors must be linearly independent.
 Lecture Notes: Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong taoyf@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Orthogonal Matrix Definition. Let u = [u
Lecture Notes: Orthogonal and Symmetric Matrices Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong taoyf@cse.cuhk.edu.hk Orthogonal Matrix Definition. Let u = [u
High-Resolution. Transmission. Electron Microscopy
 Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
Part 4 High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy 186 Significance high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM): resolve object details smaller than 1nm (10 9 m) image the interior of
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Compact Course on Linear Algebra. Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Compact Course on Linear Algebra Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello Vectors Arrays of numbers Vectors represent a point
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Compact Course on Linear Algebra Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello Vectors Arrays of numbers Vectors represent a point
 The Transactional Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics http://www.npl.washington.edu/ti John G. Cramer John G. Cramer Professor of Physics Department of Physics University of Washington Seattle, Washington,
The Transactional Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics http://www.npl.washington.edu/ti John G. Cramer John G. Cramer Professor of Physics Department of Physics University of Washington Seattle, Washington,
Pure Quantum States Are Fundamental, Mixtures (Composite States) Are Mathematical Constructions: An Argument Using Algorithmic Information Theory
 Pure Quantum States Are Fundamental, Mixtures (Composite States) Are Mathematical Constructions: An Argument Using Algorithmic Information Theory Vladik Kreinovich and Luc Longpré Department of Computer
Pure Quantum States Are Fundamental, Mixtures (Composite States) Are Mathematical Constructions: An Argument Using Algorithmic Information Theory Vladik Kreinovich and Luc Longpré Department of Computer
Wave properties of matter & Quantum mechanics I. Chapter 5
 Wave properties of matter & Quantum mechanics I Chapter 5 X-ray diffraction Max von Laue suggested that if x-rays were a form of electromagnetic radiation, interference effects should be observed. Crystals
Wave properties of matter & Quantum mechanics I Chapter 5 X-ray diffraction Max von Laue suggested that if x-rays were a form of electromagnetic radiation, interference effects should be observed. Crystals
Mobile Robotics 1. A Compact Course on Linear Algebra. Giorgio Grisetti
 Mobile Robotics 1 A Compact Course on Linear Algebra Giorgio Grisetti SA-1 Vectors Arrays of numbers They represent a point in a n dimensional space 2 Vectors: Scalar Product Scalar-Vector Product Changes
Mobile Robotics 1 A Compact Course on Linear Algebra Giorgio Grisetti SA-1 Vectors Arrays of numbers They represent a point in a n dimensional space 2 Vectors: Scalar Product Scalar-Vector Product Changes
Topic 2: The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thin
 The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
The mathematical formalism and the standard way of thinking about it http://www.wuthrich.net/ MA Seminar: Philosophy of Physics Vectors and vector spaces Vectors and vector spaces Operators Albert, Quantum
Elementary maths for GMT
 Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 2: Matrices, Elimination and Determinant m n matrices The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1
Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 2: Matrices, Elimination and Determinant m n matrices The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701
 Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/10//2017 Outline 1 One Particle Wave Function Space F 2 One Particle Wave Function Space F One Particle Wave Function Space F The set of square-integrable
Quantum Mechanics I Physics 5701 Z. E. Meziani 02/10//2017 Outline 1 One Particle Wave Function Space F 2 One Particle Wave Function Space F One Particle Wave Function Space F The set of square-integrable
Introduction to Bell s theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics
 Introduction to Bells theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics Jia Wang Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, 930 N. University Ave., Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (Received November 30,
Introduction to Bells theorem: the theory that solidified quantum mechanics Jia Wang Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, 930 N. University Ave., Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (Received November 30,
On a proposal for Quantum Signalling
 On a proposal for Quantum Signalling Padmanabhan Murali Pune, India pmurali1000@gmail.com Ver1 : 21st Nov 2015 Abstract Present understanding of non-possibility of Quantum communication rests on analysis
On a proposal for Quantum Signalling Padmanabhan Murali Pune, India pmurali1000@gmail.com Ver1 : 21st Nov 2015 Abstract Present understanding of non-possibility of Quantum communication rests on analysis
Decoherence in QM physics 491 fall 2009 friday feature M. Gold updated Oct. 1, 2015
 diffraction experiment Decoherence in QM physics 491 fall 2009 friday feature M. Gold updated Oct. 1, 2015 In reality, it contains the only mystery, the basic peculiarities of all of quantum mechanics.
diffraction experiment Decoherence in QM physics 491 fall 2009 friday feature M. Gold updated Oct. 1, 2015 In reality, it contains the only mystery, the basic peculiarities of all of quantum mechanics.
Q8 Lecture. State of Quantum Mechanics EPR Paradox Bell s Thm. Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1
 Physics 56: Lecture Q8 Lecture State of Quantum Mechanics EPR Paradox Bell s Thm Physics 01: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Question Richard Feynman said, [the double-slit experiment] has in it the heart of quantum mechanics;
Physics 56: Lecture Q8 Lecture State of Quantum Mechanics EPR Paradox Bell s Thm Physics 01: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Question Richard Feynman said, [the double-slit experiment] has in it the heart of quantum mechanics;
THE DELAYED CHOICE QUANTUM EXPERIMENT
 Project optic physics 2008 Professor: Andres La Rosa THE DELAYED CHOICE QUANTUM EXPERIMENT by THOMAS BENJAMIN 1 st of June, 2008 1 Introduction The delayed choice quantum experiment, and electron coupling.
Project optic physics 2008 Professor: Andres La Rosa THE DELAYED CHOICE QUANTUM EXPERIMENT by THOMAS BENJAMIN 1 st of June, 2008 1 Introduction The delayed choice quantum experiment, and electron coupling.
Physics General Physics II. Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter Wave Optics. Fall 2015 Semester Prof.
 Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
Physics 21900 General Physics II Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Lecture 20 Chapter 23.1-2 Wave Optics Fall 2015 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones Announcement Exam #2 will be on Thursday, November 5 th (tomorrow)
Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012
 PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
PHYS 20602 Handout 1 Vector Spaces for Quantum Mechanics J. P. Leahy January 30, 2012 Handout Contents Examples Classes Examples for Lectures 1 to 4 (with hints at end) Definitions of groups and vector
Mathematical foundations - linear algebra
 Mathematical foundations - linear algebra Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Vector space Definition (over reals) A set X is called a vector space over IR if addition and scalar
Mathematical foundations - linear algebra Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Vector space Definition (over reals) A set X is called a vector space over IR if addition and scalar
Kernel Method: Data Analysis with Positive Definite Kernels
 Kernel Method: Data Analysis with Positive Definite Kernels 2. Positive Definite Kernel and Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space Kenji Fukumizu The Institute of Statistical Mathematics. Graduate University
Kernel Method: Data Analysis with Positive Definite Kernels 2. Positive Definite Kernel and Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space Kenji Fukumizu The Institute of Statistical Mathematics. Graduate University
1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box
 1 OF 5 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider a particle of mass m confined to an infinite one-dimensional well of width L. The potential is given by V (x) = V 0 x L/2, V (x) =
1 OF 5 1 1D Schrödinger equation: Particle in an infinite box Consider a particle of mass m confined to an infinite one-dimensional well of width L. The potential is given by V (x) = V 0 x L/2, V (x) =
Double slit questions
 1) How does the intensity pattern on the screen look for an experiment with light and classical particles respectively? Similarities and differences? Intensity Double slit questions Intensity 1) How does
1) How does the intensity pattern on the screen look for an experiment with light and classical particles respectively? Similarities and differences? Intensity Double slit questions Intensity 1) How does
Comparing quantum and classical correlations in a quantum eraser
 Comparing quantum and classical correlations in a quantum eraser A. Gogo, W. D. Snyder, and M. Beck* Department of Physics, Whitman College, Walla Walla, Washington 99362, USA Received 14 February 2005;
Comparing quantum and classical correlations in a quantum eraser A. Gogo, W. D. Snyder, and M. Beck* Department of Physics, Whitman College, Walla Walla, Washington 99362, USA Received 14 February 2005;
QFT. Unit 1: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
 QFT Unit 1: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics What s QFT? Relativity deals with things that are fast Quantum mechanics deals with things that are small QFT deals with things that are both small and fast What
QFT Unit 1: Relativistic Quantum Mechanics What s QFT? Relativity deals with things that are fast Quantum mechanics deals with things that are small QFT deals with things that are both small and fast What
Linear Algebra II. 7 Inner product spaces. Notes 7 16th December Inner products and orthonormal bases
 MTH6140 Linear Algebra II Notes 7 16th December 2010 7 Inner product spaces Ordinary Euclidean space is a 3-dimensional vector space over R, but it is more than that: the extra geometric structure (lengths,
MTH6140 Linear Algebra II Notes 7 16th December 2010 7 Inner product spaces Ordinary Euclidean space is a 3-dimensional vector space over R, but it is more than that: the extra geometric structure (lengths,
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS. Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5
 BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
BASICS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 Reading: QM Course packet Ch 5 Interesting things happen when electrons are confined to small regions of space (few nm). For one thing, they can behave as if they are in an
Linear Algebra Review. Vectors
 Linear Algebra Review 9/4/7 Linear Algebra Review By Tim K. Marks UCSD Borrows heavily from: Jana Kosecka http://cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka/cs682.html Virginia de Sa (UCSD) Cogsci 8F Linear Algebra review Vectors
Linear Algebra Review 9/4/7 Linear Algebra Review By Tim K. Marks UCSD Borrows heavily from: Jana Kosecka http://cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka/cs682.html Virginia de Sa (UCSD) Cogsci 8F Linear Algebra review Vectors
5. Orthogonal matrices
 L Vandenberghe EE133A (Spring 2017) 5 Orthogonal matrices matrices with orthonormal columns orthogonal matrices tall matrices with orthonormal columns complex matrices with orthonormal columns 5-1 Orthonormal
L Vandenberghe EE133A (Spring 2017) 5 Orthogonal matrices matrices with orthonormal columns orthogonal matrices tall matrices with orthonormal columns complex matrices with orthonormal columns 5-1 Orthonormal
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers. David Miller
 Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector space Vector space We need a space in which our vectors exist
Quantum Mechanics for Scientists and Engineers David Miller Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector spaces, operators and matrices Vector space Vector space We need a space in which our vectors exist
Postulates and Theorems of Quantum Mechanics
 Postulates and Theorems of Quantum Mechanics Literally, a postulate is something taen as self-evident or assumed without proof as a basis for reasoning. It is simply is Postulate 1: State of a physical
Postulates and Theorems of Quantum Mechanics Literally, a postulate is something taen as self-evident or assumed without proof as a basis for reasoning. It is simply is Postulate 1: State of a physical
On a proposal for Quantum Signalling
 On a proposal for Quantum Signalling Padmanabhan Murali Pune, India pmurali1000@gmail.com Ver1 : 21st Nov 2015 Abstract Present understanding of non-possibility of Quantum communication rests on analysis
On a proposal for Quantum Signalling Padmanabhan Murali Pune, India pmurali1000@gmail.com Ver1 : 21st Nov 2015 Abstract Present understanding of non-possibility of Quantum communication rests on analysis
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM COMPUTING
 INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM COMPUTING Writen by: Eleanor Rieffel and Wolfgang Polak Presented by: Anthony Luaders OUTLINE: Introduction Notation Experiment Quantum Bit Quantum Key Distribution Multiple Qubits
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM COMPUTING Writen by: Eleanor Rieffel and Wolfgang Polak Presented by: Anthony Luaders OUTLINE: Introduction Notation Experiment Quantum Bit Quantum Key Distribution Multiple Qubits
2 The Failure of Classical Mechanics and Wave-Particle Duality
 2 The Failure of Classical Mechanics and Wave-Particle Duality This lecture is more qualitative than the rest of the class. Very roughly speaking, in Classical Mechanics, one can describe motion in terms
2 The Failure of Classical Mechanics and Wave-Particle Duality This lecture is more qualitative than the rest of the class. Very roughly speaking, in Classical Mechanics, one can describe motion in terms
Quantum Optics and Quantum Information Laboratory
 Quantum Optics and Quantum Information Laboratory OPT 253, Fall 2011 Institute of Optics University of Rochester Instructor: Dr. Lukishova Jonathan Papa Contents Lab 1: Entanglement and Bell s Inequalities
Quantum Optics and Quantum Information Laboratory OPT 253, Fall 2011 Institute of Optics University of Rochester Instructor: Dr. Lukishova Jonathan Papa Contents Lab 1: Entanglement and Bell s Inequalities
Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation
 Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
Chapter 3 Quantum Gates, Circuits & Teleportation Unitary Operators The third postulate of quantum physics states that the evolution of a quantum system is necessarily unitary. Geometrically, a unitary
3 a 21 a a 2N. 3 a 21 a a 2M
 APPENDIX: MATHEMATICS REVIEW G 12.1.1 Matrices and Vectors Definition of Matrix. An MxN matrix A is a two-dimensional array of numbers 2 A = 6 4 a 11 a 12... a 1N a 21 a 22... a 2N. 7..... 5 a M1 a M2...
APPENDIX: MATHEMATICS REVIEW G 12.1.1 Matrices and Vectors Definition of Matrix. An MxN matrix A is a two-dimensional array of numbers 2 A = 6 4 a 11 a 12... a 1N a 21 a 22... a 2N. 7..... 5 a M1 a M2...
Quantum Measurements: some technical background
 Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
Quantum Measurements: some technical background [From the projection postulate to density matrices & (introduction to) von Neumann measurements] (AKA: the boring lecture) First: One more example I wanted
Lecture Notes 1: Vector spaces
 Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 1: Vector spaces In this chapter we review certain basic concepts of linear algebra, highlighting their application to signal processing. 1 Vector
Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 1: Vector spaces In this chapter we review certain basic concepts of linear algebra, highlighting their application to signal processing. 1 Vector
