Tracer dispersion of non-newtonian uids in a Hele Shaw cell
|
|
|
- Alexina Shaw
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Physica A 327 (2003) Tracer dispersion of non-newtonian uids in a Hele Shaw cell A. Boschan a;, V.J. Charette a, S. Gabbanelli b, I. Ippolito a, R. Chertco a a Grupo de Medios Porosos, Facultad Ingeniera, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Paseo Colon 850, 1063, Buenos Aires, Argentina b Depto. de Matematica, Facultad Ingeniera, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Paseo Colon 850, 1063, Buenos Aires, Argentina Abstract We report here a study of the transport and tracer dispersion properties of uids in a model of fractured media. The tracer dispersion process was analyzed using Newtonian and non-newtonian uids (polymeric solutions). Experiments were carried out in a Hele Shaw cell using axial ow and dyes as tracers. We analyze the inuence of polymers presenting shear-thinning characteristics onthe dispersionproperties. It was found that the dispersioncoecient decreases when polymer concentration increases. c 2003 Published by Elsevier B.V. PACS: d; Ji; w Keywords: Dispersion; Fracture; Non-Newtonian 1. Introduction Polymers are of interest in several applications such as oil recovery, chemical engineering and others [1]. The aim of this work is to study tracer dispersionfor both Newtonian and non-newtonian ows. We have used shear-thinning polymers, that, compared to Newtonian uids, provide a higher contrast between large and small ow channels [2]. Tracer dispersion corresponds to the spreading of an initially localized tracer concentration distribution due to the combined eects of molecular diusion and Corresponding author. address: abosch@.uba.ar (A. Boschan) /03/$ - see front matter c 2003 Published by Elsevier B.V. doi: /s (03)
2 50 A. Boschan et al. / Physica A 327 (2003) the velocity eld of the ow. Inhomogeneous systems, the variationof the tracer concentration C satises the classical macroscopic advection diusionequation[3]: 9C + U 9C 9t 9x = K 9 2 C g 9x 2 ; (1) where U is the meanow velocity and K g the longitudinal dispersion coecient (where we have neglected the transverse dispersion). For x = L (L is the size of the sample) the solutionof Eq. (1) is [ ( C(L; t)= 1 1 erf 2 L Ut 2 K g t )] : (2) Solution(2) corresponds to a Gaussian tracer dispersion. The variation of the longitudinal dispersioncoecient with the meanvelocity for a ow betweentwo parallel at plates is [4] K g = D m + d2 U 2 210D m ; K g D m =1+ Pe2 210 ; (3) where d is the distance between plates, and D m is the molecular diusioncoecient (a similar result was earlier found by Taylor Aris [5] for a capillary tube). Inthe Newtonian case the velocity prole corresponds to Poiseuille ow while for non-newtonian uids the prole is plug-like [6]. Inthe last case, the coecient of dispersioncanbe obtained analytically (A. Boschan, Tesis de Licenciatura en Fisica, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires, 2002) K g = U 2 d 2 4D m n 2 (n +1) 2 (2n +1)n + (3n + 1)(5n +2) [ 1 6 n 2 2n +1 2(4n +1) (3n + 1)(4n +1) ] ; (4) where n is the ow index of the uid which characterizes the rheological properties. Replacing n = 1 ineq. (4) wendeq.(3). 2. Experimental setup The Hele Shaw cell was constructed using two rectangular and parallel at glass plates (35 cm 20 cm 1 cm). Two mylard strips (35 cm 4cm 0:0375 cm) that separate the plates (d = 0:0375 cm) are placed over the longest sides allowing to establish anaxial ow inthe cell (Fig. 1). The cell is mounted inanaluminum frame and sealed with silicone glue to avoid losses. Two 3-point acrylic distributors allow to inject (drain) the uids. They are placed at the enter (injection) and the exit (drainage) of the cell. A CCD camera (Coolsnap CF, monochrome, 4095 gray levels) is placed at 1 m around on the top of the cell getting full view, while four uorescent tubes provide required illumination through a white acrylic (2 mm-thick) light diusor (Fig. 1). The aqueous solutions used during the experiments were glycerol 10% for the Newtonian experiments and xanthan (with dierent concentrations) for the non-newtonian
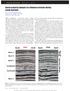
3 A. Boschan et al. / Physica A 327 (2003) CCD camera Cell Injection CCD Uniform illumination Drain Lateral guide Light diffusor Light tubes Reflecting surface Laterals Lateral guide Fig. 1. Left: Hele Shaw cell. The dyed uid (tracer) displaces the transparent uid while the camera captures the intensity variation in all the cells. Right: Scheme of the illumination system. experiments. WaterBlue (0:4 g=l) was used as a tracer for both type of experiments to color the corresponding uid. Densities were matched in all cases adding ClNa (0:4 g=l) to the transparent uid in order to avoid gravity-driven instabilities. For each experience the cell is rst lled with transparent uid. Then the distributor chamber is lled with colored uid (step-like initial condition for the tracer concentration). An experiment begins when the tracer is pumped at constant ow rate while the camera acquires images at a xed time interval (given by a digital timer) proportional to the experiment duration. The mixing zone advances while it spreads from the enter (injection distributor) to the exit of the cell. The acquisition ends when the mixing zone reaches the exit. Flow rate was varied from to 3:6 cm 3 =seg, and the corresponding Pe values were between 50 and The viscosity of the polymeric solutions used in our experiments decreases with the shear rate (shear-thinning characteristic) except for very high or low shear rates, where the viscosity is constant. The behavior in the intermediate zone can be described with the power law model = k n 1 ; where n is the ow index, is the viscosity, k is the consistence of the uid and the shear rate. We have characterized the rheological behavior of the two polymeric solutions used, obtaining ow indexes n = 0:55 and 0.65 for the highest and lowest concentrations, respectively. 3. Image processing and data analysis For each experiment we obtain a time sequence of 250 images ( pixels) which are stored ina multilayer TiFF le. The time interval betweenimages varies from 1 to 60 s according to the ow rate. The variation between maximum and minimum gray-level value is approximately The gray level is proportional to the light intensity. To obtain the spatiotemporal intensity diagram we take a given longitudinal slice of the cell image and we examine the time evolution over the 250 images. The vertical axis infig. 2 represents this time variation. From this diagram the intensity vs. time curves were obtained for 20 longitudinal positions along the cell. A calibration of the tracer concentration and the intensity (or gray level) was performed and comparing
4 52 A. Boschan et al. / Physica A 327 (2003) Fig. 2. Left: Spatiotemporal diagram. The dashed line shows how intensity curve is obtained for one longitudinal position in cell. Right: Concentration proles for dierent positions along the cell (Pe 360). to the Lambert Beer law, we have found a linear variation [7]. Inthis way we compute the curves of tracer concentration as a function of time (Fig. 2). The uniformity of the cell thickness was veried by measuring the intensity at dierent positions in the cell for a givenconcentration(the precisionis givenby the camera noise: 3%). These curves are well tted by Eq. (2). From the ttings, we compute the mean transit time T 0 and the meantime square deviationof the distributions. For a givenpe number, inall experiments T 0 varies linearly with the measuring positions indicating that the meanow velocity is constant. The meansquare deviationis related to the coecient of dispersionas follows [8]: t 2 =2 K g U 2 T 0 : (5) Then, we calculate K g from the slope of the curves t 2 vs T 0 for each Pe value. 4. Experimental results InFig. 3, we have plotted the variationof K g =D m as a function of the Pe number for Newtonian (n = 1) and non-newtonian uids with n =0:55 and The coecient of dispersionhas beennormalized by molecular diusion(d m = 2: cm 2 =s). Let us discuss rst the variationof K g =D m for experiments performed with Newtoniansolutions. We have superimposed predictiongivenby Eq. (3) as a reference. We can observe that the dimensionless dispersion coecient increases quadratically with the Pe number according with Golay [4] and Taylor Aris [5]. So we can say that this experimental technique represents an excellent tool to study tracer dispersioninthis geometry. For the non-newtonianuids the dispersioncoecient also increases proportionally to Pe 2 for both n values. The analytical predictions for the non-newtonian case, Eq. (4), are in quite good agreement with the experimental results. On the other hand, we can observe that the non-newtonian K g =D m values are smaller thannewtonianones. Evenmore, for a givenpe number, K g =D m decreases as the ow index n decreases. We think that this is due to the gradual attening of the velocity prole (parabolic for Newtonian ow and plug-like prole for non-newtonian ows) as the ow index decreases.
5 A. Boschan et al. / Physica A 327 (2003) Fig. 3. Normalized coecient of dispersion for Newtonian and non-newtonian uids. Only data points attaining Taylor regime are shown. 5. Conclusions The developed experimental technique is very useful to characterize tracer dispersion. In all cases the dispersion coecients for non-newtonian uids are smaller than for Newtonian ones. This behavior is contrary to what was observed in porous media: The dispersion coecients in the non-newtonian case are larger (shear-thinning uids) than inthe Newtoniancase [2]. The dierence is essentially due to the variations in the local velocities related to the geometry of the systems. Inorder to study that inmore detail numerical simulations are in progress. Acknowledgements This work was partially supported by Fundacion Antorchas, U.B.A PB-IO49 and the cooperationprograms PICS CNRS 561 and ECOS SUD E03-A97. References [1] F.A.L. Dullien, Porous Media, Fluids Transport and Pore Structure, Academic Press, New York, [2] A. D Onofrio, Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. de Paris VI, Univ. Buenos Aires, [3] J. Bear, Dynamics of Fluids inporous Media, AmericanElsevier, New York, [4] M.J.E. Golay, in: D.H. Destye (Ed.), Gas Chromatography, Butterworths, London, [5] R. Aris, Onthe dispersionof solute ina uid owing through a tube, Proc. Roy. Soc. LondonA 235, [6] K.S. Sorbie, Polymer-Improved Oil Recovery, Blackie, London, [7] A. Boschan, Tesis de Licenciatura en Fsica, FCEN, Universidad de Buenos Aires, [8] J. Koplik, Hydrodynamic dispersion in random networks, in: Disorder and Mixing, Serie E, Kluwer Academics Publishers, Dordrecht, 1987, pp
On the effects of Non-Newtonian fluids above the ribbing instability
 On the effects of Non-Newtonian fluids above the ribbing instability L. Pauchard, F. Varela LÓpez*, M. Rosen*, C. Allain, P. Perrot** and M. Rabaud Laboratoire FAST, Bât. 502, Campus Universitaire, 91405
On the effects of Non-Newtonian fluids above the ribbing instability L. Pauchard, F. Varela LÓpez*, M. Rosen*, C. Allain, P. Perrot** and M. Rabaud Laboratoire FAST, Bât. 502, Campus Universitaire, 91405
2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography survey optimisation of solute transport in porous media
 ArcheoSciences Revue d'archéométrie 33 (suppl.) 2009 Mémoire du sol, espace des hommes 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography survey optimisation of solute transport in porous media Gregory Lekmine, Marc
ArcheoSciences Revue d'archéométrie 33 (suppl.) 2009 Mémoire du sol, espace des hommes 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography survey optimisation of solute transport in porous media Gregory Lekmine, Marc
PARALLEL PSEUDO-SPECTRAL SIMULATIONS OF NONLINEAR VISCOUS FINGERING IN MIS- Center for Parallel Computations, COPPE / Federal University of Rio de
 PARALLEL PSEUDO-SPECTRAL SIMULATIONS OF NONLINEAR VISCOUS FINGERING IN MIS- CIBLE DISPLACEMENTS N. Mangiavacchi, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, N.F.F. Ebecken Center for Parallel Computations, COPPE / Federal University
PARALLEL PSEUDO-SPECTRAL SIMULATIONS OF NONLINEAR VISCOUS FINGERING IN MIS- CIBLE DISPLACEMENTS N. Mangiavacchi, A.L.G.A. Coutinho, N.F.F. Ebecken Center for Parallel Computations, COPPE / Federal University
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
Synchronizationinanarray of globally coupled maps with delayed interactions
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physica A 325 (2003) 186 191 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Synchronizationinanarray of globally coupled maps with delayed interactions Cristina Masoller a;, Arturo
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physica A 325 (2003) 186 191 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Synchronizationinanarray of globally coupled maps with delayed interactions Cristina Masoller a;, Arturo
6.1 Steady, One-Dimensional Rectilinear Flows Steady, Spherically Symmetric Radial Flows 42
 Contents 6 UNIDIRECTIONAL FLOWS 1 6.1 Steady, One-Dimensional Rectilinear Flows 6. Steady, Axisymmetric Rectilinear Flows 19 6.3 Steady, Axisymmetric Torsional Flows 8 6.4 Steady, Axisymmetric Radial Flows
Contents 6 UNIDIRECTIONAL FLOWS 1 6.1 Steady, One-Dimensional Rectilinear Flows 6. Steady, Axisymmetric Rectilinear Flows 19 6.3 Steady, Axisymmetric Torsional Flows 8 6.4 Steady, Axisymmetric Radial Flows
FOAM DRAINAGE part 3
 FOAM DRAINAGE part 3 gas effect : coupling coarsening and drainage () C 2 F 6 :almost «insoluble», so no coarsening N 2 : much more soluble, significantly faster coarsening Free-drainage, liquid fraction
FOAM DRAINAGE part 3 gas effect : coupling coarsening and drainage () C 2 F 6 :almost «insoluble», so no coarsening N 2 : much more soluble, significantly faster coarsening Free-drainage, liquid fraction
Spray formation with complex fluids
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Spray formation with complex fluids To cite this article: S Lustig and M Rosen 2011 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 296 012019 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Spray formation with complex fluids To cite this article: S Lustig and M Rosen 2011 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 296 012019 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
Studies on dispersive stabilization of porous media flows
 Studies on dispersive stabilization of porous media flows Prabir Daripa and Craig Gin Citation: Physics of Fluids 28, 082105 2016); doi: 10.1063/1.4961162 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4961162
Studies on dispersive stabilization of porous media flows Prabir Daripa and Craig Gin Citation: Physics of Fluids 28, 082105 2016); doi: 10.1063/1.4961162 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4961162
MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT
 MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT Osamah A. Al-Omair and Richard L. Christiansen Petroleum Engineering Department, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT A
MEASUREMENT OF CAPILLARY PRESSURE BY DIRECT VISUALIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGE EXPERIMENT Osamah A. Al-Omair and Richard L. Christiansen Petroleum Engineering Department, Colorado School of Mines ABSTRACT A
Threshold of ribbing instability with Non-Newtonian fluids
 Threshold of ribbing instability with Non-Newtonian fluids F. Varela López*, L. Pauchard, M. Rosen* and M. Rabaud Laboratoire FAST, Bât. 502, Campus Universitaire, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France * Grupo Medios
Threshold of ribbing instability with Non-Newtonian fluids F. Varela López*, L. Pauchard, M. Rosen* and M. Rabaud Laboratoire FAST, Bât. 502, Campus Universitaire, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France * Grupo Medios
Time dependence and local structure of tracer dispersion in oscillating liquid Hele-Shaw flows
 Time dependence and local structure of tracer dispersion in oscillating liquid Hele-Shaw flows Yanina Lucrecia Roth, Harold Auradou, Jean Pierre Hulin, Dominique Salin, Ricardo Chertcoff, Irene Ippolito
Time dependence and local structure of tracer dispersion in oscillating liquid Hele-Shaw flows Yanina Lucrecia Roth, Harold Auradou, Jean Pierre Hulin, Dominique Salin, Ricardo Chertcoff, Irene Ippolito
Linear stability of radial displacements in porous media: Influence of velocity-induced dispersion and concentration-dependent diffusion
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 16, NUMBER 10 OCTOBER 2004 Linear stability of radial displacements in porous media: Influence of velocity-induced dispersion and concentration-dependent diffusion A. Riaz Department
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 16, NUMBER 10 OCTOBER 2004 Linear stability of radial displacements in porous media: Influence of velocity-induced dispersion and concentration-dependent diffusion A. Riaz Department
On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell
 On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell Gelu Paşa Abstract. In this paper we study the linear stability of the displacement of two incompressible Stokes fluids in a 3D
On the displacement of two immiscible Stokes fluids in a 3D Hele-Shaw cell Gelu Paşa Abstract. In this paper we study the linear stability of the displacement of two incompressible Stokes fluids in a 3D
Erratum Experimental and numerical tools for miscible fluid displacements studies in porous media with large heterogeneities
 Eur. Phys. J. AP 7, 277 289 (1999) THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL APPLIED PHYSICS c EDP Sciences 1999 Erratum Experimental and numerical tools for miscible fluid displacements studies in porous media with
Eur. Phys. J. AP 7, 277 289 (1999) THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL APPLIED PHYSICS c EDP Sciences 1999 Erratum Experimental and numerical tools for miscible fluid displacements studies in porous media with
Flow channeling in a single fracture induced by shear displacement
 Geothermics 35 (2006) 576 588 Flow channeling in a single fracture induced by shear displacement Harold Auradou a,, German Drazer b,c, Alejandro Boschan a,d, Jean-Pierre Hulin a, Joel Koplik b a Laboratoire
Geothermics 35 (2006) 576 588 Flow channeling in a single fracture induced by shear displacement Harold Auradou a,, German Drazer b,c, Alejandro Boschan a,d, Jean-Pierre Hulin a, Joel Koplik b a Laboratoire
Polymers Reactions and Polymers Production (3 rd cycle)
 EQ, Q, DEQuim, DQuim nd semester 017/018, IST-UL Science and Technology of Polymers ( nd cycle) Polymers Reactions and Polymers Production (3 rd cycle) Lecture 5 Viscosity easurements of the viscosity
EQ, Q, DEQuim, DQuim nd semester 017/018, IST-UL Science and Technology of Polymers ( nd cycle) Polymers Reactions and Polymers Production (3 rd cycle) Lecture 5 Viscosity easurements of the viscosity
Spatial moment analysis: an application to quantitative imaging of contaminant distributions in porous media
 Spatial moment analysis: an application to quantitative imaging of contaminant distributions in porous media Ombretta Paladino a,b, Marco Massabò a,b, Federico Catania a,b, Gianangelo Bracco a,c a CIMA
Spatial moment analysis: an application to quantitative imaging of contaminant distributions in porous media Ombretta Paladino a,b, Marco Massabò a,b, Federico Catania a,b, Gianangelo Bracco a,c a CIMA
Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions. G. Fibich. University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics ABSTRACT
 Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions G. Fibich University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics Los-Angeles, CA 90095 ABSTRACT Time dispersion plays an important role in the propagation
Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions G. Fibich University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics Los-Angeles, CA 90095 ABSTRACT Time dispersion plays an important role in the propagation
Heat and Mass Transfer over Cooled Horizontal Tubes 333 x-component of the velocity: y2 u = g sin x y : (4) r 2 The y-component of the velocity eld is
 Scientia Iranica, Vol., No. 4, pp 332{338 c Sharif University of Technology, October 2004 Vapor Absorption into Liquid Films Flowing over a Column of Cooled Horizontal Tubes B. Farhanieh and F. Babadi
Scientia Iranica, Vol., No. 4, pp 332{338 c Sharif University of Technology, October 2004 Vapor Absorption into Liquid Films Flowing over a Column of Cooled Horizontal Tubes B. Farhanieh and F. Babadi
EFFECT OF CHANNEL BENDS ON TRANSVERSE MIXING
 NIJOTECH VOL. 10. NO. 1 SEPTEMBER 1986 ENGMANN 57 EFFECT OF CHANNEL BENDS ON TRANSVERSE MIXING BY E. O. ENGMANN ABSTRACT Velocity and tracer concentration measurements made in a meandering channel are
NIJOTECH VOL. 10. NO. 1 SEPTEMBER 1986 ENGMANN 57 EFFECT OF CHANNEL BENDS ON TRANSVERSE MIXING BY E. O. ENGMANN ABSTRACT Velocity and tracer concentration measurements made in a meandering channel are
Growth activity during fingering in a porous Hele-Shaw cell
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 70, 026301 (2004) Growth activity during fingering in a porous Hele-Shaw cell Grunde Løvoll, 1,2 Yves Méheust, 3,2,1 Renaud Toussaint, 1,3 Jean Schmittbuhl, 2 and Knut Jørgen Måløy 1
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 70, 026301 (2004) Growth activity during fingering in a porous Hele-Shaw cell Grunde Løvoll, 1,2 Yves Méheust, 3,2,1 Renaud Toussaint, 1,3 Jean Schmittbuhl, 2 and Knut Jørgen Måløy 1
Ordering periodic spatial structures by non-equilibrium uctuations
 Physica A 277 (2000) 327 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Ordering periodic spatial structures by non-equilibrium uctuations J.M.G. Vilar a;, J.M. Rub b a Departament de F sica Fonamental, Facultat de
Physica A 277 (2000) 327 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Ordering periodic spatial structures by non-equilibrium uctuations J.M.G. Vilar a;, J.M. Rub b a Departament de F sica Fonamental, Facultat de
Contents. Microfluidics - Jens Ducrée Physics: Laminar and Turbulent Flow 1
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Viscous Fluids. Amanda Meier. December 14th, 2011
 Viscous Fluids Amanda Meier December 14th, 2011 Abstract Fluids are represented by continuous media described by mass density, velocity and pressure. An Eulerian description of uids focuses on the transport
Viscous Fluids Amanda Meier December 14th, 2011 Abstract Fluids are represented by continuous media described by mass density, velocity and pressure. An Eulerian description of uids focuses on the transport
2 Dissipative particle dynamics with energy conservation: Heat conduction that is dissipated due to the velocity dependent forces is transformed into
 International Journal of Modern Physics C, fc World Scientic Publishing Company DISSIPATIVE PARTICLE DYNAMICS WITH ENERGY CONSERVATION: HEAT CONDUCTION M. RIPOLL, P. ESPA ~NOL Departamento de Fsica Fundamental,
International Journal of Modern Physics C, fc World Scientic Publishing Company DISSIPATIVE PARTICLE DYNAMICS WITH ENERGY CONSERVATION: HEAT CONDUCTION M. RIPOLL, P. ESPA ~NOL Departamento de Fsica Fundamental,
Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media
 1 Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media Rennes September 16, 2009 Eyvind Aker Morten Grøva Henning Arendt Knudsen Thomas Ramstad Bo-Sture Skagerstam Glenn Tørå Alex Hansen 2 Declining oil production,
1 Complexity of Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media Rennes September 16, 2009 Eyvind Aker Morten Grøva Henning Arendt Knudsen Thomas Ramstad Bo-Sture Skagerstam Glenn Tørå Alex Hansen 2 Declining oil production,
Modern Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery
 Modern Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery Theory and Practice James J. Sheng, Ph. D. AMSTERDAM BOSTON «HEIDELBERG LONDON ELSEVIER NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Gulf Professional
Modern Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery Theory and Practice James J. Sheng, Ph. D. AMSTERDAM BOSTON «HEIDELBERG LONDON ELSEVIER NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Gulf Professional
Anumerical and analytical study of the free convection thermal boundary layer or wall jet at
 REVERSED FLOW CALCULATIONS OF HIGH PRANDTL NUMBER THERMAL BOUNDARY LAYER SEPARATION 1 J. T. Ratnanather and P. G. Daniels Department of Mathematics City University London, England, EC1V HB ABSTRACT Anumerical
REVERSED FLOW CALCULATIONS OF HIGH PRANDTL NUMBER THERMAL BOUNDARY LAYER SEPARATION 1 J. T. Ratnanather and P. G. Daniels Department of Mathematics City University London, England, EC1V HB ABSTRACT Anumerical
Inlet Grid Block! Standard Grid Blocks Outlet Grid Point r Center of Rotation Equilibrium Grid Point Outlet Grid Block Figure 1 The Finite Dierence Gr
 THE CONSTANTLY-ACCELERATING CENTRIFUGE REVISITED by Douglas Ruth University ofmanitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Abstract SCA9812 In 1963, Homan described the use of a constantly-accelerating centrifuge
THE CONSTANTLY-ACCELERATING CENTRIFUGE REVISITED by Douglas Ruth University ofmanitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Abstract SCA9812 In 1963, Homan described the use of a constantly-accelerating centrifuge
Dynamics that trigger/inhibit cluster formation in a one-dimensional granular gas
 Physica A 342 (24) 62 68 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Dynamics that trigger/inhibit cluster formation in a one-dimensional granular gas Jose Miguel Pasini a;1, Patricio Cordero b; ;2 a Department of Theoretical
Physica A 342 (24) 62 68 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Dynamics that trigger/inhibit cluster formation in a one-dimensional granular gas Jose Miguel Pasini a;1, Patricio Cordero b; ;2 a Department of Theoretical
Gas hold-up and bubble diameters in a gassed oscillatory baed column
 Chemical Engineering Science 56 (2001) 6143 6148 www.elsevier.com/locate/ces Gas hold-up and bubble diameters in a gassed oscillatory baed column M. S. N. Oliveira, X. Ni Department of Mechanical and Chemical
Chemical Engineering Science 56 (2001) 6143 6148 www.elsevier.com/locate/ces Gas hold-up and bubble diameters in a gassed oscillatory baed column M. S. N. Oliveira, X. Ni Department of Mechanical and Chemical
Radial source flows in porous media: Linear stability analysis of axial and helical perturbations in miscible displacements
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2003 Radial source flows in porous media: Linear stability analysis of axial and helical perturbations in miscible displacements Amir Riaz and Eckart Meiburg
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS VOLUME 15, NUMBER 4 APRIL 2003 Radial source flows in porous media: Linear stability analysis of axial and helical perturbations in miscible displacements Amir Riaz and Eckart Meiburg
CHARACTERIZATION OF HETEROGENEITIES AT THE CORE-SCALE USING THE EQUIVALENT STRATIFIED POROUS MEDIUM APPROACH
 SCA006-49 /6 CHARACTERIZATION OF HETEROGENEITIES AT THE CORE-SCALE USING THE EQUIVALENT STRATIFIED POROUS MEDIUM APPROACH Mostafa FOURAR LEMTA Ecole des Mines de Nancy, Parc de Saurupt, 54 04 Nancy, France
SCA006-49 /6 CHARACTERIZATION OF HETEROGENEITIES AT THE CORE-SCALE USING THE EQUIVALENT STRATIFIED POROUS MEDIUM APPROACH Mostafa FOURAR LEMTA Ecole des Mines de Nancy, Parc de Saurupt, 54 04 Nancy, France
Steady-state, simultaneous two-phase flow in porous media: experiment and simulation
 Steady-state, simultaneous two-phase flow in porous media: experiment and simulation Ken Tore Tallakstad, 1, Grunde Løvoll, 1, Thomas Ramstad, 2, Henning Arendt Knudsen, 1 Knut Jørgen Måløy, 1 and Alex
Steady-state, simultaneous two-phase flow in porous media: experiment and simulation Ken Tore Tallakstad, 1, Grunde Løvoll, 1, Thomas Ramstad, 2, Henning Arendt Knudsen, 1 Knut Jørgen Måløy, 1 and Alex
On modeling pressure diusion. in non-homogeneous shear ows. By A. O. Demuren, 1 M. M. Rogers, 2 P. Durbin 3 AND S. K. Lele 3
 Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 1996 63 On modeling pressure diusion in non-homogeneous shear ows By A. O. Demuren, 1 M. M. Rogers, 2 P. Durbin 3 AND S. K. Lele 3 New models
Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 1996 63 On modeling pressure diusion in non-homogeneous shear ows By A. O. Demuren, 1 M. M. Rogers, 2 P. Durbin 3 AND S. K. Lele 3 New models
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
A simple model for a transverse dune eld
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physica A 327 (23) 554 562 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa A simple model for a transverse dune eld E.J.R. Parteli a;, H.J. Herrmann a;b a Institut fur Computeranwendungen,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physica A 327 (23) 554 562 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa A simple model for a transverse dune eld E.J.R. Parteli a;, H.J. Herrmann a;b a Institut fur Computeranwendungen,
Measurements of Dispersions (turbulent diffusion) Rates and Breaking up of Oil Droplets in Turbulent Flows
 Measurements of Dispersions (turbulent diffusion) Rates and Breaking up of Oil Droplets in Turbulent Flows Balaji Gopalan PI: Dr Joseph Katz Where do we come in? Turbulent diffusion of slightly buoyant
Measurements of Dispersions (turbulent diffusion) Rates and Breaking up of Oil Droplets in Turbulent Flows Balaji Gopalan PI: Dr Joseph Katz Where do we come in? Turbulent diffusion of slightly buoyant
Pressure Drop Separation during Aqueous Polymer Flow in Porous Media
 Pressure Drop Separation during Aqueous Polymer Flow in Porous Media D.C. Raharja 1*, R.E. Hincapie 1, M. Be 1, C.L. Gaol 1, L. Ganzer 1 1 Department of Reservoir Engineering, Clausthal University of Technology
Pressure Drop Separation during Aqueous Polymer Flow in Porous Media D.C. Raharja 1*, R.E. Hincapie 1, M. Be 1, C.L. Gaol 1, L. Ganzer 1 1 Department of Reservoir Engineering, Clausthal University of Technology
Gap size effects for the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in a Hele-Shaw cell
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 638 Gap size effects for the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in a Hele-Shaw cell L. Meignin, P. Ern, P. Gondret, and M. Rabaud Laboratoire Fluides, Automatique et Systèmes Thermiques,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 638 Gap size effects for the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in a Hele-Shaw cell L. Meignin, P. Ern, P. Gondret, and M. Rabaud Laboratoire Fluides, Automatique et Systèmes Thermiques,
Abstract Particle image velocimetry (PIV)
 Computation of Pressure Distribution Using PIV Velocity Data R. Gurka'l), A. Liberzon''), D. Hefet~'~), D. Rubinstein"), U. Shavit(')* 'I) Agricultural Engineering, Technion, Haifa 32000, Israel (anuri@tr.technian.ac.il)
Computation of Pressure Distribution Using PIV Velocity Data R. Gurka'l), A. Liberzon''), D. Hefet~'~), D. Rubinstein"), U. Shavit(')* 'I) Agricultural Engineering, Technion, Haifa 32000, Israel (anuri@tr.technian.ac.il)
APPENDIX Tidally induced groundwater circulation in an unconfined coastal aquifer modeled with a Hele-Shaw cell
 APPENDIX Tidally induced groundwater circulation in an unconfined coastal aquifer modeled with a Hele-Shaw cell AaronJ.Mango* Mark W. Schmeeckle* David Jon Furbish* Department of Geological Sciences, Florida
APPENDIX Tidally induced groundwater circulation in an unconfined coastal aquifer modeled with a Hele-Shaw cell AaronJ.Mango* Mark W. Schmeeckle* David Jon Furbish* Department of Geological Sciences, Florida
Shear instabilities in a tilting tube
 Abstract Shear instabilities in a tilting tube Edmund Tedford 1, Jeff Carpenter 2 and Greg Lawrence 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of British Columbia ttedford@eos.ubc.ca 2 Institute of
Abstract Shear instabilities in a tilting tube Edmund Tedford 1, Jeff Carpenter 2 and Greg Lawrence 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, University of British Columbia ttedford@eos.ubc.ca 2 Institute of
Dispersion relations for the convective instability of an acidity front in Hele-Shaw cells
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 2 8 JULY 2004 Dispersion relations for the convective instability of an acidity front in Hele-Shaw cells Desiderio A. Vasquez Department of Physics, Indiana
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 2 8 JULY 2004 Dispersion relations for the convective instability of an acidity front in Hele-Shaw cells Desiderio A. Vasquez Department of Physics, Indiana
Article published by EDP Sciences and available at or
 http://www.emath.fr/proc/vol.1/ Three-Dimensional Vorticity Dynamics in a Coowing Turbulent Jet Subjected to Axial and Azimuthal Perturbations Katherine Prestridge and Juan C. Lasheras Department of Applied
http://www.emath.fr/proc/vol.1/ Three-Dimensional Vorticity Dynamics in a Coowing Turbulent Jet Subjected to Axial and Azimuthal Perturbations Katherine Prestridge and Juan C. Lasheras Department of Applied
CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES. Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles
 CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Scientific questions Chemical reactions can induce changes in viscosity or density
CHEMICALLY-DRIVEN HYDRODYNAMIC INSTABILITIES Anne De Wit Nonlinear Physical Chemistry Unit Université Libre de Bruxelles 1 Scientific questions Chemical reactions can induce changes in viscosity or density
Viscosity of magmas containing highly deformable bubbles
 Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 105 (2001) 19±24 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jvolgeores Viscosity of magmas containing highly deformable bubbles M. Manga a, *, M. Loewenberg b a Department of
Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 105 (2001) 19±24 www.elsevier.nl/locate/jvolgeores Viscosity of magmas containing highly deformable bubbles M. Manga a, *, M. Loewenberg b a Department of
Experiments on capillary-gravity waves of solitary type on deep water
 Experiments on capillary-gravity waves of solitary type on deep water Michael Longuet-Higgins Institute for Nonlinear Science, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California 92093-0402 Xin Zhang
Experiments on capillary-gravity waves of solitary type on deep water Michael Longuet-Higgins Institute for Nonlinear Science, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California 92093-0402 Xin Zhang
On the solution of incompressible two-phase ow by a p-version discontinuous Galerkin method
 COMMUNICATIONS IN NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Commun. Numer. Meth. Engng 2006; 22:741 751 Published online 13 December 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/cnm.846
COMMUNICATIONS IN NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Commun. Numer. Meth. Engng 2006; 22:741 751 Published online 13 December 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/cnm.846
Lubrication and Journal Bearings
 UNIVERSITY OF HAIL College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Chapter 12 Lubrication and Journal Bearings Text Book : Mechanical Engineering Design, 9th Edition Dr. Badreddine AYADI 2016
UNIVERSITY OF HAIL College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Chapter 12 Lubrication and Journal Bearings Text Book : Mechanical Engineering Design, 9th Edition Dr. Badreddine AYADI 2016
Uncertainty in radon measurements with CR39 detector due to unknown deposition of Po
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 450 (2000) 568} 572 Uncertainty in radon measurements with CR39 detector due to unknown deposition of Po D. NikezicH, K.N. Yu* Department of Physics
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 450 (2000) 568} 572 Uncertainty in radon measurements with CR39 detector due to unknown deposition of Po D. NikezicH, K.N. Yu* Department of Physics
Viscosity * Desmond Schipper Andrew R. Barron. 1 Introduction
 OpenStax-CNX module: m50215 1 Viscosity * Desmond Schipper Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract This module discusses
OpenStax-CNX module: m50215 1 Viscosity * Desmond Schipper Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract This module discusses
ANALYSIS OF LOW DENSITY PARTICLES USING DIFFERENTIAL CENTRIFUGAL SEDIMENTATION
 ANALYSIS OF LOW DENSITY PARTICLES USING DIFFERENTIAL CENTRIFUGAL SEDIMENTATION Conventional Centrifugal Methods Centrifugal sedimentation of particles suspended in a fluid is a well known method (1, 2)
ANALYSIS OF LOW DENSITY PARTICLES USING DIFFERENTIAL CENTRIFUGAL SEDIMENTATION Conventional Centrifugal Methods Centrifugal sedimentation of particles suspended in a fluid is a well known method (1, 2)
Lecture 7: Rheology and milli microfluidic
 1 and milli microfluidic Introduction In this chapter, we come back to the notion of viscosity, introduced in its simplest form in the chapter 2. We saw that the deformation of a Newtonian fluid under
1 and milli microfluidic Introduction In this chapter, we come back to the notion of viscosity, introduced in its simplest form in the chapter 2. We saw that the deformation of a Newtonian fluid under
Flow interpretation implications for Poro-Elastic Modeling
 Flow interpretation implications for Poro-Elastic Modeling James K. Fulford Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center Stennis Space Center, Mississippi 39529 Email: jim.fulford@nrlssc.navy.mil Telephone:
Flow interpretation implications for Poro-Elastic Modeling James K. Fulford Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center Stennis Space Center, Mississippi 39529 Email: jim.fulford@nrlssc.navy.mil Telephone:
Rheological properties of polymer micro-gel dispersions
 294 DOI 10.1007/s12182-009-0047-3 Rheological properties of polymer micro-gel dispersions Dong Zhaoxia, Li Yahua, Lin Meiqin and Li Mingyuan Enhanced Oil Recovery Research Center, China University of Petroleum,
294 DOI 10.1007/s12182-009-0047-3 Rheological properties of polymer micro-gel dispersions Dong Zhaoxia, Li Yahua, Lin Meiqin and Li Mingyuan Enhanced Oil Recovery Research Center, China University of Petroleum,
SCA : A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP
 SCA2003-53: A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
SCA2003-53: A STRUCTURAL MODEL TO PREDICT TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF GRANULAR POROUS MEDIA Guy Chauveteau, IFP, Yuchun Kuang IFP and Marc Fleury, IFP This paper was prepared for presentation at the International
Plumes and jets with time-dependent sources in stratified and unstratified environments
 Plumes and jets with time-dependent sources in stratified and unstratified environments Abstract Matthew Scase 1, Colm Caulfield 2,1, Stuart Dalziel 1 & Julian Hunt 3 1 DAMTP, Centre for Mathematical Sciences,
Plumes and jets with time-dependent sources in stratified and unstratified environments Abstract Matthew Scase 1, Colm Caulfield 2,1, Stuart Dalziel 1 & Julian Hunt 3 1 DAMTP, Centre for Mathematical Sciences,
Magnetic #uids in aerodynamic measuring devices
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 201 (1999) 385}390 Magnetic #uids in aerodynamic measuring devices N.C. Popa*, I. De Sabata, I. Anton, I. Potencz, L.VeH kah s Romanian Academy, Timis7 oara
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 201 (1999) 385}390 Magnetic #uids in aerodynamic measuring devices N.C. Popa*, I. De Sabata, I. Anton, I. Potencz, L.VeH kah s Romanian Academy, Timis7 oara
Evan Mitsoulis. School of Mining Engineering and Metallurgy. National Technical University of Athens. R.R. Huilgol
 Cessation of Couette and Poiseuille ows of a Bingham plastic and nite stopping times Maria Chatzimina, Georgios C. Georgiou Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Cyprus P.O. Box 2537,
Cessation of Couette and Poiseuille ows of a Bingham plastic and nite stopping times Maria Chatzimina, Georgios C. Georgiou Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Cyprus P.O. Box 2537,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002](/thumbs/74/69829551.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0212257v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 International Journal of Modern Physics B c World Scientific Publishing Company VISCOUS FINGERING IN MISCIBLE, IMMISCIBLE AND REACTIVE FLUIDS PATRICK
arxiv:cond-mat/0212257v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 11 Dec 2002 International Journal of Modern Physics B c World Scientific Publishing Company VISCOUS FINGERING IN MISCIBLE, IMMISCIBLE AND REACTIVE FLUIDS PATRICK
Viscous fingering in periodically heterogeneous porous media. II. Numerical simulations
 Viscous fingering in periodically heterogeneous porous media. II. Numerical simulations A. De Wit Service de Chimie Physique and Centre for Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems, CP 231 Université Libre
Viscous fingering in periodically heterogeneous porous media. II. Numerical simulations A. De Wit Service de Chimie Physique and Centre for Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems, CP 231 Université Libre
n i,j+1/2 q i,j * qi+1,j * S i+1/2,j
 Helsinki University of Technology CFD-group/ The Laboratory of Applied Thermodynamics MEMO No CFD/TERMO-5-97 DATE: December 9,997 TITLE A comparison of complete vs. simplied viscous terms in boundary layer
Helsinki University of Technology CFD-group/ The Laboratory of Applied Thermodynamics MEMO No CFD/TERMO-5-97 DATE: December 9,997 TITLE A comparison of complete vs. simplied viscous terms in boundary layer
Bjørnar Sandnes. Henning Arendt Knudsen. Knut Jørgen Måløy. Eirik Grude Flekkøy. Grunde Løvoll. Yves Meheust. Renaud Toussaint Univ.
 Pattern formation: building mazes with grains Bjørnar Sandnes Henning Arendt Knudsen Knut Jørgen Måløy Eirik Grude Flekkøy x (a) z (b) (c) Grunde Løvoll Yves Meheust NTNU Renaud Toussaint Univ. Strasbourg
Pattern formation: building mazes with grains Bjørnar Sandnes Henning Arendt Knudsen Knut Jørgen Måløy Eirik Grude Flekkøy x (a) z (b) (c) Grunde Løvoll Yves Meheust NTNU Renaud Toussaint Univ. Strasbourg
(a). t = 0 (b). t = 0.276
 10 (a). t = 0 (b). t = 0.276 Figure 8: Snapshots of the sedimentation of 5040 disks of diameter 10/192 cm in 2D (W =8 cm). The initial lattice is disordered. from t = 0:026 to t = 0:476. In Figure 6, a
10 (a). t = 0 (b). t = 0.276 Figure 8: Snapshots of the sedimentation of 5040 disks of diameter 10/192 cm in 2D (W =8 cm). The initial lattice is disordered. from t = 0:026 to t = 0:476. In Figure 6, a
Buoyancy-induced #ows and phase-change heat transfer in a vertical capillary structure with symmetric heating
 Chemical Engineering Science 55 (2000) 2653}2661 Buoyancy-induced #ows and phase-change heat transfer in a vertical capillary structure with symmetric heating T. S. Zhao*, P. Cheng, C. Y. Wang Department
Chemical Engineering Science 55 (2000) 2653}2661 Buoyancy-induced #ows and phase-change heat transfer in a vertical capillary structure with symmetric heating T. S. Zhao*, P. Cheng, C. Y. Wang Department
Diffusion and Adsorption in porous media. Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 Diffusion and Adsorption in porous media Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Devices used to Measure Diffusion in Porous Solids Modes of transport in
Diffusion and Adsorption in porous media Ali Ahmadpour Chemical Eng. Dept. Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Contents Introduction Devices used to Measure Diffusion in Porous Solids Modes of transport in
Experimental setup. Chapter Rheometer
 21 Chapter 2 Experimental setup The current experiments are designed to examine the effect of volume fraction and Stokes number (and equivalently the Reynolds number) at shear rates sufficiently high enough
21 Chapter 2 Experimental setup The current experiments are designed to examine the effect of volume fraction and Stokes number (and equivalently the Reynolds number) at shear rates sufficiently high enough
A microfluidic-based hydrodynamic trap: Design and implementation
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL A microfluidic-based hydrodynamic trap: Design and implementation Melikhan Tanyeri, a Mikhil Ranka, a Natawan Sittipolkul a and Charles M. Schroeder* a,b a Department of Chemical
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL A microfluidic-based hydrodynamic trap: Design and implementation Melikhan Tanyeri, a Mikhil Ranka, a Natawan Sittipolkul a and Charles M. Schroeder* a,b a Department of Chemical
Source Free Surface x
 Finite-dierence time-domain model for elastic waves in the ground Christoph T. Schroeder and Waymond R. Scott, Jr. School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Finite-dierence time-domain model for elastic waves in the ground Christoph T. Schroeder and Waymond R. Scott, Jr. School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Shear instability of two-fluid parallel flow in a Hele Shaw cell
 Shear instability of two-fluid parallel flow in a Hele Shaw cell P. Gondret and M. Rabaud Laboratoire Fluides, Automatique et Systèmes Thermiques, Universités P. & M. Curie et Paris-Sud et CNRS (URA 871),
Shear instability of two-fluid parallel flow in a Hele Shaw cell P. Gondret and M. Rabaud Laboratoire Fluides, Automatique et Systèmes Thermiques, Universités P. & M. Curie et Paris-Sud et CNRS (URA 871),
Expansions-contractions Flows
 III Expansions-contractions Flows III.1 Introduction Flows of viscoplastic materials through internal passages of abruptly varying cross sections are found in a wide variety of industrial and natural processes.
III Expansions-contractions Flows III.1 Introduction Flows of viscoplastic materials through internal passages of abruptly varying cross sections are found in a wide variety of industrial and natural processes.
Applications of statistical mechanics in subcontinuum uid dynamics
 Physica A 274 (1999) 281 293 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Applications of statistical mechanics in subcontinuum uid dynamics Marek Cieplak a;, Joel Koplik b, Jayanth R. Banavar c a Institute of Physics,
Physica A 274 (1999) 281 293 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Applications of statistical mechanics in subcontinuum uid dynamics Marek Cieplak a;, Joel Koplik b, Jayanth R. Banavar c a Institute of Physics,
Asymptotic solution of the Boltzmann equation for the shear ow of smooth inelastic disks
 Physica A 275 (2000) 483 504 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Asymptotic solution of the Boltzmann equation for the shear ow of smooth inelastic disks V. Kumaran Department of Chemical Engineering, Indian
Physica A 275 (2000) 483 504 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Asymptotic solution of the Boltzmann equation for the shear ow of smooth inelastic disks V. Kumaran Department of Chemical Engineering, Indian
Determination of Capillary pressure & relative permeability curves
 Determination of Capillary pressure & relative permeability curves With Refrigerated Centrifuge Multi speed centrifuge experiments Introduction As the porous diaphragm method see Vinci s CAPRI, the centrifuge
Determination of Capillary pressure & relative permeability curves With Refrigerated Centrifuge Multi speed centrifuge experiments Introduction As the porous diaphragm method see Vinci s CAPRI, the centrifuge
Extending the Visco-Plastic Lubrication Concept to Near Net Shape Products and Encapsulation
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Extending the Visco-Plastic Lubrication Concept to Near Net Shape Products and Encapsulation Sarah Hormozi 1,2, Geoff Dunbrack 1, Ian A.
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Extending the Visco-Plastic Lubrication Concept to Near Net Shape Products and Encapsulation Sarah Hormozi 1,2, Geoff Dunbrack 1, Ian A.
A LABORATORY STUDY OF FOAM FOR EOR IN NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS. William R. Rossen Bander. I. AlQuaimi
 A LABORATORY STUDY OF FOAM FOR EOR IN NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS William R. Rossen Bander. I. AlQuaimi Gravity Backround Gas-injection EOR can displace nearly all oil contacted, but sweep efficiency
A LABORATORY STUDY OF FOAM FOR EOR IN NATURALLY FRACTURED RESERVOIRS William R. Rossen Bander. I. AlQuaimi Gravity Backround Gas-injection EOR can displace nearly all oil contacted, but sweep efficiency
Simultaneous Velocity and Concentration Measurements of a Turbulent Jet Mixing Flow
 Simultaneous Velocity and Concentration Measurements of a Turbulent Jet Mixing Flow HUI HU, a TETSUO SAGA, b TOSHIO KOBAYASHI, b AND NOBUYUKI TANIGUCHI b a Department of Mechanical Engineering, Michigan
Simultaneous Velocity and Concentration Measurements of a Turbulent Jet Mixing Flow HUI HU, a TETSUO SAGA, b TOSHIO KOBAYASHI, b AND NOBUYUKI TANIGUCHI b a Department of Mechanical Engineering, Michigan
The Hangingstone steam-assisted gravity drainage
 SPECIAL Heavy SECTION: oil H e a v y o i l Elastic property changes in a bitumen reservoir during steam injection AYATO KATO, University of Houston, USA SHIGENOBU ONOZUKA, JOGMEC, Chiba, Japan TORU NAKAYAMA,
SPECIAL Heavy SECTION: oil H e a v y o i l Elastic property changes in a bitumen reservoir during steam injection AYATO KATO, University of Houston, USA SHIGENOBU ONOZUKA, JOGMEC, Chiba, Japan TORU NAKAYAMA,
Shell Balances in Fluid Mechanics
 Shell Balances in Fluid Mechanics R. Shankar Subramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University When fluid flow occurs in a single direction everywhere in a system, shell
Shell Balances in Fluid Mechanics R. Shankar Subramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University When fluid flow occurs in a single direction everywhere in a system, shell
Two-phase flow in a fissurized-porous media
 Two-phase low in a issurized-porous media P. Ø. Andersen and S. Evje Citation: AIP Con. Proc. 479, 234 (22); doi:.63/.4756663 View online: http://dx.doi.org/.63/.4756663 View Table o Contents: http://proceedings.aip.org/dbt/dbt.jsp?key=apcpcs&volume=479&issue=
Two-phase low in a issurized-porous media P. Ø. Andersen and S. Evje Citation: AIP Con. Proc. 479, 234 (22); doi:.63/.4756663 View online: http://dx.doi.org/.63/.4756663 View Table o Contents: http://proceedings.aip.org/dbt/dbt.jsp?key=apcpcs&volume=479&issue=
Interfacial Flows of Contact Line Dynamics and Liquid Displacement in a Circular Microchannel
 Proceedings of the 3 rd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'17) Rome, Italy June 8 10, 2017 Paper No. HTFF 159 ISSN: 2369-8136 DOI: 10.11159/htff17.159 Interfacial Flows
Proceedings of the 3 rd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'17) Rome, Italy June 8 10, 2017 Paper No. HTFF 159 ISSN: 2369-8136 DOI: 10.11159/htff17.159 Interfacial Flows
Transport by convection. Coupling convection-diffusion
 Transport by convection. Coupling convection-diffusion 24 mars 2017 1 When can we neglect diffusion? When the Peclet number is not very small we cannot ignore the convection term in the transport equation.
Transport by convection. Coupling convection-diffusion 24 mars 2017 1 When can we neglect diffusion? When the Peclet number is not very small we cannot ignore the convection term in the transport equation.
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 25 Feb 1994
 A Model for Fracture in Fibrous Materials A. T. Bernardes Departamento de Física - ICEB arxiv:cond-mat/9402110v1 25 Feb 1994 Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto Campus do Morro do Cruzeiro 35410-000 Ouro
A Model for Fracture in Fibrous Materials A. T. Bernardes Departamento de Física - ICEB arxiv:cond-mat/9402110v1 25 Feb 1994 Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto Campus do Morro do Cruzeiro 35410-000 Ouro
Modular Microscope Accessory
 Modular Microscope Accessory Modular Microscope Accessory SAMPLE STRUCTURE OBSERVATION DHR MMA Key Features Compact, modular design that directly installs to the DHR frame for easy alignment and minimal
Modular Microscope Accessory Modular Microscope Accessory SAMPLE STRUCTURE OBSERVATION DHR MMA Key Features Compact, modular design that directly installs to the DHR frame for easy alignment and minimal
Change of ow patterns in thermocapillary convection in liquid bridge
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Acta Astronautica 54 (2004) 493 501 www.elsevier.com/locate/actaastro Change of ow patterns in thermocapillary convection in liquid bridge V.M. Shevtsova, D.E.
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Acta Astronautica 54 (2004) 493 501 www.elsevier.com/locate/actaastro Change of ow patterns in thermocapillary convection in liquid bridge V.M. Shevtsova, D.E.
2 The second case, in which Problem (P 1 ) reduces to the \one-phase" problem (P 2 ) 8 >< >: u t = u xx + uu x t > 0, x < (t) ; u((t); t) = q t > 0 ;
 1 ON A FREE BOUNDARY PROBLEM ARISING IN DETONATION THEORY: CONVERGENCE TO TRAVELLING WAVES 1. INTRODUCTION. by M.Bertsch Dipartimento di Matematica Universita di Torino Via Principe Amedeo 8 10123 Torino,
1 ON A FREE BOUNDARY PROBLEM ARISING IN DETONATION THEORY: CONVERGENCE TO TRAVELLING WAVES 1. INTRODUCTION. by M.Bertsch Dipartimento di Matematica Universita di Torino Via Principe Amedeo 8 10123 Torino,
Concentrated suspensions under flow in microfluidic channel and migration effect
 Mid-Term Review June 16-17 2011 Concentrated suspensions under flow in microfluidic channel and migration effect Florinda SCHEMBRI*, Hugues BODIGUEL, Annie COLIN LOF Laboratory of the Future University
Mid-Term Review June 16-17 2011 Concentrated suspensions under flow in microfluidic channel and migration effect Florinda SCHEMBRI*, Hugues BODIGUEL, Annie COLIN LOF Laboratory of the Future University
Msc Thesis: Modeling Single & Multi-phase flows in petroleum reservoirs using Comsol Multiphysics: ''Pore to field-scale effects''
 Technical University of Crete School of Mineral Resources Engineering Postgraduate Program in Petroleum Engineering Msc Thesis: Modeling Single & Multi-phase flows in petroleum reservoirs using Comsol
Technical University of Crete School of Mineral Resources Engineering Postgraduate Program in Petroleum Engineering Msc Thesis: Modeling Single & Multi-phase flows in petroleum reservoirs using Comsol
Amélie Neuville. Advanced Materials and Complex Systems group (AMCS) University of Oslo Norway
 Amélie Neuville Advanced Materials and Complex Systems group (AMCS) University of Oslo Norway The Research Council of Norway Postdoc within a PETROMAKS project Mobility grant for young researchers YGGDRASIL,
Amélie Neuville Advanced Materials and Complex Systems group (AMCS) University of Oslo Norway The Research Council of Norway Postdoc within a PETROMAKS project Mobility grant for young researchers YGGDRASIL,
A j = 0.1 cm 2 10 cm 10 cm 10 cm. W j Wj. W j W j. W j. 10 cm 10 cm 10 cm. r i
 ME 131B Fluid Mechanics Solutions to Week Eight Problem Session: Angular Momentum Principle (3/2/98) 1. In control volume analysis, all governing principles share the same common structure: storage = inow
ME 131B Fluid Mechanics Solutions to Week Eight Problem Session: Angular Momentum Principle (3/2/98) 1. In control volume analysis, all governing principles share the same common structure: storage = inow
PHYSICAL REALITIES FOR IN DEPTH PROFILE MODIFICATION. RANDY SERIGHT, New Mexico Tech
 PHYSICAL REALITIES FOR IN DEPTH PROFILE MODIFICATION RANDY SERIGHT, New Mexico Tech 1. Gel treatments (of any kind) are not polymer floods. 2. Crossflow makes gel placement challenging. 3. Adsorbed polymers,
PHYSICAL REALITIES FOR IN DEPTH PROFILE MODIFICATION RANDY SERIGHT, New Mexico Tech 1. Gel treatments (of any kind) are not polymer floods. 2. Crossflow makes gel placement challenging. 3. Adsorbed polymers,
48 K. B. Korotchenko, Yu. L. Pivovarov, Y. Takabayashi where n is the number of quantum states, L is the normalization length (N = 1 for axial channel
 Pis'ma v ZhETF, vol. 95, iss. 8, pp. 481 { 485 c 01 April 5 Quantum Eects for Parametric X-ray Radiation during Channeling: Theory and First Experimental Observation K. B. Korotchenko 1), Yu. L. Pivovarov,
Pis'ma v ZhETF, vol. 95, iss. 8, pp. 481 { 485 c 01 April 5 Quantum Eects for Parametric X-ray Radiation during Channeling: Theory and First Experimental Observation K. B. Korotchenko 1), Yu. L. Pivovarov,
Complete Wetting of Acrylic Solid Substrate with Silicone Oil at the Center of the Substrate
 Complete Wetting of Acrylic Solid Substrate with Silicone Oil at the Center of the Substrate Derrick O. Njobuenwu * Department of Chemical Engineering, Loughborough University Leicestershire LE11 3TU,
Complete Wetting of Acrylic Solid Substrate with Silicone Oil at the Center of the Substrate Derrick O. Njobuenwu * Department of Chemical Engineering, Loughborough University Leicestershire LE11 3TU,
Experiments on the perturbation of a channel flow by a triangular ripple
 Experiments on the perturbation of a channel flow by a triangular ripple F. Cúñez *, E. Franklin Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, University of Campinas, Brazil * Correspondent author: fernandodcb@fem.unicamp.br
Experiments on the perturbation of a channel flow by a triangular ripple F. Cúñez *, E. Franklin Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, University of Campinas, Brazil * Correspondent author: fernandodcb@fem.unicamp.br
Les Houches School of Foam: Rheology of Complex Fluids
 Les Houches School of Foam: Rheology of Complex Fluids Andrew Belmonte The W. G. Pritchard Laboratories Department of Mathematics, Penn State University 1 Fluid Dynamics (tossing a coin) Les Houches Winter
Les Houches School of Foam: Rheology of Complex Fluids Andrew Belmonte The W. G. Pritchard Laboratories Department of Mathematics, Penn State University 1 Fluid Dynamics (tossing a coin) Les Houches Winter
WETTING-LAYER EFFECTS ON HELE-SHAW FLOW
 WETTING-LAYER EFFECTS ON HELE-SHAW FLOW GELU PASA Communicated by Vasile Br nzänescu Chan and Liang noticed a new instability phenomenon related with the displacing process in a vertical Hele-Shaw cell.
WETTING-LAYER EFFECTS ON HELE-SHAW FLOW GELU PASA Communicated by Vasile Br nzänescu Chan and Liang noticed a new instability phenomenon related with the displacing process in a vertical Hele-Shaw cell.
Visualization of Convective Structures by Methods of the Hilbert Optics and Phase-Shift Interferometry
 Visualization of Convective Structures by Methods of the Hilbert Optics and Phase-Shift Interferometry Yu.N. Dubnishchev 1, 2, V.A. Arbuzov 1, 2, E.V. Arbuzov 3, V.S. Berdnikov 1, O.S. Melekhina 2, and
Visualization of Convective Structures by Methods of the Hilbert Optics and Phase-Shift Interferometry Yu.N. Dubnishchev 1, 2, V.A. Arbuzov 1, 2, E.V. Arbuzov 3, V.S. Berdnikov 1, O.S. Melekhina 2, and
On steady hydromagnetic flow of a radiating viscous fluid through a horizontal channel in a porous medium
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 1, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 153-649X doi:1.551/ajsir.1.1..33.38 On steady hydromagnetic flow of a radiating viscous fluid through
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 1, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 153-649X doi:1.551/ajsir.1.1..33.38 On steady hydromagnetic flow of a radiating viscous fluid through
