The Chain Rule. This is a generalization of the (general) power rule which we have already met in the form: then f (x) = r [g(x)] r 1 g (x).
|
|
|
- Pamela Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Chain Rule This is a generalization of the general) power rule which we have already met in the form: If f) = g)] r then f ) = r g)] r g ). Here, g) is any differentiable function and r is any real number. It may be easier to remember it in the form The derivative of ) r is r ) r Derivative of what is in ) You may put any differentiable epression inside ). Of course if you put in, you get what you already know, that the derivative of r is r r. To get something new, you have to put in epressions like +, 2, 4 2, etc. This etends to the trigonometric and the eponential functions as follows:. The derivative of sin ) is cos )] Derivative of what is in ). In practice, it is more convenient to write it as The derivative of sin ) is Derivative of what is in )] cos )]. If you put inside ), you get what you already know, that the derivative of sin is cos.) Eample a) Given f) = sin 6, view it as f) = sin6). Then f ) = 6] cos 6] = 6 cos 6. b) Let g) = sin 2 ). Then g ) = 2 cos 2 ). 2. The derivative of cos ) is Derivative of what is in )] sin )]. Eample 2 a) Given f) = cos 2, view it as f) = cos 2 ). Then f ) = 2)] sin 2 )] = 2 sin 2. b) Let g) = cos + 2 ). Then g ) = ) sin + 2 ). The derivative of tan ) is Derivative of what is in )] sec 2 ) ]. Eample a) Given f) = tan 4, view it as f) = tan4). Then f ) = 4] sec 2 4) ] = 4 sec 2 4. b) Let g) = tan ). Then g ) = + ) sec 2 2 ). 4. The derivative of csc ) is Derivative of what is in )] csc ) cot )].
2 Eample 4 a) Given f) = csc 7, view it as f) = csc7). Then f ) = 7] csc 7) cot 7)] = 7 csc 7 cot 7. b) Let g) = csc 2 ). Then g ) = 2 csc 2 ) cot 2 ) 5. The derivative of sec ) is Derivative of what is in )] sec ) tan )]. Eample 5 a) Given f) = sec 9, view it as f) = sec9). Then f ) = 9] sec 9) tan 9)] = 9 sec 9 tan b) Let g) = sec + 2 ). Then g ) = 6 ) sec + 2 ) tan + 2 ) The derivative of cot ) is Derivative of what is in )] csc 2 ) ]. Eample 6 a) If f) = cot 2 ) then f ) = 2] csc 2 2 )] = 2 csc2 2. b) If g) = cot 5 ) then g ) = ) csc 2 5 ). 7. The derivative of e ) is Derivative of what is in )] e )]. Eample 7 a) Given f) = e 4, view it as f) = e 4). Then f ) = 4] e 4)] = 4e 4. b) If g) = e sin then g ) = cos ] e sin ] = e sin cos The following is a summary of what we have described: Function Derivative. ) n n ) n Derivative of what is in ) 2. sin ) Derivative of what is in )] cos )]. cos ) Derivative of what is in )] sin )] 4. e ) Derivative of what is in )] e )] 5. tan ) Derivative of what is in )] sec 2 ) ] 6. cot ) Derivative of what is in )] csc 2 ) ] ) 7. sec ) Derivative of what is in )] sec ) tan )] 8. csc ) Derivative of what is in )] cot ) csc )] 2
3 Quite often, you may have to use the chain rule more than once. For an eample, take f) = sin. If we write sin as sin ) /2 then the derivative of f is 2 sin ) /2 Derivative of sin ) We have to use the chain rule a second time to find the derivative of sin. This turns out to be cos ). Therefore f ) = 2 sin ) /2 cos ) = 2 sin ) /2 cos ) Eercise 8. Determine the derivative of each function and simplify it when possible. a) f) = 2 sin c) v) = 2 sec 4 7 b) w) = 2 sin cos 2 d) f) = csc 2 e) g) = e 2 f) h) = 2 tan g) u) = 4 cos sec ) h) u) = 2e cot 5 i) f) = 4 7 tan j) g) = 2 tan k) h) = 4 2 sin 2 l) u) = sec 2 m) v) = sin n) w) = cos + 2 o) f) = e 2 sin cos ) p) g) = cot q) h) = tan 2 csc ) 2 2 r) u) = e +sec 2 2 The Chain Rule as a Rule for Computing Derivatives of Compositions The chain rule, in its general form, is a rule for computing derivatives of compositions of functions. It provides us with a method of computing the derivative of a composition f g of differentiable functions f and g if we know the derivative of g at a point and the derivative of f at g). More precisely, it states that the derivative of f g at is given by the formula f g) ) = f g)) g ). An outline of a proof is at the end of this section.) The results in table on page 2 are all special cases of this general form. Here is an illustration: Eample 9 To find the derivative of h) = sec 2 + ) using the formula f g) ) = f g)) g ), write h) as the composition h) = f g) where g) = 2 + and f) = sec. Then f g)) = sec 2 + ) tan 2 + ) and g ) = 2 +. Therefore h ) = f g)) g ) = 2 + ) sec 2 + ) tan 2 + )] For comparison to the result of using formula 7) in table, write h) as sec ). The term sec ) tan )] is sec 2 + ) tan 2 + )], which corresponds to f g)). The term Derivative of what is in ) is 2 + ), which corresponds to g ). Table cannot be used to find the required derivative in the net eample: Eample 0 To find f g) 2) given that g2) =, g 2) = 8 and f ) = 4. By the chain rule, f g) 2) = f g2))g 2) = f )g 2) = 4 8 = 6
4 Eercise. In the figure below, you are given the graph of a function f and the tangents to its graph at the two points with -coordinates 2 and.5. Let g) = Use the chain rule and the given tangents to estimate f g) 2) and f g) ) Use the chain rule, in the form f g) ) = f g)) g ), to find the derivative of the given function. In each case, you should write the given function as a composition of functions f and g of your choice. a) h) = b) u) = 2 + ) 4 c) v) = 2 cos +5 cos2 Another way of applying the chain rule We illustrate with eamples: Eample 2 Let h) = tan ). We reduce it to a more familiar function by introducing a new variable u =. Then h) = tan u. Let fu) = tan u. We can now write h) = fu) = tan u. The derivative of f, its variable is u), is df du = sec2 u. The derivative of u, its variable is ), is du d = 2. The chain rule states that the derivative of h is dh d = df du du d = sec 2 u ) 2) = 2 sec 2 ) As you have probably figured out already, this is similar to writing h) as a composition h) = f g) where g) = and f) = tan. The only difference here is that we have written g) as a new variable u; therefore we must write fg)) as fu). In the epression df du du for the derivative of h, d df du is really f g)) and du d is g ). Eample Let h) = 4 csc 2) + sec 2 4 csc u + sec u. Clearly, derivative of h is ). To find its derivative, we let u =. Then h) = fu) = 2 d =. By the chain rule, the 22 df du = 4 csc u cot u + sec u tan u and du dh d = df du du d = 4 csc u cot u + sec u tan u) ) 2 2 = 4 csc 2 2) cot 2) sec 2) tan )] 2 2 4
5 Remark 4 The chain rule, in the form of table, is easier to use in reverse to guess antiderivatives of functions. Eercise 5 Find the derivative of each function: i) h) = 7e 2 ii)v) = 4 tan iii) w) = e tan iv) z) = 2 + ) Sketch of a Proof of the Chain Rule Let f and g be differentiable functions, f g be their composition and c be a point in the domain of g. The derivative of g at c is the number g c) given by g c) = lim c g) gc) c The derivative of f at gc) is the number f gc)) given by f gc)) = fu) fgc)) lim u gc) u gc) The derivative of f g) at c is the number f g) c) given by fg)) fgc)) Now write as c tools, it can be shown that f g) c) = lim c fg)) fgc)) c fg)) fgc)) g) gc) and denote g) by u. Then, with appropriate g) gc) c f g) fg)) fgc)) g) gc) c) = lim = c g) gc) c lim c ) fu) fgc)) u gc) fu) fgc)) fu) fgc)) It can also be shown that lim = lim. Therefore c u gc) u gc) u gc) ) ) f g) fu) fgc)) g) gc) c) = lim lim = f gc))g c) u gc) u gc) c c lim c ) g) gc) c In general, if g is differentiable at and f is differentiable at g), then f g is differentiable at and You are asked to give another proof in the eercises. Eercise 6 f g) ) = f g))g ) 2). Determine the derivative of each function and simplify when possible. a) f) = cos sin ) 2/ b) g) = tan ) c) h) = cos 2 d) u) = csc sec e) v) = sin 2 f) w) = 4 sec 2 g) f) = 4 cot j) u) = sin 5 ) ) Let f) =. Show that f ) = 2 +. Let g) =. Show that g ) = h) g) = e 2 sin 2 i) h) = + cot 4 k) v) = csc ) l) w) = tan )
6 a sin + b cos 4. Let a, b, c, and d be constants. Show that f) = c sin + d cos has derivative f ad bc ) = c sin + d cos ) Copy and fill in the missing details in the following sketch for the proof of the chain rule: Let f and g be differentiable functions, f g be their composition and c be a point in the domain of g. The derivative of g at c is the number g c) with the property that g) = gc) + c) g c) + c) b ) ) where b ) is a function whose values approach 0 as approaches c. Likewise, the derivative of f at gc) is the number f gc)) with the property that fu) = fgc)) + u gc)) f gc)) + u gc)) b 2 u) 4) where b 2 u) is a function whose values approach zero as u approaches gc). By substituting ) into 4), show that fg)) = fgc))+ c) g c) + c) b )] f gc))+ c) g c) + c) b )] b 2 g)) This simplifies into fg)) = fgc)) + c) f gc))g c) + c) ] b )f gc)) + g c)b 2 g)) + b )b 2 g)) But g) approaches gc) as approaches c, therefore b 2 g)) approaches 0 as approaches c. Show hat the epression b )f gc)) + g c)b 2 g)) + b )b 2 g)) inside the above square brackets approaches 0 as approaches c. Denote it by b ) and write fg)) as f g) to conclude that f g) = fgc)) + c) f gc))g c) + c) b ) 5) where b ) approaches 0 as approaches c. But we know that the derivative of f g at c is the number denoted by f g) c) with the property that f g) = fgc)) + c) f g) c) + c) b) 6) where b) approaches 0 as approaches c. Compare 5) and 6), and deduce that the second term in 5) must be identical to the second term in 6). Therefore f g) c) = f gc))g c) 6
6.5 Trigonometric Equations
 6. Trigonometric Equations In this section, we discuss conditional trigonometric equations, that is, equations involving trigonometric functions that are satisfied only by some values of the variable (or
6. Trigonometric Equations In this section, we discuss conditional trigonometric equations, that is, equations involving trigonometric functions that are satisfied only by some values of the variable (or
11.4. Differentiating ProductsandQuotients. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Differentiating ProductsandQuotients 11.4 Introduction We have seen, in the first three Sections, how standard functions like n, e a, sin a, cos a, ln a may be differentiated. In this Section we see how
Differentiating ProductsandQuotients 11.4 Introduction We have seen, in the first three Sections, how standard functions like n, e a, sin a, cos a, ln a may be differentiated. In this Section we see how
Chapter 2 Section 3. Partial Derivatives
 Chapter Section 3 Partial Derivatives Deinition. Let be a unction o two variables and. The partial derivative o with respect to is the unction, denoted b D1 1 such that its value at an point (,) in the
Chapter Section 3 Partial Derivatives Deinition. Let be a unction o two variables and. The partial derivative o with respect to is the unction, denoted b D1 1 such that its value at an point (,) in the
Integration Techniques for the AB exam
 For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
Inverse Relations. 5 are inverses because their input and output are switched. For instance: f x x. x 5. f 4
 Inverse Functions Inverse Relations The inverse of a relation is the set of ordered pairs obtained by switching the input with the output of each ordered pair in the original relation. (The domain of the
Inverse Functions Inverse Relations The inverse of a relation is the set of ordered pairs obtained by switching the input with the output of each ordered pair in the original relation. (The domain of the
Trigonometric Identities Exam Questions
 Trigonometric Identities Exam Questions Name: ANSWERS January 01 January 017 Multiple Choice 1. Simplify the following expression: cos x 1 cot x a. sin x b. cos x c. cot x d. sec x. Identify a non-permissible
Trigonometric Identities Exam Questions Name: ANSWERS January 01 January 017 Multiple Choice 1. Simplify the following expression: cos x 1 cot x a. sin x b. cos x c. cot x d. sec x. Identify a non-permissible
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES 3.6 Derivatives of Logarithmic Functions In this section, we: use implicit differentiation to find the derivatives of the logarithmic functions and, in particular,
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES 3.6 Derivatives of Logarithmic Functions In this section, we: use implicit differentiation to find the derivatives of the logarithmic functions and, in particular,
In this note we will evaluate the limits of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0. f(x)
 L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
Derivatives of Inverse Functions
 Derivatives of Inverse Functions Implicit differentiation enables us to determine the derivatives of inverse functions. determine the derivatives of arcsin, arccos, arctan, and ln. In this lecture, we
Derivatives of Inverse Functions Implicit differentiation enables us to determine the derivatives of inverse functions. determine the derivatives of arcsin, arccos, arctan, and ln. In this lecture, we
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued)
 Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
Exercise Set 4.3: Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Eercise Set.: Unit Circle Trigonometr Sketch each of the following angles in standard position. (Do not use a protractor; just draw a quick sketch of each angle. Sketch each of the following angles in
Eercise Set.: Unit Circle Trigonometr Sketch each of the following angles in standard position. (Do not use a protractor; just draw a quick sketch of each angle. Sketch each of the following angles in
Worksheet Week 7 Section
 Worksheet Week 7 Section 8.. 8.4. This worksheet is for improvement of your mathematical writing skill. Writing using correct mathematical epression and steps is really important part of doing math. Please
Worksheet Week 7 Section 8.. 8.4. This worksheet is for improvement of your mathematical writing skill. Writing using correct mathematical epression and steps is really important part of doing math. Please
THEOREM: THE CONSTANT RULE
 MATH /MYERS/ALL FORMULAS ON THIS REVIEW MUST BE MEMORIZED! DERIVATIVE REVIEW THEOREM: THE CONSTANT RULE The erivative of a constant function is zero. That is, if c is a real number, then c 0 Eample 1:
MATH /MYERS/ALL FORMULAS ON THIS REVIEW MUST BE MEMORIZED! DERIVATIVE REVIEW THEOREM: THE CONSTANT RULE The erivative of a constant function is zero. That is, if c is a real number, then c 0 Eample 1:
Limits and Their Properties
 Chapter 1 Limits and Their Properties Course Number Section 1.1 A Preview of Calculus Objective: In this lesson you learned how calculus compares with precalculus. I. What is Calculus? (Pages 42 44) Calculus
Chapter 1 Limits and Their Properties Course Number Section 1.1 A Preview of Calculus Objective: In this lesson you learned how calculus compares with precalculus. I. What is Calculus? (Pages 42 44) Calculus
Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
 SECTION 4.1 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Special Right Triangles Trigonometric Ratios
SECTION 4.1 Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions Section 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Special Right Triangles Trigonometric Ratios
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus MATH 6 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 208 Remarks The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC) will make the evaluation of definite integrals
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus MATH 6 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 208 Remarks The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC) will make the evaluation of definite integrals
(ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9
![(ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9 (ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9](/thumbs/89/100579300.jpg) Study Guide for Eam 1 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its epression to be well-defined. Some eamples of the conditions are: What is inside
Study Guide for Eam 1 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its epression to be well-defined. Some eamples of the conditions are: What is inside
Trigonometric integrals by basic methods
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 7 Trigonometric integrals by basic methods What you need to know already: Integrals of basic trigonometric functions. Basic trigonometric
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 7 Trigonometric integrals by basic methods What you need to know already: Integrals of basic trigonometric functions. Basic trigonometric
Integration Techniques for the AB exam
 For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
Exercise Set 4.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios
 Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
Eercise Set.1: Special Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios Answer the following. 9. 1. If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the opposite those sides are also congruent. 2. If two angles
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
3.5 Derivatives of Trig Functions
 3.5 Derivatives of Trig Functions Problem 1 (a) Suppose we re given the right triangle below. Epress sin( ) and cos( ) in terms of the sides of the triangle. sin( ) = B C = B and cos( ) = A C = A (b) Suppose
3.5 Derivatives of Trig Functions Problem 1 (a) Suppose we re given the right triangle below. Epress sin( ) and cos( ) in terms of the sides of the triangle. sin( ) = B C = B and cos( ) = A C = A (b) Suppose
171, Calculus 1. Summer 1, CRN 50248, Section 001. Time: MTWR, 6:30 p.m. 8:30 p.m. Room: BR-43. CRN 50248, Section 002
 171, Calculus 1 Summer 1, 018 CRN 5048, Section 001 Time: MTWR, 6:0 p.m. 8:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CRN 5048, Section 00 Time: MTWR, 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CONTENTS Syllabus Reviews for tests 1 Review
171, Calculus 1 Summer 1, 018 CRN 5048, Section 001 Time: MTWR, 6:0 p.m. 8:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CRN 5048, Section 00 Time: MTWR, 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Room: BR-4 CONTENTS Syllabus Reviews for tests 1 Review
AP Calculus (AB/BC) Prerequisite Packet Paint Branch High School Math Department
 Updated 6/015 The problems in this packet are designed to help ou review topics from previous math courses that are important to our success in AP Calculus AB / BC. It is important that ou take time during
Updated 6/015 The problems in this packet are designed to help ou review topics from previous math courses that are important to our success in AP Calculus AB / BC. It is important that ou take time during
6.1 Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus
 6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
TOTAL NAME DATE PERIOD AP CALCULUS AB UNIT 4 ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION TECHNIQUES DATE TOPIC ASSIGNMENT /6 10/8 10/9 10/10 X X X X 10/11 10/12
 NAME DATE PERIOD AP CALCULUS AB UNIT ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION TECHNIQUES DATE TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 0 0 0/6 0/8 0/9 0/0 X X X X 0/ 0/ 0/5 0/6 QUIZ X X X 0/7 0/8 0/9 0/ 0/ 0/ 0/5 UNIT EXAM X X X TOTAL AP Calculus
NAME DATE PERIOD AP CALCULUS AB UNIT ADVANCED DIFFERENTIATION TECHNIQUES DATE TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 0 0 0/6 0/8 0/9 0/0 X X X X 0/ 0/ 0/5 0/6 QUIZ X X X 0/7 0/8 0/9 0/ 0/ 0/ 0/5 UNIT EXAM X X X TOTAL AP Calculus
CHAPTER 2 DIFFERENTIATION 2.1 FIRST ORDER DIFFERENTIATION. What is Differentiation?
 BA01 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS 01 CHAPTER DIFFERENTIATION.1 FIRST ORDER DIFFERENTIATION What is Differentiation? Differentiation is all about finding rates of change of one quantity compared to another.
BA01 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS 01 CHAPTER DIFFERENTIATION.1 FIRST ORDER DIFFERENTIATION What is Differentiation? Differentiation is all about finding rates of change of one quantity compared to another.
Section Inverse Trigonometry. In this section, we will define inverse since, cosine and tangent functions. x is NOT one-to-one.
 Section 5.4 - Inverse Trigonometry In this section, we will define inverse since, cosine and tangent functions. RECALL Facts about inverse functions: A function f ) is one-to-one if no two different inputs
Section 5.4 - Inverse Trigonometry In this section, we will define inverse since, cosine and tangent functions. RECALL Facts about inverse functions: A function f ) is one-to-one if no two different inputs
Name: Top Ten Things You ve Learned #10: Graphing Lines, Parabolas, and other Functions I. No Calculator: Sketch a graph of each equation
 Name: #: Graphing Lines, Parabolas, and other Functions I. No Calculator: Sketch a graph of each equation... - - - - - -.. 6. - - - - - - 7. 8. 9. - - - - - - ... a f - - - - - - II. Use a graphing calculator
Name: #: Graphing Lines, Parabolas, and other Functions I. No Calculator: Sketch a graph of each equation... - - - - - -.. 6. - - - - - - 7. 8. 9. - - - - - - ... a f - - - - - - II. Use a graphing calculator
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Regent College Maths Department. Core Mathematics 4 Trapezium Rule. C4 Integration Page 1
 Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics Trapezium Rule C Integration Page Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics Trapezium Rule C Integration Page Integration It might appear to be a bit obvious but you must remember all of your C work on differentiation if you are
CHAIN RULE: DAY 2 WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS. Section 2.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised /30/2018 1:44 AM 2.4A: Chain Rule Day 2 1
 CHAIN RULE: DAY WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS Section.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/018 1:44 AM.4A: Chain Rule Day 1 THE CHAIN RULE A. d dx f g x = f g x g x B. If f(x) is a differentiable
CHAIN RULE: DAY WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS Section.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/018 1:44 AM.4A: Chain Rule Day 1 THE CHAIN RULE A. d dx f g x = f g x g x B. If f(x) is a differentiable
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions. Name Class. (a) (b) ln x (c) (a) (b) (c) 1 x. y e (a) 0 (b) y.
 90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
Brief Revision Notes and Strategies
 Brief Revision Notes and Strategies Straight Line Distance Formula d = ( ) + ( y y ) d is distance between A(, y ) and B(, y ) Mid-point formula +, y + M y M is midpoint of A(, y ) and B(, y ) y y Equation
Brief Revision Notes and Strategies Straight Line Distance Formula d = ( ) + ( y y ) d is distance between A(, y ) and B(, y ) Mid-point formula +, y + M y M is midpoint of A(, y ) and B(, y ) y y Equation
Chapter 2 Overview: Anti-Derivatives. As noted in the introduction, Calculus is essentially comprised of four operations.
 Chapter Overview: Anti-Derivatives As noted in the introduction, Calculus is essentially comprised of four operations. Limits Derivatives Indefinite Integrals (or Anti-Derivatives) Definite Integrals There
Chapter Overview: Anti-Derivatives As noted in the introduction, Calculus is essentially comprised of four operations. Limits Derivatives Indefinite Integrals (or Anti-Derivatives) Definite Integrals There
Module FP2. Further Pure 2. Cambridge University Press Further Pure 2 and 3 Hugh Neill and Douglas Quadling Excerpt More information
 5548993 - Further Pure an 3 Moule FP Further Pure 5548993 - Further Pure an 3 Differentiating inverse trigonometric functions Throughout the course you have graually been increasing the number of functions
5548993 - Further Pure an 3 Moule FP Further Pure 5548993 - Further Pure an 3 Differentiating inverse trigonometric functions Throughout the course you have graually been increasing the number of functions
Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule
 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at certain points. INDETERMINATE FORM TYPE
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at certain points. INDETERMINATE FORM TYPE
CHAPTER 3 DIFFERENTIATION
 CHAPTER 3 DIFFERENTIATION 3.1 THE DERIVATIVE AND THE TANGENT LINE PROBLEM You will be able to: - Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a point - Use the limit definition to find the derivative
CHAPTER 3 DIFFERENTIATION 3.1 THE DERIVATIVE AND THE TANGENT LINE PROBLEM You will be able to: - Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a point - Use the limit definition to find the derivative
DISCOVERING THE PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES LEARNING TASK:
 Name: Class Period: DISCOVERING THE PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES LEARNING TASK: An identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable for which the epressions in the equation are defined. You
Name: Class Period: DISCOVERING THE PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES LEARNING TASK: An identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable for which the epressions in the equation are defined. You
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC. Complex Fractions
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Problems with an # after the number are the only ones that a calculator is required for in the solving process.
 Instructions: Make sure all problems are numbered in order. All work is in pencil, and is shown completely. Graphs are drawn out by hand. If you use your calculator for some steps, intermediate work should
Instructions: Make sure all problems are numbered in order. All work is in pencil, and is shown completely. Graphs are drawn out by hand. If you use your calculator for some steps, intermediate work should
whose domain D is a set of n-tuples in is defined. The range of f is the set of all values f x1,..., x n
 Grade 1 (MCV4UE) - AP Calculus Etended Page 1 o 1 A unction o n-variales is a real-valued unction 1,..., n whose domain D is a set o n-tuples 1,..., n in which 1,..., n is deined. The range o is the set
Grade 1 (MCV4UE) - AP Calculus Etended Page 1 o 1 A unction o n-variales is a real-valued unction 1,..., n whose domain D is a set o n-tuples 1,..., n in which 1,..., n is deined. The range o is the set
MATH section 3.4 Curve Sketching Page 1 of 29
 MATH section. Curve Sketching Page of 9 The step by step procedure below is for regular rational and polynomial functions. If a function contains radical or trigonometric term, then proceed carefully because
MATH section. Curve Sketching Page of 9 The step by step procedure below is for regular rational and polynomial functions. If a function contains radical or trigonometric term, then proceed carefully because
Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet
 Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet In the table below, a function is given. Show the algebraic analysis that leads to the derivative of the function. Find the derivative by the specified
Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet In the table below, a function is given. Show the algebraic analysis that leads to the derivative of the function. Find the derivative by the specified
CHAPTER 3 DERIVATIVES (continued)
 CHAPTER 3 DERIVATIVES (continue) 3.3. RULES FOR DIFFERENTIATION A. The erivative of a constant is zero: [c] = 0 B. The Power Rule: [n ] = n (n-1) C. The Constant Multiple Rule: [c *f()] = c * f () D. The
CHAPTER 3 DERIVATIVES (continue) 3.3. RULES FOR DIFFERENTIATION A. The erivative of a constant is zero: [c] = 0 B. The Power Rule: [n ] = n (n-1) C. The Constant Multiple Rule: [c *f()] = c * f () D. The
Review of elements of Calculus (functions in one variable)
 Review of elements of Calculus (functions in one variable) Mainly adapted from the lectures of prof Greg Kelly Hanford High School, Richland Washington http://online.math.uh.edu/houstonact/ https://sites.google.com/site/gkellymath/home/calculuspowerpoints
Review of elements of Calculus (functions in one variable) Mainly adapted from the lectures of prof Greg Kelly Hanford High School, Richland Washington http://online.math.uh.edu/houstonact/ https://sites.google.com/site/gkellymath/home/calculuspowerpoints
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
±. Then. . x. lim g( x) = lim. cos x 1 sin x. and (ii) lim
 MATH 36 L'H ˆ o pital s Rule Si of the indeterminate forms of its may be algebraically determined using L H ˆ o pital's Rule. This rule is only stated for the / and ± /± indeterminate forms, but four other
MATH 36 L'H ˆ o pital s Rule Si of the indeterminate forms of its may be algebraically determined using L H ˆ o pital's Rule. This rule is only stated for the / and ± /± indeterminate forms, but four other
dx dx x sec tan d 1 4 tan 2 2 csc d 2 ln 2 x 2 5x 6 C 2 ln 2 ln x ln x 3 x 2 C Now, suppose you had observed that x 3
 CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8. Partial Fractions Understand the concept of a partial fraction decomposition. Use partial fraction decomposition with
CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8. Partial Fractions Understand the concept of a partial fraction decomposition. Use partial fraction decomposition with
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
MATH section 3.1 Maximum and Minimum Values Page 1 of 7
 MATH section. Maimum and Minimum Values Page of 7 Definition : Let c be a number in the domain D of a function f. Then c ) is the Absolute maimum value of f on D if ) c f() for all in D. Absolute minimum
MATH section. Maimum and Minimum Values Page of 7 Definition : Let c be a number in the domain D of a function f. Then c ) is the Absolute maimum value of f on D if ) c f() for all in D. Absolute minimum
Chapter 2: The Derivative
 Chapter : The Derivative Summary: Chapter builds upon the ideas of limits and continuity discussed in the previous chapter. By using limits, the instantaneous rate at which a function changes with respect
Chapter : The Derivative Summary: Chapter builds upon the ideas of limits and continuity discussed in the previous chapter. By using limits, the instantaneous rate at which a function changes with respect
CALCULUS: Graphical,Numerical,Algebraic by Finney,Demana,Watts and Kennedy Chapter 3: Derivatives 3.3: Derivative of a function pg.
 CALCULUS: Graphical,Numerical,Algebraic b Finne,Demana,Watts and Kenned Chapter : Derivatives.: Derivative of a function pg. 116-16 What ou'll Learn About How to find the derivative of: Functions with
CALCULUS: Graphical,Numerical,Algebraic b Finne,Demana,Watts and Kenned Chapter : Derivatives.: Derivative of a function pg. 116-16 What ou'll Learn About How to find the derivative of: Functions with
Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus
 Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Philippe B. Laval KSU Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Current Semester 1 / 13 Introduction In this section,
Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Philippe B. Laval KSU Current Semester Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Differentiation - Quick Review From Calculus Current Semester 1 / 13 Introduction In this section,
Section The Chain Rule and Implicit Differentiation with Application on Derivative of Logarithm Functions
 Section 3.4-3.6 The Chain Rule an Implicit Differentiation with Application on Derivative of Logarithm Functions Ruipeng Shen September 3r, 5th Ruipeng Shen MATH 1ZA3 September 3r, 5th 1 / 3 The Chain
Section 3.4-3.6 The Chain Rule an Implicit Differentiation with Application on Derivative of Logarithm Functions Ruipeng Shen September 3r, 5th Ruipeng Shen MATH 1ZA3 September 3r, 5th 1 / 3 The Chain
A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment
 A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment This assignment is due the first day of class at the beginning of the class. It will be graded and counts as your first test grade. This packet contains eight sections and
A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment This assignment is due the first day of class at the beginning of the class. It will be graded and counts as your first test grade. This packet contains eight sections and
Some commonly encountered sets and their notations
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS (This notes are based on the book Introductory Mathematics by Ng Wee Seng ) LECTURE SETS & FUNCTIONS Some commonly encountered sets and their
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS (This notes are based on the book Introductory Mathematics by Ng Wee Seng ) LECTURE SETS & FUNCTIONS Some commonly encountered sets and their
4-3 Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
 Find the exact value of each trigonometric function, if defined. If not defined, write undefined. 9. sin The terminal side of in standard position lies on the positive y-axis. Choose a point P(0, 1) on
Find the exact value of each trigonometric function, if defined. If not defined, write undefined. 9. sin The terminal side of in standard position lies on the positive y-axis. Choose a point P(0, 1) on
Rules for Differentiation Finding the Derivative of a Product of Two Functions. What does this equation of f '(
 Rules for Differentiation Finding the Derivative of a Product of Two Functions Rewrite the function f( = ( )( + 1) as a cubic function. Then, find f '(. What does this equation of f '( represent, again?
Rules for Differentiation Finding the Derivative of a Product of Two Functions Rewrite the function f( = ( )( + 1) as a cubic function. Then, find f '(. What does this equation of f '( represent, again?
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 3
 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part FTC Part Worksheet 5: Basic Rules, Initial Value Problems, Rewriting Integrands A. It s time to find anti-derivatives algebraically. Instead of saying the anti-derivative
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part FTC Part Worksheet 5: Basic Rules, Initial Value Problems, Rewriting Integrands A. It s time to find anti-derivatives algebraically. Instead of saying the anti-derivative
Math 180 Written Homework Solutions Assignment #4 Due Tuesday, September 23rd at the beginning of your discussion class.
 Math 180 Written Homework Solutions Assignment #4 Due Tuesday, September 23rd at the beginning of your discussion class. Directions. You are welcome to work on the following problems with other MATH 180
Math 180 Written Homework Solutions Assignment #4 Due Tuesday, September 23rd at the beginning of your discussion class. Directions. You are welcome to work on the following problems with other MATH 180
Integration. 5.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration. Suppose that f(x) = 5x 4. Can we find a function F (x) whose derivative is f(x)?
 5 Integration 5. Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Suppose that f() = 5 4. Can we find a function F () whose derivative is f()? Definition. A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval
5 Integration 5. Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Suppose that f() = 5 4. Can we find a function F () whose derivative is f()? Definition. A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval
Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 05 notes Summer
 Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 0 notes Summer 0 Trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions often arise in physical applications with periodic motion. They do not arise often
Calculus with business applications, Lehigh U, Lecture 0 notes Summer 0 Trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions often arise in physical applications with periodic motion. They do not arise often
Calculus 1 (AP, Honors, Academic) Summer Assignment 2018
 Calculus (AP, Honors, Academic) Summer Assignment 08 The summer assignments for Calculus will reinforce some necessary Algebra and Precalculus skills. In order to be successful in Calculus, you must have
Calculus (AP, Honors, Academic) Summer Assignment 08 The summer assignments for Calculus will reinforce some necessary Algebra and Precalculus skills. In order to be successful in Calculus, you must have
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
AP Calculus I Summer Packet
 AP Calculus I Summer Packet This will be your first grade of AP Calculus and due on the first day of class. Please turn in ALL of your work and the attached completed answer sheet. I. Intercepts The -intercept
AP Calculus I Summer Packet This will be your first grade of AP Calculus and due on the first day of class. Please turn in ALL of your work and the attached completed answer sheet. I. Intercepts The -intercept
whose domain D is a set of n-tuples in is defined. The range of f is the set of all values f x1,..., x n
 Grade (MCV4UE) - AP Calculus Etended Page o A unction o n-variales is a real-valued unction... n whose domain D is a set o n-tuples... n in which... n is deined. The range o is the set o all values...
Grade (MCV4UE) - AP Calculus Etended Page o A unction o n-variales is a real-valued unction... n whose domain D is a set o n-tuples... n in which... n is deined. The range o is the set o all values...
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES Before starting this section, you might need to review the trigonometric functions. DIFFERENTIATION RULES In particular, it is important to remember that,
Computing Derivatives Solutions
 Stuent Stuy Session Solutions We have intentionally inclue more material than can be covere in most Stuent Stuy Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions at a faster rate. Use
Stuent Stuy Session Solutions We have intentionally inclue more material than can be covere in most Stuent Stuy Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions at a faster rate. Use
FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS
 Page of 6 FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS 6. HYPERBOLIC FUNCTIONS These functions which are defined in terms of e will be seen later to be related to the trigonometic functions via comple
Page of 6 FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS 6. HYPERBOLIC FUNCTIONS These functions which are defined in terms of e will be seen later to be related to the trigonometic functions via comple
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment
 Name: AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills
Name: AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills
Math RE - Calculus I Trigonometry Limits & Derivatives Page 1 of 8. x = 1 cos x. cos x 1 = lim
 Math 0-0-RE - Calculus I Trigonometry Limits & Derivatives Page of 8 Trigonometric Limits It has been shown in class that: lim 0 sin lim 0 sin lim 0 cos cos 0 lim 0 cos lim 0 + cos + To evaluate trigonometric
Math 0-0-RE - Calculus I Trigonometry Limits & Derivatives Page of 8 Trigonometric Limits It has been shown in class that: lim 0 sin lim 0 sin lim 0 cos cos 0 lim 0 cos lim 0 + cos + To evaluate trigonometric
Algebra II B Review 5
 Algebra II B Review 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the measure of the angle below. y x 40 ο a. 135º b. 50º c. 310º d. 270º Sketch
Algebra II B Review 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the measure of the angle below. y x 40 ο a. 135º b. 50º c. 310º d. 270º Sketch
Partial Fractions. dx dx x sec tan d 1 4 tan 2. 2 csc d. csc cot C. 2x 5. 2 ln. 2 x 2 5x 6 C. 2 ln. 2 ln x
 460_080.qd //04 :08 PM Page CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8. Partial Fractions Understand the concept of a partial fraction decomposition. Use partial
460_080.qd //04 :08 PM Page CHAPTER 8 Integration Techniques, L Hôpital s Rule, and Improper Integrals Section 8. Partial Fractions Understand the concept of a partial fraction decomposition. Use partial
Transition to College Math
 Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
Transition to College Math Date: Unit 3: Trigonometr Lesson 2: Angles of Rotation Name Period Essential Question: What is the reference angle for an angle of 15? Standard: F-TF.2 Learning Target: Eplain
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART 1 MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI PART 1: 135 POINTS, PART 2: 115 POINTS, TOTAL: 250 POINTS
 SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
4.3. Differentiation Rules for Sinusoidal Functions. How do the differentiation rules apply to sinusoidal functions?
 .3 Differentiation Rules for Sinusoidal Functions Sinusoidal patterns occur frequentl in nature. Sinusoidal functions and compound sinusoidal functions are used to describe the patterns found in the stu
.3 Differentiation Rules for Sinusoidal Functions Sinusoidal patterns occur frequentl in nature. Sinusoidal functions and compound sinusoidal functions are used to describe the patterns found in the stu
Unit 3. Integration. 3A. Differentials, indefinite integration. y x. c) Method 1 (slow way) Substitute: u = 8 + 9x, du = 9dx.
 Unit 3. Integration 3A. Differentials, indefinite integration 3A- a) 7 6 d. (d(sin ) = because sin is a constant.) b) (/) / d c) ( 9 8)d d) (3e 3 sin + e 3 cos)d e) (/ )d + (/ y)dy = implies dy = / d /
Unit 3. Integration 3A. Differentials, indefinite integration 3A- a) 7 6 d. (d(sin ) = because sin is a constant.) b) (/) / d c) ( 9 8)d d) (3e 3 sin + e 3 cos)d e) (/ )d + (/ y)dy = implies dy = / d /
6.6 Substitution with All Basic Forms
 670 CHAPTER 6. BASIC INTEGRATION 6.6 Substitution with All Basic Forms In this section we will add to our forms for substitution and recall some rather general guidelines for substitution. Ecept for our
670 CHAPTER 6. BASIC INTEGRATION 6.6 Substitution with All Basic Forms In this section we will add to our forms for substitution and recall some rather general guidelines for substitution. Ecept for our
Section 4.3: Quadratic Formula
 Objective: Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. In this section we will develop a formula to solve any quadratic equation ab c 0 where a b and c are real numbers and a 0. Solve for this
Objective: Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. In this section we will develop a formula to solve any quadratic equation ab c 0 where a b and c are real numbers and a 0. Solve for this
Problems with an # after the number are the only ones that a calculator is required for in the solving process.
 Instructions: Make sure all problems are numbered in order. (Level : If the problem had an *please skip that number) All work is in pencil, and is shown completely. Graphs are drawn out by hand. If you
Instructions: Make sure all problems are numbered in order. (Level : If the problem had an *please skip that number) All work is in pencil, and is shown completely. Graphs are drawn out by hand. If you
R3.6 Solving Linear Inequalities. 3) Solve: 2(x 4) - 3 > 3x ) Solve: 3(x 2) > 7-4x. R8.7 Rational Exponents
 Level D Review Packet - MMT This packet briefly reviews the topics covered on the Level D Math Skills Assessment. If you need additional study resources and/or assistance with any of the topics below,
Level D Review Packet - MMT This packet briefly reviews the topics covered on the Level D Math Skills Assessment. If you need additional study resources and/or assistance with any of the topics below,
Definition of the Radian. Important Note Whenever the units of angle measure are not specified, the units are assumed to be radians.
 Definition of the Radian l, Investigation The Relationship among, r and l When is measured in radians, there is a very simple equation that relates r (the radius of the circle), (the angle at the centre
Definition of the Radian l, Investigation The Relationship among, r and l When is measured in radians, there is a very simple equation that relates r (the radius of the circle), (the angle at the centre
Core Mathematics 3 A2 compulsory unit for GCE Mathematics and GCE Pure Mathematics Mathematics. Unit C3. C3.1 Unit description
 Unit C3 Core Mathematics 3 A2 compulsory unit for GCE Mathematics and GCE Pure Mathematics Mathematics C3. Unit description Algebra and functions; trigonometry; eponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
Unit C3 Core Mathematics 3 A2 compulsory unit for GCE Mathematics and GCE Pure Mathematics Mathematics C3. Unit description Algebra and functions; trigonometry; eponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
National University of Singapore Department of Mathematics
 National University of Singapore Department of Mathematics Semester I, 2002/2003 MA505 Math I Suggested Solutions to T. 2. Let f() be a real function defined as follows: sin(a) if
National University of Singapore Department of Mathematics Semester I, 2002/2003 MA505 Math I Suggested Solutions to T. 2. Let f() be a real function defined as follows: sin(a) if
y sec 3 x dx sec x tan x y sec x tan 2 x dx y sec 3 x dx 1 2(sec x tan x ln sec x tan x ) C
 SECTION 7. TRIGONOETRIC INTEGRLS 465 Then sec 3 sec tan sec tan sec tan sec sec sec tan sec 3 sec Using ormula and solving for the required integral, we get sec 3 (sec tan ln sec tan ) C Integrals such
SECTION 7. TRIGONOETRIC INTEGRLS 465 Then sec 3 sec tan sec tan sec tan sec sec sec tan sec 3 sec Using ormula and solving for the required integral, we get sec 3 (sec tan ln sec tan ) C Integrals such
Methods of Integration
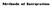 Methods of Integration Essential Formulas k d = k +C sind = cos +C n d = n+ n + +C cosd = sin +C e d = e +C tand = ln sec +C d = ln +C cotd = ln sin +C + d = tan +C lnd = ln +C secd = ln sec + tan +C cscd
Methods of Integration Essential Formulas k d = k +C sind = cos +C n d = n+ n + +C cosd = sin +C e d = e +C tand = ln sec +C d = ln +C cotd = ln sin +C + d = tan +C lnd = ln +C secd = ln sec + tan +C cscd
MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 8) Martin Li
 MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 8) Martin Li 1 L Hospital s Rule Another useful application of mean value theorems is L Hospital s Rule. It helps us to evaluate its of indeterminate
MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 8) Martin Li 1 L Hospital s Rule Another useful application of mean value theorems is L Hospital s Rule. It helps us to evaluate its of indeterminate
y sin n x dx cos x sin n 1 x n 1 y sin n 2 x cos 2 x dx y sin n xdx cos x sin n 1 x n 1 y sin n 2 x dx n 1 y sin n x dx
 SECTION 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS 57 EXAPLE 6 Prove the reduction formula N Equation 7 is called a reduction formula because the eponent n has been reduced to n and n. 7 sin n n cos sinn n n sin n where
SECTION 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS 57 EXAPLE 6 Prove the reduction formula N Equation 7 is called a reduction formula because the eponent n has been reduced to n and n. 7 sin n n cos sinn n n sin n where
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 12 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.2 The Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphs
12 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12.2 The Trigonometric Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Trigonometric Functions and Their Graphs
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
7.3 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 58 transcendental functions 73 Inverse Trigonometric Functions We now turn our attention to the inverse trigonometric functions, their properties and their graphs, focusing on properties and techniques
58 transcendental functions 73 Inverse Trigonometric Functions We now turn our attention to the inverse trigonometric functions, their properties and their graphs, focusing on properties and techniques
Integration by Triangle Substitutions
 Integration by Triangle Substitutions The Area of a Circle So far we have used the technique of u-substitution (ie, reversing the chain rule) and integration by parts (reversing the product rule) to etend
Integration by Triangle Substitutions The Area of a Circle So far we have used the technique of u-substitution (ie, reversing the chain rule) and integration by parts (reversing the product rule) to etend
An Intro to Limits Sketch to graph of 3
 Limits and Their Properties A Preview of Calculus Objectives: Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus.understand that the tangent line problem is basic to calculus. Understand
Limits and Their Properties A Preview of Calculus Objectives: Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus.understand that the tangent line problem is basic to calculus. Understand
CALCULUS II MATH Dr. Hyunju Ban
 CALCULUS II MATH 2414 Dr. Hyunju Ban Introduction Syllabus Chapter 5.1 5.4 Chapters To Be Covered: Chap 5: Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions (2 week) Chap 7: Applications of
CALCULUS II MATH 2414 Dr. Hyunju Ban Introduction Syllabus Chapter 5.1 5.4 Chapters To Be Covered: Chap 5: Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions (2 week) Chap 7: Applications of
Solutions Exam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) 1. a. Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows:
 MAT 4 Solutions Eam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) a Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows: f () = 43 e 4 e (e ) = 43 4 e = 3 (4 ) e Hence f '( ) 0 for = 0
MAT 4 Solutions Eam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) a Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows: f () = 43 e 4 e (e ) = 43 4 e = 3 (4 ) e Hence f '( ) 0 for = 0
8 Differential Calculus 1 Introduction
 8 Differential Calculus Introduction The ideas that are the basis for calculus have been with us for a ver long time. Between 5 BC and 5 BC, Greek mathematicians were working on problems that would find
8 Differential Calculus Introduction The ideas that are the basis for calculus have been with us for a ver long time. Between 5 BC and 5 BC, Greek mathematicians were working on problems that would find
Franklin High School AB Calculus Prerequisite Work
 Franklin High School AB Calculus Prerequisite Work Below you will find an assignment set based on the prerequisites needed for the AB Calculus curriculum taught at Franklin High School. The problems assigned
Franklin High School AB Calculus Prerequisite Work Below you will find an assignment set based on the prerequisites needed for the AB Calculus curriculum taught at Franklin High School. The problems assigned
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
