Sure shot questions for class XII CBSE Board Exam reg. 02(Two) Marks Questions and Answer
|
|
|
- Carmel Ashlyn Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ATOMS AND NUCLEI Sure shot questions for class XII CBSE Board Exam reg. 02(Two) Marks Questions and Answer Q.1. Define the term activity of a radio nuclide & draw the graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei. Ans.:- Activity of a radionuclide is defined as the rate of disintegration of given radioactive sample with time. Its S.I. Unit is becquerel. We know that = N Where is constant for a given radioactive material so the graph between &N is straight line as shown in diagraph given below. dn/dt N Q.2. Theenergy of the electron in the ground state of hydrogen atom is e V (n=1). i. What does the negative sign signify? ii. How much energy is required to take an electron in this atom from the ground state to the first excited state? Ans.i. Negative sign signifies that the electron is bound to the nucleus. ii.energy in ground state = ev Energy in 1 st excited state = 13.6/2 2 = -3.4 ev Energy required to carry the electron to the first excited state = -3.4 (-13.6) = = 10.2 ev Q.3. Write two characteristic features of nuclear force which distinguish it from coulomb s force? Ans.:- Characteristic features of nuclear force i. Nuclear forces are short range attractive forces (range 2 to 3 fm) while coulomb s forces are of infinite range may be attractive or repulsive. ii. Nuclear forces are charge independent forces, while coulomb s force acts only between charged particles.
2 03 Marks Questions and Answer Q.4. Draw a graph of radioactive species versus time. Two different radioactive elements with half-life T 1 & T 2 have N 1 and N 2 (undecayed) atoms respectively present at a given instant. Determine the ratio of their activities at this instant. Ans. The required graph is shown in the diagram. We know,activity R (= ) = N & decay constant = log e 2/T Therefore, Activity R = log e 2 N/T Therefore, R 1 = log e 2 N 1 /T 1, & R 2 = log e 2 N 2 /T 2 Therefore, R 1 /R 2 = N 1 T 2 /N 2 T 1
3 Q.5. Draw a graph showing the variation of binding energy per nucleon with the mass number. What are man inferences from the graph? Ans. Graph:- Main Inference from the graph i. The nuclei having mass number below 20and above 180 have relatively small binding energy per nucleon a hence they are unstable. ii. The nuclei having mass number about 56 have maximum binding energy per nucleon 8.5 Mev& hence they are stable. iii. Some nuclei have peaks (ex He 4, 2 C 12 6,O 16 8 ) this indicates that those nuclei are relatively more stable than their neighbors. Q.6. Aradioactive isotope has a half life of 5 years after how much time is its activity reduce to 3.125% of its original activity? Ans. We know = ) n Given = 3.125% = = ) n Or, = ) n Or, ) 5 n = 5 ) n We Know n = t = nt = 5*5 years ( T 5 years) = 25 years
4 05 Marks Questions&Answers Q.7. Describe Geiger- Marsden (Rutherford) experiment. Give its observations and conclusions? Ans. At the suggestion, Rutherford In 1911, H.Geiger, and E Marsden performed an experiment called Geiger-Marsden experiment (or Rutherford scattering experiment)it consists of 1. Source of α particles : Poloniums is used as a source which placed in enclosure containing a hole and few slits 2. Thin gold foil: A gold foil nearly 10-8 m thick, α-particles are scattered by this foil.the whole experimental arrangement are so in the diagram. Observation and conclusions 1. Most of α particles pass through the gold foil undeflected.this shows that most part of the atom is hollow. 2. α particles are scattered through all angles.nearly 1 in 2000, suffer scattering though angles more than 90⁰,while smaller number (nearly I in 8000,) retrace path.this implies that when fast move positive charged α particles come near gold atom then a few of them experience such a strong repulsive force that they turn back. On this basis Rutherford concluded that whole of positive charge concentrated in small center called nucleus. The distance of closest approach estimated the nuclear size r 0 = 2Ze 2 /4π 0 E k Where symbols have their usual meaning Calculating so that size of nucleus is of the order of m,while size of atom is m.therefore size of nucleus is about /10-10 = 1/10,000 times the size of atom. 3. The negative charges (electrons) do not influence the scattering process, which show that whole mass of atom is concentrated in nucleus
5 Q.8. Using Bohr s postulates, of obtain an expression for the frequency of radiation emitted when electron make a transition from the higher energy state to lower energy state. Ans:- Let m = mass of an electron v = velocity of electron in n th orbit r = radius of the n th orbit The required centripetal force to the electron is provided by electrostatic force of attraction between electron and nucleus. mv 2 /r = 1/4πε 0 x (Ze) (e)/ r (i) Or, mv 2 = 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 / r So, K. E. (K) = ½ mv 2 K = 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 /2 r P. E. = 1/4πε 0 x (Ze) (-e)/ r = - 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 / r Total Energy E = K. E. + P. E. = 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 /2 r +( - 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 / r) = - 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 /2 r For n th orbit we can write E n = - 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 /2 r n --- (ii) Now using Bohr s postulate mvr = nh/2π or, v = nh/2πmr Putting the value of v in equation (i) we get, m/r [nh/2πmr] 2 = 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 / r 2 r = ε 0 h 2 n 2 /πmze 2 r n = ε 0 h 2 n 2 /πmze 2 Substituting value of r n in equation (ii), we get E n = - 1/4πε 0 x Ze 2 /2(ε 0 h 2 n 2 /πmze 2 ) = - mz 2 e 4 /8ε 0 h 2 n 2 E n = -Z 2 Rhc/n 2, where R = me 4 /8 ε 2 0 ch 3 (R = Rydberg constant) For hydrogen atom Z = 1 E n = -Rch/n 2 If n i and n f are the quantum numbers of initial and final states and E i and E f are energies of Electron in H- atom in initial and final state, we have 2 2 E i = -Rch/n i and E f = -Rch/n f If ν = frequency of emitted radiation, we get ν = E i E f /h = -Rc/n 2 i (-Rc/n 2 f ) = Rc[1/n 2 f 1/n 2 i ]
6 Q.9. State law of radioactivity and derive the relation N t = N 0 e - λ t for radioactive decay. Ans:- Radioactive Decay Law:- The rate of decay of radioactive nuclei is directly proportional to the number of undecayed nuclei at that time. Derivation of formula:- Let initially the number of atoms in radioactive element is N 0 and N the number of atoms after time t. After time t, let dn be the number of atoms which disintegrate in a short interval dt, then rate of disintegration will be dn/dt, this is also called the activity of the substance/element. According to Rutherford-Soddy law dn/dt N OrdN/dt = -λn --- (i) Whereλ is a constant of disintegration. Its unit is s -1. Negative sign shows that the rate of disintegration decreases with the increase of time. For a given element λ is constant. Equation (i) may be written as dn/n = -λdt Integrating, log N e = -λt + C --- (ii) Where C is constant of integration. At t = 0, N = N 0 Therefore, log e N 0 = 0+C => C = log e N 0 From equation (ii), log e N = -λt + log e N 0 or, log e N log e N 0 = -λt or, log e N/N 0 = -λt or, N/N 0 = e - λ t or, N = N 0 e -λt according to above equation, the number of undecayed atoms/nuclei of a given radioactive element decreases exponentially with time (i.e. more rapidly first and slowly afterwards).
7 Q.10. Define Half-life period and decay constant of a radioactive sample. Derive the relation between them. Ans:- Half-life Period (T) :- The half-life period of an element is defined as the time in which the number of radioactive nuclei decay to half of its initial value. Decay Constant:- The decay constant of a radioactive element is defines as the reciprocal of time in which the number of undecayed nuclei of the radioactive element falls to 1/e times to its initial value. Relation:- We know the radioactive decay equation N = N 0 e -λt When t = T, N = N 0 /2 Therefore, N 0 /2 = N 0 e - λ T Or, e - λ T = ½ Taking log both sides -λt log e e = log e 1 log e 2 Or, λt = log e 2 Therefore, T = log e 2/λ = log 10 2/λ = x /λ Or, T = /λ Prepared By:- B. K. Singh PGT (Physics) K. V. Danapur Cantt (SS)
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI
 UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
Chapter 44. Nuclear Structure
 Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
= : K A
 Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Fundamental Forces. Range Carrier Observed? Strength. Gravity Infinite Graviton No. Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983)
 Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
Downloaded from
 constant UNIT VIII- ATOMS & NUCLEI FORMULAE ANDSHORTCUT FORMULAE. Rutherford s -Particle scattering experiment (Geiger Marsden experiment) IMPOTANT OBSERVATION Scattering of -particles by heavy nuclei
constant UNIT VIII- ATOMS & NUCLEI FORMULAE ANDSHORTCUT FORMULAE. Rutherford s -Particle scattering experiment (Geiger Marsden experiment) IMPOTANT OBSERVATION Scattering of -particles by heavy nuclei
Instead, the probability to find an electron is given by a 3D standing wave.
 Lecture 24-1 The Hydrogen Atom According to the Uncertainty Principle, we cannot know both the position and momentum of any particle precisely at the same time. The electron in a hydrogen atom cannot orbit
Lecture 24-1 The Hydrogen Atom According to the Uncertainty Principle, we cannot know both the position and momentum of any particle precisely at the same time. The electron in a hydrogen atom cannot orbit
Chapter 10 - Nuclear Physics
 The release of atomic energy has not created a new problem. It has merely made more urgent the necessity of solving an existing one. -Albert Einstein David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Ernest
The release of atomic energy has not created a new problem. It has merely made more urgent the necessity of solving an existing one. -Albert Einstein David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Ernest
UNIT-VIII (ATOMS AND NUCLEI)
 UNIT-VIII (ATOMS AND NUCLEI) GIST OF LESSON/FORMULAE ANDSHORTCUT FORMULAE 1. Rutherford s -Particle scattering experiment (Geiger Marsden experiment) IMPOTANT OBSERVATION Scattering of -particles by heavy
UNIT-VIII (ATOMS AND NUCLEI) GIST OF LESSON/FORMULAE ANDSHORTCUT FORMULAE 1. Rutherford s -Particle scattering experiment (Geiger Marsden experiment) IMPOTANT OBSERVATION Scattering of -particles by heavy
Nuclear Properties. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12
 Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics Chapter 6.2 Radioactivity From IB OCC, prepared by J. Domingues based on Tsokos Physics book Warm Up Define: nucleon atomic number mass number isotope. Radioactivity In 1896,
6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics Chapter 6.2 Radioactivity From IB OCC, prepared by J. Domingues based on Tsokos Physics book Warm Up Define: nucleon atomic number mass number isotope. Radioactivity In 1896,
Nuclear Properties. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12
 Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
Nuclear Properties. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12
 Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-1 THE ATOM AND ITS NUCLEUS IB Assessment Statements Topic 7.1, The Atom 7.1.1. Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-1 THE ATOM AND ITS NUCLEUS IB Assessment Statements Topic 7.1, The Atom 7.1.1. Describe a model of the atom that features a small nucleus
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 18 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear properties Binding energy Radioactivity The Decay Process Natural Radioactivity Last lecture: 1. Quantum physics Electron Clouds
General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 18 Modern Physics Nuclear Physics Nuclear properties Binding energy Radioactivity The Decay Process Natural Radioactivity Last lecture: 1. Quantum physics Electron Clouds
The Atomic Nucleus. Bloomfield Sections 14.1, 14.2, and 14.3 (download) 4/13/04 ISP A 1
 The Atomic Nucleus Bloomfield Sections 14.1, 14., and 14. (download) 4/1/04 ISP 09-1A 1 What is matter made of? Physics is a reductionist science. Beneath the surface, nature is simple! All matter is composed
The Atomic Nucleus Bloomfield Sections 14.1, 14., and 14. (download) 4/1/04 ISP 09-1A 1 What is matter made of? Physics is a reductionist science. Beneath the surface, nature is simple! All matter is composed
Chapter from the Internet course SK180N Modern Physics
 Nuclear physics 1 Chapter 10 Chapter from the Internet course SK180N Modern Physics Contents 10.4.1 Introduction to Nuclear Physics 10.4.2 Natural radioactivity 10.4.3 alpha-decay 10.4.4 beta-decay 10.4.5
Nuclear physics 1 Chapter 10 Chapter from the Internet course SK180N Modern Physics Contents 10.4.1 Introduction to Nuclear Physics 10.4.2 Natural radioactivity 10.4.3 alpha-decay 10.4.4 beta-decay 10.4.5
Bi β + Po Bismuth-214 is radioactive. It has a half-life of 20 minutes. (a) The nuclide notation for bismuth-214 is Bi.
 1 Bismuth-214 is radioactive. It has a half-life of 20 minutes. (a) The nuclide notation for bismuth-214 is Bi. State the composition of the nucleus of bismuth-214. [2] (b) Bismuth-214 decays by β-decay
1 Bismuth-214 is radioactive. It has a half-life of 20 minutes. (a) The nuclide notation for bismuth-214 is Bi. State the composition of the nucleus of bismuth-214. [2] (b) Bismuth-214 decays by β-decay
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS. Atoms. 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model. 6. Hydrogen spectrum
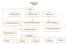 CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
Radioactivity and energy levels
 Radioactivity and energy levels Book page 497-503 Review of radioactivity β ; Free neutron proton β- decay is continuous β : Proton in nucleus neutron antineutrino neutrino Summary of useful equations
Radioactivity and energy levels Book page 497-503 Review of radioactivity β ; Free neutron proton β- decay is continuous β : Proton in nucleus neutron antineutrino neutrino Summary of useful equations
Basic science. Atomic structure. Electrons. The Rutherford-Bohr model of an atom. Electron shells. Types of Electrons. Describing an Atom
 Basic science A knowledge of basic physics is essential to understanding how radiation originates and behaves. This chapter works through what an atom is; what keeps it stable vs. radioactive and unstable;
Basic science A knowledge of basic physics is essential to understanding how radiation originates and behaves. This chapter works through what an atom is; what keeps it stable vs. radioactive and unstable;
Structure of the Atom. Thomson s Atomic Model. Knowledge of atoms in Experiments of Geiger and Marsden 2. Experiments of Geiger and Marsden
 CHAPTER 4 Structure of the Atom 4.1 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford 4. Rutherford Scattering 4.3 The Classic Atomic Model 4.4 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom 4.5 Successes & Failures of
CHAPTER 4 Structure of the Atom 4.1 The Atomic Models of Thomson and Rutherford 4. Rutherford Scattering 4.3 The Classic Atomic Model 4.4 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom 4.5 Successes & Failures of
 UNIT-VIII ATOMIC NUCLEUS 1) what conclusions were drawn from the observation in which few alpha-particle were seen rebounding from gold foil? 2) which observation led to the conclusion in the α-particle
UNIT-VIII ATOMIC NUCLEUS 1) what conclusions were drawn from the observation in which few alpha-particle were seen rebounding from gold foil? 2) which observation led to the conclusion in the α-particle
Atomic Structure. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4
 Atomic Structure Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4 Models of the Atom Required features: 1. Electrons as constituents. 2. Some positive charges to neutralize the negative charges of the electrons. 3. Some scheme
Atomic Structure Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4 Models of the Atom Required features: 1. Electrons as constituents. 2. Some positive charges to neutralize the negative charges of the electrons. 3. Some scheme
NUCLEI, RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR REACTIONS
 NUCLEI, RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR REACTIONS VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. Which of the two is bigger 1 kwh or 1 MeV? Q-2. What should be the approximate minimum energy of a gamma ray photon for pair
NUCLEI, RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR REACTIONS VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. Which of the two is bigger 1 kwh or 1 MeV? Q-2. What should be the approximate minimum energy of a gamma ray photon for pair
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Chapter 4 Atomic and nuclear physics INTRODUCTION: The technologies used in nuclear medicine for diagnostic imaging have evolved over the last century, starting with Röntgen s discovery of X rays and Becquerel
Chapter 4 Atomic and nuclear physics INTRODUCTION: The technologies used in nuclear medicine for diagnostic imaging have evolved over the last century, starting with Röntgen s discovery of X rays and Becquerel
Atoms, nuclei, particles
 Atoms, nuclei, particles Nikolaos Kidonakis Physics for Georgia Academic Decathlon September 2016 Age-old questions What are the fundamental particles of matter? What are the fundamental forces of nature?
Atoms, nuclei, particles Nikolaos Kidonakis Physics for Georgia Academic Decathlon September 2016 Age-old questions What are the fundamental particles of matter? What are the fundamental forces of nature?
Lecture 3 Radioactivity
 Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall begin with a general discussion on the nucleus. Learn about some characteristics of nucleons. Understand some concepts on stability of a
Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following We shall begin with a general discussion on the nucleus. Learn about some characteristics of nucleons. Understand some concepts on stability of a
Atomic Structure. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4
 Atomic Structure Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4 Models of the Atom Required features: 1. Electrons as constituents. 2. Some positive charges to neutralize the negative charges of the electrons. 3. Some scheme
Atomic Structure Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4 Models of the Atom Required features: 1. Electrons as constituents. 2. Some positive charges to neutralize the negative charges of the electrons. 3. Some scheme
Nuclear Powe. Bronze Buddha at Hiroshima
 Nuclear Powe Bronze Buddha at Hiroshima Nuclear Weapons Nuclear Power Is it Green & Safe? Nuclear Waste 250,000 tons of Spent Fuel 10,000 tons made per year Health Effects of Ionizing Radiation Radiocarbon
Nuclear Powe Bronze Buddha at Hiroshima Nuclear Weapons Nuclear Power Is it Green & Safe? Nuclear Waste 250,000 tons of Spent Fuel 10,000 tons made per year Health Effects of Ionizing Radiation Radiocarbon
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 7-1A DISCRETE ENERGY Essential Idea: In the microscopic world energy is discrete. Theory Of Knowledge: The role of luck/serendipity in
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 7-1A DISCRETE ENERGY Essential Idea: In the microscopic world energy is discrete. Theory Of Knowledge: The role of luck/serendipity in
NUCLEAR PHYSICS. Challenging MCQ questions by The Physics Cafe. Compiled and selected by The Physics Cafe
 NUCLEAR PHYSICS Challenging MCQ questions by The Physics Cafe Compiled and selected by The Physics Cafe 1 The activity of a radioactive sample decreases to one third of its original activity Ao in a period
NUCLEAR PHYSICS Challenging MCQ questions by The Physics Cafe Compiled and selected by The Physics Cafe 1 The activity of a radioactive sample decreases to one third of its original activity Ao in a period
Introduction to Nuclear Engineering. Ahmad Al Khatibeh
 Introduction to Nuclear Engineering Ahmad Al Khatibeh CONTENTS INTRODUCTION (Revision) RADIOACTIVITY Radioactive Decay Rates Units of Measurement for Radioactivity Variation of Radioactivity Over Time.
Introduction to Nuclear Engineering Ahmad Al Khatibeh CONTENTS INTRODUCTION (Revision) RADIOACTIVITY Radioactive Decay Rates Units of Measurement for Radioactivity Variation of Radioactivity Over Time.
SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
Topic 12: Quantum & nuclear physics - AHL 12.2 Nuclear physics
 Topic 12.2 is an extension of Topic 7.2. Essential idea: The idea of discreteness that we met in the atomic world continues to exist in the nuclear world as well. Nature of science: (1) Theoretical advances
Topic 12.2 is an extension of Topic 7.2. Essential idea: The idea of discreteness that we met in the atomic world continues to exist in the nuclear world as well. Nature of science: (1) Theoretical advances
THE EDUCARE (SIROHI CLASSES) TEST SERIES 2018
 THE EDUCARE (SIROHI CLASSES) TEST SERIES 2018 XII PHYSICS TEST MODERN PHYSICS NAME-... DATE-.. MM- 25 TIME-1 HR 1) Write one equation representing nuclear fusion reaction. (1) 2) Arrange radioactive radiations
THE EDUCARE (SIROHI CLASSES) TEST SERIES 2018 XII PHYSICS TEST MODERN PHYSICS NAME-... DATE-.. MM- 25 TIME-1 HR 1) Write one equation representing nuclear fusion reaction. (1) 2) Arrange radioactive radiations
Atomic Structure. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4
 Atomic Structure Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4 Models of the Atom Required features: 1. Electrons as constituents. 2. Some positive charges to neutralize the negative charges of the electrons. 3. Some scheme
Atomic Structure Thornton and Rex, Ch. 4 Models of the Atom Required features: 1. Electrons as constituents. 2. Some positive charges to neutralize the negative charges of the electrons. 3. Some scheme
PHYSICS CET-2014 MODEL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS NUCLEAR PHYSICS
 PHYSICS CET-2014 MODEL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS NUCLEAR PHYSICS IMPORTANT FORMULE TO BE REMEMBERED IMPORTANT FORMULE TO BE REMEMBERED 1. Identify the correct statement with regards to nuclear density a) It
PHYSICS CET-2014 MODEL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS NUCLEAR PHYSICS IMPORTANT FORMULE TO BE REMEMBERED IMPORTANT FORMULE TO BE REMEMBERED 1. Identify the correct statement with regards to nuclear density a) It
Radioactivity, Radiation and the Structure of the atom
 Radioactivity, Radiation and the Structure of the atom What do you know (or can we deduce) about radioactivity from what you have learned in the course so far? How can we learn about whether radioactive
Radioactivity, Radiation and the Structure of the atom What do you know (or can we deduce) about radioactivity from what you have learned in the course so far? How can we learn about whether radioactive
Nuclear Theory - Course 227 NUCLEAR STRUCTURE
 Nuclear Theory - Course 227 NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The Nucleus, Nuclear Particles The atomic nucleus consists of Z protons and N neutrons, where Z and N are the atomic number and neutron number respectively.
Nuclear Theory - Course 227 NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The Nucleus, Nuclear Particles The atomic nucleus consists of Z protons and N neutrons, where Z and N are the atomic number and neutron number respectively.
Chapter 42. Nuclear Physics
 Chapter 42 Nuclear Physics In the previous chapters we have looked at the quantum behavior of electrons in various potentials (quantum wells, atoms, etc) but have neglected what happens at the center of
Chapter 42 Nuclear Physics In the previous chapters we have looked at the quantum behavior of electrons in various potentials (quantum wells, atoms, etc) but have neglected what happens at the center of
CLASS 12th. Modern Physics-II
 CLASS 12th Modern Physics-II 1. Thomson s Atom Model From the study of discharge of electricity through gases, it became clear that an atom consists of positive and negative charges. As the atom is electrically
CLASS 12th Modern Physics-II 1. Thomson s Atom Model From the study of discharge of electricity through gases, it became clear that an atom consists of positive and negative charges. As the atom is electrically
NUCLEI. Atomic mass unit
 13 NUCLEI Atomic mass unit It is a unit used to express the mass of atoms and particles inside it. One atomic mass unit is the mass of atom. 1u = 1.660539 10. Chadwick discovered neutron. The sum of number
13 NUCLEI Atomic mass unit It is a unit used to express the mass of atoms and particles inside it. One atomic mass unit is the mass of atom. 1u = 1.660539 10. Chadwick discovered neutron. The sum of number
Physics 102: Lecture 26. X-rays. Make sure your grade book entries are correct. Physics 102: Lecture 26, Slide 1
 Physics 102: Lecture 26 X-rays Make sure your grade book entries are correct. Physics 102: Lecture 26, Slide 1 X-Rays Photons with energy in approx range 100eV to 100,000eV. This large energy means they
Physics 102: Lecture 26 X-rays Make sure your grade book entries are correct. Physics 102: Lecture 26, Slide 1 X-Rays Photons with energy in approx range 100eV to 100,000eV. This large energy means they
Lecture 32 April
 Lecture 32 April 08. 2016. Hydrogen Discharge Tube and Emission of Discrete Wavelengths Description of the discrete Hydrogen Emission Spectrum by the Balmer (1884) Rydberg Ritz formula (1908) Cathode Ray
Lecture 32 April 08. 2016. Hydrogen Discharge Tube and Emission of Discrete Wavelengths Description of the discrete Hydrogen Emission Spectrum by the Balmer (1884) Rydberg Ritz formula (1908) Cathode Ray
Physics 3223 Solution to Assignment #5
 Physics 3223 Solution to Assignment #5 October 20, 1999 6.1 From the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, x p h, we estimate that a typical kinetic energy of an electron in an atom would be K ( p)2 2m h 2
Physics 3223 Solution to Assignment #5 October 20, 1999 6.1 From the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, x p h, we estimate that a typical kinetic energy of an electron in an atom would be K ( p)2 2m h 2
Phys 102 Lecture 27 The strong & weak nuclear forces
 Phys 102 Lecture 27 The strong & weak nuclear forces 1 4 Fundamental forces of Nature Today Gravitational force (solar system, galaxies) Electromagnetic force (atoms, molecules) Strong force (atomic nuclei)
Phys 102 Lecture 27 The strong & weak nuclear forces 1 4 Fundamental forces of Nature Today Gravitational force (solar system, galaxies) Electromagnetic force (atoms, molecules) Strong force (atomic nuclei)
Chapter 29. Nuclear Physics
 Chapter 29 Nuclear Physics Ernest Rutherford 1871 1937 Discovery that atoms could be broken apart Studied radioactivity Nobel prize in 1908 Some Properties of Nuclei All nuclei are composed of protons
Chapter 29 Nuclear Physics Ernest Rutherford 1871 1937 Discovery that atoms could be broken apart Studied radioactivity Nobel prize in 1908 Some Properties of Nuclei All nuclei are composed of protons
The number of protons in the nucleus is known as the atomic number Z, and determines the chemical properties of the element.
 I. NUCLEAR PHYSICS I.1 Atomic Nucleus Very briefly, an atom is formed by a nucleus made up of nucleons (neutrons and protons) and electrons in external orbits. The number of electrons and protons is equal
I. NUCLEAR PHYSICS I.1 Atomic Nucleus Very briefly, an atom is formed by a nucleus made up of nucleons (neutrons and protons) and electrons in external orbits. The number of electrons and protons is equal
The Nucleus. PHY 3101 D. Acosta
 The Nucleus PHY 30 D. Acosta Rutherford Scattering Experiments by Geiger & Marsden in 909 /5/005 PHY 30 -- D. Acosta Rutherford Model of the Atom Conclusion: the atom contains a positive nucleus < 0 fm
The Nucleus PHY 30 D. Acosta Rutherford Scattering Experiments by Geiger & Marsden in 909 /5/005 PHY 30 -- D. Acosta Rutherford Model of the Atom Conclusion: the atom contains a positive nucleus < 0 fm
Z is the atomic number, the number of protons: this defines the element. Isotope: Nuclides of an element (i.e. same Z) with different N.
 Lecture : The nucleus and nuclear instability Nuclei are described using the following nomenclature: A Z Element N Z is the atomic number, the number of protons: this defines the element. A is called the
Lecture : The nucleus and nuclear instability Nuclei are described using the following nomenclature: A Z Element N Z is the atomic number, the number of protons: this defines the element. A is called the
Nuclear Binding Energy
 Nuclear Energy Nuclei contain Z number of protons and (A - Z) number of neutrons, with A the number of nucleons (mass number) Isotopes have a common Z and different A The masses of the nucleons and the
Nuclear Energy Nuclei contain Z number of protons and (A - Z) number of neutrons, with A the number of nucleons (mass number) Isotopes have a common Z and different A The masses of the nucleons and the
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-6 NUCLEAR PHYSICS IB Assessment Statements Topic 13.2, Nuclear Physics 13.2.1. Explain how the radii of nuclei may be estimated from
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 6-6 NUCLEAR PHYSICS IB Assessment Statements Topic 13.2, Nuclear Physics 13.2.1. Explain how the radii of nuclei may be estimated from
Nuclear Physics Part 1: Nuclear Structure & Reactions
 Nuclear Physics Part 1: Nuclear Structure & Reactions Last modified: 25/01/2018 Links The Atomic Nucleus Nucleons Strong Nuclear Force Nuclei Are Quantum Systems Atomic Number & Atomic Mass Number Nuclides
Nuclear Physics Part 1: Nuclear Structure & Reactions Last modified: 25/01/2018 Links The Atomic Nucleus Nucleons Strong Nuclear Force Nuclei Are Quantum Systems Atomic Number & Atomic Mass Number Nuclides
Fisika Inti Nuclear Physics 5/14/2010 1
 Fisika Inti Nuclear Physics 5/14/2010 1 Pengertian Modern: Gambar onion Modern understanding: the ``onion picture Atom Let s see what s inside! 5/14/2010 2 Pengertian Modern: Gambar onion Modern understanding:
Fisika Inti Nuclear Physics 5/14/2010 1 Pengertian Modern: Gambar onion Modern understanding: the ``onion picture Atom Let s see what s inside! 5/14/2010 2 Pengertian Modern: Gambar onion Modern understanding:
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Bohr s Correspondence Principle Bohr s Correspondence Principle states that quantum mechanics is in agreement with classical physics when the energy differences between quantized
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Bohr s Correspondence Principle Bohr s Correspondence Principle states that quantum mechanics is in agreement with classical physics when the energy differences between quantized
Introduction to Modern Physics Problems from previous Exams 3
 Introduction to Modern Physics Problems from previous Exams 3 2007 An electron of mass 9 10 31 kg moves along the x axis at a velocity.9c. a. Calculate the rest energy of the electron. b. Calculate its
Introduction to Modern Physics Problems from previous Exams 3 2007 An electron of mass 9 10 31 kg moves along the x axis at a velocity.9c. a. Calculate the rest energy of the electron. b. Calculate its
Nice Try. Introduction: Development of Nuclear Physics 20/08/2010. Nuclear Binding, Radioactivity. SPH4UI Physics
 SPH4UI Physics Modern understanding: the ``onion picture Nuclear Binding, Radioactivity Nucleus Protons tom and neutrons Let s see what s inside! 3 Nice Try Introduction: Development of Nuclear Physics
SPH4UI Physics Modern understanding: the ``onion picture Nuclear Binding, Radioactivity Nucleus Protons tom and neutrons Let s see what s inside! 3 Nice Try Introduction: Development of Nuclear Physics
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
Basic Nuclear Theory. Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability
 Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY
 PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 30.1 Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: 30.1 Structure
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 30.1 Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: 30.1 Structure
(a) e/m of a particle is called the specific charge of the particle.
 e/m of an electron (Thomson Method):- (a) e/m of a particle is called the specific charge of the particle. e/m = v/rb Here, r is the radius of curvature, B is the strength of magnetic field, v is the velocity,
e/m of an electron (Thomson Method):- (a) e/m of a particle is called the specific charge of the particle. e/m = v/rb Here, r is the radius of curvature, B is the strength of magnetic field, v is the velocity,
What do we know from GCSE?
 Radioactivity jessica.wade08@imperial.ac.uk www.makingphysicsfun.com Department of Physics & Centre for Plastic Electronics, Imperial College London Faculty of Natural & Mathematical Sciences, King s College
Radioactivity jessica.wade08@imperial.ac.uk www.makingphysicsfun.com Department of Physics & Centre for Plastic Electronics, Imperial College London Faculty of Natural & Mathematical Sciences, King s College
CURRENT ELECTRICITY LEVEL A QUESTIONS
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY LEVEL A QUESTIONS 1.Define electric current and give its SI unit. (1) 2. Define current density and give its SI unit. (1) 3. State Ohm s law. (1) 4. Derive an expression for resistivity..mention
CURRENT ELECTRICITY LEVEL A QUESTIONS 1.Define electric current and give its SI unit. (1) 2. Define current density and give its SI unit. (1) 3. State Ohm s law. (1) 4. Derive an expression for resistivity..mention
Chapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Stability and Modes of Decay
 Chapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Stability and Modes of Decay History and Discovery of Radioactivity The Discovery of Radioactivity (1896) Antoine-Henri Bequerel designed experiment to determine
Chapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Stability and Modes of Decay History and Discovery of Radioactivity The Discovery of Radioactivity (1896) Antoine-Henri Bequerel designed experiment to determine
If you cannot solve the whole problem, write down all relevant equations and explain how you will approach the solution. Show steps clearly.
 Letter ID Comprehensive Exam Session I Modern Physics (Including Stat.Mech) Physics Department- Proctor: Dr. Chris Butenhoff (Sat. Jan. 11 th, 2014) (3 hours long 9:00 to 12:00 AM) If you cannot solve
Letter ID Comprehensive Exam Session I Modern Physics (Including Stat.Mech) Physics Department- Proctor: Dr. Chris Butenhoff (Sat. Jan. 11 th, 2014) (3 hours long 9:00 to 12:00 AM) If you cannot solve
Sources of Radiation
 Radioactivity Sources of Radiation Natural Sources Cosmic Radiation The Earth is constantly bombarded by radiation from outside our solar system. interacts in the atmosphere to create secondary radiation
Radioactivity Sources of Radiation Natural Sources Cosmic Radiation The Earth is constantly bombarded by radiation from outside our solar system. interacts in the atmosphere to create secondary radiation
Class XII - Physics Atoms Chapter-wise Problems
 Class XII - Physics Atoms Chapter-wise Problems Multiple Choice Question :- 1.1 Taking the Bohr radius as a = 53pm, the radius of Li ++ ion in its ground state, on the basis of Bohr s model, will be about
Class XII - Physics Atoms Chapter-wise Problems Multiple Choice Question :- 1.1 Taking the Bohr radius as a = 53pm, the radius of Li ++ ion in its ground state, on the basis of Bohr s model, will be about
Topic 7 &13 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics
 Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
PHY293 Lecture #15. November 27, Quantum Mechanics and the Atom
 PHY293 Lecture #15 November 27, 2017 1. Quantum Mechanics and the Atom The Thompson/Plum Pudding Model Thompson discovered the electron in 1894 (Nobel Prize in 1906) Heating materials (metals) causes corpuscles
PHY293 Lecture #15 November 27, 2017 1. Quantum Mechanics and the Atom The Thompson/Plum Pudding Model Thompson discovered the electron in 1894 (Nobel Prize in 1906) Heating materials (metals) causes corpuscles
Atomic Models the Nucleus
 Atomic Models the Nucleus Rutherford (read his bio on pp 134-5), who had already won a Nobel for his work on radioactivity had also named alpha, beta, gamma radiation, developed a scattering technique
Atomic Models the Nucleus Rutherford (read his bio on pp 134-5), who had already won a Nobel for his work on radioactivity had also named alpha, beta, gamma radiation, developed a scattering technique
Nuclear Structure. chapter
 chapter 44 Nuclear Structure 44.1 Some Properties of Nuclei 44.2 Nuclear Binding Energy 44.3 Nuclear Models 44.4 Radioactivity 44.5 The Decay Processes 44.6 Natural Radioactivity 44.7 Nuclear Reactions
chapter 44 Nuclear Structure 44.1 Some Properties of Nuclei 44.2 Nuclear Binding Energy 44.3 Nuclear Models 44.4 Radioactivity 44.5 The Decay Processes 44.6 Natural Radioactivity 44.7 Nuclear Reactions
Phys102 Lecture 29, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Phys10 Lecture 9, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Key Points Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Alpha, Beta and Gamma Decays References 30-1,,3,4,5,6,7. Atomic Structure Nitrogen (N) Atom
Phys10 Lecture 9, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Key Points Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Alpha, Beta and Gamma Decays References 30-1,,3,4,5,6,7. Atomic Structure Nitrogen (N) Atom
Chapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Stability and Modes of Decay
 Chapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Stability and Modes of Decay History and Discovery of Radioactivity The Discovery of Radioactivity (1896) Antoine-Henri Bequerel designed experiment to determine
Chapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Stability and Modes of Decay History and Discovery of Radioactivity The Discovery of Radioactivity (1896) Antoine-Henri Bequerel designed experiment to determine
CHAPTER 12 The Atomic Nucleus
 CHAPTER 12 The Atomic Nucleus 12.1 Discovery of the Neutron 12.2 Nuclear Properties 12.3 The Deuteron 12.4 Nuclear Forces 12.5 Nuclear Stability 12.6 Radioactive Decay 12.7 Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay
CHAPTER 12 The Atomic Nucleus 12.1 Discovery of the Neutron 12.2 Nuclear Properties 12.3 The Deuteron 12.4 Nuclear Forces 12.5 Nuclear Stability 12.6 Radioactive Decay 12.7 Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Decay
FXA Candidates should be able to :
 1 Candidates should be able to : INTRODUCTION Describe qualitatively the alpha-particle scattering experiment and the evidence this provides for the existence, charge and small size of the nucleus. Describe
1 Candidates should be able to : INTRODUCTION Describe qualitatively the alpha-particle scattering experiment and the evidence this provides for the existence, charge and small size of the nucleus. Describe
The strong & weak nuclear forces
 Phys 102 Lecture 27 The strong & weak nuclear forces 1 4 Fundamental forces of Nature Today Gravitational force (solar system, galaxies) Electromagnetic force (atoms, molecules) Strong force (atomic nuclei)
Phys 102 Lecture 27 The strong & weak nuclear forces 1 4 Fundamental forces of Nature Today Gravitational force (solar system, galaxies) Electromagnetic force (atoms, molecules) Strong force (atomic nuclei)
Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
 Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Sascha Vogel Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher Wednesday, 14:15-16:45 FIS Lecture Hall Lecturers Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher svogel@th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de
Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics Sascha Vogel Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher Wednesday, 14:15-16:45 FIS Lecture Hall Lecturers Elena Bratkovskaya Marcus Bleicher svogel@th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de
Z is the atomic number, the number of protons: this defines the element. Isotope: Nuclides of an element (i.e. same Z) with different N.
 Lecture : The nucleus and nuclear instability Nuclei are described using the following nomenclature: A Z Element N Z is the atomic number, the number of protons: this defines the element. A is called the
Lecture : The nucleus and nuclear instability Nuclei are described using the following nomenclature: A Z Element N Z is the atomic number, the number of protons: this defines the element. A is called the
Radioactivity. Nuclear Physics. # neutrons vs# protons Where does the energy released in the nuclear 11/29/2010 A=N+Z. Nuclear Binding, Radioactivity
 Physics 1161: Lecture 25 Nuclear Binding, Radioactivity Sections 32-1 32-9 Marie Curie 1867-1934 Radioactivity Spontaneous emission of radiation from the nucleus of an unstable isotope. Antoine Henri Becquerel
Physics 1161: Lecture 25 Nuclear Binding, Radioactivity Sections 32-1 32-9 Marie Curie 1867-1934 Radioactivity Spontaneous emission of radiation from the nucleus of an unstable isotope. Antoine Henri Becquerel
THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM Models of the atom positive charge uniformly distributed over a sphere J. J. Thomson model of the atom (1907) ~2x10-10 m plum-pudding model: positive charge
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM Models of the atom positive charge uniformly distributed over a sphere J. J. Thomson model of the atom (1907) ~2x10-10 m plum-pudding model: positive charge
FLAP P9.2 Radioactive decay COPYRIGHT 1998 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY S570 V1.1
 Atoms of a given substance with differing atomic masses are said to be isotopes of that substance. The various isotopes of an element all contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Atoms of a given substance with differing atomic masses are said to be isotopes of that substance. The various isotopes of an element all contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Nuclear Spin and Stability. PHY 3101 D. Acosta
 Nuclear Spin and Stability PHY 3101 D. Acosta Nuclear Spin neutrons and protons have s = ½ (m s = ± ½) so they are fermions and obey the Pauli- Exclusion Principle The nuclear magneton is eh m µ e eh 1
Nuclear Spin and Stability PHY 3101 D. Acosta Nuclear Spin neutrons and protons have s = ½ (m s = ± ½) so they are fermions and obey the Pauli- Exclusion Principle The nuclear magneton is eh m µ e eh 1
Lecture 4. The Bohr model of the atom. De Broglie theory. The Davisson-Germer experiment
 Lecture 4 The Bohr model of the atom De Broglie theory The Davisson-Germer experiment Objectives Learn about electron energy levels in atoms and how Bohr's model can be used to determine the energy levels
Lecture 4 The Bohr model of the atom De Broglie theory The Davisson-Germer experiment Objectives Learn about electron energy levels in atoms and how Bohr's model can be used to determine the energy levels
Physics 1C. End of Chapter 30 Exam Preparationds
 Physics 1C End of Chapter 30 Exam Preparationds Radioactive Decay Example The isotope 137 Cs is a standard laboratory source of gamma rays. The half-life of 137 Cs is 30 years. (a) How many 137 Cs atoms
Physics 1C End of Chapter 30 Exam Preparationds Radioactive Decay Example The isotope 137 Cs is a standard laboratory source of gamma rays. The half-life of 137 Cs is 30 years. (a) How many 137 Cs atoms
Physics 1C. Lecture 29A. "Nuclear powered vacuum cleaners will probably be a reality within 10 years. " --Alex Lewyt, 1955
 Physics 1C Lecture 29A "Nuclear powered vacuum cleaners will probably be a reality within 10 years. " --Alex Lewyt, 1955 The Nucleus All nuclei are composed of protons and neutrons (they can also be called
Physics 1C Lecture 29A "Nuclear powered vacuum cleaners will probably be a reality within 10 years. " --Alex Lewyt, 1955 The Nucleus All nuclei are composed of protons and neutrons (they can also be called
Mass number i. Example U (uranium 235) and U (uranium 238) atomic number e. Average atomic mass weighted of the isotopes of that element i.
 CP NT Ch. 4&25 I. Atomic Theory and Structure of the Atom a. Democritus all matter consists of very small, indivisible particles, which he named i. Atom smallest particle of an element that retains all
CP NT Ch. 4&25 I. Atomic Theory and Structure of the Atom a. Democritus all matter consists of very small, indivisible particles, which he named i. Atom smallest particle of an element that retains all
Physics 2D Lecture Slides Lecture 15: Feb 2nd Vivek Sharma UCSD Physics. Where are the electrons inside the atom?
 Physics D Lecture Slides Lecture 15: Feb nd 005 Vivek Sharma UCSD Physics Where are the electrons inside the atom? Early Thought: Plum pudding model Atom has a homogenous distribution of Positive charge
Physics D Lecture Slides Lecture 15: Feb nd 005 Vivek Sharma UCSD Physics Where are the electrons inside the atom? Early Thought: Plum pudding model Atom has a homogenous distribution of Positive charge
Chapter 1. The Elements
 Chapter 1. The Elements Electronic structure of atoms (p.1-10) Excitation of atoms (p.10-13) Periodic Table (p. 13-14) References Brownlow (Geochemistry) Gunter Faure (Geochemistry) Krane (Nuclear Physics)
Chapter 1. The Elements Electronic structure of atoms (p.1-10) Excitation of atoms (p.10-13) Periodic Table (p. 13-14) References Brownlow (Geochemistry) Gunter Faure (Geochemistry) Krane (Nuclear Physics)
Introduction to Nuclei I
 Introduction to Nuclei I (The Discovery) The opposite of a correct statement is a false statement. But the opposite of a profound truth may well be another profound truth - Niels Bohr The Atom (as we know
Introduction to Nuclei I (The Discovery) The opposite of a correct statement is a false statement. But the opposite of a profound truth may well be another profound truth - Niels Bohr The Atom (as we know
H 1. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Physics. 1. Parts of Atom. A. Nuclear Structure. 2b. Nomenclature. 2. Isotopes. AstroPhysics Notes
 AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions Updated: 0Feb07 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure. Parts of Atom. Parts of
AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions Updated: 0Feb07 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure. Parts of Atom. Parts of
Atom Physics. Chapter 30. DR JJ UiTM-Cutnell & Johnson 7th ed. 1. Model of an atom-the recent model. Nuclear radius r m
 Chapter 30 Atom Physics DR JJ UiTM-Cutnell & Johnson 7th ed. 1 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom Model of an atom-the recent model Nuclear radius r 10-15 m Electron s position radius r 10-10
Chapter 30 Atom Physics DR JJ UiTM-Cutnell & Johnson 7th ed. 1 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom Model of an atom-the recent model Nuclear radius r 10-15 m Electron s position radius r 10-10
PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #12
 PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #12 Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 Rutherford Scattering Experiment and Rutherford Atomic Model The Classic Atomic Model The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom 1 Quiz 2 results Class
PHYS 3313 Section 001 Lecture #12 Monday, Feb. 24, 2014 Rutherford Scattering Experiment and Rutherford Atomic Model The Classic Atomic Model The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom 1 Quiz 2 results Class
THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION PHYSICS (Theory)
 CLASS:XII Marks : 70 General Instructions: THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2016-17 PHYSICS (Theory) Time : Hrs (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This
CLASS:XII Marks : 70 General Instructions: THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2016-17 PHYSICS (Theory) Time : Hrs (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This
U n 3 n Ba Kr (D) Br (C) Kr (B) Rb (E) 94 37
 1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
ATOMIC MODELS. Models are formulated to fit the available data. Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral.
 ATOMIC MODELS Models are formulated to fit the available data. 1900 Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral. Atom was known to give off electrons. THOMPSON MODEL To satisfy the
ATOMIC MODELS Models are formulated to fit the available data. 1900 Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral. Atom was known to give off electrons. THOMPSON MODEL To satisfy the
H 1. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Physics. 1. Parts of Atom. 2. Isotopes. AstroPhysics Notes. Dr. Bill Pezzaglia. Rough draft. A.
 AstroPhysics Notes Tom Lehrer: Elements Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics Updated: 0Feb Rough draft Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions. Parts
AstroPhysics Notes Tom Lehrer: Elements Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics Updated: 0Feb Rough draft Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions. Parts
Physics 2D Lecture Slides Feb. 2, Sunil Sinha UCSD Physics
 Physics D Lecture Slides Feb., 010 Sunil Sinha UCSD Physics Thomson s Determination of e/m of the Electron In E Field alone, electron lands at D In B field alone, electron lands at E When E and B field
Physics D Lecture Slides Feb., 010 Sunil Sinha UCSD Physics Thomson s Determination of e/m of the Electron In E Field alone, electron lands at D In B field alone, electron lands at E When E and B field
Nuclear Physics 2. D. atomic energy levels. (1) D. scattered back along the original direction. (1)
 Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
CHEM Course web page. Outline for first exam period
 CHEM 3 Course web page http://web.chemistry.gatech.edu/~barefield/3/chem3a.html Outline for first exam period Atomic structure and periodic properties Structures and bonding models for covalent compounds
CHEM 3 Course web page http://web.chemistry.gatech.edu/~barefield/3/chem3a.html Outline for first exam period Atomic structure and periodic properties Structures and bonding models for covalent compounds
