Hyper-reduction of mechanical models involving internal variables
|
|
|
- Sharyl Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hyper-reduction of mechanical models involving internal variables David Ryckelynck Centre des Matériaux Mines ParisTech, UMR CNRS 7633 V. Courtier, S. Cartel (CSDL ANR), D. Missoum Benziane (MELOXEL ANR), S. Quilici, J. Besson, G. Cailletaud, F. Feyel,... November 15, 2011
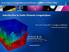
2 The main illustration of the talk: A polycristal plastic model of a specimen in duplex stainless steel We seek a model reduction method that can take into account recent research results in mechanics of materials. u = 0 1 u c2(t) 3D microstructure 2D EBSD 84 grains Iron α BCC Ferrite Prescribed displacements (mm) Umax u C1 e 1 Iron γ FCC Austenite u = 0 2 u c1(t) Ua ΔU u C2 e Time (s) ANR MELOXEL project: pitting corrosion of a duplex stainless steel V. Vignal, H. Pelletier, G. Cailletaud, D. M. Benziane, D. Ryckelynck We expect easier construction of response surfaces by using Reduced Order Models. Here the vector of parameters is µ = {U max, U a, U}. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
3 The main illustration of the talk: A polycristal plastic model of a specimen in duplex stainless steel [Meric & Cailletaud 94] The constitutive equations in the framework of continuum thermomechanics of solids: internal variables are introduced to model the history of the material changes. w(ε,ε p,α 1,...α r,...ρ 1,...ρ s,...) = w e (ε ε p ) c (α ) r 2 Q h rs ρ r ρ s r s (1) x r = c α r r r = Q h rs ρ s (Taylor model :h rs = 1) (2) s f r = τ r x r r r τ 0 τ r = σ : 1 2 (lr n r + n r l r ) (3) Z = K n + f r n+1 (4) 1 r K + ε p = γ r 1 f r 2 (lr n r + n r l r ) γ r r n = sign(τ r x r ) (5) K + f α r r n f = (sign(τ r x r ) d α r ) ρ r r n = (1 b ρ r ) (6) K + K + There is 18 internal variables at each material point. The computational complexity of the constitutive equations is not negligible compared to the complexity of the equilibrium equation. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
4 The main goal of model reduction methods is the design of surrogate models having few state variables, involving few equilibrium equations, while keeping the same material parameters. Issues: What can be the contribution of model reduction methods to nonlinear homogenization? Is it possible to split the set of internal variables into a set of explanatory variables and a set of explained variables? Is it possible to extend the concept of symmetry to define explanatory variables? Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
5 Reduced-Basis approximations We consider two kinds of Reduced-Basis approximations. The usual one, constant RB with respect to the parameters (µ D) of the model: u(x, µ, t) = u o (x, µ, t) + φ k (x) = N φ k (x) ϕ k (t, µ), x Ω µ D t ]0,T ], (7) N N i (x) A ik, k = 1,...,N (8) i=1 The multidimensional RB composed of vectors defined over Ω D: u(x, µ, t) = u o (x, µ, t) + N φ k (x, µ) ϕ k ( t), x Ω µ D t ]0,T ], (9) N φ k (x, µ) = N i (x) A ik (µ), k = 1,...,N (10) i=1 The Ammar-Chinesta point of view: (x, µ) is denoted x. It is a point of Ω = Ω D. Therefore Equation (37) is similar to Equation (7). Only a finite number of sampling points of the parameter domain are considered: F D = {µ p } P p=1. These sampling points are provided by a Design Of Experiment Method (Kriging, Full Factorial design,...). Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
6 Example of multidimensional model in crystal plasticity theory: D = R 3, P = 2 3 µ 3 µ 4 µ 7 µ 8 Ω' = R 6 µ 1 µ 2 µ 5 µ 6 This is a 2D projection of one multidimensional mesh for the simultaneous simulation of 8 cases of loading. There is 434, 000 FE dofs and 15.4e6 internal variables. k=n u(x, µ, t) = u o (x, µ, t) + φ k (x, µ p ) = α(x, µ, t) = φ k (x ) ϕ k (t), x Ω t ]0,T] (11) i=n N i (x) A jk, j = i + (p 1)N, k = 1,...,N, p = 1,...,P, (12) i=1 k=n α Υ k (x ) b k (t), x Ω t ]0,T ] (13) Here α are the internal variables: α R 18. The matrix A has 434,000 rows (N P ). Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
7 Few words on complexity in mechanics of solid materials We consider the parametrized evaluation problem: given a µ D, evaluate the response s(µ) = l(u, α;µ), where (u, α) ((u o +V ) W ) is the solution of the partial differential equation (14) coupled to the constitutive equation (15) and the initial condition (16) bellow. a Ω (v,u;α;µ; t) = 0, v V t ]0, T], (14) α = g(α; u; x; µ; t), x Ω t ]0, T ], (15) t α = α o, x Ω t = 0 (16) Here V is a Hilbert space with the associated inner product (v,u) Ω ; and a Ω is a bounded form linear with respect to v. We assume that the following property holds: for all Ω Z Ω, a Ω (v,u;α;µ; t) = a ΩZ (v,u;α;µ; t) + a Ω\ΩZ (v,u;α;µ; t) (17) In case of multidimensional problems Ω and L 2 (D;V ) are substituted for Ω and V respectively. Equation (15) can be very complex. For instance, its contribution to the computational time of the given example is 33%. Substitute V ROM V for V, has no effect on this complexity even if the dimension of V ROM is very small. Reduced Order Model may be inefficient in such a case. The Hyper-Reduction method can overcome this issue. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
8 Outline: What is hyper-reduction? A theoretical example in case of symmetry. Complexity analysis of Hyper-reduced formulations. Response surface enrichment by adding a sampling point. Response surface enrichment by adding a new dimension to the parameter domain. Incremental construction of Hyper-Reduced Model (HRM) using the APHR method (A Priori Hyper-Reduction). Various examples of Hyper-Reduced Models. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
9 What is Hyper-Reduction [Ryckelynck 2005, 2009]? The Hyper-Reduction method aims to write few governing equations having a low complexity by introducing a Reduced Integration Domain Ω Z Ω and related truncated test functions denoted {ψ k } N. The RID is designed by using the shape of the empirical modes of the ROM. The subset of truncated test functions are empirical modes set to zero outside the RID: ψ k (x) V (18) ψ k (x) = β(x) φ k x Ω (19) β(x) = 0 x Ω \ Ω Z (20) β(x) is a given bubble function equal to 1 almost everywhere in Ω Z. Therefore we introduce the following Petrov-Galerkin formulation: find u (u o + span(φ k ) N ) and α span(υ k ) Nα such that, a Ω (ψ j,u;α;µ; t) = 0, j {1,...,N} t ]0, T ], (21) α = g( α; u; x; µ; t), x Ω Z t ]0, T ], (22) t α = α o, x Ω Z t = 0, (23) k=nα 2 {b k } Nα = arg min α Υ k y k, (24) {y k } Nα Ω Z Property : a Ω (ψ j,u;α;µ; t) = a ΩZ (ψ j,u;α;µ; t), the smaller Ω Z the smaller the complexity. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
10 Property: the Hyper-reduction of symmetrical problems can be exact Several Hyper-reduced formulations of a symmetrical problem can be proposed such that the solution is unchanged. β 2 e 3 e 3 e 3 Ω Ω Z Ω Z Ω β 1 α 2 e 2 e 2 α 1 e 2 δθ δθ δθ δθ e 1 θ e r e 1 e 1 x = r e r (θ) + z e 3 Ω = Ω [0, 2Π] β(θ) = 0 over [ Π, δθ] [δθ, Π] u V ROM = {v V v θ = 0} V Z ROM = {v V v = β w, with w V ROM } The 3D Principle of Virtual Work using truncated test functions is equivalent to the classical 2D weak formulation. In a sense, the Hyper-Reduction is an extension of the symmetry concept. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
11 Proof: the Hyper-reduction of symmetrical problems can be exact v = β w + dβ f(r,z) (25) dθ a Ω (v,u;α;µ; t) = v E(r,z) v dω v F ds v V Z ROM (26) Ω F Ω δθ ( ) = β dθ w E(r,z) u r dr dz w F ds δθ Ω F Ω δθ dβ + δθ dθ Ω dθ (... dr dz) (27) δθ ( ) = β dθ w E(r,z) u r dr dz w F ds (28) δθ Ω F Ω If δθ δθ β dθ 0, then a Ω(v,u;α;µ; t) = 0 v V Z ROM is equivalent to: w E(r,z) u r dr dz w F ds = 0 Ω F Ω w V ROM Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
12 Few comments on the Hyper-Reduction method The internal variables inside Ω Z are explanatory variables. The internal variables outside Ω Z are explained variables. A similar partition of the variables has been proposed in the Partial Least Square (PLS) method [Wold & Herman 1966]. {b k } Nα = arg min {y k } Nα k=nα α Υ k y k ΩZ A minimization similar to Equation (24) was also introduced in the Gappy POD [Everson & Sirovich 1995] by using a mask similar to β. But the Hyper-reduction does not aim to create a RB by using gappy data. The trucated test functions are obtained by using a rectangular truncation matrix Z (m N ): ψ k = N N i (x) β ii A ik, (29) i=1 β = Z T Z (30) The Hyper-Reduction reduces the complexity of the assembly procedure related to the linearized equilibrium equation (J δq = R): A T Z T Z J A δϕ = A T Z T Z R (31) Truncated products for RB can also be found in the EIM method [Barrault & al. 2004]. The Hyper-Reduction of the linearized problem does not require any "off-line" computation. This facilitates adaptive procedures. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
13 An heuristic construction of the RID Ω Z Ω Π F Ω Ω u = 0 u Ω Z is built by aggregating balls whose the radius is h/2 or 2h. Each vector of reduced bases provides a center of a ball. for each mode Υ k related to an internal variable α the center of the ball is: x = arg max y Ω Υ k (y) (32) for each displacement mode φ k the center of the ball is: x = arg max y Ω ( ε(φ k )(y) : ε(φ k )(y) ) (33) One can add to the RID a zone of interest where we need the stress to be estimated. Balls having a radius equal to 2h are related to the displacement modes to facilitate the selection of equilibrium conditions. A region covering a part of the loaded boundary is also added to the RID to avoid the spurious solution u = 0. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
14 Example of RID construction arg max Y M in Ω k Y (γ ) 1 5 Y (γ ) 2 5 Y (γ ) 10 5 One element of the RID... There is about 1800 empirical modes related to A. ROM boundary arg max ε(φ k):ε(φ k) M in Ω φ 1 φ 2 φ 7... An element and its neighbour elements Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
15 The selection of a set of FE equilibrium equations The truncation matrix Z is deduced from the shape of Ω Z. We take into account the FE equilibrium equations that we are able to write knowing that the stress tensor is computed only over Ω Z. β = 0 (over Ω Ω Ζ) β = 1, Zji = 1 Ω Ζ The FE equilibrium equations that we can t take into account are related to the degrees-of-freedoms connected to Ω/Ω Z. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
16 Indicators of computational complexity reduction Let s m be the number of Z rows, ω the average number of non zero entries per row of J. A T Z T Z J A δϕ = A T Z T Z R (34) The left hand side term requires 2 ω m N + 2 m N 2 flops and the right hand side term 2 N m. The usual Galerking procedure is obtained with Ω Z = Ω and Z T Z = I d and the related number of fops are 2 ωn N + 2N N 2 and 2 N N. Therefore the related complexity reduction factor is : G Z = N m In case of multidimensional analyses this factor is : G Z = N P m An other complexity reduction factor related to the integration of the constitutive equations reads: Number of elements in Ω G I = Number of elements in Ω Z Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
17 Response Surface enrichment: by adding a new sampling point denoted µ P +1 The Reduced Bases are provided by the snapshot POD applied to the interpolated state given by the multidimensional model such that: N N α φ k (x) ϕ k (t) = Υ k (x) b k (t) = N φ k (x, µ P +1) ϕ k (t), x Ω t ]0,T ], (35) N α Υ k (x, µ P +1 ) b k (t), x Ω t ]0,T ] (36) The updated reduced variables {ϕ k } N and {b k } Nα are provided by an Hyper-Reduced simulation. APHR FE Figure: 3rd sliding system internal variable. Error < 2.5%, G Z = 149, G I = 25, Speed up = 17.7 (Response Surface speed up > 1000). All the internal variables of the reference model are estimated locally. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
18 Numerical results: The RID Full domain dof elements, internal variables Reduced Integration Domain obtained by the Hyper-Reduction method 7 empirical modes, 7 equilibrium equations 705 elements, internal variables (1/25) Error < 2.5%, G Z = 149, G I = 25, Speed up = There is 76,000 explanatory variables (inside the RID) and 1,800,000 explained internal variables. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
19 Response Surface enrichment: by adding a new dimension to the parameter domain u = 0 1 u c2(t) 3D microstructure 2D EBSD 84 grains Iron α BCC Ferrite Prescribed displacements (mm) Umax u C1 e 1 Iron γ FCC Austenite u = 0 2 u c1(t) Ua ΔU u C2 e Time (s) ANR MELOXEL project: pitting corrosion of a duplex stainless steel V. Vignal, H. Pelletier, G. Cailletaud, D. M. Benziane, D. Ryckelynck Here the former vector of parameters is µ = {U max, U a, U} and the additional parameter is ν = max t u c2 (t). Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
20 Response Surface enrichment: by adding a new dimension to the parameter domain The new parameter domain is D ν. u(x, µ, t, ν) = u o (x, µ, t, ν) + φ k (x, µ) = N φ k (x, µ) ϕ k (t,ν), x Ω µ D t ]0,T ], (37) N N i (x) A ik (µ), k = 1,...,N (38) i=1 α(x, µ, t, ν) = N α Υ k (x, µ P +1 ) b k (t,ν) (39) The updated reduced variables {ϕ k }N and {b k }Nα are provided by an Hyper-Reduced simulation. Figure: Multidimensional Reduced Integration Domain Ω Z in orange Error < 30%, G Z = 38, G I = 108, Speed up = 54 (no RS available). Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
21 Response Surface enrichment: error indicator Whatever is the accuracy of the response surface prediction, the related HROM prediction provides a physically-based error indicator. It is the norm of the truncated equilibrium residual: (v,r(u)) Ω = a Ω (v,u;α;µ; t), v V Zh, with α t The definition of the error indicator, denoted η, reads: = g(α; u; x; µ; t) (40) (v,r(u)) ΩZ η(u, α, t) = max, u u o +V h (41) v V Zh (v,v) ΩZ Here: V Zh = span(n i β ii ) N i=1 (42) Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
22 The APHR method [Ryckelynck 2005, 2010] The APHR method provides an incremental adaptive algorithm to create or update the HROM. A (0) t i t i+1 time Just a HROM prediction if η(t i+1) > ε R, then find δu in Vh and expand the RB (n) (n+1) A A The correction step reads: find δu and δα such that: a Ω (N i,u HROM + δu;α HROM + δα;µ; t) = 0, i = 1,...,N, (43) α HROM + δα = g(α HROM + δα; u HROM + δu; x; µ; t) x Ω, (44) t α HROM + δα = α o x Ω, t = 0, (45) N (n+1) N (n+1) α φ (n+1) k ϕ (n+1) Υ (n+1) k b (n+1) N (n) k = N α (n) k = φ (n) k ϕ (n) k + δu, (46) Υ (n) k b (n) k + δα (47) The PGD [Ammar, Chinesta & al. 2006] and the LATIN method [Ladeveze 1985] are alternative a priori reduction methods. Mesh and RB adaptation strategy based on the LATIN method can be found in [Pelle & Ryckelynck 2000]. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
23 3D Finite Element model: Linear Wedge Elements d.o.f. 18 or 30 scalar internal variables at each Gauss Point Gauss points Numerical results: APHR method versus FEM σ11 (MPa) FEM APHR ε x s time increments FEM Full basis increment for APHR method During the simulation using the APHR method, the reduced approximation has been enriched 26 times (+). After each correction step we obtained points close to the reference stress-strain curve. The smaller ε R the smaller is the magnitude of the deviation. The speed up is 2.2. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
24 Numerical results: The time integration, APHR method versus FEM Norm of the equilibrium residue of the FE model εr time increments 1s FEM Full basis increment for APHR method time Size of the basis related to the displacements Number of elements in the RID initial basis vectors : u 1 = x, u 2 = y, u 3= z 2 (Simulation starts with Taylor assumption) time time This illustrates the effect of the adaptation of the reduced approximations during the incremental computation. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
25 Parallel computing is tractable: The Hyper-Reduction provides "green" simulations [Ryckelynck 2010] The FETI method and the APHR have been combined to generate HROMs on parallel computers. Here the RID have been set to one subdomain Ω Z = Ω 8. This provides an amazing speed up: 360. and an energy reduction factor equal to 5,800 by using 1 processor instead of 16. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
26 Other numerical results: The APHR method is not dedicated to homogenization problems A Dammage simulation using the Rousselier model. Unstable problems require ROM adaptivity.[ryckelynck & al. 2011] 3 EF {p}2 loading on the top of the specimen 3 4 x 10 (N) EF {p}3 1.5 loading on the top of the specimen EF {p}1 4 x FE {p}1 APHR {p}1 1 EF {p} EF {p}2 EF {p} t (s) Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models t 0.4 (s) EF APHR Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
27 Work in progress: Periodic homogenization (Vivien Courtier) Periodic formulation: u(x, t ) = E(t ) x + w(x, t ) with periodic boundary conditions on w 2D FCC microstructure Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
28 Conclusion The APHR method is an a priori approach providing reduced order models and reduced integration domains. The precision and the efficiency of the surrogate model is governed by few parameters. The Reduced Integration Domain is the support of explanatory internal variables. The internal variables outside the RID are explained using the internal variables of the RID. By coupling RS model to the Hyper-Reduction method, one can obtain very fast physically-based predictions and error indicators. An open issue is: Since the Hyper-Reduction method and the APHR method exploit results of previous simulations, how can we use efficiently High Parallel Computing in order to adapt HROM and generate RS? The parallel simulation of multidimensional problems needs to be improved. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
29 Work in progress Fatigue, ductile fracture, brittle fracture with plasticity at the crack tip, non-linear damping... And pattern recognition applied to experimental results. Hyper-reduction of nonlinear mechanical models Wokshop RB/PDG/POD ENS Cachan November /29
Error estimation and adaptivity for model reduction in mechanics of materials
 Error estimation and adaptivity for model reduction in mechanics of materials David Ryckelynck Centre des Matériaux Mines ParisTech, UMR CNRS 7633 8 février 2017 Outline 1 Motivations 2 Local enrichment
Error estimation and adaptivity for model reduction in mechanics of materials David Ryckelynck Centre des Matériaux Mines ParisTech, UMR CNRS 7633 8 février 2017 Outline 1 Motivations 2 Local enrichment
Virtual tests based on model reduction strategies for fatigue analysis
 Proceedings of the 7th GACM Colloquium on Computational Mechanics for Young Scientists from Academia and Industry October 11-13, 217 in Stuttgart, Germany Virtual tests based on model reduction strategies
Proceedings of the 7th GACM Colloquium on Computational Mechanics for Young Scientists from Academia and Industry October 11-13, 217 in Stuttgart, Germany Virtual tests based on model reduction strategies
Reduced order modelling for Crash Simulation
 Reduced order modelling for Crash Simulation Fatima Daim ESI Group 28 th january 2016 Fatima Daim (ESI Group) ROM Crash Simulation 28 th january 2016 1 / 50 High Fidelity Model (HFM) and Model Order Reduction
Reduced order modelling for Crash Simulation Fatima Daim ESI Group 28 th january 2016 Fatima Daim (ESI Group) ROM Crash Simulation 28 th january 2016 1 / 50 High Fidelity Model (HFM) and Model Order Reduction
Archetype-Blending Multiscale Continuum Method
 Archetype-Blending Multiscale Continuum Method John A. Moore Professor Wing Kam Liu Northwestern University Mechanical Engineering 3/27/2014 1 1 Outline Background and Motivation Archetype-Blending Continuum
Archetype-Blending Multiscale Continuum Method John A. Moore Professor Wing Kam Liu Northwestern University Mechanical Engineering 3/27/2014 1 1 Outline Background and Motivation Archetype-Blending Continuum
An Energy Dissipative Constitutive Model for Multi-Surface Interfaces at Weld Defect Sites in Ultrasonic Consolidation
 An Energy Dissipative Constitutive Model for Multi-Surface Interfaces at Weld Defect Sites in Ultrasonic Consolidation Nachiket Patil, Deepankar Pal and Brent E. Stucker Industrial Engineering, University
An Energy Dissipative Constitutive Model for Multi-Surface Interfaces at Weld Defect Sites in Ultrasonic Consolidation Nachiket Patil, Deepankar Pal and Brent E. Stucker Industrial Engineering, University
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
An Evaluation of Simplified Methods to Compute the Mechanical Steady State
 An Evaluation of Simplified Methods to Compute the Mechanical Steady State T. Herbland a,b, G. Cailletaud a, S. Quilici a, H. Jaffal b, M. Afzali b a Mines Paris Paris Tech, CNRS UMR 7633, BP 87, 91003
An Evaluation of Simplified Methods to Compute the Mechanical Steady State T. Herbland a,b, G. Cailletaud a, S. Quilici a, H. Jaffal b, M. Afzali b a Mines Paris Paris Tech, CNRS UMR 7633, BP 87, 91003
Discontinuous Galerkin methods for nonlinear elasticity
 Discontinuous Galerkin methods for nonlinear elasticity Preprint submitted to lsevier Science 8 January 2008 The goal of this paper is to introduce Discontinuous Galerkin (DG) methods for nonlinear elasticity
Discontinuous Galerkin methods for nonlinear elasticity Preprint submitted to lsevier Science 8 January 2008 The goal of this paper is to introduce Discontinuous Galerkin (DG) methods for nonlinear elasticity
Nonlinear Model Reduction for Uncertainty Quantification in Large-Scale Inverse Problems
 Nonlinear Model Reduction for Uncertainty Quantification in Large-Scale Inverse Problems Krzysztof Fidkowski, David Galbally*, Karen Willcox* (*MIT) Computational Aerospace Sciences Seminar Aerospace Engineering
Nonlinear Model Reduction for Uncertainty Quantification in Large-Scale Inverse Problems Krzysztof Fidkowski, David Galbally*, Karen Willcox* (*MIT) Computational Aerospace Sciences Seminar Aerospace Engineering
DEIM-BASED PGD FOR PARAMETRIC NONLINEAR MODEL ORDER REDUCTION
 VI International Conference on Adaptive Modeling and Simulation ADMOS 213 J. P. Moitinho de Almeida, P. Díez, C. Tiago and N. Parés (Eds) DEIM-BASED PGD FOR PARAMETRIC NONLINEAR MODEL ORDER REDUCTION JOSE
VI International Conference on Adaptive Modeling and Simulation ADMOS 213 J. P. Moitinho de Almeida, P. Díez, C. Tiago and N. Parés (Eds) DEIM-BASED PGD FOR PARAMETRIC NONLINEAR MODEL ORDER REDUCTION JOSE
Chapter 3 Variational Formulation & the Galerkin Method
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 3 Variational Formulation & the Galerkin Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Today s Lecture Contents: Introduction Differential formulation
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 3 Variational Formulation & the Galerkin Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Today s Lecture Contents: Introduction Differential formulation
Model-independent approaches for the XFEM in fracture mechanics
 Model-independent approaches for the XFEM in fracture mechanics Safdar Abbas 1 Alaskar Alizada 2 and Thomas-Peter Fries 2 1 Aachen Institute for Computational Engineering Science (AICES), RWTH Aachen University,
Model-independent approaches for the XFEM in fracture mechanics Safdar Abbas 1 Alaskar Alizada 2 and Thomas-Peter Fries 2 1 Aachen Institute for Computational Engineering Science (AICES), RWTH Aachen University,
NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS
 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS Introduction to nonlinear continuum mechanics Descriptions of motion Measures of stresses and strains Updated and Total Lagrangian formulations Continuum shell
NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS Introduction to nonlinear continuum mechanics Descriptions of motion Measures of stresses and strains Updated and Total Lagrangian formulations Continuum shell
CSMA Towards optimal design of multiscale nonlinear structures and reduced-order modeling approaches. 1 Introduction.
 CSMA 2017 13ème Colloque National en Calcul des Structures 15-19 Mai 2017, Presqu île de Giens (Var) Towards optimal design of multiscale nonlinear structures and reduced-order modeling approaches Liang
CSMA 2017 13ème Colloque National en Calcul des Structures 15-19 Mai 2017, Presqu île de Giens (Var) Towards optimal design of multiscale nonlinear structures and reduced-order modeling approaches Liang
Cracks Jacques Besson
 Jacques Besson Centre des Matériaux UMR 7633 Mines ParisTech PSL Research University Institut Mines Télécom Aγνωστ oς Θεoς Outline 1 Some definitions 2 in a linear elastic material 3 in a plastic material
Jacques Besson Centre des Matériaux UMR 7633 Mines ParisTech PSL Research University Institut Mines Télécom Aγνωστ oς Θεoς Outline 1 Some definitions 2 in a linear elastic material 3 in a plastic material
Introduction to Finite Element computations
 Non Linear Computational Mechanics Athens MP06/2012 Introduction to Finite Element computations Vincent Chiaruttini, Georges Cailletaud vincent.chiaruttini@onera.fr Outline Continuous to discrete problem
Non Linear Computational Mechanics Athens MP06/2012 Introduction to Finite Element computations Vincent Chiaruttini, Georges Cailletaud vincent.chiaruttini@onera.fr Outline Continuous to discrete problem
Model reduction of parametrized aerodynamic flows: discontinuous Galerkin RB empirical quadrature procedure. Masayuki Yano
 Model reduction of parametrized aerodynamic flows: discontinuous Galerkin RB empirical quadrature procedure Masayuki Yano University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies Acknowledgments: Anthony
Model reduction of parametrized aerodynamic flows: discontinuous Galerkin RB empirical quadrature procedure Masayuki Yano University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies Acknowledgments: Anthony
Weld Fracture. How Residual Stresses Affect Prediction of Brittle Fracture. Outline. Residual Stress in Thick Welds
 How Residual Stresses ffect Prediction of Brittle Fracture Michael R. Hill University of California, Davis Tina L. Panontin NS-mes Research Center Weld Fracture Defects provide location for fracture initiation
How Residual Stresses ffect Prediction of Brittle Fracture Michael R. Hill University of California, Davis Tina L. Panontin NS-mes Research Center Weld Fracture Defects provide location for fracture initiation
An Algorithmic Comparison of the Hyper-Reduction and the Discrete Empirical Interpolation Method for a Nonlinear Thermal Problem
 Mathematical and Computational Applications Article An Algorithmic Comparison of the Hyper-Reduction and the Discrete Empirical Interpolation Method for a Nonlinear Thermal Problem Felix Fritzen 1, ID,
Mathematical and Computational Applications Article An Algorithmic Comparison of the Hyper-Reduction and the Discrete Empirical Interpolation Method for a Nonlinear Thermal Problem Felix Fritzen 1, ID,
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials
 Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials Georges Cailletaud Centre des Matériaux Ecole des Mines de Paris/CNRS Notations Notations (maths) (1/2) A vector v (element of a vectorial space) can be seen
Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials Georges Cailletaud Centre des Matériaux Ecole des Mines de Paris/CNRS Notations Notations (maths) (1/2) A vector v (element of a vectorial space) can be seen
Multi-scale digital image correlation of strain localization
 Multi-scale digital image correlation of strain localization J. Marty a, J. Réthoré a, A. Combescure a a. Laboratoire de Mécanique des Contacts et des Strcutures, INSA Lyon / UMR CNRS 5259 2 Avenue des
Multi-scale digital image correlation of strain localization J. Marty a, J. Réthoré a, A. Combescure a a. Laboratoire de Mécanique des Contacts et des Strcutures, INSA Lyon / UMR CNRS 5259 2 Avenue des
Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs
 Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs Junping Wang Computational Mathematics Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Arlington, VA 22230 Polytopal Element
Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs Junping Wang Computational Mathematics Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Arlington, VA 22230 Polytopal Element
FVM for Fluid-Structure Interaction with Large Structural Displacements
 FVM for Fluid-Structure Interaction with Large Structural Displacements Željko Tuković and Hrvoje Jasak Zeljko.Tukovic@fsb.hr, h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture
FVM for Fluid-Structure Interaction with Large Structural Displacements Željko Tuković and Hrvoje Jasak Zeljko.Tukovic@fsb.hr, h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture
The Finite Element Method for Computational Structural Mechanics
 The Finite Element Method for Computational Structural Mechanics Martin Kronbichler Applied Scientific Computing (Tillämpad beräkningsvetenskap) January 29, 2010 Martin Kronbichler (TDB) FEM for CSM January
The Finite Element Method for Computational Structural Mechanics Martin Kronbichler Applied Scientific Computing (Tillämpad beräkningsvetenskap) January 29, 2010 Martin Kronbichler (TDB) FEM for CSM January
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Contact analysis for the modelling of anchors in concrete structures H. Walter*, L. Baillet** & M. Brunet* *Laboratoire de Mecanique des Solides **Laboratoire de Mecanique des Contacts-CNRS UMR 5514 Institut
Contact analysis for the modelling of anchors in concrete structures H. Walter*, L. Baillet** & M. Brunet* *Laboratoire de Mecanique des Solides **Laboratoire de Mecanique des Contacts-CNRS UMR 5514 Institut
PSEUDO ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF MATERIAL NON-LINEAR PROBLEMS USING ELEMENT FREE GALERKIN METHOD
 Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 505-516 (2004) 505 PSEUDO ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF MATERIAL NON-LINEAR PROBLEMS USING ELEMENT FREE GALERKIN METHOD Raju Sethuraman* and Cherku
Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 505-516 (2004) 505 PSEUDO ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF MATERIAL NON-LINEAR PROBLEMS USING ELEMENT FREE GALERKIN METHOD Raju Sethuraman* and Cherku
BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS
 Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol.., No. 1., (2005), pp. 83 94 BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS Vladimír Kutiš and Justín Murín Department
Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol.., No. 1., (2005), pp. 83 94 BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS Vladimír Kutiš and Justín Murín Department
1 Nonlinear deformation
 NONLINEAR TRUSS 1 Nonlinear deformation When deformation and/or rotation of the truss are large, various strains and stresses can be defined and related by material laws. The material behavior can be expected
NONLINEAR TRUSS 1 Nonlinear deformation When deformation and/or rotation of the truss are large, various strains and stresses can be defined and related by material laws. The material behavior can be expected
Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains
 Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains E. Chahine 1, P. Laborde 2, J. Pommier 1, Y. Renard 3 and M. Salaün 4 (1) INSA Toulouse, laboratoire MIP, CNRS UMR 5640, Complexe scientifique de Rangueil,
Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains E. Chahine 1, P. Laborde 2, J. Pommier 1, Y. Renard 3 and M. Salaün 4 (1) INSA Toulouse, laboratoire MIP, CNRS UMR 5640, Complexe scientifique de Rangueil,
Stress Concentration. Professor Darrell F. Socie Darrell Socie, All Rights Reserved
 Stress Concentration Professor Darrell F. Socie 004-014 Darrell Socie, All Rights Reserved Outline 1. Stress Concentration. Notch Rules 3. Fatigue Notch Factor 4. Stress Intensity Factors for Notches 5.
Stress Concentration Professor Darrell F. Socie 004-014 Darrell Socie, All Rights Reserved Outline 1. Stress Concentration. Notch Rules 3. Fatigue Notch Factor 4. Stress Intensity Factors for Notches 5.
Scientific Computing I
 Scientific Computing I Module 8: An Introduction to Finite Element Methods Tobias Neckel Winter 2013/2014 Module 8: An Introduction to Finite Element Methods, Winter 2013/2014 1 Part I: Introduction to
Scientific Computing I Module 8: An Introduction to Finite Element Methods Tobias Neckel Winter 2013/2014 Module 8: An Introduction to Finite Element Methods, Winter 2013/2014 1 Part I: Introduction to
Meshfree Inelastic Frame Analysis
 Theory & Results Louie L. Yaw, Sashi Kunnath and N. Sukumar University of California, Davis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Minisymposium 47 Recent Advances in Modeling of Engineering
Theory & Results Louie L. Yaw, Sashi Kunnath and N. Sukumar University of California, Davis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Minisymposium 47 Recent Advances in Modeling of Engineering
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
CME 345: MODEL REDUCTION
 CME 345: MODEL REDUCTION Methods for Nonlinear Systems Charbel Farhat & David Amsallem Stanford University cfarhat@stanford.edu 1 / 65 Outline 1 Nested Approximations 2 Trajectory PieceWise Linear (TPWL)
CME 345: MODEL REDUCTION Methods for Nonlinear Systems Charbel Farhat & David Amsallem Stanford University cfarhat@stanford.edu 1 / 65 Outline 1 Nested Approximations 2 Trajectory PieceWise Linear (TPWL)
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems. Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture 1-20 September, 2017
 The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture 1-20 September, 2017 Institute of Structural Engineering Method of Finite Elements II 1 Course
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture 1-20 September, 2017 Institute of Structural Engineering Method of Finite Elements II 1 Course
Model reduction of parametrized aerodynamic flows: stability, error control, and empirical quadrature. Masayuki Yano
 Model reduction of parametrized aerodynamic flows: stability, error control, and empirical quadrature Masayuki Yano University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies Acknowledgments: Anthony Patera;
Model reduction of parametrized aerodynamic flows: stability, error control, and empirical quadrature Masayuki Yano University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies Acknowledgments: Anthony Patera;
Multiple integrals: Sufficient conditions for a local minimum, Jacobi and Weierstrass-type conditions
 Multiple integrals: Sufficient conditions for a local minimum, Jacobi and Weierstrass-type conditions March 6, 2013 Contents 1 Wea second variation 2 1.1 Formulas for variation........................
Multiple integrals: Sufficient conditions for a local minimum, Jacobi and Weierstrass-type conditions March 6, 2013 Contents 1 Wea second variation 2 1.1 Formulas for variation........................
Fissuration en milieux isotrope et orthotrope via les intégrales invariantes: prise en compte des effets environnementaux
 G E M H Fissuration en milieux isotrope et orthotrope via les intégrales invariantes: prise en compte des effets environnementaux R. Moutou Pitti 1,2, H. Riahi 1,2, F. Dubois 3, N. Angellier 3, A. Châteauneuf
G E M H Fissuration en milieux isotrope et orthotrope via les intégrales invariantes: prise en compte des effets environnementaux R. Moutou Pitti 1,2, H. Riahi 1,2, F. Dubois 3, N. Angellier 3, A. Châteauneuf
Mixed Finite Element Methods. Douglas N. Arnold, University of Minnesota The 41st Woudschoten Conference 5 October 2016
 Mixed Finite Element Methods Douglas N. Arnold, University of Minnesota The 41st Woudschoten Conference 5 October 2016 Linear elasticity Given the load f : Ω R n, find the displacement u : Ω R n and the
Mixed Finite Element Methods Douglas N. Arnold, University of Minnesota The 41st Woudschoten Conference 5 October 2016 Linear elasticity Given the load f : Ω R n, find the displacement u : Ω R n and the
MMJ1133 FATIGUE AND FRACTURE MECHANICS A - INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION
 A - INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION M.N.Tamin, CSMLab, UTM Course Content: A - INTRODUCTION Mechanical failure modes; Review of load and stress analysis equilibrium equations, complex stresses, stress transformation,
A - INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION M.N.Tamin, CSMLab, UTM Course Content: A - INTRODUCTION Mechanical failure modes; Review of load and stress analysis equilibrium equations, complex stresses, stress transformation,
INVERSE ANALYSIS METHODS OF IDENTIFYING CRUSTAL CHARACTERISTICS USING GPS ARRYA DATA
 Problems in Solid Mechanics A Symposium in Honor of H.D. Bui Symi, Greece, July 3-8, 6 INVERSE ANALYSIS METHODS OF IDENTIFYING CRUSTAL CHARACTERISTICS USING GPS ARRYA DATA M. HORI (Earthquake Research
Problems in Solid Mechanics A Symposium in Honor of H.D. Bui Symi, Greece, July 3-8, 6 INVERSE ANALYSIS METHODS OF IDENTIFYING CRUSTAL CHARACTERISTICS USING GPS ARRYA DATA M. HORI (Earthquake Research
UNCONVENTIONAL FINITE ELEMENT MODELS FOR NONLINEAR ANALYSIS OF BEAMS AND PLATES
 UNCONVENTIONAL FINITE ELEMENT MODELS FOR NONLINEAR ANALYSIS OF BEAMS AND PLATES A Thesis by WOORAM KIM Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the
UNCONVENTIONAL FINITE ELEMENT MODELS FOR NONLINEAR ANALYSIS OF BEAMS AND PLATES A Thesis by WOORAM KIM Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the
Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics - Energetic Approach
 University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics - Energetic Approach Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of
University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Fracture Mechanics, Damage and Fatigue Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics - Energetic Approach Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of
Reduced basis approximation and a posteriori error estimation for stress intensity factors
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng 2006; 00:1 6 [Version: 2002/09/18 v2.02] Reduced basis approximation and a posteriori error estimation for stress intensity
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng 2006; 00:1 6 [Version: 2002/09/18 v2.02] Reduced basis approximation and a posteriori error estimation for stress intensity
Numerical Simulation of Delamination in Composites via Incremental Energy Minimization
 Numerical Simulation of Delamination in Composites via Incremental Energy Minimization Pavel Gruber 1 Martin Kružík 1,2 Jan Zeman 1 1 Fakulta stavební České vysoké učení technické v Praze 2 Ústav teorie
Numerical Simulation of Delamination in Composites via Incremental Energy Minimization Pavel Gruber 1 Martin Kružík 1,2 Jan Zeman 1 1 Fakulta stavební České vysoké učení technické v Praze 2 Ústav teorie
Studies of Bimaterial Interface Fracture with Peridynamics Fang Wang 1, Lisheng Liu 2, *, Qiwen Liu 1, Zhenyu Zhang 1, Lin Su 1 & Dan Xue 1
 International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 2015) Studies of Bimaterial Interface Fracture with Peridynamics Fang Wang 1, Lisheng Liu 2, *, Qiwen Liu 1, Zhenyu Zhang 1,
International Power, Electronics and Materials Engineering Conference (IPEMEC 2015) Studies of Bimaterial Interface Fracture with Peridynamics Fang Wang 1, Lisheng Liu 2, *, Qiwen Liu 1, Zhenyu Zhang 1,
Homework Problems. ( σ 11 + σ 22 ) 2. cos (θ /2), ( σ θθ σ rr ) 2. ( σ 22 σ 11 ) 2
 Engineering Sciences 47: Fracture Mechanics J. R. Rice, 1991 Homework Problems 1) Assuming that the stress field near a crack tip in a linear elastic solid is singular in the form σ ij = rλ Σ ij (θ), it
Engineering Sciences 47: Fracture Mechanics J. R. Rice, 1991 Homework Problems 1) Assuming that the stress field near a crack tip in a linear elastic solid is singular in the form σ ij = rλ Σ ij (θ), it
The Plane Stress Problem
 The Plane Stress Problem Martin Kronbichler Applied Scientific Computing (Tillämpad beräkningsvetenskap) February 2, 2010 Martin Kronbichler (TDB) The Plane Stress Problem February 2, 2010 1 / 24 Outline
The Plane Stress Problem Martin Kronbichler Applied Scientific Computing (Tillämpad beräkningsvetenskap) February 2, 2010 Martin Kronbichler (TDB) The Plane Stress Problem February 2, 2010 1 / 24 Outline
 Code No: RT41033 R13 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November - 2016 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Common to Mechanical Engineering, Aeronautical Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
Code No: RT41033 R13 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November - 2016 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Common to Mechanical Engineering, Aeronautical Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
Finite Elements for Elastic Shell Models in
 Elastic s in Advisor: Matthias Heinkenschloss Computational and Applied Mathematics Rice University 13 April 2007 Outline Elasticity in Differential Geometry of Shell Geometry and Equations The Plate Model
Elastic s in Advisor: Matthias Heinkenschloss Computational and Applied Mathematics Rice University 13 April 2007 Outline Elasticity in Differential Geometry of Shell Geometry and Equations The Plate Model
G1RT-CT A. BASIC CONCEPTS F. GUTIÉRREZ-SOLANA S. CICERO J.A. ALVAREZ R. LACALLE W P 6: TRAINING & EDUCATION
 A. BASIC CONCEPTS 6 INTRODUCTION The final fracture of structural components is associated with the presence of macro or microstructural defects that affect the stress state due to the loading conditions.
A. BASIC CONCEPTS 6 INTRODUCTION The final fracture of structural components is associated with the presence of macro or microstructural defects that affect the stress state due to the loading conditions.
Análisis Computacional del Comportamiento de Falla de Hormigón Reforzado con Fibras Metálicas
 San Miguel de Tucuman, Argentina September 14 th, 2011 Seminary on Análisis Computacional del Comportamiento de Falla de Hormigón Reforzado con Fibras Metálicas Antonio Caggiano 1, Guillermo Etse 2, Enzo
San Miguel de Tucuman, Argentina September 14 th, 2011 Seminary on Análisis Computacional del Comportamiento de Falla de Hormigón Reforzado con Fibras Metálicas Antonio Caggiano 1, Guillermo Etse 2, Enzo
FEMxDEM double scale approach with second gradient regularization applied to granular materials modeling
 FEMxDEM double scale approach with second gradient regularization applied to granular materials modeling Albert Argilaga Claramunt Stefano Dal Pont Gaël Combe Denis Caillerie Jacques Desrues 16 december
FEMxDEM double scale approach with second gradient regularization applied to granular materials modeling Albert Argilaga Claramunt Stefano Dal Pont Gaël Combe Denis Caillerie Jacques Desrues 16 december
ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT. Identification of elastic property and loading. fields from full-field displacement. measurements
 Identification of elastic property and loading fields from full-field displacement measurements F. Amiot a,b, F. Hild a J.P. Roger b a LMT Cachan, ENS de Cachan / CNRS-UMR 8535 / Université Paris 6 61
Identification of elastic property and loading fields from full-field displacement measurements F. Amiot a,b, F. Hild a J.P. Roger b a LMT Cachan, ENS de Cachan / CNRS-UMR 8535 / Université Paris 6 61
A hierarchy of higher order and higher grade continua Application to the plasticity and fracture of metallic foams
 A hierarchy of higher order and higher grade continua Application to the plasticity and fracture of metallic foams Samuel Forest Centre des Matériaux/UMR 7633 Mines Paris ParisTech /CNRS BP 87, 91003 Evry,
A hierarchy of higher order and higher grade continua Application to the plasticity and fracture of metallic foams Samuel Forest Centre des Matériaux/UMR 7633 Mines Paris ParisTech /CNRS BP 87, 91003 Evry,
CHAPTER 7 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DEEP GROOVE BALL BEARING
 113 CHAPTER 7 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DEEP GROOVE BALL BEARING 7. 1 INTRODUCTION Finite element computational methodology for rolling contact analysis of the bearing was proposed and it has several
113 CHAPTER 7 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DEEP GROOVE BALL BEARING 7. 1 INTRODUCTION Finite element computational methodology for rolling contact analysis of the bearing was proposed and it has several
DEVELOPMENT OF MEASURING SYSTEM FOR STRESS BY MEANS OF IMAGE PLATE FOR LABORATORY X-RAY EXPERIMENT
 Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 46. 6 DEVELOPMENT OF MEASURING SYSTEM FOR STRESS BY MEANS OF IMAGE PLATE FOR LABORATORY X-RAY EXPERIMENT
Copyright JCPDS - International Centre for Diffraction Data 003, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 46. 6 DEVELOPMENT OF MEASURING SYSTEM FOR STRESS BY MEANS OF IMAGE PLATE FOR LABORATORY X-RAY EXPERIMENT
Stress concentrations, fracture and fatigue
 Stress concentrations, fracture and fatigue Piet Schreurs Department of Mechanical Engineering Eindhoven University of Technology http://www.mate.tue.nl/ piet December 1, 2016 Overview Stress concentrations
Stress concentrations, fracture and fatigue Piet Schreurs Department of Mechanical Engineering Eindhoven University of Technology http://www.mate.tue.nl/ piet December 1, 2016 Overview Stress concentrations
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A PILE SUBJECTED TO LATERAL LOADS
 IGC 009, Guntur, INDIA NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A PILE SUBJECTED TO LATERAL LOADS Mohammed Younus Ahmed Graduate Student, Earthquake Engineering Research Center, IIIT Hyderabad, Gachibowli, Hyderabad 3, India.
IGC 009, Guntur, INDIA NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A PILE SUBJECTED TO LATERAL LOADS Mohammed Younus Ahmed Graduate Student, Earthquake Engineering Research Center, IIIT Hyderabad, Gachibowli, Hyderabad 3, India.
Course in. Geometric nonlinearity. Nonlinear FEM. Computational Mechanics, AAU, Esbjerg
 Course in Nonlinear FEM Geometric nonlinearity Nonlinear FEM Outline Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometric nonlinearity Lecture 3 Material nonlinearity Lecture 4 Material nonlinearity it continued
Course in Nonlinear FEM Geometric nonlinearity Nonlinear FEM Outline Lecture 1 Introduction Lecture 2 Geometric nonlinearity Lecture 3 Material nonlinearity Lecture 4 Material nonlinearity it continued
MODELLING MIXED-MODE RATE-DEPENDENT DELAMINATION IN LAYERED STRUCTURES USING GEOMETRICALLY NONLINEAR BEAM FINITE ELEMENTS
 PROCEEDINGS Proceedings of the 25 th UKACM Conference on Computational Mechanics 12-13 April 217, University of Birmingham Birmingham, United Kingdom MODELLING MIXED-MODE RATE-DEPENDENT DELAMINATION IN
PROCEEDINGS Proceedings of the 25 th UKACM Conference on Computational Mechanics 12-13 April 217, University of Birmingham Birmingham, United Kingdom MODELLING MIXED-MODE RATE-DEPENDENT DELAMINATION IN
A model order reduction technique for speeding up computational homogenisation
 A model order reduction technique for speeding up computational homogenisation Olivier Goury, Pierre Kerfriden, Wing Kam Liu, Stéphane Bordas Cardiff University Outline Introduction Heterogeneous materials
A model order reduction technique for speeding up computational homogenisation Olivier Goury, Pierre Kerfriden, Wing Kam Liu, Stéphane Bordas Cardiff University Outline Introduction Heterogeneous materials
A Model for Local Plasticity Effects on Fatigue Crack Growth
 A Model for Local Plasticity Effects on Fatigue Crack Growth USAF Aircraft Structural Integrity Program Conference San Antonio, Texas November 28-30, 2006 R. Craig McClung Brian M. Gardner Yi-Der Lee Fraser
A Model for Local Plasticity Effects on Fatigue Crack Growth USAF Aircraft Structural Integrity Program Conference San Antonio, Texas November 28-30, 2006 R. Craig McClung Brian M. Gardner Yi-Der Lee Fraser
Constitutive and Damage Accumulation Modeling
 Workshop on Modeling and Data needs for Lead-Free Solders Sponsored by NEMI, NIST, NSF, and TMS February 15, 001 New Orleans, LA Constitutive and Damage Accumulation Modeling Leon M. Keer Northwestern
Workshop on Modeling and Data needs for Lead-Free Solders Sponsored by NEMI, NIST, NSF, and TMS February 15, 001 New Orleans, LA Constitutive and Damage Accumulation Modeling Leon M. Keer Northwestern
Preprocessor Geometry Properties )Nodes, Elements(, Material Properties Boundary Conditions(displacements, Forces )
 در برنامه يك تدوين براي بعدي دو يك سازه محيط MATLAB Preprocessor Geometry Properties )Nodes, Elements(, Material Properties Boundary Conditions(displacements, Forces ) Definition of Stiffness Matrices
در برنامه يك تدوين براي بعدي دو يك سازه محيط MATLAB Preprocessor Geometry Properties )Nodes, Elements(, Material Properties Boundary Conditions(displacements, Forces ) Definition of Stiffness Matrices
Alternative numerical method in continuum mechanics COMPUTATIONAL MULTISCALE. University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering
 University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Alternative numerical method in continuum mechanics COMPUTATIONAL MULTISCALE Van Dung NGUYEN Innocent NIYONZIMA Aerospace & Mechanical engineering
University of Liège Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Alternative numerical method in continuum mechanics COMPUTATIONAL MULTISCALE Van Dung NGUYEN Innocent NIYONZIMA Aerospace & Mechanical engineering
Contents. Prologue Introduction. Classical Approximation... 19
 Contents Prologue........................................................................ 15 1 Introduction. Classical Approximation.................................. 19 1.1 Introduction................................................................
Contents Prologue........................................................................ 15 1 Introduction. Classical Approximation.................................. 19 1.1 Introduction................................................................
MMJ1153 COMPUTATIONAL METHOD IN SOLID MECHANICS PRELIMINARIES TO FEM
 B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field
 Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field Amit Acharya November 19, 2018 Abstract It can be shown that the stress produced by a spatially uniform dislocation density field in a body comprising
Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field Amit Acharya November 19, 2018 Abstract It can be shown that the stress produced by a spatially uniform dislocation density field in a body comprising
EML4507 Finite Element Analysis and Design EXAM 1
 2-17-15 Name (underline last name): EML4507 Finite Element Analysis and Design EXAM 1 In this exam you may not use any materials except a pencil or a pen, an 8.5x11 formula sheet, and a calculator. Whenever
2-17-15 Name (underline last name): EML4507 Finite Element Analysis and Design EXAM 1 In this exam you may not use any materials except a pencil or a pen, an 8.5x11 formula sheet, and a calculator. Whenever
Structural Matrices in MDOF Systems
 in MDOF Systems http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 9, 2016 Outline Additional Static Condensation
in MDOF Systems http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 9, 2016 Outline Additional Static Condensation
Identification of the plastic zone using digital image correlation
 M. Rossi et alii, Frattura ed Integrità Strutturale, 3 (4) 55-557; DOI:.3/IGF-ESIS.3.66 Focussed on: Fracture and Structural Integrity related Issues Identification of the plastic zone using digital image
M. Rossi et alii, Frattura ed Integrità Strutturale, 3 (4) 55-557; DOI:.3/IGF-ESIS.3.66 Focussed on: Fracture and Structural Integrity related Issues Identification of the plastic zone using digital image
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) for Nonlinear Dynamical Systems. Stefan Volkwein
 Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) for Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Institute for Mathematics and Scientific Computing, Austria DISC Summerschool 5 Outline of the talk POD and singular value decomposition
Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD) for Nonlinear Dynamical Systems Institute for Mathematics and Scientific Computing, Austria DISC Summerschool 5 Outline of the talk POD and singular value decomposition
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Use various methods to determine the deflection and slope at specific pts on beams and shafts: 2. Discontinuity functions
 1. Deflections of Beams and Shafts CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Use various methods to determine the deflection and slope at specific pts on beams and shafts: 1. Integration method. Discontinuity functions 3. Method
1. Deflections of Beams and Shafts CHAPTER OBJECTIVES Use various methods to determine the deflection and slope at specific pts on beams and shafts: 1. Integration method. Discontinuity functions 3. Method
Chapter 2 Finite Element Formulations
 Chapter 2 Finite Element Formulations The governing equations for problems solved by the finite element method are typically formulated by partial differential equations in their original form. These are
Chapter 2 Finite Element Formulations The governing equations for problems solved by the finite element method are typically formulated by partial differential equations in their original form. These are
A truly meshless Galerkin method based on a moving least squares quadrature
 A truly meshless Galerkin method based on a moving least squares quadrature Marc Duflot, Hung Nguyen-Dang Abstract A new body integration technique is presented and applied to the evaluation of the stiffness
A truly meshless Galerkin method based on a moving least squares quadrature Marc Duflot, Hung Nguyen-Dang Abstract A new body integration technique is presented and applied to the evaluation of the stiffness
GENERALISED COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF CONTACT FATIGUE INITIATION
 UNIVERSITY OF MARIBOR FACULTY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING NAFEMS/FENET GENERALISED COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF CONTACT FATIGUE INITIATION M. Šraml, Z. Ren,, J. Flašker ker,, I. Potrč, M.Ulbin Zurich, June
UNIVERSITY OF MARIBOR FACULTY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING NAFEMS/FENET GENERALISED COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF CONTACT FATIGUE INITIATION M. Šraml, Z. Ren,, J. Flašker ker,, I. Potrč, M.Ulbin Zurich, June
A warping model for reinforced concrete beams under multiaxial loading
 22 ème Congrès Français de Mécanique Lyon, 24 au 28 Août 215 A warping model for reinforced concrete beams under multiaxial loading S. Capdevielle +,a,b, S. Grange a,b, F. Dufour a,b, C. Desprez c + Corresponding
22 ème Congrès Français de Mécanique Lyon, 24 au 28 Août 215 A warping model for reinforced concrete beams under multiaxial loading S. Capdevielle +,a,b, S. Grange a,b, F. Dufour a,b, C. Desprez c + Corresponding
Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface
 Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface Laurent BAILLET LGIT (Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique) Grenoble France laurent.baillet@ujf-grenoble.fr http://www-lgit.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr/users/lbaillet/
Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface Laurent BAILLET LGIT (Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique) Grenoble France laurent.baillet@ujf-grenoble.fr http://www-lgit.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr/users/lbaillet/
JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE Jeppiaar Nagar, Rajiv Gandhi Salai 600 119 DEPARTMENT OFMECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER ME6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Regulation 013 SUBJECT YEAR /SEM: III
JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE Jeppiaar Nagar, Rajiv Gandhi Salai 600 119 DEPARTMENT OFMECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER ME6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Regulation 013 SUBJECT YEAR /SEM: III
CM3. Generation of unidirectional composite SVEs from micro-structural statistical information. Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials
 Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be Generation of unidirectional composite SVEs from micro-structural statistical information Wu Ling, Bidaine Benoit, Major Zoltan,
Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be Generation of unidirectional composite SVEs from micro-structural statistical information Wu Ling, Bidaine Benoit, Major Zoltan,
Outline. Structural Matrices. Giacomo Boffi. Introductory Remarks. Structural Matrices. Evaluation of Structural Matrices
 Outline in MDOF Systems Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Milano May 8, 014 Additional Today we will study the properties of structural matrices, that is the operators that
Outline in MDOF Systems Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Milano May 8, 014 Additional Today we will study the properties of structural matrices, that is the operators that
Discrete Element Modelling of a Reinforced Concrete Structure
 Discrete Element Modelling of a Reinforced Concrete Structure S. Hentz, L. Daudeville, F.-V. Donzé Laboratoire Sols, Solides, Structures, Domaine Universitaire, BP 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9 France sebastian.hentz@inpg.fr
Discrete Element Modelling of a Reinforced Concrete Structure S. Hentz, L. Daudeville, F.-V. Donzé Laboratoire Sols, Solides, Structures, Domaine Universitaire, BP 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9 France sebastian.hentz@inpg.fr
SIMULATION OF PLANE STRAIN FIBER COMPOSITE PLATES IN BENDING THROUGH A BEM/ACA/HM FORMULATION
 8 th GRACM International Congress on Computational Mechanics Volos, 12 July 15 July 2015 SIMULATION OF PLANE STRAIN FIBER COMPOSITE PLATES IN BENDING THROUGH A BEM/ACA/HM FORMULATION Theodore V. Gortsas
8 th GRACM International Congress on Computational Mechanics Volos, 12 July 15 July 2015 SIMULATION OF PLANE STRAIN FIBER COMPOSITE PLATES IN BENDING THROUGH A BEM/ACA/HM FORMULATION Theodore V. Gortsas
Spectral methods for fuzzy structural dynamics: modal vs direct approach
 Spectral methods for fuzzy structural dynamics: modal vs direct approach S Adhikari Zienkiewicz Centre for Computational Engineering, College of Engineering, Swansea University, Wales, UK IUTAM Symposium
Spectral methods for fuzzy structural dynamics: modal vs direct approach S Adhikari Zienkiewicz Centre for Computational Engineering, College of Engineering, Swansea University, Wales, UK IUTAM Symposium
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
ROTATING RING. Volume of small element = Rdθbt if weight density of ring = ρ weight of small element = ρrbtdθ. Figure 1 Rotating ring
 ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
Large Amplitude Vibrations and Modal Sensing of Intelligent Thin Piezolaminated Structures
 Large Amplitude Vibrations and Modal Sensing of Intelligent Thin Piezolaminated Structures S. Lentzen and R. Schmidt Insitut of General Mechanics, RWTH Aachen University Contents MRT FOSD theory of shells
Large Amplitude Vibrations and Modal Sensing of Intelligent Thin Piezolaminated Structures S. Lentzen and R. Schmidt Insitut of General Mechanics, RWTH Aachen University Contents MRT FOSD theory of shells
Modelling the effects of various contents of fillers on the relaxation rate of filled rubbers
 Modelling the effects of various contents of fillers on the relaxation rate of filled rubbers L. Laiarinandrasana, A. Jean, D. Jeulin, S. Forest MINES ParisTech MAT Centre des Matériaux CNRS UMR 7633 BP
Modelling the effects of various contents of fillers on the relaxation rate of filled rubbers L. Laiarinandrasana, A. Jean, D. Jeulin, S. Forest MINES ParisTech MAT Centre des Matériaux CNRS UMR 7633 BP
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
Outline. Tensile-Test Specimen and Machine. Stress-Strain Curve. Review of Mechanical Properties. Mechanical Behaviour
 Tensile-Test Specimen and Machine Review of Mechanical Properties Outline Tensile test True stress - true strain (flow curve) mechanical properties: - Resilience - Ductility - Toughness - Hardness A standard
Tensile-Test Specimen and Machine Review of Mechanical Properties Outline Tensile test True stress - true strain (flow curve) mechanical properties: - Resilience - Ductility - Toughness - Hardness A standard
Numerical modeling of standard rock mechanics laboratory tests using a finite/discrete element approach
 Numerical modeling of standard rock mechanics laboratory tests using a finite/discrete element approach S. Stefanizzi GEODATA SpA, Turin, Italy G. Barla Department of Structural and Geotechnical Engineering,
Numerical modeling of standard rock mechanics laboratory tests using a finite/discrete element approach S. Stefanizzi GEODATA SpA, Turin, Italy G. Barla Department of Structural and Geotechnical Engineering,
Determination of Stress Intensity Factor for a Crack Emanating From a Rivet Hole and Approaching Another in Curved Sheet
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Determination of Stress Intensity Factor for a Crack Emanating From a Rivet Hole and Approaching Another in Curved Sheet Raghavendra.
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Determination of Stress Intensity Factor for a Crack Emanating From a Rivet Hole and Approaching Another in Curved Sheet Raghavendra.
Outline. Organization. Stresses in Beams
 Stresses in Beams B the end of this lesson, ou should be able to: Calculate the maimum stress in a beam undergoing a bending moment 1 Outline Curvature Normal Strain Normal Stress Neutral is Moment of
Stresses in Beams B the end of this lesson, ou should be able to: Calculate the maimum stress in a beam undergoing a bending moment 1 Outline Curvature Normal Strain Normal Stress Neutral is Moment of
Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity. Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess
 Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess geometry description Cartesian global coordinate system with base vectors of the Euclidian space orthonormal basis origin O point P domain of a deformable
Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess geometry description Cartesian global coordinate system with base vectors of the Euclidian space orthonormal basis origin O point P domain of a deformable
VORONOI APPLIED ELEMENT METHOD FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS: THEORY AND APPLICATION FOR LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR MATERIALS
 The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 008, Beijing, China VORONOI APPLIED ELEMENT METHOD FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS: THEORY AND APPLICATION FOR LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR MATERIALS K.
The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 008, Beijing, China VORONOI APPLIED ELEMENT METHOD FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS: THEORY AND APPLICATION FOR LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR MATERIALS K.
Identification of crystal plasticity law parameters using kinematic measurements in polycrystals
 Identification of crystal plasticity law parameters using kinematic measurements in polycrystals Adrien Guery, Felix Latourte, François Hild, Stéphane Roux To cite this version: Adrien Guery, Felix Latourte,
Identification of crystal plasticity law parameters using kinematic measurements in polycrystals Adrien Guery, Felix Latourte, François Hild, Stéphane Roux To cite this version: Adrien Guery, Felix Latourte,
POD for Parametric PDEs and for Optimality Systems
 POD for Parametric PDEs and for Optimality Systems M. Kahlbacher, K. Kunisch, H. Müller and S. Volkwein Institute for Mathematics and Scientific Computing University of Graz, Austria DMV-Jahrestagung 26,
POD for Parametric PDEs and for Optimality Systems M. Kahlbacher, K. Kunisch, H. Müller and S. Volkwein Institute for Mathematics and Scientific Computing University of Graz, Austria DMV-Jahrestagung 26,
