Appendix A: Data completeness
|
|
|
- Sharleen Poole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appendix A: Data completeness The fraction of relps in a given constant-resolution sphere that are lost in the blind region lie in two polar caps intersecting the rotation axis (z). That is, all points in reciprocal space that share a common d-spacing form a sphere, and as this constantresolution sphere is spun about the z-axis, most points will cross the Ewald sphere twice, some not at all (near the axis), and a few will intersect it only once. These glehit relps graze the Ewald sphere, and form the border between the two-hit and zero-hit regions. The grazing relp border is a circle, and it is illustrative to consider moving the relp circle in Fig. 1 up the z axis until it intersects the Ewald sphere at just one point. At this grazing point, Bragg s Law: (A1) λ d θ is satisfied, and so the height (h) of this circle above the z plane must be the radius of the Ewald sphere λ* times the of the take-off angle of the spot (θ): (A) h λ* θ Now, the area in either of the blind regions is a section of the surface of a sphere that is cut off by a plane at z ±h. This shape is known as a spherical cap, and the area of a spherical cap from a sphere of radius r that was cut at height h is given by: (A3) A cap π r (r-h) There are two such caps, and we are interested in the area left over after they are cut off (observable relps) relative to the original area of the sphere: (A4) f 4πr 4πr ( πr( r-h) ) r ( r h) obs r h r 1
2 Since a sphere of relps with constant d-spacing d has radius 1/d d*, we may substitute r d* and Equation (A) into Equation (A4): (A5) λ* θ d f obs θ θ d* λ Substituting in Equation (A1) for λ: (A6) f d obs θ θ θ d θ Appendix B: Average Lorentz-polarization factor Taking the product of Equations (a) and (3) from the text and, for the moment, simplifying Equation (3) by considering the case of an unpolarized beam ( ), we have: 1+ θ (B1) LP θ ζ Assuming the X-ray beam is perpendicular to the rotation axis, the polar coordinate ζ is simply the height of the relp circle pictured in Fig. 1 above the z plane if the length of the relp vector is normalized to unit wavelength. That is, if we define the angle between the relp vector and the z plane, we have: (B) ζ λ d* λ d θ The angle is when the relp circle lies exactly in the z plane, and it is 9 when the relp lies perfectly along the z-axis and the relp circle has vanished. Note that Equation (B1) is undefined at this position, and so care must be taken when approaching
3 this gularity. The value of ζ for which the relp circle just grazes the Ewald sphere at one point is when the denominator of (B1) becomes zero, or: (B3) θ ζ θ or θ Since we wish to avoid the gularity here, we shall set our limit of integration at a small value short of it and use the symbol η because it is reminiscent of mosaic spread. (B4) arc( θ ) η max Substituting B into B1 we obtain: (B5) LP 1+ θ θ 4 θ 1+ θ 4 θ θ Computing the average value of LP for all spots at a fixed resolution is equivalent to integrating LP over the accessible surface of the constant-resolution sphere, and then dividing by the accessible surface area: (B6) LP blind equator blind LP da equator da The denominator of (B6) was solved as Equation (A6), and is simply half of the accessible surface area of the constant-resolution sphere, which has radius λ/d or θ, and accessible fraction f obs θ: blind da (B7) π( θ ) θ equator Now, all the points that lie on or very near the relp circle pictured in Fig. 1 will have the same L and P factors, so we must weight the LP of each contact point on the Ewald sphere surface by the circumference of the relp circle. That is, we define the area element 3
4 in Equation (B6) with a re-casting of Equation (A3) where we can compute the area of the constant-resolution sphere above the relp circle in Fig. 1 by substituting the radius of this sphere (λ/d θ) for r and ζ from Equation (B) for h : (B8) π( θ )( θ θ ) 8π θ 8π θ A cap Differentiating with respect to, we obtain the area element: (B9) da -8π θ d Substituting (B5), (B7) and (B9) into (B6) we have: (B1a) LP max 4 θ 1+ θ θ π ( θ ) θ (-8π θ ) d (B1b) LP 1+ θ 4 θ θ max θ d We now employ the indefinite integral: (B11) C d arctan C C And substitute this into the definite integral: (B1) max (B13) ( θ η) θ ( θ η) ( θ η) θ ( ) θ ( ) ( ) θ d arctan + arctan θ θ d arctan max Clearly, as we approach the limit: ( θ η) η η 4
5 (B14) lim η max θ π d Substituting this back into Equation (B1b) we obtain the average LP factor: (6a) LP π 1+ θ 8 θ θ π 1 θ θ Multiplying LP by f obs θ, we obtain: (6b) ( 3 + 4θ ) π 1+ θ π LP f obs 8 θ 16 θ This result was validated numerically by calculating discrete spot positions, L and P for hypothetical data sets ug randomized wavelengths, unit cells and crystal orientations and then dividing the predictions into resolution bins and averaging the value of the product LP and the fraction of all possible relps that appeared in the bin (not shown). These simulations were repeated ug the full expression for the polarization factor with different values for the degree of polarization ( ), but the numerical results were identical to (not shown), and we saw no need to repeat the derivation ug the full polarization factor expression. Appendix C: Spot-fading integral Here we assume that the average spot intensity (photons/spot) at a given resolution fades exponentially, but begin with a slightly different representation of Equation (13) than in the text: 5
6 DR t H d (C1) i ( t ) i ( ) exp ln( ) where: i (t) - average intensity rate (photons/spot/s) at time t (after absorbing a dose DR t) i () - average intensity rate (photons/spot/s) from an undamaged crystal ln() - natural log of two (~.7) DR - dose deposited per unit time (D reso /t) or dose rate (MGy/s) H - Howells et al. (9) criterion (1 MGy/Å) d - d-spacing (Å) t - accumulated exposure time (seconds) Note the use of angle brackets to denote the average in a given resolution bin, and that here we use the term intensity rate to refer to a spot intensity (photons/spot) divided by the exposure time used to record it (seconds). This is because accurate spot fading experiments must record the decay curve by sampling the same spots over and over again ug per-observation exposure times that are short relative to the damage limit (T DL ). That is, when sampling a changing signal, the sampling time must be short enough so that the signal does not decay appreciably during a given sample. This is equivalent to requiring that the photons/spot per unit time (intensity rate) is constant for a given exposure. So, effectively, spot fading experiments measure changes in intensity rate. Here we use a lower case i to differentiate an intensity rate (photons/spot/s) from an integrated spot intensity (photons/spot), which we will continue to denote with a capital I, and also replace the dose D reso with DR t so that DR represents the timeinvariant factors of dose in Equation (11). Since DR, d, H, and i () do not change with time, the integral of Equation (C1) is simply the integral of an exponential decay: 6
7 T H d ln( ) DR exp() -exp - TDL ln DL (C) I i ( t ) dt i ( ) DL ( ) DR H d Where: I DL T DL DR H d - accumulated spot intensity at the damage limit (photons/spot) - accumulated exposure time at the damage limit (seconds) - dose rate (MGy/s) - Howells et al. (9) criterion (1 MGy/Å) - d-spacing in Å Since we are not considering the accumulation of background counts, T DL could be chosen to be infinity and I DL would then truly account for every last photon that will fall into a spot before it fades away completely, but in practice the damage limit is usually declared at a point where i (T DL ) is not zero, as discussed in.11. To account for potentially variable damage limit criteria, we define the decay fraction at the end of data collection as: (C3) f decayed i ( ) i ( TDL ) i ( ) Since T DL is now defined in terms of f decayed, substituting Equation (C3) into Equation (C) simplifies it to the expression: (C4) I i ( ) f H d DL decayed ln() DR where: I DL - average accumulated spot intensity (photons/spot) at the damage limit i () - average intensity rate (photons/spot/s) from an undamaged crystal DR - dose rate (MGy/s) 7
8 H d - Howells et al. (9) criterion (1 MGy/Å) - d-spacing in Å Although it may appear that I DL (photons/spot) depends on the dose rate (DR), the time component of DR (MGy/s) is actually cancelled by the time component of the initial intensity rate i () (photons/spot/s). Consider a hypothetical data collection strategy where a very large number of observations are made of each spot, and the whole data set is actually a series of mini data sets with exposure time t DS. As long as t DS is very small when compared to the damage limit (T DL ), the spot intensities (photons/spot) in the first mini data set (I ND ) will be undamaged and given by Darwin s formula (Equation (1)). The exact I ND measured will be proportional to t DS, as can easily be seen by substituting ω eff from Equation (1) into Equation (1): (C5) I t ND DS I beamre V V xtal cell 4n π symop λ V 3 cell LP A F where: I ND - spot intensity (photons/spot) from the first mini data set measured quickly enough to have suffered no radiation damage effects. It is readily apparent that the quotient I ND /t DS (photons/spot/s) is an intensity rate, as is the average value I ND/t DS. Formally, the right hand side of Equation (C5) is independent of time, but as the reality of radiation damage progresses the same t DS will record spot intensities that fade (on average) according to the exponential decay of Equation (C1). Therefore, the starting value of this decay curve is I ND/t DS, and we may substitute this intensity rate for i () in the above Equations: 8
9 I i t (C6) ( ) ND DS Now the sum of all the equivalent observations in all the mini data sets up to a given accumulated exposure time is given by Equation (C), and even if a gle data set were collected with total exposure time T DL, the average number of photons that eventually contribute to a spot ( I DL) is simply the integral of the decay over time (Equation (C4)). We now substitute I ND/t DS for i () in Equation (C4), as well as D en /t from Equation (11) for the dose rate (DR), convert the photon energy into wavelength (q e E ph hc/λ J/photon), apply the Nave-Hill fraction f NH from Equation (1) and scale to convenient units. We arrive at Equation (14) from the main text: (14) I Where: I 1. fdecayed 4 H d λ R ρ ND DL t 3 ln DS ( ) ( ) f h c I 1 T (,μ,r) NH beam I DL - maximum average spot intensity due to radiation damage limits (photons/spot) I ND - average spot intensity (photons/spot) observed ug an undamaged crystal and a very short exposure: t DS H - Howells s criterion (1 MGy/Å).1 - converting λ from Å to m, ρ from g/cm 3 to kg/m 3 and MGy to Gy λ - X-ray wavelength (Å) h - Planck s constant (6.66 x 1-34 J s) c - speed of light ( m/s) R - radius of the spherical crystal (m) ρ - density of crystal (~1. g/cm 3 ) I beam - incident beam intensity (photons/s/m ) μ en - mass energy-absorption coefficient of sphere material (m -1 ) f NH - the Nave-Hill fraction sphere en 9
10 References Howells, M. R., Beetz, T., Chapman, H. N., Cui, C., Holton, J. M., Jacobsen, C. J., Kirz, J., Lima, E., Marchei, S., Miao, H., Sayre, D., Shapiro, D. A., Spence, J. H. C. & Starodub, D. (9). J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 17,
SOLID STATE 18. Reciprocal Space
 SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
PSD '18 -- Xray lecture 4. Laue conditions Fourier Transform The reciprocal lattice data collection
 PSD '18 -- Xray lecture 4 Laue conditions Fourier Transform The reciprocal lattice data collection 1 Fourier Transform The Fourier Transform is a conversion of one space into another space with reciprocal
PSD '18 -- Xray lecture 4 Laue conditions Fourier Transform The reciprocal lattice data collection 1 Fourier Transform The Fourier Transform is a conversion of one space into another space with reciprocal
Crystal planes. Neutrons: magnetic moment - interacts with magnetic materials or nuclei of non-magnetic materials. (in Å)
 Crystallography: neutron, electron, and X-ray scattering from periodic lattice, scattering of waves by periodic structures, Miller indices, reciprocal space, Ewald construction. Diffraction: Specular,
Crystallography: neutron, electron, and X-ray scattering from periodic lattice, scattering of waves by periodic structures, Miller indices, reciprocal space, Ewald construction. Diffraction: Specular,
Class 29: Reciprocal Space 3: Ewald sphere, Simple Cubic, FCC and BCC in Reciprocal Space
 Class 29: Reciprocal Space 3: Ewald sphere, Simple Cubic, FCC and BCC in Reciprocal Space We have seen that diffraction occurs when, in reciprocal space, Let us now plot this information. Let us designate
Class 29: Reciprocal Space 3: Ewald sphere, Simple Cubic, FCC and BCC in Reciprocal Space We have seen that diffraction occurs when, in reciprocal space, Let us now plot this information. Let us designate
The Reciprocal Lattice
 59-553 The Reciprocal Lattice 61 Because of the reciprocal nature of d spacings and θ from Bragg s Law, the pattern of the diffraction we observe can be related to the crystal lattice by a mathematical
59-553 The Reciprocal Lattice 61 Because of the reciprocal nature of d spacings and θ from Bragg s Law, the pattern of the diffraction we observe can be related to the crystal lattice by a mathematical
Diffraction Geometry
 Diffraction Geometry Diffraction from a crystal - Laue equations Reciprocal lattice Ewald construction Data collection strategy Phil Evans LMB May 2013 MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology Cambridge UK
Diffraction Geometry Diffraction from a crystal - Laue equations Reciprocal lattice Ewald construction Data collection strategy Phil Evans LMB May 2013 MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology Cambridge UK
3.012 Structure An Introduction to X-ray Diffraction
 3.012 Structure An Introduction to X-ray Diffraction This handout summarizes some topics that are important for understanding x-ray diffraction. The following references provide a thorough explanation
3.012 Structure An Introduction to X-ray Diffraction This handout summarizes some topics that are important for understanding x-ray diffraction. The following references provide a thorough explanation
Handout 7 Reciprocal Space
 Handout 7 Reciprocal Space Useful concepts for the analysis of diffraction data http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ Concepts versus reality Reflection from lattice planes is just a concept that helps us
Handout 7 Reciprocal Space Useful concepts for the analysis of diffraction data http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ Concepts versus reality Reflection from lattice planes is just a concept that helps us
Contents. basic algebra. Learning outcomes. Time allocation. 1. Mathematical notation and symbols. 2. Indices. 3. Simplification and factorisation
 basic algebra Contents. Mathematical notation and symbols 2. Indices 3. Simplification and factorisation 4. Arithmetic of algebraic fractions 5. Formulae and transposition Learning outcomes In this workbook
basic algebra Contents. Mathematical notation and symbols 2. Indices 3. Simplification and factorisation 4. Arithmetic of algebraic fractions 5. Formulae and transposition Learning outcomes In this workbook
Mie Theory, Cross-Sections, Efficiency Factors and Phase Function
 Appendix C Mie Theory, Cross-Sections, Efficiency Factors and Phase Function C.1 Mie Theory The concept behind the Mie Theory is explained in section.6.1. However, the mathematical derivation of the theory
Appendix C Mie Theory, Cross-Sections, Efficiency Factors and Phase Function C.1 Mie Theory The concept behind the Mie Theory is explained in section.6.1. However, the mathematical derivation of the theory
I ν. di ν. = α ν. = (ndads) σ ν da α ν. = nσ ν = ρκ ν
 Absorption Consider a beam passing through an absorbing medium. Define the absorption coefficient, α ν, by ie the fractional loss in intensity in travelling a distance ds is α ν ds (convention: positive
Absorption Consider a beam passing through an absorbing medium. Define the absorption coefficient, α ν, by ie the fractional loss in intensity in travelling a distance ds is α ν ds (convention: positive
Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2006) Lecture 19 (11/22/06) Gamma Interactions: Compton Scattering
 .101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 006) Lecture 19 (11//06) Gamma Interactions: Compton Scattering References: R. D. Evans, Atomic Nucleus (McGraw-Hill New York, 1955), Chaps 3 5.. W. E. Meyerhof, Elements
.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 006) Lecture 19 (11//06) Gamma Interactions: Compton Scattering References: R. D. Evans, Atomic Nucleus (McGraw-Hill New York, 1955), Chaps 3 5.. W. E. Meyerhof, Elements
Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document
 Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document Background knowledge: (a) The arithmetic of integers (including HCFs and LCMs), of fractions, and of real numbers.
Core A-level mathematics reproduced from the QCA s Subject criteria for Mathematics document Background knowledge: (a) The arithmetic of integers (including HCFs and LCMs), of fractions, and of real numbers.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A: Calculation of radial distribution functions To get an effective propagator in one dimension, we first transform 1) into spherical coordinates: x a = ρ sin θ cos φ, y = ρ sin
Supporting Information A: Calculation of radial distribution functions To get an effective propagator in one dimension, we first transform 1) into spherical coordinates: x a = ρ sin θ cos φ, y = ρ sin
X-ray diffraction geometry
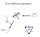 X-ray diffraction geometry Setting controls sample orientation in the diffraction plane. most important for single-crystal diffraction For any poly- (or nano-) crystalline specimen, we usually set: 1 X-ray
X-ray diffraction geometry Setting controls sample orientation in the diffraction plane. most important for single-crystal diffraction For any poly- (or nano-) crystalline specimen, we usually set: 1 X-ray
Experimental Determination of Crystal Structure
 Experimental Determination of Crystal Structure Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. PHYS 624: Introduction to Solid State Physics http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic/teaching/phys624/phys624.html
Experimental Determination of Crystal Structure Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. PHYS 624: Introduction to Solid State Physics http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic/teaching/phys624/phys624.html
[1+ m2 c 4 4EE γ. The equations of conservation of energy and momentum are. E + E γ p p γ
 Physics 403: Relativity Homework Assignment 2 Due 12 February 2007 1. Inverse Compton scattering occurs whenever a photon scatters off a particle moving with a speed very nearly equal to that of light.
Physics 403: Relativity Homework Assignment 2 Due 12 February 2007 1. Inverse Compton scattering occurs whenever a photon scatters off a particle moving with a speed very nearly equal to that of light.
APPENDIX 2.1 LINE AND SURFACE INTEGRALS
 2 APPENDIX 2. LINE AND URFACE INTEGRAL Consider a path connecting points (a) and (b) as shown in Fig. A.2.. Assume that a vector field A(r) exists in the space in which the path is situated. Then the line
2 APPENDIX 2. LINE AND URFACE INTEGRAL Consider a path connecting points (a) and (b) as shown in Fig. A.2.. Assume that a vector field A(r) exists in the space in which the path is situated. Then the line
- 1 - θ 1. n 1. θ 2. mirror. object. image
 TEST 5 (PHY 50) 1. a) How will the ray indicated in the figure on the following page be reflected by the mirror? (Be accurate!) b) Explain the symbols in the thin lens equation. c) Recall the laws governing
TEST 5 (PHY 50) 1. a) How will the ray indicated in the figure on the following page be reflected by the mirror? (Be accurate!) b) Explain the symbols in the thin lens equation. c) Recall the laws governing
PHYS 390 Lecture 23 - Photon gas 23-1
 PHYS 39 Lecture 23 - Photon gas 23-1 Lecture 23 - Photon gas What's Important: radiative intensity and pressure stellar opacity Text: Carroll and Ostlie, Secs. 9.1 and 9.2 The temperature required to drive
PHYS 39 Lecture 23 - Photon gas 23-1 Lecture 23 - Photon gas What's Important: radiative intensity and pressure stellar opacity Text: Carroll and Ostlie, Secs. 9.1 and 9.2 The temperature required to drive
LECTURE 4 PRINCIPLE OF IMAGE FORMATION KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH
 LECTURE 4 PRINCIPLE OF IMAGE FORMATION KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, student should able to: Define attenuation Explain interactions between x-rays and matter in
LECTURE 4 PRINCIPLE OF IMAGE FORMATION KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, student should able to: Define attenuation Explain interactions between x-rays and matter in
Properties of a Configuration of Repeatedly Reflected Points over Reflection-Determined Lines
 Properties of a Configuration of Repeatedly Reflected Points over Reflection-Determined Lines Matthew J Cox January 15, 2017 Abstract We explore a certain configuration of reflections of points over lines
Properties of a Configuration of Repeatedly Reflected Points over Reflection-Determined Lines Matthew J Cox January 15, 2017 Abstract We explore a certain configuration of reflections of points over lines
Notes on x-ray scattering - M. Le Tacon, B. Keimer (06/2015)
 Notes on x-ray scattering - M. Le Tacon, B. Keimer (06/2015) Interaction of x-ray with matter: - Photoelectric absorption - Elastic (coherent) scattering (Thomson Scattering) - Inelastic (incoherent) scattering
Notes on x-ray scattering - M. Le Tacon, B. Keimer (06/2015) Interaction of x-ray with matter: - Photoelectric absorption - Elastic (coherent) scattering (Thomson Scattering) - Inelastic (incoherent) scattering
Copyright 2008, University of Chicago, Department of Physics. Gamma Cross-sections. NaI crystal (~2" dia) mounted on photo-multiplier tube
 Gamma Cross-sections 1. Goal We wish to measure absorption cross-sections for γ-rays for a range of gamma energies and absorber atomic number. 2. Equipment Pulse height analyzer Oscilloscope NaI crystal
Gamma Cross-sections 1. Goal We wish to measure absorption cross-sections for γ-rays for a range of gamma energies and absorber atomic number. 2. Equipment Pulse height analyzer Oscilloscope NaI crystal
Data processing and reduction
 Data processing and reduction Leopoldo Suescun International School on Fundamental Crystallography 2014 May 1st, 2014 Reciprocal lattice c* b* b * dh' k' l' 1 dh' k' l' * dhkl 1 dhkl a a* 0 d hkl c bc
Data processing and reduction Leopoldo Suescun International School on Fundamental Crystallography 2014 May 1st, 2014 Reciprocal lattice c* b* b * dh' k' l' 1 dh' k' l' * dhkl 1 dhkl a a* 0 d hkl c bc
X-ray, Neutron and e-beam scattering
 X-ray, Neutron and e-beam scattering Introduction Why scattering? Diffraction basics Neutrons and x-rays Techniques Direct and reciprocal space Single crystals Powders CaFe 2 As 2 an example What is the
X-ray, Neutron and e-beam scattering Introduction Why scattering? Diffraction basics Neutrons and x-rays Techniques Direct and reciprocal space Single crystals Powders CaFe 2 As 2 an example What is the
Data Collection. Overview. Methods. Counter Methods. Crystal Quality with -Scans
 Data Collection Overview with a unit cell, possible space group and computer reference frame (orientation matrix); the location of diffracted x-rays can be calculated (h k l) and intercepted by something
Data Collection Overview with a unit cell, possible space group and computer reference frame (orientation matrix); the location of diffracted x-rays can be calculated (h k l) and intercepted by something
Problem Set 3: Solutions
 PH 53 / LeClair Spring 013 Problem Set 3: Solutions 1. In an experiment to find the value of h, light at wavelengths 18 and 431 nm were shone on a clean sodium surface. The potentials that stopped the
PH 53 / LeClair Spring 013 Problem Set 3: Solutions 1. In an experiment to find the value of h, light at wavelengths 18 and 431 nm were shone on a clean sodium surface. The potentials that stopped the
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Crystals, X-rays and Proteins
 Crystals, X-rays and Proteins Comprehensive Protein Crystallography Dennis Sherwood MA (Hons), MPhil, PhD Jon Cooper BA (Hons), PhD OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols xiv PART I FUNDAMENTALS
Crystals, X-rays and Proteins Comprehensive Protein Crystallography Dennis Sherwood MA (Hons), MPhil, PhD Jon Cooper BA (Hons), PhD OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols xiv PART I FUNDAMENTALS
Chapter 2 Problem Solutions
 Chapter Problem Solutions 1. If Planck's constant were smaller than it is, would quantum phenomena be more or less conspicuous than they are now? Planck s constant gives a measure of the energy at which
Chapter Problem Solutions 1. If Planck's constant were smaller than it is, would quantum phenomena be more or less conspicuous than they are now? Planck s constant gives a measure of the energy at which
1 Radiative transfer etc
 Radiative transfer etc Last time we derived the transfer equation dτ ν = S ν I v where I ν is the intensity, S ν = j ν /α ν is the source function and τ ν = R α ν dl is the optical depth. The formal solution
Radiative transfer etc Last time we derived the transfer equation dτ ν = S ν I v where I ν is the intensity, S ν = j ν /α ν is the source function and τ ν = R α ν dl is the optical depth. The formal solution
Low Emittance Machines
 Advanced Accelerator Physics Course RHUL, Egham, UK September 2017 Low Emittance Machines Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and the University of Liverpool,
Advanced Accelerator Physics Course RHUL, Egham, UK September 2017 Low Emittance Machines Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and the University of Liverpool,
X-ray Diffraction. Interaction of Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diffraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity
 X-ray Diraction Interaction o Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity Basic Principles o Interaction o Waves Periodic waves characteristic: Frequency :
X-ray Diraction Interaction o Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity Basic Principles o Interaction o Waves Periodic waves characteristic: Frequency :
LET! (de / dx) 1 Gy= 1 J/kG 1Gy=100 rad. m(kg) dose rate
 Basics of Radiation Dosimetry for the Physicist http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ionizing_radiation I. Ionizing radiation consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that ionize electrons along
Basics of Radiation Dosimetry for the Physicist http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ionizing_radiation I. Ionizing radiation consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that ionize electrons along
Since x + we get x² + 2x = 4, or simplifying it, x² = 4. Therefore, x² + = 4 2 = 2. Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
SEAFLOOR MAPPING MODELLING UNDERWATER PROPAGATION RAY ACOUSTICS
 3 Underwater propagation 3. Ray acoustics 3.. Relevant mathematics We first consider a plane wave as depicted in figure. As shown in the figure wave fronts are planes. The arrow perpendicular to the wave
3 Underwater propagation 3. Ray acoustics 3.. Relevant mathematics We first consider a plane wave as depicted in figure. As shown in the figure wave fronts are planes. The arrow perpendicular to the wave
Radiation Quantities and Units
 Radiation Quantities and Units George Starkschall, Ph.D. Lecture Objectives Define and identify units for the following: Exposure Kerma Absorbed dose Dose equivalent Relative biological effectiveness Activity
Radiation Quantities and Units George Starkschall, Ph.D. Lecture Objectives Define and identify units for the following: Exposure Kerma Absorbed dose Dose equivalent Relative biological effectiveness Activity
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 15. Optical Sources-LASER
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
Analytical Methods for Materials
 Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 15 Reciprocal Lattices and Their Roles in Diffraction Studies Suggested Reading Chs. 2 and 6 in Tilley, Crystals and Crystal Structures, Wiley (2006) Ch. 6 M. DeGraef
Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 15 Reciprocal Lattices and Their Roles in Diffraction Studies Suggested Reading Chs. 2 and 6 in Tilley, Crystals and Crystal Structures, Wiley (2006) Ch. 6 M. DeGraef
What use is Reciprocal Space? An Introduction
 What use is Reciprocal Space? An Introduction a* b* x You are here John Bargar 5th Annual SSRL Workshop on Synchrotron X-ray Scattering Techniques in Materials and Environmental Sciences June 1-3, 2010
What use is Reciprocal Space? An Introduction a* b* x You are here John Bargar 5th Annual SSRL Workshop on Synchrotron X-ray Scattering Techniques in Materials and Environmental Sciences June 1-3, 2010
3 The Friedmann-Robertson-Walker metric
 3 The Friedmann-Robertson-Walker metric 3.1 Three dimensions The most general isotropic and homogeneous metric in three dimensions is similar to the two dimensional result of eq. (43): ( ) dr ds 2 = a
3 The Friedmann-Robertson-Walker metric 3.1 Three dimensions The most general isotropic and homogeneous metric in three dimensions is similar to the two dimensional result of eq. (43): ( ) dr ds 2 = a
Bohr & Wheeler Fission Theory Calculation 4 March 2009
 Bohr & Wheeler Fission Theory Calculation 4 March 9 () Introduction The goal here is to reproduce the calculation of the limiting Z /A against spontaneous fission Z A lim a S. (.) a C as first done by
Bohr & Wheeler Fission Theory Calculation 4 March 9 () Introduction The goal here is to reproduce the calculation of the limiting Z /A against spontaneous fission Z A lim a S. (.) a C as first done by
Exercise Set 4. D s n ds + + V. s dv = V. After using Stokes theorem, the surface integral becomes
 Exercise Set Exercise - (a) Let s consider a test volum in the pellet. The substract enters the pellet by diffusion and some is created and disappears due to the chemical reaction. The two contribute to
Exercise Set Exercise - (a) Let s consider a test volum in the pellet. The substract enters the pellet by diffusion and some is created and disappears due to the chemical reaction. The two contribute to
Attenuation of Radiation in Matter. Attenuation of gamma particles
 Attenuation of Radiation in Matter In this experiment we will examine how radiation decreases in intensity as it passes through a substance. Since radiation interacts with matter, its intensity will decrease
Attenuation of Radiation in Matter In this experiment we will examine how radiation decreases in intensity as it passes through a substance. Since radiation interacts with matter, its intensity will decrease
Roger Johnson Structure and Dynamics: X-ray Diffraction Lecture 6
 6.1. Summary In this Lecture we cover the theory of x-ray diffraction, which gives direct information about the atomic structure of crystals. In these experiments, the wavelength of the incident beam must
6.1. Summary In this Lecture we cover the theory of x-ray diffraction, which gives direct information about the atomic structure of crystals. In these experiments, the wavelength of the incident beam must
Scattering. March 20, 2016
 Scattering March 0, 06 The scattering of waves of any kind, by a compact object, has applications on all scales, from the scattering of light from the early universe by intervening galaxies, to the scattering
Scattering March 0, 06 The scattering of waves of any kind, by a compact object, has applications on all scales, from the scattering of light from the early universe by intervening galaxies, to the scattering
Protein Crystallography
 Protein Crystallography Part II Tim Grüne Dept. of Structural Chemistry Prof. G. Sheldrick University of Göttingen http://shelx.uni-ac.gwdg.de tg@shelx.uni-ac.gwdg.de Overview The Reciprocal Lattice The
Protein Crystallography Part II Tim Grüne Dept. of Structural Chemistry Prof. G. Sheldrick University of Göttingen http://shelx.uni-ac.gwdg.de tg@shelx.uni-ac.gwdg.de Overview The Reciprocal Lattice The
Lecture notes 5: Diffraction
 Lecture notes 5: Diffraction Let us now consider how light reacts to being confined to a given aperture. The resolution of an aperture is restricted due to the wave nature of light: as light passes through
Lecture notes 5: Diffraction Let us now consider how light reacts to being confined to a given aperture. The resolution of an aperture is restricted due to the wave nature of light: as light passes through
Green s function for the wave equation
 Green s function for the wave equation Non-relativistic case January 2018 1 The wave equations In the Lorentz Gauge, the wave equations for the potentials are (Notes 1 eqns 44 and 43): 1 2 2 2 2 0 (1)
Green s function for the wave equation Non-relativistic case January 2018 1 The wave equations In the Lorentz Gauge, the wave equations for the potentials are (Notes 1 eqns 44 and 43): 1 2 2 2 2 0 (1)
If light travels past a system faster than the time scale for which the system evolves then t I ν = 0 and we have then
 6 LECTURE 2 Equation of Radiative Transfer Condition that I ν is constant along rays means that di ν /dt = 0 = t I ν + ck I ν, (29) where ck = di ν /ds is the ray-path derivative. This is equation is the
6 LECTURE 2 Equation of Radiative Transfer Condition that I ν is constant along rays means that di ν /dt = 0 = t I ν + ck I ν, (29) where ck = di ν /ds is the ray-path derivative. This is equation is the
The next three lectures will address interactions of charged particles with matter. In today s lecture, we will talk about energy transfer through
 The next three lectures will address interactions of charged particles with matter. In today s lecture, we will talk about energy transfer through the property known as stopping power. In the second lecture,
The next three lectures will address interactions of charged particles with matter. In today s lecture, we will talk about energy transfer through the property known as stopping power. In the second lecture,
Chapter 21. Electric Fields
 Chapter 21 Electric Fields The Origin of Electricity The electrical nature of matter is inherent in the atoms of all substances. An atom consists of a small relatively massive nucleus that contains particles
Chapter 21 Electric Fields The Origin of Electricity The electrical nature of matter is inherent in the atoms of all substances. An atom consists of a small relatively massive nucleus that contains particles
Elastic Scattering. R = m 1r 1 + m 2 r 2 m 1 + m 2. is the center of mass which is known to move with a constant velocity (see previous lectures):
 Elastic Scattering In this section we will consider a problem of scattering of two particles obeying Newtonian mechanics. The problem of scattering can be viewed as a truncated version of dynamic problem
Elastic Scattering In this section we will consider a problem of scattering of two particles obeying Newtonian mechanics. The problem of scattering can be viewed as a truncated version of dynamic problem
Electron Diffraction
 Electron iffraction o moving electrons display wave nature? To answer this question you will direct a beam of electrons through a thin layer of carbon and analyze the resulting pattern. Theory Louis de
Electron iffraction o moving electrons display wave nature? To answer this question you will direct a beam of electrons through a thin layer of carbon and analyze the resulting pattern. Theory Louis de
Essential Mathematics 2 Introduction to the calculus
 Essential Mathematics Introduction to the calculus As you will alrea know, the calculus may be broadly separated into two major parts. The first part the Differential Calculus is concerned with finding
Essential Mathematics Introduction to the calculus As you will alrea know, the calculus may be broadly separated into two major parts. The first part the Differential Calculus is concerned with finding
Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell
 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell 9.2 The Blackbody as the Ideal Radiator A material that absorbs 100 percent of the energy incident on it from all directions
Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell 9.2 The Blackbody as the Ideal Radiator A material that absorbs 100 percent of the energy incident on it from all directions
The ideal fiber pattern exhibits 4-quadrant symmetry. In the ideal pattern the fiber axis is called the meridian, the perpendicular direction is
 Fiber diffraction is a method used to determine the structural information of a molecule by using scattering data from X-rays. Rosalind Franklin used this technique in discovering structural information
Fiber diffraction is a method used to determine the structural information of a molecule by using scattering data from X-rays. Rosalind Franklin used this technique in discovering structural information
Equations of Stellar Structure
 Equations of Stellar Structure Stellar structure and evolution can be calculated via a series of differential equations involving mass, pressure, temperature, and density. For simplicity, we will assume
Equations of Stellar Structure Stellar structure and evolution can be calculated via a series of differential equations involving mass, pressure, temperature, and density. For simplicity, we will assume
Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth
 Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth We begin a more detailed look at stellar atmospheres by defining the fundamental variable, which is called the Specific Intensity. It may be specified
Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth We begin a more detailed look at stellar atmospheres by defining the fundamental variable, which is called the Specific Intensity. It may be specified
Electron Diffraction
 Exp-3-Electron Diffraction.doc (TJR) Physics Department, University of Windsor Introduction 64-311 Laboratory Experiment 3 Electron Diffraction In 1924 de Broglie predicted that the wavelength of matter
Exp-3-Electron Diffraction.doc (TJR) Physics Department, University of Windsor Introduction 64-311 Laboratory Experiment 3 Electron Diffraction In 1924 de Broglie predicted that the wavelength of matter
Lecture 2 Solutions to the Transport Equation
 Lecture 2 Solutions to the Transport Equation Equation along a ray I In general we can solve the static transfer equation along a ray in some particular direction. Since photons move in straight lines
Lecture 2 Solutions to the Transport Equation Equation along a ray I In general we can solve the static transfer equation along a ray in some particular direction. Since photons move in straight lines
Radiation Heat Transfer Prof. J. Srinivasan Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 Radiation Heat Transfer Prof. J. Srinivasan Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture - 7 Evaluations of shape factors (Refer Slide Time: 00:18) The last
Radiation Heat Transfer Prof. J. Srinivasan Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Lecture - 7 Evaluations of shape factors (Refer Slide Time: 00:18) The last
Liouville Equation. q s = H p s
 Liouville Equation In this section we will build a bridge from Classical Mechanics to Statistical Physics. The bridge is Liouville equation. We start with the Hamiltonian formalism of the Classical Mechanics,
Liouville Equation In this section we will build a bridge from Classical Mechanics to Statistical Physics. The bridge is Liouville equation. We start with the Hamiltonian formalism of the Classical Mechanics,
Nuclear Fusion and Radiation
 Nuclear Fusion and Radiation Lecture 9 (Meetings 23 & 24) Eugenio Schuster schuster@lehigh.edu Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics Lehigh University Nuclear Fusion and Radiation p. 1/42 Radiation Interactions
Nuclear Fusion and Radiation Lecture 9 (Meetings 23 & 24) Eugenio Schuster schuster@lehigh.edu Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics Lehigh University Nuclear Fusion and Radiation p. 1/42 Radiation Interactions
Physics 2135 Exam 3 April 18, 2017
 Physics 2135 Exam 3 April 18, 2017 Exam Total / 200 Printed Name: Rec. Sec. Letter: Solutions for problems 6 to 10 must start from official starting equations. Show your work to receive credit for your
Physics 2135 Exam 3 April 18, 2017 Exam Total / 200 Printed Name: Rec. Sec. Letter: Solutions for problems 6 to 10 must start from official starting equations. Show your work to receive credit for your
Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric)
 Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric) crystal Y X-ray source 2θ X direct beam tan 2θ = Y X d = resolution 2d sinθ = λ detector 1 Unit Cell: two vectors in plane of image c* Observe: b*
Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric) crystal Y X-ray source 2θ X direct beam tan 2θ = Y X d = resolution 2d sinθ = λ detector 1 Unit Cell: two vectors in plane of image c* Observe: b*
Lecture 6, September 1, 2017
 Engineering Mathematics Fall 07 Lecture 6, September, 07 Escape Velocity Suppose we have a planet (or any large near to spherical heavenly body) of radius R and acceleration of gravity at the surface of
Engineering Mathematics Fall 07 Lecture 6, September, 07 Escape Velocity Suppose we have a planet (or any large near to spherical heavenly body) of radius R and acceleration of gravity at the surface of
CERN Accelerator School. Intermediate Accelerator Physics Course Chios, Greece, September Low Emittance Rings
 CERN Accelerator School Intermediate Accelerator Physics Course Chios, Greece, September 2011 Low Emittance Rings Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and
CERN Accelerator School Intermediate Accelerator Physics Course Chios, Greece, September 2011 Low Emittance Rings Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and
The Compton Effect. Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA (Dated: November 26, 2002)
 The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
The Compton Effect Martha Buckley MIT Department of Physics, Cambridge, MA 02139 marthab@mit.edu (Dated: November 26, 2002) We measured the angular dependence of the energies of 661.6 kev photons scattered
Lecture 23 X-Ray & UV Techniques
 Lecture 23 X-Ray & UV Techniques Schroder: Chapter 11.3 1/50 Announcements Homework 6/6: Will be online on later today. Due Wednesday June 6th at 10:00am. I will return it at the final exam (14 th June).
Lecture 23 X-Ray & UV Techniques Schroder: Chapter 11.3 1/50 Announcements Homework 6/6: Will be online on later today. Due Wednesday June 6th at 10:00am. I will return it at the final exam (14 th June).
4. The interaction of light with matter
 4. The interaction of light with matter The propagation of light through chemical materials is described by a wave equation similar to the one that describes light travel in a vacuum (free space). Again,
4. The interaction of light with matter The propagation of light through chemical materials is described by a wave equation similar to the one that describes light travel in a vacuum (free space). Again,
A few principles of classical and quantum mechanics
 A few principles of classical and quantum mechanics The classical approach: In classical mechanics, we usually (but not exclusively) solve Newton s nd law of motion relating the acceleration a of the system
A few principles of classical and quantum mechanics The classical approach: In classical mechanics, we usually (but not exclusively) solve Newton s nd law of motion relating the acceleration a of the system
E d. h, c o, k are all parameters from quantum physics. We need not worry about their precise definition here.
 The actual form of Plank s law is: b db d b 5 e C C2 1 T 1 where: C 1 = 2hc o 2 = 3.7210 8 Wm /m 2 C 2 = hc o /k = 1.3910 mk Where: h, c o, k are all parameters from quantum physics. We need not worry
The actual form of Plank s law is: b db d b 5 e C C2 1 T 1 where: C 1 = 2hc o 2 = 3.7210 8 Wm /m 2 C 2 = hc o /k = 1.3910 mk Where: h, c o, k are all parameters from quantum physics. We need not worry
Math 350 Solutions for Final Exam Page 1. Problem 1. (10 points) (a) Compute the line integral. F ds C. z dx + y dy + x dz C
 Math 35 Solutions for Final Exam Page Problem. ( points) (a) ompute the line integral F ds for the path c(t) = (t 2, t 3, t) with t and the vector field F (x, y, z) = xi + zj + xk. (b) ompute the line
Math 35 Solutions for Final Exam Page Problem. ( points) (a) ompute the line integral F ds for the path c(t) = (t 2, t 3, t) with t and the vector field F (x, y, z) = xi + zj + xk. (b) ompute the line
Compton Scattering II
 Compton Scattering II 1 Introduction In the previous chapter we considered the total power produced by a single electron from inverse Compton scattering. This is useful but limited information. Here we
Compton Scattering II 1 Introduction In the previous chapter we considered the total power produced by a single electron from inverse Compton scattering. This is useful but limited information. Here we
4.1b - Cavity Theory Lecture 2 Peter R Al mond 2011 Overview of Lecture Exposure (W/e)air Exposure Exposure and and and Air Air Kerma
 4.1b - Cavity Theory Lecture 2 Peter R Almond 2011 Overview of Lecture Exposure (W/e) air Exposure and Air Kerma Exposure Exposure is symbolized as X and defined by the ICRU as the quotient of dq by dm,
4.1b - Cavity Theory Lecture 2 Peter R Almond 2011 Overview of Lecture Exposure (W/e) air Exposure and Air Kerma Exposure Exposure is symbolized as X and defined by the ICRU as the quotient of dq by dm,
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Goal: The theory behind the electromagnetic radiation in remote sensing. 2.1 Maxwell Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Goal: The theory behind the electromagnetic radiation in remote sensing. 2.1 Maxwell Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves do not need a medium to
Chapter 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Goal: The theory behind the electromagnetic radiation in remote sensing. 2.1 Maxwell Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves do not need a medium to
Penning Traps. Contents. Plasma Physics Penning Traps AJW August 16, Introduction. Clasical picture. Radiation Damping.
 Penning Traps Contents Introduction Clasical picture Radiation Damping Number density B and E fields used to increase time that an electron remains within a discharge: Penning, 936. Can now trap a particle
Penning Traps Contents Introduction Clasical picture Radiation Damping Number density B and E fields used to increase time that an electron remains within a discharge: Penning, 936. Can now trap a particle
Problem Set 2: Solution
 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 53 / LeClair Fall 1 Problem Set : Solution 1. In a hydrogen atom an electron of charge e orbits around a proton of charge +e. (a) Find the total
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 53 / LeClair Fall 1 Problem Set : Solution 1. In a hydrogen atom an electron of charge e orbits around a proton of charge +e. (a) Find the total
ANTENNAS. Vector and Scalar Potentials. Maxwell's Equations. E = jωb. H = J + jωd. D = ρ (M3) B = 0 (M4) D = εe
 ANTENNAS Vector and Scalar Potentials Maxwell's Equations E = jωb H = J + jωd D = ρ B = (M) (M) (M3) (M4) D = εe B= µh For a linear, homogeneous, isotropic medium µ and ε are contant. Since B =, there
ANTENNAS Vector and Scalar Potentials Maxwell's Equations E = jωb H = J + jωd D = ρ B = (M) (M) (M3) (M4) D = εe B= µh For a linear, homogeneous, isotropic medium µ and ε are contant. Since B =, there
The Black Body Radiation
 The Black Body Radiation = Chapter 4 of Kittel and Kroemer The Planck distribution Derivation Black Body Radiation Cosmic Microwave Background The genius of Max Planck Other derivations Stefan Boltzmann
The Black Body Radiation = Chapter 4 of Kittel and Kroemer The Planck distribution Derivation Black Body Radiation Cosmic Microwave Background The genius of Max Planck Other derivations Stefan Boltzmann
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL EXAM. December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours)
 SOLUTIONS TO THE 18.02 FINAL EXAM BJORN POONEN December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours) 1) For each of (a)-(e) below: If the statement is true, write TRUE. If the statement is false, write FALSE. (Please
SOLUTIONS TO THE 18.02 FINAL EXAM BJORN POONEN December 14, 2010, 9:00am-12:00 (3 hours) 1) For each of (a)-(e) below: If the statement is true, write TRUE. If the statement is false, write FALSE. (Please
Moment of inertia. Contents. 1 Introduction and simple cases. January 15, Introduction. 1.2 Examples
 Moment of inertia January 15, 016 A systematic account is given of the concept and the properties of the moment of inertia. Contents 1 Introduction and simple cases 1 1.1 Introduction.............. 1 1.
Moment of inertia January 15, 016 A systematic account is given of the concept and the properties of the moment of inertia. Contents 1 Introduction and simple cases 1 1.1 Introduction.............. 1 1.
2. Passage of Radiation Through Matter
 2. Passage of Radiation Through Matter Passage of Radiation Through Matter: Contents Energy Loss of Heavy Charged Particles by Atomic Collision (addendum) Cherenkov Radiation Energy loss of Electrons and
2. Passage of Radiation Through Matter Passage of Radiation Through Matter: Contents Energy Loss of Heavy Charged Particles by Atomic Collision (addendum) Cherenkov Radiation Energy loss of Electrons and
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT)
 Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 9 1) Coulomb s Law and Field Intensity 2) Electric Fields Due to Continuous Charge Distributions Line Charge Surface Charge Volume Charge Coulomb's Law Coulomb's
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 9 1) Coulomb s Law and Field Intensity 2) Electric Fields Due to Continuous Charge Distributions Line Charge Surface Charge Volume Charge Coulomb's Law Coulomb's
Neutron Physics. The De Broglie relation for matter is: h mv (1) λ =
 Neutron Physics Emily P. Wang MIT Department of Physics (Dated: November 11, 2004) Thermal neutrons in a beam emerging from the MIT research reactor were used to study the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution,
Neutron Physics Emily P. Wang MIT Department of Physics (Dated: November 11, 2004) Thermal neutrons in a beam emerging from the MIT research reactor were used to study the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution,
MURI teleconference 28 May Optical Antimatter. John Pendry and Sebastien Guenneau Imperial College London. 24 May 2004 page 1
 24 May 2004 page 1 MURI teleconference 28 May 2004 Optical Antimatter John Pendry and Sebastien Guenneau Imperial College London 05 March 2004 page 2 A Conventional Lens Contributions of the far field
24 May 2004 page 1 MURI teleconference 28 May 2004 Optical Antimatter John Pendry and Sebastien Guenneau Imperial College London 05 March 2004 page 2 A Conventional Lens Contributions of the far field
Radiative heat transfer
 Radiative heat transfer 22 mars 2017 Energy can be transported by the electromagnetic field radiated by an object at finite temperature. A very important example is the infrared radiation emitted towards
Radiative heat transfer 22 mars 2017 Energy can be transported by the electromagnetic field radiated by an object at finite temperature. A very important example is the infrared radiation emitted towards
How DLS Works: Interference of Light
 Static light scattering vs. Dynamic light scattering Static light scattering measures time-average intensities (mean square fluctuations) molecular weight radius of gyration second virial coefficient Dynamic
Static light scattering vs. Dynamic light scattering Static light scattering measures time-average intensities (mean square fluctuations) molecular weight radius of gyration second virial coefficient Dynamic
Crystal Structure and Electron Diffraction
 Crystal Structure and Electron Diffraction References: Kittel C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics, 8 th ed. Wiley 005 University of Michigan, PHY441-44 (Advanced Physics Laboratory Experiments, Electron
Crystal Structure and Electron Diffraction References: Kittel C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics, 8 th ed. Wiley 005 University of Michigan, PHY441-44 (Advanced Physics Laboratory Experiments, Electron
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions.
 Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
3.012 PS Issued: Fall 2003 Graded problems due:
 3.012 PS 4 3.012 Issued: 10.07.03 Fall 2003 Graded problems due: 10.15.03 Graded problems: 1. Planes and directions. Consider a 2-dimensional lattice defined by translations T 1 and T 2. a. Is the direction
3.012 PS 4 3.012 Issued: 10.07.03 Fall 2003 Graded problems due: 10.15.03 Graded problems: 1. Planes and directions. Consider a 2-dimensional lattice defined by translations T 1 and T 2. a. Is the direction
AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski)
 AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.). If f(x) = 0x 4 3 + x, then f (8) = (A) (B) 4 3 (C) 83 3 (D) 2 3 (E) 2
AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.). If f(x) = 0x 4 3 + x, then f (8) = (A) (B) 4 3 (C) 83 3 (D) 2 3 (E) 2
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 8 LC Transmission Line Wave Reflection
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 8 LC Transmission Line Wave Reflection Midterm Exam #1 Midterm #1 has been graded Class average = 80.4 Standard deviation = 14.6 Your exam will be returned in the section
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 8 LC Transmission Line Wave Reflection Midterm Exam #1 Midterm #1 has been graded Class average = 80.4 Standard deviation = 14.6 Your exam will be returned in the section
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
2. NOTES ON RADIATIVE TRANSFER The specific intensity I ν
 1 2. NOTES ON RADIATIVE TRANSFER 2.1. The specific intensity I ν Let f(x, p) be the photon distribution function in phase space, summed over the two polarization states. Then fdxdp is the number of photons
1 2. NOTES ON RADIATIVE TRANSFER 2.1. The specific intensity I ν Let f(x, p) be the photon distribution function in phase space, summed over the two polarization states. Then fdxdp is the number of photons
BEM Formulation plane orthotropic bodies a modification for exterior regions and its proof
 Ŕ periodica polytechnica Civil Engineering 5/ 7 3 web: http:// www.pp.bme.hu/ ci c Periodica Polytechnica 7 BEM Formulation plane orthotropic bodies a modification for exterior regions its proof RESEARCH
Ŕ periodica polytechnica Civil Engineering 5/ 7 3 web: http:// www.pp.bme.hu/ ci c Periodica Polytechnica 7 BEM Formulation plane orthotropic bodies a modification for exterior regions its proof RESEARCH
New algoritms for electron diffraction of 3D protein crystals. JP Abrahams, D Georgieva, L Jiang, I Sikhuralidze, NS Pannu
 New algoritms for electron diffraction of 3D protein crystals JP Abrahams, D Georgieva, L Jiang, I Sikhuralidze, NS Pannu Why new algorithms? New research questions New experimental techniques Better insight
New algoritms for electron diffraction of 3D protein crystals JP Abrahams, D Georgieva, L Jiang, I Sikhuralidze, NS Pannu Why new algorithms? New research questions New experimental techniques Better insight
