3. The Electric Flux
|
|
|
- Annabel George
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3. The Electric Flux S. G. Rajeev January 20, Electric Field Lines The most important idea we discussed so far so far is the electric field. If you place a charge at any point, the electric force it feels is proportional to its charge. Thus the force divided by the charge is the same for all particles at that point. This quantity is the electric field at that point. It is a vector E :thedirection of the electric field is the same as the direction of the force felt by a positive charge placed at that point. A negative charge would be pushed in the direction opposite to the electric field. F = qe. Thus the electric field created by a positive charge points outward along the radial lines from its position; for a negative charge, the field points towards its position. It is useful to think of an electric field at each point as a little arrow at that point, giving its direction. Imagine moving along a curve that at each point points in the direction of the electric field. This is called a field line. These line start at a poistive charge and end at a negative charges. They cross only at points where you don t know the direction of the electric field: where the electric field vanishes. Or at the location of point charges where the electric field is infinite. 1
2 2 The Path of a Charged Particle The field lines are not the path of a charged particle in the electric field. It gives the direction of the force- and hence the acceleration- at each point: the direction in which a particle moves is given by the velocity. Velocity and acceleration don t have to point in the same direction. For example, a negative charge can move in a circle around a positive charge which is at rest. Its acceleration points to the positive charge, although its velocity points tangential to the circle. 2.1 A Charged Particle in a Constant Electric Field The path of a charged particle in a constant electric field is a parabola. This is very much like the path of a ball you throw into the air: the gravitational force is constant, so the acceleration is constant. If the electric field E is constant, the acceleration is constant as well: a = q m E. The velocity is then a linear function of time: v = at + v 0 where v 0 is the velocity at time t =0. The position at any time t must be a function whose derivative is equal to velocity 2
3 r(t) = 1 2 at2 + v 0 t + r 0 where r 0 is the position at time t =0. This is the equation of a parabola. Every shape (curve) can be described by a picture or an equation. The equation is by far the more powerful way of thinking of about it: it tell you much more about the curve than a mere picture. They say a picture is worth a thousand words. I say an equation is worth a thousand pictures. I can differentiate and integrate an equation. Try doing that with a picture. 3 The Electric Flux Karl Friedrich Gauss is one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. Some would say he is the greatest. ( Not me. That would be Isaac Newton.) Gauss found a way of thinking about Coulomb s law that allows us to calculate the electric field of charge distributions in a simple way. Although Gauss did not discover a new law of physics, his restatement of Coulomb s law was just as important a contribution. To understand Gauss s law we need to master the idea of the Electric Flux across a surface. It is a way of measuring the total electric field that crosses a surface. 3.1 Constant Field and Planar Surface Again we start with the simplest situation: the field is a constant and the surface is part of a plane perpendicular to it. The electric flux across the surface is defined to be the area of the surface A times the electric field. Φ=EA In this situation the electric field lines cross the surface: the flux is a way of counting how many field lines cross the surface. If we tilt the surface so that the lines cross at an angle, we can imagine fewer of them cross it. If the surface is lying parallel to the lines, nothing crosses it. The flux crossing a surface whose normal is at an angle θ to the field lines is defined to be Φ=EAcos θ Every surface has a direction associated to it, which is its normal. The area of a surface can be thought of as a vector, whose direction is along the normal. The flux is the dot product of the electric field and this area vector. Φ=E A. 3
4 3.2 Curved Surfaces Alas, most surfaces we encounter are not planes. Here is where the ideas of calculus come in handy. We can think of any smooth surface as tiled by small flat pieces: like the roof a house. If the tiles are small enoough, this is becomes a better and better way to think of the surface. Each tile has a small area and its normal points in a different direction. We can calculate the flux through each tile and then add them all up to get the total flux through the surface. This is called a surface integral. It is denoted by ˆ Φ= E da Flux of a Point Charge As an example, let us find the flux through a sphere surrounding a point charge. The electric field is E = k Q r 2ˆr. 4
5 A little piece of the sphere will alwas have a normal that points radially outward: that is a special property of the sphere. So we are in luck: although the normal to the sphere and the electric have directions that change with position, they are always parallel in this case. Moreover, the magnitude of the electric field is a constant. So the total flux in this case is just the magnitude of the electric field at a sphere of radius r times the area of the sphere of radius r. Φ=k Q r 2 4πr2 This is the same for all sphere, the radius actualy cancels out: Φ=4πkQ. In other words Q = Φ 4πk 5
6 3.3 An Annoying Constant 1 The constant 4πk appears very often in this subject, so it has a standard name. It is called the permittivity of free space (don t ask) and is denoted by the symbol 0 = 1 4πk. Its value is C 2 N 1 m 2. The total flux out of a point charge Q is Φ= Q The Direction of the Normal The area of a surface points along its normal. If a surface is closed (is the boundary of a volume) we always choose this direction to be the outward normal. The total flux out of a closed surface is denoted by :thelittleloopistoremind us that we are integrating over a closed surface. 4 Gauss s Law Gauss realized that Coulomb s law can be stated in another way: The electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the total charge contained inside it. In other words E da = Q 0. We saw this for the simplest case of the electric charge and a sphere. It was Gauss s insight that this is also true of all surfaces and any electric field. We will find it enormously useful in calculating the electric field of many shapes of charges. References [1] We used diagrams from notes online by Profs. Frank Wolfs (U of R), J. F. Becker (SJSU) and by resourcefulphysics.org 6
Welcome. to Electrostatics
 Welcome to Electrostatics Outline 1. Coulomb s Law 2. The Electric Field - Examples 3. Gauss Law - Examples 4. Conductors in Electric Field Coulomb s Law Coulomb s law quantifies the magnitude of the electrostatic
Welcome to Electrostatics Outline 1. Coulomb s Law 2. The Electric Field - Examples 3. Gauss Law - Examples 4. Conductors in Electric Field Coulomb s Law Coulomb s law quantifies the magnitude of the electrostatic
4. Gauss s Law. S. G. Rajeev. January 27, The electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the total charge contained inside it.
 4. Gauss s Law S. G. Rajeev January 27, 2009 1 Statement of Gauss s Law The electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the total charge contained inside it. In other words E da = Q ɛ 0.
4. Gauss s Law S. G. Rajeev January 27, 2009 1 Statement of Gauss s Law The electric flux through any closed surface is proportional to the total charge contained inside it. In other words E da = Q ɛ 0.
3: Gauss s Law July 7, 2008
 3: Gauss s Law July 7, 2008 3.1 Electric Flux In order to understand electric flux, it is helpful to take field lines very seriously. Think of them almost as real things that stream out from positive charges
3: Gauss s Law July 7, 2008 3.1 Electric Flux In order to understand electric flux, it is helpful to take field lines very seriously. Think of them almost as real things that stream out from positive charges
Chapter 24. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Electric Field and Gauss s law. January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1
 Electric Field and Gauss s law January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1 Missing clickers! The following clickers are not yet registered! If your clicker number is in this list,
Electric Field and Gauss s law January 17, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 22 1 Missing clickers! The following clickers are not yet registered! If your clicker number is in this list,
ELECTROSTATICS. kq q SUPERPOSITION
 ELECTROSTATICS As seen in class, we observe both attractive and repulsive forces. This requires at least two kinds of charge. Although more is possible we choose the simplest explanation consistent with
ELECTROSTATICS As seen in class, we observe both attractive and repulsive forces. This requires at least two kinds of charge. Although more is possible we choose the simplest explanation consistent with
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #6
 PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #6 Monday, Sept. 18, 2017 Chapter 21 Motion of a Charged Particle in an Electric Field Electric Dipoles Chapter 22 Electric Flux Gauss Law with many charges What is Gauss
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #6 Monday, Sept. 18, 2017 Chapter 21 Motion of a Charged Particle in an Electric Field Electric Dipoles Chapter 22 Electric Flux Gauss Law with many charges What is Gauss
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 Electromagnetism Physics 15b Lecture #2 Guass s Law Electric Field and Flux Purcell 1.7 1.15 Administravia Online sectioning due Wednesday (tudy Card Day) Go to http://www.section.fas.harvard.edu/ Do both
Electromagnetism Physics 15b Lecture #2 Guass s Law Electric Field and Flux Purcell 1.7 1.15 Administravia Online sectioning due Wednesday (tudy Card Day) Go to http://www.section.fas.harvard.edu/ Do both
Gauss s law for electric fields
 1 Gauss s law for electric fields In Maxwell s Equations, you ll encounter two kinds of electric field: the electrostatic field produced by electric charge and the induced electric field produced by a
1 Gauss s law for electric fields In Maxwell s Equations, you ll encounter two kinds of electric field: the electrostatic field produced by electric charge and the induced electric field produced by a
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law. Last Lecture: Electric Field Lines
 Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Last Lecture: Electric Field Lines 1 iclicker Charged particles are fixed on grids having the same spacing. Each charge has the same magnitude Q with signs given
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Last Lecture: Electric Field Lines 1 iclicker Charged particles are fixed on grids having the same spacing. Each charge has the same magnitude Q with signs given
3/22/2016. Chapter 27 Gauss s Law. Chapter 27 Preview. Chapter 27 Preview. Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2.
 Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-3 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-4 1 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-5 Chapter 27 Preview Slide
Chapter 27 Gauss s Law Chapter Goal: To understand and apply Gauss s law. Slide 27-2 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-3 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-4 1 Chapter 27 Preview Slide 27-5 Chapter 27 Preview Slide
Gauss s Law. Lecture 4. Chapter 27. Channel 61 (clicker) Physics II
 Lecture 4 Chapter 27 Physics II 01.30.2015 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov201415/physics2spring.html
Lecture 4 Chapter 27 Physics II 01.30.2015 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov201415/physics2spring.html
PHYSICS. Chapter 24 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 24 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 24 Gauss s Law IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about and apply Gauss s law. Slide 24-2 Chapter
Gauss s Law. Lecture 3. Chapter Course website:
 Lecture 3 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 24: Section 24.2 Idea of Flux Section 24.3 Electric
Lecture 3 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 24: Section 24.2 Idea of Flux Section 24.3 Electric
Chapter (2) Gauss s Law
 Chapter (2) Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface! What is meant by electric flux and how you can calculate it. How
Chapter (2) Gauss s Law How you can determine the amount of charge within a closed surface by examining the electric field on the surface! What is meant by electric flux and how you can calculate it. How
The Basic Definition of Flux
 The Basic Definition of Flux Imagine holding a rectangular wire loop of area A in front of a fan. The volume of air flowing through the loop each second depends on the angle between the loop and the direction
The Basic Definition of Flux Imagine holding a rectangular wire loop of area A in front of a fan. The volume of air flowing through the loop each second depends on the angle between the loop and the direction
Physics 202, Lecture 3. The Electric Field
 Physics 202, Lecture 3 Today s Topics Electric Field (Review) Motion of charged particles in external E field Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium (Ch. 21.9) Gauss s Law (Ch. 22) Reminder: HW #1 due
Physics 202, Lecture 3 Today s Topics Electric Field (Review) Motion of charged particles in external E field Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium (Ch. 21.9) Gauss s Law (Ch. 22) Reminder: HW #1 due
IClicker question. We have a negative charge q=-e. How electric field is directed at point X? q=-e (negative charge) X A: B: C: D: E: E=0
 We have a negative charge q=-e. How electric field is directed at point X? IClicker question q=-e (negative charge) X A: B: C: D: E: E=0 1 A: q=-e (negative charge) F X E Place positive charge q0 Force
We have a negative charge q=-e. How electric field is directed at point X? IClicker question q=-e (negative charge) X A: B: C: D: E: E=0 1 A: q=-e (negative charge) F X E Place positive charge q0 Force
Chapter 24. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Let s return to the field lines and consider the flux through a surface. The number of lines per unit area is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field. This means that
Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Let s return to the field lines and consider the flux through a surface. The number of lines per unit area is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field. This means that
Electric Flux. To investigate this, we have to understand electric flux.
 Problem 21.72 A charge q 1 = +5. nc is placed at the origin of an xy-coordinate system, and a charge q 2 = -2. nc is placed on the positive x-axis at x = 4. cm. (a) If a third charge q 3 = +6. nc is now
Problem 21.72 A charge q 1 = +5. nc is placed at the origin of an xy-coordinate system, and a charge q 2 = -2. nc is placed on the positive x-axis at x = 4. cm. (a) If a third charge q 3 = +6. nc is now
3 Chapter. Gauss s Law
 3 Chapter Gauss s Law 3.1 Electric Flux... 3-2 3.2 Gauss s Law (see also Gauss s Law Simulation in Section 3.10)... 3-4 Example 3.1: Infinitely Long Rod of Uniform Charge Density... 3-9 Example 3.2: Infinite
3 Chapter Gauss s Law 3.1 Electric Flux... 3-2 3.2 Gauss s Law (see also Gauss s Law Simulation in Section 3.10)... 3-4 Example 3.1: Infinitely Long Rod of Uniform Charge Density... 3-9 Example 3.2: Infinite
Phys102 General Physics II. Chapter 24: Gauss s Law
 Phys102 General Physics II Gauss Law Chapter 24: Gauss s Law Flux Electric Flux Gauss Law Coulombs Law from Gauss Law Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor Application of Gauss Law Charged
Phys102 General Physics II Gauss Law Chapter 24: Gauss s Law Flux Electric Flux Gauss Law Coulombs Law from Gauss Law Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor Application of Gauss Law Charged
PHY102 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law
 PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
PHY1 Electricity Topic 3 (Lectures 4 & 5) Gauss s Law In this topic, we will cover: 1) Electric Flux ) Gauss s Law, relating flux to enclosed charge 3) Electric Fields and Conductors revisited Reading
Forces. A force is a push or a pull on an object
 Forces Forces A force is a push or a pull on an object Arrows are used to represent forces. The direction of the arrow represent the direction the force that exist or being applied. Forces A net force
Forces Forces A force is a push or a pull on an object Arrows are used to represent forces. The direction of the arrow represent the direction the force that exist or being applied. Forces A net force
Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux
 Lecture 3 Chapter 23 Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter
Lecture 3 Chapter 23 Motion of a charged particle in an electric field. Electric flux 95.144 Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter
Problem Solving 1: The Mathematics of 8.02 Part I. Coordinate Systems
 Problem Solving 1: The Mathematics of 8.02 Part I. Coordinate Systems In 8.02 we regularly use three different coordinate systems: rectangular (Cartesian), cylindrical and spherical. In order to become
Problem Solving 1: The Mathematics of 8.02 Part I. Coordinate Systems In 8.02 we regularly use three different coordinate systems: rectangular (Cartesian), cylindrical and spherical. In order to become
Circular motion. Aug. 22, 2017
 Circular motion Aug. 22, 2017 Until now, we have been observers to Newtonian physics through inertial reference frames. From our discussion of Newton s laws, these are frames which obey Newton s first
Circular motion Aug. 22, 2017 Until now, we have been observers to Newtonian physics through inertial reference frames. From our discussion of Newton s laws, these are frames which obey Newton s first
Ideas from Vector Calculus Kurt Bryan
 Ideas from Vector Calculus Kurt Bryan Most of the facts I state below are for functions of two or three variables, but with noted exceptions all are true for functions of n variables..1 Tangent Line Approximation
Ideas from Vector Calculus Kurt Bryan Most of the facts I state below are for functions of two or three variables, but with noted exceptions all are true for functions of n variables..1 Tangent Line Approximation
Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
 Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields Outline 19-1 Electric Charge 19-2 Insulators and Conductors 19-3 Coulomb s Law 19-4 The Electric Field 19-5 Electric Field Lines 19-6 Shield and Charging
Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields Outline 19-1 Electric Charge 19-2 Insulators and Conductors 19-3 Coulomb s Law 19-4 The Electric Field 19-5 Electric Field Lines 19-6 Shield and Charging
Electric Flux. If we know the electric field on a Gaussian surface, we can find the net charge enclosed by the surface.
 Chapter 23 Gauss' Law Instead of considering the electric fields of charge elements in a given charge distribution, Gauss' law considers a hypothetical closed surface enclosing the charge distribution.
Chapter 23 Gauss' Law Instead of considering the electric fields of charge elements in a given charge distribution, Gauss' law considers a hypothetical closed surface enclosing the charge distribution.
Mechanics Lecture Notes
 Mechanics Lecture Notes Lectures 0 and : Motion in a circle. Introduction The important result in this lecture concerns the force required to keep a particle moving on a circular path: if the radius of
Mechanics Lecture Notes Lectures 0 and : Motion in a circle. Introduction The important result in this lecture concerns the force required to keep a particle moving on a circular path: if the radius of
Chapter 23: Gauss Law. PHY2049: Chapter 23 1
 Chapter 23: Gauss Law PHY2049: Chapter 23 1 Two Equivalent Laws for Electricity Coulomb s Law equivalent Gauss Law Derivation given in Sec. 23-5 (Read!) Not derived in this book (Requires vector calculus)
Chapter 23: Gauss Law PHY2049: Chapter 23 1 Two Equivalent Laws for Electricity Coulomb s Law equivalent Gauss Law Derivation given in Sec. 23-5 (Read!) Not derived in this book (Requires vector calculus)
Physics 2B. Lecture 24B. Gauss 10 Deutsche Mark
 Physics 2B Lecture 24B Gauss 10 Deutsche Mark Electric Flux Flux is the amount of something that flows through a given area. Electric flux, Φ E, measures the amount of electric field lines that passes
Physics 2B Lecture 24B Gauss 10 Deutsche Mark Electric Flux Flux is the amount of something that flows through a given area. Electric flux, Φ E, measures the amount of electric field lines that passes
Reading: Chapter 28. 4πε r. For r > a. Gauss s Law
 Reading: Chapter 8 Q 4πε r o k Q r e For r > a Gauss s Law 1 Chapter 8 Gauss s Law lectric Flux Definition: lectric flux is the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area, A, perpendicular
Reading: Chapter 8 Q 4πε r o k Q r e For r > a Gauss s Law 1 Chapter 8 Gauss s Law lectric Flux Definition: lectric flux is the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area, A, perpendicular
Electric Field Lines. lecture 4.1.1
 Electric Field Lines Two protons, A and B, are in an electric field. Which proton has the larger acceleration? A. Proton A B. Proton B C. Both have the same acceleration. lecture 4.1.1 Electric Field Lines
Electric Field Lines Two protons, A and B, are in an electric field. Which proton has the larger acceleration? A. Proton A B. Proton B C. Both have the same acceleration. lecture 4.1.1 Electric Field Lines
Course Updates. Reminders: 1) Quiz today. 2) Written problems: 21.96, 22.6, 22.58, ) Complete Chapter 22 (all this information on web page)
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phy272-pr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Quiz today 2) Written problems: 21.96, 22.6, 22.58, 22.30 3) Complete Chapter 22 (all this information on web
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phy272-pr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Quiz today 2) Written problems: 21.96, 22.6, 22.58, 22.30 3) Complete Chapter 22 (all this information on web
Chapter 21: Gauss s Law
 Chapter 21: Gauss s Law Electric field lines Electric field lines provide a convenient and insightful way to represent electric fields. A field line is a curve whose direction at each point is the direction
Chapter 21: Gauss s Law Electric field lines Electric field lines provide a convenient and insightful way to represent electric fields. A field line is a curve whose direction at each point is the direction
Physics 212. Lecture 3. Gauss s Law. Today's Concepts: Electric Flux and Field Lines. Physics 212 Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Physics 212 Lecture 3 Today's Concepts: lectric Flux and Field Lines Gauss s Law Physics 212 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Introduce a new constant: 0 q k r r 2 ˆ k 1 4 0 k = 9 x 10 9 N m 2 / C 2 0 = 8.85 x 10-12
Physics 212 Lecture 3 Today's Concepts: lectric Flux and Field Lines Gauss s Law Physics 212 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Introduce a new constant: 0 q k r r 2 ˆ k 1 4 0 k = 9 x 10 9 N m 2 / C 2 0 = 8.85 x 10-12
Math 234 Exam 3 Review Sheet
 Math 234 Exam 3 Review Sheet Jim Brunner LIST OF TOPIS TO KNOW Vector Fields lairaut s Theorem & onservative Vector Fields url Divergence Area & Volume Integrals Using oordinate Transforms hanging the
Math 234 Exam 3 Review Sheet Jim Brunner LIST OF TOPIS TO KNOW Vector Fields lairaut s Theorem & onservative Vector Fields url Divergence Area & Volume Integrals Using oordinate Transforms hanging the
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law
 Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
Electro Magnetic Field Dr. Harishankar Ramachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Electro Magnetic Field Dr. Harishankar Ramachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 7 Gauss s Law Good morning. Today, I want to discuss two or three
Electro Magnetic Field Dr. Harishankar Ramachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture - 7 Gauss s Law Good morning. Today, I want to discuss two or three
PHY114 S11 Term Exam 1
 PHY114 S11 Term Exam 1 S. G. Rajeev Feb 15 2011 12:30 pm to 1:45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams
PHY114 S11 Term Exam 1 S. G. Rajeev Feb 15 2011 12:30 pm to 1:45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams
Gauss s Law. Name. I. The Law: , where ɛ 0 = C 2 (N?m 2
 Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
Name Gauss s Law I. The Law:, where ɛ 0 = 8.8510 12 C 2 (N?m 2 1. Consider a point charge q in three-dimensional space. Symmetry requires the electric field to point directly away from the charge in all
Chapter 22 Gauss s law. Electric charge and flux (sec &.3) Gauss s Law (sec &.5) Charges on conductors (sec. 22.6)
 Chapter 22 Gauss s law Electric charge and flux (sec. 22.2 &.3) Gauss s Law (sec. 22.4 &.5) Charges on conductors (sec. 22.6) 1 Learning Goals for CH 22 Determine the amount of charge within a closed surface
Chapter 22 Gauss s law Electric charge and flux (sec. 22.2 &.3) Gauss s Law (sec. 22.4 &.5) Charges on conductors (sec. 22.6) 1 Learning Goals for CH 22 Determine the amount of charge within a closed surface
Integrals in Electrostatic Problems
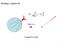
 PHYS 119 Integrals in Electrostatic Problems Josh McKenney University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (Dated: January 6, 2016) 1 FIG. 1. Three positive charges positioned at equal distances around an
PHYS 119 Integrals in Electrostatic Problems Josh McKenney University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (Dated: January 6, 2016) 1 FIG. 1. Three positive charges positioned at equal distances around an
Practice Questions Exam 1/page1. PES Physics 2 Practice Exam 1 Questions. Name: Score: /.
 Practice Questions Exam 1/page1 PES 110 - Physics Practice Exam 1 Questions Name: Score: /. Instructions Time allowed for this is exam is 1 hour 15 minutes 5 multiple choice (5 points) 3 to 5 written problems
Practice Questions Exam 1/page1 PES 110 - Physics Practice Exam 1 Questions Name: Score: /. Instructions Time allowed for this is exam is 1 hour 15 minutes 5 multiple choice (5 points) 3 to 5 written problems
Chapter 23. Gauss Law. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 Electric Flux Electric field vectors and field lines pierce an imaginary, spherical Gaussian surface that encloses a particle with charge +Q. Now the enclosed particle
Chapter 23 Gauss Law Copyright 23-1 Electric Flux Electric field vectors and field lines pierce an imaginary, spherical Gaussian surface that encloses a particle with charge +Q. Now the enclosed particle
Physics 11b Lecture #3. Electric Flux Gauss s Law
 Physics 11b Lecture #3 lectric Flux Gauss s Law What We Did Last Time Introduced electric field by Field lines and the rules From a positive charge to a negative charge No splitting, merging, or crossing
Physics 11b Lecture #3 lectric Flux Gauss s Law What We Did Last Time Introduced electric field by Field lines and the rules From a positive charge to a negative charge No splitting, merging, or crossing
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law
 Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
Electric Flux and Gauss s Law Electric Flux Figure (1) Consider an electric field that is uniform in both magnitude and direction, as shown in Figure 1. The total number of lines penetrating the surface
6 Div, grad curl and all that
 6 Div, grad curl and all that 6.1 Fundamental theorems for gradient, divergence, and curl Figure 1: Fundamental theorem of calculus relates df/dx over[a, b] and f(a), f(b). You will recall the fundamental
6 Div, grad curl and all that 6.1 Fundamental theorems for gradient, divergence, and curl Figure 1: Fundamental theorem of calculus relates df/dx over[a, b] and f(a), f(b). You will recall the fundamental
Physics 2A Chapter 3 - Motion in Two Dimensions Fall 2017
 These notes are seen pages. A quick summary: Projectile motion is simply horizontal motion at constant elocity with ertical motion at constant acceleration. An object moing in a circular path experiences
These notes are seen pages. A quick summary: Projectile motion is simply horizontal motion at constant elocity with ertical motion at constant acceleration. An object moing in a circular path experiences
MATH 228: Calculus III (FALL 2016) Sample Problems for FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 228: Calculus III (FALL 216) Sample Problems for FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS MATH 228 Page 2 Problem 1. (2pts) Evaluate the line integral C xy dx + (x + y) dy along the parabola y x2 from ( 1, 1) to (2,
MATH 228: Calculus III (FALL 216) Sample Problems for FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS MATH 228 Page 2 Problem 1. (2pts) Evaluate the line integral C xy dx + (x + y) dy along the parabola y x2 from ( 1, 1) to (2,
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields
 Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
Chapter 1 Electric Charges, Forces, and Fields 1 Units of Chapter 1 Electric Charge Insulators and Conductors Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric Fields Generated by simple distributions
Electric flux. You must be able to calculate the electric flux through a surface.
 Today s agenda: Announcements. lectric field lines. You must be able to draw electric field lines, and interpret diagrams that show electric field lines. A dipole in an external electric field. You must
Today s agenda: Announcements. lectric field lines. You must be able to draw electric field lines, and interpret diagrams that show electric field lines. A dipole in an external electric field. You must
Week 4. Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential
 Week 4 Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential Electric Charge - A property of matter Matter is made up of two kinds of electric charges (positive and negative). Like charges repel, unlike
Week 4 Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential Electric Charge - A property of matter Matter is made up of two kinds of electric charges (positive and negative). Like charges repel, unlike
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law
 Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 22 To use the electric field at a surface to determine the charge within the surface To learn the meaning of electric flux and how to calculate
Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals for Chapter 22 To use the electric field at a surface to determine the charge within the surface To learn the meaning of electric flux and how to calculate
Chapter 24. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Chapter 24 Gauss s Law Gauss Law Gauss Law can be used as an alternative procedure for calculating electric fields. Gauss Law is based on the inverse-square behavior of the electric force between point
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Central Potential and Central Force Ready now to take up the idea
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 21 Central Potential and Central Force Ready now to take up the idea
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Kinematics
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Kinematics Module 10 - Lecture 24 Kinematics of a particle moving on a curve Today,
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Kinematics Module 10 - Lecture 24 Kinematics of a particle moving on a curve Today,
Physics 114 Exam 1 Spring 2013
 Physics 114 Exam 1 Spring 2013 Name: For grading purposes (do not write here): Question 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the following questions and each of the problems. Points for each question
Physics 114 Exam 1 Spring 2013 Name: For grading purposes (do not write here): Question 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the following questions and each of the problems. Points for each question
2. Gauss Law [1] Equipment: This is a theoretical lab so your equipment is pencil, paper, and textbook.
![2. Gauss Law [1] Equipment: This is a theoretical lab so your equipment is pencil, paper, and textbook. 2. Gauss Law [1] Equipment: This is a theoretical lab so your equipment is pencil, paper, and textbook.](/thumbs/76/74190723.jpg) Purpose: Theoretical study of Gauss law. 2. Gauss Law [1] Equipment: This is a theoretical lab so your equipment is pencil, paper, and textbook. When drawing field line pattern around charge distributions
Purpose: Theoretical study of Gauss law. 2. Gauss Law [1] Equipment: This is a theoretical lab so your equipment is pencil, paper, and textbook. When drawing field line pattern around charge distributions
FLUX OF VECTOR FIELD INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
Chapter 3 GAUSS LAW ntroduction Flux of vector field Solid angle Gauss s Law Symmetry Spherical symmetry Cylindrical symmetry Plane symmetry Superposition of symmetric geometries Motion of point charges
Chapter 28. Gauss s Law
 Chapter 28. Gauss s Law Using Gauss s law, we can deduce electric fields, particularly those with a high degree of symmetry, simply from the shape of the charge distribution. The nearly spherical shape
Chapter 28. Gauss s Law Using Gauss s law, we can deduce electric fields, particularly those with a high degree of symmetry, simply from the shape of the charge distribution. The nearly spherical shape
free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]
![free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m] free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]](/thumbs/79/79624275.jpg) Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
ES.182A Topic 36 Notes Jeremy Orloff
 ES.82A Topic 36 Notes Jerem Orloff 36 Vector fields and line integrals in the plane 36. Vector analsis We now will begin our stud of the part of 8.2 called vector analsis. This is the stud of vector fields
ES.82A Topic 36 Notes Jerem Orloff 36 Vector fields and line integrals in the plane 36. Vector analsis We now will begin our stud of the part of 8.2 called vector analsis. This is the stud of vector fields
Physics 1B Electricity & Magne4sm
 Physics 1B Electricity & Magne4sm Frank Wuerthwein (Prof) Edward Ronan (TA) UCSD 1/19/12 1 Outline of Today Electric Flux & Gauss Law Quiz prepara4on: A reminder of geometry Quiz 1 on Friday January 27
Physics 1B Electricity & Magne4sm Frank Wuerthwein (Prof) Edward Ronan (TA) UCSD 1/19/12 1 Outline of Today Electric Flux & Gauss Law Quiz prepara4on: A reminder of geometry Quiz 1 on Friday January 27
Lecture 4-1 Physics 219 Question 1 Aug Where (if any) is the net electric field due to the following two charges equal to zero?
 Lecture 4-1 Physics 219 Question 1 Aug.31.2016. Where (if any) is the net electric field due to the following two charges equal to zero? y Q Q a x a) at (-a,0) b) at (2a,0) c) at (a/2,0) d) at (0,a) and
Lecture 4-1 Physics 219 Question 1 Aug.31.2016. Where (if any) is the net electric field due to the following two charges equal to zero? y Q Q a x a) at (-a,0) b) at (2a,0) c) at (a/2,0) d) at (0,a) and
PHY2048 Physics with Calculus I
 PHY2048 Physics with Calculus I Section 584761 Prof. Douglas H. Laurence Exam 1 (Chapters 2 6) February 14, 2018 Name: Solutions 1 Instructions: This exam is composed of 10 multiple choice questions and
PHY2048 Physics with Calculus I Section 584761 Prof. Douglas H. Laurence Exam 1 (Chapters 2 6) February 14, 2018 Name: Solutions 1 Instructions: This exam is composed of 10 multiple choice questions and
Math 5BI: Problem Set 9 Integral Theorems of Vector Calculus
 Math 5BI: Problem et 9 Integral Theorems of Vector Calculus June 2, 2010 A. ivergence and Curl The gradient operator = i + y j + z k operates not only on scalar-valued functions f, yielding the gradient
Math 5BI: Problem et 9 Integral Theorems of Vector Calculus June 2, 2010 A. ivergence and Curl The gradient operator = i + y j + z k operates not only on scalar-valued functions f, yielding the gradient
Quick Questions. 1. Two charges of +1 µc each are separated by 1 cm. What is the force between them?
 92 3.10 Quick Questions 3.10 Quick Questions 1. Two charges of +1 µc each are separated by 1 cm. What is the force between them? 0.89 N 90 N 173 N 15 N 2. The electric field inside an isolated conductor
92 3.10 Quick Questions 3.10 Quick Questions 1. Two charges of +1 µc each are separated by 1 cm. What is the force between them? 0.89 N 90 N 173 N 15 N 2. The electric field inside an isolated conductor
P - f = m a x. Now, if the box is already moving, for the frictional force, we use
 Chapter 5 Class Notes This week, we return to forces, and consider forces pointing in different directions. Previously, in Chapter 3, the forces were parallel, but in this chapter the forces can be pointing
Chapter 5 Class Notes This week, we return to forces, and consider forces pointing in different directions. Previously, in Chapter 3, the forces were parallel, but in this chapter the forces can be pointing
Episode 402: Fields, field lines and field strength
 Episode 402: Fields, field lines and field strength This episode introduces the notion of a field of force and how we can diagrammatically represent such a field using field lines. The actual strength
Episode 402: Fields, field lines and field strength This episode introduces the notion of a field of force and how we can diagrammatically represent such a field using field lines. The actual strength
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 08 Vectors in a Plane, Scalars & Pseudoscalers Let us continue today with
Mechanics, Heat, Oscillations and Waves Prof. V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 08 Vectors in a Plane, Scalars & Pseudoscalers Let us continue today with
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University. Shari Ultman
 Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Quiz Fun! This box contains. 1. a net positive charge. 2. no net charge. 3. a net negative charge. 4. a positive charge. 5. a negative charge.
 Quiz Fun! This box contains 1. a net positive charge. 2. no net charge. 3. a net negative charge. 4. a positive charge. 5. a negative charge. Quiz Fun! This box contains 1. a net positive charge. 2. no
Quiz Fun! This box contains 1. a net positive charge. 2. no net charge. 3. a net negative charge. 4. a positive charge. 5. a negative charge. Quiz Fun! This box contains 1. a net positive charge. 2. no
Gauss s Law & Potential
 Gauss s Law & Potential Lecture 7: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Flux of an Electric Field : In this lecture we introduce Gauss s law which happens to
Gauss s Law & Potential Lecture 7: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay Flux of an Electric Field : In this lecture we introduce Gauss s law which happens to
PHY 2049: Introductory Electromagnetism
 PHY 2049: Introductory Electromagnetism Notes From the Text 1 Introduction Chris Mueller Dept. of Physics, University of Florida 3 January, 2009 The subject of this course is the physics of electricity
PHY 2049: Introductory Electromagnetism Notes From the Text 1 Introduction Chris Mueller Dept. of Physics, University of Florida 3 January, 2009 The subject of this course is the physics of electricity
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration
 Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_24 Sunday, February 03, 2008 Page 1
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_4 Sunday, February 03, 008 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. A point charged particle is placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface. The net electric flux Φ net
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_4 Sunday, February 03, 008 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. A point charged particle is placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface. The net electric flux Φ net
Physics 212 Lecture 3
 Physics 212 Lecture 3 Today's Concepts: lectric Flux and Field Lines Gauss s Law Physics 212 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Music Who is the Artist? A) Professor Longhair B) Henry Butler C) David gan D) Dr. John )
Physics 212 Lecture 3 Today's Concepts: lectric Flux and Field Lines Gauss s Law Physics 212 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Music Who is the Artist? A) Professor Longhair B) Henry Butler C) David gan D) Dr. John )
Electricity and Magnetism Magnetic Field from Moving Charges
 Electricity and Magnetism Magnetic Field from Moving Charges Lana Sheridan De Anza College Nov 17, 2015 Last time force on a wire with a current in a B-field torque on a wire loop in a B-field motors relating
Electricity and Magnetism Magnetic Field from Moving Charges Lana Sheridan De Anza College Nov 17, 2015 Last time force on a wire with a current in a B-field torque on a wire loop in a B-field motors relating
Summary: Applications of Gauss Law
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2006, Lecture 15 1 Summary: Applications of Gauss Law 1. Field outside of a uniformly charged sphere of radius a: 2. An infinite, uniformly charged plane
Calculus Workshop. Calculus Workshop 1
 Physics 251 Laboratory Calculus Workshop For the next three lab periods we will be reviewing the concept of density and learning the calculus techniques necessary to succeed in Physics 251. The first week
Physics 251 Laboratory Calculus Workshop For the next three lab periods we will be reviewing the concept of density and learning the calculus techniques necessary to succeed in Physics 251. The first week
Chapter 23. Electric Fields
 Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electric Charges There are two kinds of electric charges Called positive and negative Negative charges are the type possessed by electrons Positive charges are the type possessed
Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electric Charges There are two kinds of electric charges Called positive and negative Negative charges are the type possessed by electrons Positive charges are the type possessed
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 4 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 4 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/
To receive full credit, you must show your work (including calculations and formulas used).
 Page Score Problem : Problem 2: Problem 3: Problem 4: Problem 5: TOTAL: (25 pts) To receive full credit, you must show your work (including calculations and formulas used). If you do not wish your quiz
Page Score Problem : Problem 2: Problem 3: Problem 4: Problem 5: TOTAL: (25 pts) To receive full credit, you must show your work (including calculations and formulas used). If you do not wish your quiz
Potential/density pairs and Gauss s law
 Potential/density pairs and Gauss s law We showed last time that the motion of a particle in a cluster will evolve gradually, on the relaxation time scale. This time, however, is much longer than the typical
Potential/density pairs and Gauss s law We showed last time that the motion of a particle in a cluster will evolve gradually, on the relaxation time scale. This time, however, is much longer than the typical
Coordinate systems and vectors in three spatial dimensions
 PHYS2796 Introduction to Modern Physics (Spring 2015) Notes on Mathematics Prerequisites Jim Napolitano, Department of Physics, Temple University January 7, 2015 This is a brief summary of material on
PHYS2796 Introduction to Modern Physics (Spring 2015) Notes on Mathematics Prerequisites Jim Napolitano, Department of Physics, Temple University January 7, 2015 This is a brief summary of material on
Electric Field Lines
 Electric Field Lines Electric forces Electric fields: - Electric field lines emanate from positive charges - Electric field lines disappear at negative charges If you see a bunch of field lines emanating
Electric Field Lines Electric forces Electric fields: - Electric field lines emanate from positive charges - Electric field lines disappear at negative charges If you see a bunch of field lines emanating
Circular Motion Ch. 10 in your text book
 Circular Motion Ch. 10 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Define rotation and revolution 2) Calculate the rotational speed of an object 3) Calculate the centripetal acceleration
Circular Motion Ch. 10 in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: 1) Define rotation and revolution 2) Calculate the rotational speed of an object 3) Calculate the centripetal acceleration
Gravity and Coulomb s Law
 AP PHYSICS 1 Gravity and Coulomb s Law 016 EDITION Click on the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright 016 National
AP PHYSICS 1 Gravity and Coulomb s Law 016 EDITION Click on the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright 016 National
Lecture 3: Vectors. Any set of numbers that transform under a rotation the same way that a point in space does is called a vector.
 Lecture 3: Vectors Any set of numbers that transform under a rotation the same way that a point in space does is called a vector i.e., A = λ A i ij j j In earlier courses, you may have learned that a vector
Lecture 3: Vectors Any set of numbers that transform under a rotation the same way that a point in space does is called a vector i.e., A = λ A i ij j j In earlier courses, you may have learned that a vector
Phys 122 Lecture 3 G. Rybka
 Phys 122 Lecture 3 G. Rybka A few more Demos Electric Field Lines Example Calculations: Discrete: Electric Dipole Overview Continuous: Infinite Line of Charge Next week Labs and Tutorials begin Electric
Phys 122 Lecture 3 G. Rybka A few more Demos Electric Field Lines Example Calculations: Discrete: Electric Dipole Overview Continuous: Infinite Line of Charge Next week Labs and Tutorials begin Electric
Gauss s Law. Chapter 22. Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition. Applications of Gauss s Law
 Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law Uniform Charged Sphere Infinite Line of Charge Infinite Sheet of Charge Two infinite sheets of charge Phys 2435:
Electric Flux Gauss s Law: Definition Chapter 22 Gauss s Law Applications of Gauss s Law Uniform Charged Sphere Infinite Line of Charge Infinite Sheet of Charge Two infinite sheets of charge Phys 2435:
Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law
 Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law F F Last modified: 07/02/2018 Contents Links Electric Charge & Coulomb s Law Electric Charge Coulomb s Law Example 1: Coulomb s Law Electric Field Electric Field Vector
Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law F F Last modified: 07/02/2018 Contents Links Electric Charge & Coulomb s Law Electric Charge Coulomb s Law Example 1: Coulomb s Law Electric Field Electric Field Vector
Midterm 1 Review. Distance = (x 1 x 0 ) 2 + (y 1 y 0 ) 2.
 Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS
 MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT100 is a fast-paced and thorough tour of precalculus mathematics, where the choice of topics is primarily motivated by the conceptual and technical knowledge
MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT100 is a fast-paced and thorough tour of precalculus mathematics, where the choice of topics is primarily motivated by the conceptual and technical knowledge
Calculus Relationships in AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
 C: Electricity This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your C: Mechanics course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the
C: Electricity This chapter focuses on some of the quantitative skills that are important in your C: Mechanics course. These are not all of the skills that you will learn, practice, and apply during the
CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULUS. We ve spent a lot of time so far just looking at all the different ways you can graph
 CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULUS We ve spent a lot of time so far just looking at all the different ways you can graph things and describe things in three dimensions, and it certainly seems like there is a lot
CHAPTER 6 VECTOR CALCULUS We ve spent a lot of time so far just looking at all the different ways you can graph things and describe things in three dimensions, and it certainly seems like there is a lot
18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. V9. Surface Integrals Surface
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. V9. Surface Integrals Surface
