Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Fields. Part A Motion of a charged particle due to the presence of another charged particle
|
|
|
- Kelley Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Fields We will be looking at two situations in which a charged particle is moving in an electric field. The first situation occurs when the motion of the charged particle is due to the presence of a fixed charged particle. The other analysis will involve the motion of a charged particle through a uniform electric field, such as that between two parallel plates. Part A Motion of a charged particle due to the presence of another charged particle Consider a small positive charge q, with a very small mass m, a distance r from a fixed positive charge Q. We will assume that m is so small that gravitational effects can be ignored. Describing the object s motion in terms of dynamics is difficult. As it begins to move, r increases, causing F E to decrease, so that a decreases as well. Motion with changing acceleration is difficult to analyze using dynamics. If we use conservation of energy to analyze its motion, it becomes much simpler. As the separation between the charges increases, the electric potential energy decreases and the charge q begins to acquire kinetic energy. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that the total energy remains constant. At r 1 E = PE E = + kqq r 1
2 At r 2 E = PE E + E k = + kqq + 1 r 2 2 mv 2 f Therefore, kqq r 1 = kqq r mv 2 f kqq kqq r 2 r = mv 2 f ΔPE E = ΔE k Where, r 1 is the initial separation between the two charges r 2 is the separation after being accelerated (gaining E k ) v f is the final speed of the particle Example 1 A small pith ball of mass kg and charge C is at rest 25 cm from a fixed positive charge of C. Neglecting gravitational effects and air resistance, with what speed will the pith ball be moving when it is 50 cm from the other charge?
3 Part B Motion of a charged particle in a uniform electric field When the electric field in which the charged particle is moving is a uniform electric field, its motion is much simpler. In a uniform electric field Therefore, F E = qe = constant a = F E m = constant Thus, the charged particle moves with constant acceleration, allowing us to analyze its motion using dynamics. This will be the case for small particles (such as protons, electrons, and ions) moving between parallel plates. In the case of parallel plates, it is often desirable to analyze the motion in terms of conservation of energy. In a parallel plate apparatus, whose separation is d, the work done in moving a charge q from one plate to the other is W = F E d = qed = q ΔV d d W = qδv This amount of work is equal in magnitude to the change in kinetic energy of the particle as it moves from one plate to the other. Example 2 The potential difference between two parallel plates is 8000 V. If a free electron of mass kg and charge C, is released at the negative plate, with what speed does it hit the positive plate?
4
5 Charges in Electric Fields Worksheet #1 1. The potential difference between two parallel plates is V. If 0.24 J of work is required to move a small charge from one plate to the other, what is the magnitude of the charge? ( C ) 2. An alpha particle has a positive charge of 2e and a mass of kg. With what velocity would an alpha particle reach the negative plate of a parallel plate apparatus with a potential difference of V, if it started, at rest, a. next to the positive plate? ( m / s ) b. at the midpoint between the plates? ( m / s ) 3. A pith ball of mass kg with a positive charge of C is slowly pulled by a string a distance of 50 cm through a potential difference of V. It is then released from rest and falls back to its original position. Calculate: a. the work done by the string in moving the pith ball. ( J ) b. the average force required to do this work. ( N ) c. the kinetic energy with which the pith ball reaches its original position. ( J ) d. its speed just as it reaches its original position. (8.0 m/s) 4. Two electrons are held, at rest, m apart, and then released. With what kinetic energy and speed is each moving when they are a large distance apart? ( J, m / s ) 5. What potential difference is required to accelerate a deuteron, of mass kg and charge C, from rest to a speed of m / s? ( V ) 6. An electron is accelerated by a constant electric field of 300 N/C. a. Find the acceleration of the electron. ( m / s 2 ) b. Find the electron s speed after s assuming it starts from rest.( m / s ) 7. A constant electric field directed along the positive x-axis has a strength of N / C. a. Find the electric force exerted on a proton by the field. ( N along the positive x-axis) b. Find the acceleration of the proton. ( m / s 2 ) c. Find the time required for the proton to reach a speed of m / s, assuming it starts from rest. ( s ) 8. Consider an electron that is released from rest in a uniform electric field. a. If the electron is accelerated to 1.0 percent of the speed of light after traveling 2.0 mm, what is the strength of the electric field? ( N / C ) b. What speed does the electron have after traveling 4.0 mm from rest? ( m / s )
6 9. A proton has a kinetic energy of J. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field that will stop this proton in a distance of 1.25 m? ( N / C in the direction opposite to the proton s velocity)
CHAPTER 19 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL. Sections 1-5
 CHAPTER 19 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Sections 1-5 Objectives: After completing this unit, you should be able to: Understand an apply the concepts of electric potential energy,
CHAPTER 19 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Sections 1-5 Objectives: After completing this unit, you should be able to: Understand an apply the concepts of electric potential energy,
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
Section 1 Measuring Electric Fields: Practice Problems
 Section 1 Measuring Electric Fields: Practice Problems 1. A positive test charge of 5.0 10 6 C is in an electric field that exerts a force of 2.0 10 4 N on it. What is the magnitude of the electric field
Section 1 Measuring Electric Fields: Practice Problems 1. A positive test charge of 5.0 10 6 C is in an electric field that exerts a force of 2.0 10 4 N on it. What is the magnitude of the electric field
Physics The Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Fields Figure 1 use considerations of energy to analyze its motion Figure 2
 Physics 12 The Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Fields In Figure 1, the charge q 1 experiences a Coulomb force, to the right in this case, whose magnitude is given by It simply means that if q 1,
Physics 12 The Motion of Charged Particles in Electric Fields In Figure 1, the charge q 1 experiences a Coulomb force, to the right in this case, whose magnitude is given by It simply means that if q 1,
Physics 2010 Work and Energy Recitation Activity 5 (Week 9)
 Physics 2010 Work and Energy Recitation Activity 5 (Week 9) Name Section Tues Wed Thu 8am 10am 12pm 2pm 1. The figure at right shows a hand pushing a block as it moves through a displacement Δ! s. a) Suppose
Physics 2010 Work and Energy Recitation Activity 5 (Week 9) Name Section Tues Wed Thu 8am 10am 12pm 2pm 1. The figure at right shows a hand pushing a block as it moves through a displacement Δ! s. a) Suppose
Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS
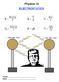 Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS F = kq 1Q 2 r2 E = V d V = kq r E p = kq 1Q 2 r F = qe V = E p Q 1 000 000 Volts 1 000 000 Volts NAME: Block: Text References 3 rd Ed. Giancolli Pg. 416-30 4 th Ed. Giancolli
Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS F = kq 1Q 2 r2 E = V d V = kq r E p = kq 1Q 2 r F = qe V = E p Q 1 000 000 Volts 1 000 000 Volts NAME: Block: Text References 3 rd Ed. Giancolli Pg. 416-30 4 th Ed. Giancolli
Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law
 Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law Matter is made of particles which are or charged. The unit of charge is the ( ) Charges are, meaning that they cannot be It is thought that the total charge
Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law Matter is made of particles which are or charged. The unit of charge is the ( ) Charges are, meaning that they cannot be It is thought that the total charge
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Electric Fields
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 22 Electric Fields Electric field Point charge in an electric field Electric dipole 1. Two identical charges, each of charge Q, are positioned at points A (5.0 m,
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 22 Electric Fields Electric field Point charge in an electric field Electric dipole 1. Two identical charges, each of charge Q, are positioned at points A (5.0 m,
47 CHARGE. 1. What are the basic particles of charge?
 47 CHARGE 1. What are the basic particles of charge? 2. There are three variables for charge listed to the right. Tell the typical circumstances when each is used. 3. Charge What are the units of charge?
47 CHARGE 1. What are the basic particles of charge? 2. There are three variables for charge listed to the right. Tell the typical circumstances when each is used. 3. Charge What are the units of charge?
[1] (b) State one difference and one similarity between the electric field of a point charge and the gravitational field of a point mass....
![[1] (b) State one difference and one similarity between the electric field of a point charge and the gravitational field of a point mass.... [1] (b) State one difference and one similarity between the electric field of a point charge and the gravitational field of a point mass....](/thumbs/76/73399850.jpg) 1 (a) An electric field always exists around a charged particle. Explain what is meant by an electric field.... [1] (b) State one difference and one similarity between the electric field of a point charge
1 (a) An electric field always exists around a charged particle. Explain what is meant by an electric field.... [1] (b) State one difference and one similarity between the electric field of a point charge
Objects can be charged by rubbing
 Electrostatics Objects can be charged by rubbing Charge comes in two types, positive and negative; like charges repel and opposite charges attract Electric charge is conserved the arithmetic sum of the
Electrostatics Objects can be charged by rubbing Charge comes in two types, positive and negative; like charges repel and opposite charges attract Electric charge is conserved the arithmetic sum of the
Supplemental Questions 12U
 Supplemental Questions 12U Gravitational, Electric and Magnetic Fields Questions A satellite of mass 5.00x10² kg is in a circular orbit of radius 2r around Earth. Then it is moved to a circular orbit radius
Supplemental Questions 12U Gravitational, Electric and Magnetic Fields Questions A satellite of mass 5.00x10² kg is in a circular orbit of radius 2r around Earth. Then it is moved to a circular orbit radius
Chapter 20 Electric Potential and Electric potential Energy
 Outline Chapter 20 Electric Potential and Electric potential Energy 20-1 Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential 20-2 Energy Conservation 20-3 The Electric Potential of Point Charges 20-4
Outline Chapter 20 Electric Potential and Electric potential Energy 20-1 Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential 20-2 Energy Conservation 20-3 The Electric Potential of Point Charges 20-4
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 2 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 2 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 11
 1 Two protons are held a distance d apart. The electrostatic force and the gravitational force that one protons exerts on the other are F e and F g, respectively. Which of the following correctly compares
1 Two protons are held a distance d apart. The electrostatic force and the gravitational force that one protons exerts on the other are F e and F g, respectively. Which of the following correctly compares
(a) On the dots below that represent the students, draw and label free-body diagrams showing the forces on Student A and on Student B.
 2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
Electric Potential Energy
 Electric Potential Energy the electric potential energy of two charges depends on the distance between the charges when two like charges are an infinite distance apart, the potential energy is zero An
Electric Potential Energy the electric potential energy of two charges depends on the distance between the charges when two like charges are an infinite distance apart, the potential energy is zero An
P Q 2 = -3.0 x 10-6 C
 1. Which one of the following represents correct units for electric field strength? A. T B. N/C C. J / C D. N m 2 /C 2 2. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. P Q 2Q Which
1. Which one of the following represents correct units for electric field strength? A. T B. N/C C. J / C D. N m 2 /C 2 2. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. P Q 2Q Which
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object.
 1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
1. The diagram below shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object. The area between the line of the graph and the time-axis represents A. the average velocity of the object. B. the displacement
Recap: Electric Field Lines Positive Charge: field lines outwards direction Negative Charge: converge F + In both cases density
 Recap: Electric Field Lines Concept of electric field lines initially used by Michael Faraday (19 th century) to aid visualizing electric (and magnetic) forces and their effects. James Clerk Maxwell (19
Recap: Electric Field Lines Concept of electric field lines initially used by Michael Faraday (19 th century) to aid visualizing electric (and magnetic) forces and their effects. James Clerk Maxwell (19
Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles
 Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles 1. In the arrangement shown below, 2 C of positive charge is moved from plate S, which is at a potential of 250 V, to plate T, which is at a potential of 750 V.
Homework 2: Forces on Charged Particles 1. In the arrangement shown below, 2 C of positive charge is moved from plate S, which is at a potential of 250 V, to plate T, which is at a potential of 750 V.
Chapter Assignment Solutions
 Chapter 20-21 Assignment Solutions Table of Contents Page 558 #22, 24, 29, 31, 36, 37, 40, 43-48... 1 Lightning Worksheet (Transparency 20-4)... 4 Page 584 #42-46, 58-61, 66-69, 76-79, 84-86... 5 Chapter
Chapter 20-21 Assignment Solutions Table of Contents Page 558 #22, 24, 29, 31, 36, 37, 40, 43-48... 1 Lightning Worksheet (Transparency 20-4)... 4 Page 584 #42-46, 58-61, 66-69, 76-79, 84-86... 5 Chapter
Fields. Electric Field Strength Section 13.6
 Fields Electric Field Strength Section 13.6 Outcomes In this lesson you will : define electric field strength and use the definition to express the concept mathematically use Coulomb's Law to write a second
Fields Electric Field Strength Section 13.6 Outcomes In this lesson you will : define electric field strength and use the definition to express the concept mathematically use Coulomb's Law to write a second
Electromagnetism Unit- Electrostatics Sub-Unit
 Electromagnetism Unit Electrostatics SubUnit 4.1.1 Elementary Charge Atomic Structure Review electrons nucleus two types of nucleons charge 0 charge Nucleons are not allowed to move around WITHIN matter
Electromagnetism Unit Electrostatics SubUnit 4.1.1 Elementary Charge Atomic Structure Review electrons nucleus two types of nucleons charge 0 charge Nucleons are not allowed to move around WITHIN matter
Questions Chapter 22 Electric Fields
 Questions Chapter 22 Electric Fields 22-1 What is Physics? 22-2 The Electric Field 22-3 Electric Field Lines 22-4 Electric Field due to a Point Charge 22-5 Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole 22-6
Questions Chapter 22 Electric Fields 22-1 What is Physics? 22-2 The Electric Field 22-3 Electric Field Lines 22-4 Electric Field due to a Point Charge 22-5 Electric Field due to an Electric Dipole 22-6
Potential Energy. Serway 7.6, 7.7;
 Potential Energy Conservative and non-conservative forces Gravitational and elastic potential energy Mechanical Energy Serway 7.6, 7.7; 8.1 8.2 Practice problems: Serway chapter 7, problems 41, 43 chapter
Potential Energy Conservative and non-conservative forces Gravitational and elastic potential energy Mechanical Energy Serway 7.6, 7.7; 8.1 8.2 Practice problems: Serway chapter 7, problems 41, 43 chapter
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy. No Recitation Quiz this week
 Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Today: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy HW #4 due Thursday, 11:59 p.m. pm No Recitation Quiz this week 1 What is Energy? Mechanical Electromagnetic PHY 11 PHY 13 Chemical CHE 105 Nuclear PHY 555
Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020
 Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020 1. You are throwing a ball straight up in the air. At the highest point, the ball s a) velocity and acceleration are zero b) velocity is nonzero, but
Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020 1. You are throwing a ball straight up in the air. At the highest point, the ball s a) velocity and acceleration are zero b) velocity is nonzero, but
PHYSICS LAB Experiment 6 Fall 2004 WORK AND ENERGY GRAVITY
 PHYSICS 183 - LAB Experiment 6 Fall 004 WORK AND ENERGY GRAVITY In this experiment we will study the effects of the work-energy theorem, which states that the change in the kinetic energy (1/Mv ) of an
PHYSICS 183 - LAB Experiment 6 Fall 004 WORK AND ENERGY GRAVITY In this experiment we will study the effects of the work-energy theorem, which states that the change in the kinetic energy (1/Mv ) of an
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. An electron orbits a nucleus which carries a charge of +9.6 x10-19 C. If the electron s orbital radius is 2.0 x10-10 m, what is its electric potential energy? A. -6.9 x10-18
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. An electron orbits a nucleus which carries a charge of +9.6 x10-19 C. If the electron s orbital radius is 2.0 x10-10 m, what is its electric potential energy? A. -6.9 x10-18
Chapter 4. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not
Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not
Department of Natural Sciences Clayton College & State University. Physics 1111 Quiz 5. a. Calculate the work done by each force on the crate.
 Clayton College & State University October, 00 Physics 1111 Quiz 5 Name SOLUTION A crate of 50.0 kg mass containing a new lab instrument is dragged by enthusiastic physics students a distance of 30.0 m
Clayton College & State University October, 00 Physics 1111 Quiz 5 Name SOLUTION A crate of 50.0 kg mass containing a new lab instrument is dragged by enthusiastic physics students a distance of 30.0 m
REVISING MECHANICS (LIVE) 30 JUNE 2015 Exam Questions
 REVISING MECHANICS (LIVE) 30 JUNE 2015 Exam Questions Question 1 (Adapted from DBE November 2014, Question 2) Two blocks of masses 20 kg and 5 kg respectively are connected by a light inextensible string,
REVISING MECHANICS (LIVE) 30 JUNE 2015 Exam Questions Question 1 (Adapted from DBE November 2014, Question 2) Two blocks of masses 20 kg and 5 kg respectively are connected by a light inextensible string,
Conceptual Questions. Fig.8.51 EXERCISES. 8. Why can t electric field lines cross? 9. In which direction do charges always move in an electric field?
 EXERCISES Conceptual Questions 1. Explain why a neutral object can be attracted to a charged object. Why can this neutral object not be repelled by a charged object? 2. What is the function of an electroscope?
EXERCISES Conceptual Questions 1. Explain why a neutral object can be attracted to a charged object. Why can this neutral object not be repelled by a charged object? 2. What is the function of an electroscope?
2. To study circular motion, two students use the hand-held device shown above, which consists of a rod on which a spring scale is attached.
 1. A ball of mass M attached to a string of length L moves in a circle in a vertical plane as shown above. At the top of the circular path, the tension in the string is twice the weight of the ball. At
1. A ball of mass M attached to a string of length L moves in a circle in a vertical plane as shown above. At the top of the circular path, the tension in the string is twice the weight of the ball. At
Electricity Final Unit Final Assessment
 Electricity Final Unit Final Assessment Name k = 1/ (4pe 0 ) = 9.0 10 9 N m 2 C -2 mass of an electron = 9.11 10-31 kg mass of a proton = 1.67 10-27 kg G = 6.67 10-11 N m 2 kg -2 C = 3 x10 8 m/s Show all
Electricity Final Unit Final Assessment Name k = 1/ (4pe 0 ) = 9.0 10 9 N m 2 C -2 mass of an electron = 9.11 10-31 kg mass of a proton = 1.67 10-27 kg G = 6.67 10-11 N m 2 kg -2 C = 3 x10 8 m/s Show all
Handout 3: Electric potential and electric potential energy. Electric potential
 Handout 3: Electric potential and electric potential energy Electric potential Consider a charge + fixed in space as in Figure. Electric potential V at any point in space is defined as the work done by
Handout 3: Electric potential and electric potential energy Electric potential Consider a charge + fixed in space as in Figure. Electric potential V at any point in space is defined as the work done by
21.4 Electric Field and Electric Forces
 21.4 Electric Field and Electric Forces How do charged particles interact in empty space? How do they know the presence of each other? What goes on in the space between them? Body A produces an electric
21.4 Electric Field and Electric Forces How do charged particles interact in empty space? How do they know the presence of each other? What goes on in the space between them? Body A produces an electric
Electric Fields Electric charges exert forces on each other when they are a distance apart. The word Electric field is used to explain this action at
 Electricity & Magnetism Electric Fields Marline Kurishingal Electric Fields Electric charges exert forces on each other when they are a distance apart. The word Electric field is used to explain this action
Electricity & Magnetism Electric Fields Marline Kurishingal Electric Fields Electric charges exert forces on each other when they are a distance apart. The word Electric field is used to explain this action
Electric Field Intensity
 Electric Field Intensity Every charged object creates an electric field of force in the space around it. Any other charged object in that space will experience a force of attraction or repulsion from the
Electric Field Intensity Every charged object creates an electric field of force in the space around it. Any other charged object in that space will experience a force of attraction or repulsion from the
SPH 4U: Unit 3 - Electric and Magnetic Fields
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ SPH 4U: Unit 3 - Electric and Magnetic Fields Modified True/False (1 point each) Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ SPH 4U: Unit 3 - Electric and Magnetic Fields Modified True/False (1 point each) Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
- Work/Energy Theorem Notes Teacher Key -
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: HON. PHYSICS - Work/Energy Theorem Notes Teacher Key - - Mechanical Energy - The MECHANICAL ENERGY that an object has is simply the SUM of potential and kinetic energy forms. Gravitational
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: HON. PHYSICS - Work/Energy Theorem Notes Teacher Key - - Mechanical Energy - The MECHANICAL ENERGY that an object has is simply the SUM of potential and kinetic energy forms. Gravitational
Objects usually are charged up through the transfer of electrons from one object to the other.
 1 Part 1: Electric Force Review of Vectors Review your vectors! You should know how to convert from polar form to component form and vice versa add and subtract vectors multiply vectors by scalars Find
1 Part 1: Electric Force Review of Vectors Review your vectors! You should know how to convert from polar form to component form and vice versa add and subtract vectors multiply vectors by scalars Find
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics. Student name:
 Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
4 r 2. r 2. Solved Problems
 CHAP. 24] COULOMB'S LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELDS 233 AN ELECTRIC FIELD is said to exist at any point in space when a test charge, placed at that point, experiences an electrical force. The direction of the
CHAP. 24] COULOMB'S LAW AND ELECTRIC FIELDS 233 AN ELECTRIC FIELD is said to exist at any point in space when a test charge, placed at that point, experiences an electrical force. The direction of the
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Fiona Website:
 Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
Electrical energy & Capacitance
 Electrical energy & Capacitance PHY232 Remco Zegers zegers@nscl.msu.edu Room W109 cyclotron building http://www.nscl.msu.edu/~zegers/phy232.html work previously A force is conservative if the work done
Electrical energy & Capacitance PHY232 Remco Zegers zegers@nscl.msu.edu Room W109 cyclotron building http://www.nscl.msu.edu/~zegers/phy232.html work previously A force is conservative if the work done
Electricity and Magnetism. Electric Potential Energy and Voltage
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Work and Potential Energy Recall from Mechanics that E mech = K + U is a conserved quantity for particles that interact via conservative
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Work and Potential Energy Recall from Mechanics that E mech = K + U is a conserved quantity for particles that interact via conservative
Electric potential energy The concept of electric potential and potential difference Motion of charges in electric field
 In this chapter, you will learn: Electric potential energy The concept of electric potential and potential difference Motion of charges in electric field 2.1 Electric potential energy When a charged particle
In this chapter, you will learn: Electric potential energy The concept of electric potential and potential difference Motion of charges in electric field 2.1 Electric potential energy When a charged particle
A 12-V battery does 1200 J of work transferring charge. How much charge is transferred? A source of 1.0 µc is meters is from a positive test
 1 A source of 1.0 µc is 0.030 meters is from a positive test charge of 2.0 µc. (a) What is the force on the test charge? (b) What is the potential energy of the test charge? (c) What is the strength of
1 A source of 1.0 µc is 0.030 meters is from a positive test charge of 2.0 µc. (a) What is the force on the test charge? (b) What is the potential energy of the test charge? (c) What is the strength of
Electrostatics Notes 2 Electric Field on a Single Charge
 Electrostatics Notes 2 Electric Field on a Single Charge There are many similarities between gravitational and electrostatic forces. One such similarity is that both forces can be exerted on objects that
Electrostatics Notes 2 Electric Field on a Single Charge There are many similarities between gravitational and electrostatic forces. One such similarity is that both forces can be exerted on objects that
Find the acceleration of the train B Find the distance traveled during this 20 s? C D
 75 A train with a mass of 25000 kg increases its speed from 10 m/s to 25 m/s in 20 seconds. Assume that the acceleration is constant and that you can neglect friction. A Find the acceleration of the train
75 A train with a mass of 25000 kg increases its speed from 10 m/s to 25 m/s in 20 seconds. Assume that the acceleration is constant and that you can neglect friction. A Find the acceleration of the train
Unit 3: Gravitational, Electric and Magnetic Fields Unit Test
 Unit 3: Gravitational, Electric and Magnetic Fields Unit Test Name: Knowledge & Understanding Application Thinking & Inquiry Communication Total 15 18 5 6 44 Part 1: Multiple Choice 1. Two charged spheres
Unit 3: Gravitational, Electric and Magnetic Fields Unit Test Name: Knowledge & Understanding Application Thinking & Inquiry Communication Total 15 18 5 6 44 Part 1: Multiple Choice 1. Two charged spheres
AP Physics 2012 Practice Quiz 4, Conduction & Electric Fields
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A AP Physics 01 Practice Quiz 4, Conduction & Electric Fields Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. ( points) A repelling
Name: Class: Date: ID: A AP Physics 01 Practice Quiz 4, Conduction & Electric Fields Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. ( points) A repelling
2. E A 3. E A 4. E A 5. E A
 west (mrw3223) HW 23 lyle (16001) 1 This print-out should have 32 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Reading assignment: Hecht
west (mrw3223) HW 23 lyle (16001) 1 This print-out should have 32 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Reading assignment: Hecht
Electrical Energy and Capacitance
 6 Electrical Energy and Capacitance QUICK QUIZZES. Choice. The field exerts a force on the electron, causing it to accelerate in the direction opposite to that of the field. In this process, electrical
6 Electrical Energy and Capacitance QUICK QUIZZES. Choice. The field exerts a force on the electron, causing it to accelerate in the direction opposite to that of the field. In this process, electrical
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
Electrostatics Electrostatics
 Electrostatics You will get a charge out of these questions... 1. A combination of four electrons and two protons would have a net charge of... d) 3.2 E 19 Coulombs c) +3.2 E 19 Coulombs b) 2 a) +2 2.
Electrostatics You will get a charge out of these questions... 1. A combination of four electrons and two protons would have a net charge of... d) 3.2 E 19 Coulombs c) +3.2 E 19 Coulombs b) 2 a) +2 2.
= 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ. T.E. initial. = T.E. Final. = P.E. final. + K.E. initial. + P.E. initial. K.E. initial =
 Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Work. Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d
 ENERGY CHAPTER 11 Work Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d Units = Joules Work and energy transferred are equivalent in ideal systems. Two Types of Energy
ENERGY CHAPTER 11 Work Work is the measure of energy transferred. Energy: the capacity to do work. W = F X d Units = Joules Work and energy transferred are equivalent in ideal systems. Two Types of Energy
Motion. Argument: (i) Forces are needed to keep things moving, because they stop when the forces are taken away (evidence horse pulling a carriage).
 1 Motion Aristotle s Study Aristotle s Law of Motion This law of motion was based on false assumptions. He believed that an object moved only if something was pushing it. His arguments were based on everyday
1 Motion Aristotle s Study Aristotle s Law of Motion This law of motion was based on false assumptions. He believed that an object moved only if something was pushing it. His arguments were based on everyday
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I
 PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 6 Last Lecture: Gravity Normal forces Strings, ropes and Pulleys Today: Friction Work and Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Frictional Forces
Solutions Midterm Exam 1 October 3, surface. You push to the left on the right block with a constant force F.
 Problem 1 (2.5 points) Two blocks of mass m 1 and m 3, connected by a rod of mass m 2, are sitting on a frictionless surface. You push to the left on the right block with a constant force F. What is the
Problem 1 (2.5 points) Two blocks of mass m 1 and m 3, connected by a rod of mass m 2, are sitting on a frictionless surface. You push to the left on the right block with a constant force F. What is the
Physics 231 Lecture 9
 Physics 31 Lecture 9 Mi Main points o today s lecture: Potential energy: ΔPE = PE PE = mg ( y ) 0 y 0 Conservation o energy E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Reading Quiz 3. I you raise an object to a greater
Physics 31 Lecture 9 Mi Main points o today s lecture: Potential energy: ΔPE = PE PE = mg ( y ) 0 y 0 Conservation o energy E = KE + PE = KE 0 + PE 0 Reading Quiz 3. I you raise an object to a greater
Physics 111. = Δ p. F net. p f. p i. = F net. m v i. = v i. v f. = m v i. + m a(δt) m v f. m v f. Δt = Δ p. I F net. = m a = m Δ v
 ics Announcements day, ober 07, 004 Ch 9: Momentum Conservation of Momentum Ch 7: Work Kinetic Energy Help this week: Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements p = mv
ics Announcements day, ober 07, 004 Ch 9: Momentum Conservation of Momentum Ch 7: Work Kinetic Energy Help this week: Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements p = mv
Electrostatics Test Review Hons. All work must be shown,including givens, equations used, and units. Draw diagrams as appropriate.
 Electrostatics Test Review Hons. All work must be shown,including givens, equations used, and units. Draw diagrams as appropriate. 1. If a charged rod A attracts another rod B, you can conclude that a.
Electrostatics Test Review Hons. All work must be shown,including givens, equations used, and units. Draw diagrams as appropriate. 1. If a charged rod A attracts another rod B, you can conclude that a.
Chapter 21: Electric Potential Solutions
 Chapter 21: Electric Potential Solutions Questions: 2, 7, 14 Exercises & Problems: 1, 6, 10, 12, 16, 21, 25, 27, 71 Q21.2: Charge q is fired through a small hole in the positive plate of a capacitor. a)
Chapter 21: Electric Potential Solutions Questions: 2, 7, 14 Exercises & Problems: 1, 6, 10, 12, 16, 21, 25, 27, 71 Q21.2: Charge q is fired through a small hole in the positive plate of a capacitor. a)
PHY2020 Practice Problems Fall 2015
 PHY2020 Practice Problems Fall 2015 Some of these practice problems are easy and some are not. Most of them should require between 5 and 15 minutes for you to solve. The more of them that you attempt on
PHY2020 Practice Problems Fall 2015 Some of these practice problems are easy and some are not. Most of them should require between 5 and 15 minutes for you to solve. The more of them that you attempt on
Los Altos Physics Honors. Electrostatics: Electric Fields, Electric Forces, Electric Potentials and. Electric Potential Energy.
 Los Altos Physics Honors Electrostatics: Electric Fields, Electric Forces, Electric Potentials and Electric Potential Energy Workbook adam.randall@mvla.net www.laphysics.com dls.mvla.net/los_altos Spring
Los Altos Physics Honors Electrostatics: Electric Fields, Electric Forces, Electric Potentials and Electric Potential Energy Workbook adam.randall@mvla.net www.laphysics.com dls.mvla.net/los_altos Spring
Coulomb s Law. Phys102 Lecture 2. Key Points. Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References
 Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture 2-1 Coulomb s Law Key Points Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References SFU Ed: 21-5,6,7,8,9,10. 6 th Ed: 16-6,7,8,9,+. Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture
Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture 2-1 Coulomb s Law Key Points Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References SFU Ed: 21-5,6,7,8,9,10. 6 th Ed: 16-6,7,8,9,+. Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture
Physics. Student Materials Advanced Higher. Tutorial Problems Electrical Phenomena HIGHER STILL. Spring 2000
 Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Electrical Phenomena TUTORIAL 1 Coulomb's Inverse Square Law 1 A charge of 2.0 x 10-8 C is placed a distance of 2.0
Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Electrical Phenomena TUTORIAL 1 Coulomb's Inverse Square Law 1 A charge of 2.0 x 10-8 C is placed a distance of 2.0
AP physics B web review ch 15 electric forces and fields
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B web review ch 15 electric forces and fields Please do not write on my tests Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B web review ch 15 electric forces and fields Please do not write on my tests Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
the electrical nature of matter is inherent in its atomic structure E & M atoms are made up of p+, n, and e- the nucleus has p+ and n
 Electric Forces and Fields E & M the electrical nature of matter is inherent in its atomic structure atoms are made up of p+, n, and e- a.k.a Electricity and Magnetism the nucleus has p+ and n surrounding
Electric Forces and Fields E & M the electrical nature of matter is inherent in its atomic structure atoms are made up of p+, n, and e- a.k.a Electricity and Magnetism the nucleus has p+ and n surrounding
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: Q5. Q7.
 Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
Exam 1--PHYS 102--S14
 Class: Date: Exam 1--PHYS 102--S14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The magnitude of the charge on an electron is approximately: a. 10-23
Class: Date: Exam 1--PHYS 102--S14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The magnitude of the charge on an electron is approximately: a. 10-23
Polarization. Polarization is not necessarily a charge imbalance!
 Electrostatics Polarization Polarization is the separation of charge In a conductor, free electrons can move around the surface of the material, leaving one side positive and the other side negative. In
Electrostatics Polarization Polarization is the separation of charge In a conductor, free electrons can move around the surface of the material, leaving one side positive and the other side negative. In
RELEASED. Go to next page. 2. The graph shows the acceleration of a car over time.
 1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
Energy Whiteboard Problems
 Energy Whiteboard Problems 1. (a) Consider an object that is thrown vertically up into the air. Draw a graph of gravitational force vs. height for that object. (b) Based on your experience with the formula
Energy Whiteboard Problems 1. (a) Consider an object that is thrown vertically up into the air. Draw a graph of gravitational force vs. height for that object. (b) Based on your experience with the formula
Electric Fields Practice Multiple Choice
 Choose the best response and place your answers, using HB pencil, on the Scantron sheet provided. 1. The number of excess electrons that must be collected on a sphere to give it a charge of 5.6 x 10 6
Choose the best response and place your answers, using HB pencil, on the Scantron sheet provided. 1. The number of excess electrons that must be collected on a sphere to give it a charge of 5.6 x 10 6
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
1N the force that a 100g bar of chocolate exerts on your hand.
 Forces: - - > cause change in motions Newton's first law = law of inertia In absence of a net external force acting upon it, a body will either remain at rest or continue in its rectilinear uniform motion.
Forces: - - > cause change in motions Newton's first law = law of inertia In absence of a net external force acting upon it, a body will either remain at rest or continue in its rectilinear uniform motion.
PHYSICS 30 ELECTRIC FIELDS ASSIGNMENT 1 55 MARKS
 For each of the following questions complete communication must be shown. Communication consists of an introduction to the physics of the situation, diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well
For each of the following questions complete communication must be shown. Communication consists of an introduction to the physics of the situation, diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well
PHY112 Chapter 16 Problems Electrical Energy and Capacitance
 PHY112 Chapter 16 Problems Electrical Energy and Capacitance 1. A uniform electric field of magnitude 375 N/C pointing in the positive x-direction acts on an electron, which is initially at rest. After
PHY112 Chapter 16 Problems Electrical Energy and Capacitance 1. A uniform electric field of magnitude 375 N/C pointing in the positive x-direction acts on an electron, which is initially at rest. After
Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power
 Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
Potential energy Basic energy Lecture 10 Mechanical Energy Conservation; Power ACT: Zero net work The system of pulleys shown below is used to lift a bag of mass M at constant speed a distance h from the
University of Houston Mathematics Contest: Physics Exam 2017
 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Vectors x, y, and z are unit vectors along x, y, and z, respectively. Let G be the universal gravitational
Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Vectors x, y, and z are unit vectors along x, y, and z, respectively. Let G be the universal gravitational
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
Electrostatics. 4πε 2) + Q / 2 4) 4 Q
 Two spheres A and B of radius a and b respectively are at the same potential The ratio of the surface charge density of A to B is: ) a / b ) b / a a / b b / a Two free protons are separated by a distance
Two spheres A and B of radius a and b respectively are at the same potential The ratio of the surface charge density of A to B is: ) a / b ) b / a a / b b / a Two free protons are separated by a distance
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the 1) A small sphere with a mass of 441 g is moving upward along the vertical +y-axis when it encounters
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the 1) A small sphere with a mass of 441 g is moving upward along the vertical +y-axis when it encounters
Electric Fields, Dipoles and Torque Challenge Problem Solutions
 Electric Fields, Dipoles and Torque Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Three charges equal to Q, +Q and +Q are located a distance a apart along the x axis (see sketch). The point P is located on the
Electric Fields, Dipoles and Torque Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Three charges equal to Q, +Q and +Q are located a distance a apart along the x axis (see sketch). The point P is located on the
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
 Multiple Choice Portion Unit 2: Vector Dynamics 1. Which one of the following best describes the motion of a projectile close to the surface of the Earth? (Assume no friction) Vertical Acceleration Horizontal
Multiple Choice Portion Unit 2: Vector Dynamics 1. Which one of the following best describes the motion of a projectile close to the surface of the Earth? (Assume no friction) Vertical Acceleration Horizontal
E&M: Worksheet 6 Fields, Potential, and Energy
 Name Date Pd () (-) E&M: Worksheet 6 Fields, Potential, and Energy 1. Below are two parallel conducting plates, each carrying an equal quantity of excess charge of opposite type. The plates are separated
Name Date Pd () (-) E&M: Worksheet 6 Fields, Potential, and Energy 1. Below are two parallel conducting plates, each carrying an equal quantity of excess charge of opposite type. The plates are separated
Electrical energy & Capacitance
 Electrical energy & Capacitance PHY232 Remco Zegers zegers@nscl.msu.edu Room W109 cyclotron building http://www.nscl.msu.edu/~zegers/phy232.html work previously A force is conservative if the work done
Electrical energy & Capacitance PHY232 Remco Zegers zegers@nscl.msu.edu Room W109 cyclotron building http://www.nscl.msu.edu/~zegers/phy232.html work previously A force is conservative if the work done
Physical Science (SCI101) Final Exam
 Department of Mathematics and General Sciences Final Exam Second Semester, Term 132 Date: Wednesday 28/5/2014 Name: ID number: Section number or time: Instructor s name: Important instructions: 1. Examination
Department of Mathematics and General Sciences Final Exam Second Semester, Term 132 Date: Wednesday 28/5/2014 Name: ID number: Section number or time: Instructor s name: Important instructions: 1. Examination
Electrostatics Review A. A B. B C. C D. D
 Name: ate: 1. Which sketch best represents the charge distribution around a neutral electroscope when a positively charged strip is brought near, but does not touch, the electroscope? 4. In the diagram
Name: ate: 1. Which sketch best represents the charge distribution around a neutral electroscope when a positively charged strip is brought near, but does not touch, the electroscope? 4. In the diagram
Electrostatics. 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative object: excess of electrons. Particle Mass Electric Charge. m e = 9.
 Electrostatics 1) electric charge: 2 types of electric charge: positive and negative 2) charging by friction: transfer of electrons from one object to another 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative
Electrostatics 1) electric charge: 2 types of electric charge: positive and negative 2) charging by friction: transfer of electrons from one object to another 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative
Question 16.1a Electric Potential Energy I
 Question 16.1a Electric Potential Energy I A proton and an electron are in a constant electric field created by oppositely charged plates. You release the proton from the positive side and the electron
Question 16.1a Electric Potential Energy I A proton and an electron are in a constant electric field created by oppositely charged plates. You release the proton from the positive side and the electron
NAME DATE CLASS. HOLT PHYSICS Graph Skills. Momentum and Impulse
 6-1 Graph Skills Momentum and Impulse 1. A soccer ball with a mass of 0.950 kg is traveling east at 10.0 m/s. Using a ruler and a scale of 1.0 square per 1.0 kg m/s, draw a vector representing the momentum
6-1 Graph Skills Momentum and Impulse 1. A soccer ball with a mass of 0.950 kg is traveling east at 10.0 m/s. Using a ruler and a scale of 1.0 square per 1.0 kg m/s, draw a vector representing the momentum
Version PREVIEW Semester 1 Review Slade (22222) 1
 Version PREVIEW Semester 1 Review Slade () 1 This print-out should have 48 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Holt SF 0Rev 10A
Version PREVIEW Semester 1 Review Slade () 1 This print-out should have 48 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Holt SF 0Rev 10A
