Convexity of level sets for solutions to nonlinear elliptic problems in convex rings. Paola Cuoghi and Paolo Salani
|
|
|
- Amy Richard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Convexity of level sets for solutions to nonlinear elliptic problems in convex rings Paola Cuoghi and Paolo Salani Dip.to di Matematica U. Dini - Firenze - Italy 1
2 Let u be a solution of a Dirichlet problem of elliptic type in a domain Ω: { F (x, u, u, D 2 u) = 0 in Ω u = g on Ω - F is degenerate elliptic, i.e. F (x, t, p, A) F (x, t, p, B), for every A, B Γ such that A B, where A B means that B A is positive semidefinite. - F is proper, i.e. F (x, t, p, A) F (x, s, p, A) if s t. A quite natural question is the following: is there any relationship between the geometry of the domain Ω and the geometry of the solution u? Is it possible to find assumptions on the elliptic operator F which ensure that some geometric property of the domain is inherited, in some sense, by the solution? For instance, if the domain Ω is convex and the Dirichlet data is a constant, we may ask whether the function u must be convex too. 2
3 Precisely, the problem we are here involved with is the following: Ω is a convex ring, i.e. Ω = Ω 0 \ Ω 1 where Ω 0 and Ω 1 are convex, bounded and open subsets of R n such that Ω 1 Ω 0. u is a solution of the following Dirichlet problem F (x, u, u, D 2 u) = 0 in Ω u = 0 on Ω 0 u = 1 on Ω 1. (1) Hence, two level sets of the solution, are convex surfaces: namely, {u = 0} = Ω 0 and {u = 1} = Ω 1. MAIN QUESTION: Is it possible to find suitable assumptions on F which ensure that all the level sets of u are convex? 3
4 This problem and related questions have been faced by many authors; we recall, for instance, the classic work of Gabriel (1957) and more recent important contributions by Acker, Caffarelli, Korevaar, Lewis, Spruck, as well as many papers and a well-known monograph by Kawohl. The method here adopted is a generalization of the method introduced in [CS] - A. Colesanti & P. S. Quasi-concave Envelope of a Function and Convexity of Level Sets of Solutions to Elliptic Equations Math. Nach. 258 (2003), It makes use of the quasi-concave envelope u of a function u. Roughly speaking, u is the function whose superlevel sets are the convex hulls of the corresponding superlevel sets of u (we sistematically extend u 1 in Ω 1 ), i.e. {u t} = conv({u t}. 4
5 Ω t = { u t } Ω t = { u t } Ω1= { u 1} Ω 0 = { u 0} More explicitely, we can define u in the following way: { u (x) = max min {u(x 1 ),..., u(x n+1 )} : x 1,..., x n+1 Ω, x = n+1 i=1 λ ix i, λ 1 0,..., λ n+1 0, } n+1 i=1 λ i = 1. 5
6 We look for conditions that imply u = u. Notice that u u by definition (to obtain u we enlarge the superlevel sets of u), then it suffices to prove the reverse inequality; the latter can be obtained by a suitable Comparison Principle, if u is a viscosity subsolution of problem (1). In this way we reduce ourselves to the following question: Can we find suitable assumptions on F that force u to be a viscosity subsolution of (1)? A positive answer was given in [CS], but only for operators whose principal can be decomposed in a normal and a tangential part (normal and tangential with respect to level sets of the solution, we mean). 6
7 Basically, the operators which share such a structure are: - the laplacian u = f(x, u, u ); - the p-laplacian p u = div( u p 2 u) = f(x, u, u ); - the mean curvature operator Mu = n(1 + u 2 ) 3/2 H = f(x, u, u ). There, we proved that under suitable concavity assumption on f, the solutions to Dirichlet problems in convex rings for these equations have convex level sets. Now we are able to treat much more general operator! In particular, we are able to treat the Hessian operators, defined, for k = 1,..., n, as the k-th elementary symmetric function of the eigenvalues of the Hessian matrix of u, i.e. for k = 1,..., n S k (D 2 u) = S k (λ 1,..., λ n ) = λ i1 λ ik 1 i 1 < <i k n where λ 1,..., λ n are the eigenvalues of D 2 u. 7
8 MAIN THEOREM. Let Ω = Ω 0 \Ω 1 be a convex ring and let F (x, u, θ, A) be a proper, continuous and degenerate elliptic operator in Ω (0, 1) R n Γ F. Assume that there exists p < 0 such that, for every p p and for every θ R n, the application ( ) (x, t, A) F x, tp, 1 tp 1 1 θ, tp 1 3 A (2) is concave in Ω (1, + ) Γ F. If u C 2 (Ω) C(Ω) is an admissible classical solution of (1) such that u > 0 in Ω, then u is a viscosity subsolution of (1). Remarks 1. The above theorem holds also for viscosity solutions. 2. The assumption u > 0 is typical for this kind of investigation; in fact, we can relax it a little bit, but not in an essential way. To prove geometric properties of solutions to elliptic problems without this assumption it is a difficult task. In fact, this assumption is often automatically satisfied by classical solutions, thanks to some maximum principle applied to u. 3. Admissible solution means that D 2 u(x) Γ F for every x Ω, i.e. u is an elliptic solution. 8
9 To prove the main theorem, we need some preliminaries. First of all we recall the notion of p-means of m nonnegative real numbers. Given a = (a 1,..., a m ) > 0, λ Λ m and p [, + ], the quantity [λ 1 a p λ ma p m] 1/p for p, 0, + M p (a, λ) = max{a 1,..., a m } p = + a λ 1 1 aλ m m p = 0 min{a 1, a 2,..., a m } p = is the p-(weighted) mean of a. For a 0, we define M p (a, λ) as above if p 0 and we set M p (a, λ) = 0 if p < 0 and a i = 0, for some i = 1,..., m. Let us fix λ Λ n+1 and consider p [, + ]. Definition 0.1 The (p, λ) envelope of u is the function u p,λ : Ω [0, 1] defined as follows { u p,λ (x) = sup M p (u(x 1 ),..., u(x n+1 ), λ) : x i Ω, x = n+1 i=1 λ (3) ix i }. Notice that, as Ω is compact and M p is continuous, the supremum of the definition is in fact a maximum. 9
10 Hence, for every x Ω, there exist (x 1,p,..., x n+1,p ) Ω n+1 such that x = n+1 i=1 λ i x i,p, u p,λ (x) = M p (u(x 1 ),..., u(x n+1 ), λ). An immediate consequence of the definition is that u p,λ (x) u(x), x Ω, p [,, + ]; moreover, from the monotonicity of means, we have u p,λ (x) u q,λ (x), for p q, x Ω. For convenience, we will refer to u,λ as u λ. Notice that u (x) = sup {u λ(x) : λ Λ n+1 } (4) and the above supremum is in fact a maximum as Λ n+1 is compact. Theorem. u p,λ converge uniformly to u λ as p. 10
11 Sketch of the proof of the main thm. i. We fix λ Λ n+1 and we prove that, for every compact subset K of Ω, u p,λ is a viscosity subsolution, for p large enough (depending on K). ii. Then passing to the limit for p, thanks to uniform convergence, we obtain that u λ is a subsolution. iii. Thanks to (4) and since the supremum of subsolutions is a subsolution, the proof is concluded. How do we prove the first item? By definition, u p,λ is a viscosity subsolution of F = 0 if, for every C 2 function φ touching u p,λ from above at any point x Ω, it holds F (x, φ(x), φ(x), D 2 φ(x)) 0. If u is an admissible classical solution, this task is somewhat simplified, since u can be used as a test function. 11
12 Indeed, for every point x Ω, we can use u to construct a C 2 function ϕ p,λ that touches u p,λ from below at x. This function is defined as follows: [ n+1 ] 1/p ϕ p,λ (x) = λ i u (x i,p + a i,p (x x)) p, (5) where i=1 a i,p = u(x i,p) p u p,λ (x) p, for i = 1,..., n + 1, (6) and the points x i,p are the ones which realize the maximum in the definition of u p,λ (x). If all the points x 1,p,..., x n+1,p belong to Ω, we can write the gradient and the Hessian matrix of φ p,λ at the point x as a convex combination of the gradients and the Hessian matrices of u at these points and our concavity assumption on F makes the rest. But we cannot be sure, in general, that any one of these points belongs to Ω; notice that, if for some p we could be able to prove this, we would obtain that u coincide with its p-concave envelope and finally it is p-concave, which is of course much more than quasi-concave. On the other hand, it is easily seen that this actually happens for p =, hence restricting to any compact subset of Ω, we can prove that it must also happen for p enough large and this conclude the proof. 12
Brunn-Minkowski inequality for the 1-Riesz capacity and level set convexity for the 1/2-Laplacian
 Brunn-Minkowski inequality for the 1-Riesz capacity and level set convexity for the 1/2-Laplacian M. Novaga, B. Ruffini January 13, 2014 Abstract We prove that that the 1-Riesz capacity satisfies a Brunn-Minkowski
Brunn-Minkowski inequality for the 1-Riesz capacity and level set convexity for the 1/2-Laplacian M. Novaga, B. Ruffini January 13, 2014 Abstract We prove that that the 1-Riesz capacity satisfies a Brunn-Minkowski
Asymptotic behavior of infinity harmonic functions near an isolated singularity
 Asymptotic behavior of infinity harmonic functions near an isolated singularity Ovidiu Savin, Changyou Wang, Yifeng Yu Abstract In this paper, we prove if n 2 x 0 is an isolated singularity of a nonegative
Asymptotic behavior of infinity harmonic functions near an isolated singularity Ovidiu Savin, Changyou Wang, Yifeng Yu Abstract In this paper, we prove if n 2 x 0 is an isolated singularity of a nonegative
Brunn-Minkowski inequalities for two functionals involving the p-laplace operator
 Brunn-Minkowski inequalities for two functionals involving the p-laplace operator Andrea Colesanti Paola Cuoghi Paolo Salani Abstract In the family of n-dimensional convex bodies, we prove a Brunn-Minkowski
Brunn-Minkowski inequalities for two functionals involving the p-laplace operator Andrea Colesanti Paola Cuoghi Paolo Salani Abstract In the family of n-dimensional convex bodies, we prove a Brunn-Minkowski
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
 VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LUIS SILVESTRE These are the notes from the summer course given in the Second Chicago Summer School In Analysis, in June 2015. We introduce the notion of viscosity
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS LUIS SILVESTRE These are the notes from the summer course given in the Second Chicago Summer School In Analysis, in June 2015. We introduce the notion of viscosity
Brunn-Minkowski inequality for the 1-Riesz capacity and level set convexity for the 1/2-Laplacian
 Brunn-Minkowski inequality for the 1-Riesz capacity and level set convexity for the 1/2-Laplacian M. Novaga, B. Ruffini Abstract We prove that that the 1-Riesz capacity satisfies a Brunn-Minkowski inequality,
Brunn-Minkowski inequality for the 1-Riesz capacity and level set convexity for the 1/2-Laplacian M. Novaga, B. Ruffini Abstract We prove that that the 1-Riesz capacity satisfies a Brunn-Minkowski inequality,
Convex Functions and Optimization
 Chapter 5 Convex Functions and Optimization 5.1 Convex Functions Our next topic is that of convex functions. Again, we will concentrate on the context of a map f : R n R although the situation can be generalized
Chapter 5 Convex Functions and Optimization 5.1 Convex Functions Our next topic is that of convex functions. Again, we will concentrate on the context of a map f : R n R although the situation can be generalized
Numerical Solutions of Geometric Partial Differential Equations. Adam Oberman McGill University
 Numerical Solutions of Geometric Partial Differential Equations Adam Oberman McGill University Sample Equations and Schemes Fully Nonlinear Pucci Equation! "#+ "#* "#) "#( "#$ "#' "#& "#% "#! "!!!"#$ "
Numerical Solutions of Geometric Partial Differential Equations Adam Oberman McGill University Sample Equations and Schemes Fully Nonlinear Pucci Equation! "#+ "#* "#) "#( "#$ "#' "#& "#% "#! "!!!"#$ "
Asymptotic Behavior of Infinity Harmonic Functions Near an Isolated Singularity
 Savin, O., and C. Wang. (2008) Asymptotic Behavior of Infinity Harmonic Functions, International Mathematics Research Notices, Vol. 2008, Article ID rnm163, 23 pages. doi:10.1093/imrn/rnm163 Asymptotic
Savin, O., and C. Wang. (2008) Asymptotic Behavior of Infinity Harmonic Functions, International Mathematics Research Notices, Vol. 2008, Article ID rnm163, 23 pages. doi:10.1093/imrn/rnm163 Asymptotic
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS. We follow Han and Lin, Elliptic Partial Differential Equations, 5.
 VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS PETER HINTZ We follow Han and Lin, Elliptic Partial Differential Equations, 5. 1. Motivation Throughout, we will assume that Ω R n is a bounded and connected domain and that a ij C(Ω)
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS PETER HINTZ We follow Han and Lin, Elliptic Partial Differential Equations, 5. 1. Motivation Throughout, we will assume that Ω R n is a bounded and connected domain and that a ij C(Ω)
On a Fractional Monge Ampère Operator
 Ann. PDE (015) 1:4 DOI 10.1007/s40818-015-0005-x On a Fractional Monge Ampère Operator Luis Caffarelli 1 Fernando Charro Received: 16 November 015 / Accepted: 19 November 015 / Published online: 18 December
Ann. PDE (015) 1:4 DOI 10.1007/s40818-015-0005-x On a Fractional Monge Ampère Operator Luis Caffarelli 1 Fernando Charro Received: 16 November 015 / Accepted: 19 November 015 / Published online: 18 December
SYMMETRY OF POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF SOME NONLINEAR EQUATIONS. M. Grossi S. Kesavan F. Pacella M. Ramaswamy. 1. Introduction
 Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 12, 1998, 47 59 SYMMETRY OF POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF SOME NONLINEAR EQUATIONS M. Grossi S. Kesavan F. Pacella M. Ramaswamy
Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 12, 1998, 47 59 SYMMETRY OF POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF SOME NONLINEAR EQUATIONS M. Grossi S. Kesavan F. Pacella M. Ramaswamy
Gradient Estimate of Mean Curvature Equations and Hessian Equations with Neumann Boundary Condition
 of Mean Curvature Equations and Hessian Equations with Neumann Boundary Condition Xinan Ma NUS, Dec. 11, 2014 Four Kinds of Equations Laplace s equation: u = f(x); mean curvature equation: div( Du ) =
of Mean Curvature Equations and Hessian Equations with Neumann Boundary Condition Xinan Ma NUS, Dec. 11, 2014 Four Kinds of Equations Laplace s equation: u = f(x); mean curvature equation: div( Du ) =
Example 1. Hamilton-Jacobi equation. In particular, the eikonal equation. for some n( x) > 0 in Ω. Here 1 / 2
 Oct. 1 0 Viscosity S olutions In this lecture we take a glimpse of the viscosity solution theory for linear and nonlinear PDEs. From our experience we know that even for linear equations, the existence
Oct. 1 0 Viscosity S olutions In this lecture we take a glimpse of the viscosity solution theory for linear and nonlinear PDEs. From our experience we know that even for linear equations, the existence
COINCIDENCE SETS IN THE OBSTACLE PROBLEM FOR THE p-harmonic OPERATOR
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 95, Number 3, November 1985 COINCIDENCE SETS IN THE OBSTACLE PROBLEM FOR THE p-harmonic OPERATOR SHIGERU SAKAGUCHI Abstract. We consider the obstacle
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 95, Number 3, November 1985 COINCIDENCE SETS IN THE OBSTACLE PROBLEM FOR THE p-harmonic OPERATOR SHIGERU SAKAGUCHI Abstract. We consider the obstacle
Asymptotic behavior of the degenerate p Laplacian equation on bounded domains
 Asymptotic behavior of the degenerate p Laplacian equation on bounded domains Diana Stan Instituto de Ciencias Matematicas (CSIC), Madrid, Spain UAM, September 19, 2011 Diana Stan (ICMAT & UAM) Nonlinear
Asymptotic behavior of the degenerate p Laplacian equation on bounded domains Diana Stan Instituto de Ciencias Matematicas (CSIC), Madrid, Spain UAM, September 19, 2011 Diana Stan (ICMAT & UAM) Nonlinear
The general programming problem is the nonlinear programming problem where a given function is maximized subject to a set of inequality constraints.
 1 Optimization Mathematical programming refers to the basic mathematical problem of finding a maximum to a function, f, subject to some constraints. 1 In other words, the objective is to find a point,
1 Optimization Mathematical programming refers to the basic mathematical problem of finding a maximum to a function, f, subject to some constraints. 1 In other words, the objective is to find a point,
A LOCALIZATION PROPERTY AT THE BOUNDARY FOR MONGE-AMPERE EQUATION
 A LOCALIZATION PROPERTY AT THE BOUNDARY FOR MONGE-AMPERE EQUATION O. SAVIN. Introduction In this paper we study the geometry of the sections for solutions to the Monge- Ampere equation det D 2 u = f, u
A LOCALIZATION PROPERTY AT THE BOUNDARY FOR MONGE-AMPERE EQUATION O. SAVIN. Introduction In this paper we study the geometry of the sections for solutions to the Monge- Ampere equation det D 2 u = f, u
Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications The Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia. 1. Introduction
 ON LOCALLY CONVEX HYPERSURFACES WITH BOUNDARY Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia Wang Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications The Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia Abstract. In this
ON LOCALLY CONVEX HYPERSURFACES WITH BOUNDARY Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia Wang Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications The Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia Abstract. In this
On Generalized and Viscosity Solutions of Nonlinear Elliptic Equations
 Advanced Nonlinear Studies 4 (2004), 289 306 On Generalized and Viscosity Solutions of Nonlinear Elliptic Equations David Hartenstine, Klaus Schmitt Department of Mathematics, University of Utah, 155 South
Advanced Nonlinear Studies 4 (2004), 289 306 On Generalized and Viscosity Solutions of Nonlinear Elliptic Equations David Hartenstine, Klaus Schmitt Department of Mathematics, University of Utah, 155 South
On John type ellipsoids
 On John type ellipsoids B. Klartag Tel Aviv University Abstract Given an arbitrary convex symmetric body K R n, we construct a natural and non-trivial continuous map u K which associates ellipsoids to
On John type ellipsoids B. Klartag Tel Aviv University Abstract Given an arbitrary convex symmetric body K R n, we construct a natural and non-trivial continuous map u K which associates ellipsoids to
Local strong convexity and local Lipschitz continuity of the gradient of convex functions
 Local strong convexity and local Lipschitz continuity of the gradient of convex functions R. Goebel and R.T. Rockafellar May 23, 2007 Abstract. Given a pair of convex conjugate functions f and f, we investigate
Local strong convexity and local Lipschitz continuity of the gradient of convex functions R. Goebel and R.T. Rockafellar May 23, 2007 Abstract. Given a pair of convex conjugate functions f and f, we investigate
Eigenfunctions for versions of the p-laplacian
 Eigenfunctions for versions of the p-laplacian Bernd Kawohl Universität zu Köln www.mi.uni-koeln.de/ kawohl *Joint work with C. Nitsch, L.Esposito, C.Trombetti and others B. Kawohl (Universität zu Köln)
Eigenfunctions for versions of the p-laplacian Bernd Kawohl Universität zu Köln www.mi.uni-koeln.de/ kawohl *Joint work with C. Nitsch, L.Esposito, C.Trombetti and others B. Kawohl (Universität zu Köln)
TOPICS IN NONLINEAR ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS. Dipartimento di Matematica e Applicazioni Università di Milano Bicocca March 15-16, 2017
 TOPICS IN NONLINEAR ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS Dipartimento di Matematica e Applicazioni Università di Milano Bicocca March 15-16, 2017 Abstracts of the talks Spectral stability under removal of small capacity
TOPICS IN NONLINEAR ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS Dipartimento di Matematica e Applicazioni Università di Milano Bicocca March 15-16, 2017 Abstracts of the talks Spectral stability under removal of small capacity
MEAN VALUE PROPERTY FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 40, Number 7, July 0, Pages 453 463 S 000-9939(0)8-X Article electronically published on November, 0 MEAN VALUE PROPERTY FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 40, Number 7, July 0, Pages 453 463 S 000-9939(0)8-X Article electronically published on November, 0 MEAN VALUE PROPERTY FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS
REGULARITY RESULTS FOR THE EQUATION u 11 u 22 = Introduction
 REGULARITY RESULTS FOR THE EQUATION u 11 u 22 = 1 CONNOR MOONEY AND OVIDIU SAVIN Abstract. We study the equation u 11 u 22 = 1 in R 2. Our results include an interior C 2 estimate, classical solvability
REGULARITY RESULTS FOR THE EQUATION u 11 u 22 = 1 CONNOR MOONEY AND OVIDIU SAVIN Abstract. We study the equation u 11 u 22 = 1 in R 2. Our results include an interior C 2 estimate, classical solvability
A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF A MONOTONE SCHEME FOR THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION 1. INTRODUCTION
 A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF A MONOTONE SCHEME FOR THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION GERARD AWANOU AND LEOPOLD MATAMBA MESSI ABSTRACT. We give a proof of existence of a solution to the discrete problem
A VARIATIONAL METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF A MONOTONE SCHEME FOR THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION GERARD AWANOU AND LEOPOLD MATAMBA MESSI ABSTRACT. We give a proof of existence of a solution to the discrete problem
Class Meeting # 1: Introduction to PDEs
 MATH 18.152 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 1 18.152 Introduction to PDEs, Spring 2017 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 1: Introduction to PDEs 1. What is a PDE? We will be studying functions u =
MATH 18.152 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 1 18.152 Introduction to PDEs, Spring 2017 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 1: Introduction to PDEs 1. What is a PDE? We will be studying functions u =
SHARP BOUNDARY TRACE INEQUALITIES. 1. Introduction
 SHARP BOUNDARY TRACE INEQUALITIES GILES AUCHMUTY Abstract. This paper describes sharp inequalities for the trace of Sobolev functions on the boundary of a bounded region R N. The inequalities bound (semi-)norms
SHARP BOUNDARY TRACE INEQUALITIES GILES AUCHMUTY Abstract. This paper describes sharp inequalities for the trace of Sobolev functions on the boundary of a bounded region R N. The inequalities bound (semi-)norms
Hausdorff Continuous Viscosity Solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi Equations
 Hausdorff Continuous Viscosity Solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi Equations R Anguelov 1,2, S Markov 2,, F Minani 3 1 Department of Mathematics and Applied Mathematics, University of Pretoria 2 Institute of
Hausdorff Continuous Viscosity Solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi Equations R Anguelov 1,2, S Markov 2,, F Minani 3 1 Department of Mathematics and Applied Mathematics, University of Pretoria 2 Institute of
Obstacle Problems Involving The Fractional Laplacian
 Obstacle Problems Involving The Fractional Laplacian Donatella Danielli and Sandro Salsa January 27, 2017 1 Introduction Obstacle problems involving a fractional power of the Laplace operator appear in
Obstacle Problems Involving The Fractional Laplacian Donatella Danielli and Sandro Salsa January 27, 2017 1 Introduction Obstacle problems involving a fractional power of the Laplace operator appear in
Dedicated to Professor Linda Rothchild on the occasion of her 60th birthday
 REARKS ON THE HOOGENEOUS COPLEX ONGE-APÈRE EQUATION PENGFEI GUAN Dedicated to Professor Linda Rothchild on the occasion of her 60th birthday This short note concerns the homogeneous complex onge-ampère
REARKS ON THE HOOGENEOUS COPLEX ONGE-APÈRE EQUATION PENGFEI GUAN Dedicated to Professor Linda Rothchild on the occasion of her 60th birthday This short note concerns the homogeneous complex onge-ampère
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 18 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 18 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 18 Jan 2019](/thumbs/88/115225534.jpg) manuscripta mathematica manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Yongpan Huang Dongsheng Li Kai Zhang Pointwise Boundary Differentiability of Solutions of Elliptic Equations Received: date / Revised
manuscripta mathematica manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Yongpan Huang Dongsheng Li Kai Zhang Pointwise Boundary Differentiability of Solutions of Elliptic Equations Received: date / Revised
1 Convexity, concavity and quasi-concavity. (SB )
 UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ECON 600 Summer 2010 Lecture Two: Unconstrained Optimization 1 Convexity, concavity and quasi-concavity. (SB 21.1-21.3.) For any two points, x, y R n, we can trace out the line of
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND ECON 600 Summer 2010 Lecture Two: Unconstrained Optimization 1 Convexity, concavity and quasi-concavity. (SB 21.1-21.3.) For any two points, x, y R n, we can trace out the line of
A Brunn Minkowski inequality for the Hessian eigenvalue in three-dimensional convex domain
 Advances in Mathematics 5 010 1616 1633 www.elsevier.com/locate/aim A Brunn Minkowski inequality for the Hessian eigenvalue in three-dimensional convex domain Pan Liu a, Xi-Nan Ma b,,luxu c a Department
Advances in Mathematics 5 010 1616 1633 www.elsevier.com/locate/aim A Brunn Minkowski inequality for the Hessian eigenvalue in three-dimensional convex domain Pan Liu a, Xi-Nan Ma b,,luxu c a Department
Degenerate Monge-Ampère equations and the smoothness of the eigenfunction
 Degenerate Monge-Ampère equations and the smoothness of the eigenfunction Ovidiu Savin Columbia University November 2nd, 2015 Ovidiu Savin (Columbia University) Degenerate Monge-Ampère equations November
Degenerate Monge-Ampère equations and the smoothness of the eigenfunction Ovidiu Savin Columbia University November 2nd, 2015 Ovidiu Savin (Columbia University) Degenerate Monge-Ampère equations November
HESSIAN MEASURES III. Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia
 HESSIAN MEASURES III Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia Wang Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia 1 HESSIAN MEASURES III Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia
HESSIAN MEASURES III Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia Wang Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia 1 HESSIAN MEASURES III Neil S. Trudinger Xu-Jia
On a weighted total variation minimization problem
 On a weighted total variation minimization problem Guillaume Carlier CEREMADE Université Paris Dauphine carlier@ceremade.dauphine.fr Myriam Comte Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions, Université Pierre et Marie
On a weighted total variation minimization problem Guillaume Carlier CEREMADE Université Paris Dauphine carlier@ceremade.dauphine.fr Myriam Comte Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions, Université Pierre et Marie
Written Examination
 Division of Scientific Computing Department of Information Technology Uppsala University Optimization Written Examination 202-2-20 Time: 4:00-9:00 Allowed Tools: Pocket Calculator, one A4 paper with notes
Division of Scientific Computing Department of Information Technology Uppsala University Optimization Written Examination 202-2-20 Time: 4:00-9:00 Allowed Tools: Pocket Calculator, one A4 paper with notes
COMPARISON PRINCIPLES FOR CONSTRAINED SUBHARMONICS PH.D. COURSE - SPRING 2019 UNIVERSITÀ DI MILANO
 COMPARISON PRINCIPLES FOR CONSTRAINED SUBHARMONICS PH.D. COURSE - SPRING 2019 UNIVERSITÀ DI MILANO KEVIN R. PAYNE 1. Introduction Constant coefficient differential inequalities and inclusions, constraint
COMPARISON PRINCIPLES FOR CONSTRAINED SUBHARMONICS PH.D. COURSE - SPRING 2019 UNIVERSITÀ DI MILANO KEVIN R. PAYNE 1. Introduction Constant coefficient differential inequalities and inclusions, constraint
AN INTRODUCTION TO VISCOSITY SOLUTION THEORY. In this note, we study the general second-order fully nonlinear equations arising in various fields:
 AN INTRODUCTION TO VISCOSITY SOLUTION THEORY QING LIU AND XIAODAN ZHOU 1. Introduction to Fully Nonlinear Equations In this note, we study the general second-order fully nonlinear equations arising in
AN INTRODUCTION TO VISCOSITY SOLUTION THEORY QING LIU AND XIAODAN ZHOU 1. Introduction to Fully Nonlinear Equations In this note, we study the general second-order fully nonlinear equations arising in
Integro-differential equations: Regularity theory and Pohozaev identities
 Integro-differential equations: Regularity theory and Pohozaev identities Xavier Ros Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya PhD Thesis Advisor: Xavier Cabré Xavier
Integro-differential equations: Regularity theory and Pohozaev identities Xavier Ros Oton Departament Matemàtica Aplicada I, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya PhD Thesis Advisor: Xavier Cabré Xavier
PROD. TYPE: COM ARTICLE IN PRESS. Andrea Colesanti. Received 4 August 2003; accepted 8 June 2004 Communicated by Michael Hopkins
 YAIMA28.0. pp: - (col.fig.: nil) PROD. TYPE: COM ED: Suraina PAGN: Vidya -- SCAN: Girish Advances in Mathematics ( ) www.elsevier.com/locate/aim 2 2 Brunn Minkowski inequalities for variational functionals
YAIMA28.0. pp: - (col.fig.: nil) PROD. TYPE: COM ED: Suraina PAGN: Vidya -- SCAN: Girish Advances in Mathematics ( ) www.elsevier.com/locate/aim 2 2 Brunn Minkowski inequalities for variational functionals
GERARD AWANOU. i 1< <i k
 ITERATIVE METHODS FOR k-hessian EQUATIONS GERARD AWANOU Abstract. On a domain of the n-dimensional Euclidean space, and for an integer k = 1,..., n, the k-hessian equations are fully nonlinear elliptic
ITERATIVE METHODS FOR k-hessian EQUATIONS GERARD AWANOU Abstract. On a domain of the n-dimensional Euclidean space, and for an integer k = 1,..., n, the k-hessian equations are fully nonlinear elliptic
On the second differentiability of convex surfaces
 On the second differentiability of convex surfaces Gabriele Bianchi, Andrea Colesanti, Carlo Pucci Abstract Properties of pointwise second differentiability of real valued convex functions in IR n are
On the second differentiability of convex surfaces Gabriele Bianchi, Andrea Colesanti, Carlo Pucci Abstract Properties of pointwise second differentiability of real valued convex functions in IR n are
Applications of the periodic unfolding method to multi-scale problems
 Applications of the periodic unfolding method to multi-scale problems Doina Cioranescu Université Paris VI Santiago de Compostela December 14, 2009 Periodic unfolding method and multi-scale problems 1/56
Applications of the periodic unfolding method to multi-scale problems Doina Cioranescu Université Paris VI Santiago de Compostela December 14, 2009 Periodic unfolding method and multi-scale problems 1/56
EQUAZIONI A DERIVATE PARZIALI. STEKLOV EIGENVALUES FOR THE -LAPLACIAN
 EQUAZIONI A DERIVATE PARZIALI. STEKLOV EIGENVALUES FOR THE -LAPLACIAN J. GARCIA-AZORERO, J. J. MANFREDI, I. PERAL AND J. D. ROSSI Abstract. We study the Steklov eigenvalue problem for the - laplacian.
EQUAZIONI A DERIVATE PARZIALI. STEKLOV EIGENVALUES FOR THE -LAPLACIAN J. GARCIA-AZORERO, J. J. MANFREDI, I. PERAL AND J. D. ROSSI Abstract. We study the Steklov eigenvalue problem for the - laplacian.
Fast convergent finite difference solvers for the elliptic Monge-Ampère equation
 Fast convergent finite difference solvers for the elliptic Monge-Ampère equation Adam Oberman Simon Fraser University BIRS February 17, 211 Joint work [O.] 28. Convergent scheme in two dim. Explicit solver.
Fast convergent finite difference solvers for the elliptic Monge-Ampère equation Adam Oberman Simon Fraser University BIRS February 17, 211 Joint work [O.] 28. Convergent scheme in two dim. Explicit solver.
Lecture No 2 Degenerate Diffusion Free boundary problems
 Lecture No 2 Degenerate Diffusion Free boundary problems Columbia University IAS summer program June, 2009 Outline We will discuss non-linear parabolic equations of slow diffusion. Our model is the porous
Lecture No 2 Degenerate Diffusion Free boundary problems Columbia University IAS summer program June, 2009 Outline We will discuss non-linear parabolic equations of slow diffusion. Our model is the porous
Convex analysis and profit/cost/support functions
 Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Convex analysis and profit/cost/support functions KC Border October 2004 Revised January 2009 Let A be a subset of R m Convex analysts may give one of two
Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences Convex analysis and profit/cost/support functions KC Border October 2004 Revised January 2009 Let A be a subset of R m Convex analysts may give one of two
On the spectrum of the Hodge Laplacian and the John ellipsoid
 Banff, July 203 On the spectrum of the Hodge Laplacian and the John ellipsoid Alessandro Savo, Sapienza Università di Roma We give upper and lower bounds for the first eigenvalue of the Hodge Laplacian
Banff, July 203 On the spectrum of the Hodge Laplacian and the John ellipsoid Alessandro Savo, Sapienza Università di Roma We give upper and lower bounds for the first eigenvalue of the Hodge Laplacian
1. Introduction Boundary estimates for the second derivatives of the solution to the Dirichlet problem for the Monge-Ampere equation
 POINTWISE C 2,α ESTIMATES AT THE BOUNDARY FOR THE MONGE-AMPERE EQUATION O. SAVIN Abstract. We prove a localization property of boundary sections for solutions to the Monge-Ampere equation. As a consequence
POINTWISE C 2,α ESTIMATES AT THE BOUNDARY FOR THE MONGE-AMPERE EQUATION O. SAVIN Abstract. We prove a localization property of boundary sections for solutions to the Monge-Ampere equation. As a consequence
Convex Optimization. Convex Analysis - Functions
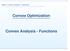 Convex Optimization Convex Analsis - Functions p. 1 A function f : K R n R is convex, if K is a convex set and x, K,x, λ (,1) we have f(λx+(1 λ)) λf(x)+(1 λ)f(). (x, f(x)) (,f()) x - strictl convex,
Convex Optimization Convex Analsis - Functions p. 1 A function f : K R n R is convex, if K is a convex set and x, K,x, λ (,1) we have f(λx+(1 λ)) λf(x)+(1 λ)f(). (x, f(x)) (,f()) x - strictl convex,
Appeared in Commun. Contemp. Math. 11 (1) (2009) ZERO ORDER PERTURBATIONS TO FULLY NONLINEAR EQUATIONS: COMPARISON, EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS
 Appeared in Commun. Contemp. Math. 11 1 2009 1 34. ZERO ORDER PERTURBATIONS TO FULLY NONLINEAR EQUATIONS: COMPARISON, EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS FERNANDO CHARRO AND IRENEO PERAL Abstract. We study existence
Appeared in Commun. Contemp. Math. 11 1 2009 1 34. ZERO ORDER PERTURBATIONS TO FULLY NONLINEAR EQUATIONS: COMPARISON, EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS FERNANDO CHARRO AND IRENEO PERAL Abstract. We study existence
GENERALIZED CONVEXITY AND OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS IN SCALAR AND VECTOR OPTIMIZATION
 Chapter 4 GENERALIZED CONVEXITY AND OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS IN SCALAR AND VECTOR OPTIMIZATION Alberto Cambini Department of Statistics and Applied Mathematics University of Pisa, Via Cosmo Ridolfi 10 56124
Chapter 4 GENERALIZED CONVEXITY AND OPTIMALITY CONDITIONS IN SCALAR AND VECTOR OPTIMIZATION Alberto Cambini Department of Statistics and Applied Mathematics University of Pisa, Via Cosmo Ridolfi 10 56124
Lecture Introduction
 Lecture 1 1.1 Introduction The theory of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) is central to mathematics, both pure and applied. The main difference between the theory of PDEs and the theory of Ordinary
Lecture 1 1.1 Introduction The theory of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) is central to mathematics, both pure and applied. The main difference between the theory of PDEs and the theory of Ordinary
AN ASYMPTOTIC MEAN VALUE CHARACTERIZATION FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS
 AN ASYMPTOTIC MEAN VALUE CHARACTERIZATION FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS JUAN J. MANFREDI, MIKKO PARVIAINEN, AND JULIO D. ROSSI Abstract. We characterize p-harmonic functions in terms of an asymptotic mean value
AN ASYMPTOTIC MEAN VALUE CHARACTERIZATION FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS JUAN J. MANFREDI, MIKKO PARVIAINEN, AND JULIO D. ROSSI Abstract. We characterize p-harmonic functions in terms of an asymptotic mean value
INTERIOR CURVATURE BOUNDS FOR A CLASS OF CURVATURE EQUATIONS
 d2321rev5.jl 2004/4/28 15:18 page 1 #1 INTERIOR CURVATURE BOUNDS FOR A CLASS OF CURVATURE EQUATIONS WEIMIN SHENG, JOHN URBAS, and XU-JIA WANG Abstract We derive interior curvature bounds for admissible
d2321rev5.jl 2004/4/28 15:18 page 1 #1 INTERIOR CURVATURE BOUNDS FOR A CLASS OF CURVATURE EQUATIONS WEIMIN SHENG, JOHN URBAS, and XU-JIA WANG Abstract We derive interior curvature bounds for admissible
The location of the hot spot in a grounded convex conductor
 The location of the hot spot in a grounded convex conductor ROLANDO MAGNANINI joint paper with Lorenzo BRASCO and Paolo SALANI R. Magnanini (Università di Firenze) The location of the hot spot Cortona,
The location of the hot spot in a grounded convex conductor ROLANDO MAGNANINI joint paper with Lorenzo BRASCO and Paolo SALANI R. Magnanini (Università di Firenze) The location of the hot spot Cortona,
CONVEX SOLUTIONS OF ELLIPTIC DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS IN CLASSICAL DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY. 1. Introduction
 CONVEX SOLUTIONS OF ELLIPTIC DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS IN CLASSICAL DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY PENGFEI GUAN AND XI-NAN MA 1. Introduction The issue of convexity is fundamental in the theory of partial differential
CONVEX SOLUTIONS OF ELLIPTIC DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS IN CLASSICAL DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY PENGFEI GUAN AND XI-NAN MA 1. Introduction The issue of convexity is fundamental in the theory of partial differential
MATH Final Project Mean Curvature Flows
 MATH 581 - Final Project Mean Curvature Flows Olivier Mercier April 30, 2012 1 Introduction The mean curvature flow is part of the bigger family of geometric flows, which are flows on a manifold associated
MATH 581 - Final Project Mean Curvature Flows Olivier Mercier April 30, 2012 1 Introduction The mean curvature flow is part of the bigger family of geometric flows, which are flows on a manifold associated
N. L. P. NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING (NLP) deals with optimization models with at least one nonlinear function. NLP. Optimization. Models of following form:
 0.1 N. L. P. Katta G. Murty, IOE 611 Lecture slides Introductory Lecture NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING (NLP) deals with optimization models with at least one nonlinear function. NLP does not include everything
0.1 N. L. P. Katta G. Murty, IOE 611 Lecture slides Introductory Lecture NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING (NLP) deals with optimization models with at least one nonlinear function. NLP does not include everything
Fifth Abel Conference : Celebrating the Mathematical Impact of John F. Nash Jr. and Louis Nirenberg
 Fifth Abel Conference : Celebrating the Mathematical Impact of John F. Nash Jr. and Louis Nirenberg Some analytic aspects of second order conformally invariant equations Yanyan Li Rutgers University November
Fifth Abel Conference : Celebrating the Mathematical Impact of John F. Nash Jr. and Louis Nirenberg Some analytic aspects of second order conformally invariant equations Yanyan Li Rutgers University November
Comparison Results for Semilinear Elliptic Equations in Equimeasurable Domains
 Comparison Results for Semilinear Elliptic Equations in Equimeasurable Domains François HAMEL Aix-Marseille University & Institut Universitaire de France In collaboration with Emmanuel RUSS Workshop on
Comparison Results for Semilinear Elliptic Equations in Equimeasurable Domains François HAMEL Aix-Marseille University & Institut Universitaire de France In collaboration with Emmanuel RUSS Workshop on
ALEKSANDROV-TYPE ESTIMATES FOR A PARABOLIC MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No. 11, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) ALEKSANDROV-TYPE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2005(2005), No. 11, pp. 1 8. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) ALEKSANDROV-TYPE
Math 328 Course Notes
 Math 328 Course Notes Ian Robertson March 3, 2006 3 Properties of C[0, 1]: Sup-norm and Completeness In this chapter we are going to examine the vector space of all continuous functions defined on the
Math 328 Course Notes Ian Robertson March 3, 2006 3 Properties of C[0, 1]: Sup-norm and Completeness In this chapter we are going to examine the vector space of all continuous functions defined on the
On the definition and properties of p-harmonious functions
 On the definition and properties of p-harmonious functions University of Pittsburgh, UBA, UAM Workshop on New Connections Between Differential and Random Turn Games, PDE s and Image Processing Pacific
On the definition and properties of p-harmonious functions University of Pittsburgh, UBA, UAM Workshop on New Connections Between Differential and Random Turn Games, PDE s and Image Processing Pacific
Lecture 2: Convex functions
 Lecture 2: Convex functions f : R n R is convex if dom f is convex and for all x, y dom f, θ [0, 1] f is concave if f is convex f(θx + (1 θ)y) θf(x) + (1 θ)f(y) x x convex concave neither x examples (on
Lecture 2: Convex functions f : R n R is convex if dom f is convex and for all x, y dom f, θ [0, 1] f is concave if f is convex f(θx + (1 θ)y) θf(x) + (1 θ)f(y) x x convex concave neither x examples (on
Lecture Unconstrained optimization. In this lecture we will study the unconstrained problem. minimize f(x), (2.1)
 Lecture 2 In this lecture we will study the unconstrained problem minimize f(x), (2.1) where x R n. Optimality conditions aim to identify properties that potential minimizers need to satisfy in relation
Lecture 2 In this lecture we will study the unconstrained problem minimize f(x), (2.1) where x R n. Optimality conditions aim to identify properties that potential minimizers need to satisfy in relation
PERTURBATION THEORY FOR NONLINEAR DIRICHLET PROBLEMS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 28, 2003, 207 222 PERTURBATION THEORY FOR NONLINEAR DIRICHLET PROBLEMS Fumi-Yuki Maeda and Takayori Ono Hiroshima Institute of Technology, Miyake,
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 28, 2003, 207 222 PERTURBATION THEORY FOR NONLINEAR DIRICHLET PROBLEMS Fumi-Yuki Maeda and Takayori Ono Hiroshima Institute of Technology, Miyake,
SOLUTIONS OF NONLINEAR PDES IN THE SENSE OF AVERAGES
 SOLUTIONS OF NONLINEAR PDES IN THE SENSE OF AVERAGES BERND KAWOHL, JUAN MANFREDI, AND MIKKO PARVIAINEN Abstract. We characterize p-harmonic functions including p = 1 and p = by using mean value properties
SOLUTIONS OF NONLINEAR PDES IN THE SENSE OF AVERAGES BERND KAWOHL, JUAN MANFREDI, AND MIKKO PARVIAINEN Abstract. We characterize p-harmonic functions including p = 1 and p = by using mean value properties
Differentiable Functions
 Differentiable Functions Let S R n be open and let f : R n R. We recall that, for x o = (x o 1, x o,, x o n S the partial derivative of f at the point x o with respect to the component x j is defined as
Differentiable Functions Let S R n be open and let f : R n R. We recall that, for x o = (x o 1, x o,, x o n S the partial derivative of f at the point x o with respect to the component x j is defined as
AN ASYMPTOTIC MEAN VALUE CHARACTERIZATION FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS. To the memory of our friend and colleague Fuensanta Andreu
 AN ASYMPTOTIC MEAN VALUE CHARACTERIZATION FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS JUAN J. MANFREDI, MIKKO PARVIAINEN, AND JULIO D. ROSSI Abstract. We characterize p-harmonic functions in terms of an asymptotic mean value
AN ASYMPTOTIC MEAN VALUE CHARACTERIZATION FOR p-harmonic FUNCTIONS JUAN J. MANFREDI, MIKKO PARVIAINEN, AND JULIO D. ROSSI Abstract. We characterize p-harmonic functions in terms of an asymptotic mean value
Math (P)Review Part II:
 Math (P)Review Part II: Vector Calculus Computer Graphics Assignment 0.5 (Out today!) Same story as last homework; second part on vector calculus. Slightly fewer questions Last Time: Linear Algebra Touched
Math (P)Review Part II: Vector Calculus Computer Graphics Assignment 0.5 (Out today!) Same story as last homework; second part on vector calculus. Slightly fewer questions Last Time: Linear Algebra Touched
Murat Akman. The Brunn-Minkowski Inequality and a Minkowski Problem for Nonlinear Capacities. March 10
 The Brunn-Minkowski Inequality and a Minkowski Problem for Nonlinear Capacities Murat Akman March 10 Postdoc in HA Group and Postdoc at the University of Connecticut Minkowski Addition of Sets Let E 1
The Brunn-Minkowski Inequality and a Minkowski Problem for Nonlinear Capacities Murat Akman March 10 Postdoc in HA Group and Postdoc at the University of Connecticut Minkowski Addition of Sets Let E 1
Flux-limited solutions for quasi-convex Hamilton-Jacobi equations on networks
 Flux-limited solutions for quasi-convex Hamilton-Jacobi equations on networks C. Imbert and R. Monneau June 24, 2014 Abstract We study Hamilton-Jacobi equations on networks in the case where Hamiltonians
Flux-limited solutions for quasi-convex Hamilton-Jacobi equations on networks C. Imbert and R. Monneau June 24, 2014 Abstract We study Hamilton-Jacobi equations on networks in the case where Hamiltonians
A BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM FOR MINIMAL LAGRANGIAN GRAPHS. Simon Brendle & Micah Warren. Abstract. The associated symplectic structure is given by
 j. differential geometry 84 (2010) 267-287 A BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM FOR MINIMAL LAGRANGIAN GRAPHS Simon Brendle & Micah Warren Abstract Let Ω and Ω be uniformly convex domains in R n with smooth boundary.
j. differential geometry 84 (2010) 267-287 A BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEM FOR MINIMAL LAGRANGIAN GRAPHS Simon Brendle & Micah Warren Abstract Let Ω and Ω be uniformly convex domains in R n with smooth boundary.
Sébastien Chaumont a a Institut Élie Cartan, Université Henri Poincaré Nancy I, B. P. 239, Vandoeuvre-lès-Nancy Cedex, France. 1.
 A strong comparison result for viscosity solutions to Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations with Dirichlet condition on a non-smooth boundary and application to parabolic problems Sébastien Chaumont a a Institut
A strong comparison result for viscosity solutions to Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations with Dirichlet condition on a non-smooth boundary and application to parabolic problems Sébastien Chaumont a a Institut
Constrained Optimal Stopping Problems
 University of Bath SAMBa EPSRC CDT Thesis Formulation Report For the Degree of MRes in Statistical Applied Mathematics Author: Benjamin A. Robinson Supervisor: Alexander M. G. Cox September 9, 016 Abstract
University of Bath SAMBa EPSRC CDT Thesis Formulation Report For the Degree of MRes in Statistical Applied Mathematics Author: Benjamin A. Robinson Supervisor: Alexander M. G. Cox September 9, 016 Abstract
Parabolic quasi-concavity for solutions to parabolic problems in convex rings
 Math. Nachr. 283, No. 11, 1526 1548 (2010) / DOI 10.1002/mana.200910242 Editor s Choice Parabolic quasi-concavity for solutions to parabolic problems in convex rings Kazuhiro Ishige 1 and Paolo Salani
Math. Nachr. 283, No. 11, 1526 1548 (2010) / DOI 10.1002/mana.200910242 Editor s Choice Parabolic quasi-concavity for solutions to parabolic problems in convex rings Kazuhiro Ishige 1 and Paolo Salani
ON THE REGULARITY OF SAMPLE PATHS OF SUB-ELLIPTIC DIFFUSIONS ON MANIFOLDS
 Bendikov, A. and Saloff-Coste, L. Osaka J. Math. 4 (5), 677 7 ON THE REGULARITY OF SAMPLE PATHS OF SUB-ELLIPTIC DIFFUSIONS ON MANIFOLDS ALEXANDER BENDIKOV and LAURENT SALOFF-COSTE (Received March 4, 4)
Bendikov, A. and Saloff-Coste, L. Osaka J. Math. 4 (5), 677 7 ON THE REGULARITY OF SAMPLE PATHS OF SUB-ELLIPTIC DIFFUSIONS ON MANIFOLDS ALEXANDER BENDIKOV and LAURENT SALOFF-COSTE (Received March 4, 4)
A Geometric Approach to Free Boundary Problems
 A Geometric Approach to Free Boundary Problems Luis Caffarelli Sandro Salsa Graduate Studies in Mathematics Volume 68 a,,,,. n American Mathematical Society Providence, Rhode Island Introduction vii Part
A Geometric Approach to Free Boundary Problems Luis Caffarelli Sandro Salsa Graduate Studies in Mathematics Volume 68 a,,,,. n American Mathematical Society Providence, Rhode Island Introduction vii Part
Fractional convexity maximum principle
 Fractional convexity maximum principle Antonio Greco Department of Mathematics and Informatics via Ospedale 7, 0914 Cagliari, Italy E-mail: greco@unica.it Abstract We construct an anisotropic, degenerate,
Fractional convexity maximum principle Antonio Greco Department of Mathematics and Informatics via Ospedale 7, 0914 Cagliari, Italy E-mail: greco@unica.it Abstract We construct an anisotropic, degenerate,
Lecture Notes (Math 90): Week IX (Thursday)
 Lecture Notes (Math 90): Week IX (Thursday) Alicia Harper November 13, 2017 Monotonic functions/convexity and Concavity 1 The Story 1.1 Monotonic Functions Recall that we say a function is increasing if
Lecture Notes (Math 90): Week IX (Thursday) Alicia Harper November 13, 2017 Monotonic functions/convexity and Concavity 1 The Story 1.1 Monotonic Functions Recall that we say a function is increasing if
A CONNECTION BETWEEN A GENERAL CLASS OF SUPERPARABOLIC FUNCTIONS AND SUPERSOLUTIONS
 A CONNECTION BETWEEN A GENERAL CLASS OF SUPERPARABOLIC FUNCTIONS AND SUPERSOLUTIONS RIIKKA KORTE, TUOMO KUUSI, AND MIKKO PARVIAINEN Abstract. We show to a general class of parabolic equations that every
A CONNECTION BETWEEN A GENERAL CLASS OF SUPERPARABOLIC FUNCTIONS AND SUPERSOLUTIONS RIIKKA KORTE, TUOMO KUUSI, AND MIKKO PARVIAINEN Abstract. We show to a general class of parabolic equations that every
Linear vector spaces and subspaces.
 Math 2051 W2008 Margo Kondratieva Week 1 Linear vector spaces and subspaces. Section 1.1 The notion of a linear vector space. For the purpose of these notes we regard (m 1)-matrices as m-dimensional vectors,
Math 2051 W2008 Margo Kondratieva Week 1 Linear vector spaces and subspaces. Section 1.1 The notion of a linear vector space. For the purpose of these notes we regard (m 1)-matrices as m-dimensional vectors,
THE DIRICHLET PROBLEM FOR THE CONVEX ENVELOPE
 THE DIRICHLET PROBLEM FOR THE CONVEX ENVELOPE LUIS SILVESTRE AND ADAM M. OBERMAN Abstract. This work studies the Dirichlet problem for the Convex Envelope. While the convex envelope is a natural object
THE DIRICHLET PROBLEM FOR THE CONVEX ENVELOPE LUIS SILVESTRE AND ADAM M. OBERMAN Abstract. This work studies the Dirichlet problem for the Convex Envelope. While the convex envelope is a natural object
EXISTENCE AND REGULARITY RESULTS FOR SOME NONLINEAR PARABOLIC EQUATIONS
 EXISTECE AD REGULARITY RESULTS FOR SOME OLIEAR PARABOLIC EUATIOS Lucio BOCCARDO 1 Andrea DALL AGLIO 2 Thierry GALLOUËT3 Luigi ORSIA 1 Abstract We prove summability results for the solutions of nonlinear
EXISTECE AD REGULARITY RESULTS FOR SOME OLIEAR PARABOLIC EUATIOS Lucio BOCCARDO 1 Andrea DALL AGLIO 2 Thierry GALLOUËT3 Luigi ORSIA 1 Abstract We prove summability results for the solutions of nonlinear
U.C. Berkeley CS294: Spectral Methods and Expanders Handout 11 Luca Trevisan February 29, 2016
 U.C. Berkeley CS294: Spectral Methods and Expanders Handout Luca Trevisan February 29, 206 Lecture : ARV In which we introduce semi-definite programming and a semi-definite programming relaxation of sparsest
U.C. Berkeley CS294: Spectral Methods and Expanders Handout Luca Trevisan February 29, 206 Lecture : ARV In which we introduce semi-definite programming and a semi-definite programming relaxation of sparsest
Around the Brunn-Minkowski inequality
 Around the Brunn-Minkowski inequality Andrea Colesanti Technische Universität Berlin - Institut für Mathematik January 28, 2015 Summary Summary The Brunn-Minkowski inequality Summary The Brunn-Minkowski
Around the Brunn-Minkowski inequality Andrea Colesanti Technische Universität Berlin - Institut für Mathematik January 28, 2015 Summary Summary The Brunn-Minkowski inequality Summary The Brunn-Minkowski
SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS. Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S. L. Yadava. 1. Introduction
 Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
Motivation Power curvature flow Large exponent limit Analogues & applications. Qing Liu. Fukuoka University. Joint work with Prof.
 On Large Exponent Behavior of Power Curvature Flow Arising in Image Processing Qing Liu Fukuoka University Joint work with Prof. Naoki Yamada Mathematics and Phenomena in Miyazaki 2017 University of Miyazaki
On Large Exponent Behavior of Power Curvature Flow Arising in Image Processing Qing Liu Fukuoka University Joint work with Prof. Naoki Yamada Mathematics and Phenomena in Miyazaki 2017 University of Miyazaki
Boundary value problems for the infinity Laplacian. regularity and geometric results
 : regularity and geometric results based on joint works with Graziano Crasta, Roma La Sapienza Calculus of Variations and Its Applications - Lisboa, December 2015 on the occasion of Luísa Mascarenhas 65th
: regularity and geometric results based on joint works with Graziano Crasta, Roma La Sapienza Calculus of Variations and Its Applications - Lisboa, December 2015 on the occasion of Luísa Mascarenhas 65th
Elliptic stability for stationary Schrödinger equations by Emmanuel Hebey. Part III/VI A priori blow-up theories March 2015
 Elliptic stability for stationary Schrödinger equations by Emmanuel Hebey Part III/VI A priori blow-up theories March 2015 Nonlinear analysis arising from geometry and physics Conference in honor of Professor
Elliptic stability for stationary Schrödinger equations by Emmanuel Hebey Part III/VI A priori blow-up theories March 2015 Nonlinear analysis arising from geometry and physics Conference in honor of Professor
Multiple positive solutions for a class of quasilinear elliptic boundary-value problems
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20032003), No. 07, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp) Multiple positive
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 20032003), No. 07, pp. 1 5. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu login: ftp) Multiple positive
Regularity of flat level sets in phase transitions
 Annals of Mathematics, 69 (2009), 4 78 Regularity of flat level sets in phase transitions By Ovidiu Savin Abstract We consider local minimizers of the Ginzburg-Landau energy functional 2 u 2 + 4 ( u2 )
Annals of Mathematics, 69 (2009), 4 78 Regularity of flat level sets in phase transitions By Ovidiu Savin Abstract We consider local minimizers of the Ginzburg-Landau energy functional 2 u 2 + 4 ( u2 )
Landesman-Lazer type results for second order Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations
 Author manuscript, published in "Journal of Functional Analysis 258, 12 (2010) 4154-4182" Landesman-Lazer type results for second order Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations Patricio FELMER, Alexander QUAAS,
Author manuscript, published in "Journal of Functional Analysis 258, 12 (2010) 4154-4182" Landesman-Lazer type results for second order Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equations Patricio FELMER, Alexander QUAAS,
PHASE TRANSITIONS: REGULARITY OF FLAT LEVEL SETS
 PHASE TRANSITIONS: REGULARITY OF FLAT LEVEL SETS OVIDIU SAVIN Abstract. We consider local minimizers of the Ginzburg-Landau energy functional 2 u 2 + 4 ( u2 ) 2 dx and prove that, if the level set is included
PHASE TRANSITIONS: REGULARITY OF FLAT LEVEL SETS OVIDIU SAVIN Abstract. We consider local minimizers of the Ginzburg-Landau energy functional 2 u 2 + 4 ( u2 ) 2 dx and prove that, if the level set is included
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 10 Apr 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 10 Apr 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 10 Apr 2013](/thumbs/71/66250579.jpg) QUASI-STATIC EVOLUTION AND CONGESTED CROWD TRANSPORT DAMON ALEXANDER, INWON KIM, AND YAO YAO arxiv:1304.3072v1 [math.ap] 10 Apr 2013 Abstract. We consider the relationship between Hele-Shaw evolution with
QUASI-STATIC EVOLUTION AND CONGESTED CROWD TRANSPORT DAMON ALEXANDER, INWON KIM, AND YAO YAO arxiv:1304.3072v1 [math.ap] 10 Apr 2013 Abstract. We consider the relationship between Hele-Shaw evolution with
REGULARITY OF SUBELLIPTIC MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATIONS IN THE PLANE
 REGULARITY OF SUBELLIPTIC MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATIONS IN THE PLANE PENGFEI GUAN AND ERIC SAWYER (.). Introduction There is a vast body of elliptic regularity results for the Monge-Ampère equation det D u (x)
REGULARITY OF SUBELLIPTIC MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATIONS IN THE PLANE PENGFEI GUAN AND ERIC SAWYER (.). Introduction There is a vast body of elliptic regularity results for the Monge-Ampère equation det D u (x)
A note on W 1,p estimates for quasilinear parabolic equations
 200-Luminy conference on Quasilinear Elliptic and Parabolic Equations and Systems, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 08, 2002, pp 2 3. http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu
200-Luminy conference on Quasilinear Elliptic and Parabolic Equations and Systems, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 08, 2002, pp 2 3. http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu
