PHYS 221 General Physics II
|
|
|
- Janis Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYS 221 General Physics II Elec. Potential Energy, Voltage, Equipotentials Spring 2015 Assigned Reading: Lecture 4
2 Review: Gauss Law Last Lecture E q enc o E EAcos Gauss Law Very useful to determine E when there is symmetry Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 2
3 From Mechanics (PHYS 220) Energy Kinetic Energy: associated with the state of motion KE 1 2 mv2 Potential Energy: associated with the configuration of the system PE W Conservative Forces: W Fx cos W=F x if F and x are parallel Work done by a conservative force is independent of path. PE(gravity) mgh PE(spring) k 2 x2 Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 3
4 Potential Energy of Two Point Charges m1m G r U g 2 PE elec k q 1 q 2 r Gravity: always attraction. U is more negative ( lower ) when objects are closer q 1 q 2 < 0 : attraction. U is more negative ( lower ) when objects are closer q 1 q 2 > 0 : repulsion. U is lower when objects are farther apart Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 4
5 Potential Energy: Gravitational vs Electric Gravitational potential energy Electric potential energy PE = -W grav.field W = F. d. cos() m1m 2 F g G 2 r PE=0 at r= PE G m m 1 2 r PE = -W elec.field W = F. d. cos() q1q 2 F e k 2 r PE k q q 1 2 r Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 5
6 BB i>clicker question BB C F A B What is the direction of the force on the negative charge at point A? 1) left 2) right 3) up Uniform E Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 6
7 BB i>clicker question BB C A B When a negative charge is moved from A to C the ELECTRIC force does 1) positive work. 2) zero work. 3) negative work. Uniform E Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 7
8 Zero because the path is perpendicular to the field W Fx cos qex cos 0 F F F F F motion C A Uniform E B When a negative charge is moved from A to C the ELECTRIC force does A. positive work. B. zero work. C. negative work. Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 8
9 Potential Energy of Several Point Charges: An Example with 3 charges PE 13 k q 1q 3 q 1 -q 3 PE 12 k q 1 q 2 r 12 PE 23 k q 2q 3 q 2 r 13 r 23 Total potential energy PE: PE PE 12 PE 23 PE 13 PE k q 1q 2 q 2q 3 q 1q 3 r 12 r 23 r 13 Potential energy of many charges is a scalar sum of potential energies of all the pairs of charges in the system. Note: each pair should be counted only once. Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 9
10 Electric Potential q 5 q 4 q 1 Suppose a test charge q moves through the area with many fixed charges around q 6 q 3 q 2 q Since the distance from this charge to other charges changes, the potential energy changes PE elec k qq 1 qq 2... q q 1 2 q q r 1 r 2 r 12 r 13 The changes in potential energy are proportional to that charge Electric potential V: electric potential energy per unit charge: V PE elec q Units: J/CV (Volt) Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 10
11 Electric Potential vs Electric Potential Energy Electric Potential is a property of an electric field and is measured in J/C or V Electric Potential Energy is an energy of system consisting of the charged object and the external electric field, and is measured in Joules. *Electric potential energy PE elec electric potential (or potential) V Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 11
12 Potential Difference The potential difference between two points is the negative of the work done by the electrostatic force to move a unit charge from one point to another. Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 12
13 Potential & Electric Fields The electric field points in the direction in which the potential decreases most rapidly. PE W Fx qex V PE q Ex V Ex E V E V x x V ˆx, y V ŷ, z ẑ Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 13
14 Potential Difference The potential difference between two points is the negative of the work done by the electrostatic force to move a unit charge from one point to another. V V B V A PE q W q A B Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 14
15 Potential Difference *independent of path *independent of test charge To find V, find work done on a positive charge q o by the electric field as it moves from i to f. i E At any point, the work done on the particle by electrostatic force: θ x f Potential Difference: W elec = q 0 E cos Δx The potential energy is: PE W elec q 0 E cos x V f V i PE q 0 E cos x Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 15
16 Potential due to a point charge: V in space around a charged particle relative to the zero potential at infinity: For a point charge V(r) to V q 4 0 r V(r 0) r Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 16
17 Potential due to a Group of Point Charges Find the Potential at the center of the square. N V(r) V n (r) 1 n1 4 o N n1 q n r n Principle of superposition q 1 = 12 nc q 2 = -24 nc - r 1 r 2 r 3 q 3 =31 nc q 4 =17 nc r 4 Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 17
18 Electric Potential and Electric Field Calculate Electric Potential from the Electric Field V Ex Calculate Electric Field from the Electric Potential E V x Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 18
19 Potential Energy Gravitational Potential Energy m m r Electric Potential Energy F e k q q F g G 2 2 PE G m 1 m 2 r U=0 at r = Potential energy: can be positive or negative Field force pushes a system to a configuration with lower potential energy: Field force does work on a system, leading to a decrease in its potential energy. But, the total energy is conserved, if there are no other forces. Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture r PE k q 1 q 2 r
20 BB i>clicker question An electron moves a distance of 1.5 m through a region where the electric field E is constant and parallel to the displacement. The electron s potential energy increases by J. What is the magnitude of E? E V x PE qx Nm C a) 3.1 N/C b) N/C c) 2.0 N/C d) J e) N/C e = C 1.5m k = Nm 2 /C 2 0 = C 2 /(Nm 2 ) 2N / C Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture BB
21 Equipotentials Definition: locus of points with the same potential. General Property: The electric field is always perpendicular to an equipotential surface. Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 21
22 Equipotentials Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 22
23 E due to an infinite line charge Corona discharge around a high voltage power line, which roughly indicates the electric field lines. Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 23
24 Equipotential Surface: Examples Point charge infinite positive charge sheet electric dipole Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 24
25 Potential inside & outside a conducting sphere V ref 0 at r. Common mistake: thinking that potential must be zero inside because electric field is zero inside. Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 25
26 Demo PE q V Get energy out charge flow R V kq R r 1 r 2 V V(r 1 ) V(r 2 ) across fluorescent light bulb Phys 221 Spring 2014 Lecture 04 26
Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1
 Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1 Two Parallel Conducting Sheets Find the electric field to the left of the sheets, between the sheets and to the right of the sheets. 1/28/2018 2 Uniform
Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1 Two Parallel Conducting Sheets Find the electric field to the left of the sheets, between the sheets and to the right of the sheets. 1/28/2018 2 Uniform
Chapter 24. QUIZ 6 January 26, Example: Three Point Charges. Example: Electrostatic Potential Energy 1/30/12 1
 QUIZ 6 January 26, 2012 An electron moves a distance of 1.5 m through a region where the electric field E is constant and parallel to the displacement. The electron s potential energy increases by 3.2
QUIZ 6 January 26, 2012 An electron moves a distance of 1.5 m through a region where the electric field E is constant and parallel to the displacement. The electron s potential energy increases by 3.2
Physics 1202: Lecture 3 Today s Agenda
 Physics 1202: Lecture 3 Today s Agenda Announcements: Lectures posted on: www.phys.uconn.edu/~rcote/ HW assignments, solutions etc. Homework #1: On Masterphysics: due this coming Friday Go to the syllabus
Physics 1202: Lecture 3 Today s Agenda Announcements: Lectures posted on: www.phys.uconn.edu/~rcote/ HW assignments, solutions etc. Homework #1: On Masterphysics: due this coming Friday Go to the syllabus
Electric Potential II
 Electric Potential II Physics 2415 Lecture 7 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics Field lines and equipotentials Partial derivatives Potential along a line from two charges Electric breakdown of air Potential
Electric Potential II Physics 2415 Lecture 7 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics Field lines and equipotentials Partial derivatives Potential along a line from two charges Electric breakdown of air Potential
Chapter 25. Electric Potential
 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law
 Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law F F Last modified: 07/02/2018 Contents Links Electric Charge & Coulomb s Law Electric Charge Coulomb s Law Example 1: Coulomb s Law Electric Field Electric Field Vector
Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law F F Last modified: 07/02/2018 Contents Links Electric Charge & Coulomb s Law Electric Charge Coulomb s Law Example 1: Coulomb s Law Electric Field Electric Field Vector
What will the electric field be like inside the cavity?
 What will the electric field be like inside the cavity? 1. There is no charge inside the gaussian surface so E = 0 2. There is no net flux through the surface but there is an E field 3. Gauss s law doesn
What will the electric field be like inside the cavity? 1. There is no charge inside the gaussian surface so E = 0 2. There is no net flux through the surface but there is an E field 3. Gauss s law doesn
Electrical Potential Energy. Chapter 25. Electric Potential Energy, final. Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential.
 Chapter 25 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electrical Potential Energy! When a test charge, q 0 is placed in an electric field E, it experiences a force: F = q E 0! Is this force conservative? 1 2 Electric
Chapter 25 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electrical Potential Energy! When a test charge, q 0 is placed in an electric field E, it experiences a force: F = q E 0! Is this force conservative? 1 2 Electric
Chapter 25. Electric Potential
 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
r 4 r 2 q 2 r 3 V () r En dln (r) 1 q 1 Negative sign from integration of E field cancels the negative sign from the original equation.
 Question from last class Potential due to a Group of Point Charges rr V () r E dl r r 1 q 1 X rr N V () r E dl r n n N V(r) V n (r) 1 n1 4 o 1/30/2018 2 q 2 N r r N r r q n V () r En dln dr 2 n n r n r
Question from last class Potential due to a Group of Point Charges rr V () r E dl r r 1 q 1 X rr N V () r E dl r n n N V(r) V n (r) 1 n1 4 o 1/30/2018 2 q 2 N r r N r r q n V () r En dln dr 2 n n r n r
MTE1 results. Mean 75% = 90/120
 MTE1 results Mean 75% = 90/120 Scores available at Learn@UW, your TAs have exams If your score is an F or a D, talk to us and your TAs for suggestions on how to improve From last times Electric charges
MTE1 results Mean 75% = 90/120 Scores available at Learn@UW, your TAs have exams If your score is an F or a D, talk to us and your TAs for suggestions on how to improve From last times Electric charges
Recall Gravitational Potential Energy
 Electric Potential Recall Gravitational Potential Energy How can you increase the gravitational potential energy of an object? Raise it above the surface of the earth. The amount of work done against earth
Electric Potential Recall Gravitational Potential Energy How can you increase the gravitational potential energy of an object? Raise it above the surface of the earth. The amount of work done against earth
Electric Potential Energy Chapter 16
 Electric Potential Energy Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Sections: 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy
Electric Potential Energy Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Sections: 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy
Electrostatics so far
 Electrostatics so far F = 1 2 1 2 2 Electric Force b/n q and q : qq 1 2 kq Electric Field E due to q : E = 1 1 r 2 kq q r q e = 1.6 x10-19 C k = 9 x 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 Tesla Envy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jl
Electrostatics so far F = 1 2 1 2 2 Electric Force b/n q and q : qq 1 2 kq Electric Field E due to q : E = 1 1 r 2 kq q r q e = 1.6 x10-19 C k = 9 x 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 Tesla Envy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jl
Physics 1051 Lecture 14. Electric Potential. Physics General Physics II Oscillations, Waves and Magnetism
 Physics 1051 Lecture 14 Electric Potential Lecture 14 - Contents 20.0 Describing Electric Phenomenon using Electric Potential 20.1 Electric Potential Difference and Electric Potential 20.2 Potential Difference
Physics 1051 Lecture 14 Electric Potential Lecture 14 - Contents 20.0 Describing Electric Phenomenon using Electric Potential 20.1 Electric Potential Difference and Electric Potential 20.2 Potential Difference
What You Already Know
 What You Already Know Coulomb s law Electric fields Gauss law Electric fields for several configurations Point Line Plane (nonconducting) Sheet (conducting) Ring (along axis) Disk (along axis) Sphere Cylinder
What You Already Know Coulomb s law Electric fields Gauss law Electric fields for several configurations Point Line Plane (nonconducting) Sheet (conducting) Ring (along axis) Disk (along axis) Sphere Cylinder
Electrical Potential Energy and Electric Potential (Chapter 29)
 Electrical Potential Energy and Electric Potential (Chapter 29) A Refresher Course on Gravity and Mechanical Energy Total mechanical energy: E mech = K + U, K= 1 2 mv2,u = potential energy f W = F!" ids
Electrical Potential Energy and Electric Potential (Chapter 29) A Refresher Course on Gravity and Mechanical Energy Total mechanical energy: E mech = K + U, K= 1 2 mv2,u = potential energy f W = F!" ids
The electric potential energy of charge q in a uniform electric field is
 The electric potential energy of charge q in a uniform electric field is where s is measured from the negative plate and U 0 is the potential energy at the negative plate (s = 0). It will often be convenient
The electric potential energy of charge q in a uniform electric field is where s is measured from the negative plate and U 0 is the potential energy at the negative plate (s = 0). It will often be convenient
What You Already Know
 What You Already Know Coulomb s law Electric fields Gauss law Electric fields for several configurations Point Line Plane (nonconducting) Sheet (conducting) Ring (along axis) Disk (along axis) Sphere Cylinder
What You Already Know Coulomb s law Electric fields Gauss law Electric fields for several configurations Point Line Plane (nonconducting) Sheet (conducting) Ring (along axis) Disk (along axis) Sphere Cylinder
Electricity and Magnetism. Electric Potential Energy and Voltage
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Work and Potential Energy Recall from Mechanics that E mech = K + U is a conserved quantity for particles that interact via conservative
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Work and Potential Energy Recall from Mechanics that E mech = K + U is a conserved quantity for particles that interact via conservative
Chapter 2. Electric Fields Field Intensity Due to a Point Charge
 Chapter 2 Electric Fields An electric field exists in a region if electrical forces are exerted on charged bodies in that region. The direction of an electric field at a point is the direction in which
Chapter 2 Electric Fields An electric field exists in a region if electrical forces are exerted on charged bodies in that region. The direction of an electric field at a point is the direction in which
PHYSICS 1/23/2019. Chapter 25 Lecture. Chapter 25 The Electric Potential. Chapter 25 Preview
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 25 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 25 The Electric Potential IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the electric potential and electric
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 25 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 25 The Electric Potential IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the electric potential and electric
Chapter 16. Electric Energy and Capacitance
 Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Electric Potential Energy The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy function with this force Work
Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Electric Potential Energy The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy function with this force Work
Chapter 17. Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential
 Chapter 17 Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential Consider gravity near the surface of the Earth The gravitational field is uniform. This means it always points in the same direction with
Chapter 17 Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential Consider gravity near the surface of the Earth The gravitational field is uniform. This means it always points in the same direction with
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 4 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 4 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/
7 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
 Chapter 7 Electric Potential 285 7 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Figure 7.1 The energy released in a lightning strike is an excellent illustration of the vast quantities of energy that may be stored and released
Chapter 7 Electric Potential 285 7 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Figure 7.1 The energy released in a lightning strike is an excellent illustration of the vast quantities of energy that may be stored and released
Finishing Chapter 26 on dipoles.. Electric Potential Energy of: Point Charges Dipoles Electric Potential: V Voltage: ΔV
 PHY132 Introduction to Physics II Class 11 Outline: Finishing Chapter 26 on dipoles.. Electric Potential Energy of: Point Charges Dipoles Electric Potential: V Voltage: ΔV QuickCheck 26.13 Which dipole
PHY132 Introduction to Physics II Class 11 Outline: Finishing Chapter 26 on dipoles.. Electric Potential Energy of: Point Charges Dipoles Electric Potential: V Voltage: ΔV QuickCheck 26.13 Which dipole
Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field
 Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field The electrostatic force is a conservative force. Therefore, it is possible to define an electrical potential energy function with this force. Work done
Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field The electrostatic force is a conservative force. Therefore, it is possible to define an electrical potential energy function with this force. Work done
Physics 102: Lecture 3 Electric Potential Energy & Electric Potential. Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1
 Physics 102: Lecture 3 Electric Potential Energy & Electric Potential Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1 Overview for Today s Lecture Electric Potential Energy & Work Uniform fields Point charges Electric
Physics 102: Lecture 3 Electric Potential Energy & Electric Potential Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1 Overview for Today s Lecture Electric Potential Energy & Work Uniform fields Point charges Electric
Phys 2102 Spring 2002 Exam 1
 Phys 2102 Spring 2002 Exam 1 February 19, 2002 1. When a positively charged conductor touches a neutral conductor, the neutral conductor will: (a) Lose protons (b) Gain electrons (c) Stay neutral (d) Lose
Phys 2102 Spring 2002 Exam 1 February 19, 2002 1. When a positively charged conductor touches a neutral conductor, the neutral conductor will: (a) Lose protons (b) Gain electrons (c) Stay neutral (d) Lose
CHAPTER 19 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL. Sections 1-5
 CHAPTER 19 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Sections 1-5 Objectives: After completing this unit, you should be able to: Understand an apply the concepts of electric potential energy,
CHAPTER 19 - ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Sections 1-5 Objectives: After completing this unit, you should be able to: Understand an apply the concepts of electric potential energy,
Electric Potential Energy
 Electric Potential Energy the electric potential energy of two charges depends on the distance between the charges when two like charges are an infinite distance apart, the potential energy is zero An
Electric Potential Energy the electric potential energy of two charges depends on the distance between the charges when two like charges are an infinite distance apart, the potential energy is zero An
Chapter 17 & 18. Electric Field and Electric Potential
 Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
Chapter 17 & 18 Electric Field and Electric Potential Electric Field Maxwell developed an approach to discussing fields An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a charged object
Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work
 Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric potential energy Relate it to work Ex: charge in uniform electric field, point charges Apply these concepts
Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric potential energy Relate it to work Ex: charge in uniform electric field, point charges Apply these concepts
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 2 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 2 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/
Chapter 16 Electrical Energy Capacitance. HW: 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 12, 13, 17, 21, 25, 27 33, 35, 37a, 43, 45, 49, 51
 Chapter 16 Electrical Energy Capacitance HW: 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 12, 13, 17, 21, 25, 27 33, 35, 37a, 43, 45, 49, 51 Electrical Potential Reminder from physics 1: Work done by a conservative force, depends only
Chapter 16 Electrical Energy Capacitance HW: 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 12, 13, 17, 21, 25, 27 33, 35, 37a, 43, 45, 49, 51 Electrical Potential Reminder from physics 1: Work done by a conservative force, depends only
Electric Potential Lecture 5
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential Lecture 5 Dr. Armen Kocharian Electrical Potential Energy When a test charge is placed in an electric field, it experiences a force F = q o E The force is conservative ds
Chapter 23 Electric Potential Lecture 5 Dr. Armen Kocharian Electrical Potential Energy When a test charge is placed in an electric field, it experiences a force F = q o E The force is conservative ds
Electric Potential. Capacitors (Chapters 28, 29)
 Electric Potential. Capacitors (Chapters 28, 29) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength
Electric Potential. Capacitors (Chapters 28, 29) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength
Electric Potential. Chapter 23. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Reza Khanbabaie Goals for Chapter 23 Reminder about gravitational
Chapter 23 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Reza Khanbabaie Goals for Chapter 23 Reminder about gravitational
ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS
 ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS Electric charge Ordinary matter is made up of atoms which have positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons surrounding them. A body can become charged if it loses or
ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS Electric charge Ordinary matter is made up of atoms which have positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons surrounding them. A body can become charged if it loses or
Chapter 21 Electric Potential
 Chapter 21 Electric Potential Chapter Goal: To calculate and use the electric potential and electric potential energy. Slide 21-1 Chapter 21 Preview Looking Ahead Text: p. 665 Slide 21-2 Review of Potential
Chapter 21 Electric Potential Chapter Goal: To calculate and use the electric potential and electric potential energy. Slide 21-1 Chapter 21 Preview Looking Ahead Text: p. 665 Slide 21-2 Review of Potential
As we discussed in class, here are the key properties of the topographical map:
 Ch21P Page 1 1P22/1P92 Problems (2011) Chapter 21 Electric Potential Friday, January 14, 2011 10:03 AM In the previous chapter we learned about the use of the electric field concept to describe electric
Ch21P Page 1 1P22/1P92 Problems (2011) Chapter 21 Electric Potential Friday, January 14, 2011 10:03 AM In the previous chapter we learned about the use of the electric field concept to describe electric
Chapter 20. Electric Potential Electric Potential Energy
 Chapter 20 Electric Potential Electric Potential Energy CONSERVTIVE FORCES conservative force gives back work that has been done against it Gravitational and electrostatic forces are conservative Friction
Chapter 20 Electric Potential Electric Potential Energy CONSERVTIVE FORCES conservative force gives back work that has been done against it Gravitational and electrostatic forces are conservative Friction
Physics 102: Lecture 3 Electric Potential Energy & Electric Potential. Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1
 Physics 102: Lecture 3 Electric Potential Energy & Electric Potential Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1 Overview for Today s Lecture Electric Potential Energy & Work Uniform fields Point charges Electric
Physics 102: Lecture 3 Electric Potential Energy & Electric Potential Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1 Overview for Today s Lecture Electric Potential Energy & Work Uniform fields Point charges Electric
Essential University Physics
 Essential University Physics Richard Wolfson 22 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lecture prepared by Richard Wolfson Slide 22-1 In this lecture you ll learn The concept of electric potential difference Including
Essential University Physics Richard Wolfson 22 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lecture prepared by Richard Wolfson Slide 22-1 In this lecture you ll learn The concept of electric potential difference Including
Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS
 Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS F = kq 1Q 2 r2 E = V d V = kq r E p = kq 1Q 2 r F = qe V = E p Q 1 000 000 Volts 1 000 000 Volts NAME: Block: Text References 3 rd Ed. Giancolli Pg. 416-30 4 th Ed. Giancolli
Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS F = kq 1Q 2 r2 E = V d V = kq r E p = kq 1Q 2 r F = qe V = E p Q 1 000 000 Volts 1 000 000 Volts NAME: Block: Text References 3 rd Ed. Giancolli Pg. 416-30 4 th Ed. Giancolli
Chapter 22 Electric Potential (Voltage)
 Chapter 22 Electric Potential (Voltage) Question 29.5 Work and Electric Potential I Which requires the most work, to move a positive charge from P to points 1, 2, 3 or 4? All points are the same distance
Chapter 22 Electric Potential (Voltage) Question 29.5 Work and Electric Potential I Which requires the most work, to move a positive charge from P to points 1, 2, 3 or 4? All points are the same distance
Physics 2112 Unit 6: Electric Potential
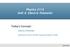 Physics 2112 Unit 6: Electric Potential Today s Concept: Electric Potential (Defined in terms of Path Integral of Electric Field) Unit 6, Slide 1 Stuff you asked about: I am very confused about the integrals
Physics 2112 Unit 6: Electric Potential Today s Concept: Electric Potential (Defined in terms of Path Integral of Electric Field) Unit 6, Slide 1 Stuff you asked about: I am very confused about the integrals
Agenda for Today. Elements of Physics II. Conductors and Insulators Movement of charges Conservation of charge Static electricity Electroscope
 Physics 132: Lecture e 5 Elements of Physics II Agenda for Today Conductors and Insulators Movement of charges Conservation of charge Static electricity Electroscope Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Problem
Physics 132: Lecture e 5 Elements of Physics II Agenda for Today Conductors and Insulators Movement of charges Conservation of charge Static electricity Electroscope Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Problem
Physics 1302W.500 Lecture 9 Introductory Physics for Scientists and Engineering II
 Physics 1302W.500 Lecture 9 Introductory Physics for Scientists and Engineering II In today s lecture, we will finish our discussion of Gauss law. Slide 25-1 Applying Gauss s law Procedure: Calculating
Physics 1302W.500 Lecture 9 Introductory Physics for Scientists and Engineering II In today s lecture, we will finish our discussion of Gauss law. Slide 25-1 Applying Gauss s law Procedure: Calculating
Intermediate Physics PHYS102
 Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
Intermediate Physics PHYS102 Dr Richard H. Cyburt Assistant Professor of Physics My office: 402c in the Science Building My phone: (304) 384-6006 My email: rcyburt@concord.edu My webpage: www.concord.edu/rcyburt
ELECTROSTATIC CBSE BOARD S IMPORTANT QUESTIONS OF 1 MARKS
 ELECTROSTATIC CBSE BOARD S IMPORTANT QUESTIONS OF 1 MARKS 1. Name any two basic properties of electric charge. [1] 2. Define the term electric dipole-moment. [1] 3. Write the physical quantity, which has
ELECTROSTATIC CBSE BOARD S IMPORTANT QUESTIONS OF 1 MARKS 1. Name any two basic properties of electric charge. [1] 2. Define the term electric dipole-moment. [1] 3. Write the physical quantity, which has
Lecture 24 Chapter 22 Electrostatics II Electric Field & Potential. Chapter 23 Electric Current. From last time--
 Lecture 24 Chapter 22 Electrostatics II Electric Field & Potential Chapter 23 Electric Current 21-Oct-10 From last time-- Electric charge (q), measured in Coulombs (C) Positive and negative charge Electric
Lecture 24 Chapter 22 Electrostatics II Electric Field & Potential Chapter 23 Electric Current 21-Oct-10 From last time-- Electric charge (q), measured in Coulombs (C) Positive and negative charge Electric
Danger High Voltage! Your friend starts to climb on this... You shout Get away! That s High Voltage!!! After you save his life, your friend asks:
 Danger High Voltage! Your friend starts to climb on this... You shout Get away! That s High Voltage!!! After you save his life, your friend asks: What is Voltage anyway? Voltage... Is the energy (in Joules)
Danger High Voltage! Your friend starts to climb on this... You shout Get away! That s High Voltage!!! After you save his life, your friend asks: What is Voltage anyway? Voltage... Is the energy (in Joules)
Electricity and Magnetism
 Electricity and Magnetism Review Electric Charge and Coulomb s Force Electric Field and Field Lines Superposition principle E.S. Induction Electric Dipole Electric Flux and Gauss Law Electric Potential
Electricity and Magnetism Review Electric Charge and Coulomb s Force Electric Field and Field Lines Superposition principle E.S. Induction Electric Dipole Electric Flux and Gauss Law Electric Potential
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
Los Altos Physics Honors. Electrostatics: Electric Fields, Electric Forces, Electric Potentials and. Electric Potential Energy.
 Los Altos Physics Honors Electrostatics: Electric Fields, Electric Forces, Electric Potentials and Electric Potential Energy Workbook adam.randall@mvla.net www.laphysics.com dls.mvla.net/los_altos Spring
Los Altos Physics Honors Electrostatics: Electric Fields, Electric Forces, Electric Potentials and Electric Potential Energy Workbook adam.randall@mvla.net www.laphysics.com dls.mvla.net/los_altos Spring
Lecture 7. Capacitors and Electric Field Energy. Last lecture review: Electrostatic potential
 Lecture 7. Capacitors and Electric Field Energy Last lecture review: Electrostatic potential V r = U r q Q Iclicker question The figure shows cross sections through two equipotential surfaces. In both
Lecture 7. Capacitors and Electric Field Energy Last lecture review: Electrostatic potential V r = U r q Q Iclicker question The figure shows cross sections through two equipotential surfaces. In both
Lecture 4 Electric Potential and/ Potential Energy Ch. 25
 Lecture 4 Electric Potential and/ Potential Energy Ch. 5 Review from Lecture 3 Cartoon - There is an electric energy associated with the position of a charge. Opening Demo - Warm-up problems Physlet Topics
Lecture 4 Electric Potential and/ Potential Energy Ch. 5 Review from Lecture 3 Cartoon - There is an electric energy associated with the position of a charge. Opening Demo - Warm-up problems Physlet Topics
Electrostatics Notes 2 Electric Field on a Single Charge
 Electrostatics Notes 2 Electric Field on a Single Charge There are many similarities between gravitational and electrostatic forces. One such similarity is that both forces can be exerted on objects that
Electrostatics Notes 2 Electric Field on a Single Charge There are many similarities between gravitational and electrostatic forces. One such similarity is that both forces can be exerted on objects that
Work and Energy Definition of work Examples. Definition of Mechanical Energy. Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Pg 1
 Work and Energy Definition of work Examples Work and Energy Today s Agenda Definition of Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical Energy Conservative forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Pg 1
Work and Energy Definition of work Examples Work and Energy Today s Agenda Definition of Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical Energy Conservative forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Pg 1
b) What is its position when its velocity (magnitude) is largest? When it is at x=0 all the energy is kinetic.
 Question 1. The electrostatic force between two charges, Q 1 and F 1 /4 Q 2 a separated by a distance D, is F 1. What is the force between them after they are moved to a distance 2D apart? (Give in terms
Question 1. The electrostatic force between two charges, Q 1 and F 1 /4 Q 2 a separated by a distance D, is F 1. What is the force between them after they are moved to a distance 2D apart? (Give in terms
PHY481 - Outline of solutions to Homework 3
 1 PHY481 - Outline of solutions to Homework 3 Problem 3.8: We consider a charge outside a conducting sphere that is neutral. In order that the sphere be neutral, we have to introduce a new image charge
1 PHY481 - Outline of solutions to Homework 3 Problem 3.8: We consider a charge outside a conducting sphere that is neutral. In order that the sphere be neutral, we have to introduce a new image charge
Electric Potential. 1/22/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1
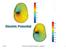 Electric Potential 1/22/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1 Announcements! First exam is next Tuesday, January 28 45 minute exam during lecture time You can bring a 5 by 8 size cheat
Electric Potential 1/22/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1 Announcements! First exam is next Tuesday, January 28 45 minute exam during lecture time You can bring a 5 by 8 size cheat
Lecture 15. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 15 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Q23.11 A solid spherical conductor has a spherical cavity in its interior. The cavity is not centered on the center of the conductor. If there is a net positive charge on
Lecture 15 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Q23.11 A solid spherical conductor has a spherical cavity in its interior. The cavity is not centered on the center of the conductor. If there is a net positive charge on
Physics 201. Professor P. Q. Hung. 311B, Physics Building. Physics 201 p. 1/1
 Physics 201 p. 1/1 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/1 Summary of last lecture Force on a point charge q 0 in the presence of an electric field: F = q 0 E(r) Physics
Physics 201 p. 1/1 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/1 Summary of last lecture Force on a point charge q 0 in the presence of an electric field: F = q 0 E(r) Physics
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Fiona Website:
 Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
Electric Potential. 1/28/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1
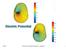 Electric Potential 1/28/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1 Notes! Correction set 1 Due Thursday evening at 10pm Name: Correction #1 RS Must answer all questions correctly to receive
Electric Potential 1/28/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1 Notes! Correction set 1 Due Thursday evening at 10pm Name: Correction #1 RS Must answer all questions correctly to receive
PH 222-2A Spring 2015
 PH 222-2A Spring 215 Electric Potential Lectures 5-6 Chapter 24 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 24 Electric Potential In this chapter we will define the electric
PH 222-2A Spring 215 Electric Potential Lectures 5-6 Chapter 24 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 24 Electric Potential In this chapter we will define the electric
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law
 Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Attention: the list of unregistered iclickers will be posted on our Web page after this lecture. From the concept of electric field flux to the calculation of
Lecture 3. Electric Field Flux, Gauss Law Attention: the list of unregistered iclickers will be posted on our Web page after this lecture. From the concept of electric field flux to the calculation of
Section 1: Electric Fields
 PHY 132 Outline of Lecture Notes i Section 1: Electric Fields A property called charge is part of the basic nature of protons and electrons. Large scale objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons.
PHY 132 Outline of Lecture Notes i Section 1: Electric Fields A property called charge is part of the basic nature of protons and electrons. Large scale objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons.
Review. Spring Semester /21/14. Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 1
 Review Spring Semester 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 1 Notes! Homework set 13 extended to Tuesday, 4/22! Remember to fill out SIRS form: https://sirsonline.msu.edu Physics for Scientists &
Review Spring Semester 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 1 Notes! Homework set 13 extended to Tuesday, 4/22! Remember to fill out SIRS form: https://sirsonline.msu.edu Physics for Scientists &
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th
![Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th](/thumbs/73/68267691.jpg) Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th Administrative Items Assignments this week: read Ch 21 and Ch 22 in the textbook complete Pre-Lecture Ch22 HW assignment complete Ch 21 HW assignment [Pre-Lecture
Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th Administrative Items Assignments this week: read Ch 21 and Ch 22 in the textbook complete Pre-Lecture Ch22 HW assignment complete Ch 21 HW assignment [Pre-Lecture
Some differences: Some basic similarities: Charges. Electrons vs. Protons 3/25/12. Chapters 22-25: Electromagnetism!
 Chapters 22-25: Electromagnetism! Electric Force vs. Gravitational Force What properties does the gravitational force depend on? What properties does the electric force depend on? F grav = G*m 1 *m 2 /d
Chapters 22-25: Electromagnetism! Electric Force vs. Gravitational Force What properties does the gravitational force depend on? What properties does the electric force depend on? F grav = G*m 1 *m 2 /d
Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field Sunday, January 31, Key concepts:
 Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy when dealing
Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy when dealing
Electric Fields and Potentials
 Electric Fields and Potentials Please do not write on the conducting sheet, and do not use more than 5 volts from the power supply. Introduction The force between electric charges is intriguing. Why are
Electric Fields and Potentials Please do not write on the conducting sheet, and do not use more than 5 volts from the power supply. Introduction The force between electric charges is intriguing. Why are
INTRODUCTION ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL ENERGY. Introduction. Electrostatic potential energy. Electric potential. for a system of point charges
 Chapter 4 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Introduction Electrostatic potential energy Electric potential for a system of point charges for a continuous charge distribution Why determine electic potential? Determination
Chapter 4 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Introduction Electrostatic potential energy Electric potential for a system of point charges for a continuous charge distribution Why determine electic potential? Determination
Potential from a distribution of charges = 1
 Lecture 7 Potential from a distribution of charges V = 1 4 0 X Smooth distribution i q i r i V = 1 4 0 X i q i r i = 1 4 0 Z r dv Calculating the electric potential from a group of point charges is usually
Lecture 7 Potential from a distribution of charges V = 1 4 0 X Smooth distribution i q i r i V = 1 4 0 X i q i r i = 1 4 0 Z r dv Calculating the electric potential from a group of point charges is usually
Introduction to Charges. BCLN PHYSICS 12 - Rev. Sept/2012
 Electrostatics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
Electrostatics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
Algebra Based Physics Electric Field, Potential Energy and Voltage
 1 Algebra Based Physics Electric Field, Potential Energy and Voltage 2016 04 19 www.njctl.org 2 Electric Field, Potential Energy and Voltage Click on the topic to go to that section Electric Field *Electric
1 Algebra Based Physics Electric Field, Potential Energy and Voltage 2016 04 19 www.njctl.org 2 Electric Field, Potential Energy and Voltage Click on the topic to go to that section Electric Field *Electric
Objects can be charged by rubbing
 Electrostatics Objects can be charged by rubbing Charge comes in two types, positive and negative; like charges repel and opposite charges attract Electric charge is conserved the arithmetic sum of the
Electrostatics Objects can be charged by rubbing Charge comes in two types, positive and negative; like charges repel and opposite charges attract Electric charge is conserved the arithmetic sum of the
is at the origin, and charge q μc be located if the net force on q
 Term: 152 Saturday, April 09, 2016 Page: 1 Q1. Three point charges are arranged along the x-axis. Charge q 3.0 0 μc 1 is at the origin, and charge q 5.0 0 μc 2 is at x = 0.200 m. Where should a third charge
Term: 152 Saturday, April 09, 2016 Page: 1 Q1. Three point charges are arranged along the x-axis. Charge q 3.0 0 μc 1 is at the origin, and charge q 5.0 0 μc 2 is at x = 0.200 m. Where should a third charge
PHYS 1444 Section 003 Lecture #6
 PHYS 1444 Section 003 Lecture #6 Thursday Sep. 13, 2012 Dr. Andrew Brandt Chapter 23: Electric Potential 1 Electric Potential Energy Concept of energy is very useful solving mechanical problems Conservation
PHYS 1444 Section 003 Lecture #6 Thursday Sep. 13, 2012 Dr. Andrew Brandt Chapter 23: Electric Potential 1 Electric Potential Energy Concept of energy is very useful solving mechanical problems Conservation
25/01/2014. Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power. Work of a force. Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (First part) Work = Force x Displacement
 5/0/04 Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power King Saud University College o Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. Phys 45 (General Physics) Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (Part ) Week n 5 This presentation
5/0/04 Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power King Saud University College o Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. Phys 45 (General Physics) Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power (Part ) Week n 5 This presentation
Some differences: Some basic similarities: Charges. Electrons vs. Protons 4/3/15. Chapters 22-25: Electromagnetism!
 Chapters 22-25: Electromagnetism! Electric Force vs. Gravitational Force What properties does the gravitational force depend on? What properties does the electric force depend on? F grav = Gm 1 m 2 /d
Chapters 22-25: Electromagnetism! Electric Force vs. Gravitational Force What properties does the gravitational force depend on? What properties does the electric force depend on? F grav = Gm 1 m 2 /d
Conductors & Electric Fields
 Conductors & Electric Fields suppose you have a conductor (that may have charge on it) any electric field in the bulk of it would cause charges to move therefore: electric field is zero inside a conductor
Conductors & Electric Fields suppose you have a conductor (that may have charge on it) any electric field in the bulk of it would cause charges to move therefore: electric field is zero inside a conductor
Practice Problem Solutions
 Chapter 14 Fields and Forces Practice Problem Solutions Student Textbook page 638 1. Conceptualize the Problem - Force, charge and distance are related by Coulomb s law. The electrostatic force, F, between
Chapter 14 Fields and Forces Practice Problem Solutions Student Textbook page 638 1. Conceptualize the Problem - Force, charge and distance are related by Coulomb s law. The electrostatic force, F, between
d) (6) If a third charge q = 2.0 µc is now placed 12.0 cm to the left of Q 1, what magnitude electric force will it experience?
 Gen. Phys. II Exam 1 - Chs. 16,17,18A - Electric Fields, Potential, Current Sep. 12, 2013 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
Gen. Phys. II Exam 1 - Chs. 16,17,18A - Electric Fields, Potential, Current Sep. 12, 2013 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
Electric Potential Energy
 Electric Potential Energy The work done on q2 (and the change in potential energy) is path independent. lecture 5.1.1 Electric Potential Energy Going to P1 to P2 independent of path taken. lecture 5.1.2
Electric Potential Energy The work done on q2 (and the change in potential energy) is path independent. lecture 5.1.1 Electric Potential Energy Going to P1 to P2 independent of path taken. lecture 5.1.2
Electric Potential (Chapter 25)
 Electric Potential (Chapter 25) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength The potential
Electric Potential (Chapter 25) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength The potential
4 Chapter. Electric Potential
 4 Chapter Electric Potential 4.1 Potential and Potential Energy... 4-3 4.2 Electric Potential in a Uniform Field... 4-7 4.3 Electric Potential due to Point Charges... 4-8 4.3.1 Potential Energy in a System
4 Chapter Electric Potential 4.1 Potential and Potential Energy... 4-3 4.2 Electric Potential in a Uniform Field... 4-7 4.3 Electric Potential due to Point Charges... 4-8 4.3.1 Potential Energy in a System
PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 1
 PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) The figure shows three electric charges labeled Q 1, Q 2, Q 3, and some electric field lines in the region surrounding the charges. What are the
PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 1 Multiple Choice Questions 1) The figure shows three electric charges labeled Q 1, Q 2, Q 3, and some electric field lines in the region surrounding the charges. What are the
3/5/2009 PHYS202 SPRING Lecture notes Electrostatics
 PHYS0 SPRING 009 Lecture notes Electrostatics 1 What is Electricity Static effects known since ancient times. Static charges can be made by rubbing certain materials together. Described by Benjamin Franklin
PHYS0 SPRING 009 Lecture notes Electrostatics 1 What is Electricity Static effects known since ancient times. Static charges can be made by rubbing certain materials together. Described by Benjamin Franklin
Solution. ANSWERS - AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Electrostatics. Answer
 NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Practice lectrostatics Solution nswer 1. y definition. Since charge is free to move around on/in a conductor, excess charges will repel each other to the outer surface
NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Practice lectrostatics Solution nswer 1. y definition. Since charge is free to move around on/in a conductor, excess charges will repel each other to the outer surface
Chapter 19 Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Sunday, January 31, Key concepts:
 Chapter 19 Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy
Chapter 19 Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy
Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law
 Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law Matter is made of particles which are or charged. The unit of charge is the ( ) Charges are, meaning that they cannot be It is thought that the total charge
Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law Matter is made of particles which are or charged. The unit of charge is the ( ) Charges are, meaning that they cannot be It is thought that the total charge
Chapter 7. Kinetic energy and work. Energy is a scalar quantity associated with the state (or condition) of one or more objects.
 Chapter 7 Kinetic energy and work 7.2 What is energy? One definition: Energy is a scalar quantity associated with the state (or condition) of one or more objects. Some characteristics: 1.Energy can be
Chapter 7 Kinetic energy and work 7.2 What is energy? One definition: Energy is a scalar quantity associated with the state (or condition) of one or more objects. Some characteristics: 1.Energy can be
- there will be midterm extra credit available (described after 2 nd midterm)
 Lecture 13: Energy & Work Today s Announcements: * Midterm # 1 still being graded. Stay tuned - there will be midterm extra credit available (described after 2 nd midterm) * Midterm # 1 solutions being
Lecture 13: Energy & Work Today s Announcements: * Midterm # 1 still being graded. Stay tuned - there will be midterm extra credit available (described after 2 nd midterm) * Midterm # 1 solutions being
You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of:
 OCR B Physics H557 Module 6: Field and Particle Physics You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 6.1: Fields (Charge and Field) Field: A potential gradient Field Strength: Indicates
OCR B Physics H557 Module 6: Field and Particle Physics You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 6.1: Fields (Charge and Field) Field: A potential gradient Field Strength: Indicates
