Introduction to Orbital-Free Density-Functional Theory. Ralf Gehrke FHI Berlin, February 8th 2005
|
|
|
- Amice McGee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intoduction to Obital-Fee Density-Functional heoy Ralf Gehke FHI Belin, Febuay 8th 005
2 Outline Basics of functional deivatives I Pinciples of Obital-fee Density-Functional heoy basics of Density-Functional heoy motivation fo OF-DF basics of the numeical implementation II Appoximations to the kinetic-enegy functional he homas-femi Appoximation he von-weizsäcke tem Linea-Response heoy Combination of F and vw he Conventional Gadient Expansion Aveage-Density Appoximation
3 Basics of functional deivatives function of multiple agument functional { y, L 0 y N } F[ y( x ] F, analogous { y i } numbe y( x numbe y i df F dyi y(x yi δ F δf δy ( x 0 δy ( x 0 x i dy i x δy( x 0 x 0 x df F y i i dy i δf δf F[ y + δy] F[ y] dx δy x δy ( x (
4 Basics of functional deivatives F [ y( x ] dx f ( y( x some ules δ F δ y [ y ] f ( x y δf δy Poof : δf [ y] F[ y + δy] F[ y] dx f ( y + δy f 44 f ( y + δy+ O( δy y [ y( x ] dx f ( y( x y ( x F, dx f ( y f dx δy { y [ y] f f f d f d f d f ( y y y dx ( ( ( y / x dx y / x dx y / x δf δy ( x ( x δf δy [ y ] f d f ( x y dx y
5 Basics of functional deivatives Poof : some ules F [ y + δ y] dx f ( y + δy, y + δy δf dx f [ y] ( x f y f d f dx δy x y dx y δf δy f y ( y + δy + δy F[ y] ( + f dx δy + y ( y( x 0 x ± f dx δy y 44 d f dx δy dx y
6 Basics of functional deivatives some ules chain ule [ G( [ y( x ] x ] F, ( x δg( [ y], x ([ y], x y( x δ F δf δg dx δy δ J [ ρ] ρ - ( ρ( d d some examples V H ([ ρ], [ ρ] ( δj d ρ - ( [ ρ] ( ( - δ J
7 Basics of DF Fist Hohenbeg-Kohn-heoem Enegy of goundstate is a mee function of the electon density ρ E ext [ ρ] F[ ρ] + d V (( ρ [ ρ ] [ ρ ] + E [ ρ ] [ ρ ] + J [ ρ ] E [ ρ ] F + ee S XC J [ ρ] S [ ] ρ [ ] ρ E XC ρ - ( ρ( d d classical coulomb inteaction kinetic enegy of a non-inteacting system with density ρ exchange-coelation enegy
8 Basics of DF Second Hohenbeg-Kohn-heoem (Vaiational Pinciple δ ( ( [ ] ( ( E ρ µ d ρ N 0 [ ] ( δe ρ µ Eule-Lagange-Equation µ chemical potential (negative of fist ionization enegy of system
9 Basics of DF What is the kinetic enegy ρ? ϕ ϕ δ ϕ ( ρ( i j ij q i 0 obitals ae solutions of single-paticle Schödinge-equations (Kohn-Sham-equations effective potential has to be detemined self-consistently S i + V [ ] intoduction of a efeence-system of non-inteacting paticles { } ϕ i KS eff ϕ i ε iϕi [ ρ] δe [ ρ] KS δj V eff ([ ρ] + XC, + + Vext VH + VXC Vext S i ϕ ϕ i i
10 Motivation fo OF-DF Intoduction of obitals in DF is not desiable matix diagonalization scales cubically with basis size many data have to be stoed duing computation the goal is to get id of KS-obitals and to expess each enegy contibution in tems of the electon chage density a functional [ ] ρ S has to be found S [ ] high accuacy fo ρ is equied since ρ is of the same ode as E[ ρ] (viial theoem E XC [ ρ] is much smalle than E[ ρ] many schemes fo appoximating E XC [ ρ] might be inappopiate fo ρ S [ ] S [ ]
11 Basics of numeical implementation Once an appopiate appoximation fo S ρ exists, how can the total enegy E ρ of the goundstate be calculated? [ ] [ ] two diffeent appoaches: diect minimization of the total enegy self-consistent calculation
12 Basics of numeical implementation diect minimization enegy has to be minimized unde the constained of constant paticle numbes Π E d ρ ρ µ ρ N ( [ ] [ ] ( vaiable substitution to ensue positivity of electon density ρ minimization of Π with steepest descend, conjugate-gadients, etc. [ ρ] ( δπ δϕ 0 ϕ ( ρ( ϕ n+ ( ϕ ( n [ ρ ] δπ τ δϕ ( ϕ ( n
13 Basics of numeical implementation self-consistent calculation add and subtact kinetic enegy of a bosonic system E [ ρ] [ ρ] + [ ρ] + J[ ρ] + E [ ρ] + d V ( ρ( [ ρ] B S XC B [ ρ] d ρ( ρ( inset total enegy expession in Eule-Lagange-equation ext B integation by pats and chain ule δb [ ] ρ ( L ϕ ϕ ( (
14 Basics of numeical implementation self-consistent calculation Eule-Lagange-equation is tansfeed to a Kohn-Sham-like equation with an additional potential tem δe [ ρ] ( µ ϕ ϕ ( δ δ S VH VXC Vext B ( ( ( µ Ĥϕ µϕ Hˆ + V H + V XC + V ext δ S δb + ( ( same solution methods can be used as in the case of the KS-scheme, but only with one obital no othogonalization
15 KS-scheme OF-scheme solve poisson-equation ( 4 ( VH πρ k solve poisson-equation ( 4 ( VH πρ k calculate exchange-coelation potential ([ ], VˆXC ρ k V ([ ρ ], Gˆ [ ρ ], ˆXC k calculate potentials δˆ ( ( ([ ] ˆ S δb, ( ([ ], k ρk ρk ceate hamiltonian ˆ H + Vˆ ˆ ˆ H + VXC + V ext ceate pseudo-hamiltonian ˆ H + Vˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ H + VXC + G + V ext Hˆ ϕ ε ϕ, i 0, L, q i i solve i solve Ĥϕ µϕ calculate new electon density ~ ρ ρ ( ~ ρ, ρ,, q k + ϕ i i 0 k + f k + 0 L ρk calculate new electon density ~ ρ ϕ ρ ( k + k + f ρk +, ρ0, L, ρk ~ self-consistency achieved? ρ ρ < ε k + k no k k + self-consistency k + ρk ε achieved? ρ < no k k + yes k : inteation index q : numbe of KS-obitals yes
16 he homas-femi appoximation conside a system, consisting of non-inteacting, fee electons H ˆ i ( ( exp k k C i i ϕ ρ ( intoducing peiodic bounday conditions ( C const. k k n π, i L x, y i i, i 8 k kx k y kz ( z π V k F / π ρ
17 he homas-femi appoximation kinetic enegy can be calculated exactly k k k F kf k F V F V k k d k k dk k 8π π k k 0 0 k 4 V π 5 kf 5 V C C, π 0 5/ ρ ( / kinetic enegy density t / V may be used to appoximate the kinetic enegy of a non-homogenous system with sufficiently slowly vaying electon density t V 5/ Cρ d t ρ( [ ]
18 he homas-femi appoximation by constuction, the F appoximation is coect in the limit of a homogenous electon gas F is coect in the limit of infinite nuclea chage ( Z flaws infinite chage density at the nucleus bad total enegies compaed to Kohn-Sham 6 algebaical decay of chage density instead of exponential ( exp( µ no binding of atoms to fom molecules o solids no shell stuctue in atoms (
19 he von-weizsäcke tem oiginally, von-weizsäcke deived intuitively a coection to the homas-femi appoximation to descibe the kinetic enegy of coe paticles to explain mass defects F + vw vw d t ρ ( ρ, the von-weizsäcke tem is exact fo one-obital systems (e.g. bosonic systems, one o two electons
20 he von-weizsäcke tem deivation fo a one-obital system, the kinetic enegy can be calculated exactly vw f d ϕ * ( ϕ( integation by pats d ϕ f g( g g ( ( ( d ρ( vw 8 ( ϕ( 0 d ρ ρ ( ( ρ ( ρ ( ρ (
21 he von-weizsäcke tem impovements compaed to F exponential decay of electonic density finite chage at the nucleus flaws in a homogenous system vw 0, but fo a one-obital system + does not epoduce the two limits S F vw F 0 attempts to impove the bidge between the two extemes: ( vw S G N F + numbe of electons ( ( empiical paametes A A G N δ + N δ N N N expeiences indicated that the pefacto of the vw-em might be too lage
22 Linea-Response heoy Why Linea-Response heoy? elationship between Linea Response and functional deivative of S can be deived coect Linea Response is impotant to descibe chage oscillations in solids definition small change in potential causes a fist-ode change of the chage density 44 ( d χ( - δν ( ( q χ( q δν ( q δν ( ( fouie tansfomation
23 Linea-Response heoy he Linea-Response Function invesion theoem of functional deivatives: δ ( - d δν ( ( δν ( ( d χ ( - δν f ( ( ( - fouie tansfomation: ( ˆ δν ( q ˆ δν χ F F ( ( ( χ( q
24 Linea-Response heoy ˆ H + V Linea-Response in the DF scheme E S + E eff eff δv eff ( ( ( δe V eff ( E S δ S ( ( ( ( δ Eeff δ eff ( δe ( µ const. χ Fˆ δ ( ( ( q goundstate S unknown!
25 ( ( ( ( q F f Lindhad - S ˆ 0 χ δ ρ Linea-Response heoy he Fee-Electon-Gas limit of the LR-function ˆ 0 H F F Lindhad, ln 4 k q k + + η η η η η π χ homogenous system due to symmety...
26 Linea-Response heoy weak logaithmic singulaity fouie tansfomation lim ( cos ( k F Fiedel oscillations singulaity is impotant to descibe the physics of a solid popely
27 Combination of F and vw goal is to put the combination of F and vw on a physical basis by consideing the linea-esponse S F + λ vw conside a nealy homogeneous electon gas with small fluctuations ρ ρ + ρ d ρ ( ( 0 ( 0 kinetic enegy may be expanded aound the aveage density S [ ρ] [ ρ ] S 0 F + d δs ( ρ0 44 const. ρ ( + linea tem vanishes d d S δ ρ ( ( ρ ˆ F χ Lindhad ( q ( ρ(
28 χ Combination of F and vw Lindhad χf λ vw k π F η q L, small η k F K, lage η η Kompaneets, Pavlovskii (957 Kizhnits (957 Le Couteu (964 Stoddat, Beattie, Mach (970 λη, small η λ kf k 9 F π + λη π λ λη, lage η
29 Combination of F and vw λ / 9 valid fo long wavelength petubation e.g. appopiate fo impuity poblems whee long wavelength components of potential ae dominant λ valid fo shot wavelength petubation e.g. appopiate fo pefect lattices flaws bad estimation of total enegy: λ oveestimation, λ / 9 undeestimation (intepolation leads to λ / 5 still no shell stuctues in atoms
30 Conventional Gadient Expansion Basic Idea include highe ode gadient coections to the kinetic enegy functional by expanding the Lindhad function to highe odes χ Lindhad 4 [ ρ] k π F η 4 η 5 L ( ρ 9 ρ( ρ ( ρ ( d ρ π ρ 8ρ ρ F 9 4 vw +L 6[ ρ] L (extemely complicated... (Hodges, 97 (Muphy, 98
31 Conventional Gadient Expansion flaws not suitable fo isolated systems with exponential decay of chage density kinetic enegy potential diveges fo ode fou and highe diveges fo ode six δ in self-consistent calculations, chage density shows wong decay behaviou linea esponse is wong, since expansion does only convege fo η < CGE is of no pactical use
32 Aveage-Density Appoximation Basic idea include non-local effects to the kinetic enegy functional example: (Gacia-Gonzales et al., PRA 54, 897 (996 S 5 [ ρ] [ ρ] + [ ρ] + d ρ( t ( ~ ρ( F F vw [ ρ] d ρ( t ( ρ( coect linea-esponse behaviou is enfoced by appopiate chose of the weight function Ω, ( Fˆ δ S ( ( χ ( q ρ 0 0! ~ ρ ( d ρ( Ω(, Lindhad
33 Aveage-Density Appoximation K Kohn-Sham symmetic ADA non-symmetic ADA FλvW Ω Ω (, Ω(, (, Ω(, non-local functionals can impove numeical esults significantly (Gacia-Gonzales et al., PRA 54, 897 (996
34 Summay goal is to get id of the Kohn-Sham-obitals to educe the computational time tade-off ae less acuate esults due to the necessity of appoximating the kinetic enegy functional state-of-the-at ae non-local functionals which impove the esults of the classical functionals significantly
35 Liteatue Wang, Y.A., Cate, E.A. 000, Obital-fee kinetic enegy density functional theoy, heoetical Methods in Condensed Phase Chemisty, S.D. Schwatz, Ed. Kluwe, 7-84 P. Gacia-Gonzales, J.E. Alvaellos and E. Chacon, Kinetic-enegy density functional: Atoms and shell stuctue, Phys. Rev. A, 54, 897 (996 M. Levy, J.P. Pedew and V. Sahni, Exact diffeential equation fo the density and ionization enegy of a many-paticle system, Phys. Rev. A, 0, 745 (984 C.H. Hodges, Quantum Coections to the homas-femi Appoximation-he Kizhnits Methods, Can. J. Phys., 54, 48 (97 R.G. Pa, S. Liu, A.A. Kugle and A. Nagy, Some identities in density-functional theoy, Phys. Rev. A, 5, 969 (995 Y. Wang and R.G. Pa, Constuction of exact Kohn-Sham obitals fom a given electon density, Phys. Rev. A, 47, R59 (99. Gal and A. Nagy, A method to get an analytical expession fo the non-inteacting kinetic enegy density functional, J. Mol. Stuc , 67 (000
Teoría del Funcional de la Densidad (Density Functional Theory)
 Teoía del Funcional de la Densidad (Density Functional Theoy) Motivation: limitations of the standad appoach based on the wave function. The electonic density n() as the key vaiable: Functionals & Thomas-Femi
Teoía del Funcional de la Densidad (Density Functional Theoy) Motivation: limitations of the standad appoach based on the wave function. The electonic density n() as the key vaiable: Functionals & Thomas-Femi
DENSITY-FUNCTIONAL THEORY, AND DENSITY-FUNCTIONAL PRACTICE
 3.320: Lectue 7 Feb 24 2005 DENSITY-FUNCTIONAL THEORY, AND DENSITY-FUNCTIONAL PRACTICE Feb 24 2005 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Mateials -- Geband Cede and Nicola Mazai Hatee-Fock Equations ψ,,..., = 1
3.320: Lectue 7 Feb 24 2005 DENSITY-FUNCTIONAL THEORY, AND DENSITY-FUNCTIONAL PRACTICE Feb 24 2005 3.320 Atomistic Modeling of Mateials -- Geband Cede and Nicola Mazai Hatee-Fock Equations ψ,,..., = 1
EM Boundary Value Problems
 EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
EM Bounday Value Poblems 10/ 9 11/ By Ilekta chistidi & Lee, Seung-Hyun A. Geneal Desciption : Maxwell Equations & Loentz Foce We want to find the equations of motion of chaged paticles. The way to do
3.320: Lecture 6 (Feb ) Photos of Hartree, Fock, Hohenberg, Kohn, and Sham removed for copyright reasons.
 3.30: Lectue 6 Feb 7 005 HARTREE-FOCK AND DFT Photos of Hatee, Fock, Hohenbeg, Kohn, and Sham emoved fo copyight easons. Feb 7 005 3.30 Atomistic Modeling of Mateials -- Geband Cede and Nicola Mazai Matix
3.30: Lectue 6 Feb 7 005 HARTREE-FOCK AND DFT Photos of Hatee, Fock, Hohenbeg, Kohn, and Sham emoved fo copyight easons. Feb 7 005 3.30 Atomistic Modeling of Mateials -- Geband Cede and Nicola Mazai Matix
Many Electron Atoms. Electrons can be put into approximate orbitals and the properties of the many electron systems can be catalogued
 Many Electon Atoms The many body poblem cannot be solved analytically. We content ouselves with developing appoximate methods that can yield quite accuate esults (but usually equie a compute). The electons
Many Electon Atoms The many body poblem cannot be solved analytically. We content ouselves with developing appoximate methods that can yield quite accuate esults (but usually equie a compute). The electons
( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.
![( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx. ( ) [ ] [ ] [ ] δf φ = F φ+δφ F. xdx.](/thumbs/90/103689049.jpg) 9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
9. LAGRANGIAN OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD In the pevious section the Lagangian and Hamiltonian of an ensemble of point paticles was developed. This appoach is based on a qt. This discete fomulation can
Quantum Mechanics II
 Quantum Mechanics II Pof. Bois Altshule Apil 25, 2 Lectue 25 We have been dicussing the analytic popeties of the S-matix element. Remembe the adial wave function was u kl () = R kl () e ik iπl/2 S l (k)e
Quantum Mechanics II Pof. Bois Altshule Apil 25, 2 Lectue 25 We have been dicussing the analytic popeties of the S-matix element. Remembe the adial wave function was u kl () = R kl () e ik iπl/2 S l (k)e
5.61 Physical Chemistry Lecture #23 page 1 MANY ELECTRON ATOMS
 5.6 Physical Chemisty Lectue #3 page MAY ELECTRO ATOMS At this point, we see that quantum mechanics allows us to undestand the helium atom, at least qualitatively. What about atoms with moe than two electons,
5.6 Physical Chemisty Lectue #3 page MAY ELECTRO ATOMS At this point, we see that quantum mechanics allows us to undestand the helium atom, at least qualitatively. What about atoms with moe than two electons,
PROBLEM SET #1 SOLUTIONS by Robert A. DiStasio Jr.
 POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
POBLM S # SOLUIONS by obet A. DiStasio J. Q. he Bon-Oppenheime appoximation is the standad way of appoximating the gound state of a molecula system. Wite down the conditions that detemine the tonic and
An Exact Solution of Navier Stokes Equation
 An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
2. Electrostatics. Dr. Rakhesh Singh Kshetrimayum 8/11/ Electromagnetic Field Theory by R. S. Kshetrimayum
 2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
2. Electostatics D. Rakhesh Singh Kshetimayum 1 2.1 Intoduction In this chapte, we will study how to find the electostatic fields fo vaious cases? fo symmetic known chage distibution fo un-symmetic known
Physics 505 Homework No. 9 Solutions S9-1
 Physics 505 Homewok No 9 s S9-1 1 As pomised, hee is the tick fo summing the matix elements fo the Stak effect fo the gound state of the hydogen atom Recall, we need to calculate the coection to the gound
Physics 505 Homewok No 9 s S9-1 1 As pomised, hee is the tick fo summing the matix elements fo the Stak effect fo the gound state of the hydogen atom Recall, we need to calculate the coection to the gound
Numerical Integration
 MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
MCEN 473/573 Chapte 0 Numeical Integation Fall, 2006 Textbook, 0.4 and 0.5 Isopaametic Fomula Numeical Integation [] e [ ] T k = h B [ D][ B] e B Jdsdt In pactice, the element stiffness is calculated numeically.
Quantum Chemistry Notes:
 Quantum Chemisty otes: Hatee-Fock equations The Hatee-Fock method is the undelying appoximation to nealy all methods of computational chemisty, both ab initio and semi-empiical. Theefoe, a clea undestanding
Quantum Chemisty otes: Hatee-Fock equations The Hatee-Fock method is the undelying appoximation to nealy all methods of computational chemisty, both ab initio and semi-empiical. Theefoe, a clea undestanding
Physics 506 Winter 2006 Homework Assignment #9 Solutions
 Physics 506 Winte 2006 Homewok Assignment #9 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.2, 12.9, 12.13, 12.14 12.2 a) Show fom Hamilton s pinciple that Lagangians that diffe only by a total time deivative
Physics 506 Winte 2006 Homewok Assignment #9 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.2, 12.9, 12.13, 12.14 12.2 a) Show fom Hamilton s pinciple that Lagangians that diffe only by a total time deivative
Question 1: The dipole
 Septembe, 08 Conell Univesity, Depatment of Physics PHYS 337, Advance E&M, HW #, due: 9/5/08, :5 AM Question : The dipole Conside a system as discussed in class and shown in Fig.. in Heald & Maion.. Wite
Septembe, 08 Conell Univesity, Depatment of Physics PHYS 337, Advance E&M, HW #, due: 9/5/08, :5 AM Question : The dipole Conside a system as discussed in class and shown in Fig.. in Heald & Maion.. Wite
Let us next consider how one can calculate one- electron elements of the long- range nuclear- electron potential:
 Hatee- Fock Long Range In the following assume the patition of 1/ into shot ange and long ance components 1 efc( / a) ef ( / a) + Hee a is a paamete detemining the patitioning between shot ange and long
Hatee- Fock Long Range In the following assume the patition of 1/ into shot ange and long ance components 1 efc( / a) ef ( / a) + Hee a is a paamete detemining the patitioning between shot ange and long
1D2G - Numerical solution of the neutron diffusion equation
 DG - Numeical solution of the neuton diffusion equation Y. Danon Daft: /6/09 Oveview A simple numeical solution of the neuton diffusion equation in one dimension and two enegy goups was implemented. Both
DG - Numeical solution of the neuton diffusion equation Y. Danon Daft: /6/09 Oveview A simple numeical solution of the neuton diffusion equation in one dimension and two enegy goups was implemented. Both
Perturbation to Symmetries and Adiabatic Invariants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of Relative Motion
 Commun. Theo. Phys. Beijing, China) 43 25) pp. 577 581 c Intenational Academic Publishes Vol. 43, No. 4, Apil 15, 25 Petubation to Symmeties and Adiabatic Invaiants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of
Commun. Theo. Phys. Beijing, China) 43 25) pp. 577 581 c Intenational Academic Publishes Vol. 43, No. 4, Apil 15, 25 Petubation to Symmeties and Adiabatic Invaiants of Nonholonomic Dynamical System of
Problem Set 10 Solutions
 Chemisty 6 D. Jean M. Standad Poblem Set 0 Solutions. Give the explicit fom of the Hamiltonian opeato (in atomic units) fo the lithium atom. You expession should not include any summations (expand them
Chemisty 6 D. Jean M. Standad Poblem Set 0 Solutions. Give the explicit fom of the Hamiltonian opeato (in atomic units) fo the lithium atom. You expession should not include any summations (expand them
Conjugate Gradient Methods. Michael Bader. Summer term 2012
 Gadient Methods Outlines Pat I: Quadatic Foms and Steepest Descent Pat II: Gadients Pat III: Summe tem 2012 Pat I: Quadatic Foms and Steepest Descent Outlines Pat I: Quadatic Foms and Steepest Descent
Gadient Methods Outlines Pat I: Quadatic Foms and Steepest Descent Pat II: Gadients Pat III: Summe tem 2012 Pat I: Quadatic Foms and Steepest Descent Outlines Pat I: Quadatic Foms and Steepest Descent
Modeling Fermi Level Effects in Atomistic Simulations
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Poc. Vol. 717 Mateials Reseach Society Modeling Femi Level Effects in Atomistic Simulations Zudian Qin and Scott T. Dunham Depatment of Electical Engineeing, Univesity of Washington,
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Poc. Vol. 717 Mateials Reseach Society Modeling Femi Level Effects in Atomistic Simulations Zudian Qin and Scott T. Dunham Depatment of Electical Engineeing, Univesity of Washington,
A Relativistic Electron in a Coulomb Potential
 A Relativistic Electon in a Coulomb Potential Alfed Whitehead Physics 518, Fall 009 The Poblem Solve the Diac Equation fo an electon in a Coulomb potential. Identify the conseved quantum numbes. Specify
A Relativistic Electon in a Coulomb Potential Alfed Whitehead Physics 518, Fall 009 The Poblem Solve the Diac Equation fo an electon in a Coulomb potential. Identify the conseved quantum numbes. Specify
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
Exceptional regular singular points of second-order ODEs. 1. Solving second-order ODEs
 (May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
(May 14, 2011 Exceptional egula singula points of second-ode ODEs Paul Gaett gaett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ gaett/ 1. Solving second-ode ODEs 2. Examples 3. Convegence Fobenius method fo solving
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Classical Mechanics Homework set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions
 Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
Classical Mechanics Homewok set 7, due Nov 8th: Solutions 1. Do deivation 8.. It has been asked what effect does a total deivative as a function of q i, t have on the Hamiltonian. Thus, lets us begin with
But for simplicity, we ll define significant as the time it takes a star to lose all memory of its original trajectory, i.e.,
 Stella elaxation Time [Chandasekha 1960, Pinciples of Stella Dynamics, Chap II] [Ostike & Davidson 1968, Ap.J., 151, 679] Do stas eve collide? Ae inteactions between stas (as opposed to the geneal system
Stella elaxation Time [Chandasekha 1960, Pinciples of Stella Dynamics, Chap II] [Ostike & Davidson 1968, Ap.J., 151, 679] Do stas eve collide? Ae inteactions between stas (as opposed to the geneal system
Solutions. V in = ρ 0. r 2 + a r 2 + b, where a and b are constants. The potential at the center of the atom has to be finite, so a = 0. r 2 + b.
 Solutions. Plum Pudding Model (a) Find the coesponding electostatic potential inside and outside the atom. Fo R The solution can be found by integating twice, 2 V in = ρ 0 ε 0. V in = ρ 0 6ε 0 2 + a 2
Solutions. Plum Pudding Model (a) Find the coesponding electostatic potential inside and outside the atom. Fo R The solution can be found by integating twice, 2 V in = ρ 0 ε 0. V in = ρ 0 6ε 0 2 + a 2
is the instantaneous position vector of any grid point or fluid
 Absolute inetial, elative inetial and non-inetial coodinates fo a moving but non-defoming contol volume Tao Xing, Pablo Caica, and Fed Sten bjective Deive and coelate the govening equations of motion in
Absolute inetial, elative inetial and non-inetial coodinates fo a moving but non-defoming contol volume Tao Xing, Pablo Caica, and Fed Sten bjective Deive and coelate the govening equations of motion in
DFT functionals in WIEN2k
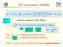 d E xc DFT functionals in WIEN2k ] [ 2 1 ] [ xc ext o E d d d V T E 1-electon equations Kohn Sham } 2 1 { 2 V V V i i i xc C ext E F i i 2 vay de/d=0 -Z/ E xc = E x + E c : exchange-coelation enegy V xc
d E xc DFT functionals in WIEN2k ] [ 2 1 ] [ xc ext o E d d d V T E 1-electon equations Kohn Sham } 2 1 { 2 V V V i i i xc C ext E F i i 2 vay de/d=0 -Z/ E xc = E x + E c : exchange-coelation enegy V xc
EQUATIONS OF MOTION LUCA GUIDO MOLINARI
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION LUCA GUIDO MOLINARI 1. Equation of motion of destuction opeatos Conside a system of bosons o femions descibed by a Hamiltonian H = H 1 + H 2, whee H 1 and H 2 ae espectively the one
EQUATIONS OF MOTION LUCA GUIDO MOLINARI 1. Equation of motion of destuction opeatos Conside a system of bosons o femions descibed by a Hamiltonian H = H 1 + H 2, whee H 1 and H 2 ae espectively the one
Adiabatic evolution of the constants of motion in resonance (I)
 Adiabatic evolution of the constants of motion in esonance (I) BH Gavitational 重 力力波 waves Takahio Tanaka (YITP, Kyoto univesity) R. Fujita, S. Isoyama, H. Nakano, N. Sago PTEP 013 (013) 6, 063E01 e-pint:
Adiabatic evolution of the constants of motion in esonance (I) BH Gavitational 重 力力波 waves Takahio Tanaka (YITP, Kyoto univesity) R. Fujita, S. Isoyama, H. Nakano, N. Sago PTEP 013 (013) 6, 063E01 e-pint:
Annihilation of Relativistic Positrons in Single Crystal with production of One Photon
 Annihilation of Relativistic Positons in Single Cystal with poduction of One Photon Kalashnikov N.P.,Mazu E.A.,Olczak A.S. National Reseach Nuclea Univesity MEPhI (Moscow Engineeing Physics Institute),
Annihilation of Relativistic Positons in Single Cystal with poduction of One Photon Kalashnikov N.P.,Mazu E.A.,Olczak A.S. National Reseach Nuclea Univesity MEPhI (Moscow Engineeing Physics Institute),
Plasmonics and non-local interactions from TDDFT: graphene and metal surfaces
 Plasmonics and non-local inteactions fom TDDFT: gaphene and metal sufaces Thomas Olsen Cente fo Atomic-scale Mateials Design CAMD Depatment of Physics Technical Univesity of Denmak Outline Linea esponse
Plasmonics and non-local inteactions fom TDDFT: gaphene and metal sufaces Thomas Olsen Cente fo Atomic-scale Mateials Design CAMD Depatment of Physics Technical Univesity of Denmak Outline Linea esponse
Nuclear and Particle Physics - Lecture 20 The shell model
 1 Intoduction Nuclea and Paticle Physics - Lectue 0 The shell model It is appaent that the semi-empiical mass fomula does a good job of descibing tends but not the non-smooth behaviou of the binding enegy.
1 Intoduction Nuclea and Paticle Physics - Lectue 0 The shell model It is appaent that the semi-empiical mass fomula does a good job of descibing tends but not the non-smooth behaviou of the binding enegy.
Nuclear models: Shell model
 Lectue 3 Nuclea models: Shell model WS0/3: Intoduction to Nuclea and Paticle Physics,, Pat I Nuclea models Nuclea models Models with stong inteaction between the nucleons Liquid dop model α-paticle model
Lectue 3 Nuclea models: Shell model WS0/3: Intoduction to Nuclea and Paticle Physics,, Pat I Nuclea models Nuclea models Models with stong inteaction between the nucleons Liquid dop model α-paticle model
3. Electromagnetic Waves II
 Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Right-handed screw dislocation in an isotropic solid
 Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Nuclear size corrections to the energy levels of single-electron atoms
 Nuclea size coections to the enegy levels of single-electon atoms Babak Nadii Nii a eseach Institute fo Astonomy and Astophysics of Maagha (IAAM IAN P. O. Box: 554-44. Abstact A study is made of nuclea
Nuclea size coections to the enegy levels of single-electon atoms Babak Nadii Nii a eseach Institute fo Astonomy and Astophysics of Maagha (IAAM IAN P. O. Box: 554-44. Abstact A study is made of nuclea
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Circuit Synthesizable Guaranteed Passive Modeling for Multiport Structures
 Cicuit Synthesizable Guaanteed Passive Modeling fo Multipot Stuctues Zohaib Mahmood, Luca Daniel Massachusetts Institute of Technology BMAS Septembe-23, 2010 Outline Motivation fo Compact Dynamical Passive
Cicuit Synthesizable Guaanteed Passive Modeling fo Multipot Stuctues Zohaib Mahmood, Luca Daniel Massachusetts Institute of Technology BMAS Septembe-23, 2010 Outline Motivation fo Compact Dynamical Passive
8 Separation of Variables in Other Coordinate Systems
 8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
8 Sepaation of Vaiables in Othe Coodinate Systems Fo the method of sepaation of vaiables to succeed you need to be able to expess the poblem at hand in a coodinate system in which the physical boundaies
2. Plane Elasticity Problems
 S0 Solid Mechanics Fall 009. Plane lasticity Poblems Main Refeence: Theoy of lasticity by S.P. Timoshenko and J.N. Goodie McGaw-Hill New Yok. Chaptes 3..1 The plane-stess poblem A thin sheet of an isotopic
S0 Solid Mechanics Fall 009. Plane lasticity Poblems Main Refeence: Theoy of lasticity by S.P. Timoshenko and J.N. Goodie McGaw-Hill New Yok. Chaptes 3..1 The plane-stess poblem A thin sheet of an isotopic
2 Lecture 2: The Bohr atom (1913) and the Schrödinger equation (1925)
 1 Lectue 1: The beginnings of quantum physics 1. The Sten-Gelach expeiment. Atomic clocks 3. Planck 1900, blackbody adiation, and E ω 4. Photoelectic effect 5. Electon diffaction though cystals, de Boglie
1 Lectue 1: The beginnings of quantum physics 1. The Sten-Gelach expeiment. Atomic clocks 3. Planck 1900, blackbody adiation, and E ω 4. Photoelectic effect 5. Electon diffaction though cystals, de Boglie
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW)
 PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
PHYS 301 HOMEWORK #10 (Optional HW) 1. Conside the Legende diffeential equation : 1 - x 2 y'' - 2xy' + m m + 1 y = 0 Make the substitution x = cos q and show the Legende equation tansfoms into d 2 y 2
you of a spring. The potential energy for a spring is given by the parabola U( x)
 Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
Small oscillations The theoy of small oscillations is an extemely impotant topic in mechanics. Conside a system that has a potential enegy diagam as below: U B C A x Thee ae thee points of stable equilibium,
Gradient-based Neural Network for Online Solution of Lyapunov Matrix Equation with Li Activation Function
 Intenational Confeence on Infomation echnology and Management Innovation (ICIMI 05) Gadient-based Neual Netwok fo Online Solution of Lyapunov Matix Equation with Li Activation unction Shiheng Wang, Shidong
Intenational Confeence on Infomation echnology and Management Innovation (ICIMI 05) Gadient-based Neual Netwok fo Online Solution of Lyapunov Matix Equation with Li Activation unction Shiheng Wang, Shidong
Local Density Functional Theory for Superfluid Fermionic Systems. The Unitary Fermi Gas
 Local Density unctional Theoy fo Supefluid emionic Systems The Unitay emi Gas Unitay emi gas in a hamonic tap Chang and Betsch, physics/070390 Outline: What is a unitay emi gas Vey bief/sewed summay of
Local Density unctional Theoy fo Supefluid emionic Systems The Unitay emi Gas Unitay emi gas in a hamonic tap Chang and Betsch, physics/070390 Outline: What is a unitay emi gas Vey bief/sewed summay of
Chem 453/544 Fall /08/03. Exam #1 Solutions
 Chem 453/544 Fall 3 /8/3 Exam # Solutions. ( points) Use the genealized compessibility diagam povided on the last page to estimate ove what ange of pessues A at oom tempeatue confoms to the ideal gas law
Chem 453/544 Fall 3 /8/3 Exam # Solutions. ( points) Use the genealized compessibility diagam povided on the last page to estimate ove what ange of pessues A at oom tempeatue confoms to the ideal gas law
Germán Sierra Instituto de Física Teórica CSIC-UAM, Madrid, Spain
 Gemán Siea Instituto de Física Teóica CSIC-UAM, Madid, Spain Wo in pogess done in collaboation with J. Lins and S. Y. Zhao (Univ. Queensland, Austalia) and M. Ibañez (IFT, Madid) Taled pesented at the
Gemán Siea Instituto de Física Teóica CSIC-UAM, Madid, Spain Wo in pogess done in collaboation with J. Lins and S. Y. Zhao (Univ. Queensland, Austalia) and M. Ibañez (IFT, Madid) Taled pesented at the
Is there a magnification paradox in gravitational lensing?
 Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? Olaf Wucknitz wucknitz@asto.uni-bonn.de Astophysics semina/colloquium, Potsdam, 6 Novembe 7 Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? gavitational
Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? Olaf Wucknitz wucknitz@asto.uni-bonn.de Astophysics semina/colloquium, Potsdam, 6 Novembe 7 Is thee a magnification paadox in gavitational ing? gavitational
Single Particle State AB AB
 LECTURE 3 Maxwell Boltzmann, Femi, and Bose Statistics Suppose we have a gas of N identical point paticles in a box of volume V. When we say gas, we mean that the paticles ae not inteacting with one anothe.
LECTURE 3 Maxwell Boltzmann, Femi, and Bose Statistics Suppose we have a gas of N identical point paticles in a box of volume V. When we say gas, we mean that the paticles ae not inteacting with one anothe.
Introduction to General Relativity 2
 Intoduction to Geneal Relativity 2 Geneal Relativity Diffeential geomety Paallel tanspot How to compute metic? Deviation of geodesics Einstein equations Consequences Tests of Geneal Relativity Sola system
Intoduction to Geneal Relativity 2 Geneal Relativity Diffeential geomety Paallel tanspot How to compute metic? Deviation of geodesics Einstein equations Consequences Tests of Geneal Relativity Sola system
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Question Bank. Section A. is skew-hermitian matrix. is diagonalizable. (, ) , Evaluate (, ) 12 about = 1 and = Find, if
 Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Calculation of Quark-antiquark Potential Coefficient and Charge Radius of Light Mesons
 Applied Physics Reseach ISSN: 96-9639 Vol., No., May E-ISSN: 96-9647 Calculation of Quak-antiquak Potential Coefficient and Chage Radius of Light Mesons M.R. Shojaei (Coesponding autho ) Depatment of Physics
Applied Physics Reseach ISSN: 96-9639 Vol., No., May E-ISSN: 96-9647 Calculation of Quak-antiquak Potential Coefficient and Chage Radius of Light Mesons M.R. Shojaei (Coesponding autho ) Depatment of Physics
Contact impedance of grounded and capacitive electrodes
 Abstact Contact impedance of gounded and capacitive electodes Andeas Hödt Institut fü Geophysik und extateestische Physik, TU Baunschweig The contact impedance of electodes detemines how much cuent can
Abstact Contact impedance of gounded and capacitive electodes Andeas Hödt Institut fü Geophysik und extateestische Physik, TU Baunschweig The contact impedance of electodes detemines how much cuent can
ON THE TWO-BODY PROBLEM IN QUANTUM MECHANICS
 ON THE TWO-BODY PROBLEM IN QUANTUM MECHANICS L. MICU Hoia Hulubei National Institute fo Physics and Nuclea Engineeing, P.O. Box MG-6, RO-0775 Buchaest-Maguele, Romania, E-mail: lmicu@theoy.nipne.o (Received
ON THE TWO-BODY PROBLEM IN QUANTUM MECHANICS L. MICU Hoia Hulubei National Institute fo Physics and Nuclea Engineeing, P.O. Box MG-6, RO-0775 Buchaest-Maguele, Romania, E-mail: lmicu@theoy.nipne.o (Received
Homework # 3 Solution Key
 PHYSICS 631: Geneal Relativity Homewok # 3 Solution Key 1. You e on you hono not to do this one by hand. I ealize you can use a compute o simply look it up. Please don t. In a flat space, the metic in
PHYSICS 631: Geneal Relativity Homewok # 3 Solution Key 1. You e on you hono not to do this one by hand. I ealize you can use a compute o simply look it up. Please don t. In a flat space, the metic in
AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism 2001 Scoring Guidelines
 AP Physics C: Electicity and Magnetism 1 Scoing Guidelines The mateials included in these files ae intended fo non-commecial use by AP teaches fo couse and exam pepaation; pemission fo any othe use must
AP Physics C: Electicity and Magnetism 1 Scoing Guidelines The mateials included in these files ae intended fo non-commecial use by AP teaches fo couse and exam pepaation; pemission fo any othe use must
Appendix B The Relativistic Transformation of Forces
 Appendix B The Relativistic Tansfomation of oces B. The ou-foce We intoduced the idea of foces in Chapte 3 whee we saw that the change in the fou-momentum pe unit time is given by the expession d d w x
Appendix B The Relativistic Tansfomation of oces B. The ou-foce We intoduced the idea of foces in Chapte 3 whee we saw that the change in the fou-momentum pe unit time is given by the expession d d w x
Mobility of atoms and diffusion. Einstein relation.
 Mobility of atoms and diffusion. Einstein elation. In M simulation we can descibe the mobility of atoms though the mean squae displacement that can be calculated as N 1 MS ( t ( i ( t i ( 0 N The MS contains
Mobility of atoms and diffusion. Einstein elation. In M simulation we can descibe the mobility of atoms though the mean squae displacement that can be calculated as N 1 MS ( t ( i ( t i ( 0 N The MS contains
d 2 x 0a d d =0. Relative to an arbitrary (accelerating frame) specified by x a = x a (x 0b ), the latter becomes: d 2 x a d 2 + a dx b dx c
 Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Chapte 6 Geneal Relativity 6.1 Towads the Einstein equations Thee ae seveal ways of motivating the Einstein equations. The most natual is pehaps though consideations involving the Equivalence Pinciple.
Scattering in Three Dimensions
 Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
Scatteing in Thee Dimensions Scatteing expeiments ae an impotant souce of infomation about quantum systems, anging in enegy fom vey low enegy chemical eactions to the highest possible enegies at the LHC.
MA557/MA578/CS557. Lecture 14. Prof. Tim Warburton. Spring
 MA557/MA578/CS557 Lectue 4 Sping 3 Pof. Tim Wabuton timwa@math.unm.edu Matlab Notes To ceate a symbolic vaiable (say theta) use the command: theta = sym( theta ); Example manipulation: Matlab cont To evaluate
MA557/MA578/CS557 Lectue 4 Sping 3 Pof. Tim Wabuton timwa@math.unm.edu Matlab Notes To ceate a symbolic vaiable (say theta) use the command: theta = sym( theta ); Example manipulation: Matlab cont To evaluate
A thermodynamic degree of freedom solution to the galaxy cluster problem of MOND. Abstract
 A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
A themodynamic degee of feedom solution to the galaxy cluste poblem of MOND E.P.J. de Haas (Paul) Nijmegen, The Nethelands (Dated: Octobe 23, 2015) Abstact In this pape I discus the degee of feedom paamete
Physics 221 Lecture 41 Nonlinear Absorption and Refraction
 Physics 221 Lectue 41 Nonlinea Absoption and Refaction Refeences Meye-Aendt, pp. 97-98. Boyd, Nonlinea Optics, 1.4 Yaiv, Optical Waves in Cystals, p. 22 (Table of cystal symmeties) 1. Intoductoy Remaks.
Physics 221 Lectue 41 Nonlinea Absoption and Refaction Refeences Meye-Aendt, pp. 97-98. Boyd, Nonlinea Optics, 1.4 Yaiv, Optical Waves in Cystals, p. 22 (Table of cystal symmeties) 1. Intoductoy Remaks.
Electromagnetic scattering. Graduate Course Electrical Engineering (Communications) 1 st Semester, Sharif University of Technology
 Electomagnetic scatteing Gaduate Couse Electical Engineeing (Communications) 1 st Semeste, 1390-1391 Shaif Univesity of Technology Geneal infomation Infomation about the instucto: Instucto: Behzad Rejaei
Electomagnetic scatteing Gaduate Couse Electical Engineeing (Communications) 1 st Semeste, 1390-1391 Shaif Univesity of Technology Geneal infomation Infomation about the instucto: Instucto: Behzad Rejaei
This gives rise to the separable equation dr/r = 2 cot θ dθ which may be integrated to yield r(θ) = R sin 2 θ (3)
 Physics 506 Winte 2008 Homewok Assignment #10 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.10, 12.13, 12.16, 12.19 12.10 A chaged paticle finds itself instantaneously in the equatoial plane of the eath s magnetic
Physics 506 Winte 2008 Homewok Assignment #10 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.10, 12.13, 12.16, 12.19 12.10 A chaged paticle finds itself instantaneously in the equatoial plane of the eath s magnetic
c n ψ n (r)e ient/ h (2) where E n = 1 mc 2 α 2 Z 2 ψ(r) = c n ψ n (r) = c n = ψn(r)ψ(r)d 3 x e 2r/a0 1 πa e 3r/a0 r 2 dr c 1 2 = 2 9 /3 6 = 0.
 Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
Poblem {a} Fo t : Ψ(, t ψ(e iet/ h ( whee E mc α (α /7 ψ( e /a πa Hee we have used the gound state wavefunction fo Z. Fo t, Ψ(, t can be witten as a supeposition of Z hydogenic wavefunctions ψ n (: Ψ(,
Many Electron Theory: Particles and holes. Unitary transformations.
 Many Electon Theoy: Paticles and holes. Unitay tansfomations. Continued notes fo a wokgoup Septembe-Octobe 00. Notes pepaed by Jan Lindebeg, Septembe 00 Heny Eying Cente fo Theoetical Chemisty Equivalencies
Many Electon Theoy: Paticles and holes. Unitay tansfomations. Continued notes fo a wokgoup Septembe-Octobe 00. Notes pepaed by Jan Lindebeg, Septembe 00 Heny Eying Cente fo Theoetical Chemisty Equivalencies
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Lecture 5 Solving Problems using Green s Theorem. 1. Show how Green s theorem can be used to solve general electrostatic problems 2.
 Lectue 5 Solving Poblems using Geen s Theoem Today s topics. Show how Geen s theoem can be used to solve geneal electostatic poblems. Dielectics A well known application of Geen s theoem. Last time we
Lectue 5 Solving Poblems using Geen s Theoem Today s topics. Show how Geen s theoem can be used to solve geneal electostatic poblems. Dielectics A well known application of Geen s theoem. Last time we
Scientific Computing II
 Scientific Computing II Conjugate Gadient Methods Michael Bade Summe 2014 Conjugate Gadient Methods, Summe 2014 1 Families of Iteative Solves elaxation methods: Jacobi-, Gauss-Seidel-Relaxation,... Ove-Relaxation-Methods
Scientific Computing II Conjugate Gadient Methods Michael Bade Summe 2014 Conjugate Gadient Methods, Summe 2014 1 Families of Iteative Solves elaxation methods: Jacobi-, Gauss-Seidel-Relaxation,... Ove-Relaxation-Methods
by numerous studies); ii) MSWT spectrum is symmetric with respect to point while numerical methods give asymmetrical spectrum with gap = = 2.
 SPIN-WAVE THEORY FOR S= ANTIFERROMAGNETIC ISOTROPIC CHAIN D. V. Spiin V.I. Venadsii Tauida National Univesity, Yaltinsaya st. 4, Simfeopol, 957, Cimea, Uaine E-mail: spiin@cimea.edu, spiin@tnu.cimea.ua
SPIN-WAVE THEORY FOR S= ANTIFERROMAGNETIC ISOTROPIC CHAIN D. V. Spiin V.I. Venadsii Tauida National Univesity, Yaltinsaya st. 4, Simfeopol, 957, Cimea, Uaine E-mail: spiin@cimea.edu, spiin@tnu.cimea.ua
( n x ( ) Last Time Exam 3 results. Question. 3-D particle in box: summary. Modified Bohr model. 3-D Hydrogen atom. r n. = n 2 a o
 Last Time Exam 3 esults Quantum tunneling 3-dimensional wave functions Deceasing paticle size Quantum dots paticle in box) This week s honos lectue: Pof. ad histian, Positon Emission Tomogaphy Tue. Dec.
Last Time Exam 3 esults Quantum tunneling 3-dimensional wave functions Deceasing paticle size Quantum dots paticle in box) This week s honos lectue: Pof. ad histian, Positon Emission Tomogaphy Tue. Dec.
f(k) e p 2 (k) e iax 2 (k a) r 2 e a x a a 2 + k 2 e a2 x 1 2 H(x) ik p (k) 4 r 3 cos Y 2 = 4
 Fouie tansfom pais: f(x) 1 f(k) e p 2 (k) p e iax 2 (k a) 2 e a x a a 2 + k 2 e a2 x 1 2, a > 0 a p k2 /4a2 e 2 1 H(x) ik p 2 + 2 (k) The fist few Y m Y 0 0 = Y 0 1 = Y ±1 1 = l : 1 Y2 0 = 4 3 ±1 cos Y
Fouie tansfom pais: f(x) 1 f(k) e p 2 (k) p e iax 2 (k a) 2 e a x a a 2 + k 2 e a2 x 1 2, a > 0 a p k2 /4a2 e 2 1 H(x) ik p 2 + 2 (k) The fist few Y m Y 0 0 = Y 0 1 = Y ±1 1 = l : 1 Y2 0 = 4 3 ±1 cos Y
A Lattice Energy Calculation for LiH
 A Lattice Enegy Calculation fo LiH Fank Riou Lithium hyie is a white cystalline soli with the face-centee cubic cystal stuctue (see lattice shown below). The moel fo LiH(s) popose in this stuy constists
A Lattice Enegy Calculation fo LiH Fank Riou Lithium hyie is a white cystalline soli with the face-centee cubic cystal stuctue (see lattice shown below). The moel fo LiH(s) popose in this stuy constists
6 Matrix Concentration Bounds
 6 Matix Concentation Bounds Concentation bounds ae inequalities that bound pobabilities of deviations by a andom vaiable fom some value, often its mean. Infomally, they show the pobability that a andom
6 Matix Concentation Bounds Concentation bounds ae inequalities that bound pobabilities of deviations by a andom vaiable fom some value, often its mean. Infomally, they show the pobability that a andom
Analytic Evaluation of two-electron Atomic Integrals involving Extended Hylleraas-CI functions with STO basis
 Analytic Evaluation of two-electon Atomic Integals involving Extended Hylleaas-CI functions with STO basis B PADHY (Retd.) Faculty Membe Depatment of Physics, Khalikote (Autonomous) College, Behampu-760001,
Analytic Evaluation of two-electon Atomic Integals involving Extended Hylleaas-CI functions with STO basis B PADHY (Retd.) Faculty Membe Depatment of Physics, Khalikote (Autonomous) College, Behampu-760001,
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Method for Approximating Irrational Numbers
 Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
Method fo Appoximating Iational Numbes Eic Reichwein Depatment of Physics Univesity of Califonia, Santa Cuz June 6, 0 Abstact I will put foth an algoithm fo poducing inceasingly accuate ational appoximations
The evolution of the phase space density of particle beams in external fields
 The evolution of the phase space density of paticle beams in extenal fields E.G.Bessonov Lebedev Phys. Inst. RAS, Moscow, Russia, COOL 09 Wokshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics August 31 Septembe 4,
The evolution of the phase space density of paticle beams in extenal fields E.G.Bessonov Lebedev Phys. Inst. RAS, Moscow, Russia, COOL 09 Wokshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics August 31 Septembe 4,
b Ψ Ψ Principles of Organic Chemistry lecture 22, page 1
 Pinciples of Oganic Chemisty lectue, page. Basis fo LCAO and Hückel MO Theoy.. Souces... Hypephysics online. http://hypephysics.phy-ast.gsu.edu/hbase/quantum/qm.html#c... Zimmeman, H. E., Quantum Mechanics
Pinciples of Oganic Chemisty lectue, page. Basis fo LCAO and Hückel MO Theoy.. Souces... Hypephysics online. http://hypephysics.phy-ast.gsu.edu/hbase/quantum/qm.html#c... Zimmeman, H. E., Quantum Mechanics
Computational Methods of Solid Mechanics. Project report
 Computational Methods of Solid Mechanics Poject epot Due on Dec. 6, 25 Pof. Allan F. Bowe Weilin Deng Simulation of adhesive contact with molecula potential Poject desciption In the poject, we will investigate
Computational Methods of Solid Mechanics Poject epot Due on Dec. 6, 25 Pof. Allan F. Bowe Weilin Deng Simulation of adhesive contact with molecula potential Poject desciption In the poject, we will investigate
Pseudopotentials (Part I):
 seudopotentials at : eog nstitut fü Mateialphysik and ente fo omputational Mateials cience nivesität ien, ensengasse, A- ien, Austia b-initio ienna ackage imulation, OONAL A age Oveview the vey basics
seudopotentials at : eog nstitut fü Mateialphysik and ente fo omputational Mateials cience nivesität ien, ensengasse, A- ien, Austia b-initio ienna ackage imulation, OONAL A age Oveview the vey basics
Transverse Wakefield in a Dielectric Tube with Frequency Dependent Dielectric Constant
 ARDB-378 Bob Siemann & Alex Chao /4/5 Page of 8 Tansvese Wakefield in a Dielectic Tube with Fequency Dependent Dielectic Constant This note is a continuation of ARDB-368 that is now extended to the tansvese
ARDB-378 Bob Siemann & Alex Chao /4/5 Page of 8 Tansvese Wakefield in a Dielectic Tube with Fequency Dependent Dielectic Constant This note is a continuation of ARDB-368 that is now extended to the tansvese
Doublet structure of Alkali spectra:
 Doublet stuctue of : Caeful examination of the specta of alkali metals shows that each membe of some of the seies ae closed doublets. Fo example, sodium yellow line, coesponding to 3p 3s tansition, is
Doublet stuctue of : Caeful examination of the specta of alkali metals shows that each membe of some of the seies ae closed doublets. Fo example, sodium yellow line, coesponding to 3p 3s tansition, is
The Unitary Fermi Gas
 Local Density unctional Theoy fo Supefluid emionic Systems The Unitay emi Gas A. Bulgac, Univesity of Washington axiv:cond-mat/070356, PRA, R, in pess (007 Unitay emi gas in a hamonic tap Chang and Betsch,
Local Density unctional Theoy fo Supefluid emionic Systems The Unitay emi Gas A. Bulgac, Univesity of Washington axiv:cond-mat/070356, PRA, R, in pess (007 Unitay emi gas in a hamonic tap Chang and Betsch,
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Electricity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination
 E&M poblems Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Depatment of Physics Electicity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination Januay 3, 6 9. am : pm Full cedit can be achieved fom completely coect answes to 4 questions.
E&M poblems Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Depatment of Physics Electicity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination Januay 3, 6 9. am : pm Full cedit can be achieved fom completely coect answes to 4 questions.
Preliminary Exam: Quantum Physics 1/14/2011, 9:00-3:00
 Peliminay Exam: Quantum Physics /4/ 9:-: Answe a total of SIX questions of which at least TWO ae fom section A and at least THREE ae fom section B Fo you answes you can use eithe the blue books o individual
Peliminay Exam: Quantum Physics /4/ 9:-: Answe a total of SIX questions of which at least TWO ae fom section A and at least THREE ae fom section B Fo you answes you can use eithe the blue books o individual
, and the curve BC is symmetrical. Find also the horizontal force in x-direction on one side of the body. h C
 Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Dynamics (Stömningsläa), 2013-05-31, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the textbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Dynamics (Stömningsläa), 2013-05-31, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the textbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
Geometry of the homogeneous and isotropic spaces
 Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
HOW TO TEACH THE FUNDAMENTALS OF INFORMATION SCIENCE, CODING, DECODING AND NUMBER SYSTEMS?
 6th INTERNATIONAL MULTIDISCIPLINARY CONFERENCE HOW TO TEACH THE FUNDAMENTALS OF INFORMATION SCIENCE, CODING, DECODING AND NUMBER SYSTEMS? Cecília Sitkuné Göömbei College of Nyíegyháza Hungay Abstact: The
6th INTERNATIONAL MULTIDISCIPLINARY CONFERENCE HOW TO TEACH THE FUNDAMENTALS OF INFORMATION SCIENCE, CODING, DECODING AND NUMBER SYSTEMS? Cecília Sitkuné Göömbei College of Nyíegyháza Hungay Abstact: The
FE FORMULATIONS FOR PLASTICITY
 G These slides ae designed based on the book: Finite Elements in Plasticity Theoy and Pactice, D.R.J. Owen and E. Hinton, 970, Pineidge Pess Ltd., Swansea, UK. Couse Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW
G These slides ae designed based on the book: Finite Elements in Plasticity Theoy and Pactice, D.R.J. Owen and E. Hinton, 970, Pineidge Pess Ltd., Swansea, UK. Couse Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW
Moment-free numerical approximation of highly oscillatory integrals with stationary points
 Moment-fee numeical appoximation of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points Sheehan Olve Abstact We pesent a method fo the numeical quadatue of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points.
Moment-fee numeical appoximation of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points Sheehan Olve Abstact We pesent a method fo the numeical quadatue of highly oscillatoy integals with stationay points.
Inseting this into the left hand side of the equation of motion above gives the most commonly used algoithm in classical molecula dynamics simulations
 Chem465 in 2000 Univesity of Washington Lectue notes Hannes Jonsson Classical dynamics When we ae dealing with heavy atoms and high enough enegy o tempeatue, it is often suciently accuate to neglect quantum
Chem465 in 2000 Univesity of Washington Lectue notes Hannes Jonsson Classical dynamics When we ae dealing with heavy atoms and high enough enegy o tempeatue, it is often suciently accuate to neglect quantum
arxiv:gr-qc/ v2 8 Jun 2006
 On Quantization of the Electical Chage Mass Dmitiy M Palatnik 1 6400 N Sheidan Rd 2605, Chicago, IL 60626 axiv:g-qc/060502v2 8 Jun 2006 Abstact Suggested a non-linea, non-gauge invaiant model of Maxwell
On Quantization of the Electical Chage Mass Dmitiy M Palatnik 1 6400 N Sheidan Rd 2605, Chicago, IL 60626 axiv:g-qc/060502v2 8 Jun 2006 Abstact Suggested a non-linea, non-gauge invaiant model of Maxwell
A New Approach to General Relativity
 Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
Apeion, Vol. 14, No. 3, July 7 7 A New Appoach to Geneal Relativity Ali Rıza Şahin Gaziosmanpaşa, Istanbul Tukey E-mail: aizasahin@gmail.com Hee we pesent a new point of view fo geneal elativity and/o
