Precision spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium
|
|
|
- Alice Scott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hyperfine Interact (009) 194:15 0 DOI /s Precision spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium Vladimir I. Korobov Zhan-Xiang Zhong Published online: 1 August 009 Springer Science + Business Media B.V. 009 Abstract We survey recent progress in the theoretical study of vibrational transitions in the antiprotonic helium atom. Along with the latest experiment they allow to achieve a competitive accuracy in determination of the atomic mass of an electron and thus they have been included into the CODATA06 analysis of the fundamental constants. Improved theoretical calculation of the hyperfine structure in 4 He p atom will be considered as well. We will discuss contributions of order R α 4 to the electron spin-orbit interaction. These corrections are necessary to confirm the latest measurements of the 1.9 MHz intervals of the (n, l) = (37, 35) state in 4 He + p and for precise determination of the antiproton magnetic moment. Keywords Antiprotonic helium Relativistic and radiative corrections Atomic mass of an electron HFS 1 Introduction In past few yearsexperimental [1] and theoretical [] efforts brought the antiprotonic helium spectroscopy to the new level of precision, which allowed to use it in determination of the atomic mass of an electron ( codata.pdf). At present the most precise measurements of m p /m e are the penning trap mass spectroscopy (uncertainty )[3] andtheg factor of a bound electron in 1 C 5+ (uncertainty )[4]. Among these experiments only the first one can V. I. Korobov (B) Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, , Dubna, Russia korobov@theor.jinr.ru Z.-X. Zhong Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Science, , Wuhan, People s Republic of China
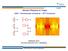
2 16 V.I. Korobov, Z.-X. Zhong be considered as direct, the g factor experiment requires sophisticated theoretical efforts to take account of the high order QED corrections. The atomic mass deduced from comparison of the antiprotonic helium theory and experiment ( A r (e) = (91)[ ]. That means that this system can be competitive in measuring of the fundamental constants. In our contribution we want to report the present status of the theoretical studies, discuss the main sources of uncertainties and the program for future improvements of the theoretical accuracy of the ro-vibrational transition intervals. The second part will be devoted to the R α 4 order corrections to the fine structure in the (37, 35) state of 4 He + p. Ro-vibrational transitions The numerical calculation of the ro-vibrational transitions has been published recently in [], where the contributions up to and including the R α 4 order to the nonrelativistic energies have been taken into account. The radiative corrections of order R α 5 have not been calculated so far but can be approximately evaluated as follows E (5) se = α 5[ 1 ]{ Z 3 He ln (Z He α) δ(r He ) + Z 3 p ln (Z p α) δ(r p ) }, E (5 ) se [ ] δ(rhe = α 5 ZHe 3 A 61 ln (Z He α) + A 60 ), E (5) loop = α5 π Z He [ ] B50 δ(rhe ), (1) where the constants A 61, A 60,andB 50 are taken equal to the constants of the 1s state of the hydrogen atom A 61 = [5], A 60 = [6], and B 50 = [7, 8]. Some examples of the ro-vibrational transitions are shown in Table 1. The theoretical uncertainty is determined by the total contribution of the terms of the last two equations in (1). It is seen that the numerical error is significantly smaller and the major limit for the better theoretical prediction comes from the not yet calculated radiative corrections of order R α 5. Especially that is important for the two-photon transitions ( n = ). The numerical uncertainty is primarily determined by the uncertainty in the daughter state decaying via Auger channel and is about the same for one- and two-photon transitions, while the frequency interval of the two-photon transition is doubled. So, the relative error from the numerical uncertainty is about 10 10, or about an order of magnitude smaller than the theoretical error (Fig. 1). As a proposition for the future work we plan to calculate directly the R α 5 order contribution in the nonrecoil limit of the two-center problem. To do that we will use
3 Precision spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium 17 Table 1 The theoretical ro-vibrational transition intervals (in MHz) Transition Theory 4 He + p (3, 31) (31, 30) (0.8)(0.) (36, 34) (34, 3) (.1)(0.3) 3 He + p (35, 33) (33, 31) (.1)(0.) The state is denoted by (n, l), the principal quantum numbers of the antiprotonic orbital. In parentheses the first error is the theoretical uncertainty due to yet uncalculated higher order corrections. The last error is the numerical uncertainty Fig. 1 Comparison of theory and experiment for some transitions in 4 He + p. Squares are the theoretical data from [, 14], triangles are the data from [15] the analytical expression for the one-loop self-energy correction at this order derived in [9] E (5) se { ( α(zα)6 5 = L + π 9 + [ ]) 1 3 ln (Z α) VQ(E H) 1 QH R + 1 σ ij i Vp j Q(E H) 1 QH R ( [ ]) 1 10 ln (Z α) 4 V ( [ ]) 1 iσ 4 ln (Z α) ij p i Vp j ( [ ]) 1 ( V) 3 ln (Z α) + 3 p V 1 p σ ij i Vp j }, 80 8 where Q is the projector operator on the subspace orthogonal to Ψ 0, V = Z He Z p, r He r p H R = p V σ ij i Vp j. and L is the relativistic correction to the mean excitation energy (the Bethe logarithm). ()
4 18 V.I. Korobov, Z.-X. Zhong Concluding the consideration of the ro-vibrational spectroscopy of the antiprotonic helium atoms we may state. The best present theoretical relative accuracy is , that is still large to compete with the g factor experiment [3]. Direct calculation of R α 5 one loop self-energy corrections is strongly desirable and would allow to reach precision of in the ro-vibrational transition frequency intervals. In its turn, that would probably makes the antiprotonic helium spectroscopy the best tool for measuring of the electron atomic mass. 3 HFS of the (37, 35) state in 4 He + p atom Another interesting issue related to the high precision spectroscopy of the antiprotonic helium is an accurate measurement of the hyperfine structure of the metastable states. It has two-fold interest. First, it is expected that it may be a way to obtain improved value of the magnetic moment of an antiproton. The other point is that it can be a good benchmark for testing QED theoretical methods for the Coulomb three-body bound states to a high precision. Recently, the ASACUSA experiment has provided new precise values for the two HFS transitions of the (37, 35) state in the 4 He + p atom [10]: τ + = (39) GHz, τ = (39) GHz. Transitions τ + and τ are shown on Fig. That should be compared with the theoretical prediction [11]: τ + = (69) GHz, τ = (69) GHz. It is seen that experimental results are more than an order of magnitude better and have some systematic shift toward larger values. We have to say that so far the theoretical numbers were carried out within the leading order Breit-Pauli approximation taking account of the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron. This approximation is limited by the relative order O(α ) and corrections of order R α 4 should be included into consideration in order to comply with the experimental level of accuracy. In terms of the effective Hamiltonian of the hyperfine interaction { H eff = E 1 (s e L) + E (s p L) + E 3 (s e s p ) + E 4 L(L+1)(se s p ) 3 [ (s p L)(s e L) + (s ]} (3) e L)(s p L), one needs to get an improved value for the electron spin-orbit interaction coefficient E 1. It may be done with the use of the NRQED [1]. Some details of the derivation of the R α 6 order contribution may be found in [13]. This contribution may be expressed in terms of the second order term, E A = α 4 He BP Q(E 0 H 0 ) 1 Q (1 + a e )Z a 1 (r m e ra 3 a p e )s e +α 4 He BP Q(E 0 H 0 ) 1 Q (1 + a e)z j 1 (r a P a )s e, m e m (4) a H BP e = p4 e + π [Z 8m 3 e m 1 δ(r 1 ) + Z δ(r )]. e r 3 a
5 Precision spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium 19 Fig. Schematic diagram of hyperfine sublevels of the (37, 35) state of 4 He + p atom And the effective interaction of this order: H (6) = V 1 + V + V 3. The expressions to the effective interactions V i are obtained via NRQED Feynman rules. For the tree-level diagrams one has ( V 1 = e i 3σ e P[q p e](p e + p e ) ) 1 3m 4 e ( V = e i [σ e P q](p e + p e ) ) 8m 3 e q (Z a) 1 q ( Z i P a M a ), a = 1, ( 4 he, p), here in parentheses are the vertex functions, and 1/q is the photon propagator connecting heavy particles and electron. In addition we have the seagull interaction diagram with one Coulomb and one transverse photon lines: V 3 = e 4 σ e P [ {[ ( 1 4m e q δ ij qi q j q )] ( P Z + P ) } M [ ] ] iq1 (Z 1 ) + (1 ). Radiative corrections (from form factors) have been already included into consideration as contributions from the anomalous magnetic moment. Transforming potentials V i to the coordinate space and atomic units one gets (r a = r e R a, a = 1, ): q 1 V 1 = α 6 c 3Z { a p 16m 4 e, 1 } [r e ra 3 a p e ] s e, { V = α 6 c Z a 4m 3 e M p e, 1 } [r a ra 3 a P a ] s e. (5) (6)
6 0 V.I. Korobov, Z.-X. Zhong and V 3 = α 6 c Z 1 Z 4m e { [r1 P ] M r 3 1 r + [r P 1 ] M 1 r 1 r 3 [r 1 r ] r 3 1 r3 [ (r1 P 1 ) (r ]} P ) s e. M 1 M The numerical work on evaluation of these contributions is now carried out and results should appear soon. Acknowledgements The Russian Foundation for Basic Research under Grant No is gratefully acknowledged. References 1. Hori, M., Dax, A., Eades, J., Gomikawa, K., Hayano, R.S., Ono, N., Pirkl, W., Widmann, E., Torii, H.A., Juhász, B., Barna, D., Horváth, D.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, (006). Korobov, V.I.: Phys. Rev., A 77, (008) 3. Farnham, D.L., Van Dyck, Jr., R.S., Schwinberg, P.B.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3598 (1995) 4. Beier, T., Häffner, H., Hermanspahn, N., Karshenboim, S.G., Kluge, H.-J., Quint, W., Stahl, S., Verdú, J., Werth, G.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, (00) 5. Layzer, A.J.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 4, 580 (1960) 6. Pachucki, K.: Ann. Phys. (N.Y.) 6, 1 (1993) 7. Pachucki, K.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 7, 3154 (1994) 8. Eides, M.I., Shelyuto, V.A.: Phys. Rev., A 5, 954 (1995) 9. Jentschura, U., Czarnecki, A., Pachucki, K.: Phys. Rev., A 7, 0610 (005) 10. Pask, T., Barna, D., Dax, A., Hayano, R.S., Hori, M., Horváth, D., Juhász, B., Malbrunot, C., Marton, J., Ono, N., Suzuki, K., Zmeskal, J., Widmann, E.: J. Phys. B 41, (008) 11. Korobov, V.I., Bakalov, D.: J. Phys. B 34, L519 L53 (001) 1. Kinoshita, T., Nio, M.: Phys. Rev., D 53, 4909 (1996) 13. Korobov, V.I., Hilico, L., Karr, J.-P.: Phys. Rev., A 79, (009) 14. Korobov, V.I.: Phys. Rev., A 67, (003) 15. Kino, Y., Kudo, H., Kamimura, M.: Mod. Phys. Lett. A 18, 388 (003)
Ro-vibrational spectroscopy of the hydrogen molecular ion and antiprotonic helium
 of the hydrogen molecular ion and antiprotonic helium V.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research 141980, Dubna, Russia korobov@theor.jinr.ru Fundamental Constants 2015, February 2015 Status of Theory. 2014
of the hydrogen molecular ion and antiprotonic helium V.I. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research 141980, Dubna, Russia korobov@theor.jinr.ru Fundamental Constants 2015, February 2015 Status of Theory. 2014
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 2 Jun 2003
 The g factor of proton Savely G. Karshenboim a,b and Vladimir G. Ivanov c,a a D. I. Mendeleev Institute for Metrology (VNIIM), St. Petersburg 198005, Russia b Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, 85748
The g factor of proton Savely G. Karshenboim a,b and Vladimir G. Ivanov c,a a D. I. Mendeleev Institute for Metrology (VNIIM), St. Petersburg 198005, Russia b Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, 85748
good agreement with the experiment. Thus investigations on the magnetic moment anomaly represent one of the most stringent tests of QED of a free part
 The Magnetic Moment Anomaly of the Electron Bound in Hydrogenic Ions W. Quint Λ, T. Beier Λ, H. Häffner Λ;y1, N. Hermanspahn y2, S. Karshenboim +, H.-J. Kluge Λ, G. Marx Λ, T. Valenzuela y, J. Verdú Λ
The Magnetic Moment Anomaly of the Electron Bound in Hydrogenic Ions W. Quint Λ, T. Beier Λ, H. Häffner Λ;y1, N. Hermanspahn y2, S. Karshenboim +, H.-J. Kluge Λ, G. Marx Λ, T. Valenzuela y, J. Verdú Λ
Study of the hyperfine structure of antiprotonic helium
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 214 (2004) 89 93 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Study of the hyperfine structure of antiprotonic helium J. Sakaguchi a, J. Eades a, R.S. Hayano a, M.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 214 (2004) 89 93 www.elsevier.com/locate/nimb Study of the hyperfine structure of antiprotonic helium J. Sakaguchi a, J. Eades a, R.S. Hayano a, M.
Sub-Doppler two-photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton-toelectron
 Sub-Doppler two-photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton-toelectron mass ratio Fukuoka, August 2012 Masaki Hori Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics A. Sótér, D. Barna, A.
Sub-Doppler two-photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton-toelectron mass ratio Fukuoka, August 2012 Masaki Hori Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics A. Sótér, D. Barna, A.
Helium fine structure theory for determination of α
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Helium fine structure theory for determination of α To cite this article: Krzysztof Pachucki and Vladimir A Yerokhin 0 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 64 0007 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Helium fine structure theory for determination of α To cite this article: Krzysztof Pachucki and Vladimir A Yerokhin 0 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 64 0007 View the article
High-Order QED Calculations in Physics of Positronium
 current status and future perspectives of High-Order QED Calculations in Physics of Positronium Alexander A. Penin II. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Hamburg, Germany and Institute for Nuclear
current status and future perspectives of High-Order QED Calculations in Physics of Positronium Alexander A. Penin II. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Hamburg, Germany and Institute for Nuclear
Antiprotonic Helium: Measuring the Antiproton Mass and Magnetic Moment
 Dezső Horváth Antiprotonic Helium 10-14 September 2012, Stara Lesna, Slovakia p. 1/37 Antiprotonic Helium: Measuring the Antiproton Mass and Magnetic Moment Dezső Horváth on behalf of the ASACUSA Collaboration
Dezső Horváth Antiprotonic Helium 10-14 September 2012, Stara Lesna, Slovakia p. 1/37 Antiprotonic Helium: Measuring the Antiproton Mass and Magnetic Moment Dezső Horváth on behalf of the ASACUSA Collaboration
arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 31 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 31 Oct 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.atom-ph] 31 Oct 2017](/thumbs/86/94100151.jpg) Proton-electron mass ratio from HD + revisited Sayan Patra 1, J.-Ph. Karr,3, L. Hilico,3, M. Germann 1, V. I. Korobov 4, and J. C. J. Koelemeij 1 arxiv:1710.11537v1 [physics.atom-ph] 31 Oct 017 1 LaserLaB
Proton-electron mass ratio from HD + revisited Sayan Patra 1, J.-Ph. Karr,3, L. Hilico,3, M. Germann 1, V. I. Korobov 4, and J. C. J. Koelemeij 1 arxiv:1710.11537v1 [physics.atom-ph] 31 Oct 017 1 LaserLaB
Continuous Stern-Gerlach effect and the Magnetic Moment of the Antiproton
 Continuous Stern-Gerlach effect and the Magnetic Moment of the Antiproton W. Quint a, J. Alonso b, S. Djekić b, H.-J. Kluge a, S. Stahl b, T. Valenzuela b, J. Verdú b, M. Vogel b, and G. Werth b a Gesellschaft
Continuous Stern-Gerlach effect and the Magnetic Moment of the Antiproton W. Quint a, J. Alonso b, S. Djekić b, H.-J. Kluge a, S. Stahl b, T. Valenzuela b, J. Verdú b, M. Vogel b, and G. Werth b a Gesellschaft
Proton charge radius puzzle
 Proton charge radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw KMMF, January 24, 2013 Proton charge radius puzzle global fit to H and D spectrum: r p = 0.8758(77)
Proton charge radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw KMMF, January 24, 2013 Proton charge radius puzzle global fit to H and D spectrum: r p = 0.8758(77)
Nuclear Structure-Dependent Radiative Corrections to the Hydrogen Hyperfine Splitting
 arxiv:hep-ph/9608484v1 29 Aug 1996 Nuclear Structure-Dependent Radiative Corrections to the Hydrogen Hyperfine Splitting Savely G. Karshenboim D. I. Mendeleev Institute for Metrology (VNIIM), St. Petersburg
arxiv:hep-ph/9608484v1 29 Aug 1996 Nuclear Structure-Dependent Radiative Corrections to the Hydrogen Hyperfine Splitting Savely G. Karshenboim D. I. Mendeleev Institute for Metrology (VNIIM), St. Petersburg
Higher-order recoil corrections in Helium and Helium-like ions
 Higher-order recoil corrections in Helium and Helium-like ions Vojtěch Patkóš Department of Chemical Physics and Optics Charles University in Prague 19th May 2017 Motivation Motivation Hydrogenic systems
Higher-order recoil corrections in Helium and Helium-like ions Vojtěch Patkóš Department of Chemical Physics and Optics Charles University in Prague 19th May 2017 Motivation Motivation Hydrogenic systems
ASACUSA: Measuring the Antiproton Mass and Magnetic Moment
 Dezső Horváth ASACUSA 9 October 2013, St. Petersburg, Russia p. 1/41 ASACUSA: Measuring the Antiproton Mass and Magnetic Moment Dezső Horváth on behalf of the ASACUSA Collaboration horvath.dezso@wigner.mta.hu
Dezső Horváth ASACUSA 9 October 2013, St. Petersburg, Russia p. 1/41 ASACUSA: Measuring the Antiproton Mass and Magnetic Moment Dezső Horváth on behalf of the ASACUSA Collaboration horvath.dezso@wigner.mta.hu
Direct Measurement of the Proton Magnetic Moment
 Direct Measurement of the Proton Magnetic Moment J. DiSciacca 1 and G. Gabrielse 1, 1 Dept. of Physics, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138 (Dated: 14 Jan. 2012 (submitted to PRL); 31 Jan. 2012 (accepted
Direct Measurement of the Proton Magnetic Moment J. DiSciacca 1 and G. Gabrielse 1, 1 Dept. of Physics, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138 (Dated: 14 Jan. 2012 (submitted to PRL); 31 Jan. 2012 (accepted
The Lamb shift in hydrogen and muonic hydrogen and the proton charge radius
 The Lamb shift in hydrogen and muonic hydrogen and the proton charge radius Savely Karshenboim Pulkovo Observatory (ГАО( РАН) ) (St. Petersburg) & Max-Planck Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik (Garching)
The Lamb shift in hydrogen and muonic hydrogen and the proton charge radius Savely Karshenboim Pulkovo Observatory (ГАО( РАН) ) (St. Petersburg) & Max-Planck Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik (Garching)
Forbidden Electric Dipole Transitions in the Hydrogen Molecular Ion First Estimates
 Bulg. J. Phys. 44 (2017) 76 83 Forbidden Electric Dipole Transitions in the Hydrogen Molecular Ion First Estimates P. Danev Institute for Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
Bulg. J. Phys. 44 (2017) 76 83 Forbidden Electric Dipole Transitions in the Hydrogen Molecular Ion First Estimates P. Danev Institute for Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
Lamb shift in muonic hydrogen and the proton charge radius puzzle
 Lamb shift in muonic hydrogen and the proton charge radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw Mainz, April 17, 2013 Proton charge radius puzzle global fit
Lamb shift in muonic hydrogen and the proton charge radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw Mainz, April 17, 2013 Proton charge radius puzzle global fit
Fine and hyperfine structure of helium atom
 Fine and hyperfine structure of helium atom Vladimir A. Yerokhin St. Petersburg State Polytechnical University in collaboration with Krzysztof Pachucki Warsaw University Fundamental Constants Meeting,
Fine and hyperfine structure of helium atom Vladimir A. Yerokhin St. Petersburg State Polytechnical University in collaboration with Krzysztof Pachucki Warsaw University Fundamental Constants Meeting,
Anomalous magnetic moments of free and bound leptons
 Anomalous magnetic moments of free and bound leptons Andrzej Czarnecki, Ulrich D. Jentschura, Krzysztof Pachucki, and Vladimir A. Yerokhin 1 1. Introduction Abstract: We review the theoretical knowledge
Anomalous magnetic moments of free and bound leptons Andrzej Czarnecki, Ulrich D. Jentschura, Krzysztof Pachucki, and Vladimir A. Yerokhin 1 1. Introduction Abstract: We review the theoretical knowledge
New Physics Hypotheses on Muonic Hydrogen and the Proton Radius Puzzle (Part II)
 New Physics Hypotheses on Muonic Hydrogen and the Proton Radius Puzzle (Part II) Ulrich D. Jentschura Missouri University of Science and Technology Rolla, Missouri, USA Bled Workshop on What Comes Beyond
New Physics Hypotheses on Muonic Hydrogen and the Proton Radius Puzzle (Part II) Ulrich D. Jentschura Missouri University of Science and Technology Rolla, Missouri, USA Bled Workshop on What Comes Beyond
Directions toward the resolution of the proton charge radius puzzle
 Directions toward the resolution of the proton charge radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw ECT workshop on the proton radius puzzle, November 1, 2012
Directions toward the resolution of the proton charge radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Institute of Theoretical Physics, University of Warsaw ECT workshop on the proton radius puzzle, November 1, 2012
Sponsored document from Physics Letters. [Part B] First observation of two hyperfine transitions in antiprotonic 3 He
![Sponsored document from Physics Letters. [Part B] First observation of two hyperfine transitions in antiprotonic 3 He Sponsored document from Physics Letters. [Part B] First observation of two hyperfine transitions in antiprotonic 3 He](/thumbs/73/69017849.jpg) Sponsored document from Physics Letters. [Part B] First observation of two hyperfine transitions in antiprotonic 3 He S. Friedreich a,, D. Barna b,c, F. Caspers d, A. Dax b, R.S. Hayano b, M. Hori b,e,
Sponsored document from Physics Letters. [Part B] First observation of two hyperfine transitions in antiprotonic 3 He S. Friedreich a,, D. Barna b,c, F. Caspers d, A. Dax b, R.S. Hayano b, M. Hori b,e,
Complete Result for Positronium Energy Levels at Order α 6 m. Abstract
 version 1.0 Complete Result for Positronium Energy Levels at Order α 6 m Krzysztof Pachucki ab and Savely G. Karshenboim ac a Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, Hans-Kopfermann-Str. 1, 85748 Garching,
version 1.0 Complete Result for Positronium Energy Levels at Order α 6 m Krzysztof Pachucki ab and Savely G. Karshenboim ac a Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, Hans-Kopfermann-Str. 1, 85748 Garching,
Observing a single hydrogen-like ion in a Penning trap at T = 4K
 Hyperfine Interactions 115 (1998) 185 192 185 Observing a single hydrogen-like ion in a Penning trap at T = 4K M. Diederich a,h.häffner a, N. Hermanspahn a,m.immel a,h.j.kluge b,r.ley a, R. Mann b,w.quint
Hyperfine Interactions 115 (1998) 185 192 185 Observing a single hydrogen-like ion in a Penning trap at T = 4K M. Diederich a,h.häffner a, N. Hermanspahn a,m.immel a,h.j.kluge b,r.ley a, R. Mann b,w.quint
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 28 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 28 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 28 Dec 2018](/thumbs/95/123227284.jpg) Hyperfine Splitting in Muonium: Accuracy of the Theoretical Prediction Michael I. Eides arxiv:1812.10881v1 [hep-ph] 28 Dec 2018 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY
Hyperfine Splitting in Muonium: Accuracy of the Theoretical Prediction Michael I. Eides arxiv:1812.10881v1 [hep-ph] 28 Dec 2018 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY
MAGNETIC MOMENT OF THE TWO-PARTICLE BOUND STATE IN QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS 1
 Preprint SSU-HEP-00/09 Samara State University MAGNETIC MOMENT OF THE TWO-PARTICLE BOUND STATE IN QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS R.N. Faustov Scientific Council Cybernetics RAS 7, Moscow, Vavilov, 40, Russia,
Preprint SSU-HEP-00/09 Samara State University MAGNETIC MOMENT OF THE TWO-PARTICLE BOUND STATE IN QUANTUM ELECTRODYNAMICS R.N. Faustov Scientific Council Cybernetics RAS 7, Moscow, Vavilov, 40, Russia,
Helium fine structure Ingvar Lindgren (mod )
 Helium fine structure Ingvar Lindgren 2004.09.20 (mod. 2005.01.23) The leading contributions to the helium fine structure beyond the first-order relativistic contribution were first derived by Araki [1]
Helium fine structure Ingvar Lindgren 2004.09.20 (mod. 2005.01.23) The leading contributions to the helium fine structure beyond the first-order relativistic contribution were first derived by Araki [1]
Bound Electron g Factor
 Bound Electron g Factor Lepton Moments ' 06 Cape Cod, 20 JUN 2006 Ulrich D. Jentschura Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Contents Theory of hydrogen and deuterium spectra and
Bound Electron g Factor Lepton Moments ' 06 Cape Cod, 20 JUN 2006 Ulrich D. Jentschura Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics, Heidelberg, Germany Contents Theory of hydrogen and deuterium spectra and
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 23 Sep 2000
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 23 Sep 2000 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 23 Sep 2000](/thumbs/91/107319551.jpg) Lamb Shift in Light Hydrogen-Like Atoms arxiv:physics/0009069v1 [physics.atom-ph] 23 Sep 2000 Vladimir G. Ivanov 1 and Savely G. Karshenboim 2,3 1 Pulkovo Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia 2 D. I. Mendeleev
Lamb Shift in Light Hydrogen-Like Atoms arxiv:physics/0009069v1 [physics.atom-ph] 23 Sep 2000 Vladimir G. Ivanov 1 and Savely G. Karshenboim 2,3 1 Pulkovo Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia 2 D. I. Mendeleev
Probing QED in strong fields via the magnetic moment of highly charged ions. Sven Sturm May 25 th, 2016
 Probing QED in strong fields via the magnetic moment of highly charged ions Sven Sturm May 25 th, 2016 Quantum ElectroDynamics (QED) Quantum Electrodynamics (QED is tested and proven in the weak field
Probing QED in strong fields via the magnetic moment of highly charged ions Sven Sturm May 25 th, 2016 Quantum ElectroDynamics (QED) Quantum Electrodynamics (QED is tested and proven in the weak field
Fundamental constants and tests of theory in Rydberg states of hydrogen like ions
 International Conference on Precision Physics of Simple Atomic Systems University of Windsor, July 21 26, 2008 Fundamental constants and tests of theory in Rydberg states of hydrogen like ions Ulrich Jentschura,
International Conference on Precision Physics of Simple Atomic Systems University of Windsor, July 21 26, 2008 Fundamental constants and tests of theory in Rydberg states of hydrogen like ions Ulrich Jentschura,
Atomic Physics with Stored and Cooled Ions
 Lecture #5 Atomic Physics with Stored and Cooled Ions Klaus Blaum Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI, Darmstadt and CERN, Physics Department, Geneva, Switzerland Summer School, Lanzhou, China,
Lecture #5 Atomic Physics with Stored and Cooled Ions Klaus Blaum Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI, Darmstadt and CERN, Physics Department, Geneva, Switzerland Summer School, Lanzhou, China,
RECENT ADVANCES IN THE THEORY OF THE HYDROGEN LAMB SHIFT
 Vol. 85 (1994) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 RECENT ADVANCES IN THE THEORY OF THE HYDROGEN LAMB SHIFT H. GROTCH 104 Davey Laboratory, Department of Physics, Penn State University University Park, PA 16802,
Vol. 85 (1994) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 4 RECENT ADVANCES IN THE THEORY OF THE HYDROGEN LAMB SHIFT H. GROTCH 104 Davey Laboratory, Department of Physics, Penn State University University Park, PA 16802,
arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 24 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 24 Mar 2012 arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 24 Mar 2012](/thumbs/94/118674402.jpg) UK/1-01 Weak Interaction Contributions in Light Muonic Atoms Michael I. Eides Department of Physics and Astronomy, arxiv:101.979v [physics.atom-ph] 4 Mar 01 University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506,
UK/1-01 Weak Interaction Contributions in Light Muonic Atoms Michael I. Eides Department of Physics and Astronomy, arxiv:101.979v [physics.atom-ph] 4 Mar 01 University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506,
Interaction between antiprotonic helium ion and He atom: Potential Energy Surface
 Interaction between antiprotonic helium ion and He atom: Potential Energy Surface S.N. Yudin 1, I.V. Bodrenko 2, and G.Ya. Korenman 1 1 D.V.Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, M.V. Lomonosov Moscow
Interaction between antiprotonic helium ion and He atom: Potential Energy Surface S.N. Yudin 1, I.V. Bodrenko 2, and G.Ya. Korenman 1 1 D.V.Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, M.V. Lomonosov Moscow
Cavity Control in a Single-Electron Quantum Cyclotron
 Cavity Control in a Single-Electron Quantum Cyclotron An Improved Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment David Hanneke Michelson Postdoctoral Prize Lectures 13 May 2010 The Quantum Cyclotron Single
Cavity Control in a Single-Electron Quantum Cyclotron An Improved Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment David Hanneke Michelson Postdoctoral Prize Lectures 13 May 2010 The Quantum Cyclotron Single
arxiv:physics/ v3 27 Jun 2005
 Lamb Shift in Muonic Hydrogen arxiv:physics/45 v3 7 Jun 5 E. Borie Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut für Hochleistungsimpuls and Mikrowellentechnik IHM, Hermann-von-Helmholtzplatz, 76344 Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen,
Lamb Shift in Muonic Hydrogen arxiv:physics/45 v3 7 Jun 5 E. Borie Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut für Hochleistungsimpuls and Mikrowellentechnik IHM, Hermann-von-Helmholtzplatz, 76344 Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen,
Two- photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton- to- electron mass ratio
 Two- photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton- to- electron mass ratio Masaki Hori 1,2, Anna Sótér 1, Daniel Barna 2,4, Andreas Dax 2, Ryugo Hayano 2, Susanne Friedreich 3, Bertalan
Two- photon laser spectroscopy of antiprotonic helium and the antiproton- to- electron mass ratio Masaki Hori 1,2, Anna Sótér 1, Daniel Barna 2,4, Andreas Dax 2, Ryugo Hayano 2, Susanne Friedreich 3, Bertalan
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 8 Oct 2004
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 8 Oct 2004 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.atom-ph] 8 Oct 2004](/thumbs/81/83175157.jpg) Lamb Shift in Muonic Hydrogen arxiv:physics/45v [physics.atom-ph] 8 Oct 24 E. Borie Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut für Hochleistungsimpuls and Mikrowellentechnik IHM), Hermann-von-Helmholtzplatz,
Lamb Shift in Muonic Hydrogen arxiv:physics/45v [physics.atom-ph] 8 Oct 24 E. Borie Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut für Hochleistungsimpuls and Mikrowellentechnik IHM), Hermann-von-Helmholtzplatz,
Fully Quantum Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment
 Fully Quantum Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment prepared by Maren Padeffke (presented by N. Herrmann) Outline Motivation and History Experimental Methods Results Conclusion Sources Motivation
Fully Quantum Measurement of the Electron Magnetic Moment prepared by Maren Padeffke (presented by N. Herrmann) Outline Motivation and History Experimental Methods Results Conclusion Sources Motivation
Proton radius puzzle
 Proton radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Universiy of Warsaw Frascati, December 21, 2016 Measurements of atomic spectra Measurement of transition frequencies can be very accurate [Garching, 2013] ν(1s 2S)
Proton radius puzzle Krzysztof Pachucki Universiy of Warsaw Frascati, December 21, 2016 Measurements of atomic spectra Measurement of transition frequencies can be very accurate [Garching, 2013] ν(1s 2S)
Experiments with hydrogen - discovery of the Lamb shift
 Experiments with hydrogen - discovery of the Lamb shift Haris Ðapo Relativistic heavy ion seminar, October 26, 2006 Outline 1 Pre-Lamb experiment The beginning (Bohr s formula) Fine structure (Dirac s
Experiments with hydrogen - discovery of the Lamb shift Haris Ðapo Relativistic heavy ion seminar, October 26, 2006 Outline 1 Pre-Lamb experiment The beginning (Bohr s formula) Fine structure (Dirac s
Lecture 4. Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects
 Lecture 4 Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects Plan of the lecture Reminder from the last lecture: Bound-state solutions of Dirac equation Higher-order corrections to Dirac energies: Radiative
Lecture 4 Beyound the Dirac equation: QED and nuclear effects Plan of the lecture Reminder from the last lecture: Bound-state solutions of Dirac equation Higher-order corrections to Dirac energies: Radiative
QED on background Coulomb field
 Department of Chemical Physics and Optics Charles University in Prague May 2017 Plan of the talk Motivation for study bound-state QED Solution of Dirac equation for external Coulomb field Evaluation of
Department of Chemical Physics and Optics Charles University in Prague May 2017 Plan of the talk Motivation for study bound-state QED Solution of Dirac equation for external Coulomb field Evaluation of
Fine Structure Calculations of Atomic Data for Ar XVI
 Journal of Modern Physics, 2015, 6, 1609-1630 Published Online September 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jmp.2015.611163 Fine Structure Calculations of Atomic
Journal of Modern Physics, 2015, 6, 1609-1630 Published Online September 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jmp.2015.611163 Fine Structure Calculations of Atomic
Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places
 The 64 th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 5: Using the Fine Structure Constant to Push
The 64 th Compton Lecture Series Unsolved Mysteries of the Universe: Looking for Clues in Surprising Places http://kicp.uchicago.edu/~odom/compton.htm Lecture 5: Using the Fine Structure Constant to Push
New Physics Searches with Muons. Electromagnetic Interactions with Nucleons and Nuclei Paphos, Cyprus November 4, 2015
 New Physics Searches with Muons Electromagnetic Interactions with Nucleons and Nuclei Paphos, Cyprus November 4, 2015 Andrzej Czarnecki University of Alberta Outline Three promising directions in low-energy
New Physics Searches with Muons Electromagnetic Interactions with Nucleons and Nuclei Paphos, Cyprus November 4, 2015 Andrzej Czarnecki University of Alberta Outline Three promising directions in low-energy
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 12 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 12 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 12 Oct 2018](/thumbs/96/126603323.jpg) Precision electroweak shift of muonium hyperfine splitting arxiv:1810.05429v1 [hep-ph] 12 Oct 2018 T. Asaka, M. Tanaka, K. Tsumura, and M. Yoshimura Department of Physics, Niigata University, 950-2181
Precision electroweak shift of muonium hyperfine splitting arxiv:1810.05429v1 [hep-ph] 12 Oct 2018 T. Asaka, M. Tanaka, K. Tsumura, and M. Yoshimura Department of Physics, Niigata University, 950-2181
Excerpted from CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2002
 Excerpted from CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2002 Peter J. Mohr and Barry N. Taylor National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899-801,
Excerpted from CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2002 Peter J. Mohr and Barry N. Taylor National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899-801,
The most stringent test of QED in strong fields: The g-factor of 28 Si 13+
 The most stringent test of QED in strong fields: The g-factor of 28 Si 13+ Sven Sturm, Anke Wagner, Klaus Blaum March 27 th, 2012 PTB Helmholtz-Symposium Quantum ElectroDynamics (QED) QED describes the
The most stringent test of QED in strong fields: The g-factor of 28 Si 13+ Sven Sturm, Anke Wagner, Klaus Blaum March 27 th, 2012 PTB Helmholtz-Symposium Quantum ElectroDynamics (QED) QED describes the
Atomic Physics in Traps
 Atomic Physics in Traps QED Fundamental Constants CPT Invariance Wolfgang Quint GSI Darmstadt and Univ. Heidelberg Quantum mechanics, Relativity, and P.A.M. Dirac Quantum mechanics Special Relativity Dirac
Atomic Physics in Traps QED Fundamental Constants CPT Invariance Wolfgang Quint GSI Darmstadt and Univ. Heidelberg Quantum mechanics, Relativity, and P.A.M. Dirac Quantum mechanics Special Relativity Dirac
221B Lecture Notes Quantum ElectroDynamics
 221B Lecture Notes Quantum ElectroDynamics 1 Putting Everything Together Now we are in the position to discuss a truly relativistic, quantum formulation of electrodynamics. We have discussed all individual
221B Lecture Notes Quantum ElectroDynamics 1 Putting Everything Together Now we are in the position to discuss a truly relativistic, quantum formulation of electrodynamics. We have discussed all individual
On The Method of Precise Calculations Of Energy Levels of Hydrogen-like Atoms. N. A. Boikova, Y. N. Tyukhtyaev, R. N. Faustov
 On The Method of Precise alculations Of Energy Levels of Hydrogen-like Atoms N. A. Boikova, Y. N. Tyukhtyaev, R. N. Faustov Abstract: We describe a method for deriving logarithmic corrections in the mass
On The Method of Precise alculations Of Energy Levels of Hydrogen-like Atoms N. A. Boikova, Y. N. Tyukhtyaev, R. N. Faustov Abstract: We describe a method for deriving logarithmic corrections in the mass
ASACUSA STATUS REPORT
 January, 217 ASACUSA STATUS REPORT Recent progress and plans for 217 CERN-SPSC-217-5 / SPSC-SR-23 17/1/217 ASACUSA collaboration H. Aghai-Khozani h, C. Amsler g, S. Arguedas Cuendis g, D. Barna I, H. Breuker
January, 217 ASACUSA STATUS REPORT Recent progress and plans for 217 CERN-SPSC-217-5 / SPSC-SR-23 17/1/217 ASACUSA collaboration H. Aghai-Khozani h, C. Amsler g, S. Arguedas Cuendis g, D. Barna I, H. Breuker
Positronium molecule
 Positronium molecule e + e - e - (0γ) 2γ (4γ) (1γ) 3γ (5γ) e + PSAS 2008 University of Windsor, July 26, 2008 Andrzej Czarnecki University of Alberta Outline Positronium, its ion, and the molecule 1951
Positronium molecule e + e - e - (0γ) 2γ (4γ) (1γ) 3γ (5γ) e + PSAS 2008 University of Windsor, July 26, 2008 Andrzej Czarnecki University of Alberta Outline Positronium, its ion, and the molecule 1951
Relativistic corrections of energy terms
 Lectures 2-3 Hydrogen atom. Relativistic corrections of energy terms: relativistic mass correction, Darwin term, and spin-orbit term. Fine structure. Lamb shift. Hyperfine structure. Energy levels of the
Lectures 2-3 Hydrogen atom. Relativistic corrections of energy terms: relativistic mass correction, Darwin term, and spin-orbit term. Fine structure. Lamb shift. Hyperfine structure. Energy levels of the
Precision physics of simple atoms:qed tests, nuclear structure and fundamental constants
 Physics Reports 422 (2005) 1 63 www.elsevier.com/locate/physrep Precision physics of simple atoms:qed tests, nuclear structure and fundamental constants Savely G. Karshenboim a,b, a D.I. Mendeleev Institute
Physics Reports 422 (2005) 1 63 www.elsevier.com/locate/physrep Precision physics of simple atoms:qed tests, nuclear structure and fundamental constants Savely G. Karshenboim a,b, a D.I. Mendeleev Institute
arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 30 May 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 30 May 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.atom-ph] 30 May 2013](/thumbs/77/75170619.jpg) Proton Radius Puzzle 1 Muonic hydrogen and the proton radius arxiv:1301.0905v2 [physics.atom-ph] 30 May 2013 puzzle Randolf Pohl Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, 85748 Garching, Germany Ronald Gilman
Proton Radius Puzzle 1 Muonic hydrogen and the proton radius arxiv:1301.0905v2 [physics.atom-ph] 30 May 2013 puzzle Randolf Pohl Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, 85748 Garching, Germany Ronald Gilman
Fine structure of helium and light helium-like ions
 Fine structure of helium and light helium-like ions Krzysztof Pachucki and Vladimir A. Yerokhin Abstract: Calculational results are presented for the fine-structure splitting of the 3 P state of helium
Fine structure of helium and light helium-like ions Krzysztof Pachucki and Vladimir A. Yerokhin Abstract: Calculational results are presented for the fine-structure splitting of the 3 P state of helium
CONTINUOUS STERN GERLACH EFFECT ON ATOMIC IONS
 ADVANCES IN ATOMIC, MOLECULAR, AND OPTICAL PHYSICS, VOL. 48 CONTINUOUS STERN GERLACH EFFECT ON ATOMIC IONS GÜNTHER WERTH 1, HARTMUT HÄFFNER 1 and WOLFGANG QUINT 2 1 Johannes Gutenberg University, Department
ADVANCES IN ATOMIC, MOLECULAR, AND OPTICAL PHYSICS, VOL. 48 CONTINUOUS STERN GERLACH EFFECT ON ATOMIC IONS GÜNTHER WERTH 1, HARTMUT HÄFFNER 1 and WOLFGANG QUINT 2 1 Johannes Gutenberg University, Department
Proton Size Puzzle: Fat or Thin?
 Proton Size Puzzle: Fat or Thin? A.E. Dorokhov (JINR, Dubna) Fat and Thin famous Anton Chekhov novel R.N. Faustov (Institute of Informatics in Education, FRC CSC RAS, Moscow) N.I. Kochelev (JINR, Dubna;
Proton Size Puzzle: Fat or Thin? A.E. Dorokhov (JINR, Dubna) Fat and Thin famous Anton Chekhov novel R.N. Faustov (Institute of Informatics in Education, FRC CSC RAS, Moscow) N.I. Kochelev (JINR, Dubna;
Lowest vibrational states of 4 He 3 He + : Non-Born-Oppenheimer calculations
 Lowest vibrational states of He 3 He + : Non-Born-Oppenheimer calculations Monika Stanke,, * Dariusz Kȩdziera, Sergiy Bubin, Marcin Molski, 3 and Ludwik Adamowicz, Department of Chemistry, University of
Lowest vibrational states of He 3 He + : Non-Born-Oppenheimer calculations Monika Stanke,, * Dariusz Kȩdziera, Sergiy Bubin, Marcin Molski, 3 and Ludwik Adamowicz, Department of Chemistry, University of
Global properties of atomic nuclei
 Global properties of atomic nuclei How to probe nuclear size? Electron Sca5ering from nuclei For low energies and under condi0ons where the electron does not penetrate the nucleus, the electron sca5ering
Global properties of atomic nuclei How to probe nuclear size? Electron Sca5ering from nuclei For low energies and under condi0ons where the electron does not penetrate the nucleus, the electron sca5ering
Global properties of atomic nuclei
 Global properties of atomic nuclei How to probe nuclear size? Electron Sca5ering from nuclei For low energies and under condi0ons where the electron does not penetrate the nucleus, the electron sca5ering
Global properties of atomic nuclei How to probe nuclear size? Electron Sca5ering from nuclei For low energies and under condi0ons where the electron does not penetrate the nucleus, the electron sca5ering
Atomic structure and dynamics
 Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
Atomic structure and dynamics -- need and requirements for accurate atomic calculations Analysis and interpretation of optical and x-ray spectra (astro physics) Isotope shifts and hyperfine structures
Ion traps. Trapping of charged particles in electromagnetic. Laser cooling, sympathetic cooling, optical clocks
 Ion traps Trapping of charged particles in electromagnetic fields Dynamics of trapped ions Applications to nuclear physics and QED The Paul trap Laser cooling, sympathetic cooling, optical clocks Coulomb
Ion traps Trapping of charged particles in electromagnetic fields Dynamics of trapped ions Applications to nuclear physics and QED The Paul trap Laser cooling, sympathetic cooling, optical clocks Coulomb
Improved Coulomb Potential. Abstract
 THEF-NIJM 8.18 Improved Coulomb Potential G. J. M. Austen and J. J. de Swart Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Abstract An improved Coulomb potential
THEF-NIJM 8.18 Improved Coulomb Potential G. J. M. Austen and J. J. de Swart Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands Abstract An improved Coulomb potential
Energy Level Energy Level Diagrams for Diagrams for Simple Hydrogen Model
 Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics Lecture 20: Real Hydrogen Atom /Identical particles http://www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/361 physics edu/ugrad/361 Prof. Sean Oh Last time Hydrogen atom: electron in
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics Lecture 20: Real Hydrogen Atom /Identical particles http://www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/361 physics edu/ugrad/361 Prof. Sean Oh Last time Hydrogen atom: electron in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature1306 Statistical measurement uncertainty The statistical uncertainty of the experimentally determined ratio of Larmor- and cyclotron frequencies, which we denote
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature1306 Statistical measurement uncertainty The statistical uncertainty of the experimentally determined ratio of Larmor- and cyclotron frequencies, which we denote
arxiv:hep-ph/ v2 25 May 2000
 Theory of Light Hydrogenlike Atoms PSU/TH/226; hep-ph/0002158 Michael I. Eides Department of Physics, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA and Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute,
Theory of Light Hydrogenlike Atoms PSU/TH/226; hep-ph/0002158 Michael I. Eides Department of Physics, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA and Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute,
Testing CPT Invariance with Antiprotonic Atoms 1
 Testing CPT Invariance with Antiprotonic Atoms 1 Dezső Horváth KFKI Research Institute for Particle and Nuclear Physics, H 1525 Budapest, Hungary and Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Debrecen, Hungary
Testing CPT Invariance with Antiprotonic Atoms 1 Dezső Horváth KFKI Research Institute for Particle and Nuclear Physics, H 1525 Budapest, Hungary and Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Debrecen, Hungary
Feynman diagrams in nuclear physics at low and intermediate energies
 «Избранные вопросы теоретической физики и астрофизики». Дубна: ОИЯИ, 2003. С. 99 104. Feynman diagrams in nuclear physics at low and intermediate energies L. D. Blokhintsev Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear
«Избранные вопросы теоретической физики и астрофизики». Дубна: ОИЯИ, 2003. С. 99 104. Feynman diagrams in nuclear physics at low and intermediate energies L. D. Blokhintsev Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear
Development of a detector setup to determine the 2s hyperfine transition of 209 Bi 80+ at the Experimental Storage Ring at GSI
 Denis Anielski 28.01.2011 1 Development of a detector setup to determine the 2s hyperfine transition of 209 Bi 80+ at the Experimental Storage Ring at GSI Denis Anielski Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität
Denis Anielski 28.01.2011 1 Development of a detector setup to determine the 2s hyperfine transition of 209 Bi 80+ at the Experimental Storage Ring at GSI Denis Anielski Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 5 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 5 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 5 Jan 2018](/thumbs/84/89368398.jpg) Access to improve the muon mass and magnetic moment anomaly via the bound-muon g factor arxiv:1801.02501v1 [hep-ph] 5 Jan 2018 B. Sikora, 1, H. Cakir, 1 N. ichel, 1 V. Debierre, 1 N. S. Oreshkina, 1 N.
Access to improve the muon mass and magnetic moment anomaly via the bound-muon g factor arxiv:1801.02501v1 [hep-ph] 5 Jan 2018 B. Sikora, 1, H. Cakir, 1 N. ichel, 1 V. Debierre, 1 N. S. Oreshkina, 1 N.
Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom
 Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom Jayash Panigrahi August 17, 2013 Abstract Saturated absorption spectroscopy has various application in laser cooling which have many relevant uses in
Saturation Absorption Spectroscopy of Rubidium Atom Jayash Panigrahi August 17, 2013 Abstract Saturated absorption spectroscopy has various application in laser cooling which have many relevant uses in
Experimental Tests of CPT Invariance at CERN
 Dezső Horváth: CPT Tests at CERN Szegedi Egyetem, 2018.10.15. p. 1 Experimental Tests of CPT Invariance at CERN Szegedi Egyetem, Elm-Fiz. Tanszék, 2018.10.15. Horváth Dezső horvath.dezso@wigner.mta.hu
Dezső Horváth: CPT Tests at CERN Szegedi Egyetem, 2018.10.15. p. 1 Experimental Tests of CPT Invariance at CERN Szegedi Egyetem, Elm-Fiz. Tanszék, 2018.10.15. Horváth Dezső horvath.dezso@wigner.mta.hu
QED, Lamb shift, `proton charge radius puzzle' etc.
 QED, Lamb shift, `proton charge radius puzzle' etc. Savely Karshenboim Pulkovo Observatory (ГАО РАН) (St. Petersburg) & Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik (Garching) Outline Different methods to determine
QED, Lamb shift, `proton charge radius puzzle' etc. Savely Karshenboim Pulkovo Observatory (ГАО РАН) (St. Petersburg) & Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik (Garching) Outline Different methods to determine
Testing CPT Invariance with Antiprotonic Atoms
 Testing CPT Invariance with Antiprotonic Atoms Dezső Horváth horvath@rmki.kfki.hu. KFKI Research Institute for Particle and Nuclear Physics, Budapest, Hungary & ATOMKI, Debrecen, Hungary Outline CPT Invariance
Testing CPT Invariance with Antiprotonic Atoms Dezső Horváth horvath@rmki.kfki.hu. KFKI Research Institute for Particle and Nuclear Physics, Budapest, Hungary & ATOMKI, Debrecen, Hungary Outline CPT Invariance
Calculation of the Isotope Shifts on 5S 1/2 4D 3/2,5/2 Transitions of 87,88 Sr +
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 37 (22) pp 76 7 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 37, No. 6, June 5, 22 Calculation of the Isotope Shifts on 5S /2 4D 3/2,5/2 Transitions of 87,88 Sr + LI Yong,,2
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 37 (22) pp 76 7 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 37, No. 6, June 5, 22 Calculation of the Isotope Shifts on 5S /2 4D 3/2,5/2 Transitions of 87,88 Sr + LI Yong,,2
P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman. Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION
 P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1997 Introduction and orientation 1 Black-body radiation 1 Heat capacities 2 The
P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman Molecular Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Oxford New York Tokyo OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1997 Introduction and orientation 1 Black-body radiation 1 Heat capacities 2 The
ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY: Introduction to the Theory of Hyperfine Structure
 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY: Introduction to the Theory of Hyperfine Structure ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY: Introduction to the Theory of Hyperfine Structure ANATOLI ANDREEV M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University Moscow.
ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY: Introduction to the Theory of Hyperfine Structure ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY: Introduction to the Theory of Hyperfine Structure ANATOLI ANDREEV M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University Moscow.
The Fine Structure Constant
 3.6, 00 AMO Seinar The Fine Structure Constant Li-Bang Wang Physics Departent, National Tsing-Hua University Origin of fine structure constant Introduced by Soerfeld in 96, as relativistic correction of
3.6, 00 AMO Seinar The Fine Structure Constant Li-Bang Wang Physics Departent, National Tsing-Hua University Origin of fine structure constant Introduced by Soerfeld in 96, as relativistic correction of
A natural solution of the proton charge radius puzzle.
 A natural solution of the proton charge radius puzzle. Thomas Walcher Institute for Nuclear Physics Johannes-Gutenberg University Mainz INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS 37th Course Probing Hadron
A natural solution of the proton charge radius puzzle. Thomas Walcher Institute for Nuclear Physics Johannes-Gutenberg University Mainz INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS 37th Course Probing Hadron
New Determination of the Fine Structure Constant from the Electron g Value and QED
 2 JULY 2006 New Determination of the Fine Structure Constant from the Electron g Value and QED G. Gabrielse, D. Hanneke, T. Kinoshita, 2 M. Nio, 3 and B. Odom, * Lyman Laboratory, Harvard University, Cambridge,
2 JULY 2006 New Determination of the Fine Structure Constant from the Electron g Value and QED G. Gabrielse, D. Hanneke, T. Kinoshita, 2 M. Nio, 3 and B. Odom, * Lyman Laboratory, Harvard University, Cambridge,
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 27 Sep 2001
 EPJ manuscript No. will be inserted by the editor Hyperfine Structure of the Ground and First Excited States in Light Hydrogen-Like Atoms and High-Precision Tests of QED arxiv:hep-ph/010973v1 7 Sep 001
EPJ manuscript No. will be inserted by the editor Hyperfine Structure of the Ground and First Excited States in Light Hydrogen-Like Atoms and High-Precision Tests of QED arxiv:hep-ph/010973v1 7 Sep 001
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing. Course Outline 2009
 Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Fundamentals of Spectroscopy for Optical Remote Sensing Course Outline 2009 Part I. Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics Chapter 1. Concepts of Quantum and Experimental Facts 1.1. Blackbody Radiation and
Fundamental physics with antihydrogen and antiprotons at the AD. Michael Doser CERN
 Fundamental physics with antihydrogen and antiprotons at the AD Michael Doser CERN What measurements are we talking about? 1) Precise spectroscopic comparison between H and H tests of fundamental symmetry
Fundamental physics with antihydrogen and antiprotons at the AD Michael Doser CERN What measurements are we talking about? 1) Precise spectroscopic comparison between H and H tests of fundamental symmetry
The Magnetic Moment of the Proton. A. Mooser for the BASE collaboration
 The Magnetic Moment of the Proton A. Mooser for the BASE collaboration Motivation CPT-Symmetry fundamental cornerstone of Standard Model Strategy: Compare properties of matter and antimatter conjugates
The Magnetic Moment of the Proton A. Mooser for the BASE collaboration Motivation CPT-Symmetry fundamental cornerstone of Standard Model Strategy: Compare properties of matter and antimatter conjugates
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 22 Mar 2001
 Quantum Electrodynamics of the Helium Atom hep-ph/010341 arxiv:hep-ph/010341v1 Mar 001 Alexander Yelkhovsky Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, and Physics Department, Novosibirsk University, Novosibirsk,
Quantum Electrodynamics of the Helium Atom hep-ph/010341 arxiv:hep-ph/010341v1 Mar 001 Alexander Yelkhovsky Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, and Physics Department, Novosibirsk University, Novosibirsk,
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 43, NO. 2 APRIL Ming-Keh Chen
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 43, NO. 2 APRIL 2004 Doubly Excited 1,3 P e Resonances in He Between the N=2 and 3 He + Thresholds Ming-Keh Chen Department of Physics, National Chung-Hsing University,
CHINESE JOURNAL OF PHYSICS VOL. 43, NO. 2 APRIL 2004 Doubly Excited 1,3 P e Resonances in He Between the N=2 and 3 He + Thresholds Ming-Keh Chen Department of Physics, National Chung-Hsing University,
Atomic Structure and Processes
 Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and Processes 5.1 Elementary atomic structure Bohr Orbits correspond to principal quantum number n. Hydrogen atom energy levels where the Rydberg energy is R y = m e ( e E n
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and Processes 5.1 Elementary atomic structure Bohr Orbits correspond to principal quantum number n. Hydrogen atom energy levels where the Rydberg energy is R y = m e ( e E n
Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga
 Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
Pramana J. Phys. (2017) 89:79 DOI 10.1007/s12043-017-1469-x Indian Academy of Sciences Energy levels and radiative rates for Ne-like ions from Cu to Ga NARENDRA SINGH and SUNNY AGGARWAL Department of Physics,
Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540
 Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540 Questions about organization Second quantization Questions about last class? Comments? Similar strategy N-particles Consider Two-body operators in Fock
Quantum Theory of Many-Particle Systems, Phys. 540 Questions about organization Second quantization Questions about last class? Comments? Similar strategy N-particles Consider Two-body operators in Fock
CPT ALPHA CPT 2.1 CPT , CERN. TRIUMF Canada s National Laboratory for Particle and Nuclear Physics
 258 501 ALPHA (CERN) CPT, CERN ishida@icepp.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp TRIUMF Canada s National Laboratory for Particle and Nuclear Physics Makoto.Fujiwara@triumf.ca 2015 2 26 ( H ) (p ) ( e + ) CPT ( ) CERN (AD;
258 501 ALPHA (CERN) CPT, CERN ishida@icepp.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp TRIUMF Canada s National Laboratory for Particle and Nuclear Physics Makoto.Fujiwara@triumf.ca 2015 2 26 ( H ) (p ) ( e + ) CPT ( ) CERN (AD;
Nicola Fabiano Perugia University and INFN, via Pascoli I-06100, Perugia, Italy. Abstract
 η b Decay into Two Photons Nicola Fabiano Perugia University and INFN, via Pascoli I-06100, Perugia, Italy Abstract We discuss the theoretical predictions for the two photon decay width of the pseudoscalar
η b Decay into Two Photons Nicola Fabiano Perugia University and INFN, via Pascoli I-06100, Perugia, Italy Abstract We discuss the theoretical predictions for the two photon decay width of the pseudoscalar
A more comprehensive theory was needed. 1925, Schrödinger and Heisenberg separately worked out a new theory Quantum Mechanics.
 Ch28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms Bohr s model was very successful to explain line spectra and the ionization energy for hydrogen. However, it also had many limitations: It was not able to predict the line
Ch28 Quantum Mechanics of Atoms Bohr s model was very successful to explain line spectra and the ionization energy for hydrogen. However, it also had many limitations: It was not able to predict the line
Preliminary Quantum Questions
 Preliminary Quantum Questions Thomas Ouldridge October 01 1. Certain quantities that appear in the theory of hydrogen have wider application in atomic physics: the Bohr radius a 0, the Rydberg constant
Preliminary Quantum Questions Thomas Ouldridge October 01 1. Certain quantities that appear in the theory of hydrogen have wider application in atomic physics: the Bohr radius a 0, the Rydberg constant
Form Factors with Electrons and Positrons
 HUGS2013, JLab, May 28 June 14, 2013 Form Factors with Electrons and Positrons Part 2: Proton form factor measurements Michael Kohl Hampton University, Hampton, VA 23668 Jefferson Laboratory, Newport News,
HUGS2013, JLab, May 28 June 14, 2013 Form Factors with Electrons and Positrons Part 2: Proton form factor measurements Michael Kohl Hampton University, Hampton, VA 23668 Jefferson Laboratory, Newport News,
Prospects for a Million-fold Improvement in the Comparison of Antiproton and Proton Magnetic Moments
 Prospects for a Million-fold Improvement in the Comparison of Antiproton and Proton Magnetic Moments Nicholas Guise Harvard University Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA LEPTON MOMENTS 19 July 2010 Prospects
Prospects for a Million-fold Improvement in the Comparison of Antiproton and Proton Magnetic Moments Nicholas Guise Harvard University Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA LEPTON MOMENTS 19 July 2010 Prospects
