Chapter 4 AD AS. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos. Computational Economics: a concise introduction
|
|
|
- Junior York
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 4 AD AS O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 32
2 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Numerical solution 4 Computational implementation 5 Numerical results and simulation 6 Highlights 7 Main references O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 2 / 32
3 Introduction The AD AS model, Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply is an aggregation of the elementary microeconomic demand-and-supply model. The AD curve can be obtained from the IS LM curves, by removing the fixed price level, representing the set of output and price level combinations that guarantee equilibrium of goods and services and monetary markets. The AS curve represents the set of output and price level combinations that maximise profits of firms. The equilibrium levels of the main variables, GDP and price level, P, are determined by the interaction of the AD and AS curves. MATLAB/Octave is used to solve the nonlinear model (Newton method and variants). O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 3 / 32
4 Economic model The set-up of the typical AD AS model specifies relationships among aggregate variables. This model can be used to study the effect of changes either in policy variables or in the specification of the interaction between endogenous variables: product equals aggregate demand, Y = C + I + G; consumption function, C = C + cy (1 t); investment function, I = I br; public spending function, G = G; income taxes function, T = ty ; money demand, L = L + ky hr; money supply function, M P ; production function, Y = A K α H 1 α. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 4 / 32
5 Economic model Endogenous variables are: product, Y ; consumption, C; investment, I; interest rate, R; prices, P. Exogenous variables are: government/public spending, G; independent/autonomous consumption, C; independent/autonomous investment, I; money supply, M; nominal wages, W ; Capital, K ; labour (which is given), H; total productivity of factors, A. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 5 / 32
6 Economic model Parameters: 0 < c < 1 is the propensity to consume; b > 0 is the interest sensitivity of investment; k > 0 is the output sensitivity of the demand for money; h > 0 is the interest sensitivity of the demand for money; t 0 is the tax rate; 0 < α < 1 is the share of labour in production; 1 α is the share of capital in production. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 6 / 32
7 Economic model AD curve: aggregate demand The AD curve represents the various amounts of real GDP, IS-LM equilibrium output, that buyers will desire to purchase at each possible price level. Y = ( ) ( ) 1 h L M P 1 b C + I + G c(1 t) 1 b k h. (1) Representing (Y, P), respectively, in the x axis and y axis, it can be stated that: the position of the AD curve is affected by any factor that affects the position of IS and LM curves; Y < 0 (negative slope); P points on the left (right) side of the curve imply excess (scarcity) of aggregate demand. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 7 / 32
8 Economic model AS curve: aggregate supply The AS curve represents the real domestic output level that is supplied by the economy at different price levels, having three distinct segments Horizontal range: the price level remains constant, P = P, with substantial output variation, and the economy is far from full employment Keynesian (or short-run aggregate supply) curve (implicit in the IS LM model). Intermediate (up sloping) range: the expansion of real output is accompanied by a rising price level, near to a full employment level the hybrid (or intermediate or medium-run aggregate supply) curve (AS mr ), Y = A K α ( W P K α (1 α)a ) α 1 α. (2) Vertical range: absolute full capacity is assumed and full employment occurs at the natural rate of unemployment, Y = Y N Classical AS (or long-run aggregate supply) curve. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 8 / 32
9 Economic model AS curve: aggregate supply It can be stated that: AS mr position depends on a change in input prices, change in productivity and change in legal institutional environment; Y P > 0 (positive slope). O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 9 / 32
10 Economic model Putting the AD and the AS curves together Equilibrium price and quantity are found where the AD and AS curves intersect. If the AD curve shifts right, in the intermediate and vertical AS curve ranges it will cause demand-pull inflation, whereas in the horizontal it will only cause output changes. The multiplier effect is weakened by price level changes in intermediate and vertical AS curve ranges: the more price level increases the smaller the effect on real GDP is. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 10 / 32
11 Numerical solution Computing the zeros of a real function f, or equivalently the roots of the equation f (x) = 0, is a frequent problem in economy. Contrary to linear systems, this computation cannot be accomplished in a finite number of operations; thus, one must rely on iterative methods. Iterative methods. Starting from x 0, build a sequence x k, k = 1, 2,..., convergent to a zero of f. The quality of the solution can be measured by the residual, f (x k ), or by the error, x k x, where x is the solution sought. The convergence rate r of the iterative process is linear, super-linear or quadratic, if x k+1 x lim k x k x r = c for a nonzero constant c, respectively, r = 1, r > 1 or r = 2. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 11 / 32
12 Numerical solution Scalar nonlinear equations Bisection method. If f on [a 0, b 0 ] satisfies f (a 0 )f (b 0 ) < 0, then it has at least one zero in the segment ]a 0, b 0 [. Taking m 0 = (a 0 + b 0 )/2, new intervals can be iteratively defined by halving the previous one according to { ]ak, m ]a k+1, b k+1 [ = k [, f (m k )f (b k ) > 0 ]m k, b k [, f (m k )f (b k ) < 0. Advantage: independent of the regularity of f. Disadvantage: low rate of convergence. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 12 / 32
13 Numerical solution Scalar nonlinear equations Newton method x k+1 = x k f (x k ) 1 f (x k ), f (x k ) 0, k = 0, 1, 2,... computes the zero by locally replacing f by its tangent line. Advantage: rate of (local) convergence of this method is quadratic. Disadvantage: requires f, expensive to compute and often not explicitly available. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 13 / 32
14 Numerical solution Scalar nonlinear equations Secant method x k+1 = x k x k x k 1 f (x k ) f (x k 1 ) f (x k), k = 0, 1, 2,..., where f (x k ) is approximated by finite differences using two successive iterates. (Local) super-linear convergence. Convergence can be improved by considering a higher order degree interpolation polynomial. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 14 / 32
15 Numerical solution Nonlinear system of equations Compute the zeros of a system of n nonlinear equations, f (x) = 0 with f : lr n lr n, x k a vector with n components, using Newton method x k+1 = x k f (x k ) 1 f (x k ), k = 0, 1, 2,... f (x k ) = J(x k ) = f 1 f 1 x 1 (x k ) x n (x k )..... f n f x 1 (x k ) n x n (x k ) where the Jacobian matrix at x k (J(x k ) is nonsingular). O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 15 / 32
16 Numerical solution Nonlinear system of equations Variants of the Newton method: use the same Jacobian several iterations; updating factorisation methods rather than re-factorising the Jacobian matrix. Disadvantage: Newton method (or variants) may not converge for x(0) far from the solution. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 16 / 32
17 Numerical solution Nonlinear (system) of equations in practice MATLAB/Octave: zeros of a continuous function of one variable: fzero(f,x0), where f is the function and x 0 an initial approximation; system of nonlinear equations: fsolve(f,x0), where f is the vector function and x 0 an initial approximation. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 17 / 32
18 Computational implementation The following baseline values are considered: c = 0.6, b = 1500, k = 0.2, b = 1500, h = 1000, t = 0.2, α = 0.5, A = 1, K = 30000, C = 160, I = 100, G = 200, M = 1000, W = 50 and L = 225. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 18 / 32
19 Computational implementation Presentation and parameters %% AD AS model % Medium run e q u i l i b r i u m % Implemented by : P. B. Vasconcelos and O. Afonso function adas global C_bar I_bar G_bar M_bar W_bar L_bar A_bar K_bar... c b t k h alpha aux disp ( ) ; disp ( AD AS model ) ; disp ( ) ; %% parameters c = 0. 6 ; % marginal p r o p e n s i t y to consume b = 1500; % s e n s i b i l i t y of the investment to the i n t e r e s t r a t e k = 0. 2 ; % s e n s i b i l i t y of the money demand to the product h = 1000; % s e n s i b i l i t y of the money demand to the i n t e r e s t r a t e t = 0. 2 ; % tax on consumption alpha = 0. 5 ; % c a p i t a l share i n production O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 19 / 32
20 Computational implementation Exogenous and endogeneous variables %% exogenous v a r i a b l e s ( autonomous components ) A_bar = 1; % exogenous p r o d u c t i v i t y K_bar = 30000; % stock of c a p i t a l C_bar = 160; % autonomous consumption I_ bar = 100; % autonomous investment G_bar = 200; % government spending M_bar = 1000; % money supply W_bar = 50; % wage L_bar = 225; % autonomous money demand disp ( exogenous v a r i a b l e s ( autonomous components ) : ) f p r i n t f ( G_bar = %d ; M_bar = %d ; W_bar = %d ; L_bar = %d \ n,... G_bar, M_bar, W_bar, L_bar ) ; %% endogenous v a r i a b l e s % Y, product % P, p r i c e O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 20 / 32
21 Computational implementation Compute, show and plot the solution %% model s o l u t i o n : compute the endogenous v a r i a b l e s x0 = [500 5 ] ; % i n i t i a l approximation f o r Y and P, resp. aux = ( c (1 t ) 1) / b k / h ; % a u x i l i a r y v a r i a b l e f o r AD curve x = f s o l v e (@ADAS_system, x0 ) ; %% show the s o l u t i o n disp ( computed endogenous v a r i a b l e s : ) f p r i n t f ( product, Y : %6.2 f \ n, x ( 1 ) ) ; f p r i n t f ( price, P : %6.2 f \ n, x ( 2 ) ) ; % show v a r i a b l e of i n t e r e s t R = 1/ h ( L_bar M_bar / x ( 2 ) +k x ( 1 ) ) ; f p r i n t f ( i n t e r e s t r a t e (%%), R: %6.2 f \ n, R 100) ; %% p l o t the s o l u t i o n P = 0 : 0. 1 : 1. 5 x ( 2 ) ; AS = A_bar K_bar^ alpha ( W_bar. / P... K_bar.^( alpha ) /((1 alpha ) A_bar ) ). ^ ( ( alpha 1) / alpha ) ; AD = 1/ h ( L_bar M_bar. / P) / aux 1/b ( C_bar+ I_bar+G_bar ) / aux ; plot (AS, P, b,ad, P, r ) ; xlim ([ ]) ; xlabel ( product ) ; ylabel ( p r i c e ) ; legend ( AS, AD ) ; O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 21 / 32
22 Computational implementation System of nonlinear equations %% AD AS system function f = ADAS_system ( x ) global C_bar I_ bar G_bar M_bar W_bar L_bar A_bar K_bar b h alpha aux ; f = [ x ( 1 ) 1/h ( L_bar M_bar / x ( 2 ) ) / aux +1/b ( C_bar+ I_bar+G_bar ) / aux ; x ( 1 ) A_bar K_bar^ alpha (W_bar / x ( 2 )... K_bar^( alpha ) /((1 alpha ) A_bar ) ) ^ ( ( alpha 1) / alpha ) ; ] ; O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 22 / 32
23 Numerical results and simulation AD-AS model exogenous variables (autonomous components): G_bar = 200; M_bar = 1000; W_bar = 50; L_bar = 225 computed endogenous variables: product, Y: price, P: 2.73 interest rate (%), R: 2.27 O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 23 / 32
24 Numerical results and simulation AS AD price product AD AS diagram O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 24 / 32
25 Numerical results and simulation Expansion of governmental spending (G increases 20%) G_bar from to initial eq. eq. after shock product, Y: price, P: interest rate, R (%): O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 25 / 32
26 Numerical results and simulation interest rate equilibrium after expansion of governamental spending LM IS LM new IS new product price AS AD AD new product Increase in G O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 26 / 32
27 Numerical results and simulation Expansion of money supply (M increases 20%) M_bar from 1000 to 1200 initial eq. eq. after shock product, Y: price, P: interest rate, R (%): O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 27 / 32
28 Numerical results and simulation interest rate equilibrium after expansion of governamental spending LM IS LM new product price AS AD AD new product Increase in M O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 28 / 32
29 Numerical results and simulation A positive supply shock (A increases 5%) A_bar from 1 to 1.05 initial eq. eq. after shock product, Y: price, P: interest rate, R (%): O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 29 / 32
30 Numerical results and simulation interest rate equilibrium after expansion of governamental spending LM IS LM new IS new product price AS AD AS new AD new product Increase in A O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 30 / 32
31 Highlights The AD AS model explains price level and output considering the relationship between aggregate demand and aggregate supply. The AD curve is defined by the IS LM equilibrium and the AS curve reflects the labour market. Iterative numerical methods for nonlinear problems are introduced. Newton and quasi-newton methods for the approximate solution of nonlinear (system of) equation(s) are briefly explained. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 31 / 32
32 Main references M. Burda and C. Wyplosz Macroeconomics: a European text Oxford University Press (2009) G. Dahlquist and Å Björck Numerical methods in scientific computing Society for Industrial Mathematics (2008) R. J. Gordon Macroeconomics Pearson Education (2011) C. T. Kelley Iterative Methods for Linear and Nonlinear Equations Society for Industrial Mathematics (1995) N. G. Mankiw Macroeconomics Worth Publishers (2009) O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 32 / 32
Mankiw Chapter 11. Aggregate Demand I. Building the IS-LM Model
 Mankiw Chapter 11 Building the IS-LM Model 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: the IS curve and its relation to: the Keynesian cross the LM curve and its relation to: the theory of liquidity preference how
Mankiw Chapter 11 Building the IS-LM Model 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: the IS curve and its relation to: the Keynesian cross the LM curve and its relation to: the theory of liquidity preference how
Chapter 9 Solow. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos. Computational Economics: a concise introduction
 Chapter 9 Solow O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 27 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Computational
Chapter 9 Solow O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 27 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Computational
IS-LM Analysis. Math 202. Brian D. Fitzpatrick. Duke University. February 14, 2018 MATH
 IS-LM Analysis Math 202 Brian D. Fitzpatrick Duke University February 14, 2018 MATH Overview Background History Variables The GDP Equation Definition of GDP Assumptions The GDP Equation with Assumptions
IS-LM Analysis Math 202 Brian D. Fitzpatrick Duke University February 14, 2018 MATH Overview Background History Variables The GDP Equation Definition of GDP Assumptions The GDP Equation with Assumptions
Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory
 2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
Chapter 7 Duopoly. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos. Computational Economics: a concise introduction
 Chapter 7 Duopoly O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 21 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Numerical
Chapter 7 Duopoly O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 21 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Numerical
Chapter 12 Ramsey Cass Koopmans model
 Chapter 12 Ramsey Cass Koopmans model O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 33 Overview 1 Introduction 2
Chapter 12 Ramsey Cass Koopmans model O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 33 Overview 1 Introduction 2
Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis
 Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis Yulei Luo Econ, HKU November 13, 2017 Luo, Y. (Econ, HKU) ECON2220CB: Intermediate Macro November 13, 2017 1 / 14 The
Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis Yulei Luo Econ, HKU November 13, 2017 Luo, Y. (Econ, HKU) ECON2220CB: Intermediate Macro November 13, 2017 1 / 14 The
Test code: ME I/ME II, 2004 Syllabus for ME I. Matrix Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matrix Operations, Determinants,
 Test code: ME I/ME II, 004 Syllabus for ME I Matri Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matri Operations, Determinants, Nonsingularity, Inversion, Cramer s rule. Calculus: Limits, Continuity, Differentiation
Test code: ME I/ME II, 004 Syllabus for ME I Matri Algebra: Matrices and Vectors, Matri Operations, Determinants, Nonsingularity, Inversion, Cramer s rule. Calculus: Limits, Continuity, Differentiation
Chapter 10 Skill biased technological change
 Chapter 10 Skill biased technological change O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 29 Overview 1 Introduction
Chapter 10 Skill biased technological change O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 29 Overview 1 Introduction
MTAEA Implicit Functions
 School of Economics, Australian National University February 12, 2010 Implicit Functions and Their Derivatives Up till now we have only worked with functions in which the endogenous variables are explicit
School of Economics, Australian National University February 12, 2010 Implicit Functions and Their Derivatives Up till now we have only worked with functions in which the endogenous variables are explicit
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 2: Dynamics in Aggregate Demand and Supply
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 2 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 2: Dynamics in Aggregate Demand and Supply Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics:
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 2 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 2: Dynamics in Aggregate Demand and Supply Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics:
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction
 The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam?
 The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
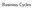 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium
 Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey
 Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey Chapter 5 Nonlinear Equations Prof. Michael T. Heath Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Copyright c 2002. Reproduction
Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey Chapter 5 Nonlinear Equations Prof. Michael T. Heath Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Copyright c 2002. Reproduction
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 4: Anticipation effects and economic policy BJ Heijdra Department of Economics, Econometrics & Finance University of Groningen 1 September 2009
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 4: Anticipation effects and economic policy BJ Heijdra Department of Economics, Econometrics & Finance University of Groningen 1 September 2009
ECON2285: Mathematical Economics
 ECON2285: Mathematical Economics Yulei Luo FBE, HKU September 2, 2018 Luo, Y. (FBE, HKU) ME September 2, 2018 1 / 35 Course Outline Economics: The study of the choices people (consumers, firm managers,
ECON2285: Mathematical Economics Yulei Luo FBE, HKU September 2, 2018 Luo, Y. (FBE, HKU) ME September 2, 2018 1 / 35 Course Outline Economics: The study of the choices people (consumers, firm managers,
Theoretical premises of the Keynesian approach
 origin of Keynesian approach to Growth can be traced back to an article written after the General Theory (1936) Roy Harrod, An Essay in Dynamic Theory, Economic Journal, 1939 Theoretical premises of the
origin of Keynesian approach to Growth can be traced back to an article written after the General Theory (1936) Roy Harrod, An Essay in Dynamic Theory, Economic Journal, 1939 Theoretical premises of the
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
The Real Business Cycle Model
 The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
Monetary Economics. Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one. Chris Edmond. 2nd Semester 2014
 Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case.
 Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV
 Keynes and the Classics Notes on the Monetary Theory of Production Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV Social production, value and distribution (436-445) The starting point is a Leontief price system:
Keynes and the Classics Notes on the Monetary Theory of Production Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV Social production, value and distribution (436-445) The starting point is a Leontief price system:
Econ Review Set 2 - Answers
 Econ 4808 Review Set 2 - Answers EQUILIBRIUM ANALYSIS 1. De ne the concept of equilibrium within the con nes of an economic model. Provide an example of an economic equilibrium. Economic models contain
Econ 4808 Review Set 2 - Answers EQUILIBRIUM ANALYSIS 1. De ne the concept of equilibrium within the con nes of an economic model. Provide an example of an economic equilibrium. Economic models contain
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model
 Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
V. The Speed of adjustment of Endogenous Variables and Overshooting
 V. The Speed of adjustment of Endogenous Variables and Overshooting The second section of Chapter 11 of Dornbusch (1980) draws on Dornbusch (1976) Expectations and Exchange Rate Dynamics, Journal of Political
V. The Speed of adjustment of Endogenous Variables and Overshooting The second section of Chapter 11 of Dornbusch (1980) draws on Dornbusch (1976) Expectations and Exchange Rate Dynamics, Journal of Political
Assignment #5. 1 Keynesian Cross. Econ 302: Intermediate Macroeconomics. December 2, 2009
 Assignment #5 Econ 0: Intermediate Macroeconomics December, 009 Keynesian Cross Consider a closed economy. Consumption function: C = C + M C(Y T ) () In addition, suppose that planned investment expenditure
Assignment #5 Econ 0: Intermediate Macroeconomics December, 009 Keynesian Cross Consider a closed economy. Consumption function: C = C + M C(Y T ) () In addition, suppose that planned investment expenditure
Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade
 Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 147-158 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade Michiya Nozaki Gifu Keizai
Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 147-158 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade Michiya Nozaki Gifu Keizai
Study Skills in Mathematics. Edited by D. Burkhardt and D. Rutherford. Nottingham: Shell Centre for Mathematical Education (Revised edn 1981).
 Study Skills in Mathematics. Edited by D. Burkhardt and D. Rutherford. Nottingham: Shell Centre for Mathematical Education (Revised edn 1981). (Copies are available from the Shell Centre for Mathematical
Study Skills in Mathematics. Edited by D. Burkhardt and D. Rutherford. Nottingham: Shell Centre for Mathematical Education (Revised edn 1981). (Copies are available from the Shell Centre for Mathematical
Lecture Notes to Accompany. Scientific Computing An Introductory Survey. by Michael T. Heath. Chapter 5. Nonlinear Equations
 Lecture Notes to Accompany Scientific Computing An Introductory Survey Second Edition by Michael T Heath Chapter 5 Nonlinear Equations Copyright c 2001 Reproduction permitted only for noncommercial, educational
Lecture Notes to Accompany Scientific Computing An Introductory Survey Second Edition by Michael T Heath Chapter 5 Nonlinear Equations Copyright c 2001 Reproduction permitted only for noncommercial, educational
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World
 Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin November 28, 2016 Lindé and Trabandt Multipliers () in Nonlinear Models November 28, 2016
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin November 28, 2016 Lindé and Trabandt Multipliers () in Nonlinear Models November 28, 2016
Outline. Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey. Nonlinear Equations. Nonlinear Equations. Examples: Nonlinear Equations
 Methods for Systems of Methods for Systems of Outline Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey Chapter 5 1 Prof. Michael T. Heath Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Methods for Systems of Methods for Systems of Outline Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey Chapter 5 1 Prof. Michael T. Heath Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
ECONOMICS TRIPOS PART I. Friday 15 June to 12. Paper 3 QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS
 ECONOMICS TRIPOS PART I Friday 15 June 2007 9 to 12 Paper 3 QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS This exam comprises four sections. Sections A and B are on Mathematics; Sections C and D are on Statistics.
ECONOMICS TRIPOS PART I Friday 15 June 2007 9 to 12 Paper 3 QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS This exam comprises four sections. Sections A and B are on Mathematics; Sections C and D are on Statistics.
CS 450 Numerical Analysis. Chapter 5: Nonlinear Equations
 Lecture slides based on the textbook Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey by Michael T. Heath, copyright c 2018 by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. http://www.siam.org/books/cl80
Lecture slides based on the textbook Scientific Computing: An Introductory Survey by Michael T. Heath, copyright c 2018 by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. http://www.siam.org/books/cl80
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
A Summary of Economic Methodology
 A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT AND ECONOMICS Royal Military College of Canada. ECE Modelling in Economics Instructor: Lenin Arango-Castillo
 Page 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT AND ECONOMICS Royal Military College of Canada ECE 256 - Modelling in Economics Instructor: Lenin Arango-Castillo Final Examination 13:00-16:00, December 11, 2017 INSTRUCTIONS
Page 1 of 5 DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT AND ECONOMICS Royal Military College of Canada ECE 256 - Modelling in Economics Instructor: Lenin Arango-Castillo Final Examination 13:00-16:00, December 11, 2017 INSTRUCTIONS
Exercises for Chapter 7
 Exercises for Chapter 7 Exercise 7.1 The following simple macroeconomic model has four equations relating government policy variables to aggregate income and investment. Aggregate income equals consumption
Exercises for Chapter 7 Exercise 7.1 The following simple macroeconomic model has four equations relating government policy variables to aggregate income and investment. Aggregate income equals consumption
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory
 ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models. December 4, 2007
 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models December 4, 2007 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models Random shocks to generate trajectories that look like the observed national accounts. Rational
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models December 4, 2007 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models Random shocks to generate trajectories that look like the observed national accounts. Rational
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital
 Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Extended IS-LM model - construction and analysis of behavior
 Extended IS-LM model - construction and analysis of behavior David Martinčík Department of Economics and Finance, Faculty of Economics, University of West Bohemia, martinci@kef.zcu.cz Blanka Šedivá Department
Extended IS-LM model - construction and analysis of behavior David Martinčík Department of Economics and Finance, Faculty of Economics, University of West Bohemia, martinci@kef.zcu.cz Blanka Šedivá Department
PROBLEM SET 1 (Solutions) (MACROECONOMICS cl. 15)
 PROBLEM SET (Solutions) (MACROECONOMICS cl. 5) Exercise Calculating GDP In an economic system there are two sectors A and B. The sector A: - produces value added or a value o 50; - pays wages or a value
PROBLEM SET (Solutions) (MACROECONOMICS cl. 5) Exercise Calculating GDP In an economic system there are two sectors A and B. The sector A: - produces value added or a value o 50; - pays wages or a value
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
ECON0702: Mathematical Methods in Economics
 ECON0702: Mathematical Methods in Economics Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 12, 2009 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) MME January 12, 2009 1 / 35 Course Outline Economics: The study of the choices people (consumers,
ECON0702: Mathematical Methods in Economics Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 12, 2009 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) MME January 12, 2009 1 / 35 Course Outline Economics: The study of the choices people (consumers,
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment
 Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) September 2014 1 / 44 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 44 Motivation
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) September 2014 1 / 44 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 44 Motivation
Learning, Expectations, and Endogenous Business Cycles
 Learning, Expectations, and Endogenous Business Cycles I.S.E.O. Summer School June 19, 2013 Introduction A simple model Simulations Stability Monetary Policy What s next Who we are Two students writing
Learning, Expectations, and Endogenous Business Cycles I.S.E.O. Summer School June 19, 2013 Introduction A simple model Simulations Stability Monetary Policy What s next Who we are Two students writing
(a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies
 Journal of Regional Development Studies2010 131 Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies Ken-ichi ISHIYAMA 1. Introduction We have observed large increases in trade and
Journal of Regional Development Studies2010 131 Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies Ken-ichi ISHIYAMA 1. Introduction We have observed large increases in trade and
Assumption 5. The technology is represented by a production function, F : R 3 + R +, F (K t, N t, A t )
 6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment
 Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) July 2014 1 / 46 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 46 Motivation
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) July 2014 1 / 46 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 46 Motivation
Maria Cameron. f(x) = 1 n
 Maria Cameron 1. Local algorithms for solving nonlinear equations Here we discuss local methods for nonlinear equations r(x) =. These methods are Newton, inexact Newton and quasi-newton. We will show that
Maria Cameron 1. Local algorithms for solving nonlinear equations Here we discuss local methods for nonlinear equations r(x) =. These methods are Newton, inexact Newton and quasi-newton. We will show that
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital
 Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano Gerzensee, August 27 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano Gerzensee, August 27 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1
 Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
Functions of One Variable
 Functions of One Variable Mathematical Economics Vilen Lipatov Fall 2014 Outline Functions of one real variable Graphs Linear functions Polynomials, powers and exponentials Reading: Sydsaeter and Hammond,
Functions of One Variable Mathematical Economics Vilen Lipatov Fall 2014 Outline Functions of one real variable Graphs Linear functions Polynomials, powers and exponentials Reading: Sydsaeter and Hammond,
Business Cycles: The Classical Approach
 San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy
 Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy Economics 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Kam Yu Winter 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Basic DGE Closed Economy 3 Golden Rule Solution 4 Optimal Solution The Euler Equation
Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy Economics 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Kam Yu Winter 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Basic DGE Closed Economy 3 Golden Rule Solution 4 Optimal Solution The Euler Equation
A Modern Equilibrium Model. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
Endogenous Growth Theory
 Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
ES10006: Core skills for economists: Mathematics 2
 ES10006: Core skills for economists: Mathematics 2 Seminar 6 Problem set no. 4: Questions 1c, 1d, 2, 4, 7, 8b First-order linear differential equations From Chiang and Wainwright (2005, Section 15.1),
ES10006: Core skills for economists: Mathematics 2 Seminar 6 Problem set no. 4: Questions 1c, 1d, 2, 4, 7, 8b First-order linear differential equations From Chiang and Wainwright (2005, Section 15.1),
The Keynesian Model of Income Determination (revised)
 Economics 32 Menzie D. Chinn Spring 2 Social Sciences 748 University of Wisconsin-Madison The Keynesian Model of Income Determination revised This set of notes outlines the Keynesian model of national
Economics 32 Menzie D. Chinn Spring 2 Social Sciences 748 University of Wisconsin-Madison The Keynesian Model of Income Determination revised This set of notes outlines the Keynesian model of national
ECON0702: Mathematical Methods in Economics
 ECON0702: Mathematical Methods in Economics Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 14, 2009 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) MME January 14, 2009 1 / 44 Comparative Statics and The Concept of Derivative Comparative Statics
ECON0702: Mathematical Methods in Economics Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 14, 2009 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) MME January 14, 2009 1 / 44 Comparative Statics and The Concept of Derivative Comparative Statics
Monetary Economics Notes
 Monetary Economics Notes Nicola Viegi 2 University of Pretoria - School of Economics Contents New Keynesian Models. Readings...............................2 Basic New Keynesian Model...................
Monetary Economics Notes Nicola Viegi 2 University of Pretoria - School of Economics Contents New Keynesian Models. Readings...............................2 Basic New Keynesian Model...................
3. Medium Run AS-AD Model 3.1 Labor Market Equilibrium (2)
 3. Medium Run AS-AD Model 3. Labor Market Equilibrium () Medium-run GD Equilibrium: Demand roduction Un-/Employment Labor Market Wage/Cost Goods Market rice Income Demand articipation Rate Unemployment
3. Medium Run AS-AD Model 3. Labor Market Equilibrium () Medium-run GD Equilibrium: Demand roduction Un-/Employment Labor Market Wage/Cost Goods Market rice Income Demand articipation Rate Unemployment
Chap. II: Fiscal Multipliers. L3 TSE: Macroeconomics 2014
 Chap. II: Fiscal Multipliers Patrick Fève Toulouse School of Economics GREMAQ, IDEI and IUF Adresse e-mail: patrick.feve@tse-eu.fr Internet: See the Website of TSE MF 508 L3 TSE: Macroeconomics 2014 Thomas
Chap. II: Fiscal Multipliers Patrick Fève Toulouse School of Economics GREMAQ, IDEI and IUF Adresse e-mail: patrick.feve@tse-eu.fr Internet: See the Website of TSE MF 508 L3 TSE: Macroeconomics 2014 Thomas
Final Exam. You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind.
 Professor Christiano Economics 311, Winter 2005 Final Exam IMPORTANT: read the following notes You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind. A total of 100 points is possible, with the distribution
Professor Christiano Economics 311, Winter 2005 Final Exam IMPORTANT: read the following notes You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind. A total of 100 points is possible, with the distribution
Does Pleasing Export-Oriented Foreign Investors Help Your. Balance of Payments? A General Equilibrium Analysis. (Available on Request Appendix)
 Does Pleasing Export-Oriented Foreign Investors Help Your Balance of Payments? A General Equilibrium Analysis (Available on Request Appendix) Derivation of the Excess Demand Equations, the IS Equation,
Does Pleasing Export-Oriented Foreign Investors Help Your Balance of Payments? A General Equilibrium Analysis (Available on Request Appendix) Derivation of the Excess Demand Equations, the IS Equation,
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8
 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Online Appendix for Investment Hangover and the Great Recession
 ONLINE APPENDIX INVESTMENT HANGOVER A1 Online Appendix for Investment Hangover and the Great Recession By MATTHEW ROGNLIE, ANDREI SHLEIFER, AND ALP SIMSEK APPENDIX A: CALIBRATION This appendix describes
ONLINE APPENDIX INVESTMENT HANGOVER A1 Online Appendix for Investment Hangover and the Great Recession By MATTHEW ROGNLIE, ANDREI SHLEIFER, AND ALP SIMSEK APPENDIX A: CALIBRATION This appendix describes
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research
 This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: A Theoretical Framework for Monetary Analysis Volume Author/Editor: Milton Friedman Volume
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the National Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: A Theoretical Framework for Monetary Analysis Volume Author/Editor: Milton Friedman Volume
Toulouse School of Economics, M2 Macroeconomics 1 Professor Franck Portier. Exam Solution
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2013-2014 M2 Macroeconomics 1 Professor Franck Portier Exam Solution This is a 3 hours exam. Class slides and any handwritten material are allowed. You must write legibly.
Toulouse School of Economics, 2013-2014 M2 Macroeconomics 1 Professor Franck Portier Exam Solution This is a 3 hours exam. Class slides and any handwritten material are allowed. You must write legibly.
The Ramsey Model. (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 2013)
 The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
Foundation of (virtually) all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model) is Solow growth model
 THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
KÖZGAZDASÁGI ALAPISMERETEK (ELMÉLETI GAZDASÁGTAN) ANGOL NYELVEN
 Közgazdasági alapismeretek (elméleti gazdaságtan) középszint angol nyelven Javítási-értékelésiútmutató 1212 ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA 2012. május 25. KÖZGAZDASÁGI ALAPISMERETEK (ELMÉLETI GAZDASÁGTAN) ANGOL NYELVEN
Közgazdasági alapismeretek (elméleti gazdaságtan) középszint angol nyelven Javítási-értékelésiútmutató 1212 ÉRETTSÉGI VIZSGA 2012. május 25. KÖZGAZDASÁGI ALAPISMERETEK (ELMÉLETI GAZDASÁGTAN) ANGOL NYELVEN
General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 2013
 HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999)
 Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model
 A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
Wooldridge, Introductory Econometrics, 3d ed. Chapter 16: Simultaneous equations models. An obvious reason for the endogeneity of explanatory
 Wooldridge, Introductory Econometrics, 3d ed. Chapter 16: Simultaneous equations models An obvious reason for the endogeneity of explanatory variables in a regression model is simultaneity: that is, one
Wooldridge, Introductory Econometrics, 3d ed. Chapter 16: Simultaneous equations models An obvious reason for the endogeneity of explanatory variables in a regression model is simultaneity: that is, one
Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions
 Monetary Economics Problem Set #4 Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions This problem set is marked out of 100 points. The weight given to each part is indicated below. Please contact me asap if
Monetary Economics Problem Set #4 Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions This problem set is marked out of 100 points. The weight given to each part is indicated below. Please contact me asap if
problem. max Both k (0) and h (0) are given at time 0. (a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
Economics 203: Intermediate Microeconomics. Calculus Review. A function f, is a rule assigning a value y for each value x.
 Economics 203: Intermediate Microeconomics Calculus Review Functions, Graphs and Coordinates Econ 203 Calculus Review p. 1 Functions: A function f, is a rule assigning a value y for each value x. The following
Economics 203: Intermediate Microeconomics Calculus Review Functions, Graphs and Coordinates Econ 203 Calculus Review p. 1 Functions: A function f, is a rule assigning a value y for each value x. The following
Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy
 Class handout Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy Giovanni Di Bartolomeo University of Teramo 1. The Phillips menu In the 190s, econometricians estimated a negative relationship
Class handout Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy Giovanni Di Bartolomeo University of Teramo 1. The Phillips menu In the 190s, econometricians estimated a negative relationship
Solution for Problem Set 3
 Solution for Problem Set 3 Q. Heterogeneous Expectations. Consider following dynamic IS-LM economy in Lecture Notes 8: IS curve: y t = ar t + u t (.) where y t is output, r t is the real interest rate,
Solution for Problem Set 3 Q. Heterogeneous Expectations. Consider following dynamic IS-LM economy in Lecture Notes 8: IS curve: y t = ar t + u t (.) where y t is output, r t is the real interest rate,
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model
 Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Tutorial 2: Comparative Statics
 Tutorial 2: Comparative Statics ECO42F 20 Derivatives and Rules of Differentiation For each of the functions below: (a) Find the difference quotient. (b) Find the derivative dx. (c) Find f (4) and f (3)..
Tutorial 2: Comparative Statics ECO42F 20 Derivatives and Rules of Differentiation For each of the functions below: (a) Find the difference quotient. (b) Find the derivative dx. (c) Find f (4) and f (3)..
Equilibrium in a Production Economy
 Equilibrium in a Production Economy Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2012 Sims (ND) Equilibrium in a Production Economy Fall 2012 1 / 23 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in
Equilibrium in a Production Economy Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2012 Sims (ND) Equilibrium in a Production Economy Fall 2012 1 / 23 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective
 Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE April 215 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment April 215 1 / 16
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE April 215 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment April 215 1 / 16
h Edition Money in Search Equilibrium
 In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Money in Search Equilibrium Diamond (1984) Navid Raeesi Spring 2014 Page 1 Introduction: Markets with Search
In the Name of God Sharif University of Technology Graduate School of Management and Economics Money in Search Equilibrium Diamond (1984) Navid Raeesi Spring 2014 Page 1 Introduction: Markets with Search
Lecture 7. The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium. ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter Kam Yu Department of Economics Lakehead University
 Lecture 7 The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 2013 Phillips Department of Economics Lakehead University 7.1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Phillips Phillips 7.2 Market Equilibrium:
Lecture 7 The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 2013 Phillips Department of Economics Lakehead University 7.1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Phillips Phillips 7.2 Market Equilibrium:
Introductory Mathematics and Statistics Summer Practice Questions
 University of Warwick Introductory Mathematics and Statistics Summer Practice Questions Jeremy Smith Piotr Z. Jelonek Nicholas Jackson This version: 22nd August 2017 Please find below a list of warm-up
University of Warwick Introductory Mathematics and Statistics Summer Practice Questions Jeremy Smith Piotr Z. Jelonek Nicholas Jackson This version: 22nd August 2017 Please find below a list of warm-up
Differentiation. 1. What is a Derivative? CHAPTER 5
 CHAPTER 5 Differentiation Differentiation is a technique that enables us to find out how a function changes when its argument changes It is an essential tool in economics If you have done A-level maths,
CHAPTER 5 Differentiation Differentiation is a technique that enables us to find out how a function changes when its argument changes It is an essential tool in economics If you have done A-level maths,
Equilibrium in Factors Market: Properties
 Equilibrium in Factors Market: Properties Ram Singh Microeconomic Theory Lecture 12 Ram Singh: (DSE) Factor Prices Lecture 12 1 / 17 Questions What is the relationship between output prices and the wage
Equilibrium in Factors Market: Properties Ram Singh Microeconomic Theory Lecture 12 Ram Singh: (DSE) Factor Prices Lecture 12 1 / 17 Questions What is the relationship between output prices and the wage
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models
 Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Stagnation Traps. Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro
 Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Masanori Yokoo. 1 Introduction
 Masanori Yokoo Abstract In many standard undergraduate textbooks of macroeconomics, open economies are discussed by means of the Mundell Fleming model, an open macroeconomic version of the IS LM model.
Masanori Yokoo Abstract In many standard undergraduate textbooks of macroeconomics, open economies are discussed by means of the Mundell Fleming model, an open macroeconomic version of the IS LM model.
