Theoretical premises of the Keynesian approach
|
|
|
- Rebecca Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 origin of Keynesian approach to Growth can be traced back to an article written after the General Theory (1936) Roy Harrod, An Essay in Dynamic Theory, Economic Journal, 1939 Theoretical premises of the Keynesian approach uncertainty and expectations play a role in investment decisions nominal rigidities (money wage and prices) follow from institutional rules forged by social selection: more instability with flexible prices and wages under employment equilibria: capitalistic economies normally operate at less than full employment of labor and at less than full utilization of capacity quantity adjustment (Keynesian income multiplier): output is demandconstrained, and an increase in demand is met by a more efficient use of existing resources.
2 Nominal rigidities and desired K* / Y one good economy: price of output Py = 1 competitive firms minimize costs at given money prices w, r constant returns to scale technology L employment labor supply at money wage w K existing capital stock from past entrepreneurial decisions Y = F (K, L) ay = F(aK, al) a > 0
3 Intensive production function y Y / L k K / L y = F (k, 1) f(k) f (k) = F(K, L) / K at k = K/L f (k) > 0 f (k) < 0 f (k) decreasing function of k f(k)/k decreasing function of k
4 Constant returns to scale implies: Y / K is well defined decreasing function of k Y / L is well defined increasing function of k cost minimizing (desired) k Y / K = f (k) = r (assume depreciation δ=0) Y / L = f(k) k f (k) = w
5 Price rigidities Suppose r, w are fixed cost minimizing k is fixed cost minimizing y = f(k) is fixed k / f(k) desired capital output rao is fixed! K / Y = k / y K / Y is fixed by prices K / Y v desired rao between capital stock and output
6 Alternative interpretation of fixed Capital / Output ratio v Modern technologies are Leontief type: Y min ( K, L) Static efficiency (cost minimization) = α K = αl L = K Y K = K full capacity output Static efficiency: K / Y K = α cost minimizing K/Y Firms need prompt response to unexpected peaks in demand: they plan desired capacity utilization u n < 1 Capacity utilization = u = 1 implies Y = L = K Uncertainty + fast adjustment (dynamic efficiency) require: Desired capacity utilization u n < 1 implies Desired = Remark: because Y = L, desired = desired = v
7 min, K = v (desired) (cost minimizing) u < 1 u = 1 If firms expect otput, they wish and plan to have capital sock, such that. In this way, the buy a margin of flexibility, and can meet an unexpected peak in output up to. L
8 Harrod (1939) Macroeconomic growth model 1 good economy for simplicity Part 1. explain equilibrium growth path of the economy defined as the growth path realizing: macroeconomic equilibrium in the good market (agg. demand = agg. supply) at every t > 0 Capacity produced by investment is optimally utilized Demand expectations supporting those investments are fulfilled
9 Building blocks: 1. Savings St = s Yt s marginal and average savings rate (1) 2. Keynesian expenditure and income multiplier syt = It It Kt+1 Kt = investment demand at time t (2) K = capital stock
10 3. Investment accelerator v = desired ratio between capital stock and output planned by firms Y e t+1 = expectation on demand at t+1, formulated at t Kt+1 = vy e t+1 Kt = vy e t I t = Kt+1 Kt = vy e t+1 vy e t = v(y e t+1 Y e t) (3)
11 4. Endogenous variable: growth expectations g e t g e t (Y e t+1 Y e t) / Y e t growth rate of expected demand Y e t+1 = Y e t (1+ g e t ) (4) (Y e t+1 Y e t) = Y e t (1+ g e t ) Y e t = Y e t g e t (4 ) Substituting for (Y e t+1 Y e t) in I t = v(y e t+1 Y e t) (3) 5. Investment as determined by growth expectations I t = vy e t g e t (5)
12 6. Investments as determinants of current effective demand vy e t g e t = I t = s Y t (6) Interpretation: vy e t g e t I t Y t Notice that entrepreneurs take their investment decisions I t an instant before income Y t is realized
13 7. Equilibrium growth equilibrium is a state in which agents are not induced to revise their decisions. fulfilled predictions : Y e t = Y t (6) desired investment vy e t g e t = I t = s Y t desired saving (7) Substituting from (6) into (7): vy t g e t= s Y t vg e t = s g e t = s / v g*
14 Compare Harrod s warranted path with Solow s equilibrium path: Harrod: v = K/Y = constant, in general Solow: y = kα δ = 0 for simplicity v = = in steady state, v is flexible and is determined fixed by factor supply + full employment
15 Harrod s Proposition 1. The unique growth rate of expected demand consistent with equilibrium in the goods market and fulfilled entrepreneurs expectations is: g* = s / v if g e t g* then predictions are not self-fulfilling g e t g t
16 Interpretation: If the economy is on a warranted equilibrium path, at t entrepreneurs are happy with past investment decisions giving rise to the existing stock K t. This implies that Y t is such that v Y t = K t Because Y t depends on current investment (through the income multiplier), and investment depends on growth expectations, equilibrium requires that entrepreneurs expectations at time t are such that g e t = g* s / v
17 Part 2. Study the dynamic stability of warranted growth path actual growth rate g t 1 (Yt Yt 1) / Yt 1 will materialize at end of t Assume the adjustment rule: g t 1 > g e t 1 g e t > g e t 1 g t 1 < g e t 1 g e t < g e t 1 (8) g t 1 = g e t 1 g e t = g e t 1
18 expectation formation more plausible adjustment rules exploit longer sequence of data?? Harrod : uncertainty surrounding long term prospects is very high entrepreneurs are forced to consider only immediate prospects Immediate prospects are closely linked to recent observations but different expectation formation may yield different stability properties
19 Remark: if at (t 1) the economy is on the warranted path (expectations fulfilled) g t 1 = g e t 1 = g* g* = g e t 1 = g e t = g t Without shocks, the economy will be on the warranted path for ever But what happens if there are small exogenous changes in expectations?
20 Dynamic instability: problem set up Suppose at time t 1 the economy is on the warranted path so that Y t 1 = Y e t 1 (9) g e t 1 = g e t 1 = g* for some reason (a discovery, exogenous change in animal spirits ) at time t entrepreneurs become more optimistic, and expect increase of the growth rate: g e t > g e t 1 = g* (10) Harrod s instability proposition: the chain of events following from g e t > g* will induce growth expectations to be revised in the wrong direction
21 Interpretation: Initial condition: g e t 1 = g* Y t 1 = Y* t 1 Exogenous shock on expectations at t: g e t > g* I t > I* t Y t > Y* t (Y t / Y t 1 ) 1 g t > g e t > g* g e t+1 > g e t > g* g e t is revised in the wrong direction
22 Proof from 6 from 4 I t = vy e t g e t = s Y t Y e t = Y e t 1 (1+ g e t 1 )= Y e t 1 (1+ g*) using 9 s Y t = v g e t Y e t 1 (1+ g*) = v g e t Y t 1 (1+ g*) (11) from 11 (1 + g t ) = Y t / Y t 1 = (v / s) (1+ g*) g e t = (g e t + g e t g*) (v / s) = = (g e t + g e t g*) / g* = (g e t / g*) + g e t (12) from 12 and 10 (1 + g t ) = (g e t / g*) + g e t > 1 + g e t
23 Proposition 2: Under the adjustment rule (8), the warranted growth rate g* is dynamically unstable: the warranted path is a knife edge. Remark: different adjustment rules may yield different stability results
24 g e t < g* cumulative departure from sustained growth towards depression g e t > g* cumulative departure from sustained growth towards full employment working population grows at rate n: natural growth rate no endogenous economic force drives g* towards n, or vice versa Remark: in Solow the equilibrium growth rate g* converges to n (steady state growth without technological progress) through price flexibility and changes in K/L.
25 Proposition 3: Under Harrod s conditions, persistent growth, at a constant rate trough time, can take place only if the following conditions obtain: g e t = g* s / v g* = n all t
26 Corollary 4: As a result of the fact that: expectations are made under strong uncertainty in general g* n sustained growth over extended periods of time can only result from appropriate measures of economic policy.
27 Harrod growth model with autonomous government expenditure Hicks (1950) adds autonomous investment expenditure I A Assume I A growing at exogenous constant rate g A I(t) = induced investment + autonomous investment I(t) = vg e Y e (t) + I A (t) Remark: Notice that autonomous expenditure (here investment) does not interfere with firms investment decisions: autonomous expenditure is not capacity creating
28 Investment : I(t) = vg e Y e (t) + I A (t) Fulfilled predictions : Y(t) = Y e (t) g e = g Y Income multiplier : sy(t) Y(t)(1 c) = I(t) = vg e Y(t) + I A (t) Y(t) (1 c vg e ) = I A (t) (1 c vg e ) > 0
29 g e = g Y on a fulfilled predictions path with fulfilled predictions: 1 1 On a growth path such that g = constant, And = constant The exogenous growth rate of autonomous expenditure determines the equilibrium growth rate of the economy.
30 Conclusions 1. If equilibrium path is dynamically stable, or there are bounded fluctuations around the equilibrium path: long run growth determined by growth of autonomous expenditure in the long run g A influenced by population growth (infrastructure) Harrod (1951) criticized Hick s notion of autonomous expenditure
31 Conclusions 2. Boundedness of fluctuations around equilibrium path may result from: income ceiling of full employment income floor supported by infrastructure autonomous investment related to population growth non linear adjustment behavior in the very long run: actual growth rate g is influenced by n (natural growth rate) but underemployment equilibria may be a normal state of affairs
32 Limits wage and price dynamics may be relevant in the long run autonomous expenditure is not only government expenditure, and may not be exogenous. Other examples are: Exports (Kaldor) Autonomous consumption R&D expenditure
Assumption 5. The technology is represented by a production function, F : R 3 + R +, F (K t, N t, A t )
 6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
Solution for Problem Set 3
 Solution for Problem Set 3 Q. Heterogeneous Expectations. Consider following dynamic IS-LM economy in Lecture Notes 8: IS curve: y t = ar t + u t (.) where y t is output, r t is the real interest rate,
Solution for Problem Set 3 Q. Heterogeneous Expectations. Consider following dynamic IS-LM economy in Lecture Notes 8: IS curve: y t = ar t + u t (.) where y t is output, r t is the real interest rate,
Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade
 Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 147-158 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade Michiya Nozaki Gifu Keizai
Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 147-158 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade Michiya Nozaki Gifu Keizai
Endogenous Growth Theory
 Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
The Solow Growth Model
 The Solow Growth Model Lectures 5, 6 & 7 Topics in Macroeconomics Topic 2 October 20, 21 & 27, 2008 Lectures 5, 6 & 7 1/37 Topics in Macroeconomics From Growth Accounting to the Solow Model Goal 1: Stylized
The Solow Growth Model Lectures 5, 6 & 7 Topics in Macroeconomics Topic 2 October 20, 21 & 27, 2008 Lectures 5, 6 & 7 1/37 Topics in Macroeconomics From Growth Accounting to the Solow Model Goal 1: Stylized
Equilibrium in a Production Economy
 Equilibrium in a Production Economy Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2012 Sims (ND) Equilibrium in a Production Economy Fall 2012 1 / 23 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in
Equilibrium in a Production Economy Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2012 Sims (ND) Equilibrium in a Production Economy Fall 2012 1 / 23 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in
A Summary of Economic Methodology
 A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
The Solow Model. Prof. Lutz Hendricks. January 26, Econ520
 The Solow Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ520 January 26, 2017 1 / 28 Issues The production model measures the proximate causes of income gaps. Now we start to look at deep causes. The Solow model answers
The Solow Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ520 January 26, 2017 1 / 28 Issues The production model measures the proximate causes of income gaps. Now we start to look at deep causes. The Solow model answers
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
The Real Business Cycle Model
 The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
The Ramsey Model. (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 2013)
 The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
Lecture notes on modern growth theory
 Lecture notes on modern growth theory Part 2 Mario Tirelli Very preliminary material Not to be circulated without the permission of the author October 25, 2017 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Optimal economic
Lecture notes on modern growth theory Part 2 Mario Tirelli Very preliminary material Not to be circulated without the permission of the author October 25, 2017 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Optimal economic
IS-LM Analysis. Math 202. Brian D. Fitzpatrick. Duke University. February 14, 2018 MATH
 IS-LM Analysis Math 202 Brian D. Fitzpatrick Duke University February 14, 2018 MATH Overview Background History Variables The GDP Equation Definition of GDP Assumptions The GDP Equation with Assumptions
IS-LM Analysis Math 202 Brian D. Fitzpatrick Duke University February 14, 2018 MATH Overview Background History Variables The GDP Equation Definition of GDP Assumptions The GDP Equation with Assumptions
A Modern Equilibrium Model. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
From Difference to Differential Equations I
 From Difference to Differential Equations I Start with a simple difference equation x (t + 1) x (t) = g(x (t)). (30) Now consider the following approximation for any t [0, 1], x (t + t) x (t) t g(x (t)),
From Difference to Differential Equations I Start with a simple difference equation x (t + 1) x (t) = g(x (t)). (30) Now consider the following approximation for any t [0, 1], x (t + t) x (t) t g(x (t)),
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam?
 The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
Economic Growth
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 14.452 Economic Growth Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 14.452 Economic Growth Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture
Economic Growth: Lecture 13, Stochastic Growth
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 13, Stochastic Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT December 10, 2013. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 13 December 10, 2013. 1 / 52 Stochastic Growth Models Stochastic
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 13, Stochastic Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT December 10, 2013. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 13 December 10, 2013. 1 / 52 Stochastic Growth Models Stochastic
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model
 Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Foundation of (virtually) all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model) is Solow growth model
 THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
Lecture 15. Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model. Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD I Semestre 2017 Last updated: July 3, 2017
 Lecture 15 Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD I Semestre 2017 Last updated: July 3, 2017 Universidad de Costa Rica EC3201 - Teoría Macroeconómica 2 Table of contents
Lecture 15 Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Model Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD I Semestre 2017 Last updated: July 3, 2017 Universidad de Costa Rica EC3201 - Teoría Macroeconómica 2 Table of contents
Mankiw Chapter 11. Aggregate Demand I. Building the IS-LM Model
 Mankiw Chapter 11 Building the IS-LM Model 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: the IS curve and its relation to: the Keynesian cross the LM curve and its relation to: the theory of liquidity preference how
Mankiw Chapter 11 Building the IS-LM Model 0 IN THIS CHAPTER, WE WILL COVER: the IS curve and its relation to: the Keynesian cross the LM curve and its relation to: the theory of liquidity preference how
Stagnation Traps. Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro
 Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Advanced Macroeconomics
 Advanced Macroeconomics Endogenous Growth Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Endogenous growth 1 / 18 Introduction The Solow and Ramsey models are exogenous growth
Advanced Macroeconomics Endogenous Growth Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Endogenous growth 1 / 18 Introduction The Solow and Ramsey models are exogenous growth
New Notes on the Solow Growth Model
 New Notes on the Solow Growth Model Roberto Chang September 2009 1 The Model The firstingredientofadynamicmodelisthedescriptionofthetimehorizon. In the original Solow model, time is continuous and the
New Notes on the Solow Growth Model Roberto Chang September 2009 1 The Model The firstingredientofadynamicmodelisthedescriptionofthetimehorizon. In the original Solow model, time is continuous and the
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
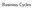 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies
 Journal of Regional Development Studies2010 131 Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies Ken-ichi ISHIYAMA 1. Introduction We have observed large increases in trade and
Journal of Regional Development Studies2010 131 Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies Ken-ichi ISHIYAMA 1. Introduction We have observed large increases in trade and
One-Sector Models of Endogenous Growth. Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko
 One-Sector Models of Endogenous Growth Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 Mid-1980s: dissatisfaction with exogenously driven explanations of long-run productivity growth. 2 It led to construction of models in
One-Sector Models of Endogenous Growth Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 Mid-1980s: dissatisfaction with exogenously driven explanations of long-run productivity growth. 2 It led to construction of models in
Sentiments and Aggregate Fluctuations
 Sentiments and Aggregate Fluctuations Jess Benhabib Pengfei Wang Yi Wen October 15, 2013 Jess Benhabib Pengfei Wang Yi Wen () Sentiments and Aggregate Fluctuations October 15, 2013 1 / 43 Introduction
Sentiments and Aggregate Fluctuations Jess Benhabib Pengfei Wang Yi Wen October 15, 2013 Jess Benhabib Pengfei Wang Yi Wen () Sentiments and Aggregate Fluctuations October 15, 2013 1 / 43 Introduction
Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory
 2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
Learning, Expectations, and Endogenous Business Cycles
 Learning, Expectations, and Endogenous Business Cycles I.S.E.O. Summer School June 19, 2013 Introduction A simple model Simulations Stability Monetary Policy What s next Who we are Two students writing
Learning, Expectations, and Endogenous Business Cycles I.S.E.O. Summer School June 19, 2013 Introduction A simple model Simulations Stability Monetary Policy What s next Who we are Two students writing
Economic Growth: Lecture 9, Neoclassical Endogenous Growth
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 9, Neoclassical Endogenous Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT November 28, 2017. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 9 November 28, 2017. 1 / 41 First-Generation Models
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 9, Neoclassical Endogenous Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT November 28, 2017. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 9 November 28, 2017. 1 / 41 First-Generation Models
Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy: Basic features
 Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy: Basic features Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 41 I Motivation This Lecture introduces the basic
Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy: Basic features Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 41 I Motivation This Lecture introduces the basic
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Introduction to Real Business Cycles: The Solow Model and Dynamic Optimization
 Introduction to Real Business Cycles: The Solow Model and Dynamic Optimization Vivaldo Mendes a ISCTE IUL Department of Economics 24 September 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes ) Macroeconomics (M8674) 24 September
Introduction to Real Business Cycles: The Solow Model and Dynamic Optimization Vivaldo Mendes a ISCTE IUL Department of Economics 24 September 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes ) Macroeconomics (M8674) 24 September
Solow Growth Model. Michael Bar. February 28, Introduction Some facts about modern growth Questions... 4
 Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
14.05: Section Handout #1 Solow Model
 14.05: Section Handout #1 Solow Model TA: Jose Tessada September 16, 2005 Today we will review the basic elements of the Solow model. Be prepared to ask any questions you may have about the derivation
14.05: Section Handout #1 Solow Model TA: Jose Tessada September 16, 2005 Today we will review the basic elements of the Solow model. Be prepared to ask any questions you may have about the derivation
ECON 582: The Neoclassical Growth Model (Chapter 8, Acemoglu)
 ECON 582: The Neoclassical Growth Model (Chapter 8, Acemoglu) Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 / 21 Consider the neoclassical economy without population growth and technological progress. The optimal growth
ECON 582: The Neoclassical Growth Model (Chapter 8, Acemoglu) Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko 1 / 21 Consider the neoclassical economy without population growth and technological progress. The optimal growth
Advanced Macroeconomics
 Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
Financialization and Distribution in a Kaleckian Model with Firms Debt Accumulation
 Kyoto University, Graduate School of Economics Discussion Paper Series Financialization and Distribution in a Kaleckian Model with Firms Debt Accumulation Hiroaki Sasaki Discussion Paper No. E-16-013 Graduate
Kyoto University, Graduate School of Economics Discussion Paper Series Financialization and Distribution in a Kaleckian Model with Firms Debt Accumulation Hiroaki Sasaki Discussion Paper No. E-16-013 Graduate
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1
 Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
Monetary Economics. Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one. Chris Edmond. 2nd Semester 2014
 Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 2: Dynamics in Aggregate Demand and Supply
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 2 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 2: Dynamics in Aggregate Demand and Supply Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics:
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics: Chapter 2 1 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics B. J. Heijdra & F. van der Ploeg Chapter 2: Dynamics in Aggregate Demand and Supply Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics:
Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 20, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 8 November 20, 2018 1 / 46 Growth with Overlapping Generations
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 20, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 8 November 20, 2018 1 / 46 Growth with Overlapping Generations
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I. Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form:
 Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I
 14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
Economics 2: Growth (Growth in the Solow Model)
 Economics 2: Growth (Growth in the Solow Model) Lecture 3, Week 7 Solow Model - I Definition (Solow Model I) The most basic Solow model with no population growth or technological progress. Solow Model
Economics 2: Growth (Growth in the Solow Model) Lecture 3, Week 7 Solow Model - I Definition (Solow Model I) The most basic Solow model with no population growth or technological progress. Solow Model
Chapter 9 Solow. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos. Computational Economics: a concise introduction
 Chapter 9 Solow O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 27 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Computational
Chapter 9 Solow O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 27 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Computational
Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path
 Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path Ryoji Ohdoi Dept. of Industrial Engineering and Economics, Tokyo Tech This lecture note is mainly based on Ch. 8 of Acemoglu
Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path Ryoji Ohdoi Dept. of Industrial Engineering and Economics, Tokyo Tech This lecture note is mainly based on Ch. 8 of Acemoglu
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Lecture 5: The neoclassical growth model
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Paul Klein Office: Murray Building, 3005 Email: p.klein@soton.ac.uk URL: http://paulklein.se Economics 3010 Topics in Macroeconomics 3 Autumn 2010 Lecture 5: The neoclassical
THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Paul Klein Office: Murray Building, 3005 Email: p.klein@soton.ac.uk URL: http://paulklein.se Economics 3010 Topics in Macroeconomics 3 Autumn 2010 Lecture 5: The neoclassical
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory
 ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital
 Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
Lecture 15 Real Business Cycle Model. Noah Williams
 Lecture 15 Real Business Cycle Model Noah Williams University of Wisconsin - Madison Economics 702/312 Real Business Cycle Model We will have a shock: change in technology. Then we will have a propagation
Lecture 15 Real Business Cycle Model Noah Williams University of Wisconsin - Madison Economics 702/312 Real Business Cycle Model We will have a shock: change in technology. Then we will have a propagation
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 4: Anticipation effects and economic policy BJ Heijdra Department of Economics, Econometrics & Finance University of Groningen 1 September 2009
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 4: Anticipation effects and economic policy BJ Heijdra Department of Economics, Econometrics & Finance University of Groningen 1 September 2009
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions
 Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
(a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
Chapter 4 AD AS. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos. Computational Economics: a concise introduction
 Chapter 4 AD AS O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 32 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Numerical
Chapter 4 AD AS O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 32 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Numerical
Productivity Losses from Financial Frictions: Can Self-financing Undo Capital Misallocation?
 Productivity Losses from Financial Frictions: Can Self-financing Undo Capital Misallocation? Benjamin Moll G Online Appendix: The Model in Discrete Time and with iid Shocks This Appendix presents a version
Productivity Losses from Financial Frictions: Can Self-financing Undo Capital Misallocation? Benjamin Moll G Online Appendix: The Model in Discrete Time and with iid Shocks This Appendix presents a version
Modern Urban and Regional Economics
 Modern Urban and Regional Economics SECOND EDITION Philip McCann OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of figures List of tables Introduction xii xiv xvii Part I Urban and Regional Economic Models and
Modern Urban and Regional Economics SECOND EDITION Philip McCann OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of figures List of tables Introduction xii xiv xvii Part I Urban and Regional Economic Models and
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model. Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany
 Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model
 Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model
 A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
Advanced Macroeconomics II. Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities. Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 2018
 Advanced Macroeconomics II Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 208 Motivation Empirical Evidence Macro evidence on the e ects of monetary policy shocks (i)
Advanced Macroeconomics II Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 208 Motivation Empirical Evidence Macro evidence on the e ects of monetary policy shocks (i)
Problem 1 (30 points)
 Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Online Appendix for Investment Hangover and the Great Recession
 ONLINE APPENDIX INVESTMENT HANGOVER A1 Online Appendix for Investment Hangover and the Great Recession By MATTHEW ROGNLIE, ANDREI SHLEIFER, AND ALP SIMSEK APPENDIX A: CALIBRATION This appendix describes
ONLINE APPENDIX INVESTMENT HANGOVER A1 Online Appendix for Investment Hangover and the Great Recession By MATTHEW ROGNLIE, ANDREI SHLEIFER, AND ALP SIMSEK APPENDIX A: CALIBRATION This appendix describes
Lecture 3 - Solow Model
 Lecture 3 - Solow Model EC308 Advanced Macroeconomics 16/02/2016 (EC308) Lecture 3 - Solow Model 16/02/2016 1 / 26 Introduction Solow Model Sometimes known as Solow-Swan Model: Solow (1956): General Production
Lecture 3 - Solow Model EC308 Advanced Macroeconomics 16/02/2016 (EC308) Lecture 3 - Solow Model 16/02/2016 1 / 26 Introduction Solow Model Sometimes known as Solow-Swan Model: Solow (1956): General Production
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Fall 2015 P. Gourinchas/D. Romer MIDTERM EXAM
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 202A DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Fall 2015 P. Gourinchas/D. Romer MIDTERM EXAM The exam consists of two parts. There are 85 points total. Part I has 18 points and Part II
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 202A DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Fall 2015 P. Gourinchas/D. Romer MIDTERM EXAM The exam consists of two parts. There are 85 points total. Part I has 18 points and Part II
Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy
 Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy Economics 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Kam Yu Winter 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Basic DGE Closed Economy 3 Golden Rule Solution 4 Optimal Solution The Euler Equation
Lecture 2 The Centralized Economy Economics 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Kam Yu Winter 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Basic DGE Closed Economy 3 Golden Rule Solution 4 Optimal Solution The Euler Equation
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models. December 4, 2007
 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models December 4, 2007 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models Random shocks to generate trajectories that look like the observed national accounts. Rational
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models December 4, 2007 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models Random shocks to generate trajectories that look like the observed national accounts. Rational
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction
 The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Growth: Facts and Theories
 Notes on Growth: Facts and Theories Intermediate Macroeconomics Spring 2006 Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania Growth In the last part of the course we are going to study economic growth, i.e. the
Notes on Growth: Facts and Theories Intermediate Macroeconomics Spring 2006 Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania Growth In the last part of the course we are going to study economic growth, i.e. the
Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth
 Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) D(S)GE and Growth Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 43 Macroeconomics is Dynamic
Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) D(S)GE and Growth Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 43 Macroeconomics is Dynamic
EC9A2 Advanced Macro Analysis - Class #1
 EC9A2 Advanced Macro Analysis - Class #1 Jorge F. Chávez University of Warwick October 29, 2012 Outline 1. Some math 2. Shocking the Solow model 3. The Golden Rule 4. CES production function (more math)
EC9A2 Advanced Macro Analysis - Class #1 Jorge F. Chávez University of Warwick October 29, 2012 Outline 1. Some math 2. Shocking the Solow model 3. The Golden Rule 4. CES production function (more math)
Solution to Homework 2 - Exogeneous Growth Models
 Solution to Homework 2 - Exogeneous Growth Models ECO-3211 Macroeconomia Aplicada (Applied Macroeconomics Question 1: Solow Model with a Fixed Factor 1 The law of motion for capital in the Solow economy
Solution to Homework 2 - Exogeneous Growth Models ECO-3211 Macroeconomia Aplicada (Applied Macroeconomics Question 1: Solow Model with a Fixed Factor 1 The law of motion for capital in the Solow economy
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital
 Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano March, 28 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand. Derive
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano March, 28 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand. Derive
Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis
 Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis Yulei Luo Econ, HKU November 13, 2017 Luo, Y. (Econ, HKU) ECON2220CB: Intermediate Macro November 13, 2017 1 / 14 The
Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis Yulei Luo Econ, HKU November 13, 2017 Luo, Y. (Econ, HKU) ECON2220CB: Intermediate Macro November 13, 2017 1 / 14 The
problem. max Both k (0) and h (0) are given at time 0. (a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium
 Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
Dynamic Optimization: An Introduction
 Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Nova SBE February 2012 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/31 Housekeeping Website TA: none No "Mas-Collel" in macro One midterm, one final, problem sets
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Nova SBE February 2012 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/31 Housekeeping Website TA: none No "Mas-Collel" in macro One midterm, one final, problem sets
Monetary Economics Notes
 Monetary Economics Notes Nicola Viegi 2 University of Pretoria - School of Economics Contents New Keynesian Models. Readings...............................2 Basic New Keynesian Model...................
Monetary Economics Notes Nicola Viegi 2 University of Pretoria - School of Economics Contents New Keynesian Models. Readings...............................2 Basic New Keynesian Model...................
Equilibrium Conditions (symmetric across all differentiated goods)
 MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION IN A DSGE MODEL: PART II SEPTEMBER 30, 200 Canonical Dixit-Stiglitz Model MONOPOLISTICALLY-COMPETITIVE EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium Conditions (symmetric across all differentiated goods)
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION IN A DSGE MODEL: PART II SEPTEMBER 30, 200 Canonical Dixit-Stiglitz Model MONOPOLISTICALLY-COMPETITIVE EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium Conditions (symmetric across all differentiated goods)
Structural change in a multi-sector model of the climate and the economy
 Structural change in a multi-sector model of the climate and the economy Gustav Engström The Beijer Institute of Environmental Economics Stockholm, December 2012 G. Engström (Beijer) Stockholm, December
Structural change in a multi-sector model of the climate and the economy Gustav Engström The Beijer Institute of Environmental Economics Stockholm, December 2012 G. Engström (Beijer) Stockholm, December
1 The Basic RBC Model
 IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination
 Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination August 2016 Department of Economics UNC Chapel Hill Instructions: This examination consists of 4 questions. Answer all questions. If you believe a question is ambiguously
Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination August 2016 Department of Economics UNC Chapel Hill Instructions: This examination consists of 4 questions. Answer all questions. If you believe a question is ambiguously
Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations
 George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco (FEUNL) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 18 Road Map Research question: we want to understand businesses cycles.
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco (FEUNL) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 18 Road Map Research question: we want to understand businesses cycles.
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment
 Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) September 2014 1 / 44 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 44 Motivation
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) September 2014 1 / 44 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 44 Motivation
Problem Set #2: Overlapping Generations Models Suggested Solutions - Q2 revised
 University of Warwick EC9A Advanced Macroeconomic Analysis Problem Set #: Overlapping Generations Models Suggested Solutions - Q revised Jorge F. Chavez December 6, 0 Question Consider the following production
University of Warwick EC9A Advanced Macroeconomic Analysis Problem Set #: Overlapping Generations Models Suggested Solutions - Q revised Jorge F. Chavez December 6, 0 Question Consider the following production
Economics 210B Due: September 16, Problem Set 10. s.t. k t+1 = R(k t c t ) for all t 0, and k 0 given, lim. and
 Economics 210B Due: September 16, 2010 Problem 1: Constant returns to saving Consider the following problem. c0,k1,c1,k2,... β t Problem Set 10 1 α c1 α t s.t. k t+1 = R(k t c t ) for all t 0, and k 0
Economics 210B Due: September 16, 2010 Problem 1: Constant returns to saving Consider the following problem. c0,k1,c1,k2,... β t Problem Set 10 1 α c1 α t s.t. k t+1 = R(k t c t ) for all t 0, and k 0
Markov Perfect Equilibria in the Ramsey Model
 Markov Perfect Equilibria in the Ramsey Model Paul Pichler and Gerhard Sorger This Version: February 2006 Abstract We study the Ramsey (1928) model under the assumption that households act strategically.
Markov Perfect Equilibria in the Ramsey Model Paul Pichler and Gerhard Sorger This Version: February 2006 Abstract We study the Ramsey (1928) model under the assumption that households act strategically.
Solow Growth Model. Sang Yoon (Tim) Lee. Jan 9-16, last updated: January 20, Toulouse School of Economics
 Solow Growth Model Sang Yoon (Tim) Lee Toulouse School of Economics Jan 9-16, 2018 last updated: January 20, 2018 This Week: Industrialized Countries Kaldor Facts: since we ever measured such things, 1.
Solow Growth Model Sang Yoon (Tim) Lee Toulouse School of Economics Jan 9-16, 2018 last updated: January 20, 2018 This Week: Industrialized Countries Kaldor Facts: since we ever measured such things, 1.
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment
 Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) July 2014 1 / 46 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 46 Motivation
Aggregate Demand, Idle Time, and Unemployment Pascal Michaillat (LSE) & Emmanuel Saez (Berkeley) July 2014 1 / 46 Motivation 11% Unemployment rate 9% 7% 5% 3% 1974 1984 1994 2004 2014 2 / 46 Motivation
