Chemical Instrumentation CHEM*3440 Mid-Term Examination Fall 2005 TUESDAY, OCTOBER 25, 2005
|
|
|
- Dustin Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemical Instrumentation CHEM*3440 Mid-Term Examination Fall 2005 TUESDAY, OCTOBER 25, 2005 Duration: 2 hours. You may use a calculator. No additional aids will be necessary as a series of data and equation sheets are included as part of the examination paper. 1. (8 points) Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that have important toxicological effects. Their detection and measurement in environmental conditions is a vital health concern. A method was developed to measure these compounds from waste water samples. The first step was the extraction of the PAH from the water into methylene chloride. The efficiency of this step was tested by injecting known amounts of various PAH substances into an aqueous sample and then quantifying the extracted amount. The following table reports the results of several trials for four different compounds. Note the different added amounts in each case. The mean recovered values and the standard deviation of those means are shown at the bottom. Chrysene Benzofluoranthenes Benzo(a)pyrene Dibenz(a,h)anthracene Amount added 1.0 µg/m µg/m 3 10 µg/m 3 50 µg/m Mean St. Dev (a) Calculate the relative standard deviation for each substance. (b) Which substance is most completely recovered? (c) Which substance is most unreliably recovered? (d) What are the 95% confidence limits for the recovery of benzo(a)pyrene?
2 2. (6 points) An experiment provided a rapidly and chaotically time varying signal. On average, however, the input signal current was 1.5 µa. It was decided that the signal could be smoothed by integrating it for a fixed length of time. The op amps are driven by a ± 10.0 V source. Here is a basic schematic of the arrangement. R = kω C = 0.1 µf I in = 1.5 µa - A R = 100 kω - B (a) What will be the average voltage at point A? (b) What will be the maximum useful integration time for the circuit? 3. (4 points) A spectrophotometric assay was undertaken with a substance with a molar absorptivity of 4000 M -1 cm -1. A stock solution is available whose concentration is M. The instrumental path length is cm. A final absorbance in the range between is desired to calibrate in the range of the unknown solutions. You are to make up.0 ml of the calibration solution in a volumetric flask. Do you need to pipette 1.00, 2.00, 3.00, 4.00 or 5.00 ml of the stock solution into the.0 ml volumetric flask to provide a solution in this absorbance range? Show your work, 4. (6 points) Look at the six spectra on the next page. The background has already been corrected for all spectra. Read the scales and the titles very carefully. The unknown sample contains a mixture of Cu and Zn ions. What is the concentration of each ion in the unknown? 5. (4 points) Your instrument is using a 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to digitize an input signal. The range of this device is 0 to 10 V. (a) What is the voltage resolution of this device? (b) What decimal number would be produced if an input voltage of 2.50 V was converted? 6. (12 points) Describe the following terms in a couple of sentences each. When appropriate, give both and equation and an explanation. (a) Limit of quantitation. (b) Dynamic range. (c) Impedance. (d) 1/f noise. (e) Alias (in the context of digital signal acquisition). (f) Auxochrome.
3 7. (8 points) The following data were obtained for forming a calibration curve in a spectroscopic experiment. The concentrations are in ppm and the instrument signal is in mv. The calibration curve is given in the following graph, along with the parameters of the fit. Concentration (ppm) Average Signal (mv) Calibration Curve Signal Concentration (ppm) The fit parameters are: m = mv/ppm b = mv s r = mv s m = mv/ppm s b = mv An unknown sample was measured 5 times, giving the following results: , , , (a) What is the concentration of the unknown sample? (b) What are the 95% confidence limits on that concentration?
4 CHEM*3440 Mid-Term Examination Fall 2005 ANSWERS 1. (a) The relative standard deviation is just the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean (divide the standard deviation by the mean). We find Chrysene Benzofluoranthenes Benzo(a)pyrene Dibenz(a,h)anthracene (b) The highest recovery rate comes from the ones whose mean is the largest fraction of the originally added amount. We can easily see that chrysene is recovered at a rate of about 70.4% and is the largest of the four. (c) The one which is most unreliably recovered is the one with the largest relative standard deviation. We can compare the standard deviation directly because that depends upon how much was recovered. In fact, benzofluoranthenes is the most unreliably recovered material with its relative standard deviation of 49.1%. (d) The equation needs a value for Student s t from the tables. To find that, we need the number of degrees of freedom, which is N-1. There are 14 measurements, so dof = 13. From the table, t = for 95% confidence. The result then is ts ^2.160h^1.419h = = N ! ng m3 at the 95% confidence level. 2. (a) First element is just a current-to-voltage amplifier. We simply have VA =- ^1.5 # 10-6 Ah^ # 10 3 Xh = V (b) This 0.75 V will be integrated at a rate given by the RC time constant of the integrator until the integrator is saturated (reaches its maximum or minimum output). The time required to do this is the maximum useful integration time. x = RC = ^100 kxh_ 0.1 nfi = 0.01s Voutput =- RC 1 Vmax = 10.0 V 0 t # Vinput dt =- ^-0.75 V h t 0.01s tmax = ^10.0 Vh 0.01s = s =133 ms 0.75 V 3. This is a common activity one would need to do: form a calibration solution whose absorbance falls within a particular range. There are two approaches. You could solve Beer s Law to find the volumes that would give the two ends of the desired absorbance range; they would then bracket the desired volume. Or you could solve Beer s Law for each of the possible volumes and find which one falls within the desired range. I ll so the work for the last procedure.
5 It is obviously central to the problem to consider the dilution of the concentration. This is easily accounted for by scaling the original concentration by the ratio of the added volume to the final volume (.0 ml). The final concentration in each of the five cases is then C1 V1= C2 V2 V1 C1 V2 = C2 Z 1 = 3.90 # 10-5 M 2 = 7.80 # 10-5 M M # [ 3 = 1.17 # 10-4 M 4 = 1.56 # 10-4 M 5 = 1.95 # 10-4 M \ Now we use these five concentrations in Beer s Law to find the expected absorbance in each case. A = fbc Z 3.90 # 10-5 M = # 10-5 M = M - 1 cm - 1 # cm # [ 1.17 # 10-4 M = # 10-4 M = \ 1.95 # 10-4 M = Clearly the third entry falls within the desired absorbance range of We need to add 3.00 ml of the stock solution to make the desired calibration standard solution. 4. Note the spectra are for three different solutions a Zn 2 calibration standard, a Cu 2 calibration standard, and an unknown containing both ions. The spectra are taken at two different wavelength ranges. After looking at them, you should realized that zinc provide a signal a one wavelength while copper provides a signal at both wavelengths. We assume and a casual inspection of the spectra confirms it is true that the spectra all have the same shape meaning they have the same linewidth and are Gaussian in form. This is to be expected when the lineshape is governed by the instrument as is typically the case in spectrometry. It is also reasonable to assume that the same pathlength is used in each case. We can therefore relate the signal intensity to the peak height. It should be peak area but since the peaks all have the same linewidth, their heights are all proportional to their areas. While it would be possible to solve this problem when both calibration solutions have a measurable signal at both wavelengths it is just a problem of two equations in two unknowns this case is made particularly simple by having only one entity give rise
6 to a signal and on of the wavelengths. Therefore, Cu 2 can be identified by comparing the unknown to the calibration signal at nm. Then, knowing the Cu 2 concentration, we can find the Zn 2 from the signal at nm. I (Cu(10.0 ppm)) = 240 I (unknown) = Cu = 10.0 ppm # = 6.29 ppm I (Zn(1.00 ppm)) = 4.2 I (Cu(10.0 ppm)) = 1.3 I (unknown) = Zn 6.7 = 4.2 f unknown p 6.29 ppm 1.3 d n 1.00 ppm 10.0 ppm 6.7 = 4.26 Zn unknown Zn unknown = = 1.4 ppm 5. (a) A 12-bit device means that it has 2 12 = 4096 resolution elements. Since these 4096 resolution steps are spread over 10 V in this case (device range is from 0-10 V), then each digital step spans a voltage step of = V= 2.44 mv which is the voltage resolution of the device. (b) The decimal number (meaning a base-10 number) which is an integer between 0 and 4095 can be found in two ways. Either we can use the step size of 2.44 mv and see how many steps would be needed to reach the desired voltage of 2.50 V, or we can realize that the range of integers is spread smoothly of over the voltage range. Both procedures give us the result of I will accept 1024 ± 1. R V int S 2.50 V W= 1024 steps V S step W T X or 2.50 V # 4096 steps = 1024 steps 10.0 V 6. (a) Limit of Quantitation. This is the lower concentration limit at which an experimental technique can provide a reliable quantitative result. It is chosen to be a concentration equal to 10 times the standard deviation of the blank signal. LOQ = 10 s blank. (b) Dynamic range. The concentration range between the LOQ and the upper limit of linearity LOL, or the point after which the instrumental method s response is no longer linear. A technique is able to readily measure concentration throughout its dynamic range. (c) Impedance. The vector sum of a circuit s resistance and reactance. The overall tendency for the circuit to impede the flow of current. I = (R 2 X 2 ) 1/2.
7 (d) 1/f noise. Also known as drift or pink noise. It is more pronounced at low frequencies (hence the reciprocal dependence on frequency). Its origins are uncertain and difficult to specify. Try to shift the frequency range of an experiment away from the DC condition. (e) Alias. A higher frequency signal masquerades as a lower frequency signal due to undersampling when digitizing. Anything above the Nyquist frequency (given by the reciprocal of twice the sampling rate) will appear as an alias and will be folded over into the spectrum. (f) Auxochrome. A molecular feature which is not itself photoactive, but whose presence does alter the frequency and intensity of nearby chromophores. 7. PROBLEM!! The raw data given in this problem did not give rise to the parameters as given. Sorry about that. You will be given full marks if you refit the data and used the correct slop and intercept values, etc. or if you just took my word for it and used the data as given into the equations. (a) The least squares parameters for the fitting line readily give the concentration for the unknown once we find the average signal. The average of the five measurements of the unknown is We solve the equation for the line given the slope and intercept in the problem. We have S = mc b C x = S - b m = = 4.25 ppm (b) To calculate the confidence limits, we need the standard deviation of the result, given as s calc on the equation sheet. While the problem gives s r as part of the data, we also need to calculate S xx First we calculate S xx ; the x i are the concentration values for each point on the calibration curve, of which there are 7, it also being the variable N in the calculation. We need to find the square of each concentration value, and then sum all the concentration values (and square them) and then sum all the squares of the concentration values. `!x i j 2 Sxx =! x i2 - N = ^33.47h 2 7 = = We can now find s calc. M = 5, the number of measurements of the unknown; N = 7, the number of points in the calibration plot; m = slope of calibration curve. We also need to find the average of the y values for the calibration curve. It is Scalc = m sr M 1 N 1 `y unknown - y calib j 2 m 2 Sxx = ^ h 2 = ^3.407h 2 ^81.76h We now use the equation with Student s t to specify the confidence limits. We measured the average with 5 experiments. The degrees of freedom is 4. At 95%, we find that t = Note that the equation uses N and not N-1. We obtain Confidence limits =! t s ^ =! 2.776h^0.074h = N 5 The final answer is 4.25 ± ppm with 95% confidence.
Chemical Instrumentation CHEM*3440 Mid-Term Examination Fall 2006 Tuesday, October 24
 Chemical Instrumentation CHEM*3440 Mid-Term Examination Fall 006 Tuesday, October 4 Duration: hours. You may use a calculator. No additional aids will be necessary as a series of data and equation sheets
Chemical Instrumentation CHEM*3440 Mid-Term Examination Fall 006 Tuesday, October 4 Duration: hours. You may use a calculator. No additional aids will be necessary as a series of data and equation sheets
Experiment 1 (Part A): Plotting the Absorption Spectrum of Iron (II) Complex with 1,10- Phenanthroline
 Experiment (Part A): Plotting the Absorption Spectrum of Iron (II) Complex with,0- Phenanthroline Background The first step of an analytical spectrophotometric procedure for quantitative determination
Experiment (Part A): Plotting the Absorption Spectrum of Iron (II) Complex with,0- Phenanthroline Background The first step of an analytical spectrophotometric procedure for quantitative determination
CHEM 334 Quantitative Analysis Laboratory
 The Methods of Calibration Curve and Standard Addition Introduction One of the principle activities in the Quantitative Analysis Laboratory is the measurement of the concentration or total quantity of
The Methods of Calibration Curve and Standard Addition Introduction One of the principle activities in the Quantitative Analysis Laboratory is the measurement of the concentration or total quantity of
Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 18 - Spectrophotometry 10/31/13 In the lab you will use spectrophotometric techniques to determine the amount of iron, calcium and magnesium in unknowns. Although
Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical]
![Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical] Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves. BCH 312 [Practical]](/thumbs/78/77692425.jpg) Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves BCH 312 [Practical] Spectrophotometer: Spectrophotometer can be used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a solution. It consist of two parts:
Beer's- Lambert Law and Standard Curves BCH 312 [Practical] Spectrophotometer: Spectrophotometer can be used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a solution. It consist of two parts:
CEM 333 Instrumental Analysis
 CEM 333 Instrumental Analysis Simon J. Garrett Room: CEM 234 Phone: 355 9715 ext 208 E-mail: garrett@cem.msu.edu Lectures: Tuesday, Thursday 9:00-9:50 am Room 136 Office Hours: Tuesdays 10:00-11:00 am
CEM 333 Instrumental Analysis Simon J. Garrett Room: CEM 234 Phone: 355 9715 ext 208 E-mail: garrett@cem.msu.edu Lectures: Tuesday, Thursday 9:00-9:50 am Room 136 Office Hours: Tuesdays 10:00-11:00 am
Brooklyn College Department of Chemistry
 Brooklyn College Department of Chemistry Instrumental Analysis (Chem 42/790) Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy An atomic absorption spectrometer is used in this experiment to analyze a copper-base alloy for
Brooklyn College Department of Chemistry Instrumental Analysis (Chem 42/790) Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy An atomic absorption spectrometer is used in this experiment to analyze a copper-base alloy for
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer
 Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
Skill Building Activity 2 Determining the Concentration of a Species using a Vernier Spectrometer Purpose To use spectroscopy to prepare a Beer s Law plot of known dilutions of copper(ii) sulfate so that
1. The range of frequencies that a measurement is sensitive to is called the frequency
 CHEM 3 Name Exam 1 Fall 014 Complete these problems on separate paper and staple it to this sheet when you are finished. Please initial each sheet as well. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR
CHEM 3 Name Exam 1 Fall 014 Complete these problems on separate paper and staple it to this sheet when you are finished. Please initial each sheet as well. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR
CHEM 1471 Kinetics of Phenolphthalein Decolorization Fall 2010 (Buckley) Lab Under Development
 CHEM 1471 Kinetics of Phenolphthalein Decolorization Fall 2010 (Buckley) Lab Under Development Objective: Use spectrophotometry to determine the order of the kinetics of decolorization of phenolphthalein
CHEM 1471 Kinetics of Phenolphthalein Decolorization Fall 2010 (Buckley) Lab Under Development Objective: Use spectrophotometry to determine the order of the kinetics of decolorization of phenolphthalein
EXPERIMENT 14. ACID DISSOCIATION CONSTANT OF METHYL RED 1
 EXPERIMET 14. ACID DISSOCIATIO COSTAT OF METHYL RED 1 The acid dissociation constant, Ka, of a dye is determined using spectrophotometry. Introduction In aqueous solution, methyl red is a zwitterion and
EXPERIMET 14. ACID DISSOCIATIO COSTAT OF METHYL RED 1 The acid dissociation constant, Ka, of a dye is determined using spectrophotometry. Introduction In aqueous solution, methyl red is a zwitterion and
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE. 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation Estimation of Drugs
 CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
Introduction to Chemistry Techniques Prelab (Week 1) 2. Determine the number of significant figures in each of the following numbers.
 Introduction to Chemistry Techniques Prelab (Week 1) Name Total /10 SHOW ALL WORK NO WORK = NO CREDIT 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. Determine the number of significant figures in each of
Introduction to Chemistry Techniques Prelab (Week 1) Name Total /10 SHOW ALL WORK NO WORK = NO CREDIT 1. What is the purpose of this experiment? 2. Determine the number of significant figures in each of
Developing a Spectrophotometric Quantitative Assay for p-nitrophenol
 Developing a Spectrophotometric Quantitative Assay for p-nitrophenol The insecticide parathion (O,O-diethyl-o-p-nitrophenyl phosphorothioate) undergoes a welldefined pathway of biodegradation. In the first
Developing a Spectrophotometric Quantitative Assay for p-nitrophenol The insecticide parathion (O,O-diethyl-o-p-nitrophenyl phosphorothioate) undergoes a welldefined pathway of biodegradation. In the first
Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS
 Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS FV 10/21/10 MATERIALS: Spectronic 20 spectrophotometers, 2 cuvettes, brass sample, 7 M HNO 3, 0.100 M CuSO 4, 2 M NH 3, two 50 ml beakers, 100 ml beaker, two 25 ml volumetric
Experiment 7A ANALYSIS OF BRASS FV 10/21/10 MATERIALS: Spectronic 20 spectrophotometers, 2 cuvettes, brass sample, 7 M HNO 3, 0.100 M CuSO 4, 2 M NH 3, two 50 ml beakers, 100 ml beaker, two 25 ml volumetric
Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum.
 Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum. a. Is the spectrum above a band spectrum or a line spectrum? This is a band spectra, there are what
Answers to spectroscopy questions. 1. Consider the spectrum below. Questions a f refer to this spectrum. a. Is the spectrum above a band spectrum or a line spectrum? This is a band spectra, there are what
REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES
 Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample
 Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Chemistry 1215 Experiment #11 Spectrophotometric Analysis of an Unknown Brass Sample Objective In this experiment you will use spectrophotometric measurements to determine the copper concentration of a
Spectroscopy Primer. for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy. by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015
 Spectroscopy Primer for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015 Abstract: An overview of uv vis absorbance spectroscopy including Beer s Law, calibration curves,
Spectroscopy Primer for ultraviolet and visible absorbance spectroscopy by Stephanie Myers Summer 2015 Abstract: An overview of uv vis absorbance spectroscopy including Beer s Law, calibration curves,
Dr. Julie J. Nazareth
 Name: Dr. Julie J. Nazareth Lab Partner(s): Physics: 133L Date lab performed: Section: Capacitors Parts A & B: Measurement of capacitance single, series, and parallel combinations Table 1: Voltage and
Name: Dr. Julie J. Nazareth Lab Partner(s): Physics: 133L Date lab performed: Section: Capacitors Parts A & B: Measurement of capacitance single, series, and parallel combinations Table 1: Voltage and
AIM To verify Beer - Lambert s law and to determine the dissociation constant (Ka) of methyl red, Spectrophotometrically.
 C 141(Expt. No. ) NAME : ROLL No. : SIGNATURE : BATCH : DATE : VERIFICATION OF BEER - LAMBERT S LAW & DETERMINATION OF DISSOCIATION CONSTANT (Ka) OF METHYLRED, SPECTROPHOTOMETRICALLY AIM To verify Beer
C 141(Expt. No. ) NAME : ROLL No. : SIGNATURE : BATCH : DATE : VERIFICATION OF BEER - LAMBERT S LAW & DETERMINATION OF DISSOCIATION CONSTANT (Ka) OF METHYLRED, SPECTROPHOTOMETRICALLY AIM To verify Beer
Measurement and Instrumentation. Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition
 2141-375 Measurement and Instrumentation Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Basic Data Acquisition System Analog Form Analog Form Digital Form Display Physical varialble Sensor Signal conditioning
2141-375 Measurement and Instrumentation Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Basic Data Acquisition System Analog Form Analog Form Digital Form Display Physical varialble Sensor Signal conditioning
Application of mathematical, statistical, graphical or symbolic methods to maximize chemical information.
 Application of mathematical, statistical, graphical or symbolic methods to maximize chemical information. -However, this definition can be expanded to include: biology (biometrics), environmental science
Application of mathematical, statistical, graphical or symbolic methods to maximize chemical information. -However, this definition can be expanded to include: biology (biometrics), environmental science
EXPERIMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study
 OBJECTVES: EXPERMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study To operate a Spectronic 20 To convert from percent transmission to absorbance units To plot absorbance versus wavelength and find max To plot absorbance versus
OBJECTVES: EXPERMENT #3 A Beer's Law Study To operate a Spectronic 20 To convert from percent transmission to absorbance units To plot absorbance versus wavelength and find max To plot absorbance versus
Chem 310 rd. 3 Homework Set Answers
 -1- Chem 310 rd 3 Homework Set Answers 1. A double line labeled S 0 represents the _ground electronic_ state and the _ground vibrational_ state of a molecule in an excitation state diagram. Light absorption
-1- Chem 310 rd 3 Homework Set Answers 1. A double line labeled S 0 represents the _ground electronic_ state and the _ground vibrational_ state of a molecule in an excitation state diagram. Light absorption
REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES
 Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
Experiment 1 REVIEW OF LAB TECHNIQUES Prepared by Masanobu M. Yamauchi and Ross S. Nord, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE To review density calculations, Beer s Law and the use of electronic balances,
This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact
 This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact pogil@pogil.org The BEER-LAMBERT LAW Learning Objectives Students
This activity has been password protected to prevent modification. In order to request an unprotected version of this activity, contact pogil@pogil.org The BEER-LAMBERT LAW Learning Objectives Students
Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant
 Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant v021214 Objective To determine the equilibrium constant (K c ) for the reaction of iron (III) ion with thiocyanate (SCN - ) to form the thiocyanatoiron(iii)
Spectrophotometric Determination of an Equilibrium Constant v021214 Objective To determine the equilibrium constant (K c ) for the reaction of iron (III) ion with thiocyanate (SCN - ) to form the thiocyanatoiron(iii)
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution 2.47 ml of solution 50.00 ml delivered delivered Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution 2.47 ml of solution 50.00 ml delivered delivered Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
Concepts, Techniques. Concepts, Techniques 9/11/2012. & Beer s Law. For a simple, transparent, COLORED material, e.g. ROYGBV
 9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
9//22 OBJECTIVES Spectrophotometry of Food Dyes & Beer s Law Last Update: 9//22 9:54 AM What is the quantitative basis for the color of substances? How is the absorption/transmission of light measured?
Experiment 13. Dilutions and Data Handling in a Spreadsheet rev 1/2013
 Absorbance Experiment 13 Dilutions and Data Handling in a Spreadsheet rev 1/2013 GOAL: This lab experiment will provide practice in making dilutions using pipets and introduce basic spreadsheet skills
Absorbance Experiment 13 Dilutions and Data Handling in a Spreadsheet rev 1/2013 GOAL: This lab experiment will provide practice in making dilutions using pipets and introduce basic spreadsheet skills
Investigating Transition Metal Complexes
 Exercise 4 Investigating Transition Metal Complexes 4 Introduction Colour is a well known property of the transition metals. The colour produced as parts of the visible spectrum are due to electron transitions
Exercise 4 Investigating Transition Metal Complexes 4 Introduction Colour is a well known property of the transition metals. The colour produced as parts of the visible spectrum are due to electron transitions
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law.
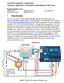 The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
The ROXI Colorimeter & Fluorimeter. Laboratory Application I. Colorimetric measurements via Beer s Law. Required Supplies & Costs: RGB LED; $1.95 Light Sensors; $3.95 ea 3-way switch; $6.54 3 ohm resistor;
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Thousands of years ago, copper was abundant enough in quantity that it could be found on the Earth s surface. Prospecting for copper then was relatively
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Thousands of years ago, copper was abundant enough in quantity that it could be found on the Earth s surface. Prospecting for copper then was relatively
Experiment 8: DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 Experiment 8: DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT Purpose: The equilibrium constant for the formation of iron(iii) thiocyanate complex ion is to be determined. Introduction: In the previous week,
Experiment 8: DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT Purpose: The equilibrium constant for the formation of iron(iii) thiocyanate complex ion is to be determined. Introduction: In the previous week,
Chapter 4: Verification of compendial methods
 Chapter 4: Verification of compendial methods Introduction In order to ensure accurate and reliable test results, the quality control laboratory (QCL) needs to use analytical methods (and accompanying
Chapter 4: Verification of compendial methods Introduction In order to ensure accurate and reliable test results, the quality control laboratory (QCL) needs to use analytical methods (and accompanying
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium
 Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium Introduction The word equilibrium suggests balance or stability. The fact that a chemical reaction
Chemistry 112 Laboratory Experiment 7: Determination of Reaction Stoichiometry and Chemical Equilibrium Introduction The word equilibrium suggests balance or stability. The fact that a chemical reaction
Experiment. Quantification of Ascorbic acid by Fluorescence Spectroscopy1
 Experiment. Quantification of Ascorbic acid by Fluorescence Spectroscopy Modified 10/2017 Experiment. Quantification of Ascorbic acid by Fluorescence Spectroscopy1 Objective: The goal of this experiment
Experiment. Quantification of Ascorbic acid by Fluorescence Spectroscopy Modified 10/2017 Experiment. Quantification of Ascorbic acid by Fluorescence Spectroscopy1 Objective: The goal of this experiment
MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION!
 Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
Name Partner(s) Section Date MORE LIGHTS, COLOR, ABSORPTION! PRE-LAB QUERIES 1. The terms absorption and transmittance are often used when describing the interaction of light with matter. Explain what
For simplicity, we ll represent BTB s ionization in a solution by the equilibrium: HBTB = H + + BTB -
 Chemistry 160 Please have the following pages ready before class on Wednesday, April 11. An abstract (see the end of this handout) is needed for this write-up. The abstract and photocopied pages of the
Chemistry 160 Please have the following pages ready before class on Wednesday, April 11. An abstract (see the end of this handout) is needed for this write-up. The abstract and photocopied pages of the
Time Varying Circuit Analysis
 MAS.836 Sensor Systems for Interactive Environments th Distributed: Tuesday February 16, 2010 Due: Tuesday February 23, 2010 Problem Set # 2 Time Varying Circuit Analysis The purpose of this problem set
MAS.836 Sensor Systems for Interactive Environments th Distributed: Tuesday February 16, 2010 Due: Tuesday February 23, 2010 Problem Set # 2 Time Varying Circuit Analysis The purpose of this problem set
CHEM 254 EXPERIMENT 9. Chemical Equilibrium-Colorimetric determination of equilibrium constant of a weak acid
 CHEM 254 EXPERIMENT 9 Chemical Equilibrium-Colorimetric determination of equilibrium constant of a weak acid For a weak acid that can only partly dissociate the equilibrium constant is related to activities
CHEM 254 EXPERIMENT 9 Chemical Equilibrium-Colorimetric determination of equilibrium constant of a weak acid For a weak acid that can only partly dissociate the equilibrium constant is related to activities
Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION
 Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
Sample Experiment 12: SPECTROSCOPY: EMISSION & ABSORPTION Purpose: Emission and absorption spectroscopy is to be explored from different perspectives in a multipart experiment. Part I: Certain elements
Pelagia Research Library. Spectrophotometric determination of Ametoctradin and in its commercial formulations
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2016, 7(4):7-14 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Spectrophotometric determination of Ametoctradin and in its commercial formulations
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2016, 7(4):7-14 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Spectrophotometric determination of Ametoctradin and in its commercial formulations
you-try-it-04.xlsx Step-by-Step Guide ver. 9/4/2009
 you-try-it-04.xlsx Step-by-Step Guide ver. 9/4/2009 Abstract This document provides step-by-step instructions for the Excel workbook you-try-it-04.xlsx (Excel 2007). The worksheets contain data for practice
you-try-it-04.xlsx Step-by-Step Guide ver. 9/4/2009 Abstract This document provides step-by-step instructions for the Excel workbook you-try-it-04.xlsx (Excel 2007). The worksheets contain data for practice
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Level
 *348375840* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 970/52 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation May/June 203 hour 5 minutes Candidates
*348375840* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 970/52 Paper 5 Planning, Analysis and Evaluation May/June 203 hour 5 minutes Candidates
Instrumental methods of analysis
 Instrumental methods of analysis By Dr Hisham Ezzat Abdellatef Prof. of Analytical Chemistry Background: Analytical Chemistry: The Science of Chemical Measurements. Analyte: The compound or chemical species
Instrumental methods of analysis By Dr Hisham Ezzat Abdellatef Prof. of Analytical Chemistry Background: Analytical Chemistry: The Science of Chemical Measurements. Analyte: The compound or chemical species
Spectrometric Determination of the Acid Dissociation Constant of an Acid-base Indicator
 Spectrometric Determination of the Acid Dissociation Constant of an Acid-base Indicator Learning Goals 1. Gain appreciation of the dynamics of perturbing a chemical equilibrium 2. Gain an understanding
Spectrometric Determination of the Acid Dissociation Constant of an Acid-base Indicator Learning Goals 1. Gain appreciation of the dynamics of perturbing a chemical equilibrium 2. Gain an understanding
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution delivered 2.47 ml of solution delivered 50.00 ml Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Using a Buret and Volumetric Flask: 2.06 ml of solution delivered 2.47 ml of solution delivered 50.00 ml Volumetric Flask Reading a buret: Burets are
International Journal of Chemistry Research Vol 1, Issue 1, 2010
 International Journal of Chemistry Research Vol 1, Issue 1, 0 Research Article DEVELOPMENT OF SIMULTANEOUS SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHOD OF AMOXICILLIN TRIHYDRATE AND RANITIDINE BISMUTH CITRATE IN SAME DOSAGES
International Journal of Chemistry Research Vol 1, Issue 1, 0 Research Article DEVELOPMENT OF SIMULTANEOUS SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHOD OF AMOXICILLIN TRIHYDRATE AND RANITIDINE BISMUTH CITRATE IN SAME DOSAGES
Schedule. Draft Section of Lab Report Monday 6pm (Jan 27) Summary of Paper 2 Monday 2pm (Feb 3)
 Schedule Assignment Due Date Draft Section of Lab Report Monday 6pm (Jan 27) Quiz for Lab 2 Peer Review of Draft Complete Lab Report 1 Tuesday 9:30am Wednesday 6pm Friday 6pm Summary of Paper 2 Monday
Schedule Assignment Due Date Draft Section of Lab Report Monday 6pm (Jan 27) Quiz for Lab 2 Peer Review of Draft Complete Lab Report 1 Tuesday 9:30am Wednesday 6pm Friday 6pm Summary of Paper 2 Monday
Complete the following. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT.
 CHEM 322 Name Exam 3 Spring 2013 Complete the following. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT. Warm-up (3 points each). 1. In Raman Spectroscopy, molecules are promoted
CHEM 322 Name Exam 3 Spring 2013 Complete the following. Clearly mark your answers. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE CREDIT. Warm-up (3 points each). 1. In Raman Spectroscopy, molecules are promoted
Activity 6: Spectroscopy
 Activity 6: Spectroscopy Reference: Kenkel (p 149-237) and arris, (hp 17-21) Turn in a hardcopy of this activity. If you do not, you will not receive credit. Dropbox submission is not valid. / Score Name
Activity 6: Spectroscopy Reference: Kenkel (p 149-237) and arris, (hp 17-21) Turn in a hardcopy of this activity. If you do not, you will not receive credit. Dropbox submission is not valid. / Score Name
A Fluorometric Analysis of Quinine in Tonic Water
 A Fluorometric Analysis of Quinine in Tonic Water Introduction In this Laboratory Exercise, we will determine the amount of quinine in Tonic Water using a fluorometric analysis. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
A Fluorometric Analysis of Quinine in Tonic Water Introduction In this Laboratory Exercise, we will determine the amount of quinine in Tonic Water using a fluorometric analysis. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
CHEM Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy
 CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
CHEM 0012 Lab 7: Determination of an Equilibrium Constant using Spectroscopy 1 Determination of the equilibrium constant of the following equilibrium system at room temperature. Fe 3+ (aq) + SCN- (aq)
Basics of UV-Visible Spectroscopy *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m34525 1 Basics of UV-Visible Spectroscopy * Brittany L. Oliva-Chatelain Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m34525 1 Basics of UV-Visible Spectroscopy * Brittany L. Oliva-Chatelain Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Shigeya SnTO and SUIIllO UCHIKAWA. Faculty of Education, Kumamoto University, Kurokami, Kumamoto 860
 ANALYTICAL SCIENCES FEBRUARY 1986, VOL. 2 47 Extraction-Spectrophotometric Determination of Antimony(V) with 2-Hydroxyisocaproic Acid and Citrate, with Application to Differential Determination of Antimony(V)
ANALYTICAL SCIENCES FEBRUARY 1986, VOL. 2 47 Extraction-Spectrophotometric Determination of Antimony(V) with 2-Hydroxyisocaproic Acid and Citrate, with Application to Differential Determination of Antimony(V)
Topic 2 Measurement and Calculations in Chemistry
 Topic Measurement and Calculations in Chemistry Nature of Measurement Quantitative observation consisting of two parts. number scale (unit) Examples 0 grams 6.63 10 34 joule seconds The Fundamental SI
Topic Measurement and Calculations in Chemistry Nature of Measurement Quantitative observation consisting of two parts. number scale (unit) Examples 0 grams 6.63 10 34 joule seconds The Fundamental SI
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13)
 An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
An Introduction to Ultraviolet-Visible Molecular Spectrometry (Chapter 13) Beer s Law: A = -log T = -logp 0 / P = e x b x C See Table 13-1 for terms. In measuring absorbance or transmittance, one should
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Absorbance Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious
Absorbance Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious
Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT INTRODUCTION The principle underlying a spectrophotometric method of analysis involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation
Chemistry 112 SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT INTRODUCTION The principle underlying a spectrophotometric method of analysis involves the interaction of electromagnetic radiation
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore
 Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious mining sites
Introduction to Spectroscopy: Analysis of Copper Ore Introduction The goal of this lab is to determine the unknown concentration of two different copper solution samples, taken from fictitious mining sites
A Fluorometric Analysis of Quinine in Tonic Water
 A Fluorometric Analysis of Quinine in Tonic Water CHEM 329 Professor Vogt TA: Sam Rosolina Allison Poget Date Performed: March 29, 2016 Date Submitted: April 5, 2016 ABSTRACT In this experimental, various
A Fluorometric Analysis of Quinine in Tonic Water CHEM 329 Professor Vogt TA: Sam Rosolina Allison Poget Date Performed: March 29, 2016 Date Submitted: April 5, 2016 ABSTRACT In this experimental, various
PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES
 PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES CHAPTER General Principles of Spectrophotometry 123 In absorption spectroscopy, absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet light and visible radiation find application
PART SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC STUDIES CHAPTER General Principles of Spectrophotometry 123 In absorption spectroscopy, absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet light and visible radiation find application
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS
 2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
2 SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS 2.1 Introduction Chemical analysis falls into two basic categories: qualitative what is present quantitative how much is present Spectroscopy is capable of both types of analysis,
GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Colour intensity of liquids GPM.1.2.1.0006.15 Replaces the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XII, Part 1 Monograph,
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION GENERAL PHARMACOPOEIA MONOGRAPH Colour intensity of liquids GPM.1.2.1.0006.15 Replaces the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation XII, Part 1 Monograph,
The LM741C Integrated Circuit As A Differential Amplifier Building The Electronic Thermometer
 BE 209 Group BEW6 Jocelyn Poruthur, Justin Tannir Alice Wu, & Jeffrey Wu November 19, 1999 The LM741C Integrated Circuit As A Differential Amplifier Building The Electronic Thermometer INTRODUCTION: A
BE 209 Group BEW6 Jocelyn Poruthur, Justin Tannir Alice Wu, & Jeffrey Wu November 19, 1999 The LM741C Integrated Circuit As A Differential Amplifier Building The Electronic Thermometer INTRODUCTION: A
11.1 Uncertainty and error in measurement (1 Hour) 11.2 Uncertainties in calculated results (0.5 Hour) 11.3 Graphical techniques (0.
 Chapter 11 Measurement and Data Processing Page 1 Students are to read and complete any part that requires answers and will submit this assignment on the first day of class. You may use internet sources
Chapter 11 Measurement and Data Processing Page 1 Students are to read and complete any part that requires answers and will submit this assignment on the first day of class. You may use internet sources
Determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper in Effluent Sample
 Determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper in Effluent Sample Branch: General analytical chemistry, water, waste water, environmental protection Key Words 797 / polarography / VA / 8 / Zn / Cd / Pb
Determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead and Copper in Effluent Sample Branch: General analytical chemistry, water, waste water, environmental protection Key Words 797 / polarography / VA / 8 / Zn / Cd / Pb
Beer-Lambert law Decomposition of the manganese oxalate ion
 A34 Beer-Lambert law Decomposition of the manganese oxalate ion Task: 1. Determine the wavelength of maximal absorbance λ max of a hydrated Cu(NH 3 ) 4 2+ complex in the wavelength region of 400 to 800
A34 Beer-Lambert law Decomposition of the manganese oxalate ion Task: 1. Determine the wavelength of maximal absorbance λ max of a hydrated Cu(NH 3 ) 4 2+ complex in the wavelength region of 400 to 800
VISIBLE SPECTROSCOPY
 INTRODUCTION SPECTROPHOTOMETRY OF Co 2+ (Revised: 1-24-93) In this experiment, the Beer-Lambert Law, A = åcl, will be applied to a series of aqueous solutions of CoCl 2. The pink color of the solutions
INTRODUCTION SPECTROPHOTOMETRY OF Co 2+ (Revised: 1-24-93) In this experiment, the Beer-Lambert Law, A = åcl, will be applied to a series of aqueous solutions of CoCl 2. The pink color of the solutions
Colorimetric analysis of aspirin content in a commercial tablet
 Colorimetric analysis of aspirin content in a commercial tablet v010214 Objective In this lab, you will prepare standard solutions, and use Beer s Law to construct a calibration curve. You will determine
Colorimetric analysis of aspirin content in a commercial tablet v010214 Objective In this lab, you will prepare standard solutions, and use Beer s Law to construct a calibration curve. You will determine
Research Article Spectrophotometric Estimation of Didanosine in Bulk Drug and its Formulation
 Research Article Spectrophotometric Estimation of Didanosine in Bulk Drug and its Formulation RN. Kane, PS. Bhokare*, CC. Nalawade, MS Sayyed and RD. Paliwal Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Singhad
Research Article Spectrophotometric Estimation of Didanosine in Bulk Drug and its Formulation RN. Kane, PS. Bhokare*, CC. Nalawade, MS Sayyed and RD. Paliwal Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Singhad
MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer
 Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
ESE319 Introduction to Microelectronics. Output Stages
 Output Stages Power amplifier classification Class A amplifier circuits Class A Power conversion efficiency Class B amplifier circuits Class B Power conversion efficiency Class AB amplifier circuits Class
Output Stages Power amplifier classification Class A amplifier circuits Class A Power conversion efficiency Class B amplifier circuits Class B Power conversion efficiency Class AB amplifier circuits Class
Chapter 28 Solutions
 Chapter 8 Solutions 8.1 (a) P ( V) R becomes 0.0 W (11.6 V) R so R 6.73 Ω (b) V IR so 11.6 V I (6.73 Ω) and I 1.7 A ε IR + Ir so 15.0 V 11.6 V + (1.7 A)r r 1.97 Ω Figure for Goal Solution Goal Solution
Chapter 8 Solutions 8.1 (a) P ( V) R becomes 0.0 W (11.6 V) R so R 6.73 Ω (b) V IR so 11.6 V I (6.73 Ω) and I 1.7 A ε IR + Ir so 15.0 V 11.6 V + (1.7 A)r r 1.97 Ω Figure for Goal Solution Goal Solution
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE DEVELOPMENT OF VALIDATED UV SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF BETAXOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE IN BULK AND PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORM SIDHARTH
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE DEVELOPMENT OF VALIDATED UV SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF BETAXOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE IN BULK AND PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORM SIDHARTH
Quality Assurance is what we do to get the right answer for our purpose FITNESS FOR PURPOSE
 Quality Assurance is what we do to get the right answer for our purpose FITNESS FOR PURPOSE Use objectives: state purpose for which results will be used. Specifications: How good should the numbers be
Quality Assurance is what we do to get the right answer for our purpose FITNESS FOR PURPOSE Use objectives: state purpose for which results will be used. Specifications: How good should the numbers be
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash
 Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
Chemistry 141 Laboratory Spectrometric Determination of Iron Concentration Lab Lecture Notes 8/29/2011 Dr. Abrash What is the purpose of this experiment? We re going to learn a way to quantify the amount
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
BENG 186B Winter 2012 Final
 Name (Last, First): BENG 186B Winter 2012 Final This exam is closed book, closed note, calculators are OK. Circle and put your final answers in the space provided; show your work only on the pages provided.
Name (Last, First): BENG 186B Winter 2012 Final This exam is closed book, closed note, calculators are OK. Circle and put your final answers in the space provided; show your work only on the pages provided.
A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal
 CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 1.2 A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal In this laboratory exercise, we will determine the amount of Calium in a serving of cereal. We
CHEM 311L Quantitative Analysis Laboratory Revision 1.2 A Spectrophotometric Analysis of Calcium in Cereal In this laboratory exercise, we will determine the amount of Calium in a serving of cereal. We
9/28/10. Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Valence Electronic Structure. n σ* transitions
 Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
Title Quantitative Analysis of a Solution Containing Cobalt and Copper
 Title Quantitative Analysis of a Solution Containing Cobalt and Copper Name Manraj Gill (Lab partner: Tanner Adams) Abstract In this series of experiments, we determine the concentrations of two metal
Title Quantitative Analysis of a Solution Containing Cobalt and Copper Name Manraj Gill (Lab partner: Tanner Adams) Abstract In this series of experiments, we determine the concentrations of two metal
The Underground Experimental Investigation of Thermocouples
 The Underground Experimental Investigation of Thermocouples April 14, 21 Abstract This experiment investigates a K-type thermocouple in order to demonstrate the Seebeck and Peltier coefficients. Temperature
The Underground Experimental Investigation of Thermocouples April 14, 21 Abstract This experiment investigates a K-type thermocouple in order to demonstrate the Seebeck and Peltier coefficients. Temperature
Portable type TXRF analyzer: Ourstex 200TX
 Excerpted from Adv. X-Ray. Chem. Anal., Japan: 42, pp. 115-123 (2011) H. Nagai, Y. Nakajima, S. Kunimura, J. Kawai Improvement in Sensitivity and Quantification by Using a Portable Total Reflection X-Ray
Excerpted from Adv. X-Ray. Chem. Anal., Japan: 42, pp. 115-123 (2011) H. Nagai, Y. Nakajima, S. Kunimura, J. Kawai Improvement in Sensitivity and Quantification by Using a Portable Total Reflection X-Ray
2. A bottle of a concentrated aqueous sulfuric acid is labeled 98.0 wt % H 2 SO 4 (Molecular weight is g/mol) has a concentration of 18.0 M.
 Chem201, Winter 2006 Midterm N1 01/26/06 Name Answer key SID 1. A solution is prepared by dissolving 25.8 grams on magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 ) in water to produce 250.0 ml of solution. Molecular weight
Chem201, Winter 2006 Midterm N1 01/26/06 Name Answer key SID 1. A solution is prepared by dissolving 25.8 grams on magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 ) in water to produce 250.0 ml of solution. Molecular weight
Experiment 13H THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1
 Experiment 13H 08/03/2017 AHRM THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1 PROBLEM: Determine the rate law for the chemical reaction between FD&C Red Dye #3 and sodium hypochlorite. LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
Experiment 13H 08/03/2017 AHRM THE REACTION OF RED FOOD COLOR WITH BLEACH 1 PROBLEM: Determine the rate law for the chemical reaction between FD&C Red Dye #3 and sodium hypochlorite. LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
RATE LAW DETERMINATION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET HYDROXYLATION
 Rate Law Determination of Crystal Violet Hydroxylation Revised 5/22/12 RATE LAW DETERMINATION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET HYDROXYLATION Adapted from "Chemistry with Computers" Vernier Software, Portland OR, 1997
Rate Law Determination of Crystal Violet Hydroxylation Revised 5/22/12 RATE LAW DETERMINATION OF CRYSTAL VIOLET HYDROXYLATION Adapted from "Chemistry with Computers" Vernier Software, Portland OR, 1997
DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
 DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT In this experiment the equilibrium properties of the reaction between the iron(iii) ion and the thiocyanate ion will be studied. The relevant chemical equation
DETERMINATION OF AN EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT In this experiment the equilibrium properties of the reaction between the iron(iii) ion and the thiocyanate ion will be studied. The relevant chemical equation
Analytical Performance & Method. Validation
 Analytical Performance & Method Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451 Saudi Arabia Building:
Analytical Performance & Method Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451 Saudi Arabia Building:
Preparation of Standard Curves. Principle
 Preparation of Standard urves Principle Many laboratory tests require the measurement of concentration be evaluated or read in a photometer (colorimeter or spectrophotometer). Since these instruments are
Preparation of Standard urves Principle Many laboratory tests require the measurement of concentration be evaluated or read in a photometer (colorimeter or spectrophotometer). Since these instruments are
CHEM 122 LABORATORY SKILLS EXAMINATION
 Form 2014 CHEM 122 LABORATORY SKILLS EXAMINATION Prepared by Ross S. Nord and colleagues, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE Assess each student s ability to work independently in the lab using the techniques
Form 2014 CHEM 122 LABORATORY SKILLS EXAMINATION Prepared by Ross S. Nord and colleagues, Eastern Michigan University PURPOSE Assess each student s ability to work independently in the lab using the techniques
Equilibrium and Ionic Strength Effects
 Equilibrium and Ionic Strength Effects Objectives You will determine the thermodynamic equilibrium constant for the reaction between iron(iii) ion and thiocyanate ion to form iron(iii)-thiocyanate. Fe
Equilibrium and Ionic Strength Effects Objectives You will determine the thermodynamic equilibrium constant for the reaction between iron(iii) ion and thiocyanate ion to form iron(iii)-thiocyanate. Fe
CHM112 Lab Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Grading Rubric
 Name Team Name CHM112 Lab Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Grading Rubric Criteria Points possible Points earned Lab Performance Printed lab handout and rubric was brought to lab 3 Initial concentrations
Name Team Name CHM112 Lab Determination of an Equilibrium Constant Grading Rubric Criteria Points possible Points earned Lab Performance Printed lab handout and rubric was brought to lab 3 Initial concentrations
Chem 321 Name Answer Key D. Miller
 1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
Name Lab Exercise 2 - Standard Curves Nitrate, Ammonia, Phosphorus, and Chlorophyll
 Name Lab Exercise 2 - Standard Curves Nitrate, Ammonia, Phosphorus, and Chlorophyll For most analytical chemical procedures, we use "standard curves" to calibrate our measurements. For example, we want
Name Lab Exercise 2 - Standard Curves Nitrate, Ammonia, Phosphorus, and Chlorophyll For most analytical chemical procedures, we use "standard curves" to calibrate our measurements. For example, we want
Method development and validation for the estimation of metronidazole in tablet dosage form by UV spectroscopy and derivative spectroscopy
 IJPAR Volume 3 Issue 2 April-June-2014 ISSN: 2320-2831 Available Online at: www.ijpar.com [Research article] Method development and validation for the estimation of metronidazole in tablet dosage form
IJPAR Volume 3 Issue 2 April-June-2014 ISSN: 2320-2831 Available Online at: www.ijpar.com [Research article] Method development and validation for the estimation of metronidazole in tablet dosage form
Chem 434 Instrumental Analysis Test 1
 Chem 434 Instrumental Analysis Test 1 Name: 1. (15 points) In Chapter 5 we discussed four sources of instrumental noise: Thermal Noise, Shot Noise, Flicker Noise, and Environmental noise. Discuss the differences
Chem 434 Instrumental Analysis Test 1 Name: 1. (15 points) In Chapter 5 we discussed four sources of instrumental noise: Thermal Noise, Shot Noise, Flicker Noise, and Environmental noise. Discuss the differences
6. The default plot created by Excel meets all of the requirements for a formal report plot in ME 360.
 ME 360 Fall 2008 Semester Test #1 9/24/08 Closed book, closed notes portion of test. When you turn in this part of the test you will get the second part which allows a page of handwritten formulas. There
ME 360 Fall 2008 Semester Test #1 9/24/08 Closed book, closed notes portion of test. When you turn in this part of the test you will get the second part which allows a page of handwritten formulas. There
