What are the characteristics of a transverse wave?
|
|
|
- Simon Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guiding Question What are the characteristics of a transverse wave? 1
2 Key Vocabulary Key Vocabulary } amplitude } frequency } function } longitudinal } transverse } structure } wavelength 2
3 Get Started Modeling waves with a spring } Scientists and engineers create models to show how thinks work, to describe and explain why things happen, and to make predictions. 3
4 Introduction Read the introduction and look for key ideas 4
5 Get Started Venn diagram 5
6 Do the Activity Safety } Handle the springs with care and never let go suddenly when the spring is under tension. If released when tension is being applied, the spring can move rapidly and unpredictably and could scratch someone. Wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from such an event. 6
7 Do the Activity Teacher demonstration 7
8 Do the Activity Complete procedure part A: Wave Pulses } Record your data in your notebook. 8
9 Do the Activity Did 100% of the energy that you put into the pulse make it to the end of the spring? } Share your thoughts with the class. 9
10 Do the Activity Complete procedure part B: Transverse } Record your data in your notebook. 10
11 Do the Activity Interpreting Graphs 11
12 Do the Activity Interpreting Graphs 12
13 Do the Activity Relationship between variables } proportion } graph } mathematical symbols 13
14 Build Understanding Science practices and crosscutting concepts } Used evidence to build knowledge } Patterns 14
15 Analysis Analysis 1 } Describe what happened when a. the wave pulses reached the end of the spring. b. the transverse wave reached the end of the spring. a. the wave pulses reached the end of the spring. The pulses reflected off the fixed end on the opposite side. b. the transverse wave reached the end of the spring. Both sides of the wave reflected onto the opposite sides, like with the pulse, but they did so simultaneously so it looked like the top and bottom of the wave switched sides when reflected. 15
16 Analysis Analysis 2 } What happened when the spring was stretched to double its length?. The wave traveled faster and its amplitude decreased. 16
17 Analysis Analysis 3 } What happened to the amplitude of the wave pulse when it traveled along the spring? Suggest an explanation for your observations.. The wave pulse got smaller and, therefore, its amplitude must have decreased.this is probably because the wave used some of its energy to overcome friction as it moved across the surface of the floor. 17
18 Analysis Analysis 4 } Do you think that sound also has a wavelength? Explain why or why not. Sound must have a wavelength. because it has a frequency, and they go together. Since a wavelength is the distance of one cycle, I think the wavelength is the distance between compressions. 18
19 Analysis Analysis 5 } Look at the diagram shown on the right of a wave made with a spring. a. Describe the motion of the spring at points B and C. a. Describe the motion of the spring at points B and C. The motion of the spring at B is up and down from the maximum height to minimum height.the spring at position C moves up and down but does so at a slightly later time than the spring at position B. 19
20 Analysis Analysis 5 continued } Look at the diagram shown on the right of a wave made with a spring. b. Is the energy transfer of the wave parallel or perpendicular to the motion of the spring at point B? Explain.. Is the energy transfer of the wave parallel or perpendicular to the motion of the spring at Point B? Explain. The energy transfer is from end to end, or between points A and D. The motion of the spring at part B is up and down, which is perpendicular to the energy transfer. 20
21 Analysis Analysis 6 } Trace the diagram from the previous question above, and then a. draw what the wave would look like if the amplitude was doubled. b. draw what the wave would look like if the frequency was doubled. c. draw what the wave would look like if the wavelength was doubled. Show page 73 from teacher s notebook. 21
22 Analysis Analysis 7 } Make two tables like the ones shown, and fill in the missing diagrams to show changes in wavelength and frequency. Then explain what your diagrams model. } Show answer from teacher s book page 74 22
23 Analysis Analysis 8 } For a wave of a given speed, what is the relationship between the wavelength and the frequency? Use your diagrams from the activity and the model from the previous item to look for patterns.. As the wavelength of a wave increases, if everything else is constant, the frequency will decrease.when the wavelength decreases, the frequency increases. 23
24 Analysis Analysis 9 } A transverse wave with constant speed has an increase in amplitude over time, as shown in the lefthand column of the table shown. Some of the data for energy and wavelength is missing. 24
25 Analysis Analysis 9 continued a. Look at the patterns in the data and predict the missing energies and wavelengths of the wave. In your science notebook, copy the last two rows of the table and complete the data. Then explain the pattern you followed to fill in the data. The pattern is that the energy is equal to the square of the amplitude times 10.The energy is not related to the wavelength or time. 25
26 Analysis Analysis 9 continued b. Make a graph of amplitude (x-axis) vs. energy (y-axis) that includes all five times. Make sure to label your graph. See teacher page 76 d. Use your graph to predict the energy and wavelength for the amplitude of 7 m. For the amplitude of 7m, the energy is 490 J and the wavelength is 0.3 m. 26
27 Analysis Scoring Guide: Organizing Data for Analysis 27
28 Revisit the Guiding Question What are the characteristics of a transverse wave? 28
29 Review Key Vocabulary definitions } amplitude - The maximum displacement of a wave from its state of rest. For a mechanical wave, amplitude can be measured as a distance or a pressure. } frequency - The number of times an event repeats in a given time. For sound it is the number of vibrations per second. 29
30 Review Key Vocabulary definitions } function - A purpose or function which a particular thing can perform. } longitudinal wave - A wave that transfers energy through compressions and rarefactions in the material through which the energy travels. 30
31 Review Key Vocabulary definitions } transverse wave - A wave that consists of vibrations that are perpendicular to the direction that the energy travels. } structure - The way something is formed, built, or organized. } wavelength - The length of one wave cycle. 31
32 Extension Extension } Investigate a standing wave and model them with your long spring. 32
How can we model sound waves?
 Guiding Question How can we model sound waves? Activity 2: Making Sound 1 Key Vocabulary Key Vocabulary } audiogram } compression } frequency } function } hertz } pattern } rarefaction } sound intensity
Guiding Question How can we model sound waves? Activity 2: Making Sound 1 Key Vocabulary Key Vocabulary } audiogram } compression } frequency } function } hertz } pattern } rarefaction } sound intensity
Virbations and Waves
 Virbations and Waves 1.1 Observe and find a pattern Try the following simple experiments and describe common patterns concerning the behavior of the block. (a) Fill in the table that follows. Experiment
Virbations and Waves 1.1 Observe and find a pattern Try the following simple experiments and describe common patterns concerning the behavior of the block. (a) Fill in the table that follows. Experiment
Class 35. Wave properties. PHY 231 Fall 2004 Prof. S. Billinge
 Class 35 Wave properties Announcements Clicker scores were sent by message to LONCAPA. Please check and report problems to me ASAP Concepts overview 1. Wavelength, amplitude, frequency, period 2. Superposition
Class 35 Wave properties Announcements Clicker scores were sent by message to LONCAPA. Please check and report problems to me ASAP Concepts overview 1. Wavelength, amplitude, frequency, period 2. Superposition
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
STANDING WAVES AND RESONANCE
 Name: PHYSICS 119 SPRING 2008 S.N.: SECTION: Experiment 2 PARTNER: DATE: STANDING WAVES AND RESONANCE Objectives Observe standing waves in a stretched string Examine how an external oscillator can cause
Name: PHYSICS 119 SPRING 2008 S.N.: SECTION: Experiment 2 PARTNER: DATE: STANDING WAVES AND RESONANCE Objectives Observe standing waves in a stretched string Examine how an external oscillator can cause
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam
 G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Second Semester Review
 Second Semester Review Name Section 4.2 1. Define energy What is energy? Explain if it is scalar or vector in nature. 2. Explain what factors affect the speed of a rollercoaster. Whether a rollercoaster
Second Semester Review Name Section 4.2 1. Define energy What is energy? Explain if it is scalar or vector in nature. 2. Explain what factors affect the speed of a rollercoaster. Whether a rollercoaster
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Speed of waves. Apparatus: Long spring, meter stick, spring scale, stopwatch (or cell phone stopwatch)
 Name: Speed of waves Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Apparatus: Long spring, meter stick, spring scale, stopwatch (or cell phone stopwatch) Objectives 1. To directly calculate the speed of waves in a stretched
Name: Speed of waves Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Apparatus: Long spring, meter stick, spring scale, stopwatch (or cell phone stopwatch) Objectives 1. To directly calculate the speed of waves in a stretched
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion
 Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Introduction to Waves
 Introduction to Waves 4 January 2016 PHYC 1290 Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Water waves Sound waves Radio waves Waves are everywhere in nature Visible Light X-rays Matter waves Waves and
Introduction to Waves 4 January 2016 PHYC 1290 Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Water waves Sound waves Radio waves Waves are everywhere in nature Visible Light X-rays Matter waves Waves and
Chapter 15. Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Standing waves [49 marks]
![Standing waves [49 marks] Standing waves [49 marks]](/thumbs/92/110837906.jpg) Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Be a Scientist Notebook. Student Journal. Grade 5
 Be a Scientist Notebook Student Journal Grade 5 MODULE OPENER Name Date Structure and Properties of Matter Science in Our World Barges can be used to transport large quantities of goods from one place
Be a Scientist Notebook Student Journal Grade 5 MODULE OPENER Name Date Structure and Properties of Matter Science in Our World Barges can be used to transport large quantities of goods from one place
When you throw a ball, increasing the speed of your hand increases the speed of the ball. Does the same apply to a wave pulse?
 Tutorial Finding mechanism: Pulses Name I. One traveling pulse: The effect of flicking the spring faster When you throw a ball, increasing the speed of your hand increases the speed of the ball. Does the
Tutorial Finding mechanism: Pulses Name I. One traveling pulse: The effect of flicking the spring faster When you throw a ball, increasing the speed of your hand increases the speed of the ball. Does the
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Simple Harmonic Motion Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring
 17 Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring A spring that is hanging vertically from a support with no mass at the end of the spring has a length L (called its rest length). When a mass is added to
17 Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring A spring that is hanging vertically from a support with no mass at the end of the spring has a length L (called its rest length). When a mass is added to
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
PH206 Exam II Spring 2000
 Name PH206 Exam II Spring 2000 Some Constants: % = 3.14159 sin(a±b)=sinacosb ± cosasinb ) = 5.6696 10-8 W/m 2 #K 4 cos(a±b)=cosacosb. sinasinb k B = 1.38 10-23 J/K sina ± sinb = 2 sin ½(A±B) cos½(a.b)
Name PH206 Exam II Spring 2000 Some Constants: % = 3.14159 sin(a±b)=sinacosb ± cosasinb ) = 5.6696 10-8 W/m 2 #K 4 cos(a±b)=cosacosb. sinasinb k B = 1.38 10-23 J/K sina ± sinb = 2 sin ½(A±B) cos½(a.b)
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Simple Harmonic Oscillator Challenge Problems
 Simple Harmonic Oscillator Challenge Problems Problem 1: Dimensional Analysis, Estimation and Concepts Imagine that one drilled a hole with smooth sides straight through the center of the earth, of radius
Simple Harmonic Oscillator Challenge Problems Problem 1: Dimensional Analysis, Estimation and Concepts Imagine that one drilled a hole with smooth sides straight through the center of the earth, of radius
Mahopac Central School District Curriculum Introduction to Science 8
 Introduction to Science 8 A. The goal of science is to understand the natural world 1. As you make new observations and test new explanations your view of the natural world may change again and again 2.
Introduction to Science 8 A. The goal of science is to understand the natural world 1. As you make new observations and test new explanations your view of the natural world may change again and again 2.
Lesson Plan: Star Gazing By: Darby Feldwinn
 Lesson Plan: Star Gazing By: Darby Feldwinn Target Grade: 5 th Teacher Prep Time: 10 (1 hour if you need to print and laminate star cards.) Lesson Time: 3 hours (we recommend doing this lesson over three
Lesson Plan: Star Gazing By: Darby Feldwinn Target Grade: 5 th Teacher Prep Time: 10 (1 hour if you need to print and laminate star cards.) Lesson Time: 3 hours (we recommend doing this lesson over three
DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN. Physics FINAL EXAMINATION June 2011.
 Name: Teacher: DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN Value: 80 Marks Physics 2204 FINAL EXAMINATION June 2011 General Instructions This examination consists of
Name: Teacher: DO NOT OPEN THE EXAMINATION PAPER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD BY THE SUPERVISOR TO BEGIN Value: 80 Marks Physics 2204 FINAL EXAMINATION June 2011 General Instructions This examination consists of
Fineman CP Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
Scientific Inquiry. Standards B 1.2 & B 1.9
 Scientific Inquiry Standards B 1.2 & B 1.9 Scientific Inquiry The student will demonstrate an understanding of how scientific inquiry and technological design, including mathematical analysis, can be used
Scientific Inquiry Standards B 1.2 & B 1.9 Scientific Inquiry The student will demonstrate an understanding of how scientific inquiry and technological design, including mathematical analysis, can be used
Section 2.7 Solving Linear Inequalities
 Section.7 Solving Linear Inequalities Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Add and multiply an inequality. Solving equations (.1,.,
Section.7 Solving Linear Inequalities Objectives In this section, you will learn to: To successfully complete this section, you need to understand: Add and multiply an inequality. Solving equations (.1,.,
Physics Unit: Force & Motion
 Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
General Physics I Spring Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 General Physics I Spring 2011 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion 1 Forces and Interactions The central concept in understanding why things move is force. If a tractor pushes or pulls a trailer, the tractor
General Physics I Spring 2011 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion 1 Forces and Interactions The central concept in understanding why things move is force. If a tractor pushes or pulls a trailer, the tractor
14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions
 14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions Required Accessories o (2) Table stops (wooden bars) o (4) C-Clamps o (2) Recording Timers (#15210 or #15215) o (5) Bricks or Books (or other identical
14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions Required Accessories o (2) Table stops (wooden bars) o (4) C-Clamps o (2) Recording Timers (#15210 or #15215) o (5) Bricks or Books (or other identical
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Chapter 16: Oscillatory Motion and Waves. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion
 1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
AP PHYSICS 1. Energy 2016 EDITION
 AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Chapter 5 The Force Vector
 Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 5 The Force Vector Section Review 5.1 1. Indicate whether each of the following units of measurement are scalar or vector units: Speed _scalar time scalar mass
Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 5 The Force Vector Section Review 5.1 1. Indicate whether each of the following units of measurement are scalar or vector units: Speed _scalar time scalar mass
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 9
 1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance
 Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance Part Introduction The sound from a vibrating tuning fork is much louder if it is held over an air column whose length allows it to vibrate in sympathy with the tuning
Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance Part Introduction The sound from a vibrating tuning fork is much louder if it is held over an air column whose length allows it to vibrate in sympathy with the tuning
Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4
 Name Date Period Objectives: Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4 1) Find the energy stored within the rubber band cannon for various displacements. 2) Find the
Name Date Period Objectives: Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4 1) Find the energy stored within the rubber band cannon for various displacements. 2) Find the
Energy Review Guide Name: Date: Period:
 Name: Date: Period: You are to use this review guide in addition to the study cards you should have already created using the guide previously given to you. I can state and explain the Law of Conservation
Name: Date: Period: You are to use this review guide in addition to the study cards you should have already created using the guide previously given to you. I can state and explain the Law of Conservation
Chapter 13. F =!kx. Vibrations and Waves. ! = 2" f = 2" T. Hooke s Law Reviewed. Sinusoidal Oscillation Graphing x vs. t. Phases.
 Chapter 13 Vibrations and Waves Hooke s Law Reviewed F =!k When is positive, F is negative ; When at equilibrium (=0, F = 0 ; When is negative, F is positive ; 1 2 Sinusoidal Oscillation Graphing vs. t
Chapter 13 Vibrations and Waves Hooke s Law Reviewed F =!k When is positive, F is negative ; When at equilibrium (=0, F = 0 ; When is negative, F is positive ; 1 2 Sinusoidal Oscillation Graphing vs. t
Physics Common Assessment Unit 5-8 3rd Nine Weeks
 1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
[2] [2] Fig. 4.1
![[2] [2] Fig. 4.1 [2] [2] Fig. 4.1](/thumbs/79/80000819.jpg) 1 (a) (i) Explain what is meant by a progressive wave.... [2] (ii) State two differences between a progressive and a stationary wave. 1... 2... [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows, at time t = 0, the shape of a section
1 (a) (i) Explain what is meant by a progressive wave.... [2] (ii) State two differences between a progressive and a stationary wave. 1... 2... [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows, at time t = 0, the shape of a section
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 2
 6.5.1 Forces and their interactions 6.5.2 Work done and energy transfer AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and
6.5.1 Forces and their interactions 6.5.2 Work done and energy transfer AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and
Earthquake Investigation
 Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Chapter 1, Lesson 3: The Ups and Downs of Thermometers
 Chapter 1, Lesson 3: The Ups and Downs of Thermometers Key Concepts The way a thermometer works is an example of heating and cooling a liquid. When heated, the molecules of the liquid in the thermometer
Chapter 1, Lesson 3: The Ups and Downs of Thermometers Key Concepts The way a thermometer works is an example of heating and cooling a liquid. When heated, the molecules of the liquid in the thermometer
Lab 14. Simple Harmonic Motion and Springs: What Is the Mathematical Model of the Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass Hanging From a Spring?
 Simple Harmonic Motion and Springs What Is the Mathematical Model of the Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass Hanging From a Spring? Lab Handout Lab 14. Simple Harmonic Motion and Springs: What Is the Mathematical
Simple Harmonic Motion and Springs What Is the Mathematical Model of the Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass Hanging From a Spring? Lab Handout Lab 14. Simple Harmonic Motion and Springs: What Is the Mathematical
2. What are the 4 steps of the Scientific Method as described by Mr. Martin?
 Ch.1 Study Guide Outline Study the Review that is posted on the website. Make a note card to use for the test. 1. What is science and physics? 2. What are the 4 steps of the Scientific Method as described
Ch.1 Study Guide Outline Study the Review that is posted on the website. Make a note card to use for the test. 1. What is science and physics? 2. What are the 4 steps of the Scientific Method as described
Equipotential and Electric Field Mapping
 Experiment 2 Equipotential and Electric Field Mapping 2.1 Objectives 1. Determine the lines of constant electric potential for two simple configurations of oppositely charged conductors. 2. Determine the
Experiment 2 Equipotential and Electric Field Mapping 2.1 Objectives 1. Determine the lines of constant electric potential for two simple configurations of oppositely charged conductors. 2. Determine the
What is a force? How can a force be measured? How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect objects?
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION Matter in Motion 2 What Is a Force? BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a force? How can a force be measured? How do balanced
CHAPTER 12 SECTION Matter in Motion 2 What Is a Force? BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a force? How can a force be measured? How do balanced
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Scientific Processes 1. Read through the following scenario and identify the claim, evidence and reasoning.
 PS Physics Study Guide End of Course Exam Scientific Processes 1. Read through the following scenario and identify the claim, evidence and reasoning. Lea just finished her lunch. All that is left is her
PS Physics Study Guide End of Course Exam Scientific Processes 1. Read through the following scenario and identify the claim, evidence and reasoning. Lea just finished her lunch. All that is left is her
AS Physics. PHYA2 Mechanics, Materials and Waves Mark scheme June Version: 1.0 Final
 AS Physics PHYA Mechanics, Materials and Waves Mark scheme 450 June 017 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions,
AS Physics PHYA Mechanics, Materials and Waves Mark scheme 450 June 017 Version: 1.0 Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions,
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Fineman Honors Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
Final Worksheet. Equation And Constant Summary
 Equation And Constant Summary Final Worksheet These equations will be provided for you on the final. Know what they mean! Make notes on this page with which to study. v = d t t = d v d=vt If the speed
Equation And Constant Summary Final Worksheet These equations will be provided for you on the final. Know what they mean! Make notes on this page with which to study. v = d t t = d v d=vt If the speed
Activity Template. Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY
 Activity Template Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: Density and Pitch, is there a relationship? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity
Activity Template Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: Density and Pitch, is there a relationship? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA THE MATRICULATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION INTERMEDIATE LEVEL. PHYSICS May 2012 EXAMINERS REPORT
 UNIVERSITY OF MALTA THE MATRICULATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION INTERMEDIATE LEVEL PHYSICS May 2012 EXAMINERS REPORT MATRICULATION AND SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS BOARD Part 1: Statistical
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA THE MATRICULATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION INTERMEDIATE LEVEL PHYSICS May 2012 EXAMINERS REPORT MATRICULATION AND SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS BOARD Part 1: Statistical
LECTURE 5 WAVES ON STRINGS & HARMONIC WAVES. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 5 WAVES ON STRINGS & HARMONIC WAVES Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 5 2 Reading chapter 14.2 14.3 Waves on a string Speed of waves on a string Reflections Harmonic waves Speed of waves 3 The
LECTURE 5 WAVES ON STRINGS & HARMONIC WAVES Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 5 2 Reading chapter 14.2 14.3 Waves on a string Speed of waves on a string Reflections Harmonic waves Speed of waves 3 The
Physics. Puyallup Fair
 Newspapers In Education Presents Physics. and the, Puyallup Fair Teacher s Guide for Grades 4 12 Puyallup Fair Make your escape Physics and the Puyallup Fair Teacher s Guide Introduction Nearly every teacher
Newspapers In Education Presents Physics. and the, Puyallup Fair Teacher s Guide for Grades 4 12 Puyallup Fair Make your escape Physics and the Puyallup Fair Teacher s Guide Introduction Nearly every teacher
Section 2.6 Solving Linear Inequalities
 Section 2.6 Solving Linear Inequalities INTRODUCTION Solving an inequality is much like solving an equation; there are, though, some special circumstances of which you need to be aware. In solving an inequality
Section 2.6 Solving Linear Inequalities INTRODUCTION Solving an inequality is much like solving an equation; there are, though, some special circumstances of which you need to be aware. In solving an inequality
University of Maryland Department of Physics. Spring 2009 Final Exam 20. May (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No
 University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
Investigating a pendulum
 P3 3.6 Student practical sheet Investigating a pendulum The period of a pendulum is the time it takes to complete one swing. Different pendulums have different periods, so what determines the period of
P3 3.6 Student practical sheet Investigating a pendulum The period of a pendulum is the time it takes to complete one swing. Different pendulums have different periods, so what determines the period of
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
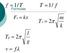 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
Name Class Date. marker and the meterstick to mark points on the string that are 50 cm, 70 cm, and 90 cm away from the mass.
 Name Class Date A pendulum clock is a compound machine that uses stored energy to do work. A spring stores energy, and with each swing of the pendulum, some of that stored energy is used to move the hands
Name Class Date A pendulum clock is a compound machine that uses stored energy to do work. A spring stores energy, and with each swing of the pendulum, some of that stored energy is used to move the hands
The Ocean s Tides. Standards. Ocean Literacy. 46 Rocky Shore Lesson 5. Focus Question. Overview. Objectives. Materials Needed. Teacher Preparation
 The Ocean s Tides Topic Tides, Change Duration One session Vocabulary gravitational force neap tides orbit rotation spring tides tides Standards Practices Planning and Carrying Out Investigations Core
The Ocean s Tides Topic Tides, Change Duration One session Vocabulary gravitational force neap tides orbit rotation spring tides tides Standards Practices Planning and Carrying Out Investigations Core
Introductory Quantum Chemistry Prof. K. L. Sebastian Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Introductory Quantum Chemistry Prof. K. L. Sebastian Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 4 Postulates Part 1 (Refer Slide Time: 00:59) So, I
Introductory Quantum Chemistry Prof. K. L. Sebastian Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 4 Postulates Part 1 (Refer Slide Time: 00:59) So, I
glass Calculate the magnitude of the Young modulus for glass. State your answer to (a) in terms of SI fundamental units.
 Q1.The term ultrasound refers to vibrations in a material that occur at frequencies too high to be detected by a human ear. When ultrasound waves move through a solid, both longitudinal and transverse
Q1.The term ultrasound refers to vibrations in a material that occur at frequencies too high to be detected by a human ear. When ultrasound waves move through a solid, both longitudinal and transverse
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 2
 4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
Forces and Motion ENERGY FUNDAMENTALS LESSON PLAN 1.1
 ENERGY FUNDAMENTALS LESSON PLAN 1.1 Forces and Motion This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven states
ENERGY FUNDAMENTALS LESSON PLAN 1.1 Forces and Motion This lesson is designed for 3rd 5th grade students in a variety of school settings (public, private, STEM schools, and home schools) in the seven states
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) κ I ω = g L L g T = 2π mgh rot com I rot
 α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
spring mass equilibrium position +v max
 Lecture 20 Oscillations (Chapter 11) Review of Simple Harmonic Motion Parameters Graphical Representation of SHM Review of mass-spring pendulum periods Let s review Simple Harmonic Motion. Recall we used
Lecture 20 Oscillations (Chapter 11) Review of Simple Harmonic Motion Parameters Graphical Representation of SHM Review of mass-spring pendulum periods Let s review Simple Harmonic Motion. Recall we used
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
Energy Transformations IDS 101
 Energy Transformations IDS 101 It is difficult to design experiments that reveal what something is. As a result, scientists often define things in terms of what something does, what something did, or what
Energy Transformations IDS 101 It is difficult to design experiments that reveal what something is. As a result, scientists often define things in terms of what something does, what something did, or what
Transverse Traveling Waves
 Purpose: To observe and study the behavior of standing transverse waves and to determine the speed of standing and traveling waves. Equipment: Cenco String Vibrator Hooked Mass Set Pulley Table Clamp String
Purpose: To observe and study the behavior of standing transverse waves and to determine the speed of standing and traveling waves. Equipment: Cenco String Vibrator Hooked Mass Set Pulley Table Clamp String
PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION
 PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION Scientific Method: an organized set of investigative procedures which scientists follow to answer testable questions. Steps include: 1. Identify the problem or question.
PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION Scientific Method: an organized set of investigative procedures which scientists follow to answer testable questions. Steps include: 1. Identify the problem or question.
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Introduction. Pre-Lab Questions: Physics 1CL PERIODIC MOTION - PART II Fall 2009
 Introduction This is the second of two labs on simple harmonic motion (SHM). In the first lab you studied elastic forces and elastic energy, and you measured the net force on a pendulum bob held at an
Introduction This is the second of two labs on simple harmonic motion (SHM). In the first lab you studied elastic forces and elastic energy, and you measured the net force on a pendulum bob held at an
Physics GCSE (9-1) Energy
 Topic Student Checklist R A G Define a system as an object or group of objects and State examples of changes in the way energy is stored in a system Describe how all the energy changes involved in an energy
Topic Student Checklist R A G Define a system as an object or group of objects and State examples of changes in the way energy is stored in a system Describe how all the energy changes involved in an energy
Waves. Waves on a string
 Waves Waves on a string From Warmup Will understanding how waves travel through strings attached to walls--a situation I imagine we will rarely encounter--help us understand how waves travel through other
Waves Waves on a string From Warmup Will understanding how waves travel through strings attached to walls--a situation I imagine we will rarely encounter--help us understand how waves travel through other
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
Academic Physics Spring Semester Final Review
 Spring Semester Final Review The Final will be 70 multiple choice questions. This review is intended to be a review and not all inclusive. You must study your notes, labs, quizzes and tests in order to
Spring Semester Final Review The Final will be 70 multiple choice questions. This review is intended to be a review and not all inclusive. You must study your notes, labs, quizzes and tests in order to
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
B3 Relating Launch Speed and Range
 Key Question: What function relates the range and launch speed of a projectile? In this investigation, students identify the function relating projectile range to launch speed. In doing so, students are
Key Question: What function relates the range and launch speed of a projectile? In this investigation, students identify the function relating projectile range to launch speed. In doing so, students are
Middle School - Physical Science. SAS Standards. Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards SAS Standards Assessment Anchor Eligible Content Pure substances are made from a single type of atom or compound; each
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards SAS Standards Assessment Anchor Eligible Content Pure substances are made from a single type of atom or compound; each
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Physical Science B. Syllabus. Course Overview. Course Goals. General Skills
 Syllabus Physical Science B Course Overview Physical science is part physics and part chemistry. It s a branch of science that deals with matter, energy, forces, and motion. Energy is the capacity to do
Syllabus Physical Science B Course Overview Physical science is part physics and part chemistry. It s a branch of science that deals with matter, energy, forces, and motion. Energy is the capacity to do
Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab. Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed?
 Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Grade / 20 Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed? Hypothesis Starters: 1.
Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Grade / 20 Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed? Hypothesis Starters: 1.
