Lifting Surfaces. Lifting Surfaces
|
|
|
- Edward Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lifting Sufaces A lifting suface geneates a foce pependicula to the undistued flow, lift foce, much lage than the foce in the diection of the undistued flow, dag foce. L D Aeodynamic foce Dag Lifting Sufaces The typical example of a lifting suface is the wing of an aiplane. The lades of a popelle o an axial tuomachine o the aileons of acing cas ae also lifting sufaces
2 Lifting Sufaces The classic aeodynamic theoy of lifting sufaces divides the polem in two pats: - Two-dimensional of the section (aifoil) - Tip effects Finite wings Lifting Sufaces Nomenclatue - Span - S Pojected aea - Λ Aspect Ratio Λ S - Coss-section (Ai)foil
3 Aifoils Lifting Sufaces Nomenclatue - L Leading edge - T Tailing edge - c Chod Aifoils Lifting Sufaces Nomenclatue - Came line contains the centes of all cicles inscied in the aifoil - Maximum thickness, d, is the maximum diamete of the inscied cicles - Relative thickness is the atio etween the maximum thickness and the chod, d/c
4 Aifoils Lifting Sufaces Nomenclatue - Maximum came is the maximum distance etween the came line and the staight line that connects the edges of the came line (chod) V - Angle of attack, α, is the angle etween the diection of the undistued flow,, and the chod V Aifoils Lifting Sufaces Nomenclatue
5 Lifting Sufaces Nomenclatue Lift, L. Foce pependicula to the diection of the undistued flow U C C L l L ρ V L ρ V S c (3 D) ( D) V Lifting Sufaces Nomenclatue Dag, D. Foce in the diection of the undistued flow U C C D d D ρ V D ρ V S c (3 D) ( D) V
6 Aifoils Joukowski tansfom is a confomal mapping that tansfoms a cicula cylinde into an aifoil accoding to the following expession(s) z z + ( ) ( + ) + z z + z + Aifoils z + The aifoil is in plane z (tansfomed plane) The cicula cylinde is in plane (stating plane) The cylinde is a continuous line. The only way to geneate the tailing edge (cone) is to guaantee that the point that is tansfomed to the tailing edge () is a mapping singulaity
7 Mapping deivative Aifoils z + Mapping singulaities ae located at dz d dz 0 ± d Aifoils z + Mapping singulaities ae located at dz 0 ± d The tailing edge is otained fom the point in the plane. is the distance etween the intesection of the cylinde with the positive eal axis and the oigin of the coodinate system
8 Aifoils Kutta condition Velocity in aifoil plane (z) is otained fom dw dz dw d dz d Velocity in the cylinde plane Mapping deivative The point in the stating plane must e a stagnation point to avoid an infinite velocity at the tailing edge Aifoils Kutta condition The point in the stating plane must e a stagnation point to avoid an infinite velocity at the tailing edge dw dz odo de fuga dw d dz d 0 0 Kutta condition states that the velocity at the tailing edge must e finite. This condition defines the ciculation of the flow aound the aifoil
9 Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ - Complex potential fo a coodinate system with the eal axis aligned with the undistued flow and the cente of the cylinde at the oigin W a Γ V + i ln π ( ) Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ - Complex velocity fo a coodinate system with the eal axis aligned with the undistued flow and the cente of the cylinde at the oigin dw a Γ V V i d π
10 Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ - Stagnation points Γ z i 4π V ± a Γ 4πa V - It only makes sense to conside Γ < 4πa V Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ - The agument of the stagnation points, θ, is given y Γ sen( θ ) 4πaV Γ 4πaV sen ( θ ) θ θ Γ < 0
11 Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ - The agument of the stagnation points, θ, is given y Γ > 0 Γ sen( θ ) 4πaV Γ 4πaV sen ( θ ) θ θ Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ. Cylinde cente at the oigin
12 Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis
13 Aifoils Stating flow in plane is the flow aound a cicula cylinde of adius a with ciculation, Γ 4. Cylinde cente on the nd o 3 d quadants Aifoils. Cylinde cente at the oigin o 0 + i 0, a - Mapping of the geomety e iθ iθ z e + e z cos iθ ( θ ) The cicumfeence is tansfomed into a flat plate with a length of 4
14 Aifoils. Cylinde cente at the oigin η z + y ξ - x Aifoils. Cilinde cente at the oigin - Kutta condition must e a stagnation point in the cylinde plane () η Γ 4πa V sen( α ) Γ α ξ
15 Aifoils. Cylinde cente at the oigin α 0 º, Γ 0 Aifoils. Cylinde cente at the oigin α 0º, Γ 4πa V sen ( ) α
16 . Cylinde cente at the oigin - Lift coefficient, Cl Aifoils L ρ V Γ Cl ρ V ρ c V c Γ 4πaV sen, c 4, C ( α ) π sen ( ) α - Fo small angles of attack πα l C l Γ Γ V c a sen( α ) α Aifoils. Cylinde cente at the oigin - Velocity at the tailing edge dw d ( V ) odode fuga dz d - Solving the indetemination U V ( V ) odode fuga V cos( α ) V cos ( α )
17 . Cylinde cente at the oigin - Pessue distiution on the plate suface -C p Aifoils x/c Extadoso, α3 o Intadoso, α3 o Extadoso, α0 o Intadoso, α0 o C p p p ρ V Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis ( β ), cos( β ) 0 + i asen a o η β a ξ
18 Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis η z + y ξ - f β f f tan ( β ) c c x The cicumfeence is tansfomed into a cameed plate (ac of a cicle) with chod 4 Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis - Kutta condition must e a stagnation point in the cylinde plane () Γ 4π av sen( α + β ) η Γ β β α ξ
19 Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis f α 0º, β 0º 0, 088 c Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis f α 0º, β 0º 0, 088 c
20 Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis f α 0º, β 0º 0, 088 c Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis - Lift coefficient, C l L ρ V Γ Γ Γ Cl ρ V ρ c V c V c Γ 4πaV sen α + β, c 4, a cos β C l ( ) ( ) sen( α + β ) π cos( β )
21 . Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis - Lift coefficient, Aifoils C l - Fo small angles of attack (α) and small values of β sen α + β α + β, cos β ( ) ( ) C l ( α β ) π + - The cuvatue poduces an hoizontal tanslation of β in the line C l f ( α ). Fo the same angle of attack a cameed plate geneates a lage lift than a flat plate. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis - Lift coefficient, Cl Aifoils C l ( α β ) π + ( ) - A cameed plate poduces lift C l 0 fo an angle of attack of zeo degees, without exhiiting stagnation points and suction peak - The angle α β is the zeo lift angle
22 Aifoils. Cylinde cente on the imaginay axis - Pessue distiution on the plate suface -C p x/c Extadoso, α0 o Intadoso, α0 o Extadoso, α0 o Intadoso, α0 o Extadoso, α-0 o Intadoso, α-0 o C p p p ρ V Aifoils 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis ( + ) a o ε + i 0, ε η ε a ξ
23 Aifoils 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis η z + y d c 3 3 ε 4 ξ -- d x ε 4 + ε The cicumfeence is tansfomed into a symmetic aifoil with chod ε ε Aifoils 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis - Kutta condition must e a stagnation point in the cylinde plane () η Γ 4πa V sen( α ) Γ α ξ
24 Aifoils 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis d α 0º, ε 0,5 0, 95 c Aifoils 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis d α 0º, ε 0,5 0, 95 c
25 Aifoils 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis C l - Lift coefficient, C l L ρ V Γ ρ V ρ c V c Γ 4πaV Γ Γ V c ε sen( α ), c 4 +, ε + ε Cl π + sen( α ) + ε a + ε 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis - Lift coefficient, Cl Aifoils d C l π + 0,77 sen c - Fo small angles of attack ( ) α sen( α ) α d C l π + 0, 77 α c - The thickness inceases the slope of C l f ( ) α
26 Aifoils 3. Cylinde cente on the negative eal axis - Pessue distiution on the aifoil suface -C p x/c Extadoso, α0 o Intadoso, α0 o Extadoso, α0 o Intadoso, α0 o C p p p ρ V ε + i asen Aifoils 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant ( β ), ( + ε ) a cos( β ) o η β ε a ξ
27 Aifoils 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant η z + y d c 3 3 ε 4 ξ -- x ε f f 4 tan ( β ) + ε c c The cicumfeence is tansfomed into a asymmetic aifoil with chod ε ε Aifoils 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant - Kutta condition must e a stagnation point in the cylinde plane () Γ 4π av sen( α + β ) η Γ α β β ξ
28 Aifoils 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant f d α 0º, β 0º 0,088, ε 0,5 0, 95 c c Aifoils 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant f d α 0º, β 0º 0,088, ε 0,5 0, 95 c c
29 Aifoils 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant 95 0, 0,5, 0,088 0º 0º, c d c f ε β α 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant - Lift coefficient, l C ρ Γ Γ V L Aifoils ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) β β α ε ε π ε β ε ε β α π ρ ρ ρ cos sen cos, 4, sen Γ Γ Γ l l C a c av c V c V V c V L C
30 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant - Lift coefficient, Aifoils C l - Fo small angles of attack (α) and small values of β sen α + β α + β, cos β ( ) ( ) d C l π + 0, 77 + c ( α β ) - The aifoil includes came and thickness effects: - Hoizontal tanslation of β in the line C l f ( α ) - Incease of the slope of C l f α ( ) Aifoils 4. Cylinde cente on the nd quadant - Pessue distiution on the aifoil suface -C p x/c Extadoso, α0 o Intadoso, α0 o Extadoso, α0 o Intadoso, α0 o Extadoso, α-0 o Intadoso, α-0 o C p p p ρ V
31 Aifoils.5 Vaiation of C l with α.5 C l α (Gaus) Aifoils Pitching moment elative to the aifoil cente yη C C is the aifoil cente xξ iα [ i πρu ] QΓ M 0 ρ + R Μe π Fo a Joukowski aifoil Q0 M 0 R iα [ i πρu ] Μe
32 Aifoils Pitching moment elative to the aifoil cente Μ is the tem popotional to z - of the complex velocity at lage distances fom the aifoil Μ V e a V e iα iα so M c πρ V sen α ( ) Aifoils Pitching moment elative to the aifoil cente Fo small values of α ( ) α M c sen α 4 πρ V α Assuming that a Joukowski aifoil as a chod appoximately equal to c 4, the pitching moment aound the aifoil cente is given y C M c M c π α ρ V c
Lifting Surfaces. Lifting Surfaces
 Lifting Sufaces A lifting suface geneates a foce pependicula to the undistued flow, lift foce, much lage than the foce in the diection of the undistued flow, dag foce. L D Aeodynamic foce Dag Lifting Sufaces
Lifting Sufaces A lifting suface geneates a foce pependicula to the undistued flow, lift foce, much lage than the foce in the diection of the undistued flow, dag foce. L D Aeodynamic foce Dag Lifting Sufaces
Final Review of AerE 243 Class
 Final Review of AeE 4 Class Content of Aeodynamics I I Chapte : Review of Multivaiable Calculus Chapte : Review of Vectos Chapte : Review of Fluid Mechanics Chapte 4: Consevation Equations Chapte 5: Simplifications
Final Review of AeE 4 Class Content of Aeodynamics I I Chapte : Review of Multivaiable Calculus Chapte : Review of Vectos Chapte : Review of Fluid Mechanics Chapte 4: Consevation Equations Chapte 5: Simplifications
Applied Aerodynamics
 Applied Aeodynamics Def: Mach Numbe (M), M a atio of flow velocity to the speed of sound Compessibility Effects Def: eynolds Numbe (e), e ρ c µ atio of inetial foces to viscous foces iscous Effects If
Applied Aeodynamics Def: Mach Numbe (M), M a atio of flow velocity to the speed of sound Compessibility Effects Def: eynolds Numbe (e), e ρ c µ atio of inetial foces to viscous foces iscous Effects If
ME 425: Aerodynamics
 ME 5: Aeodynamics D ABM Toufique Hasan Pofesso Depatment of Mechanical Engineeing, BUET Lectue- 8 Apil 7 teachebuetacbd/toufiquehasan/ toufiquehasan@mebuetacbd ME5: Aeodynamics (Jan 7) Flow ove a stationay
ME 5: Aeodynamics D ABM Toufique Hasan Pofesso Depatment of Mechanical Engineeing, BUET Lectue- 8 Apil 7 teachebuetacbd/toufiquehasan/ toufiquehasan@mebuetacbd ME5: Aeodynamics (Jan 7) Flow ove a stationay
CBN 98-1 Developable constant perimeter surfaces: Application to the end design of a tape-wound quadrupole saddle coil
 CBN 98-1 Developale constant peimete sufaces: Application to the end design of a tape-wound quadupole saddle coil G. Dugan Laoatoy of Nuclea Studies Conell Univesity Ithaca, NY 14853 1. Intoduction Constant
CBN 98-1 Developale constant peimete sufaces: Application to the end design of a tape-wound quadupole saddle coil G. Dugan Laoatoy of Nuclea Studies Conell Univesity Ithaca, NY 14853 1. Intoduction Constant
Physics 111 Lecture 5 Circular Motion
 Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
11.2. Area of a Circle. Lesson Objective. Derive the formula for the area of a circle.
 11.2 Aea of a Cicle Lesson Objective Use fomulas to calculate the aeas of cicles, semicicles, and quadants. Lean Deive the fomula fo the aea of a cicle. A diamete divides a cicle of adius into 2 semicicles.
11.2 Aea of a Cicle Lesson Objective Use fomulas to calculate the aeas of cicles, semicicles, and quadants. Lean Deive the fomula fo the aea of a cicle. A diamete divides a cicle of adius into 2 semicicles.
Ch 30 - Sources of Magnetic Field! The Biot-Savart Law! = k m. r 2. Example 1! Example 2!
 Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2016
 Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
MENSURATION-III
 MENSURATION-III CIRCLE: A cicle is a geometical figue consisting of all those points in a plane which ae at a given distance fom a fixed point in the same plane. The fixed point is called the cente and
MENSURATION-III CIRCLE: A cicle is a geometical figue consisting of all those points in a plane which ae at a given distance fom a fixed point in the same plane. The fixed point is called the cente and
Physics 2B Chapter 22 Notes - Magnetic Field Spring 2018
 Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
 Page 1 of 6 Physics II Exam 1 155 points Name Discussion day/time Pat I. Questions 110. 8 points each. Multiple choice: Fo full cedit, cicle only the coect answe. Fo half cedit, cicle the coect answe and
Page 1 of 6 Physics II Exam 1 155 points Name Discussion day/time Pat I. Questions 110. 8 points each. Multiple choice: Fo full cedit, cicle only the coect answe. Fo half cedit, cicle the coect answe and
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Question Bank. Section A. is skew-hermitian matrix. is diagonalizable. (, ) , Evaluate (, ) 12 about = 1 and = Find, if
 Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
Subject: Mathematics-I Question Bank Section A T T. Find the value of fo which the matix A = T T has ank one. T T i. Is the matix A = i is skew-hemitian matix. i. alculate the invese of the matix = 5 7
A moving charged particle creates a magnetic field vector at every point in space except at its position.
 1 Pat 3: Magnetic Foce 3.1: Magnetic Foce & Field A. Chaged Paticles A moving chaged paticle ceates a magnetic field vecto at evey point in space ecept at its position. Symbol fo Magnetic Field mks units
1 Pat 3: Magnetic Foce 3.1: Magnetic Foce & Field A. Chaged Paticles A moving chaged paticle ceates a magnetic field vecto at evey point in space ecept at its position. Symbol fo Magnetic Field mks units
Faraday s Law (continued)
 Faaday s Law (continued) What causes cuent to flow in wie? Answe: an field in the wie. A changing magnetic flux not only causes an MF aound a loop but an induced electic field. Can wite Faaday s Law: ε
Faaday s Law (continued) What causes cuent to flow in wie? Answe: an field in the wie. A changing magnetic flux not only causes an MF aound a loop but an induced electic field. Can wite Faaday s Law: ε
transformation Earth V-curve (meridian) λ Conical projection. u,v curves on the datum surface projected as U,V curves on the projection surface
 . CONICAL PROJECTIONS In elementay texts on map pojections, the pojection sufaces ae often descibed as developable sufaces, such as the cylinde (cylindical pojections) and the cone (conical pojections),
. CONICAL PROJECTIONS In elementay texts on map pojections, the pojection sufaces ae often descibed as developable sufaces, such as the cylinde (cylindical pojections) and the cone (conical pojections),
Velocimetry Techniques and Instrumentation
 AeE 344 Lectue Notes Lectue # 05: elocimety Techniques and Instumentation D. Hui Hu Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Iowa State Univesity Ames, Iowa 500, U.S.A Methods to Measue Local Flow elocity - Mechanical
AeE 344 Lectue Notes Lectue # 05: elocimety Techniques and Instumentation D. Hui Hu Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Iowa State Univesity Ames, Iowa 500, U.S.A Methods to Measue Local Flow elocity - Mechanical
Phys-272 Lecture 17. Motional Electromotive Force (emf) Induced Electric Fields Displacement Currents Maxwell s Equations
 Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
Math 1105: Calculus I (Math/Sci majors) MWF 11am / 12pm, Campion 235 Written homework 3
 Math : alculus I Math/Sci majos MWF am / pm, ampion Witten homewok Review: p 94, p 977,8,9,6, 6: p 46, 6: p 4964b,c,69, 6: p 47,6 p 94, Evaluate the following it by identifying the integal that it epesents:
Math : alculus I Math/Sci majos MWF am / pm, ampion Witten homewok Review: p 94, p 977,8,9,6, 6: p 46, 6: p 4964b,c,69, 6: p 47,6 p 94, Evaluate the following it by identifying the integal that it epesents:
$ i. !((( dv vol. Physics 8.02 Quiz One Equations Fall q 1 q 2 r 2 C = 2 C! V 2 = Q 2 2C F = 4!" or. r ˆ = points from source q to observer
 Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
Physics 8.0 Quiz One Equations Fall 006 F = 1 4" o q 1 q = q q ˆ 3 4" o = E 4" o ˆ = points fom souce q to obseve 1 dq E = # ˆ 4" 0 V "## E "d A = Q inside closed suface o d A points fom inside to V =
 /6/4 5 Stuctue-Induced Sediment Scou ef: Eosion and Sedimentation, P.Y. Julien, 998 The Mechanics of Scou in the Maine Envionment, B.M. Sume and J. Fedsoe, Evaluating Scou at Bidges (HEC-8), E.. ichadson
/6/4 5 Stuctue-Induced Sediment Scou ef: Eosion and Sedimentation, P.Y. Julien, 998 The Mechanics of Scou in the Maine Envionment, B.M. Sume and J. Fedsoe, Evaluating Scou at Bidges (HEC-8), E.. ichadson
Balanced Flow. Natural Coordinates
 Balanced Flow The pessue and velocity distibutions in atmospheic systems ae elated by elatively simple, appoximate foce balances. We can gain a qualitative undestanding by consideing steady-state conditions,
Balanced Flow The pessue and velocity distibutions in atmospheic systems ae elated by elatively simple, appoximate foce balances. We can gain a qualitative undestanding by consideing steady-state conditions,
Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
 PH -C Fall 1 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents Lectue 14 Chapte 9 (Halliday/esnick/Walke, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapte 9 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents In this chapte we will exploe the elationship
PH -C Fall 1 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents Lectue 14 Chapte 9 (Halliday/esnick/Walke, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapte 9 Magnetic Fields Due to Cuents In this chapte we will exploe the elationship
Midterm Exam #2, Part A
 Physics 151 Mach 17, 2006 Midtem Exam #2, Pat A Roste No.: Scoe: Exam time limit: 50 minutes. You may use calculatos and both sides of ONE sheet of notes, handwitten only. Closed book; no collaboation.
Physics 151 Mach 17, 2006 Midtem Exam #2, Pat A Roste No.: Scoe: Exam time limit: 50 minutes. You may use calculatos and both sides of ONE sheet of notes, handwitten only. Closed book; no collaboation.
Hopefully Helpful Hints for Gauss s Law
 Hopefully Helpful Hints fo Gauss s Law As befoe, thee ae things you need to know about Gauss s Law. In no paticula ode, they ae: a.) In the context of Gauss s Law, at a diffeential level, the electic flux
Hopefully Helpful Hints fo Gauss s Law As befoe, thee ae things you need to know about Gauss s Law. In no paticula ode, they ae: a.) In the context of Gauss s Law, at a diffeential level, the electic flux
Exercise sheet 8 (Modeling large- and small-scale flows) 8.1 Volcanic ash from the Eyjafjallajökull
 Execise sheet 8 (Modeling lage- and small-scale flows) last edited June 18, 2018 These lectue notes ae based on textbooks by White [13], Çengel & al.[16], and Munson & al.[18]. Except othewise indicated,
Execise sheet 8 (Modeling lage- and small-scale flows) last edited June 18, 2018 These lectue notes ae based on textbooks by White [13], Çengel & al.[16], and Munson & al.[18]. Except othewise indicated,
r cos, and y r sin with the origin of coordinate system located at
 Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
Lectue 3-3 Kinematics of Rotation Duing ou peious lectues we hae consideed diffeent examples of motion in one and seeal dimensions. But in each case the moing object was consideed as a paticle-like object,
7.2.1 Basic relations for Torsion of Circular Members
 Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Translation and Rotation Kinematics
 Tanslation and Rotation Kinematics Oveview: Rotation and Tanslation of Rigid Body Thown Rigid Rod Tanslational Motion: the gavitational extenal foce acts on cente-of-mass F ext = dp sy s dt dv total cm
Tanslation and Rotation Kinematics Oveview: Rotation and Tanslation of Rigid Body Thown Rigid Rod Tanslational Motion: the gavitational extenal foce acts on cente-of-mass F ext = dp sy s dt dv total cm
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Dynamics of Rotational Motion Toque: the otational analogue of foce Toque = foce x moment am τ = l moment am = pependicula distance though which the foce acts a.k.a. leve am l l l l τ = l = sin φ = tan
Dynamics of Rotational Motion Toque: the otational analogue of foce Toque = foce x moment am τ = l moment am = pependicula distance though which the foce acts a.k.a. leve am l l l l τ = l = sin φ = tan
, and the curve BC is symmetrical. Find also the horizontal force in x-direction on one side of the body. h C
 Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Dynamics (Stömningsläa), 2013-05-31, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the textbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Dynamics (Stömningsläa), 2013-05-31, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the textbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
Exam 3, vers Physics Spring, 2003
 1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
Chapter 23: GAUSS LAW 343
 Chapte 23: GAUSS LAW 1 A total chage of 63 10 8 C is distibuted unifomly thoughout a 27-cm adius sphee The volume chage density is: A 37 10 7 C/m 3 B 69 10 6 C/m 3 C 69 10 6 C/m 2 D 25 10 4 C/m 3 76 10
Chapte 23: GAUSS LAW 1 A total chage of 63 10 8 C is distibuted unifomly thoughout a 27-cm adius sphee The volume chage density is: A 37 10 7 C/m 3 B 69 10 6 C/m 3 C 69 10 6 C/m 2 D 25 10 4 C/m 3 76 10
Collaborative ASSIGNMENT Assignment 3: Sources of magnetic fields Solution
 Electicity and Magnetism: PHY-04. 11 Novembe, 014 Collaboative ASSIGNMENT Assignment 3: Souces of magnetic fields Solution 1. a A conducto in the shape of a squae loop of edge length l m caies a cuent
Electicity and Magnetism: PHY-04. 11 Novembe, 014 Collaboative ASSIGNMENT Assignment 3: Souces of magnetic fields Solution 1. a A conducto in the shape of a squae loop of edge length l m caies a cuent
PHYS 1444 Lecture #5
 Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
Effect of drag on the performance for an efficient wind turbine blade design
 Available online at www.sciencediect.com Enegy Pocedia 18 (01 ) 404 415 Abstact Effect of dag on the pefomance fo an efficient wind tubine blade design D. Eng. Ali H. Almukhta Univesity of Technology Email-
Available online at www.sciencediect.com Enegy Pocedia 18 (01 ) 404 415 Abstact Effect of dag on the pefomance fo an efficient wind tubine blade design D. Eng. Ali H. Almukhta Univesity of Technology Email-
Three dimensional flow analysis in Axial Flow Compressors
 1 Thee dimensional flow analysis in Axial Flow Compessos 2 The ealie assumption on blade flow theoies that the flow inside the axial flow compesso annulus is two dimensional means that adial movement of
1 Thee dimensional flow analysis in Axial Flow Compessos 2 The ealie assumption on blade flow theoies that the flow inside the axial flow compesso annulus is two dimensional means that adial movement of
06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions )
 06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page ) A body A of mass M while falling vetically downwads unde gavity beaks into two pats, a body B of mass ( / ) M and a body C of mass ( / ) M. The cente of mass of bodies B and
06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page ) A body A of mass M while falling vetically downwads unde gavity beaks into two pats, a body B of mass ( / ) M and a body C of mass ( / ) M. The cente of mass of bodies B and
Chapter 22: Electric Fields. 22-1: What is physics? General physics II (22102) Dr. Iyad SAADEDDIN. 22-2: The Electric Field (E)
 Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Right-handed screw dislocation in an isotropic solid
 Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Dislocation Mechanics Elastic Popeties of Isolated Dislocations Ou study of dislocations to this point has focused on thei geomety and thei ole in accommodating plastic defomation though thei motion. We
Math 209 Assignment 9 Solutions
 Math 9 Assignment 9 olutions 1. Evaluate 4y + 1 d whee is the fist octant pat of y x cut out by x + y + z 1. olution We need a paametic epesentation of the suface. (x, z). Now detemine the nomal vecto:
Math 9 Assignment 9 olutions 1. Evaluate 4y + 1 d whee is the fist octant pat of y x cut out by x + y + z 1. olution We need a paametic epesentation of the suface. (x, z). Now detemine the nomal vecto:
TRANSILVANIA UNIVERSITY OF BRASOV MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ONLY FOR STUDENTS
 TNSILVNI UNIVSITY OF BSOV CHNICL NGINING FCULTY DPTNT OF CHNICL NGINING Couse 9 Cuved as 9.. Intoduction The eams with plane o spatial cuved longitudinal axes ae called cuved as. Thee ae consideed two
TNSILVNI UNIVSITY OF BSOV CHNICL NGINING FCULTY DPTNT OF CHNICL NGINING Couse 9 Cuved as 9.. Intoduction The eams with plane o spatial cuved longitudinal axes ae called cuved as. Thee ae consideed two
( ) Make-up Tests. From Last Time. Electric Field Flux. o The Electric Field Flux through a bit of area is
 Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
Superposition. Section 8.5.3
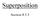 Supeposition Section 8.5.3 Simple Potential Flows Most complex potential (invicid, iotational) flows can be modeled using a combination of simple potential flows The simple flows used ae: Unifom flows
Supeposition Section 8.5.3 Simple Potential Flows Most complex potential (invicid, iotational) flows can be modeled using a combination of simple potential flows The simple flows used ae: Unifom flows
Electric Potential and Energy
 Electic Potential and Enegy Te polem: A solid spee of te adius R is omogeneously caged wit te cage Q and put inside an infinite ollow cylinde. Te cylinde inne and oute adii ae a and, R < a
Electic Potential and Enegy Te polem: A solid spee of te adius R is omogeneously caged wit te cage Q and put inside an infinite ollow cylinde. Te cylinde inne and oute adii ae a and, R < a
Position Error Estimation of a Laser Illuminated Object
 SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS OF THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NOVI PAZAR SER. A: APPL. MATH. INFORM. AND MECH. vol. 3, 1 (2011, 59-69 Position Eo Estimation of a Lase Illuminated Object Ž. P. Babaić Abstact: Position
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS OF THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NOVI PAZAR SER. A: APPL. MATH. INFORM. AND MECH. vol. 3, 1 (2011, 59-69 Position Eo Estimation of a Lase Illuminated Object Ž. P. Babaić Abstact: Position
LINEAR PLATE BENDING
 LINEAR PLATE BENDING 1 Linea plate bending A plate is a body of which the mateial is located in a small egion aound a suface in the thee-dimensional space. A special suface is the mid-plane. Measued fom
LINEAR PLATE BENDING 1 Linea plate bending A plate is a body of which the mateial is located in a small egion aound a suface in the thee-dimensional space. A special suface is the mid-plane. Measued fom
Math 259 Winter Handout 6: In-class Review for the Cumulative Final Exam
 Math 259 Winte 2009 Handout 6: In-class Review fo the Cumulative Final Exam The topics coveed by the cumulative final exam include the following: Paametic cuves. Finding fomulas fo paametic cuves. Dawing
Math 259 Winte 2009 Handout 6: In-class Review fo the Cumulative Final Exam The topics coveed by the cumulative final exam include the following: Paametic cuves. Finding fomulas fo paametic cuves. Dawing
Physics 506 Winter 2006 Homework Assignment #9 Solutions
 Physics 506 Winte 2006 Homewok Assignment #9 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.2, 12.9, 12.13, 12.14 12.2 a) Show fom Hamilton s pinciple that Lagangians that diffe only by a total time deivative
Physics 506 Winte 2006 Homewok Assignment #9 Solutions Textbook poblems: Ch. 12: 12.2, 12.9, 12.13, 12.14 12.2 a) Show fom Hamilton s pinciple that Lagangians that diffe only by a total time deivative
Describing Circular motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Descibing Cicula motion In ode to undestand cicula motion, we fist need to discuss how to subtact vectos. The easiest way to explain subtacting vectos is to descibe it as adding a
Unifom Cicula Motion Descibing Cicula motion In ode to undestand cicula motion, we fist need to discuss how to subtact vectos. The easiest way to explain subtacting vectos is to descibe it as adding a
- 5 - TEST 1R. This is the repeat version of TEST 1, which was held during Session.
 - 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
- 5 - TEST 1R This is the epeat vesion of TEST 1, which was held duing Session. This epeat test should be attempted by those students who missed Test 1, o who wish to impove thei mak in Test 1. IF YOU
Physics 101 Lecture 6 Circular Motion
 Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
Waves and Polarization in General
 Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Math 2263 Solutions for Spring 2003 Final Exam
 Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
Math 6 Solutions fo Sping Final Exam ) A staightfowad appoach to finding the tangent plane to a suface at a point ( x, y, z ) would be to expess the cuve as an explicit function z = f ( x, y ), calculate
Physics Courseware Electromagnetism
 Pysics Cousewae lectomagnetism lectic field Poblem.- a) Find te electic field at point P poduced by te wie sown in te figue. Conside tat te wie as a unifom linea cage distibution of λ.5µ C / m b) Find
Pysics Cousewae lectomagnetism lectic field Poblem.- a) Find te electic field at point P poduced by te wie sown in te figue. Conside tat te wie as a unifom linea cage distibution of λ.5µ C / m b) Find
[ ] [ ] 3.3 Given: turning corner radius, r ε = 0 mm lead angle, ψ r = 15 back rake angle, γ p = 5 side rake angle, γ f = 5
![[ ] [ ] 3.3 Given: turning corner radius, r ε = 0 mm lead angle, ψ r = 15 back rake angle, γ p = 5 side rake angle, γ f = 5 [ ] [ ] 3.3 Given: turning corner radius, r ε = 0 mm lead angle, ψ r = 15 back rake angle, γ p = 5 side rake angle, γ f = 5](/thumbs/82/86074714.jpg) 33 Given: tuning cone adius, ε = 0 mm lead angle, ψ = 5 back ake angle, γ p = 5 side ake angle, γ f = 5 initial wokpiece diamete, D w = 00 mm specific cutting and thust enegy models feed ate, f = 020 mm/ev
33 Given: tuning cone adius, ε = 0 mm lead angle, ψ = 5 back ake angle, γ p = 5 side ake angle, γ f = 5 initial wokpiece diamete, D w = 00 mm specific cutting and thust enegy models feed ate, f = 020 mm/ev
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
SPH4U Unit 6.3 Gravitational Potential Energy Page 1 of 9
 SPH4 nit 6.3 Gavitational Potential negy Page of Notes Physics ool box he gavitational potential enegy of a syste of two (spheical) asses is diectly popotional to the poduct of thei asses, and invesely
SPH4 nit 6.3 Gavitational Potential negy Page of Notes Physics ool box he gavitational potential enegy of a syste of two (spheical) asses is diectly popotional to the poduct of thei asses, and invesely
THE LAPLACE EQUATION. The Laplace (or potential) equation is the equation. u = 0. = 2 x 2. x y 2 in R 2
 THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
THE LAPLACE EQUATION The Laplace (o potential) equation is the equation whee is the Laplace opeato = 2 x 2 u = 0. in R = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 in R 2 = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 + 2 z 2 in R 3 The solutions u of the Laplace
21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
An Exact Solution of Navier Stokes Equation
 An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
An Exact Solution of Navie Stokes Equation A. Salih Depatment of Aeospace Engineeing Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiuvananthapuam, Keala, India. July 20 The pincipal difficulty in
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 5 Cental Foce Poblem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamilton s Pinciple Action integal is stationay fo the actual path Deived Lagange s Equations Used calculus
Section 26 The Laws of Rotational Motion
 Physics 24A Class Notes Section 26 The Laws of otational Motion What do objects do and why do they do it? They otate and we have established the quantities needed to descibe this motion. We now need to
Physics 24A Class Notes Section 26 The Laws of otational Motion What do objects do and why do they do it? They otate and we have established the quantities needed to descibe this motion. We now need to
Geometry of the homogeneous and isotropic spaces
 Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions
 Gaphs of Sine and Cosine Functions In pevious sections, we defined the tigonometic o cicula functions in tems of the movement of a point aound the cicumfeence of a unit cicle, o the angle fomed by the
Gaphs of Sine and Cosine Functions In pevious sections, we defined the tigonometic o cicula functions in tems of the movement of a point aound the cicumfeence of a unit cicle, o the angle fomed by the
Chapter 7-8 Rotational Motion
 Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Chapte 7-8 Rotational Motion What is a Rigid Body? Rotational Kinematics Angula Velocity ω and Acceleation α Unifom Rotational Motion: Kinematics Unifom Cicula Motion: Kinematics and Dynamics The Toque,
Between any two masses, there exists a mutual attractive force.
 YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
1 Dark Cloud Hanging over Twentieth Century Physics
 We ae Looking fo Moden Newton by Caol He, Bo He, and Jin He http://www.galaxyanatomy.com/ Wuhan FutueSpace Scientific Copoation Limited, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China E-mail: mathnob@yahoo.com Abstact Newton
We ae Looking fo Moden Newton by Caol He, Bo He, and Jin He http://www.galaxyanatomy.com/ Wuhan FutueSpace Scientific Copoation Limited, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China E-mail: mathnob@yahoo.com Abstact Newton
Phys 201A. Homework 5 Solutions
 Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
A 1. EN2210: Continuum Mechanics. Homework 7: Fluid Mechanics Solutions
 EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homewok 7: Fluid Mechanics Solutions School of Engineeing Bown Univesity 1. An ideal fluid with mass density ρ flows with velocity v 0 though a cylindical tube with cosssectional
EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homewok 7: Fluid Mechanics Solutions School of Engineeing Bown Univesity 1. An ideal fluid with mass density ρ flows with velocity v 0 though a cylindical tube with cosssectional
SMT 2013 Team Test Solutions February 2, 2013
 1 Let f 1 (n) be the numbe of divisos that n has, and define f k (n) = f 1 (f k 1 (n)) Compute the smallest intege k such that f k (013 013 ) = Answe: 4 Solution: We know that 013 013 = 3 013 11 013 61
1 Let f 1 (n) be the numbe of divisos that n has, and define f k (n) = f 1 (f k 1 (n)) Compute the smallest intege k such that f k (013 013 ) = Answe: 4 Solution: We know that 013 013 = 3 013 11 013 61
2 Governing Equations
 2 Govening Equations This chapte develops the govening equations of motion fo a homogeneous isotopic elastic solid, using the linea thee-dimensional theoy of elasticity in cylindical coodinates. At fist,
2 Govening Equations This chapte develops the govening equations of motion fo a homogeneous isotopic elastic solid, using the linea thee-dimensional theoy of elasticity in cylindical coodinates. At fist,
Dymore User s Manual Two- and three dimensional dynamic inflow models
 Dymoe Use s Manual Two- and thee dimensional dynamic inflow models Contents 1 Two-dimensional finite-state genealized dynamic wake theoy 1 Thee-dimensional finite-state genealized dynamic wake theoy 1
Dymoe Use s Manual Two- and thee dimensional dynamic inflow models Contents 1 Two-dimensional finite-state genealized dynamic wake theoy 1 Thee-dimensional finite-state genealized dynamic wake theoy 1
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
Physics 122, Fall October 2012
 hsics 1, Fall 1 3 Octobe 1 Toda in hsics 1: finding Foce between paallel cuents Eample calculations of fom the iot- Savat field law Ampèe s Law Eample calculations of fom Ampèe s law Unifom cuents in conductos?
hsics 1, Fall 1 3 Octobe 1 Toda in hsics 1: finding Foce between paallel cuents Eample calculations of fom the iot- Savat field law Ampèe s Law Eample calculations of fom Ampèe s law Unifom cuents in conductos?
ESCI 342 Atmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 3 Fundamental Forces II
 Reading: Matin, Section. ROTATING REFERENCE FRAMES ESCI 34 Atmospheic Dnamics I Lesson 3 Fundamental Foces II A efeence fame in which an object with zeo net foce on it does not acceleate is known as an
Reading: Matin, Section. ROTATING REFERENCE FRAMES ESCI 34 Atmospheic Dnamics I Lesson 3 Fundamental Foces II A efeence fame in which an object with zeo net foce on it does not acceleate is known as an
π(x, y) = u x + v y = V (x cos + y sin ) κ(x, y) = u y v x = V (y cos x sin ) v u x y
 F17 Lectue Notes 1. Unifom flow, Souces, Sinks, Doublets Reading: Andeson 3.9 3.12 Unifom Flow Definition A unifom flow consists of a velocit field whee V φ = uî + vθˆ is a constant. In 2-D, this velocit
F17 Lectue Notes 1. Unifom flow, Souces, Sinks, Doublets Reading: Andeson 3.9 3.12 Unifom Flow Definition A unifom flow consists of a velocit field whee V φ = uî + vθˆ is a constant. In 2-D, this velocit
The Law of Biot-Savart & RHR P θ
 The Law of iot-savat & RHR P R dx x Jean-aptiste iot élix Savat Phys 122 Lectue 19 G. Rybka Recall: Potential Enegy of Dipole Wok equied to otate a cuentcaying loop in a magnetic field Potential enegy
The Law of iot-savat & RHR P R dx x Jean-aptiste iot élix Savat Phys 122 Lectue 19 G. Rybka Recall: Potential Enegy of Dipole Wok equied to otate a cuentcaying loop in a magnetic field Potential enegy
Centripetal Force. Lecture 11. Chapter 8. Course website:
 Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Centipetal Foce Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylov Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics Today we ae going to discuss:
Lectue 11 Chapte 8 Centipetal Foce Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi PHYS.1410 Lectue 11 Danylov Depatment of Physics and Applied Physics Today we ae going to discuss:
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Have you eve idden on the amusement pak ide shown below? As it spins you feel as though you ae being pessed tightly against the wall. The ide then begins to tilt but you emain glued
Unifom Cicula Motion Have you eve idden on the amusement pak ide shown below? As it spins you feel as though you ae being pessed tightly against the wall. The ide then begins to tilt but you emain glued
Supplementary Figure 1. Circular parallel lamellae grain size as a function of annealing time at 250 C. Error bars represent the 2σ uncertainty in
 Supplementay Figue 1. Cicula paallel lamellae gain size as a function of annealing time at 50 C. Eo bas epesent the σ uncetainty in the measued adii based on image pixilation and analysis uncetainty contibutions
Supplementay Figue 1. Cicula paallel lamellae gain size as a function of annealing time at 50 C. Eo bas epesent the σ uncetainty in the measued adii based on image pixilation and analysis uncetainty contibutions
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Problem Solutions
 Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
Homework # 3 Solution Key
 PHYSICS 631: Geneal Relativity Homewok # 3 Solution Key 1. You e on you hono not to do this one by hand. I ealize you can use a compute o simply look it up. Please don t. In a flat space, the metic in
PHYSICS 631: Geneal Relativity Homewok # 3 Solution Key 1. You e on you hono not to do this one by hand. I ealize you can use a compute o simply look it up. Please don t. In a flat space, the metic in
Circular motion. Objectives. Physics terms. Assessment. Equations 5/22/14. Describe the accelerated motion of objects moving in circles.
 Cicula motion Objectives Descibe the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles. Use equations to analyze the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles.. Descibe in you own wods what this equation
Cicula motion Objectives Descibe the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles. Use equations to analyze the acceleated motion of objects moving in cicles.. Descibe in you own wods what this equation
MAGNETIC FIELD AROUND TWO SEPARATED MAGNETIZING COILS
 The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
Math 451: Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometry MWF 3pm, Gasson 204 Homework 9 Solutions
 Math 451: Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geomety MWF 3pm, Gasson 04 Homewok 9 Solutions Execises fom Chapte 3: 3.3, 3.8, 3.15, 3.19, 3.0, 5.11, 5.1, 5.13 Execise 3.3. Suppose that C and C ae two cicles with
Math 451: Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geomety MWF 3pm, Gasson 04 Homewok 9 Solutions Execises fom Chapte 3: 3.3, 3.8, 3.15, 3.19, 3.0, 5.11, 5.1, 5.13 Execise 3.3. Suppose that C and C ae two cicles with
HW Solutions # MIT - Prof. Please study example 12.5 "from the earth to the moon". 2GmA v esc
 HW Solutions # 11-8.01 MIT - Pof. Kowalski Univesal Gavity. 1) 12.23 Escaping Fom Asteoid Please study example 12.5 "fom the eath to the moon". a) The escape velocity deived in the example (fom enegy consevation)
HW Solutions # 11-8.01 MIT - Pof. Kowalski Univesal Gavity. 1) 12.23 Escaping Fom Asteoid Please study example 12.5 "fom the eath to the moon". a) The escape velocity deived in the example (fom enegy consevation)
BENDING OF BEAM. Compressed layer. Elongated. layer. Un-strained. layer. NA= Neutral Axis. Compression. Unchanged. Elongation. Two Dimensional View
 BNDING OF BA Compessed laye N Compession longation Un-stained laye Unchanged longated laye NA Neutal Axis Two Dimensional View A When a beam is loaded unde pue moment, it can be shown that the beam will
BNDING OF BA Compessed laye N Compession longation Un-stained laye Unchanged longated laye NA Neutal Axis Two Dimensional View A When a beam is loaded unde pue moment, it can be shown that the beam will
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Spring 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any referenced equations are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS 0B - HW #7 Sping 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any efeenced euations ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased. Poblem 0.3 fom Giffiths A point chage,, moves in a loop of adius a. At time t 0
PHYS 0B - HW #7 Sping 2004, Solutions by David Pace Any efeenced euations ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased. Poblem 0.3 fom Giffiths A point chage,, moves in a loop of adius a. At time t 0
3-Axis Vector Magnet: Construction and Characterisation of Split Coils at RT. Semester Project Petar Jurcevic
 3-Axis Vecto Magnet: Constuction and Chaacteisation of Split Coils at RT Semeste Poject Peta Jucevic Outline Field Calculation and Simulation Constuction Details Field Calculations Chaacteization at RT
3-Axis Vecto Magnet: Constuction and Chaacteisation of Split Coils at RT Semeste Poject Peta Jucevic Outline Field Calculation and Simulation Constuction Details Field Calculations Chaacteization at RT
2 E. on each of these two surfaces. r r r r. Q E E ε. 2 2 Qencl encl right left 0
 Ch : 4, 9,, 9,,, 4, 9,, 4, 8 4 (a) Fom the diagam in the textbook, we see that the flux outwad though the hemispheical suface is the same as the flux inwad though the cicula suface base of the hemisphee
Ch : 4, 9,, 9,,, 4, 9,, 4, 8 4 (a) Fom the diagam in the textbook, we see that the flux outwad though the hemispheical suface is the same as the flux inwad though the cicula suface base of the hemisphee
Math Notes on Kepler s first law 1. r(t) kp(t)
 Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
Math 7 - Notes on Keple s fist law Planetay motion and Keple s Laws We conside the motion of a single planet about the sun; fo simplicity, we assign coodinates in R 3 so that the position of the sun is
(r) = 1. Example: Electric Potential Energy. Summary. Potential due to a Group of Point Charges 9/10/12 1 R V(r) + + V(r) kq. Chapter 23.
 Eample: Electic Potential Enegy What is the change in electical potential enegy of a eleased electon in the atmosphee when the electostatic foce fom the nea Eath s electic field (diected downwad) causes
Eample: Electic Potential Enegy What is the change in electical potential enegy of a eleased electon in the atmosphee when the electostatic foce fom the nea Eath s electic field (diected downwad) causes
Radial Inflow Experiment:GFD III
 Radial Inflow Expeiment:GFD III John Mashall Febuay 6, 003 Abstact We otate a cylinde about its vetical axis: the cylinde has a cicula dain hole in the cente of its bottom. Wate entes at a constant ate
Radial Inflow Expeiment:GFD III John Mashall Febuay 6, 003 Abstact We otate a cylinde about its vetical axis: the cylinde has a cicula dain hole in the cente of its bottom. Wate entes at a constant ate
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION
 I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
I. CONSTRUCTION OF THE GREEN S FUNCTION The Helmohltz equation in 4 dimensions is 4 + k G 4 x, x = δ 4 x x. In this equation, G is the Geen s function and 4 efes to the dimensionality. In the vey end,
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Cross section dependence on ski pole sti ness
 Coss section deendence on ski ole sti ness Johan Bystöm and Leonid Kuzmin Abstact Ski equiment oduce SWIX has ecently esented a new ai of ski oles, called SWIX Tiac, which di es fom conventional (ound)
Coss section deendence on ski ole sti ness Johan Bystöm and Leonid Kuzmin Abstact Ski equiment oduce SWIX has ecently esented a new ai of ski oles, called SWIX Tiac, which di es fom conventional (ound)
