PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture #15 Wednesday, July 8, 2015
|
|
|
- Jeffery Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYS 1441 Secton 001 Lecture #15 Wednesday, July 8, 2015 Concept of the Center of Mass Center of Mass & Center of Gravty Fundamentals of the Rotatonal Moton Rotatonal Knematcs Equatons of Rotatonal Knematcs Relatonshp Between Angular and Lnear Quanttes 1
2 Announcements Readng Assgnments: CH7.9 and 7.10 Fnal exam 10:30am 12:30pm, Monday, July 13, n ths room Comprehensve exam, covers from CH1.1 what we fnsh ths Thursday, July 8, plus appendces A1 A8 Brng your calculator but DO NOT nput formula nto t! Your phones or portable computers are NOT allowed as a replacement! You can prepare a one 8.5x11.5 sheet (front and back) of handwrtten formulae and values of constants for the exam è no solutons, dervatons or defntons! No addtonal formulae or values of constants wll be provded! 2
3 Remnder: Specal Project #6 Make a lst of the rated power of all electrc and electronc devces at your home and compled them n a table. (2 ponts each for the frst 10 tems and 1 pont for each addtonal tem.) What s an tem? Smlar electrc devces count as one tem. All lght bulbs make up one tem, computers another, refrgerators, TVs, dryers (har and clothes), electrc cooktops, heaters, mcrowave ovens, electrc ovens, dshwashers, etc. All you have to do s to count add all wattages of the lght bulbs together as the power of the tem Estmate the cost of electrcty for each of the tems (takng nto account the number of hours you use the devce) on the table usng the electrcty cost per kwh of the power company that serves you and put them n a separate column n the above table for each of the tems. (2 ponts each for the frst 10 tems and 1 pont each addtonal tems). Clearly wrte down what the unt cost of the power s per kwh above the table. Estmate the the total amount of energy n Joules and the total electrcty cost per month and per year for your home. (5 ponts) Due: Begnnng of the class Monday, July 13 3
4 Specal Project Spread Sheet PHYS , Summer 15, Specal Project #6 Download ths spread sheet from URL: Just clck the fle wth the name: sp6-spreadsheet.xlsx Wrte down at the top your name and the charge per kwh by your electrcty company Item Names Lght Bulbs Heaters Fans Ar Condto ner Rated power (W) 30, 40, 60, 100, etc Number of devces 40 Average usage: Number of Hours per day Power Consumpton (kwh) Daly Energy Usage (J) Energy cost ($) Power Consumpton (kwh) Monthly Energy Usage (J) Energy cost ($) Power Consumpton (kwh) Yearly Energy Usage (J) Energy cost ($) Frdgers, Freezers Comput ers Game consoles Total
5 Center of Mass We ve been solvng physcal problems treatng objects as szeless ponts wth masses, but n realstc stuatons objects have shapes wth masses dstrbuted throughout the body. Center of mass of a system s the average poston of the system s mass and represents the moton of the system as f all the mass s on that pont. What does above statement tell you concernng the forces beng exerted on the system? The total external force exerted on the system of total mass M causes the center of mass to move at an acceleraton gven by a F / M as f the entre mass of the system s on the center of mass. Consder a massless rod wth two balls attached at ether end. m 1 m 2 The poston of the center of mass of ths system s x 1 x 2 the mass averaged poston of the system x CM mx 1 1+ mx 2 2 xcm CM s closer to the m1+ m2 heaver object 5
6 Moton of a Dver and the Center of Mass Dver performs a smple dve. The moton of the center of mass follows a parabola snce t s a projectle moton. Dver performs a complcated dve. The moton of the center of mass stll follows the same parabola snce t stll s a projectle moton. The moton of the center of mass of the dver s always the same. 6
7 Ex Center of Mass Thee people of roughly equvalent mass M on a lghtweght (ar-flled) banana boat st along the x axs at postons x 1 1.0m, x 2 5.0m, and x 3 6.0m. Fnd the poston of CM. CM M M M M M + M + M 3M x Usng the formula for CM m x m 7 4.0( m)
8 y2 m 1 (0,2) Example for Center of Mass n 2-D A system conssts of three partcles as shown n the fgure. Fnd the poston of the center of mass of ths system. r CM x CM y CM (x CM,y CM ) (1,0) m 2 x1 m x m m y m (2,0) m 3 x2 m1x 1 + m2x2 + m3x m + m + m 1 m1 y1 + m2 y2 + m3 y m + m + m Usng the formula for CM for each poston vector component x One obtans 3 3 m m + m 3 1 m CM m3 + m r CM 3 2m1 + m + m 2 3 m x m x CM If y CM + y CM j m1 2kg; m2 m3 1kg r CM j j 4 m y m ( m + 2m ) + 2m j m 1 + m 2 + m 3 8
9 Velocty of the Center of Mass Δ x cm v cm Δ mδ x + m Δx m + m x cm Δt 1 2 m1δx1 Δ t+ m2δx2 Δ t m + m 1 2 mv m + mv + m In an solated system, the total lnear momentum does not change, therefore the velocty of the center of mass does not change. 9
10 Another Look at the Ice Skater Problem Startng from rest, two skaters push off aganst each other on ce where frcton s neglgble. One s a 54-kg woman and one s a 88-kg man. The woman moves away wth a velocty of +2.5 m/s. What are the man s velocty and that of the CM? v 10 0 v cm0 m s mv m + mv + m v m s v1 f + 2.5m s v2 f 1.5m s mv 1 1f + mv 2 2 f v cmf m1+ m ( 2.5) + 88 ( 1.5) ms
11 Center of Mass and Center of Gravty The center of mass of any symmetrc object les on the axs of symmetry and on any plane of symmetry, f the object s mass s evenly dstrbuted throughout the body. How do you thnk you can determne the CM of the objects that are not symmetrc? Center of Gravty Δm g Δm F g CM Axs of One can use gravty to locate CM. symmetry 1. Hang the object by one pont and draw a vertcal lne followng a plum-bob. 2. Hang the object by another pont and do the same. 3. The pont where the two lnes meet s the CM. Snce a rgd object can be consdered as a collecton of small masses, one can see the total gravtatonal force exerted on the object as What does ths equaton tell you? F Δm g M g The net effect of these small gravtatonal forces s equvalent to a sngle force actng on a pont (Center of Gravty) wth mass M. The CoG s the pont n an object as f all the gravtatonal force s actng on! 11
12 Rotatonal Moton and Angular Dsplacement In the smplest knd of rotaton, a pont on a rgd object move on crcular paths around an axs of rotaton. The angle swept out by the lne passng through any pont on the body and ntersectng the axs of rotaton perpendcularly s called the angular dsplacement. Δ θ θ θ o It s a vector!! So there must be a drecton How do we defne drectons? +:f counter-clockwse -:f clockwse The drecton vector ponts gets determned based on the rght-hand rule. These are just conventons!! 12
13 SI Unt of the Angular Dsplacement θ (n radans) Arc length Radus s r θ 2π r r For one full revoluton: Snce the crcumference of a crcle s 2πr 2 π rad Dmenson? None 2 π rad 360 o One radan s an angle subtended by an arc of the same length as the radus! 13
14 Unt of the Angular Dsplacement How many degrees are n one radan? 1 radan s 1 rad 360 2πrad How radans s one degree? And one degrees s 2π 1 o 1 o 360 1rad 180 π π o o o o How many radans are n 10.5 revolutons? 10.5rev 10.5rev 2π rad rev o o rad 21π rad ( ) Very mportant: In solvng angular problems, all unts, degrees or revolutons, must be converted to radans. 14
15 Example 8-2 A partcular brd s eyes can just dstngush objects that subtend an angle no smaller than about 3x10-4 rad. (a) How many degrees s ths? (b) How small an object can the brd just dstngush when flyng at a heght of 100m? (a) One radan s 360 o /2π. Thus ( rad ) ( 360 o 2π rad ) rad l (b) Snce lrθ and for small angle arc length s approxmately the same as the chord length. rθ 100m rad m 3 cm 15 o
16 Ex. Adjacent Synchronous Satelltes Synchronous satelltes are put nto an orbt whose radus s m. If the angular separaton of the two satelltes s 2.00 degrees, fnd the arc length that separates them. What do we need to fnd out? The arc length!!! Convert degrees to radans s θ (n radans) Arc length Radus s r 2 π rad 2.00deg rad 360 deg rθ ( m)( rad) m (920 mles) 16
17 Ex. A Total Eclpse of the Sun The dameter of the sun s about 400 tmes greater than that of the moon. By concdence, the sun s also about 400 tmes farther from the earth than s the moon. For an observer on the earth, compare the angle subtended by the moon to the angle subtended by the sun and explan why ths result leads to a total solar eclpse. θ (n radans) Arc length Radus s r I can even cover the entre sun wth my thumb!! Why? Because the dstance (r) from my eyes to my thumb s far shorter than that to the sun. 17
18 Angular Dsplacement, Velocty, and Acceleraton Angular dsplacement s defned as Δθ How about the average angular velocty, the rate of change of angular dsplacement? Unt? rad/s θ θ f By the same token, the average angular acceleraton, rate of change of the angular velocty, s defned as Unt? rad/s 2 Dmenson? [T -1 ] Dmenson? [T -2 ] ω α θ f θ θ t ω t f f f f θ t ω t Δθ Δt Δω Δt When rotatng about a fxed axs, every partcle on a rgd object rotates through the same angle and has the same angular speed and angular acceleraton. 18
19 Ex. Gymnast on a Hgh Bar A gymnast on a hgh bar swngs through two revolutons n a tme of 1.90 s. Fnd the average angular velocty of the gymnast. What s the angular dsplacement? 2 π rad Δ θ 2.00 rev 1 rev 12.6 rad Why negatve? Because he s rotatng clockwse!! ω 12.6 rad 1.90 s 6.63rad s 19
20 Ex. A Jet Revvng Its Engnes As seen from the front of the engne, the fan blades are rotatng wth an angular velocty of -110 rad/s. As the plane takes off, the angular velocty of the blades reaches -330 rad/s n a tme of 14 s. Fnd the angular acceleraton, assumng t to be constant. α ω t f f ω t Δω Δt ( 330rad s) ( 110rad s) 2 16rad s 14 s 20
21 Rotatonal Knematcs The frst type of moton we have learned n lnear knematcs was under a constant acceleraton. We wll learn about the rotatonal moton under constant angular acceleraton (α), because these are the smplest motons n both cases. Just lke the case n lnear moton, one can obtan Angular velocty under constant angular acceleraton: Translatonal knematcs v vo + at Angular dsplacement under ω ω + αt f 0 θ θ + ω t + 1 constant angular acceleraton: f αt2 Translatonal knematcs x f x + v t + at 1 0 o 2 One can also obtan ω 2 Translatonal 2 2 v f f v + 2a( x x ) knematcs o f 2 ω ( ) 2α θ θ f 0 21
22 Rotatonal Knematcs Problem Solvng Strategy Vsualze the problem by drawng a pcture. Wrte down the values that are gven for any of the fve knematc varables and convert them to SI unts. Remember that the unt of the angle must be n radans!! Verfy that the nformaton contans values for at least three of the fve knematc varables. Select the approprate equaton. When the moton s dvded nto segments, remember that the fnal angular velocty of one segment s the ntal velocty for the next. Keep n mnd that there may be two possble answers to a knematcs problem. 22
23 Example for Rotatonal Knematcs A wheel rotates wth a constant angular acceleraton of rad/s 2. If the angular velocty of the wheel s rad/s at t 0, a) through what angle does the wheel rotate n 2.00s? Usng the angular dsplacement formula n the prevous slde, one gets θ f θ ωt+ 1 2 αt ( 2.00) rad π rev. 1.75rev. 23
24 Example for Rotatonal Knematcs cnt d What s the angular velocty at t2.00s? Usng the angular speed and acceleraton relatonshp ω f ω + αt Fnd the angle through whch the wheel rotates between t2.00 s and t3.00 s. Usng the angular knematc formula At t2.00s At t3.00s Angular dsplacement θ t rad / s θ t Δθ θ 3 θ rad rev. 1.72rev. θ ωt αt 2 f θ rad ( ) rad π 24
25 Ex. Blendng wth a Blender The blade s whrlng wth an angular velocty of +375 rad/s when the puree button s pushed n. When the blend button s pushed, the blade accelerates and reaches a greater angular velocty after the blade has rotated through an angular dsplacement of rad. The angular acceleraton has a constant value of rad/s 2. Fnd the fnal angular velocty of the blade. θ α ω ω o t +44.0rad +1740rad/s 2? +375rad/s Whch knematc eq? ω ± ω o 2 + 2αθ ω ω + 2αθ 2 2 o ± ( 375rad s) 2 + 2( 1740rad s 2 )( 44.0rad) ±542rad s Whch sgn? ω 542rad s + Why? Because the blade s acceleratng n counter-clockwse! 25
Spring 2002 Lecture #13
 44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
PHYS 1443 Section 002
 PHYS 443 Secton 00 Lecture #6 Wednesday, Nov. 5, 008 Dr. Jae Yu Collsons Elastc and Inelastc Collsons Two Dmensonal Collsons Center o ass Fundamentals o Rotatonal otons Wednesday, Nov. 5, 008 PHYS PHYS
PHYS 443 Secton 00 Lecture #6 Wednesday, Nov. 5, 008 Dr. Jae Yu Collsons Elastc and Inelastc Collsons Two Dmensonal Collsons Center o ass Fundamentals o Rotatonal otons Wednesday, Nov. 5, 008 PHYS PHYS
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Study Guide For Exam Two
 Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
CHAPTER 10 ROTATIONAL MOTION
 CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
10/23/2003 PHY Lecture 14R 1
 Announcements. Remember -- Tuesday, Oct. 8 th, 9:30 AM Second exam (coverng Chapters 9-4 of HRW) Brng the followng: a) equaton sheet b) Calculator c) Pencl d) Clear head e) Note: If you have kept up wth
Announcements. Remember -- Tuesday, Oct. 8 th, 9:30 AM Second exam (coverng Chapters 9-4 of HRW) Brng the followng: a) equaton sheet b) Calculator c) Pencl d) Clear head e) Note: If you have kept up wth
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #19
 PHYS 1441 Section 00 Lecture #19 Monday, April 8, 013 Fundamentals o the Rotational Motion Rotational Kinematics Equations o Rotational Kinematics Relationship Between Angular and Linear Quantities Rolling
PHYS 1441 Section 00 Lecture #19 Monday, April 8, 013 Fundamentals o the Rotational Motion Rotational Kinematics Equations o Rotational Kinematics Relationship Between Angular and Linear Quantities Rolling
PHYS 1443 Section 003 Lecture #17
 PHYS 144 Secton 00 ecture #17 Wednesda, Oct. 9, 00 1. Rollng oton of a Rgd od. Torque. oment of Inerta 4. Rotatonal Knetc Energ 5. Torque and Vector Products Remember the nd term eam (ch 6 11), onda, Nov.!
PHYS 144 Secton 00 ecture #17 Wednesda, Oct. 9, 00 1. Rollng oton of a Rgd od. Torque. oment of Inerta 4. Rotatonal Knetc Energ 5. Torque and Vector Products Remember the nd term eam (ch 6 11), onda, Nov.!
Chapter 11: Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
Chapter 11: ngular Momentum Statc Equlbrum In Chap. 4 we studed the equlbrum of pontobjects (mass m) wth the applcaton of Newton s aws F 0 F x y, 0 Therefore, no lnear (translatonal) acceleraton, a0 For
First Law: A body at rest remains at rest, a body in motion continues to move at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
 Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Part C Dynamics and Statics of Rigid Body. Chapter 5 Rotation of a Rigid Body About a Fixed Axis
 Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec during recitations. If you have taken the post test, don t come to recitation!
 Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Rotational Dynamics. Physics 1425 Lecture 19. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
Rotatonal Dynamcs Physcs 1425 Lecture 19 Mchael Fowler, UVa Rotatonal Dynamcs Newton s Frst Law: a rotatng body wll contnue to rotate at constant angular velocty as long as there s no torque actng on t.
So far: simple (planar) geometries
 Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Analyss Model: Nonsolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Rotatng Rgd Object Analyss Model: Isolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Partcle
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Analyss Model: Nonsolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Rotatng Rgd Object Analyss Model: Isolated System (Angular Momentum) Angular Momentum of a Partcle
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 7: Rigid Body Kinematics
 N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
N40: ynamcs and Vbratons Homewor 7: Rgd Body Knematcs School of ngneerng Brown Unversty 1. In the fgure below, bar AB rotates counterclocwse at 4 rad/s. What are the angular veloctes of bars BC and C?.
Physics 207: Lecture 27. Announcements
 Physcs 07: ecture 7 Announcements ake-up labs are ths week Fnal hwk assgned ths week, fnal quz next week Revew sesson on Thursday ay 9, :30 4:00pm, Here Today s Agenda Statcs recap Beam & Strngs» What
Physcs 07: ecture 7 Announcements ake-up labs are ths week Fnal hwk assgned ths week, fnal quz next week Revew sesson on Thursday ay 9, :30 4:00pm, Here Today s Agenda Statcs recap Beam & Strngs» What
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #15
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
Physics 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1
 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Unversty of Rochester, Lecture 14, Page 1 Physcs 141. Lecture 14. Course Informaton: Lab report # 3. Exam # 2. Mult-Partcle
A Tale of Friction Basic Rollercoaster Physics. Fahrenheit Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max height = 121 ft max speed = 58 mph
 A Tale o Frcton Basc Rollercoaster Physcs Fahrenhet Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max heght = 11 t max speed = 58 mph PLAY PLAY PLAY PLAY Rotatonal Movement Knematcs Smlar to how lnear velocty s dened, angular
A Tale o Frcton Basc Rollercoaster Physcs Fahrenhet Rollercoaster, Hershey, PA max heght = 11 t max speed = 58 mph PLAY PLAY PLAY PLAY Rotatonal Movement Knematcs Smlar to how lnear velocty s dened, angular
Moments of Inertia. and reminds us of the analogous equation for linear momentum p= mv, which is of the form. The kinetic energy of the body is.
 Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Moments of Inerta Suppose a body s movng on a crcular path wth constant speed Let s consder two quanttes: the body s angular momentum L about the center of the crcle, and ts knetc energy T How are these
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Lecture 6 Chapter 9 Physcs I 03.3.04 Lnear omentum. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.uml.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov03/physcssprng.html
Physics 207: Lecture 20. Today s Agenda Homework for Monday
 Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Week 11: Chapter 11. The Vector Product. The Vector Product Defined. The Vector Product and Torque. More About the Vector Product
 The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
ENGN 40 Dynamics and Vibrations Homework # 7 Due: Friday, April 15
 NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
Angular Momentum and Fixed Axis Rotation. 8.01t Nov 10, 2004
 Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Angular Momentum and Fxed Axs Rotaton 8.01t Nov 10, 2004 Dynamcs: Translatonal and Rotatonal Moton Translatonal Dynamcs Total Force Torque Angular Momentum about Dynamcs of Rotaton F ext Momentum of a
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 11
 Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Conservation of Angular Momentum = "Spin"
 Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Page 1 of 6 Conservaton of Angular Momentum = "Spn" We can assgn a drecton to the angular velocty: drecton of = drecton of axs + rght hand rule (wth rght hand, curl fngers n drecton of rotaton, thumb ponts
Section 8.3 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
 80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
11. Dynamics in Rotating Frames of Reference
 Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
Unversty of Rhode Island DgtalCommons@URI Classcal Dynamcs Physcs Course Materals 2015 11. Dynamcs n Rotatng Frames of Reference Gerhard Müller Unversty of Rhode Island, gmuller@ur.edu Creatve Commons
PHYS 1443 Section 004 Lecture #12 Thursday, Oct. 2, 2014
 PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
Chapter 10 Rotational motion
 Prof. Dr. I. Nasser Chapter0_I November 6, 07 Important Terms Chapter 0 Rotatonal moton Angular Dsplacement s, r n radans where s s the length of arc and r s the radus. Angular Velocty The rate at whch
Prof. Dr. I. Nasser Chapter0_I November 6, 07 Important Terms Chapter 0 Rotatonal moton Angular Dsplacement s, r n radans where s s the length of arc and r s the radus. Angular Velocty The rate at whch
τ rf = Iα I point = mr 2 L35 F 11/14/14 a*er lecture 1
 A mass s attached to a long, massless rod. The mass s close to one end of the rod. Is t easer to balance the rod on end wth the mass near the top or near the bottom? Hnt: Small α means sluggsh behavor
A mass s attached to a long, massless rod. The mass s close to one end of the rod. Is t easer to balance the rod on end wth the mass near the top or near the bottom? Hnt: Small α means sluggsh behavor
Kinematics in 2-Dimensions. Projectile Motion
 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Physics 53. Rotational Motion 3. Sir, I have found you an argument, but I am not obliged to find you an understanding.
 Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
ˆ (0.10 m) E ( N m /C ) 36 ˆj ( j C m)
 7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
Physics 181. Particle Systems
 Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Newtonian Mechanics
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Newtonan Mechancs Quck Revew of Newtonan Mechancs Basc Descrpton: -An dealzed pont partcle or a system of pont partcles n an nertal reference frame [Rgd bodes (ch. 5 later)]
Chapter 8. Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #16
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #16 Monday, Mar. 4, 008 Potental Energy Conservatve and Non-conservatve Forces Conservaton o Mechancal Energy Power Today s homework s homework #8, due 9pm, Monday, Mar. 31!!
Chapter 11 Torque and Angular Momentum
 Chapter Torque and Angular Momentum I. Torque II. Angular momentum - Defnton III. Newton s second law n angular form IV. Angular momentum - System of partcles - Rgd body - Conservaton I. Torque - Vector
Chapter Torque and Angular Momentum I. Torque II. Angular momentum - Defnton III. Newton s second law n angular form IV. Angular momentum - System of partcles - Rgd body - Conservaton I. Torque - Vector
Celestial Mechanics. Basic Orbits. Why circles? Tycho Brahe. PHY celestial-mechanics - J. Hedberg
 PHY 454 - celestal-mechancs - J. Hedberg - 207 Celestal Mechancs. Basc Orbts. Why crcles? 2. Tycho Brahe 3. Kepler 4. 3 laws of orbtng bodes 2. Newtonan Mechancs 3. Newton's Laws. Law of Gravtaton 2. The
PHY 454 - celestal-mechancs - J. Hedberg - 207 Celestal Mechancs. Basc Orbts. Why crcles? 2. Tycho Brahe 3. Kepler 4. 3 laws of orbtng bodes 2. Newtonan Mechancs 3. Newton's Laws. Law of Gravtaton 2. The
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 2
 PHYSICS 31 Revew problems for mdterm Topc 5: Energy and Work and Power Topc 6: Momentum and Collsons Topc 7: Oscllatons (sprng and pendulum) Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton The nd exam wll be Wednesday October
PHYSICS 31 Revew problems for mdterm Topc 5: Energy and Work and Power Topc 6: Momentum and Collsons Topc 7: Oscllatons (sprng and pendulum) Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton The nd exam wll be Wednesday October
MEASUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTIA
 1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
Spin-rotation coupling of the angularly accelerated rigid body
 Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
Spn-rotaton couplng of the angularly accelerated rgd body Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 E-mal: louaelzen@gmal.com November 1, 2017 All Rghts Reserved. Abstract Ths paper s
Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
EN40: Dynamcs and Vbratons Mdterm Examnaton Thursday March 5 009 Dvson of Engneerng rown Unversty NME: Isaac Newton General Instructons No collaboraton of any knd s permtted on ths examnaton. You may brng
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
AP Physics 1 & 2 Summer Assignment
 AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
AP Physcs 1 & 2 Summer Assgnment AP Physcs 1 requres an exceptonal profcency n algebra, trgonometry, and geometry. It was desgned by a select group of college professors and hgh school scence teachers
Physics 207 Lecture 6
 Physcs 207 Lecture 6 Agenda: Physcs 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 25 Chapter 4 Frames of reference Chapter 5 ewton s Law Mass Inerta s (contact and non-contact) Frcton (a external force that opposes moton) Free
Physcs 207 Lecture 6 Agenda: Physcs 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 25 Chapter 4 Frames of reference Chapter 5 ewton s Law Mass Inerta s (contact and non-contact) Frcton (a external force that opposes moton) Free
Physics 111 Final Exam, Fall 2013, Version A
 Physcs 111 Fnal Exam, Fall 013, Verson A Name (Prnt): 4 Dgt ID: Secton: Honors Code Pledge: For ethcal and farness reasons all students are pledged to comply wth the provsons of the NJIT Academc Honor
Physcs 111 Fnal Exam, Fall 013, Verson A Name (Prnt): 4 Dgt ID: Secton: Honors Code Pledge: For ethcal and farness reasons all students are pledged to comply wth the provsons of the NJIT Academc Honor
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 4: Work, Energy and Linear Momentum Due Friday March 1 st
 EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
Week 8: Chapter 9. Linear Momentum. Newton Law and Momentum. Linear Momentum, cont. Conservation of Linear Momentum. Conservation of Momentum, 2
 Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
Lnear omentum Week 8: Chapter 9 Lnear omentum and Collsons The lnear momentum of a partcle, or an object that can be modeled as a partcle, of mass m movng wth a velocty v s defned to be the product of
PHYSICS 231 Lecture 18: equilibrium & revision
 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 18: equlbrum & revson Remco Zegers Walk-n hour: Thursday 11:30-13:30 am Helproom 1 gravtaton Only f an object s near the surface of earth one can use: F gravty =mg wth g=9.81 m/s 2
PHYSICS 231 Lecture 18: equlbrum & revson Remco Zegers Walk-n hour: Thursday 11:30-13:30 am Helproom 1 gravtaton Only f an object s near the surface of earth one can use: F gravty =mg wth g=9.81 m/s 2
Section 8.1 Exercises
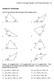 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Chapter 3. r r. Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Revisited
 Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
10/9/2003 PHY Lecture 11 1
 Announcements 1. Physc Colloquum today --The Physcs and Analyss of Non-nvasve Optcal Imagng. Today s lecture Bref revew of momentum & collsons Example HW problems Introducton to rotatons Defnton of angular
Announcements 1. Physc Colloquum today --The Physcs and Analyss of Non-nvasve Optcal Imagng. Today s lecture Bref revew of momentum & collsons Example HW problems Introducton to rotatons Defnton of angular
where v means the change in velocity, and t is the
 1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION SENIOR SECONDARY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES)
 PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 1 SESSION 1 (LEARNER NOTES) TOPIC 1: MECHANICS PROJECTILE MOTION Learner Note: Always draw a dagram of the stuaton and enter all the numercal alues onto your dagram. Remember to
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 NME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem n the space
NME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem n the space
Physics 114 Exam 3 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Mechanics Cycle 3 Chapter 9++ Chapter 9++
 Chapter 9++ More on Knetc Energy and Potental Energy BACK TO THE FUTURE I++ More Predctons wth Energy Conservaton Revst: Knetc energy for rotaton Potental energy M total g y CM for a body n constant gravty
Chapter 9++ More on Knetc Energy and Potental Energy BACK TO THE FUTURE I++ More Predctons wth Energy Conservaton Revst: Knetc energy for rotaton Potental energy M total g y CM for a body n constant gravty
Modeling of Dynamic Systems
 Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
Modelng of Dynamc Systems Ref: Control System Engneerng Norman Nse : Chapters & 3 Chapter objectves : Revew the Laplace transform Learn how to fnd a mathematcal model, called a transfer functon Learn how
I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
Work is the change in energy of a system (neglecting heat transfer). To examine what could
 Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Chapter 20 Rigid Body: Translation and Rotational Motion Kinematics for Fixed Axis Rotation
 Chapter 20 Rgd Body: Translaton and Rotatonal Moton Knematcs for Fxed Axs Rotaton 20.1 Introducton... 1 20.2 Constraned Moton: Translaton and Rotaton... 1 20.2.1 Rollng wthout slppng... 5 Example 20.1
Chapter 20 Rgd Body: Translaton and Rotatonal Moton Knematcs for Fxed Axs Rotaton 20.1 Introducton... 1 20.2 Constraned Moton: Translaton and Rotaton... 1 20.2.1 Rollng wthout slppng... 5 Example 20.1
Spring Force and Power
 Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
Physics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Solutions. Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Supplemental Instruction sessions next week
 Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutions Fall 2016 Solution:
 PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
Four Bar Linkages in Two Dimensions. A link has fixed length and is joined to other links and also possibly to a fixed point.
 Four bar lnkages 1 Four Bar Lnkages n Two Dmensons lnk has fed length and s oned to other lnks and also possbly to a fed pont. The relatve velocty of end B wth regard to s gven by V B = ω r y v B B = +y
Four bar lnkages 1 Four Bar Lnkages n Two Dmensons lnk has fed length and s oned to other lnks and also possbly to a fed pont. The relatve velocty of end B wth regard to s gven by V B = ω r y v B B = +y
PY2101 Classical Mechanics Dr. Síle Nic Chormaic, Room 215 D Kane Bldg
 PY2101 Classcal Mechancs Dr. Síle Nc Chormac, Room 215 D Kane Bldg s.ncchormac@ucc.e Lectures stll some ssues to resolve. Slots shared between PY2101 and PY2104. Hope to have t fnalsed by tomorrow. Mondays
PY2101 Classcal Mechancs Dr. Síle Nc Chormac, Room 215 D Kane Bldg s.ncchormac@ucc.e Lectures stll some ssues to resolve. Slots shared between PY2101 and PY2104. Hope to have t fnalsed by tomorrow. Mondays
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2011/2012 DYNAMICS ME247 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING ND MTHEMTICS SEMESTER EXMINTIONS 011/01 DYNMICS ME47 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ Tme allowed: THREE hours nswer: ny FOUR from SIX questons Each queston carres 5 marks Ths s a CLOSED-BOOK
s SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING ND MTHEMTICS SEMESTER EXMINTIONS 011/01 DYNMICS ME47 DR. N.D.D. MICHÉ Tme allowed: THREE hours nswer: ny FOUR from SIX questons Each queston carres 5 marks Ths s a CLOSED-BOOK
PHYS 1443 Section 002 Lecture #20
 PHYS 1443 Secton 002 Lecture #20 Dr. Jae Condtons for Equlbru & Mechancal Equlbru How to Solve Equlbru Probles? A ew Exaples of Mechancal Equlbru Elastc Propertes of Solds Densty and Specfc Gravty lud
PHYS 1443 Secton 002 Lecture #20 Dr. Jae Condtons for Equlbru & Mechancal Equlbru How to Solve Equlbru Probles? A ew Exaples of Mechancal Equlbru Elastc Propertes of Solds Densty and Specfc Gravty lud
An Algorithm to Solve the Inverse Kinematics Problem of a Robotic Manipulator Based on Rotation Vectors
 An Algorthm to Solve the Inverse Knematcs Problem of a Robotc Manpulator Based on Rotaton Vectors Mohamad Z. Al-az*, Mazn Z. Othman**, and Baker B. Al-Bahr* *AL-Nahran Unversty, Computer Eng. Dep., Baghdad,
An Algorthm to Solve the Inverse Knematcs Problem of a Robotc Manpulator Based on Rotaton Vectors Mohamad Z. Al-az*, Mazn Z. Othman**, and Baker B. Al-Bahr* *AL-Nahran Unversty, Computer Eng. Dep., Baghdad,
NEWTON S LAWS. These laws only apply when viewed from an inertial coordinate system (unaccelerated system).
 EWTO S LAWS Consder two partcles. 1 1. If 1 0 then 0 wth p 1 m1v. 1 1 2. 1.. 3. 11 These laws only apply when vewed from an nertal coordnate system (unaccelerated system). consder a collecton of partcles
EWTO S LAWS Consder two partcles. 1 1. If 1 0 then 0 wth p 1 m1v. 1 1 2. 1.. 3. 11 These laws only apply when vewed from an nertal coordnate system (unaccelerated system). consder a collecton of partcles
November 5, 2002 SE 180: Earthquake Engineering SE 180. Final Project
 SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
SE 8 Fnal Project Story Shear Frame u m Gven: u m L L m L L EI ω ω Solve for m Story Bendng Beam u u m L m L Gven: m L L EI ω ω Solve for m 3 3 Story Shear Frame u 3 m 3 Gven: L 3 m m L L L 3 EI ω ω ω
Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Exploring Calculus
 Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Explorng Calculus Part I Approxmatons and the Defnte Integral It was known n the 1600s before the calculus was developed that the area of an rregularly shaped regon could be approxmated
Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Explorng Calculus Part I Approxmatons and the Defnte Integral It was known n the 1600s before the calculus was developed that the area of an rregularly shaped regon could be approxmated
coordinates. Then, the position vectors are described by
 Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
Physics 2A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
10/24/2013. PHY 113 C General Physics I 11 AM 12:15 PM TR Olin 101. Plan for Lecture 17: Review of Chapters 9-13, 15-16
 0/4/03 PHY 3 C General Physcs I AM :5 PM T Oln 0 Plan or Lecture 7: evew o Chapters 9-3, 5-6. Comment on exam and advce or preparaton. evew 3. Example problems 0/4/03 PHY 3 C Fall 03 -- Lecture 7 0/4/03
0/4/03 PHY 3 C General Physcs I AM :5 PM T Oln 0 Plan or Lecture 7: evew o Chapters 9-3, 5-6. Comment on exam and advce or preparaton. evew 3. Example problems 0/4/03 PHY 3 C Fall 03 -- Lecture 7 0/4/03
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Equpotental Surfaces and Lnes Physcs for Scentsts & Engneers 2 Sprng Semester 2005 Lecture 9 January 25, 2005 Physcs for Scentsts&Engneers 2 1 When an electrc feld s present, the electrc potental has a
Equpotental Surfaces and Lnes Physcs for Scentsts & Engneers 2 Sprng Semester 2005 Lecture 9 January 25, 2005 Physcs for Scentsts&Engneers 2 1 When an electrc feld s present, the electrc potental has a
Lectures - Week 4 Matrix norms, Conditioning, Vector Spaces, Linear Independence, Spanning sets and Basis, Null space and Range of a Matrix
 Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
χ x B E (c) Figure 2.1.1: (a) a material particle in a body, (b) a place in space, (c) a configuration of the body
 Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
I have not received unauthorized aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Sprng 2013 Fnal Examnaton Please read and respond to the followng statement, I have not receved unauthorzed ad n the completon of ths exam. Agree Dsagree Sgnature INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
ME 270 Sprng 2013 Fnal Examnaton Please read and respond to the followng statement, I have not receved unauthorzed ad n the completon of ths exam. Agree Dsagree Sgnature INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
total If no external forces act, the total linear momentum of the system is conserved. This occurs in collisions and explosions.
 Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
How Differential Equations Arise. Newton s Second Law of Motion
 page 1 CHAPTER 1 Frst-Order Dfferental Equatons Among all of the mathematcal dscplnes the theory of dfferental equatons s the most mportant. It furnshes the explanaton of all those elementary manfestatons
page 1 CHAPTER 1 Frst-Order Dfferental Equatons Among all of the mathematcal dscplnes the theory of dfferental equatons s the most mportant. It furnshes the explanaton of all those elementary manfestatons
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
Physics 207 Lecture 13. Lecture 13
 Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
Physcs 07 Lecture 3 Goals: Lecture 3 Chapter 0 Understand the relatonshp between moton and energy Defne Potental Energy n a Hooke s Law sprng Develop and explot conservaton of energy prncple n problem
The classical spin-rotation coupling
 LOUAI H. ELZEIN 2018 All Rghts Reserved The classcal spn-rotaton couplng Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 louaelzen@gmal.com Abstract Ths paper s prepared to show that a rgd
LOUAI H. ELZEIN 2018 All Rghts Reserved The classcal spn-rotaton couplng Loua Hassan Elzen Basher Khartoum, Sudan. Postal code:11123 louaelzen@gmal.com Abstract Ths paper s prepared to show that a rgd
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Sprng 2017 Exam 1 NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name
ME 270 Sprng 2017 Exam 1 NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name
Physics 1202: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda
 Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Lecture 16. Chapter 11. Energy Dissipation Linear Momentum. Physics I. Department of Physics and Applied Physics
 Lecture 16 Chapter 11 Physcs I Energy Dsspaton Lnear Momentum Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Department o Physcs and Appled Physcs IN IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn
Lecture 16 Chapter 11 Physcs I Energy Dsspaton Lnear Momentum Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Department o Physcs and Appled Physcs IN IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn
A particle in a state of uniform motion remain in that state of motion unless acted upon by external force.
 The fundamental prncples of classcal mechancs were lad down by Galleo and Newton n the 16th and 17th centures. In 1686, Newton wrote the Prncpa where he gave us three laws of moton, one law of gravty,
The fundamental prncples of classcal mechancs were lad down by Galleo and Newton n the 16th and 17th centures. In 1686, Newton wrote the Prncpa where he gave us three laws of moton, one law of gravty,
Chapter 9. The Dot Product (Scalar Product) The Dot Product use (Scalar Product) The Dot Product (Scalar Product) The Cross Product.
 The Dot Product (Scalar Product) Chapter 9 Statcs and Torque The dot product of two vectors can be constructed by takng the component of one vector n the drecton of the other and multplyng t tmes the magntude
The Dot Product (Scalar Product) Chapter 9 Statcs and Torque The dot product of two vectors can be constructed by takng the component of one vector n the drecton of the other and multplyng t tmes the magntude
Indeterminate pin-jointed frames (trusses)
 Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
Indetermnate pn-jonted frames (trusses) Calculaton of member forces usng force method I. Statcal determnacy. The degree of freedom of any truss can be derved as: w= k d a =, where k s the number of all
Iterative General Dynamic Model for Serial-Link Manipulators
 EEL6667: Knematcs, Dynamcs and Control of Robot Manpulators 1. Introducton Iteratve General Dynamc Model for Seral-Lnk Manpulators In ths set of notes, we are gong to develop a method for computng a general
EEL6667: Knematcs, Dynamcs and Control of Robot Manpulators 1. Introducton Iteratve General Dynamc Model for Seral-Lnk Manpulators In ths set of notes, we are gong to develop a method for computng a general
Statistics MINITAB - Lab 2
 Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
