What is EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS?
|
|
|
- Dulcie King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Latvia Prof.emer., Dr.phys. A N D R I S B R O K S Mobile phone: andris.broks@lu.lv Blog: What is EXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS? ******************************************** 1. Let us start with general structure of scientific research GENERAL STRUCTURE OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH PROCESS Fundamental Science RESEARCH THEORY Applied Science RESEARCH Discription: comprehension, causality Conceptualization: understanding, factology Observation: measurements COGNITION of phenomena Consideration Use of phenomena BEHAVIOR Project development Preparation of project realization Realization of project N e e d s PRACTICE S a t i s f a c t i o n of n e e d s Full scale research process includes both fundamental and applied research activities as creative gaining of new life experience for life to satisfy definite needs of the person or society. Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
2 Experimental fundamental research of phenomenon Comprehension Conceptualization Observation of phenomenon Description (modelling) Data processing Measurement of physical quantity 2. What does it mean measurement of physical quantity? MEASUREMENT General structure of measurement Phenomenon INSTRUMENT Researcher Interaction Information Outer medium - Enviroment MATHEMETICAL PRESENTATION of the results of measurements Numbers in Mathematics and Physics All numbers in Physics are approximate numbers and must be accompanied with corresponding units Geometric presentation of numbers: p o i n t s in Mathematics and i n t e r v a l s in Physics SIGNIFICANT FIGURES Approximate number as a result of measurement in physics must contain only significant figures. Single direct measurement made with instrument on a scale with smallest division 1 should be presented as 36 units what means interval (36,0 +/- 0,5) units. Figures after the decimal point cannot be justified. Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
3 Measurements of distance and time Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
4 Measurement of temperature Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
5 Measurement of electric quantities Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
6 SINGLE and REPEATED measurements ( a, a i ) INVESTIGATION OF RELATIONSHIPS ( changes and interrelations of properties statics, kinetics, causal relationships ) Kinetics: a(t) = a 0 (t 0 ) + Δa (Δt), n Δa (Δt) = a(t) - a 0 (t 0 ) = Σ Δa i (Δt i ) i=1 a (h, g, f) MATHEMETICAL PRESENTATION of the experimental data ( tables, graphs ) a, unit t, unit a (t), unit a 0 t 0 a n a 1 t 1 a 2 t 2 a 1 a(t) = = a o (t o ) + b (t-t o ) a 3 t a 0 a i t i.... t 0 t 1 t n t, unit a n t n Analitical Table Graph functions MATHEMATICAL MODELLING of observed relationships Mathematical Physics Fund.research of physical phenomena Experimental Physics Applied research of physical phenomena Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
7 3. Precision (accuracy, uncertainty) of measurement result truth and real values of measured properties/quantities, systematic, random and total error of measured quantities Error characteristic of measured quantity precision Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
8 Treatment of random errors Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
9 Generally the contribution of an error can be neglected if the error is less than about 1/10 of the dominant or total error. If systematic error is approximately the same value as random error, systematic error θ and maximum random error ε must be presented. Maximum random error ε can be calculated using Student s coefficient t n,γ, where n is number of repeated measurements and γ = 0,95 ε = t 0.95, n [ (d a - d i ) 2 ] / [n (n-1)] n t 0.95, n 4,303 3,182 2,776 2,571 2,447 2,365 2,306 Total error of the result of measurement means account of both - systematic and random errors Direct measurement of property a Basic types of errors Absolute error Relative error Systematic error Δa s, unit δa s = (Δa s /a) 100 % Random error Δa r, unit δa r = (Δa s /a) 100 % TOTAL error Δa = (Δa s ) 2 + (Δa r ) 2, unit δa = (Δa/a) 100 % Result of the measurement of definite physical quantity - property a is presented as approximate number : a (units) alone or with its total absolute error (a +/- Δa) units and its relative (fractional) error δa = (Δa/a) 100 % If there is approximate number a (unit) alone [a = 253 units], it contains only significant figures what depend on total precision (total error) of definite measurement. If total error also is presented, total error contains not more than two significant numbers [ a= (253, 12 +/- 0,25 ) units, where 0,25 is calculated total absolute error of calculated quantity 253,12 ]. DIRECT and INDIRECT measurements Measurements DIRECT INDIRECT SINGLE a a (b, c, d.) REPEATED a i (t i ) = const a i (t i ) const a (b, c, d.) = const a i (t i ) = a i (b, c i (t i.) const Investigation of relationships Precision of indirect measurement depends on corresponding precision of direct measurements - every direct measurement comes with its total error what is producing corresponding uncertainty of indirect measurement. Determination of its total precision can be quite difficult task and special methods are used. The simplest method is corresponding adding of total relative errors of particular direct measurements. Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
10 Determination of density [ case study of solid state material what is formed as cylindrical body ] (g/cm 3 ) =? M e a s u r e m e n t p r o c e d u r e c o n s i s t s : 1) of direct measurement of diameter d (cm), height h (cm) and mass M (g) of given body what include also determination of the precision of measured quantities; 2) following final indirect measurement - calculation of density (g/cm 3 ) what again includes determination of the precision of provided indirect measurement. 1. Direct measurement of diameter d (cm) and determination of the total error No of measurement 1 (first) d 1 = 2 (second) 3 d 3 = 4 5 d 5 = 6. ( etc.) Measured values of diameter d i (cm) d av - d i (d av - d i ) 2 Totally : n measurements Calculated average value d av =... (d av - d i ) 2 = =.. Random absolute error d r = t 0.95, n * [ (d av - d i ) 2 ] / [n (n-1)] =... (cm) n - total number of measurements; = 0,95 t, n - Student s coefficient Systematic absolute error d s =. (cm) T o t a l absolute error d = d s 2 + d r 2 = (cm) Approximate number containing two significant figures! T o t a l relative error d = ( d / d av ) 100% =.. % R e s u l t : (d av +/- d ) cm, d %. Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
11 2. Direct measurement of height h (cm) and determination of the total error No of measurement 1 h 1 = 2 3 h 3 = 4 5 h 5 =. ( etc.) Totally : n measurements Measured values of height h i (cm) Calculated average value h av = h av - h i (h av - h i ) 2 (h av - h i ) 2 = = Random absolute error h r = t 0.95, n [ (h av - h i ) 2 ] / [n (n-1)] = (cm) Systematic absolute error h s =.. (cm) Total absolute error h = h s 2 + h r 2 = (cm) Total relative error h = ( h / h av ) 100% = % R e s u l t : (h av +/- h ) cm, h =. %. 3. Direct measurement of mass M (g) and determination of the total error Using digital mass meter we got M = (g) Systematic absolute error of this measurement is characterized by a half of instrument s scale smallest division: M s = (g) There was no random error effect observed when repeating mass measurements so total error of direct measurement contains only systematic error M = M s R e s u l t : ( M +/- M ) g, M= ( M/M) 100 % Final i n d i r e c t measurement - calculation of density (g/cm 3 ) and determination of the precision of corresponding indirect measurement. = 4 M / ( d 2 h) = ( g/cm 3 ) Total relative error (% ) = M (% ) + 2 d (% ) + h (% ) = (%) = (decimal fraction) Total absolute error = = g/cm 3 F I N A L R E S U LT : ( +/- ) g/cm 3, ( % ).... Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
12 4. Graphical investigation of relationships Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
13 Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
14 Plotting a graph Proportional / linear relationships Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
15 Elastic deformation of metallic string [ case study of elastic deformation (stretching, compression) of solid bodies - determination of Young modulus] Y (N/m 2 ) =? The absolute increase of string s length L when stretching force F is applied depends on the amount of force applied to stretch a rod F, cross-sectional area of the rod A and the nature of rod s material. L o F A - cross-sectional area of the string D - diameter of given cylindrical string L o - initial length of the string L - absolute increase of length when stretching force F is applied Mathematical model of the elastic behaviour - deformation for a given string can be expressed by the linear relation, if the amount of stretching is small compared to the original length of the string : L (m) (increase as well as decrease of length in meters) L = k F H o o k e s l a w : deformation (as change of string s length) and force are directly proportional to one another F (N ) (magnitude of the stretching force in newtons) where k = L o / ( Y A) means the slope of function s graph and Y is a constant, called Young modulus, what value depends on the nature of the string s material L = k F = L o / ( Y A) Y = L o / ( k A ) Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
16 Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
17 Direct measurements of metallic string L o = (mm) = 10-3 D = (mm) = 10-3 m m E x p e r i m e n t : stretching of metallic string A = D 2 / 4 = = D 2 = = = = ( m 2 ) L o L (m) F (N) = F gravitational = M F (N) = M (kg) 10 (m/s 2 ) E a r t h M (kg) L (m) F (N) L (m) M o = 0 L 0 = 0 F 0 = 0 L 18 = 10-3 M 1 = 0,5 L 1 = 10-3 F 1 = 5 1,0 1,5 2,0 2,5 3,0 3,5 4,0 4,5 L 9 = 10-3 L 9 = Determination of Young s modulus using data from graph L(F) = k F k = L (m) / F (N) = Y = L o / ( k A ) = = L(m) = (N/m 2 ) F(N) Random experimental quantities of linear function s slope are averaged graphically Teflon N/m 2 Bone (stretching ) - 1, N/m 2 Nylon N/m 2 Bone (compression) - 0, N/m 2 Aluminium - 0, N/m 2 Copper N/m 2 Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
18 Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
19 Non-linear relationships Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
20 Exponential relationships Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
21 Exponential relationships Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
22 Another example is the variation of DC electric current and voltage when charging / discharging capacitor. Direct (DC) electrical current I (t) when charging/discharging capacitor I (t) Swich I (t) + Source I of DC electric current V I charging V R A R I discharging + V C C V C V 0,63 V V C (t) I (t) V R = I R I max 0,37 I max t, s t, s = RC = RC V C (t) = q (t) / C If R=50k, C=100 F, then = 500s 8min If V =5V, then I max = 100 A I ch (t) = V / R exp ( t / RC ) I disch (t) = V / R exp ( t / RC ) q (t) = C V C (t) This is mathematical model of directly invisible physical electric phenomena. We can directly observe only formal characteristics of the flow of electric charge : electric current and corresponding voltages. Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
23 5. Organization and realization of scientific experimental research Introduction (what and why we are going to investigate?) Theoretical background of research Practical activities (organization and providing of measurements, data processing getting final results) Discussion of results Conclusions (do we have reached the goal of provided research?) Report / written and/or oral presentation of results Experimental Physics Measurement of physical properties / quantities
1 Coulomb s law, Capacitance and Dielectrics
 1 Coulomb s law, Capacitance and Dielectrics This exercise serves as an illustration of the contents of the chapters 2.1, 2.54 and 4 of the textbook: Coulomb s law, Capacitance and Dielectrics. Coulomb
1 Coulomb s law, Capacitance and Dielectrics This exercise serves as an illustration of the contents of the chapters 2.1, 2.54 and 4 of the textbook: Coulomb s law, Capacitance and Dielectrics. Coulomb
CHAPTER 1: PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AMD MEASUREMENT
 CHAPTER 1: PHYSICAL UANTITIES AMD MEASUREMENT 11 Physical uantities and Units a) State basic quantities and their respective SI units: length (m), time (s), mass (kg), electrical current (A), temperature
CHAPTER 1: PHYSICAL UANTITIES AMD MEASUREMENT 11 Physical uantities and Units a) State basic quantities and their respective SI units: length (m), time (s), mass (kg), electrical current (A), temperature
Chapter 26 Elastic Properties of Materials
 Chapter 26 Elastic Properties of Materials 26.1 Introduction... 1 26.2 Stress and Strain in Tension and Compression... 2 26.3 Shear Stress and Strain... 4 Example 26.1: Stretched wire... 5 26.4 Elastic
Chapter 26 Elastic Properties of Materials 26.1 Introduction... 1 26.2 Stress and Strain in Tension and Compression... 2 26.3 Shear Stress and Strain... 4 Example 26.1: Stretched wire... 5 26.4 Elastic
Which expression gives the elastic energy stored in the stretched wire?
 1 wire of length L and cross-sectional area is stretched a distance e by a tensile force. The Young modulus of the material of the wire is E. Which expression gives the elastic energy stored in the stretched
1 wire of length L and cross-sectional area is stretched a distance e by a tensile force. The Young modulus of the material of the wire is E. Which expression gives the elastic energy stored in the stretched
Chapter 1. A Physics Toolkit
 Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit In this chapter you will: Use mathematical tools to measure and predict. Apply accuracy and precision when measuring. Display and evaluate data graphically.
Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit Chapter 1 A Physics Toolkit In this chapter you will: Use mathematical tools to measure and predict. Apply accuracy and precision when measuring. Display and evaluate data graphically.
1. A person in an elevator begins going down. 2. The person reaches a constant velocity
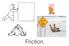 Friction. Describe what this person is feeling and why: 1. A person in an elevator begins going down 2. The person reaches a constant velocity 3. The person reaches the bottom. 4. The person then realizes
Friction. Describe what this person is feeling and why: 1. A person in an elevator begins going down 2. The person reaches a constant velocity 3. The person reaches the bottom. 4. The person then realizes
Physical World And Measurement
 Physical World And Measurement There are four fundamental forces which govern both macroscopic and microscopic phenomena. There are (i) Gravitational force (iii) Electromagnetic force (ii) Nuclear force
Physical World And Measurement There are four fundamental forces which govern both macroscopic and microscopic phenomena. There are (i) Gravitational force (iii) Electromagnetic force (ii) Nuclear force
Healy/DiMurro. Vibrations 2016
 Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
The SuperBall Lab. Objective. Instructions
 1 The SuperBall Lab Objective This goal of this tutorial lab is to introduce data analysis techniques by examining energy loss in super ball collisions. Instructions This laboratory does not have to be
1 The SuperBall Lab Objective This goal of this tutorial lab is to introduce data analysis techniques by examining energy loss in super ball collisions. Instructions This laboratory does not have to be
Hooke's Law: Stress and Strain Revisited *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42240 1 Hooke's Law: Stress and Strain Revisited * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain
OpenStax-CNX module: m42240 1 Hooke's Law: Stress and Strain Revisited * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain
Solving Problems with Labeled Numbers
 Solving Problems with Labeled Numbers When solving problems with labeled numbers (those with units such as grams or liters), the labels are treated in the same way as P or y in algebra. The problem is
Solving Problems with Labeled Numbers When solving problems with labeled numbers (those with units such as grams or liters), the labels are treated in the same way as P or y in algebra. The problem is
PSC 1121 Celebration of Knowledge 1 Fall 2002
 Fall 2002 Problem 1. (15 points) To help his teammates finish up an activity after class, Jorge agrees to find the mass (in grams) of the last four objects himself. The fours sets of measurements are shown
Fall 2002 Problem 1. (15 points) To help his teammates finish up an activity after class, Jorge agrees to find the mass (in grams) of the last four objects himself. The fours sets of measurements are shown
Physical Science Density and Measurements
 Physical Science Density and Measurements Name Date Density All matter has a mass that can be measured and a volume of space that it occupies. However, the relationship between mass and volume varies greatly
Physical Science Density and Measurements Name Date Density All matter has a mass that can be measured and a volume of space that it occupies. However, the relationship between mass and volume varies greatly
Experiment 1: Measurement & Analysis
 Experiment 1: Measurement & Analysis Figure 1.1: Measurement Materials EQUIPMENT 1-Meter Stick Digital Balance 500 g, 1 kg, 2 kg Stamped Masses Metal Cylinder (2) Vernier Calipers (10) Cylinders (Plastic,
Experiment 1: Measurement & Analysis Figure 1.1: Measurement Materials EQUIPMENT 1-Meter Stick Digital Balance 500 g, 1 kg, 2 kg Stamped Masses Metal Cylinder (2) Vernier Calipers (10) Cylinders (Plastic,
AP Physics 1. TEACHING RESOURCES Etkina, Eugenia, Michael Gentile, and Alan Van Heuvelen. College Physics. San Francisco, CA: Pearson, 2014.
 AP Physics 1 TEXTBOOK Knight, Randall D., Jones Brian, and Field, Stuart. 2015. College Physics: A Strategic Approach. 3rd edition. Pearson. San Francisco. TEACHING RESOURCES Etkina, Eugenia, Michael Gentile,
AP Physics 1 TEXTBOOK Knight, Randall D., Jones Brian, and Field, Stuart. 2015. College Physics: A Strategic Approach. 3rd edition. Pearson. San Francisco. TEACHING RESOURCES Etkina, Eugenia, Michael Gentile,
Figure 1. Before starting the investigation the student wrote the following prediction:
 Q1.A student suspended a spring from a laboratory stand and then hung a weight from the spring. Figure 1 shows the spring before and after the weight is added. Figure 1 (a) Measure the extension of the
Q1.A student suspended a spring from a laboratory stand and then hung a weight from the spring. Figure 1 shows the spring before and after the weight is added. Figure 1 (a) Measure the extension of the
Question Figure shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What are (a) Young s modulus and (b) approximate yield strength for this material?
 Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis
 Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis Advance Study Assignment Please contact Dr. Reuven at yreuven@mhrd.org if you have any questions Read the Theory part of the experiment (pages 2-14) and
Experimental Uncertainty (Error) and Data Analysis Advance Study Assignment Please contact Dr. Reuven at yreuven@mhrd.org if you have any questions Read the Theory part of the experiment (pages 2-14) and
Lab 6A: Application of Coulomb s Law, With Vernier Video Simulation
 ab 6A: Application of Coulomb s aw, With Vernier Video Simulation Physics 204, Daniel Yaverbaum John Jay College of Criminal Justice, the CUNY *** NOTE: Every Triple-Starred Direction (***) is a direction
ab 6A: Application of Coulomb s aw, With Vernier Video Simulation Physics 204, Daniel Yaverbaum John Jay College of Criminal Justice, the CUNY *** NOTE: Every Triple-Starred Direction (***) is a direction
Mostly Review. Phy 123L
 Name: Significant Digits, Unit Conversions, Graphing and Uncertainties in Measurements =========================================================== Choose the best answer. (30 pts total) 1. Do the following
Name: Significant Digits, Unit Conversions, Graphing and Uncertainties in Measurements =========================================================== Choose the best answer. (30 pts total) 1. Do the following
22 Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and Young modulus? stress strain Young modulus
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and Young modulus? 97/1/M/J/ stress strain Young modulus () x (area) (extension) x (original length) (stress) /
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and Young modulus? 97/1/M/J/ stress strain Young modulus () x (area) (extension) x (original length) (stress) /
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number
 A LEVEL PHYSICS Specimen Assessment Materials 25 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number A LEVEL PHYSICS COMPONENT 2 Electricity and the Universe SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours For Examiner s use only Question
A LEVEL PHYSICS Specimen Assessment Materials 25 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number A LEVEL PHYSICS COMPONENT 2 Electricity and the Universe SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours For Examiner s use only Question
cos(θ)sin(θ) Alternative Exercise Correct Correct θ = 0 skiladæmi 10 Part A Part B Part C Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 2015
 skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
Simple Harmonic Motion Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring
 17 Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring A spring that is hanging vertically from a support with no mass at the end of the spring has a length L (called its rest length). When a mass is added to
17 Investigating a Mass Oscillating on a Spring A spring that is hanging vertically from a support with no mass at the end of the spring has a length L (called its rest length). When a mass is added to
Topic 1.2 Measurement and Uncertainties Uncertainty and error in measurement. Random Errors
 Uncertainty and error in measurement Random Errors Definition of Random Error Random errors are sources of uncertainties in the measurement, whose effect can be reduced by a repeated experiment, and taking
Uncertainty and error in measurement Random Errors Definition of Random Error Random errors are sources of uncertainties in the measurement, whose effect can be reduced by a repeated experiment, and taking
Chapter Units and Measurement
 2 Chapter Units and Measurement 1. Identify the pair whose dimensions are equal [2002] torque and work stress and energy force and stress force and work 2. [2003] [L -1 T] ] [L -2 T 2 ] [L 2 T -2 ] [LT
2 Chapter Units and Measurement 1. Identify the pair whose dimensions are equal [2002] torque and work stress and energy force and stress force and work 2. [2003] [L -1 T] ] [L -2 T 2 ] [L 2 T -2 ] [LT
Appendix II Calculation of Uncertainties
 Part 1: Sources of Uncertainties Appendix II Calculation of Uncertainties In any experiment or calculation, uncertainties can be introduced from errors in accuracy or errors in precision. A. Errors in
Part 1: Sources of Uncertainties Appendix II Calculation of Uncertainties In any experiment or calculation, uncertainties can be introduced from errors in accuracy or errors in precision. A. Errors in
ERROR AND GRAPHICAL ANALYSIS WORKSHEET
 Student Names: Course: Section: Instructor: ERROR AND GRAPHICAL ANALYSIS WORKSHEET Instructions: For each section of this assignment, first read the relevant section in the Yellow Pages of your Lab Manual.
Student Names: Course: Section: Instructor: ERROR AND GRAPHICAL ANALYSIS WORKSHEET Instructions: For each section of this assignment, first read the relevant section in the Yellow Pages of your Lab Manual.
1. Four equal and positive charges +q are arranged as shown on figure 1.
 AP Physics C Coulomb s Law Free Response Problems 1. Four equal and positive charges +q are arranged as shown on figure 1. a. Calculate the net electric field at the center of square. b. Calculate the
AP Physics C Coulomb s Law Free Response Problems 1. Four equal and positive charges +q are arranged as shown on figure 1. a. Calculate the net electric field at the center of square. b. Calculate the
Class XI Physics. Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids. NCERT Solutions
 Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
05 the development of a kinematics problem. February 07, Area under the curve
 Area under the curve Area under the curve refers from the region the line (curve) to the x axis 1 2 3 From Graphs to equations Case 1 scatter plot reveals no apparent relationship Types of equations Case
Area under the curve Area under the curve refers from the region the line (curve) to the x axis 1 2 3 From Graphs to equations Case 1 scatter plot reveals no apparent relationship Types of equations Case
Appendix A: Significant Figures and Error Analysis
 1 Appendix A: Significant Figures and Error Analysis Every measurement of a physical quantity contains some amount of uncertainty or error. We often speak of a certain number or measurement as being precise
1 Appendix A: Significant Figures and Error Analysis Every measurement of a physical quantity contains some amount of uncertainty or error. We often speak of a certain number or measurement as being precise
Course: Phys-109 General Physics I. Text book: Physics, 6 th edition, D. C. Giancoli.
 Few Initial Remarks Course: Phys-109 General Physics I Text book: Physics, 6 th edition, D. C. Giancoli. Few Initial Remarks Instructor: Dr. Mauricio Barbi Email: barbi@uregina.ca Tel: 585-4260 Office:
Few Initial Remarks Course: Phys-109 General Physics I Text book: Physics, 6 th edition, D. C. Giancoli. Few Initial Remarks Instructor: Dr. Mauricio Barbi Email: barbi@uregina.ca Tel: 585-4260 Office:
PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion
 Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
STATICALLY INDETERMINATE STRUCTURES
 STATICALLY INDETERMINATE STRUCTURES INTRODUCTION Generally the trusses are supported on (i) a hinged support and (ii) a roller support. The reaction components of a hinged support are two (in horizontal
STATICALLY INDETERMINATE STRUCTURES INTRODUCTION Generally the trusses are supported on (i) a hinged support and (ii) a roller support. The reaction components of a hinged support are two (in horizontal
PHYS 124 Section A1 Mid-Term Examination Spring 2006 SOLUTIONS
 PHYS 14 Section A1 Mid-Term Examination Spring 006 SOLUTIONS Name Student ID Number Instructor Marc de Montigny Date Monday, May 15, 006 Duration 60 minutes Instructions Items allowed: pen or pencil, calculator
PHYS 14 Section A1 Mid-Term Examination Spring 006 SOLUTIONS Name Student ID Number Instructor Marc de Montigny Date Monday, May 15, 006 Duration 60 minutes Instructions Items allowed: pen or pencil, calculator
r r 4πε 0 r From the relations between measured or known electrical quantities, material properties and apparatus dimensions you can determine ε 0.
 8.0T Fall 001 Electrostatic Force 1 Introduction In this experiment you ll investigate aspects of the electrostatic force. This force has such varied roles as making currents flow in wires, holding atoms
8.0T Fall 001 Electrostatic Force 1 Introduction In this experiment you ll investigate aspects of the electrostatic force. This force has such varied roles as making currents flow in wires, holding atoms
Physics 11. Unit 1 Mathematical Toolkits
 Physics 11 Unit 1 Mathematical Toolkits 1 1.1 Measurement and scientific notations Système International d Unités (SI Units) The base units for measurement of fundamental quantities. Other units can be
Physics 11 Unit 1 Mathematical Toolkits 1 1.1 Measurement and scientific notations Système International d Unités (SI Units) The base units for measurement of fundamental quantities. Other units can be
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Unit 7: Energy Notes
 Unit 7: Energy Notes Energy is a conserved, substance-like quantity with the capability to produce change. Energy is conserved, neither created nor destroyed. = (Law of conservation of energy) Εnergy is
Unit 7: Energy Notes Energy is a conserved, substance-like quantity with the capability to produce change. Energy is conserved, neither created nor destroyed. = (Law of conservation of energy) Εnergy is
681. Design of elastomeric shock absorbers with a soft stiffness characteristics of type force-settlement
 681. Design of elastomeric shock absorbers with a soft stiffness characteristics of type force-settlement V. Gonca 1, J. Shvab Riga Technical University, Ezermalas 6 d, LV-1006, Riga, Latvia E-mail: 1
681. Design of elastomeric shock absorbers with a soft stiffness characteristics of type force-settlement V. Gonca 1, J. Shvab Riga Technical University, Ezermalas 6 d, LV-1006, Riga, Latvia E-mail: 1
Page 2. What is the main purpose of the steel core? To force more current into the outer sheath.
 Q1.The overhead cables used to transmit electrical power by the National Grid usually consist of a central core of steel cables surrounded by a sheath of cables of low resistivity material, such as aluminium.
Q1.The overhead cables used to transmit electrical power by the National Grid usually consist of a central core of steel cables surrounded by a sheath of cables of low resistivity material, such as aluminium.
M-3: Statics & M-10 Elasticity
 Group member names This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and explain your reasoning
Group member names This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and explain your reasoning
Keys to the Study of Chemistry. 1.1 Fundamental Definitions
 Keys to the Study of Chemistry Chemistry is the study of matter, its properties, changes, and the energy associated with these changes Matter is everything that has mass an occupies space Pure substances
Keys to the Study of Chemistry Chemistry is the study of matter, its properties, changes, and the energy associated with these changes Matter is everything that has mass an occupies space Pure substances
From Physics to Economics: the versatility of the exponential function
 From Physics to Economics: the versatility of the exponential function I. Introduction. General terms and requirements. After having completed your team and chosen your leader, you should decide on how
From Physics to Economics: the versatility of the exponential function I. Introduction. General terms and requirements. After having completed your team and chosen your leader, you should decide on how
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
Student Performance Q&A:
 Student Performance Q&A: 2006 AP Physics B Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2006 free-response questions for AP Physics B were written by the Chief Reader, William Ingham of James
Student Performance Q&A: 2006 AP Physics B Free-Response Questions The following comments on the 2006 free-response questions for AP Physics B were written by the Chief Reader, William Ingham of James
A velocity of 5 m s 1 can be resolved along perpendicular directions XY and XZ.
 T1 [154 marks] 1. A velocity of 5 m s 1 can be resolved along perpendicular directions XY and XZ. The component of the velocity in the direction XY is of magnitude 4 m s 1. What is the magnitude of the
T1 [154 marks] 1. A velocity of 5 m s 1 can be resolved along perpendicular directions XY and XZ. The component of the velocity in the direction XY is of magnitude 4 m s 1. What is the magnitude of the
REMOVING A PIECE OF ADHESIVE TAPE FROM A HORIZONTAL SURFACE
 REMOVING A PIECE OF ADHESIVE TAPE FROM A HORIZONTAL SURFACE Hossein Azizinaghsh a, Hamid Ghaednia b a Sharif University of Technology, School of Computer Engineering, I. R. Iran Hossein.Azizi@gmail.com
REMOVING A PIECE OF ADHESIVE TAPE FROM A HORIZONTAL SURFACE Hossein Azizinaghsh a, Hamid Ghaednia b a Sharif University of Technology, School of Computer Engineering, I. R. Iran Hossein.Azizi@gmail.com
HS AP Physics 1 Science
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 5 Day(s) 20 Day(s) 5 Day(s) Kinematics Course AP Physics 1 is an introductory first-year, algebra-based, college level course for the student interested
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 5 Day(s) 20 Day(s) 5 Day(s) Kinematics Course AP Physics 1 is an introductory first-year, algebra-based, college level course for the student interested
Force and Motion 20 N. Force: Net Force on 2 kg mass = N. Net Force on 3 kg mass = = N. Motion: Mass Accel. of 2 kg mass = = kg m/s 2.
 Force and Motion Team In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
Force and Motion Team In previous labs, you used a motion sensor to measure the position, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. You were not concerned about the mechanism that caused the object
[1] not to scale. Fig. 6.1
![[1] not to scale. Fig. 6.1 [1] not to scale. Fig. 6.1](/thumbs/84/89302673.jpg) 1 (a) Define work done by a force...... [1] (b) Fig. 6.1 shows a water slide. slide 32 m not to scale water Fig. 6.1 The top of the slide is 32 m above the bottom of the slide. The total distance along
1 (a) Define work done by a force...... [1] (b) Fig. 6.1 shows a water slide. slide 32 m not to scale water Fig. 6.1 The top of the slide is 32 m above the bottom of the slide. The total distance along
A420U20-1 S17-A420U20-1. PHYSICS A level component 2 Electricity and the Universe
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A LEVEL NEW A420U20-1 S17-A420U20-1 PHYSICS A level component 2 Electricity and the Universe WEDNESDAY, 21 JUNE 2017 MORNING 2 hours For s use Question
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 2 GCE A LEVEL NEW A420U20-1 S17-A420U20-1 PHYSICS A level component 2 Electricity and the Universe WEDNESDAY, 21 JUNE 2017 MORNING 2 hours For s use Question
3. What is the decimal place of the least significant figure (LSF) in the number 0.152? a. tenths place b. hundredths place c.
 Name: Significant Digits, Unit Conversions, Graphing and Uncertainties in Measurements =========================================================== Choose the best answer. (30 pts total) Significant Digits,
Name: Significant Digits, Unit Conversions, Graphing and Uncertainties in Measurements =========================================================== Choose the best answer. (30 pts total) Significant Digits,
Exam Practice Problems (3 Point Questions)
 Exam Practice Problems (3 Point Questions) Below are practice problems for the three point questions found on the exam. These questions come from past exams as well additional questions created by faculty.
Exam Practice Problems (3 Point Questions) Below are practice problems for the three point questions found on the exam. These questions come from past exams as well additional questions created by faculty.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level * 5961 585709* PHYSICS 9702/22 Paper 2 AS Structured Questions May/June
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level * 5961 585709* PHYSICS 9702/22 Paper 2 AS Structured Questions May/June
Physics Exam 2 October 11, 2007
 INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
INSTRUCTIONS: Write your NAME on the front of the blue exam booklet. The exam is closed book, and you may have only pens/pencils and a calculator (no stored equations or programs and no graphing). Show
 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
In which vector triangle does the vector Z show the magnitude and direction of vector X Y?
 1 1 Which of the following pairs of units are both SI base units? ampere, degree celsius ampere, kelvin coulomb, degree celsius coulomb, kelvin 2 The diagram shows two vectors and Y. Y In which vector
1 1 Which of the following pairs of units are both SI base units? ampere, degree celsius ampere, kelvin coulomb, degree celsius coulomb, kelvin 2 The diagram shows two vectors and Y. Y In which vector
Experiment Two (2) Torsional testing of Circular Shafts
 Experiment Two (2) Torsional testing of Circular Shafts Introduction: Torsion occurs when any shaft is subjected to a torque. This is true whether the shaft is rotating (such as drive shafts on engines,
Experiment Two (2) Torsional testing of Circular Shafts Introduction: Torsion occurs when any shaft is subjected to a torque. This is true whether the shaft is rotating (such as drive shafts on engines,
Class XI Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics
 Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
PMT. GCE AS and A Level. Physics A. AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards. Unit 2: Approved specimen question paper. Version 1.
 GCE AS and A Level Physics A AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards Unit 2: Approved specimen question paper Version 1.1 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature
GCE AS and A Level Physics A AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards Unit 2: Approved specimen question paper Version 1.1 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature
St Olave s Grammar School. AS Physics Mock Revision Checklist
 St Olave s Grammar School Mock Practical skills.. a Can you design experiments, including ones to solve problems set in a practical context?.. b Can you identify the variables that must be controlled in
St Olave s Grammar School Mock Practical skills.. a Can you design experiments, including ones to solve problems set in a practical context?.. b Can you identify the variables that must be controlled in
Experiment FT1: Measurement of Dielectric Constant
 Experiment FT1: Measurement of Dielectric Constant Name: ID: 1. Objective: (i) To measure the dielectric constant of paper and plastic film. (ii) To examine the energy storage capacity of a practical capacitor.
Experiment FT1: Measurement of Dielectric Constant Name: ID: 1. Objective: (i) To measure the dielectric constant of paper and plastic film. (ii) To examine the energy storage capacity of a practical capacitor.
Good Vibes: Introduction to Oscillations
 Good Vibes: Introduction to Oscillations Description: Several conceptual and qualitative questions related to main characteristics of simple harmonic motion: amplitude, displacement, period, frequency,
Good Vibes: Introduction to Oscillations Description: Several conceptual and qualitative questions related to main characteristics of simple harmonic motion: amplitude, displacement, period, frequency,
Dynamics Review Checklist
 Dynamics Review Checklist Newton s Laws 2.1.1 Explain Newton s 1 st Law (the Law of Inertia) and the relationship between mass and inertia. Which of the following has the greatest amount of inertia? (a)
Dynamics Review Checklist Newton s Laws 2.1.1 Explain Newton s 1 st Law (the Law of Inertia) and the relationship between mass and inertia. Which of the following has the greatest amount of inertia? (a)
Topic 2: Mechanics 2.3 Work, energy, and power
 Essential idea: The fundamental concept of energy lays the basis upon which much of science is built. Nature of science: Theories: Many phenomena can be fundamentally understood through application of
Essential idea: The fundamental concept of energy lays the basis upon which much of science is built. Nature of science: Theories: Many phenomena can be fundamentally understood through application of
GAME PHYSICS (INFOMGP) FINAL EXAM
 GAME PHYSICS (INFOMGP) FINAL EXAM 15/JUN/ 016 LECTURER: AMIR VAXMAN Student name: Student number: This exam is 3 hours long and consists of 5 exercises. The points add up to 100. Answer only in English.
GAME PHYSICS (INFOMGP) FINAL EXAM 15/JUN/ 016 LECTURER: AMIR VAXMAN Student name: Student number: This exam is 3 hours long and consists of 5 exercises. The points add up to 100. Answer only in English.
AP1 WEP. Answer: E. The final velocities of the balls are given by v = 2gh.
 1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
Experiment 2: Laboratory Experiments on Ferroelectricity
 Experiment 2: Laboratory Experiments on Ferroelectricity 1. Task: Measure the dielectric constant εr of a TGS crystal as a function of temperature from room temperature up to 70 C at a frequency of about
Experiment 2: Laboratory Experiments on Ferroelectricity 1. Task: Measure the dielectric constant εr of a TGS crystal as a function of temperature from room temperature up to 70 C at a frequency of about
Chapter 5: Energy. Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy
 Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 17
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 17 Chapter 6: Conservation of Energy 6.7 Elastic Potential Energy 6.8 Power Chapter 7: Linear Momentum 7.1 A Vector Conservation Law 7. Momentum Lecture 17 Purdue University, Physics
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 17 Chapter 6: Conservation of Energy 6.7 Elastic Potential Energy 6.8 Power Chapter 7: Linear Momentum 7.1 A Vector Conservation Law 7. Momentum Lecture 17 Purdue University, Physics
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23
 PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23 Monday, April 29, 2013 Conditions for Equilibrium Elastic Properties of Solids Young s Modulus Bulk Modulus Density and Specific Gravity luid and Pressure Today s homework
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23 Monday, April 29, 2013 Conditions for Equilibrium Elastic Properties of Solids Young s Modulus Bulk Modulus Density and Specific Gravity luid and Pressure Today s homework
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM
 1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
_CH01_p qxd 1/20/10 8:35 PM Page 1 PURPOSE
 9460218_CH01_p001-010.qxd 1/20/10 8:35 PM Page 1 1 GRAPHING AND ANALYSIS PURPOSE The purpose of this lab is to investigate the relationship between displacement and force in springs and to practice acquiring
9460218_CH01_p001-010.qxd 1/20/10 8:35 PM Page 1 1 GRAPHING AND ANALYSIS PURPOSE The purpose of this lab is to investigate the relationship between displacement and force in springs and to practice acquiring
2/28/2006 Statics ( F.Robilliard) 1
 2/28/2006 Statics (.Robilliard) 1 Extended Bodies: In our discussion so far, we have considered essentially only point masses, under the action of forces. We now broaden our considerations to extended
2/28/2006 Statics (.Robilliard) 1 Extended Bodies: In our discussion so far, we have considered essentially only point masses, under the action of forces. We now broaden our considerations to extended
Core practical 9: Investigate the relationship between the force exerted on an object and its change of momentum
 Core practical 9 Teacher sheet Core practical 9: Objective To determine the momentum change of a trolley when a force acts on it, as a function of time Safety There are trolleys and masses in motion so
Core practical 9 Teacher sheet Core practical 9: Objective To determine the momentum change of a trolley when a force acts on it, as a function of time Safety There are trolleys and masses in motion so
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
Scientific Notation. Part A: Express each of the following in standard form x x x
 Name: Course: Scientific Notation Part A: Express each of the following in standard form. 1. 5.2 x 10 3 5. 3.6 x 10 1 2. 9.65 x 10 4 6. 6.452 x 10 2 3. 8.5 x 10 2 7. 8.77 x 10 1 4. 2.71 x 10 4 8. 6.4 x
Name: Course: Scientific Notation Part A: Express each of the following in standard form. 1. 5.2 x 10 3 5. 3.6 x 10 1 2. 9.65 x 10 4 6. 6.452 x 10 2 3. 8.5 x 10 2 7. 8.77 x 10 1 4. 2.71 x 10 4 8. 6.4 x
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
Miami-Dade Community College PHY 2053 College Physics I
 Miami-Dade Community College PHY 2053 College Physics I PHY 2053 3 credits Course Description PHY 2053, College physics I, is the first semester of a two semester physics-without-calculus sequence. This
Miami-Dade Community College PHY 2053 College Physics I PHY 2053 3 credits Course Description PHY 2053, College physics I, is the first semester of a two semester physics-without-calculus sequence. This
Mechanics of Material 11/29/2017. General Information
 General Information Assistant Lecturer: Asmaa Ab. Mustafa Email : asmaa.abdulmajeed@ishik.edu.iq Department : Civil Engineering Course Title : Engineering Mechanics I Code : Credit : 2 Office Hour : Monday
General Information Assistant Lecturer: Asmaa Ab. Mustafa Email : asmaa.abdulmajeed@ishik.edu.iq Department : Civil Engineering Course Title : Engineering Mechanics I Code : Credit : 2 Office Hour : Monday
SF016: PAST YEAR PSPM QUESTIONS
 GRAPH QUESTIONS PSPM I 005/006 NO. 9 9. An experiment was carried out to determine the Young s modulus of a metal wire of length 3.0 and diameter 0.8. A vernier scale was used to measure its extension.
GRAPH QUESTIONS PSPM I 005/006 NO. 9 9. An experiment was carried out to determine the Young s modulus of a metal wire of length 3.0 and diameter 0.8. A vernier scale was used to measure its extension.
A F/4 B F/8 C 2F D 4F E 8F. Answer: Because F M A. /r 2 or eight times what it was 8F. Answer:
 Test 7 Section A 2 Core short answer questions: 50 marks Section B 2 Detailed studies short answer questions: 120 marks Suggested time: 90 2100 minutes Section A: Core short answer questions Specific instructions
Test 7 Section A 2 Core short answer questions: 50 marks Section B 2 Detailed studies short answer questions: 120 marks Suggested time: 90 2100 minutes Section A: Core short answer questions Specific instructions
Elastic Properties of Solid Materials. Notes based on those by James Irvine at
 Elastic Properties of Solid Materials Notes based on those by James Irvine at www.antonine-education.co.uk Key Words Density, Elastic, Plastic, Stress, Strain, Young modulus We study how materials behave
Elastic Properties of Solid Materials Notes based on those by James Irvine at www.antonine-education.co.uk Key Words Density, Elastic, Plastic, Stress, Strain, Young modulus We study how materials behave
PHYSICS. Unit 3 Written examination Trial Examination SOLUTIONS
 PHYSICS Unit 3 Written examination 1 2012 Trial Examination SECTION A Core Motion in one and two dimensions Question 1 SOLUTIONS Answer: 120 N Figure 1 shows that at t = 5 sec, the cart is travelling with
PHYSICS Unit 3 Written examination 1 2012 Trial Examination SECTION A Core Motion in one and two dimensions Question 1 SOLUTIONS Answer: 120 N Figure 1 shows that at t = 5 sec, the cart is travelling with
Bending Load & Calibration Module
 Bending Load & Calibration Module Objectives After completing this module, students shall be able to: 1) Conduct laboratory work to validate beam bending stress equations. 2) Develop an understanding of
Bending Load & Calibration Module Objectives After completing this module, students shall be able to: 1) Conduct laboratory work to validate beam bending stress equations. 2) Develop an understanding of
Kinematics Unit. Measurement
 Kinematics Unit Measurement The Nature of Science Observation: important first step toward scientific theory; requires imagination to tell what is important. Theories: created to explain observations;
Kinematics Unit Measurement The Nature of Science Observation: important first step toward scientific theory; requires imagination to tell what is important. Theories: created to explain observations;
Data Analysis for University Physics
 Data Analysis for University Physics by John Filaseta orthern Kentucky University Last updated on ovember 9, 004 Four Steps to a Meaningful Experimental Result Most undergraduate physics experiments have
Data Analysis for University Physics by John Filaseta orthern Kentucky University Last updated on ovember 9, 004 Four Steps to a Meaningful Experimental Result Most undergraduate physics experiments have
PHYSICS. Course Structure. Unit Topics Marks. Physical World and Measurement. 1 Physical World. 2 Units and Measurements.
 PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Chapter 5 Work and Energy
 Chapter 5 Work and Energy Work and Kinetic Energy Work W in 1D Motion: by a Constant orce by a Varying orce Kinetic Energy, KE: the Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy E and Its Conservation Potential
Chapter 5 Work and Energy Work and Kinetic Energy Work W in 1D Motion: by a Constant orce by a Varying orce Kinetic Energy, KE: the Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy E and Its Conservation Potential
Dynamics Review Checklist
 Dynamics Review Checklist Newton s Laws 2.1.1 Explain Newton s 1 st Law (the Law of Inertia) and the relationship between mass and inertia. Which of the following has the greatest amount of inertia? (a)
Dynamics Review Checklist Newton s Laws 2.1.1 Explain Newton s 1 st Law (the Law of Inertia) and the relationship between mass and inertia. Which of the following has the greatest amount of inertia? (a)
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
Pre-Comp Review Questions- 8 th Grade
 Pre-Comp Review Questions- 8 th Grade Section 1- Units 1. Fill in the missing SI and English Units Measurement SI Unit SI Symbol English Unit English Symbol Time second s. Temperature K Fahrenheit Length
Pre-Comp Review Questions- 8 th Grade Section 1- Units 1. Fill in the missing SI and English Units Measurement SI Unit SI Symbol English Unit English Symbol Time second s. Temperature K Fahrenheit Length
FRICTION. Friction: FRICARE = to rub (Latin)
 FRICTION 1 Friction: FRICARE = to rub (Latin) Resisting force (F) tangential to the interface between two bodies when, under the action of an external force, one body moves or tends to move relative to
FRICTION 1 Friction: FRICARE = to rub (Latin) Resisting force (F) tangential to the interface between two bodies when, under the action of an external force, one body moves or tends to move relative to
Forces. 3. The graph given shows the weight of three objects on planet X as a function of their mass. A. 0 N. B. between 0 N and 12 N C.
 Name: Date: 1. When a 12-newton horizontal force is applied to a box on a horizontal tabletop, the box remains at rest. The force of static friction acting on the box is 3. The graph given shows the weight
Name: Date: 1. When a 12-newton horizontal force is applied to a box on a horizontal tabletop, the box remains at rest. The force of static friction acting on the box is 3. The graph given shows the weight
PHYSICS. Written examination 1. Reading time: 15 minutes Writing time: 1 hour 30 minutes. QUESTION and ANSWER BOOK
 STUDENT NUMBER LETTER Figures Words PHYSICS Written examination 1 Reading time: 15 minutes Writing time: 1 hour 30 minutes sample QUESTION and ANSWER BOOK Section Number of questions Number of questions
STUDENT NUMBER LETTER Figures Words PHYSICS Written examination 1 Reading time: 15 minutes Writing time: 1 hour 30 minutes sample QUESTION and ANSWER BOOK Section Number of questions Number of questions
Elastic potential energy
 Elastic potential energy Objectives Investigate eamples of elastic potential energy. Provide or identify a conceptual definition of the spring constant. Calculate the potential energy, spring constant,
Elastic potential energy Objectives Investigate eamples of elastic potential energy. Provide or identify a conceptual definition of the spring constant. Calculate the potential energy, spring constant,
AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB
![AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB](/thumbs/96/128301637.jpg) 1. AP Physics C Summer Homework NAME: Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB 2. Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric
1. AP Physics C Summer Homework NAME: Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB 2. Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric
