Interaction of 28 Si Ions with Emulsion Nuclei at Momentum 4.5 AGeV/c
|
|
|
- Hannah Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics 2015, 5(1: DOI: /j.jnpp Interaction of 28 Si Ions with Emulsion Nuclei at Momentum 4.5 AGeV/c A. Abd EL-Daiem Physics Department, Faculty of science, Sohag University, Sohag, Egypt Abstract The main experimental characteristics multiplicity have been investigated from 28 Si with emulsion at 4.5 GeV/c. The nucleus-nucleus collisions are given in the energy interactions of 4 He, 24 Mg and 28 Si with emulsion nuclei at nearly the same. On the other hand the relativistic energy (a few GeV/nucleon is a special energy, at which the nuclear limiting fragmentation applies initially. Therefore, the target fragmentation is studied by selecting samples of inelastic interactions events having no emission of relativistic hadrons'. The multiplicity distribution of the produced target fragments are studied. The angular distribution of target fragmentations particles, grey and black of the interaction of 28 Si emulsions, shows statically significant peak which have been attributed to a collective phenomenon. Keywords Multiplicity secondary particles, Multiplicity correlation and angular distribution 1. Introduction The interest in high-energy nucleus-nucleus collision has greatly important during a few recent years. It allows one to obtain some information about the mechanisms of the multiparticle production and the structure of hot nuclear matter [1]. From the participant spectator model [2], the quark gluon plasma (quark matter [1] will be formed in the participant between the projectile and the target at very high incident energies and a liquid gas phase transition will occur in the spectator [3]. The interaction between the incident beam and the target emulsion nuclei is called central when the impact parameter is less than the absolute value of the difference between the interacting radii of two nuclei, i.e. b< 1R p -R t 1 where R p and R t are the projectile and target nuclei radii respectively. Such events are characterized by large multiplicities of the generated particles and the emitted target fragments. The emission of particles is symmetric with respect to the direction of the incident beam. In central collision all projectile nucleons are participants and no projectile spectators. The study of the correlation in complete destruction of Ag (Br emulsion nuclei is very interesting. The most of these interactions are due to central collision. Central collision provides a unique opportunity to investigate the consequents of nuclear compression, such as hydrodynamic effects [4-6]. Also one can study the mechanism of multiparticle production [7-12], and also obtain valuable information on the excitation and subsequent * Corresponding author: Ahmedalbiomy@yahoo.co (A. Abd EL-Daiem Published online at Copyright 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved decay of residual target nucleus. This study is restricted to events such that N h >27 (N h =N g +N b, i.e. to central collision of 28 Si with Ag (Br, where N h is the number of heavy target fragments, N g is the number of grey particles and N b is the black particles. 2. Experimental Details Three stacks of NIFKI-Br2 nuclear emulsion with dimensions of 20cm x 10cm x 600μm were irradiated by 28Si, 24Mg (4.5AGeV/c and 4He (4.1AGeV/c beam at synchrophastron in Dubna, Russia. Along the track double scanning, fast in the forward direction and slows in the backward one, was carried out using a total magnification of about 1500x. Here we could carefully extract sufficient number of statistical events. The experimental means free path λ were found to be 8.7±0.3, 10.2±0.6 and 19.9±0.1 for the interactions of 28Si, 24Mg and 4He with emulsion, respectively. The tracks of the emitted secondary charged particles in each event were classified to traditional emulsion criteria [13, 14] as follows: (a shower tracks are singly charged relativistic particles with relative ionization I/I0 1.4, were I is the track ionization and I0 is the plateau ionization for single charged minimum ionization particles. Their multiplicity was denoted by ionization Ns, (b Grey tracks having a range of L 3 mm in emulsions and relative ionization I/I These tracks are mostly due to protons with kinetic energy in the range MeV. Their multiplicity denoted by Ng, (c Black tracks, those are having range of L 3 mm corresponding to protons with kinetic energy 26 MeV. They are mainly due to evaporated target fragments. T heir multiplicity is denoted by Nb. In each event, the black and grey tracks together are called
2 Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics 2015, 5(1: heavily ionizing tracks. Their multiplicity is denoted by (Nh = Ng + Nb, and (d projectile fragments, PF`s are emitted with an angle θlab 30, with respect to the direction of incidence. They are characterized by no change in their ionization for at least 2cm from the interaction point. The single charged fragments emitted in the forward fragmentation cone were subjected to rigorous multiple scattering measurements for the momentum determination in order to distinguish them from the produced pious. 3. Secondary Particle Multiplicities In figure. (1a-c, we show the normalized multiplicity distribution of shower, grey and black particles for 28Si-and 24Mg (present work and 4He [15] with emulsion nuclei at (4.5 and 4.1AGeV/c respectively. From these figures and the results of the developed modified cascade evaporation model for A-A collision (Kawrakow et al., 1992 [16], we can conclude that, as the number of interacting projectile nucleons increase, the values of Ns slightly increases, which leads to an slightly increase in the average multiplicity of the produced shower particles, <Ns>. This may be indicate that the A-A interactions is a superposition of nucleon nucleon interaction [17]. The best fitting of the present data are: <N g >=0.56N s +2.25, <N b >=0.33N s and <N h >=0.89N s We notice that the inclination is positive which is practically signifying the appreciable dependence of <N g >, <N b > and <N h > on N s. In figure (3a-c which shows the dependence of <N s >, <N g >, and <N b > on the size of the target fragmentation N h in heavy ion interactions. This might reflect the cascading process, which is more, pronounced and consequently the energy deposition within the interaction volume is large in the heavy ion interaction [18]. The dependence of the mean number of black track on N g is non-linear throughout the energy range 6.2GeV to 400GeV in the interaction of proton with emulsion [19]. This is hold for our data of 28 Si with emulsion interaction at 4.5GeV/c with emulsion as shown in figure (4. The best fit for N g <11 take the form: <N b >=0.752N g For N g 10, a saturation of <N b >-N g correlation is reached. The correlation does not depend on the nature of the incident particle. P(N g b 28Si-4.5GeV/c He-4.1GeV/c a 28Si-4.5Gev/c He- 4.1GeV/c N g P(N s b 28Si-4.5GeV/c He-4.1GeV/c N s P(N g Figure 1a. The multiplicity distribution of shower particles for the ineraction of 28 Si(closed circle, 24 Mg(open circle at 4.5AGeV/c and 4 He(closed triangle at 4.1AGeV/c with emulsion 4. Multiplicity Correlations The correlation between the shower (s and others i.e. black (b, grey (g and heavily ionization (h track multiplicities like <N i >=a ij + k ij N j (i j as shown in figure (2. Figure 1(b-c. The multiplicity distribution of grey and black particles for the interactions of 28 Si, 24 Mg(4.5AGeV/c and 4 He(4.1 with emulsion respectively N g
3 12 A. Abd EL-Daiem: Interaction of 28 Si Ions with Emulsion Nuclei at Momentum 4.5 AGeV/c Figure 2. The dependence of the mean number of heavy tracks <Ni>,i=g,b,h, on the shower particles Ns of the interaction of 28Si-emulsion nuclei Figure 3(a-c. The dependence of <N g >, <N b > and <N s >, on the size of the target fragmentation N h for 28 Si-emulsion respectively Figure 4. The dependence of the mean number of black track <N b > on N g for 28 Si-with emulsion collision
4 Journal of Nuclear and Particle Physics 2015, 5(1: other. The target fragment angular distributions show no statistically significantly peak which could be attributed to shock wave. 6. Conclusions Figure 5a. The angular distribution of grey particles emitted in central collision and all interactions of 28 Si ions with emulsion at 4.5 GeV/c Figure 5b. The angular distribution of black particles emitted from central collision and all interactions of 28 Si ions with emulsion at 4.5 GeV/c 5. Angular Distributions of Target Fragments Figure(5a presents the angular distribution of grey particles emitted in central collision of 28 Si ions with emulsion at 4.5 GeV/c per nucleon. This distribution compared with the distribution of grey particles from all 28 Si interaction is presented in the same figure. It is seen as has been in many papers [6-12] and [20-26], that the angular distribution of grey particles tracks is very weakly dependent on variation of the projectile mass, the primary energy and the target mass. The number of participant nucleons increases as the volume of the cylinder cut by the projectile in the target nucleus increases as the mass of the projectile increases, the cross sectional area of this cylinder increased consequently the number of participants also increases. The size of the target nucleus is limited and consequently the number of evaporated particles decreases when N g increases. Figure(5b shows the angular distribution of black particles i.e. tracks with range less than or equal to 3000mm, which is equivalent to proton kinetic energy 27 MeV emitted from central collision and all interactions of 28 Si ions, within statistical errors the distributions are consistent with each From the investigation of particles emitted in the interaction of 28 Si emulsion collisions, we can make the following conclusions: 1. The multiplicity distribution of shower, grey and black particles of the present data for the interactions of 28 Si and 24 Mg (4.5AGeV/c and the other experimental one for 4 He (4.1AGeV/c with emulsion, are slightly different according to the different of their average multiplicities. 2. As the number of interacting projectile nucleons increase from 28 Si to 4 He the values of N s increases which leads to an increasing of <N s >. This may indicate the possibility of considered that nucleus-nucleus interaction is a superposition of nucleon nucleon interaction. 3. The multiplicity correlations have observed the following: for shower particles N s with the other averages<n g >, < N b >,and <N h > in emulsion is given by the relation: <N i >=a ij +k ij N j (i j. The dependence of <N s >, <N g >, and <N b >on the size of the target fragmentation N h in heavy ion interactions might reflect the cascading process. The dependence of <N b > on N g is non-linear, independent on the nature of the incident particles. 4. The angular distribution of target fragments are independent on the projectile mass, the impact parameter and on the target nucleus. 5. The target fragments angular distribution show no statistically significant peak which could be attributed to shock wave. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We would like to thanks prof. Dr. Hesham Mansour for critical reading of the manuscript useful discussions and valuable information. This work is dedicated to the memory of prof. Dr. A. El-Naghy. REFERENCES [1] G. Oyniec, int. J. Mod. phys. A17, 3107 (2002. [2] R. J. Glauber. interscience, New yourk,1959,vol.1,p315. [3] Y. G. Mu, phys.lett.83, 3617(1999. [4] D. Beavis, S.Y. Fung, W. Gorn, D. Keano, Y. M. Liu., R.T. Poe, G. Van Dalen and M. Vient, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54, 1652(1979.
5 14 A. Abd EL-Daiem: Interaction of 28 Si Ions with Emulsion Nuclei at Momentum 4.5 AGeV/c [5] P. Beckmann, H. A. Gustafasson, H. H. Gutbrod, K.H. Kalmpert, B. Kolb, H. Loehren, A. M. Posanzer, H. G. Ritter, H. R. Shmidt, and T. Siemiarcz CK, Mod. Phys. Lett.AZ (1987. [6] L.P/Csernai, P. Freier, J. Mevissen, H. Nguyen, and L. Waters, Phys. Rev.C34, 1270(1986. [7] D. Beavis, et al., Phys. Rev. 34(1986. [8] S. Z. Belenkij and L.D. Landau, ssp fiz-nauk, 56, 309(1955. [9] Meny Ta- Chung, Institute fur theroretische Physik der Freien university Berlin Report Fub, HEP (1976. [10] Y. Alek et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 41,849(1978. [11] J.P. Varg. Phys.Rev. Lett. 40,295(1978. [12] V. S. Barashenkov, V.A. Belyakov, Van-shu-Fen: Communication of JINR PI- 331, Dubna (1959. [13] F. C. Powell, H.F. Fowler and H. D. perkin. The study of Elementary particles by the pohotgraphic Method, pergamon press London, New York, Paris, Los Angles, 1958 P.474. [14] H. Barkas, Nuclear Research Emulsion, Vol.1, Technique and Theary, Acadeimic press Inc.,1963. [15] V. V. Uzhiniskii and A. S. Pak, physics of Atomic Nuclei, Vol59,No.6(1996. [16] Kawrakow, I. Mohring, H. J. and Ranft, J. Z. phys. C56, 115(1992. [17] A. El-Naghy, S. A. H. Abou-Steit, S. S. Abdel-Aziz, and A. M. El-Shimy, Proceeding of ICRC2001,1342(c Copernicus Gesellschaft [18] Jaya Roy, N.Pys.A489 ( [19] I.OTTERLUND and E.STENLUND, N.Pys.B142 ( [20] M. I. Adamovich et al., Preprint JINR E , Dubna (1977. [21] A.EL Naghy and V. D. Toneev, Z. Physik A-Atoms and Nuclei 298, 55-59(1980. [22] N. N. Abd-Allah, Physica scripta (1993. [23] K. D. Tolestov: JINR Dubna, EL (1980. [24] K.D. Tolestov: JINR Dubna PI-8662(1975. [25] S. N. Vernov, et al., Yad. Fiz 28, 1021(1978. [26] A. Abd ELDaiem, M. Abdo Khalifa and A. Abdel-hafiez, Journal of Modern Physics, (2011.
Projectile Fragmentation of relativistic nuclei in peripheral Collisions
 Projectile Fragmentation of relativistic nuclei in peripheral Collisions Swarnapratim Bhattacharyya 1, Maria Haiduc 2, Alina Tania Neagu 2 and Elena Firu 2 1 Department of Physics, New Alipore College,
Projectile Fragmentation of relativistic nuclei in peripheral Collisions Swarnapratim Bhattacharyya 1, Maria Haiduc 2, Alina Tania Neagu 2 and Elena Firu 2 1 Department of Physics, New Alipore College,
arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [nucl-ex] 1 Dec 2007](/thumbs/74/69624022.jpg) Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
Multiplicity and angular distribution of particles emitted in relativistic nuclear-nuclear interactions M. K. Suleymanov1, 2, E. U. Khan 1, A Kravchakova 3, Mahnaz Q. Haseeb 1,S. M. Saleem 1, Y. H. Huseynaliyev
Characteristics study of projectile s lightest fragment for
 1 Characteristics study of projectile s lightest fragment for 84 Kr 36 - emulsion interaction at around 1 A GeV N. Marimuthu 1, 2, V. Singh 1 *, S. S. R. Inbanathan 2 1 High Energy Physics laboratory,
1 Characteristics study of projectile s lightest fragment for 84 Kr 36 - emulsion interaction at around 1 A GeV N. Marimuthu 1, 2, V. Singh 1 *, S. S. R. Inbanathan 2 1 High Energy Physics laboratory,
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION. A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal. and. the Kr Collaboration
 AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION FUNCTIONS AS A PROBE FOR COLLECTIVE MOTION A.Kravcakova, S.Vokal and the Kr Collaboration (Dubna, Kosice, Lund, Moscow, Tashkent, Varanasi) Faculty of Science, P.J. Safarik University,
Multiplicity Characteristics of Fragments Produced in 4.5A GeV/c
 Multiplicity Characteristics of Fragments Produced in 4.5A GeV/c Mg Emulsion Interaction A. Adelsalam, E. A. Shaat, Z. Aou Moussa, B. M. Badawy (1), and Z. S. Mater Physics Department, Faculty of Science,
Multiplicity Characteristics of Fragments Produced in 4.5A GeV/c Mg Emulsion Interaction A. Adelsalam, E. A. Shaat, Z. Aou Moussa, B. M. Badawy (1), and Z. S. Mater Physics Department, Faculty of Science,
Emission of Helium Nuclei in Relativistic Proton Interactions Leading to Total Break up of Ag and Br Nuclei. Z.Physik A 279, 407 (1976).
 Emission of Helium Nuclei in Relativistic Proton Interactions Leading to Total Break up of Ag and Br Nuclei. Z.Physik A 279, 407 (1976). Inelastic Interactions of 69.0 GeV/c Protons with Emulsion Nuclei.
Emission of Helium Nuclei in Relativistic Proton Interactions Leading to Total Break up of Ag and Br Nuclei. Z.Physik A 279, 407 (1976). Inelastic Interactions of 69.0 GeV/c Protons with Emulsion Nuclei.
Scaling of multiplicity distribution in high energy hadron-nucleus interactions
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep.-Oct. 2014), PP 15-19 Scaling of multiplicity distribution in high energy hadron-nucleus interactions Tufail
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep.-Oct. 2014), PP 15-19 Scaling of multiplicity distribution in high energy hadron-nucleus interactions Tufail
Comparison of experimental and theoretical results to define centrality of heavy ion collisions. 1. Introduction.
 Oral talk for the 24 th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids (ICNTS) Bologna, Italy, 0-05 September 2008 and submitted in Radiation Measurements with Manuscript Number: RADMEAS-D-08-00227R
Oral talk for the 24 th International Conference on Nuclear Tracks in Solids (ICNTS) Bologna, Italy, 0-05 September 2008 and submitted in Radiation Measurements with Manuscript Number: RADMEAS-D-08-00227R
Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and
 Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and 12 C+ 181 Ta Collisions at 4.2 GeV/c per Nucleon* Kh. K. Olimov 1),2) **, Sayyed A. Hadi 3) 1) *** and Mahnaz Q. Haseeb Abstract
Centrality Dependence of Rapidity Spectra of Negative Pions in 12 C+ 12 C and 12 C+ 181 Ta Collisions at 4.2 GeV/c per Nucleon* Kh. K. Olimov 1),2) **, Sayyed A. Hadi 3) 1) *** and Mahnaz Q. Haseeb Abstract
Characteristics of compound multiplicity in hadron-nucleus collisions
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 48, December 2010, pp. 855-859 Characteristics of compound multiplicity in hadron-nucleus collisions Tufail Ahmad 1 *, Nazeer Ahmad 2, Shaeel Ahmad 2 & M Zafar
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 48, December 2010, pp. 855-859 Characteristics of compound multiplicity in hadron-nucleus collisions Tufail Ahmad 1 *, Nazeer Ahmad 2, Shaeel Ahmad 2 & M Zafar
What is Spallation???
 What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
What is Spallation??? Definition found in Nuclear Physics Academic press: projectile (p, n, π,...) target Spallation---a type of nuclear reaction in which the high-energy level of incident particles causes
STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI
 STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI M. Ajaz 1, 2, M. K. Suleymanov 2, 3, K. H. Khan 2, A. Zaman 2, H. Younis 2, A. Rahman 4 1 Department of Physics, Abdul Wali Khan
STUDY OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTONS USING INTERACTIONS OF LIGHT NUCLEI M. Ajaz 1, 2, M. K. Suleymanov 2, 3, K. H. Khan 2, A. Zaman 2, H. Younis 2, A. Rahman 4 1 Department of Physics, Abdul Wali Khan
Simulated nucleon nucleon and nucleon nucleus reactions in the frame of the cascade exciton model at high and intermediate energies
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 84, No. 4 journal of April 2015 physics pp. 581 590 Simulated nucleon nucleon and nucleon nucleus reactions in the frame of the cascade exciton model at high and
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 84, No. 4 journal of April 2015 physics pp. 581 590 Simulated nucleon nucleon and nucleon nucleus reactions in the frame of the cascade exciton model at high and
AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION AND COLLECTIVE BEHAVIOR IN NUCLEUS NUCLEUS COLLISIONS
 ЯДЕРНАЯ ФИЗИКА, 15, том 78, 3-4, с. 1 1 ЯДРА AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION AND COLLECTIVE BEHAVIOR IN NUCLEUS NUCLEUS COLLISIONS c 15 P. Mali 1), A. Mukhopadhyay 1)*, S. Sarkar 1), G. Singh 2) Received August
ЯДЕРНАЯ ФИЗИКА, 15, том 78, 3-4, с. 1 1 ЯДРА AZIMUTHAL CORRELATION AND COLLECTIVE BEHAVIOR IN NUCLEUS NUCLEUS COLLISIONS c 15 P. Mali 1), A. Mukhopadhyay 1)*, S. Sarkar 1), G. Singh 2) Received August
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5564/pmas.v54i4.619 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES Ts.Baatar, R.Togoo, G.Sharkhuu, B.Otgongerel Institute
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5564/pmas.v54i4.619 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SECONDARY PARTICLES FROM INTERACTIONS AT 40 GeV/c IN DIFFERENT NUCLEAR MATTER PHASES Ts.Baatar, R.Togoo, G.Sharkhuu, B.Otgongerel Institute
Two Source Emission Behavior of Helium Projectile Fragments in 84 Kr Interactions at Around 1 GeV per nucleon
 Physics International 1 (): 109-115, 010 ISSN 1948-9803 010 Science Publications Two Source Emission Behavior of Helium Projectile Fragments in 84 Kr Interactions at Around 1 GeV per nucleon 1, Manoj Kumar
Physics International 1 (): 109-115, 010 ISSN 1948-9803 010 Science Publications Two Source Emission Behavior of Helium Projectile Fragments in 84 Kr Interactions at Around 1 GeV per nucleon 1, Manoj Kumar
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)042
 Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
Multifragmentation of nuclei by photons: new approaches and results Institute for Nuclear Research RAS Prospect 60-let Octabra, 7A, 117312 Moscow, Russia E-mail: vladimir@cpc.inr.ac.ru A review on multifragmentation
A Comparative Study of Multiplicity Scaling in Nuclear Collisions at High Energies
 A Comparative Study of Multiplicity Scaling in Nuclear Collisions at High Energies N. AHMAD S. S. ALI M. MOHSIN KHAN Department of Applied Physics Z.H. College of Engineering & Technology, S. A. DAR Abstract:
A Comparative Study of Multiplicity Scaling in Nuclear Collisions at High Energies N. AHMAD S. S. ALI M. MOHSIN KHAN Department of Applied Physics Z.H. College of Engineering & Technology, S. A. DAR Abstract:
Emission Characteristics of the Projectile Fragments at Relativistic Energy
 Emission Characteristics of the Projectile Fragments at Relativistic Energy M. K. Singh* 1, A. K. Soma 2, Ramji Pathak 1 and V. Singh 2 1. Department of physics, Tilakdhari Postgraduate College, Jaunpur
Emission Characteristics of the Projectile Fragments at Relativistic Energy M. K. Singh* 1, A. K. Soma 2, Ramji Pathak 1 and V. Singh 2 1. Department of physics, Tilakdhari Postgraduate College, Jaunpur
AZIMUTHAL DEPENDENCE OF TWO-PION CORRELATIONS IN RELATIVISTIC HEAVY-ION INTERACTIONS. DIPAK GHOSH, ARGHA DEB, ASOK KUMAR MALLICK and RANJAN SENGUPTA
 ISSN 330 006 CODEN FIZBE7 AZIMUTHAL DEPENDENCE OF TWO-PION CORRELATIONS IN RELATIVISTIC HEAVY-ION INTERACTIONS DIPAK GHOSH, ARGHA DEB, ASOK KUMAR MALLICK and RANJAN SENGUPTA High Energy Physics Division,
ISSN 330 006 CODEN FIZBE7 AZIMUTHAL DEPENDENCE OF TWO-PION CORRELATIONS IN RELATIVISTIC HEAVY-ION INTERACTIONS DIPAK GHOSH, ARGHA DEB, ASOK KUMAR MALLICK and RANJAN SENGUPTA High Energy Physics Division,
Research Article Shower and Slow Particle Productions in Nucleus-Nucleus Collisions at High Energy
 Advances in High Energy Physics, Article ID 4354, 12 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/4354 Research Article Shower and Slow Particle Productions in Nucleus-Nucleus Collisions at High Energy S. Fakhraddin,
Advances in High Energy Physics, Article ID 4354, 12 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/4354 Research Article Shower and Slow Particle Productions in Nucleus-Nucleus Collisions at High Energy S. Fakhraddin,
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)072
 Cumulative protons in hadron-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus interactions E-mail: yuldashev@jinr.ru E.Kh. Bazarov S.L. Lutpullaev K. Olimov E-mail: olimov@uzsci.net V.I. Petrov New experimental data on the
Cumulative protons in hadron-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus interactions E-mail: yuldashev@jinr.ru E.Kh. Bazarov S.L. Lutpullaev K. Olimov E-mail: olimov@uzsci.net V.I. Petrov New experimental data on the
Benchmarking the CEM03.03 event generator
 Vienna meeting on inter-comparison of spallation reactions models Benchmarking the CEM03.03 event generator K. K. Gudima 1, M. I. Baznat 1 S. G. Mashnik 2, and A. J. Sierk 2 1 Institute of Applied Physics,
Vienna meeting on inter-comparison of spallation reactions models Benchmarking the CEM03.03 event generator K. K. Gudima 1, M. I. Baznat 1 S. G. Mashnik 2, and A. J. Sierk 2 1 Institute of Applied Physics,
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ MeV, 4 T 8 MeV
 Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Dedicated Arrays: MEDEA GDR studies (E γ = 10-25 MeV) Highly excited CN E*~ 250-350 MeV, 4 T 8 MeV γ-ray spectrum intermediate energy region 10 MeV/A E beam 100 MeV/A - large variety of emitted particles
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter
 Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION MODELS IN GEANT4
 Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and Monte Carlo (SNA + MC) Hitotsubashi Memorial Hall, Tokyo, Japan, October -, INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION
Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications and Monte Carlo (SNA + MC) Hitotsubashi Memorial Hall, Tokyo, Japan, October -, INCL INTRA-NUCLEAR CASCADE AND ABLA DE-EXCITATION
Estimation of Impact Parameter on event-byevent basis in Nuclear Emulsion Detector
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224944598 Estimation of Impact Parameter on event-byevent basis in Nuclear Emulsion Detector
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224944598 Estimation of Impact Parameter on event-byevent basis in Nuclear Emulsion Detector
Hadronic Showers. KIP Journal Club: Calorimetry and Jets 2009/10/28 A.Kaplan & A.Tadday
 Hadronic Showers KIP Journal Club: Calorimetry and Jets 2009/10/28 A.Kaplan & A.Tadday Hadronic Showers em + strong interaction with absorber similarities to em-showers, but much more complex different
Hadronic Showers KIP Journal Club: Calorimetry and Jets 2009/10/28 A.Kaplan & A.Tadday Hadronic Showers em + strong interaction with absorber similarities to em-showers, but much more complex different
Analysis of various projectile interactions with Nuclear Emulsion Detector nuclei at ~ 1 GeV per nucleon using Coulomb modified Glauber model
 Analysis of various projectile interactions with Nuclear Emulsion Detector nuclei at ~ 1 GeV per nucleon using Coulomb modified Glauber model N. Marimuthu 1,, V. Singh 1 *, S. S. R. Inbanathan * 1 Department
Analysis of various projectile interactions with Nuclear Emulsion Detector nuclei at ~ 1 GeV per nucleon using Coulomb modified Glauber model N. Marimuthu 1,, V. Singh 1 *, S. S. R. Inbanathan * 1 Department
Validation of Geant4 Hadronic Physics Models at Intermediate Energies. Outline
 Models at Intermediate Energies Outline Motivation Models Data Used Validation Results Summary CHEP 2009 Prague, March 23-27, 2009 Sunanda Banerjee, Fermilab (on behalf of Geant4 Hadronic Group) Motivation
Models at Intermediate Energies Outline Motivation Models Data Used Validation Results Summary CHEP 2009 Prague, March 23-27, 2009 Sunanda Banerjee, Fermilab (on behalf of Geant4 Hadronic Group) Motivation
* On leave from FLNR / JINR, Dubna
 * On leave from FLNR / JINR, Dubna 1 Introduction: Keywords of this experimental program Search for new isotopes The limits of nuclear stability provide a key benchmark of nuclear models The context of
* On leave from FLNR / JINR, Dubna 1 Introduction: Keywords of this experimental program Search for new isotopes The limits of nuclear stability provide a key benchmark of nuclear models The context of
Rapid change of multiplicity fluctuations in system size dependence at SPS energies
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper Rapid change of multiplicity fluctuations in system size dependence at SPS energies Andrey Seryakov for
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper Rapid change of multiplicity fluctuations in system size dependence at SPS energies Andrey Seryakov for
Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector
 Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector Martin Spousta for the ATLAS Collaboration Charles University in Prague DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3204/desy-proc-2014-04/275 Measurements of soft and hard
Proton-lead measurements using the ATLAS detector Martin Spousta for the ATLAS Collaboration Charles University in Prague DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3204/desy-proc-2014-04/275 Measurements of soft and hard
Partonic transport simulations of jet quenching
 Partonic transport simulations of jet quenching Z. Xu, C. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik J. W. Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt Outline motivation introduction to the model simulations of Au+Au
Partonic transport simulations of jet quenching Z. Xu, C. Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik J. W. Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt Outline motivation introduction to the model simulations of Au+Au
Lecture 12: Hydrodynamics in heavy ion collisions. Elliptic flow Last lecture we learned:
 Lecture 12: Hydrodynamics in heavy ion collisions. Elliptic flow Last lecture we learned: Particle spectral shapes in thermal model ( static medium) are exponential in m T with common slope for all particles.
Lecture 12: Hydrodynamics in heavy ion collisions. Elliptic flow Last lecture we learned: Particle spectral shapes in thermal model ( static medium) are exponential in m T with common slope for all particles.
CUMULATIVE PARTICLE PRODUCTION IN FERMILAB EXPERIMENT E665*
 SLAC-PUB-5291 June 1990 E CUMULATIVE PARTICLE PRODUCTION IN FERMILAB EXPERIMENT E665* S. Shuvalov Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford, California 94309 and Institute of Theoretical
SLAC-PUB-5291 June 1990 E CUMULATIVE PARTICLE PRODUCTION IN FERMILAB EXPERIMENT E665* S. Shuvalov Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University, Stanford, California 94309 and Institute of Theoretical
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei
 Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
Searching for high-spin toroidal isomers in collisions induced by α-conjugate nuclei X.G. Cao, K. Schmidt, E.-J. Kim, K. Hagel, M. Barbui, J. Gauthier, M. Huang, J.B. Natowitz, R. Wada, S. Wuenschel, G.Q.
PoS(DIS2017)208. Nuclear PDF studies with proton-lead measurements with the ALICE detector
 Nuclear PDF studies with proton-lead measurements with the ALICE detector a,b for the ALICE Collaboration a Institute for Subatomic Physics, Department for Physics and Astronomy and EMMEφ, Faculty of Science,
Nuclear PDF studies with proton-lead measurements with the ALICE detector a,b for the ALICE Collaboration a Institute for Subatomic Physics, Department for Physics and Astronomy and EMMEφ, Faculty of Science,
Recent Developments in Geant4. Calice Collaboration Meeting 10 March 2010 Dennis Wright (on behalf of the Geant4 hadronic working group)
 Recent Developments in Geant4 Calice Collaboration Meeting 10 March 2010 Dennis Wright (on behalf of the Geant4 hadronic working group) Outline Geant4 and Calice Geant4 Validation Physics Lists and Simplified
Recent Developments in Geant4 Calice Collaboration Meeting 10 March 2010 Dennis Wright (on behalf of the Geant4 hadronic working group) Outline Geant4 and Calice Geant4 Validation Physics Lists and Simplified
Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions studied with INDRA Comparison with models
 EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
EPJ Web of Conferences 31, 00007 (2012) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 20123100007 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences - SIF, 2012 Characterization of quasi-projectiles produced in symmetric collisions
The discovery of the antiproton and other antimatter,
 4 Antibaryons The discovery of the antiproton and other antimatter, 1955 1959 While the existence of antiparticles was established with Anderson s discovery of the positron in 1932, it was not clear in
4 Antibaryons The discovery of the antiproton and other antimatter, 1955 1959 While the existence of antiparticles was established with Anderson s discovery of the positron in 1932, it was not clear in
SHOWER PARTICLE MULTIPLICITY DISTRIBUTIONS FOR COLLISIONS OF GEV/C PROTONS WITH EMULSION UDC S. Drndarević, G. Škoro, D.
 UNIVERSITY OF NIŠ The scientific journal FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Physics, Chemistry and Technology Vol. 2, No 1, 1999 pp. 39-45 Editor of series: Momčilo Pejović, e-mail: pejovic@elfak.ni.ac.yu Address:
UNIVERSITY OF NIŠ The scientific journal FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Physics, Chemistry and Technology Vol. 2, No 1, 1999 pp. 39-45 Editor of series: Momčilo Pejović, e-mail: pejovic@elfak.ni.ac.yu Address:
Noncentral collisions
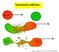 Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
Noncentral collisions Projectile Target QT E* MRS QP E* MRS: L. Gingras et al., Phys. Rev. C 65, 061604(2002) Noncentral collisions The IVS source Velocity distributions (LAB) for the 40 Ca + 40 Ca reaction
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 9 May 1996
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, arxiv:nucl-th/9605014v1
p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
 Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
Phys. Rev. C (Aug., 1996) in press. p t dependence of transverse flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions Bao-An Li, C.M. Ko and G.Q. Li Cyclotron Institute and Physics Department, Texas A&M University,
PHASE TRANSITIONS. A. Budzanowski
 PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
PHASE TRANSITIONS A. Budzanowski The H. Niewodniczański Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Radzikowskiego 152, 31-342 Kraków, Poland and V.A. Karnaukhov, H. Oeschler S.P. Avdeyev,
arxiv:nucl-th/ v1 2 Jun 2003
 CHEP 2003, La Jolla, California, USA, March 24-28 2003 1 Bertini intra-nuclear cascade implementation in Geant4 Aatos Heikkinen, Nikita Stepanov Helsinki Institute of Physics, P.O. Box 64, FIN-00014 University
CHEP 2003, La Jolla, California, USA, March 24-28 2003 1 Bertini intra-nuclear cascade implementation in Geant4 Aatos Heikkinen, Nikita Stepanov Helsinki Institute of Physics, P.O. Box 64, FIN-00014 University
SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY
 Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program
 Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Strange Hadron Production from STAR Fixed-Target Program (for the STAR Collaboration) Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 84, China E-mail: musman_mughal@yahoo.com We report
Systematic study of multiparticle production in nucleus nucleus interactions at 14.6 A GeV
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 81, No. 1 journal of July 2013 physics pp. 103 115 Systematic study of multiparticle production in nucleus nucleus interactions at 14.6 A GeV ASHWINI KUMAR 1,,
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 81, No. 1 journal of July 2013 physics pp. 103 115 Systematic study of multiparticle production in nucleus nucleus interactions at 14.6 A GeV ASHWINI KUMAR 1,,
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation
 Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
Nuclear Alpha-Particle Condensation 40 Ca+ 12 C, 25 AMeV with CHIMERA First experimental evidence of alpha-particle condensation for the Hoyle state Ad. R. Raduta, B.Borderie, N. Le Neindre, E. Geraci,
Recent Results from RHIC: On the trail of the Quark-Gluon Plasma
 Recent Results from RHIC: On the trail of the Quark-Gluon Plasma Single Au+Au Collision seen by STAR@RHIC Gunther Roland Gunther Roland/MIT July 15 2003 MPI Munich 15/7/2003 Gunther Roland/MIT www.spiegel.de
Recent Results from RHIC: On the trail of the Quark-Gluon Plasma Single Au+Au Collision seen by STAR@RHIC Gunther Roland Gunther Roland/MIT July 15 2003 MPI Munich 15/7/2003 Gunther Roland/MIT www.spiegel.de
O WILEY- MODERN NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY. WALTER D. LOVELAND Oregon State University. DAVID J. MORRISSEY Michigan State University
 MODERN NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY WALTER D. LOVELAND Oregon State University DAVID J. MORRISSEY Michigan State University GLENN T. SEABORG University of California, Berkeley O WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY &
MODERN NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY WALTER D. LOVELAND Oregon State University DAVID J. MORRISSEY Michigan State University GLENN T. SEABORG University of California, Berkeley O WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY &
arxiv:nucl-ex/ v1 10 May 2004
 arxiv:nucl-ex/0405004v1 10 May 2004 Proc. 20th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (2003) 000 000 Anisotropic flow at RHIC A. H. Tang 1 for the STAR Collaboration 1 NIKHEF and Brookhaven National Lab,
arxiv:nucl-ex/0405004v1 10 May 2004 Proc. 20th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics (2003) 000 000 Anisotropic flow at RHIC A. H. Tang 1 for the STAR Collaboration 1 NIKHEF and Brookhaven National Lab,
Nuclear Reactions A Z. Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q > 0. Exothermic Endothermic
 Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
High-p T Neutral Pion Production in Heavy Ion Collisions at SPS and RHIC
 High- Neutral Pion Production in Heavy Ion Collisions at SPS and RHIC K. Reygers for the WA98 and the PHENIX collaboration Institut für Kernphysik der Universität Münster Wilhelm-Klemm-Str. 9, D-4849 Münster,
High- Neutral Pion Production in Heavy Ion Collisions at SPS and RHIC K. Reygers for the WA98 and the PHENIX collaboration Institut für Kernphysik der Universität Münster Wilhelm-Klemm-Str. 9, D-4849 Münster,
An Analysis of Energy Dependence Parameter as Mean Charged Multiplicity for Proton-Antiproton Interactions
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 6 (June-2014) pp. 132-140 www.ijcrar.com An Analysis of Energy Dependence Parameter as Mean Charged Multiplicity for Proton-Antiproton Interactions Hardik P.Trivedi 1 and
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 6 (June-2014) pp. 132-140 www.ijcrar.com An Analysis of Energy Dependence Parameter as Mean Charged Multiplicity for Proton-Antiproton Interactions Hardik P.Trivedi 1 and
Ring like correlation in relativistic heavy ion collision: an experimental probe using continuous wavelet transform approach
 Ring like correlation in relativistic heavy ion collision: an experimental proe using continuous wavelet transform approach Gopa Bhoumik, Argha De, Swarnapratim Bhattacharyya * and Dipak Ghosh Nuclear
Ring like correlation in relativistic heavy ion collision: an experimental proe using continuous wavelet transform approach Gopa Bhoumik, Argha De, Swarnapratim Bhattacharyya * and Dipak Ghosh Nuclear
2. HEAVY QUARK PRODUCTION
 2. HEAVY QUARK PRODUCTION In this chapter a brief overview of the theoretical and experimental knowledge of heavy quark production is given. In particular the production of open beauty and J/ψ in hadronic
2. HEAVY QUARK PRODUCTION In this chapter a brief overview of the theoretical and experimental knowledge of heavy quark production is given. In particular the production of open beauty and J/ψ in hadronic
Year- 1 (Heavy- Ion) Physics with CMS at the LHC
 Year- 1 (Heavy- Ion) Physics with CMS at the LHC Edwin Norbeck and Yasar Onel (for the CMS collaboration) University of Iowa For the 26 th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics Ocho Rios, Jamaica 8 January
Year- 1 (Heavy- Ion) Physics with CMS at the LHC Edwin Norbeck and Yasar Onel (for the CMS collaboration) University of Iowa For the 26 th Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics Ocho Rios, Jamaica 8 January
Hadronic Physics I. University of Pennsylvania Geant4 Tutorial 17 May 2011 Dennis Wright. Geant4 V9.4
 Hadronic Physics I University of Pennsylvania Geant4 Tutorial 17 May 2011 Dennis Wright Geant4 V9.4 Outline Overview of hadronic physics processes, cross sections, models hadronic framework and organization
Hadronic Physics I University of Pennsylvania Geant4 Tutorial 17 May 2011 Dennis Wright Geant4 V9.4 Outline Overview of hadronic physics processes, cross sections, models hadronic framework and organization
Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams
 Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 25, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 26) March 25, 2011 1 / 35 Outline 1 Energy
Spallation, multifragmentation and radioactive beams Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 25, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 26) March 25, 2011 1 / 35 Outline 1 Energy
acta physica slovaca vol. 54 No. 4, August 2004 STUDIES OF LIGHT NUCLEUS CLUSTERING IN RELATIVISTIC MULTIFRAGMENTATION PROCESSES
 acta physica slovaca vol. 54 No. 4, 351 365 August 2004 STUDIES OF LIGHT NUCLEUS CLUSTERING IN RELATIVISTIC MULTIFRAGMENTATION PROCESSES V. Bradnová a, M.M. Chernyavsky b, A.Sh. Gaitinov c, L.A. Goncharova
acta physica slovaca vol. 54 No. 4, 351 365 August 2004 STUDIES OF LIGHT NUCLEUS CLUSTERING IN RELATIVISTIC MULTIFRAGMENTATION PROCESSES V. Bradnová a, M.M. Chernyavsky b, A.Sh. Gaitinov c, L.A. Goncharova
Stars Nuclei Baryons Quarks. STRANGENESS IN NUCLEI UNIQUE OPPORTUNITIES at FAIR Josef Pochodzalla
 Stars Nuclei Baryons Quarks STRANGENESS IN NUCLEI UNIQUE OPPORTUNITIES at FAIR Josef Pochodzalla Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research GSI, Darmstadt heavy ion physics nuclear structure atomic and plasma
Stars Nuclei Baryons Quarks STRANGENESS IN NUCLEI UNIQUE OPPORTUNITIES at FAIR Josef Pochodzalla Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research GSI, Darmstadt heavy ion physics nuclear structure atomic and plasma
The experiment at JINR: status and physics program
 The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
The 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and Astrophysics Volume 2018 Conference Paper The BM@N experiment at JINR: status and physics program D. Baranov, M. Kapishin, T. Mamontova, G. Pokatashkin,
Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment
 Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2015, 03A104 (15 pages) DOI: 10.1093/ptep/ptu069 PHYSICS at PHENIX, 15 years of discoveries Soft physics results from the PHENIX experiment ShinIchi Esumi, Institute of Physics,
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact
 Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Nuclear contribution into single-event upset in 3D on-board electronics at moderate energy cosmic proton impact N. G. Chechenin, T. V. Chuvilskaya and A. A. Shirokova Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics,
Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions
 Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Universita di Torino and INFN Torino * The selection criteria of the results presented here are (to some
Overview* of experimental results in heavy ion collisions Dipartimento di Fisica Sperimentale dell Universita di Torino and INFN Torino * The selection criteria of the results presented here are (to some
Correlations and fluctuations in p+p and Be+Be at the SPS energies from NA61/SHINE
 Correlations and fluctuations in p+p and Be+Be at the SPS energies from NA61/SHINE Andrey Seryakov 1,a, for the NA61/SHINE Collaboration 1 Saint Petersburg State University, ul. Ulyanovskaya 1, 198504,
Correlations and fluctuations in p+p and Be+Be at the SPS energies from NA61/SHINE Andrey Seryakov 1,a, for the NA61/SHINE Collaboration 1 Saint Petersburg State University, ul. Ulyanovskaya 1, 198504,
Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN. = GeV at RHIC
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Azimuthal anisotropy of the identified charged hadrons in Au+Au collisions at S NN = 39-200 GeV at RHIC To cite this article: S S Vdovkina 2017 J.
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 21 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 21 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 21 Nov 2018](/thumbs/90/104335598.jpg) arxiv:8.0889v [nucl-th] 2 Nov 208 Strongly intensive fluctuations and correlations in ultrarelativistic nuclear collisions in the model with string fusion Vladimir Kovalenko, Saint Petersburg State University
arxiv:8.0889v [nucl-th] 2 Nov 208 Strongly intensive fluctuations and correlations in ultrarelativistic nuclear collisions in the model with string fusion Vladimir Kovalenko, Saint Petersburg State University
COMPARISONS AMONG THE HADRON PRODUCTION IN ULTRA RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS IN DIFFERENT TRANSVERSE MOMENTUM RANGES. PRELIMINARY RESULTS *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 67, No. 3, P. 831 836, 2015 COMPARISONS AMONG THE HADRON PRODUCTION IN ULTRA RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS IN DIFFERENT TRANSVERSE MOMENTUM RANGES. PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 67, No. 3, P. 831 836, 2015 COMPARISONS AMONG THE HADRON PRODUCTION IN ULTRA RELATIVISTIC HEAVY ION COLLISIONS IN DIFFERENT TRANSVERSE MOMENTUM RANGES. PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Scaling between K+ and proton production in nucleus-nucleus collisions *
 Proc. Quark Matter 95 Monterey, CA January 9-, 9 9 5 I BNL-6 55 Scaling between K+ and proton production in nucleus-nucleus collisions * Ziping Chen and Chellis Chasman Dept. of Physics, Brookhaven National
Proc. Quark Matter 95 Monterey, CA January 9-, 9 9 5 I BNL-6 55 Scaling between K+ and proton production in nucleus-nucleus collisions * Ziping Chen and Chellis Chasman Dept. of Physics, Brookhaven National
Chapter 2 Radiation-Matter Interactions
 Chapter 2 Radiation-Matter Interactions The behavior of radiation and matter as a function of energy governs the degradation of astrophysical information along the path and the characteristics of the detectors.
Chapter 2 Radiation-Matter Interactions The behavior of radiation and matter as a function of energy governs the degradation of astrophysical information along the path and the characteristics of the detectors.
Heavy Ion Interactions. Beginners FLUKA Course
 Heavy Ion Interactions Beginners FLUKA Course 1 Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
Heavy Ion Interactions Beginners FLUKA Course 1 Overview The models DPMJET RQMD BME Input options Beam definition Transport thresholds 2 Heavy ion interaction models in FLUKA - 1 E > 5 GeV/n Dual Parton
Recent Developments in Geant4 Hadronic Physics
 Recent Developments in Geant4 Hadronic Physics Dennis Wright (SLAC) 1 st Geant4 Australian School Recently Released Many new features added in Geant4 9.4 (December 2010) and patch 9.4 p01 2 Energy/Momentum
Recent Developments in Geant4 Hadronic Physics Dennis Wright (SLAC) 1 st Geant4 Australian School Recently Released Many new features added in Geant4 9.4 (December 2010) and patch 9.4 p01 2 Energy/Momentum
Electromagnetic and hadronic showers development. G. Gaudio, M. Livan The Art of Calorimetry Lecture II
 Electromagnetic and hadronic showers development 1 G. Gaudio, M. Livan The Art of Calorimetry Lecture II Summary (Z dependence) Z Z 4 5 Z(Z + 1) Z Z(Z + 1) 2 A simple shower 3 Electromagnetic Showers Differences
Electromagnetic and hadronic showers development 1 G. Gaudio, M. Livan The Art of Calorimetry Lecture II Summary (Z dependence) Z Z 4 5 Z(Z + 1) Z Z(Z + 1) 2 A simple shower 3 Electromagnetic Showers Differences
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 7 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 7 Jul 2015 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 7 Jul 2015](/thumbs/72/67518689.jpg) arxiv:1507.01916v1 [hep-ph] 7 Jul 2015 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa, 50011, USA E-mail: tuchin@iastate.edu An essential part of experimental program at the future
arxiv:1507.01916v1 [hep-ph] 7 Jul 2015 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa, 50011, USA E-mail: tuchin@iastate.edu An essential part of experimental program at the future
Measurement of Charged Particle Spectra in Deep-Inelastic ep Scattering at HERA
 Measurement of Charged Particle Spectra in Deep-Inelastic ep Scattering at HERA Alexander BYLINKIN ( Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Moscow, Russia) E-mail: alexander.bylinkin@gmail.com
Measurement of Charged Particle Spectra in Deep-Inelastic ep Scattering at HERA Alexander BYLINKIN ( Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Moscow, Russia) E-mail: alexander.bylinkin@gmail.com
FRAGMENTATION OF RELATIVISTIC NUCLEI IN PERIPHERAL INTERACTIONS IN NUCLEAR TRACK EMULSION
 ЯДЕРНАЯ ФИЗИКА, 2008, том 71, 9, с. 1595 1601 ЭЛЕМЕНТАРНЫЕ ЧАСТИЦЫ И ПОЛЯ FRAGMENTATION OF RELATISTIC NUCLEI IN PERIPERAL INTERACTIONS IN NUCLEAR TRACK EMULSION c 2008 D. A. Artemenkov 1)*, V. Bradnova
ЯДЕРНАЯ ФИЗИКА, 2008, том 71, 9, с. 1595 1601 ЭЛЕМЕНТАРНЫЕ ЧАСТИЦЫ И ПОЛЯ FRAGMENTATION OF RELATISTIC NUCLEI IN PERIPERAL INTERACTIONS IN NUCLEAR TRACK EMULSION c 2008 D. A. Artemenkov 1)*, V. Bradnova
Introduction to Relativistic Heavy Ion Physics
 1 Introduction to Relativistic Heavy Ion Physics Lecture 2: Experimental Discoveries Columbia University Reminder- From Lecture 1 2 General arguments suggest that for temperatures T ~ 200 MeV, nuclear
1 Introduction to Relativistic Heavy Ion Physics Lecture 2: Experimental Discoveries Columbia University Reminder- From Lecture 1 2 General arguments suggest that for temperatures T ~ 200 MeV, nuclear
Compound and heavy-ion reactions
 Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Compound and heavy-ion reactions Introduction to Nuclear Science Simon Fraser University Spring 2011 NUCS 342 March 23, 2011 NUCS 342 (Lecture 24) March 23, 2011 1 / 32 Outline 1 Density of states in a
Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and Its Excitation Energy Dependence
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 751 756 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 5, May 15, 2004 Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 751 756 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 5, May 15, 2004 Effects of Isospin on Pre-scission Particle Multiplicity of Heavy Systems and
Neutron Interactions Part I. Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics Y2.5321
 Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI SIS-Pubblicazioni
 LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI SIS-Pubblicazioni LNF-06/22 (P) 29 August 2006 HADRON PROPERTIES IN THE NUCLEAR MEDIUM THE PANDA PROGRAM WITH pa REACTIONS Olaf N. Hartmann INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di
LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI FRASCATI SIS-Pubblicazioni LNF-06/22 (P) 29 August 2006 HADRON PROPERTIES IN THE NUCLEAR MEDIUM THE PANDA PROGRAM WITH pa REACTIONS Olaf N. Hartmann INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di
nuclear states nuclear stability
 nuclear states 1 nuclear stability 2 1 nuclear chart 3 nuclear reactions Important concepts: projectile (A) target (B) residual nuclei (C+D) q-value of a reaction Notations for the reaction B(A,C)D A+B
nuclear states 1 nuclear stability 2 1 nuclear chart 3 nuclear reactions Important concepts: projectile (A) target (B) residual nuclei (C+D) q-value of a reaction Notations for the reaction B(A,C)D A+B
A Helium-3 polarimeter using electromagnetic interference. Nigel Buttimore
 A Helium-3 polarimeter using electromagnetic interference Nigel Buttimore Trinity College Dublin 12 September 2013 PSTP 2013 09 University of Virginia OUTLINE Need a source of polarized down quarks to
A Helium-3 polarimeter using electromagnetic interference Nigel Buttimore Trinity College Dublin 12 September 2013 PSTP 2013 09 University of Virginia OUTLINE Need a source of polarized down quarks to
String Parton Models in Geant4
 String Parton Models in Geant4 G.Folger, J.P.Wellisch CERN, CH-2 Geneva, Switzerland Dual parton or quark gluon string model are the by now almost standard theoretical techniques by which one can arrive
String Parton Models in Geant4 G.Folger, J.P.Wellisch CERN, CH-2 Geneva, Switzerland Dual parton or quark gluon string model are the by now almost standard theoretical techniques by which one can arrive
Energy scan with Be+Be collisions: cross-section, centrality determination, pion spectra and mean multiplicities
 : crosssection, centrality determination, pion spectra and mean multiplicities for the NA/SHINE collaboration Institute of Physics, University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland Email: emil.aleksander.kaptur@cern.ch
: crosssection, centrality determination, pion spectra and mean multiplicities for the NA/SHINE collaboration Institute of Physics, University of Silesia, Katowice, Poland Email: emil.aleksander.kaptur@cern.ch
arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [hep-ex] 18 May 2015](/thumbs/94/118739665.jpg) ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
ALICE summary of light flavour results at intermediate and high p arxiv:55.477v [hep-ex] 8 May 5 uva Richert, on behalf of the ALICE collaboration Lund University, Department of Physics, Div. of Particle
Average multiplicities of particles emitted in the h-a reactions
 Average multiplicities of particles emitted in the h-a reactions Aatos Heikkinen aatos.heikkinen@cern.ch Geant4 Hadronic Physics Working Group Meeting October 22, 2007 Group Meeting, October 22nd, 2007
Average multiplicities of particles emitted in the h-a reactions Aatos Heikkinen aatos.heikkinen@cern.ch Geant4 Hadronic Physics Working Group Meeting October 22, 2007 Group Meeting, October 22nd, 2007
An Analytical Approach is Developed to Estimate the Values of Range of Alpha Particles Emitted from Radon Gas
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 09 (September. 2014), V1 PP 51-55 www.iosrjen.org An Analytical Approach is Developed to Estimate the Values
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 09 (September. 2014), V1 PP 51-55 www.iosrjen.org An Analytical Approach is Developed to Estimate the Values
3-D Imaging and the Generalized Parton Distribution Program at an Electron Ion Collider
 Workshop on Precision Radiative Corrections for Next Generation Experiments 6 9 May 6, Jefferson Lab, Newport News VA 3-D Imaging and the Generalized Parton Distribution Program at an Electron Ion Collider
Workshop on Precision Radiative Corrections for Next Generation Experiments 6 9 May 6, Jefferson Lab, Newport News VA 3-D Imaging and the Generalized Parton Distribution Program at an Electron Ion Collider
Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV
 Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV Samantha G Brovko June 14, 2011 1 INTRODUCTION In ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions a partonic state of
Mapping the Nuclear Matter Phase Diagram with STAR: Au+Al at 2.8 AGeV and Au+Au at 19.6 GeV Samantha G Brovko June 14, 2011 1 INTRODUCTION In ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions a partonic state of
The Quark-Gluon Plasma and the ALICE Experiment
 The Quark-Gluon Plasma and the ALICE Experiment David Evans The University of Birmingham IoP Nuclear Physics Conference 7 th April 2009 David Evans IoP Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 1 Outline of Talk
The Quark-Gluon Plasma and the ALICE Experiment David Evans The University of Birmingham IoP Nuclear Physics Conference 7 th April 2009 David Evans IoP Nuclear Physics Conference 2009 1 Outline of Talk
The interaction of radiation with matter
 Basic Detection Techniques 2009-2010 http://www.astro.rug.nl/~peletier/detectiontechniques.html Detection of energetic particles and gamma rays The interaction of radiation with matter Peter Dendooven
Basic Detection Techniques 2009-2010 http://www.astro.rug.nl/~peletier/detectiontechniques.html Detection of energetic particles and gamma rays The interaction of radiation with matter Peter Dendooven
Heavy Ions at the LHC: Selected Predictions. Georg Wolschin. Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität, Heidelberg, Germany
 Heavy Ions at the LHC: Selected Predictions Georg Wolschin Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität, Heidelberg, Germany Heavy-ion collisions at relativistic energy have been investigated for many
Heavy Ions at the LHC: Selected Predictions Georg Wolschin Institut für Theoretische Physik der Universität, Heidelberg, Germany Heavy-ion collisions at relativistic energy have been investigated for many
Threshold Photo-production of J/5 Mesons J. Dunne Jefferson Lab
 hreshold Photo-production of J/5 Mesons J. Dunne Jefferson Lab Introduction With the advent of higher energies at Jefferson Lab, the study of charmonium becomes possible. he threshold production of J/5
hreshold Photo-production of J/5 Mesons J. Dunne Jefferson Lab Introduction With the advent of higher energies at Jefferson Lab, the study of charmonium becomes possible. he threshold production of J/5
PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE ENERGIES
 EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
EPJ Web of Conferences 66, 03068 (2014) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 2014 6603068 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014 PROTON-PROTON FEMTOSCOPY AND ACCESS TO DYNAMICAL SOURCES AT INTERMEDIATE
Charged Current Quasielastic Analysis from MINERνA
 Charged Current Quasielastic Analysis from MINERνA Anushree Ghosh CBPF - Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas F sicas, Rua Dr. Xavier Sigaud 150, Urca, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, 22290-180, Brazil on behalf
Charged Current Quasielastic Analysis from MINERνA Anushree Ghosh CBPF - Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas F sicas, Rua Dr. Xavier Sigaud 150, Urca, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, 22290-180, Brazil on behalf
