MIXED NEAREST NEIGHBOR DEGENERACY FOR PARTICLES ON A ONE-DIMENSIONAL LATTICE SPACE
|
|
|
- Phoebe Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MIXED NEAREST NEIGHBOR DEGENERACY FOR PARTICLES ON A ONE-DIMENSIONAL LATTICE SPACE R.B.MC OUISTAW University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Milwaukee, Wisconsin INTRODUCTION In a recent article [1] expressions were presented which describe exactly the number of independent ways of arranging q indistinguishable particles on a one-dimensional lattice space of N equivalent compartments, in such a way as to create 1. A7 n occupied nearest neighbor pairs. /7 00 vacant nearest neighbor pairs. The present paper is concerned with the degeneracy associated with n 0l, the number of mixed (one compartment empty, one occupied) nearest neighbor pairs. Ising [] has developed relationships which describe approximately the degeneracy associated with mixed nearest neighbor pairs. The purpose of the present paper is to develop an expression which describes exactly the degeneracy of arrangements containing a prescribed number of mixed nearest neighbor pairs.. CALCULATION To determine A(n 01, q, N), the number of independent arrangements arising when q particles are placed on a one-dimensional lattice space of N equivalent compartments in such a way as to create n ol mixed nearest neighfor pairs, we must consider the situations when n 0l is odd and when it is even. 1. n 0l odd When n 0l is odd, one and only one end compartment must be occupied. (See Fig. 1.) If the occupied end compartment is on the left-hand side we construct "units" consisting of a particle or of a contiguous group of particles and the adjacent vacancy just to the right then we observe that there are permutable "units." We initially regard these "units" as identical regardless of the number of particles [> 1) of which they are composed (see cross-hatched "units" in Fig. 1). These "units" can be permuted to form other independent arrangements having the same /7 01. There are N - q vacancies but not all of these vacancies can be permuted to form independent arrangements; there are -~ + 1 vacancies which form mixed nearest neighbor pairs. Thus there are N - q - f ~ 1 permutable vacancies and a total of N - q - 1 objects which can be permuted. These can be arranged in L _ - _ - _^J I - ^ - ^ ^ J l s i i Figure 1. Shown is an arrangement of q = 10 particles on a linear array of N = 19 equivalent compartments which creates n 01 = 9 mixed nearest neighbor pairs. There are (cross-hatched) and N - q - 1 /7 n i - 1 ) 4 permutable "units" = 4 permutable vacancies (marked with *'s). Thus there are a total of eight objects to be permuted while still keeping the left-hand compartment occupied. 353
2 354 MIXED NEAREST NEIGHBOR DEGENERACY FOR [NOV. N - q - \ \ / N - q - 1 \ The "units" are, of course, not identical; the particles may be arranged to form "units" consisting of various numbers of particles subject to the constraint that n 0l mixed nearest neighbor pairs must be present. To determine the number of ways the q particles can be arranged to form the ( - ^ J "units" we consider # - 1 lines which symbolize the separation of the q particles. (See Fig..) f - 1 r ) of these lines symbolize the separation of the particles by two mixed nearest neighbor pairs and q ( - ~ r ) lines symbolize the adjacency of two particles. These q - 1 lines, of which ( - ^ - r ) are one kind and the remainder another kind can be arranged in \n 0l - 1 \ Thus, if we require that the compartment on the left end of the array is occupied (and the end compartment on the right is empty) then there are independent arrangement possible. Of course the end compartment on the right could have been occupied (and the end compartment on the left empty) so that if n ol is odd we obtain fn-q-y\l q-1 \ (D A(n 0l,q,/V) = \ n 01-1 U o o o o ojo o o o o Figure. Figure considers the particular arrangement shown in Fig. 1. There are q - 1 = 9separations between 10 particles. Of these separations ( - ~ ] = 4 are separations which constitute two mixed nearest neighbor pairs (two short horizontal lines) and q ( - 1 J = 5 represent separations between occupied nearest neighbor pairs. The q separations may be arranged in f r J = 16 independent. n ox even When n 0l is even two situations can arise: (a) the compartments on each end of the array are empty (see Fig. 3) (b) both end compartments are occupied (see Fig. 4). For arrangements consistent with situation (a) there are always ( -~ \ "units," each of which consists of a particle or a contiguous group of particles together with a facancy (if one is needed) to separate a "unit" from other "units," i.e., to create a mixed nearest neighbor pair. As before we initially regard these "units" as identin cal regardless of their composition. There are N - q vacancies but not all of them are permutable; -^ of
3 1976] PARTICLES ON A OiE-DlIVIEWSIOWAL LATTICE SPACE 355 g Mxi» a- Figure 3. In this figure N - 19, g = I = 8 and both end compartments are empty. There are ("f ) "units" (cross-hatched) and N - q f-y 1 J =4 permutable vacancies (marked withx's) or a total of 8 objects which can be permited in ( J ) ways to form independent arrangements. SKS» to Figure 4. In this figure N = 19,# = 10,/? ol = 8 and both end compartments are occupied. There are f - ^ f n 0l - 1' 3 permutable "units" (cross-hatched) and N - q = 5 permutable vacancies! - ) - (marked withx's) or a total of 8 objects which can be permited in [\\ these vacancies are required to form mixed nearest neighbor pairs because one of the "units" (either the one to the extreme right or to the extreme left of the array) does not need a vacancy to isolate it. In addition, two vacancies, one at each end, are not permutable. Thus there are j 1 N-q- 1 " o i N-qpermutable vacancies and a total of permutable objects. These can be arranged in N-q-\-"-f + n -f = N-q-\ N-q- 1 T),"-'-'-"f, independent The "units" are not identical as we have assumed. There are (f-'.j ways of arranging the q particles in the ( n -j-) "units." This can be shown by the following reasoning. There are q - 1 lines that symbolize the separation of the q particles (see Fig. 5). Of these lines represent separations of the particles by two mixed nearest neighbor pairs and -'-(V lines symbolize the separation of adjacent particles. These q - 1 lines can thus be arranged in f n, - \
4 356 MIXED NEAREST NEIGHBOR DEGENERACY FOR [NOV. o o o ofo o c4o{o o Figure 5. This figure considers the particular arrangement shown in Fig. 3. There are q - 1 = 9 separations between ^ = 1 0 particles. Of these separations -^ double horizontal lines) and J - 1 = 3 form two mixed neighbor pairs (short ( "f - 1 ) =6 are occupied nearest neighbor pairs. The 9 separations may be arranged in f g ) independent n Thus the particles may be arranged within the - ^ = 4 "units"in 1 ways so that there is at least one particle per unit. ofo ofo ofo o o{o o Figure 6. This figure considers the particular arrangement shown in Fig. 4. There are q - 1 = 9 separations between the q = 10 particles. Of these separations ( -~ ) = 4 represent separations by two mixed nearest neighbor pairs and 9-4 = 5 represent separations of occupied nearest neighbor pairs. These 9 separations may be arranged in ( ^ ) "units" when the compart- This fs^the number of ways the q particles can be arranged to form ( -~) ments on both ends are vacant. Thus when both end compartments are empty there are (N-q-\\ I q-\ \ ways of arranging the q particles to yield exactly n 01 nearest neighbor pairs. For situation (b) there are ( -^ 1 permutable "units" composed of a particle or group of contiguous particles and a vacancy to separate the "unit" for other "units." (See Fig. 4.) There are/1/ - q ( ^ J permutable vacancies or a total of N - q - 1 objects which can be permuted. These objects can be arranged in //V-q-l\ n ni - \ Within the \-7r\ "units" the particles can be arranged in (V) This arises because there are q 1 lines symbolizing the separation of the q particles (see Fig. 6); of these lines -y constitute separations of the "units" by two mixed nearest neighbor pairs and # - 1 j are lines which separate adjacent particles. These q - 1 lines can thus be arranged I
5 1976] PARTICLES ON A ONE-DIMENSIONAL LATTICE SPACE r~ 1 \ Consequently, when both end compartments are occupied the q particles may be arranged in in f N - q - \ \ ( q - \ \ Thus the total number of arrangements possible when n ol is even is / / I / \ ( q - \ \ l N - q - \ \ l q - l \ () AK *.m-y n f j \ n f _ ^ + { n f _, j [ ^ J Normalization for A(n 0im q, N) can be shown to be (3) ^A(n,q,N)= ( J f ) where /l/}? 01/ q, N) is given alternately by Eq. 1 and and where the sum is over all possible values of n REFERENCES 1. R. B. McQuistan,7o(/r. Math. Phys., 13, 1317 (197).. E. lsing,z/ 7 /7]/^,31,53(195).
Metallic and Ionic Structures and Bonding
 Metallic and Ionic Structures and Bonding Ionic compounds are formed between elements having an electronegativity difference of about 2.0 or greater. Simple ionic compounds are characterized by high melting
Metallic and Ionic Structures and Bonding Ionic compounds are formed between elements having an electronegativity difference of about 2.0 or greater. Simple ionic compounds are characterized by high melting
CRYSTAL STRUCTURES WITH CUBIC UNIT CELLS
 CRYSTAL STRUCTURES WITH CUBIC UNIT CELLS Crystalline solids are a three dimensional collection of individual atoms, ions, or whole molecules organized in repeating patterns. These atoms, ions, or molecules
CRYSTAL STRUCTURES WITH CUBIC UNIT CELLS Crystalline solids are a three dimensional collection of individual atoms, ions, or whole molecules organized in repeating patterns. These atoms, ions, or molecules
Crystal Models. Figure 1.1 Section of a three-dimensional lattice.
 Crystal Models The Solid-State Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Objectives Understand the concept of the unit cell in crystalline solids. Construct models of unit cells for several metallic and
Crystal Models The Solid-State Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Objectives Understand the concept of the unit cell in crystalline solids. Construct models of unit cells for several metallic and
A NOTE ON TENSOR CATEGORIES OF LIE TYPE E 9
 A NOTE ON TENSOR CATEGORIES OF LIE TYPE E 9 ERIC C. ROWELL Abstract. We consider the problem of decomposing tensor powers of the fundamental level 1 highest weight representation V of the affine Kac-Moody
A NOTE ON TENSOR CATEGORIES OF LIE TYPE E 9 ERIC C. ROWELL Abstract. We consider the problem of decomposing tensor powers of the fundamental level 1 highest weight representation V of the affine Kac-Moody
3-D Crystal Lattice Images
 3-D Crystal Lattice Images All of the following images are crossed-stereo pairs. To view them, cross your eyes and focus. Author's note this material has been expanded and updated, and can be found at
3-D Crystal Lattice Images All of the following images are crossed-stereo pairs. To view them, cross your eyes and focus. Author's note this material has been expanded and updated, and can be found at
Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners
 Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners Pavel Krapivsky Boston University Plan and Motivation Evolving limiting shapes in the context of Ising model endowed with T=0 spin-flip dynamics.
Limiting shapes of Ising droplets, fingers, and corners Pavel Krapivsky Boston University Plan and Motivation Evolving limiting shapes in the context of Ising model endowed with T=0 spin-flip dynamics.
4 a b 1 1 c 1 d 3 e 2 f g 6 h i j k 7 l m n o 3 p q 5 r 2 s 4 t 3 3 u v 2
 Round Solutions Year 25 Academic Year 201 201 1//25. In the hexagonal grid shown, fill in each space with a number. After the grid is completely filled in, the number in each space must be equal to the
Round Solutions Year 25 Academic Year 201 201 1//25. In the hexagonal grid shown, fill in each space with a number. After the grid is completely filled in, the number in each space must be equal to the
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Ege University, Bornova 3500, Izmir, Turkey
 The effect of anisotropy on the absorption spectrum and the density of states of two-dimensional Frenkel exciton systems with Gaussian diagonal disorder I. Avgin a and D. L. Huber b,* a Department of Electrical
The effect of anisotropy on the absorption spectrum and the density of states of two-dimensional Frenkel exciton systems with Gaussian diagonal disorder I. Avgin a and D. L. Huber b,* a Department of Electrical
AND OCCUPANCY PROBLEMS
 COMBINATIONS, COMPOSITIONS AND OCCUPANCY PROBLEMS MORTON ABRAMSON York University, Downsview, Toronto, Canada Let r < k be positive integers,, INTRODUCTION By a composition of k into r parts (an r-composition
COMBINATIONS, COMPOSITIONS AND OCCUPANCY PROBLEMS MORTON ABRAMSON York University, Downsview, Toronto, Canada Let r < k be positive integers,, INTRODUCTION By a composition of k into r parts (an r-composition
Many-Body Fermion Density Matrix: Operator-Based Truncation Scheme
 Many-Body Fermion Density Matrix: Operator-Based Truncation Scheme SIEW-ANN CHEONG and C. L. HENLEY, LASSP, Cornell U March 25, 2004 Support: NSF grants DMR-9981744, DMR-0079992 The Big Picture GOAL Ground
Many-Body Fermion Density Matrix: Operator-Based Truncation Scheme SIEW-ANN CHEONG and C. L. HENLEY, LASSP, Cornell U March 25, 2004 Support: NSF grants DMR-9981744, DMR-0079992 The Big Picture GOAL Ground
COMBINATORIAL COUNTING
 COMBINATORIAL COUNTING Our main reference is [1, Section 3] 1 Basic counting: functions and subsets Theorem 11 (Arbitrary mapping Let N be an n-element set (it may also be empty and let M be an m-element
COMBINATORIAL COUNTING Our main reference is [1, Section 3] 1 Basic counting: functions and subsets Theorem 11 (Arbitrary mapping Let N be an n-element set (it may also be empty and let M be an m-element
Cellular Automaton Growth on # : Theorems, Examples, and Problems
 Cellular Automaton Growth on : Theorems, Examples, and Problems (Excerpt from Advances in Applied Mathematics) Exactly 1 Solidification We will study the evolution starting from a single occupied cell
Cellular Automaton Growth on : Theorems, Examples, and Problems (Excerpt from Advances in Applied Mathematics) Exactly 1 Solidification We will study the evolution starting from a single occupied cell
On Moore Graphs with Diameters 2 and 3
 .., A. J. Hoffman* R. R. Singleton On Moore Graphs with Diameters 2 and 3 Abstract: This note treats the existence of connected, undirected graphs homogeneous of degree d and of diameter k, having a number
.., A. J. Hoffman* R. R. Singleton On Moore Graphs with Diameters 2 and 3 Abstract: This note treats the existence of connected, undirected graphs homogeneous of degree d and of diameter k, having a number
Phase transitions of traffic flow. Abstract
 Phase transitions of traffic flow Agustinus Peter Sahanggamu Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (Dated: May 13, 2010) Abstract This essay introduces a basic model for a traffic
Phase transitions of traffic flow Agustinus Peter Sahanggamu Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (Dated: May 13, 2010) Abstract This essay introduces a basic model for a traffic
Honeycomb arrays. Simon R. Blackburn Anastasia Panoui Maura B. Paterson and Douglas R. Stinson. November 2, 2018
 Honeycomb arrays arxiv:0911.2384v1 [math.co] 12 Nov 2009 Simon R. Blackburn Anastasia Panoui Maura B. Paterson and Douglas R. Stinson November 2, 2018 Abstract A honeycomb array is an analogue of a Costas
Honeycomb arrays arxiv:0911.2384v1 [math.co] 12 Nov 2009 Simon R. Blackburn Anastasia Panoui Maura B. Paterson and Douglas R. Stinson November 2, 2018 Abstract A honeycomb array is an analogue of a Costas
Honeycomb Arrays. Anastasia Panoui Maura B. Paterson Douglas R. Stinson
 Honeycomb Arrays Simon R. Blackburn Anastasia Panoui Maura B. Paterson Douglas R. Stinson Submitted: Nov 12, 2009; Accepted: Nov 17, 2010; Published: Dec 10, 2010 Mathematics Subject Classification: 05B30
Honeycomb Arrays Simon R. Blackburn Anastasia Panoui Maura B. Paterson Douglas R. Stinson Submitted: Nov 12, 2009; Accepted: Nov 17, 2010; Published: Dec 10, 2010 Mathematics Subject Classification: 05B30
Heinonen, J.; Koponen, I.; Merikoski, J.; Ala-Nissilä, Tapio Island diffusion on metal fcc(100) surfaces
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Heinonen, J.; Koponen, I.; Merikoski,
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Heinonen, J.; Koponen, I.; Merikoski,
Report Form for Experiment 6: Solid State Structures
 Report Form for Experiment 6: Solid State Structures Note: Many of these questions will not make sense if you are not reading the accompanying lab handout. Station 1. Simple Cubic Lattice 1. How many unit
Report Form for Experiment 6: Solid State Structures Note: Many of these questions will not make sense if you are not reading the accompanying lab handout. Station 1. Simple Cubic Lattice 1. How many unit
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 May 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 May 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 May 2005](/thumbs/89/98786755.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0505350v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 May 2005 Voter model on Sierpinski fractals Krzysztof Suchecki and Janusz A. Ho lyst Faculty of Physics and Center of Excellence for Complex Systems Research,
arxiv:cond-mat/0505350v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 13 May 2005 Voter model on Sierpinski fractals Krzysztof Suchecki and Janusz A. Ho lyst Faculty of Physics and Center of Excellence for Complex Systems Research,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004](/thumbs/93/113057924.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0306501v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004 Exactly solvable models through the generalized empty interval method: multi-species and more-than-two-site interactions Amir Aghamohammadi 1 &
arxiv:cond-mat/0306501v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 23 Apr 2004 Exactly solvable models through the generalized empty interval method: multi-species and more-than-two-site interactions Amir Aghamohammadi 1 &
Solid Thermodynamics (1)
 Solid Thermodynamics (1) Class notes based on MIT OCW by KAN K.A.Nelson and MB M.Bawendi Statistical Mechanics 2 1. Mathematics 1.1. Permutation: - Distinguishable balls (numbers on the surface of the
Solid Thermodynamics (1) Class notes based on MIT OCW by KAN K.A.Nelson and MB M.Bawendi Statistical Mechanics 2 1. Mathematics 1.1. Permutation: - Distinguishable balls (numbers on the surface of the
Ostwald Ripening: An Approach with Dynamical Systems
 Materials Research, Vol. 2, No. 3, 139-143, 1999. 1999 Ostwald Ripening: An Approach with Dynamical Systems F.S. Lameiras Centro de Desenvolvimento da Tecnologia Nuclear - CDTN / CNEN, C.P. 941, 30.123-970
Materials Research, Vol. 2, No. 3, 139-143, 1999. 1999 Ostwald Ripening: An Approach with Dynamical Systems F.S. Lameiras Centro de Desenvolvimento da Tecnologia Nuclear - CDTN / CNEN, C.P. 941, 30.123-970
Lecture 2: Receptor-ligand binding and cooperativity
 Lecture 2: Receptor-ligand binding and cooperativity Paul C Bressloff (Spring 209) A biochemical receptor is a protein molecule that receives a chemical signal in the form of ligand molecules. The ligands
Lecture 2: Receptor-ligand binding and cooperativity Paul C Bressloff (Spring 209) A biochemical receptor is a protein molecule that receives a chemical signal in the form of ligand molecules. The ligands
Fibonacci numbers. Chapter The Fibonacci sequence. The Fibonacci numbers F n are defined recursively by
 Chapter Fibonacci numbers The Fibonacci sequence The Fibonacci numbers F n are defined recursively by F n+ = F n + F n, F 0 = 0, F = The first few Fibonacci numbers are n 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 F n 0 5 8 55 89
Chapter Fibonacci numbers The Fibonacci sequence The Fibonacci numbers F n are defined recursively by F n+ = F n + F n, F 0 = 0, F = The first few Fibonacci numbers are n 0 5 6 7 8 9 0 F n 0 5 8 55 89
Circles & Interval & Set Notation.notebook. November 16, 2009 CIRCLES. OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form.
 OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form. Write the equation of a circle in standard form given a graph or two points (one being the center). Students will be able to write the domain
OBJECTIVE Graph a Circle given the equation in standard form. Write the equation of a circle in standard form given a graph or two points (one being the center). Students will be able to write the domain
Sphere Packings, Coverings and Lattices
 Sphere Packings, Coverings and Lattices Anja Stein Supervised by: Prof Christopher Smyth September, 06 Abstract This article is the result of six weeks of research for a Summer Project undertaken at the
Sphere Packings, Coverings and Lattices Anja Stein Supervised by: Prof Christopher Smyth September, 06 Abstract This article is the result of six weeks of research for a Summer Project undertaken at the
APPLICATION OF LATTICE-GAS MODEL TO THE SIMULATION OF COMPLEX ECONOMICAL SYSTEMS
 Surya Octagon Interdisciplinary Journal of Technology, September 2015, 59-71 Copyright 2015, ISSN : 2460-8777 Vol. 1, No.1 APPLICATION OF LATTICE-GAS MODEL TO THE SIMULATION OF COMPLEX ECONOMICAL SYSTEMS
Surya Octagon Interdisciplinary Journal of Technology, September 2015, 59-71 Copyright 2015, ISSN : 2460-8777 Vol. 1, No.1 APPLICATION OF LATTICE-GAS MODEL TO THE SIMULATION OF COMPLEX ECONOMICAL SYSTEMS
Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together.
 Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together. For example Nacl In the Nacl lattice, each Na atom is
Bonding in solids The interaction of electrons in neighboring atoms of a solid serves the very important function of holding the crystal together. For example Nacl In the Nacl lattice, each Na atom is
Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #5 March/April 2005 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Average team score: 86.6 Average meet for the seasion: 95.9 Meet #5 March/April 2005 Category 1 Mystery Meet #5, March/April
Meet #5 March/April 2005 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Average team score: 86.6 Average meet for the seasion: 95.9 Meet #5 March/April 2005 Category 1 Mystery Meet #5, March/April
EE301 Electronics I , Fall
 EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures
 Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures To do well in this laboratory experiment you need to be familiar with the concepts of lattice, crystal structure, unit cell, coordination number, the different
Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures To do well in this laboratory experiment you need to be familiar with the concepts of lattice, crystal structure, unit cell, coordination number, the different
MUTUALLY ORTHOGONAL LATIN SQUARES AND THEIR USES
 MUTUALLY ORTHOGONAL LATIN SQUARES AND THEIR USES LOKESH DWIVEDI M.Sc. (Agricultural Statistics), Roll No. 449 I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi 0 02 Chairperson: Dr. Cini Varghese Abstract: A Latin
MUTUALLY ORTHOGONAL LATIN SQUARES AND THEIR USES LOKESH DWIVEDI M.Sc. (Agricultural Statistics), Roll No. 449 I.A.S.R.I., Library Avenue, New Delhi 0 02 Chairperson: Dr. Cini Varghese Abstract: A Latin
Math 231E, Lecture 25. Integral Test and Estimating Sums
 Math 23E, Lecture 25. Integral Test and Estimating Sums Integral Test The definition of determining whether the sum n= a n converges is:. Compute the partial sums s n = a k, k= 2. Check that s n is a convergent
Math 23E, Lecture 25. Integral Test and Estimating Sums Integral Test The definition of determining whether the sum n= a n converges is:. Compute the partial sums s n = a k, k= 2. Check that s n is a convergent
The Vold-Sutherland and Eden Models of Cluster Formation 1
 The Vold-Sutherland and Eden Models of Cluster Formation 1 PAUL MEAKIN Central Research and Development Department, E. L du Pont de Nemours and Company, Experimental Station, Wilmington, Delaware 19898
The Vold-Sutherland and Eden Models of Cluster Formation 1 PAUL MEAKIN Central Research and Development Department, E. L du Pont de Nemours and Company, Experimental Station, Wilmington, Delaware 19898
Lecture 2 Electrons and Holes in Semiconductors
 EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 2 Electrons and Holes in Semiconductors Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 2 Electrons and Holes in Semiconductors Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
First Principles Calculation of Defect and Magnetic Structures in FeCo
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 47, No. 11 (26) pp. 2646 to 26 Special Issue on Advances in Computational Materials Science and Engineering IV #26 The Japan Institute of Metals First Principles Calculation
Materials Transactions, Vol. 47, No. 11 (26) pp. 2646 to 26 Special Issue on Advances in Computational Materials Science and Engineering IV #26 The Japan Institute of Metals First Principles Calculation
The decomposability of simple orthogonal arrays on 3 symbols having t + 1 rows and strength t
 The decomposability of simple orthogonal arrays on 3 symbols having t + 1 rows and strength t Wiebke S. Diestelkamp Department of Mathematics University of Dayton Dayton, OH 45469-2316 USA wiebke@udayton.edu
The decomposability of simple orthogonal arrays on 3 symbols having t + 1 rows and strength t Wiebke S. Diestelkamp Department of Mathematics University of Dayton Dayton, OH 45469-2316 USA wiebke@udayton.edu
Mathathon Round 1 (2 points each)
 Mathathon Round ( points each). A circle is inscribed inside a square such that the cube of the radius of the circle is numerically equal to the perimeter of the square. What is the area of the circle?
Mathathon Round ( points each). A circle is inscribed inside a square such that the cube of the radius of the circle is numerically equal to the perimeter of the square. What is the area of the circle?
Correlations to the Common Core State Standards: Kindergarten
 Correlations to the Common Core State s: Kindergarten L-1, Building the Hundreds Counting and Cardinality Know number names and the count sequence. K.CC.1. Count to 100 by ones and by tens. K.CC.2. Count
Correlations to the Common Core State s: Kindergarten L-1, Building the Hundreds Counting and Cardinality Know number names and the count sequence. K.CC.1. Count to 100 by ones and by tens. K.CC.2. Count
Consequently, the exact eigenfunctions of the Hamiltonian are also eigenfunctions of the two spin operators
 VI. SPIN-ADAPTED CONFIGURATIONS A. Preliminary Considerations We have described the spin of a single electron by the two spin functions α(ω) α and β(ω) β. In this Sect. we will discuss spin in more detail
VI. SPIN-ADAPTED CONFIGURATIONS A. Preliminary Considerations We have described the spin of a single electron by the two spin functions α(ω) α and β(ω) β. In this Sect. we will discuss spin in more detail
Adsorption from a one-dimensional lattice gas and the Brunauer Emmett Teller equation
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 1438 1433, December 1996 Chemistry Adsorption from a one-dimensional lattice gas and the Brunauer Emmett Teller equation (Ising modelreference systemgibbs ecess
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 93, pp. 1438 1433, December 1996 Chemistry Adsorption from a one-dimensional lattice gas and the Brunauer Emmett Teller equation (Ising modelreference systemgibbs ecess
0 Sets and Induction. Sets
 0 Sets and Induction Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects, called elements or members of the set. A set is said to contain its elements. We write a A to denote that a is an element of the set
0 Sets and Induction Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects, called elements or members of the set. A set is said to contain its elements. We write a A to denote that a is an element of the set
Chapter 1. Crystal structure. 1.1 Crystal lattices
 Chapter 1 Crystal structure 1.1 Crystal lattices We will concentrate as stated in the introduction, on perfect crystals, i.e. on arrays of atoms, where a given arrangement is repeated forming a periodic
Chapter 1 Crystal structure 1.1 Crystal lattices We will concentrate as stated in the introduction, on perfect crystals, i.e. on arrays of atoms, where a given arrangement is repeated forming a periodic
Human Biology Chapter 2.2: The Building Blocks of Molecules *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57963 1 Human Biology Chapter 2.2: The Building Blocks of Molecules * Willy Cushwa Based on The Building Blocks of Molecules by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
OpenStax-CNX module: m57963 1 Human Biology Chapter 2.2: The Building Blocks of Molecules * Willy Cushwa Based on The Building Blocks of Molecules by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and
MATHEMATICS K 12 SUBJECT BOOKLET
 MATHEMATICS 2018 19 K 12 SUBJECT BOOKLET Gwinnett s curriculum for grades K 12 is called the Academic Knowledge and Skills (AKS). The AKS for each grade level spells out the essential things students are
MATHEMATICS 2018 19 K 12 SUBJECT BOOKLET Gwinnett s curriculum for grades K 12 is called the Academic Knowledge and Skills (AKS). The AKS for each grade level spells out the essential things students are
Analyzing Rational Functions
 Analyzing Rational Functions These notes are intended as a summary of section 2.3 (p. 105 112) in your workbook. You should also read the section for more complete explanations and additional examples.
Analyzing Rational Functions These notes are intended as a summary of section 2.3 (p. 105 112) in your workbook. You should also read the section for more complete explanations and additional examples.
PUTNAM PROBLEMS SEQUENCES, SERIES AND RECURRENCES. Notes
 PUTNAM PROBLEMS SEQUENCES, SERIES AND RECURRENCES Notes. x n+ = ax n has the general solution x n = x a n. 2. x n+ = x n + b has the general solution x n = x + (n )b. 3. x n+ = ax n + b (with a ) can be
PUTNAM PROBLEMS SEQUENCES, SERIES AND RECURRENCES Notes. x n+ = ax n has the general solution x n = x a n. 2. x n+ = x n + b has the general solution x n = x + (n )b. 3. x n+ = ax n + b (with a ) can be
Big Idea: Ionic Bonds: Ionic Bonds: Metals: Nonmetals: Covalent Bonds: Ionic Solids: What ions do atoms form? Electron Electron
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
(1) Which of the following are propositions? If it is a proposition, determine its truth value: A propositional function, but not a proposition.
 Math 231 Exam Practice Problem Solutions WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the
Math 231 Exam Practice Problem Solutions WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the
The 6-vertex model of hydrogen-bonded crystals with bond defects
 arxiv:cond-mat/9908379v [cond-mat.stat-mech] Oct 999 The 6-vertex model of hydrogen-bonded crystals with bond defects N. Sh. Izmailian, Chin-Kun Hu and F. Y. Wu Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Nankang,
arxiv:cond-mat/9908379v [cond-mat.stat-mech] Oct 999 The 6-vertex model of hydrogen-bonded crystals with bond defects N. Sh. Izmailian, Chin-Kun Hu and F. Y. Wu Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Nankang,
Introduction to Combinatorial Mathematics
 Introduction to Combinatorial Mathematics George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 300 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Combinatorics April 2016 1 / 57
Introduction to Combinatorial Mathematics George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 300 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Combinatorics April 2016 1 / 57
f(x + y) + f(x y) = 10.
 Math Field Day 202 Mad Hatter A A Suppose that for all real numbers x and y, Then f(y x) =? f(x + y) + f(x y) = 0. A2 Find the sum + 2 + 4 + 5 + 7 + 8 + 0 + + +49 + 50 + 52 + 53 + 55 + 56 + 58 + 59. A3
Math Field Day 202 Mad Hatter A A Suppose that for all real numbers x and y, Then f(y x) =? f(x + y) + f(x y) = 0. A2 Find the sum + 2 + 4 + 5 + 7 + 8 + 0 + + +49 + 50 + 52 + 53 + 55 + 56 + 58 + 59. A3
3 rd Grade Remediation Guide
 3 rd Grade Remediation Guide Focused remediation helps target the skills students need to more quickly access and practice on-grade level content. This chart is a reference guide for teachers to help them
3 rd Grade Remediation Guide Focused remediation helps target the skills students need to more quickly access and practice on-grade level content. This chart is a reference guide for teachers to help them
Temperature dependence of the electron spin resonance linewidth in magnetic insulators
 Temperature dependence of the electron spin resonance linewidth in magnetic insulators M. Acikgoz 1 and D. L. Huber 2, a 1 Bahcesehir University, Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Besiktas,
Temperature dependence of the electron spin resonance linewidth in magnetic insulators M. Acikgoz 1 and D. L. Huber 2, a 1 Bahcesehir University, Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Besiktas,
Critical Dynamics of Two-Replica Cluster Algorithms
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Jonathan Machta 2001 Critical Dynamics of Two-Replica Cluster Algorithms X. N. Li Jonathan Machta, University of Massachusetts Amherst Available
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Jonathan Machta 2001 Critical Dynamics of Two-Replica Cluster Algorithms X. N. Li Jonathan Machta, University of Massachusetts Amherst Available
CH.8 Polymers: Solutions, Blends, Membranes, and Gels
 CH.8 Polymers: Solutions, Blends, embranes, and Gels 8. Properties of Polymers Polymers are chain-like molecules. Linear polymer Branched polymer Cross-linked polymer Polymers show little tendency to crystallize.
CH.8 Polymers: Solutions, Blends, embranes, and Gels 8. Properties of Polymers Polymers are chain-like molecules. Linear polymer Branched polymer Cross-linked polymer Polymers show little tendency to crystallize.
Combinations and Probabilities
 Combinations and Probabilities Tutor: Zhang Qi Systems Engineering and Engineering Management qzhang@se.cuhk.edu.hk November 2014 Tutor: Zhang Qi (SEEM) Tutorial 7 November 2014 1 / 16 Combination Review
Combinations and Probabilities Tutor: Zhang Qi Systems Engineering and Engineering Management qzhang@se.cuhk.edu.hk November 2014 Tutor: Zhang Qi (SEEM) Tutorial 7 November 2014 1 / 16 Combination Review
Co-rich Decagonal Al-Co-Ni predicting structure, orientatio order, and puckering
 Co-rich Decagonal Al-Co-Ni predicting structure, orientatio order, and puckering Nan Gu, Marek Mihalkovič, and C.L. Henley, Cornell University ICQ9 poster, Monday May 23, 2005 Supported by DOE grant DE-FG02-89ER-45405
Co-rich Decagonal Al-Co-Ni predicting structure, orientatio order, and puckering Nan Gu, Marek Mihalkovič, and C.L. Henley, Cornell University ICQ9 poster, Monday May 23, 2005 Supported by DOE grant DE-FG02-89ER-45405
( c ) E p s t e i n, C a r t e r a n d B o l l i n g e r C h a p t e r 1 7 : I n f o r m a t i o n S c i e n c e P a g e 1
 ( c ) E p s t e i n, C a r t e r a n d B o l l i n g e r 2 0 1 6 C h a p t e r 1 7 : I n f o r m a t i o n S c i e n c e P a g e 1 CHAPTER 17: Information Science In this chapter, we learn how data can
( c ) E p s t e i n, C a r t e r a n d B o l l i n g e r 2 0 1 6 C h a p t e r 1 7 : I n f o r m a t i o n S c i e n c e P a g e 1 CHAPTER 17: Information Science In this chapter, we learn how data can
STUDY OF SYNCHRONIZED MOTIONS IN A ONE-DIMENSIONAL ARRAY OF COUPLED CHAOTIC CIRCUITS
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol 9, No 11 (1999) 19 4 c World Scientific Publishing Company STUDY OF SYNCHRONIZED MOTIONS IN A ONE-DIMENSIONAL ARRAY OF COUPLED CHAOTIC CIRCUITS ZBIGNIEW
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol 9, No 11 (1999) 19 4 c World Scientific Publishing Company STUDY OF SYNCHRONIZED MOTIONS IN A ONE-DIMENSIONAL ARRAY OF COUPLED CHAOTIC CIRCUITS ZBIGNIEW
Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 114 Worksheet Sections (4.1),
 Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 114 Worksheet Sections (4.1), 4.-4.6 1. Find the polynomial function with zeros: -1 (multiplicity ) and 1 (multiplicity ) whose graph passes
Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 114 Worksheet Sections (4.1), 4.-4.6 1. Find the polynomial function with zeros: -1 (multiplicity ) and 1 (multiplicity ) whose graph passes
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules
 Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
SCIS-HIS. Teaching and Learning Standards January Mathematics Grades K - 5
 SCIS-HIS Teaching and Learning Standards January 2015 Mathematics Grades K - 5 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Kindergarten... 3 Counting & Cardinality... 3 Operations & Algebraic Thinking... 4 Number
SCIS-HIS Teaching and Learning Standards January 2015 Mathematics Grades K - 5 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Kindergarten... 3 Counting & Cardinality... 3 Operations & Algebraic Thinking... 4 Number
K K.OA.2 1.OA.2 2.OA.1 3.OA.3 4.OA.3 5.NF.2 6.NS.1 7.NS.3 8.EE.8c
 K.OA.2 1.OA.2 2.OA.1 3.OA.3 4.OA.3 5.NF.2 6.NS.1 7.NS.3 8.EE.8c Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add and subtract within 10, e.g., by using objects or drawings to Solve word problems that
K.OA.2 1.OA.2 2.OA.1 3.OA.3 4.OA.3 5.NF.2 6.NS.1 7.NS.3 8.EE.8c Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add and subtract within 10, e.g., by using objects or drawings to Solve word problems that
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC)
 Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Kinetic Monte Carlo (KMC) Molecular Dynamics (MD): high-frequency motion dictate the time-step (e.g., vibrations). Time step is short: pico-seconds. Direct Monte Carlo (MC): stochastic (non-deterministic)
Discrete Math, Spring Solutions to Problems V
 Discrete Math, Spring 202 - Solutions to Problems V Suppose we have statements P, P 2, P 3,, one for each natural number In other words, we have the collection or set of statements {P n n N} a Suppose
Discrete Math, Spring 202 - Solutions to Problems V Suppose we have statements P, P 2, P 3,, one for each natural number In other words, we have the collection or set of statements {P n n N} a Suppose
Chapter 13: Phenomena
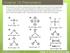 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Probability and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Probability and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Stephen R. Addison January 24, 200 Introduction Over the next several class periods we will be reviewing the basic results of probability and relating probability
Probability and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Stephen R. Addison January 24, 200 Introduction Over the next several class periods we will be reviewing the basic results of probability and relating probability
variational principle and Schrödinger equation
 variational principle and Schrödinger equation normalized wavefunctions energy functional E[ ]= H variation E[ + ] = H + H + H + H = E[ ]+ E[ ]+O 2 ( ) functional derivative E[ ] = E[ + ] E[ ] ensure normalization
variational principle and Schrödinger equation normalized wavefunctions energy functional E[ ]= H variation E[ + ] = H + H + H + H = E[ ]+ E[ ]+O 2 ( ) functional derivative E[ ] = E[ + ] E[ ] ensure normalization
Module 16. Diffusion in solids II. Lecture 16. Diffusion in solids II
 Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
Module 16 Diffusion in solids II Lecture 16 Diffusion in solids II 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Keywords: Micro mechanisms of diffusion,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 1982 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 198 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS 1. Matrix Algebra Margenau and Murphy, The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry, Chapter 10, give almost
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Chemistry 5.76 Revised February, 198 NOTES ON MATRIX METHODS 1. Matrix Algebra Margenau and Murphy, The Mathematics of Physics and Chemistry, Chapter 10, give almost
Energy band of manipulated atomic structures on an insulator substrate
 Energy band of manipulated atomic structures on an insulator substrate Toshishige Yamada and Yoshihisa Yamamoto ERATO Quantum Fluctuation Project, Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford,
Energy band of manipulated atomic structures on an insulator substrate Toshishige Yamada and Yoshihisa Yamamoto ERATO Quantum Fluctuation Project, Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford,
Bijective Proofs with Spotted Tilings
 Brian Hopkins, Saint Peter s University, New Jersey, USA Visiting Scholar, Mahidol University International College Editor, The College Mathematics Journal MUIC Mathematics Seminar 2 November 2016 outline
Brian Hopkins, Saint Peter s University, New Jersey, USA Visiting Scholar, Mahidol University International College Editor, The College Mathematics Journal MUIC Mathematics Seminar 2 November 2016 outline
WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014)
 WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014) LIST OF PROBLEMS Chapter 1: Magnetism of Free Electrons and Atoms 1. Orbital and spin moments of an electron: Using the theory of angular momentum, calculate the orbital
WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014) LIST OF PROBLEMS Chapter 1: Magnetism of Free Electrons and Atoms 1. Orbital and spin moments of an electron: Using the theory of angular momentum, calculate the orbital
Domino tilings with barriers. In memory of Gian-Carlo Rota
 Domino tilings with barriers In memory of Gian-Carlo Rota James Propp Richard Stanley University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706 Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139 In this paper,
Domino tilings with barriers In memory of Gian-Carlo Rota James Propp Richard Stanley University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI 53706 Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139 In this paper,
Maximizing the descent statistic
 Maximizing the descent statistic Richard EHRENBORG and Swapneel MAHAJAN Abstract For a subset S, let the descent statistic β(s) be the number of permutations that have descent set S. We study inequalities
Maximizing the descent statistic Richard EHRENBORG and Swapneel MAHAJAN Abstract For a subset S, let the descent statistic β(s) be the number of permutations that have descent set S. We study inequalities
L11.P1 Lecture 11. Quantum statistical mechanics: summary
 Lecture 11 Page 1 L11.P1 Lecture 11 Quantum statistical mechanics: summary At absolute zero temperature, a physical system occupies the lowest possible energy configuration. When the temperature increases,
Lecture 11 Page 1 L11.P1 Lecture 11 Quantum statistical mechanics: summary At absolute zero temperature, a physical system occupies the lowest possible energy configuration. When the temperature increases,
Ionic Bonds. H He: ... Li Be B C :N :O :F: :Ne:
 Ionic Bonds Valence electrons - the electrons in the highest occupied energy level - always electrons in the s and p orbitals - maximum of 8 valence electrons - elements in the same group have the same
Ionic Bonds Valence electrons - the electrons in the highest occupied energy level - always electrons in the s and p orbitals - maximum of 8 valence electrons - elements in the same group have the same
Hashing. Why Hashing? Applications of Hashing
 12 Hashing Why Hashing? Hashing A Search algorithm is fast enough if its time performance is O(log 2 n) For 1 5 elements, it requires approx 17 operations But, such speed may not be applicable in real-world
12 Hashing Why Hashing? Hashing A Search algorithm is fast enough if its time performance is O(log 2 n) For 1 5 elements, it requires approx 17 operations But, such speed may not be applicable in real-world
CHAPTER 4 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 4-1 CHAPTER 4 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 4.1 In order to compute the fraction of atom sites that are vacant in copper at 1357 K, we must employ Equation
4-1 CHAPTER 4 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 4.1 In order to compute the fraction of atom sites that are vacant in copper at 1357 K, we must employ Equation
Homework 7 Solutions, Math 55
 Homework 7 Solutions, Math 55 5..36. (a) Since a is a positive integer, a = a 1 + b 0 is a positive integer of the form as + bt for some integers s and t, so a S. Thus S is nonempty. (b) Since S is nonempty,
Homework 7 Solutions, Math 55 5..36. (a) Since a is a positive integer, a = a 1 + b 0 is a positive integer of the form as + bt for some integers s and t, so a S. Thus S is nonempty. (b) Since S is nonempty,
A Correlation of. Student Activity Book. to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics. Grade 2
 A Correlation of Student Activity Book to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 2 Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved Grade 2 Units Unit 1 -
A Correlation of Student Activity Book to the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics Grade 2 Copyright 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved Grade 2 Units Unit 1 -
Some Correlation Inequalities for Ising Antiferromagnets
 Some Correlation Inequalities for Ising Antiferromagnets David Klein Wei-Shih Yang Department of Mathematics Department of Mathematics California State University University of Colorado Northridge, California
Some Correlation Inequalities for Ising Antiferromagnets David Klein Wei-Shih Yang Department of Mathematics Department of Mathematics California State University University of Colorado Northridge, California
A practical method for enumerating cosets of a finite abstract group
 A practical method for enumerating cosets of a finite abstract group By J. A. ODD (University of Manchester), and H.. M. COXBEB (University of Cambridge). (Received nd January,. Mead th February,.) Introduction.
A practical method for enumerating cosets of a finite abstract group By J. A. ODD (University of Manchester), and H.. M. COXBEB (University of Cambridge). (Received nd January,. Mead th February,.) Introduction.
PROCESSING AND TRANSMISSION OF INFORMATION*
 IX. PROCESSING AND TRANSMISSION OF INFORMATION* Prof. P. Elias E. Ferretti E. T. Schoen Prof. R. M. Fano K. Joannou F. F. Tung Prof. D. A. Huffman R. M. Lerner S. H. Unger Prof. C. E. Shannon J. B. O'Loughlin
IX. PROCESSING AND TRANSMISSION OF INFORMATION* Prof. P. Elias E. Ferretti E. T. Schoen Prof. R. M. Fano K. Joannou F. F. Tung Prof. D. A. Huffman R. M. Lerner S. H. Unger Prof. C. E. Shannon J. B. O'Loughlin
Sets and Functions. (As we will see, in describing a set the order in which elements are listed is irrelevant).
 Sets and Functions 1. The language of sets Informally, a set is any collection of objects. The objects may be mathematical objects such as numbers, functions and even sets, or letters or symbols of any
Sets and Functions 1. The language of sets Informally, a set is any collection of objects. The objects may be mathematical objects such as numbers, functions and even sets, or letters or symbols of any
Statistical Physics. Solutions Sheet 11.
 Statistical Physics. Solutions Sheet. Exercise. HS 0 Prof. Manfred Sigrist Condensation and crystallization in the lattice gas model. The lattice gas model is obtained by dividing the volume V into microscopic
Statistical Physics. Solutions Sheet. Exercise. HS 0 Prof. Manfred Sigrist Condensation and crystallization in the lattice gas model. The lattice gas model is obtained by dividing the volume V into microscopic
1 Polynomial approximation of the gamma function
 AM05: Solutions to take-home midterm exam 1 1 Polynomial approximation of the gamma function Part (a) One way to answer this question is by constructing the Vandermonde linear system Solving this matrix
AM05: Solutions to take-home midterm exam 1 1 Polynomial approximation of the gamma function Part (a) One way to answer this question is by constructing the Vandermonde linear system Solving this matrix
Atoms? All matters on earth made of atoms (made up of elements or combination of elements).
 Chapter 1 Atoms? All matters on earth made of atoms (made up of elements or combination of elements). Atomic Structure Atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exist in a stable or independent
Chapter 1 Atoms? All matters on earth made of atoms (made up of elements or combination of elements). Atomic Structure Atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exist in a stable or independent
In this chapter we focus our attention on the model (3.1) in the hard-core. the model (3.1) can be mapped into spin-2 XX model in the presence of
 Chapter 4 Hard core Bosons 4.1 Introduction In this chapter we focus our attention on the model (3.1) in the hard-core limit, i.e., taking U = oo. In this limit with density of bosons p = 1/2 the model
Chapter 4 Hard core Bosons 4.1 Introduction In this chapter we focus our attention on the model (3.1) in the hard-core limit, i.e., taking U = oo. In this limit with density of bosons p = 1/2 the model
o Two-wire transmission line (end view is shown, the radius of the conductors = a, the distance between the centers of the two conductors = d)
 Homework 2 Due Monday, 14 June 1. There is a small number of simple conductor/dielectric configurations for which we can relatively easily find the capacitance. Students of electromagnetics should be sure
Homework 2 Due Monday, 14 June 1. There is a small number of simple conductor/dielectric configurations for which we can relatively easily find the capacitance. Students of electromagnetics should be sure
The Periodic Table. You have learned the names of several of the groups in previous science courses:
 The Periodic Table The periodic law, which is the basis for the modern periodic table, states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties
The Periodic Table The periodic law, which is the basis for the modern periodic table, states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties
MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 19: Subgroups (continued). Error-detecting and error-correcting codes.
 MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 19: Subgroups (continued). Error-detecting and error-correcting codes. Subgroups Definition. A group H is a called a subgroup of a group G if H is a subset of G and the
MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 19: Subgroups (continued). Error-detecting and error-correcting codes. Subgroups Definition. A group H is a called a subgroup of a group G if H is a subset of G and the
Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions
 134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
a. Ensembles of Aggregates of the Same Aggregation Number
 Mathematical Descriptions of Ensembles ote: The following mathematical descriptions of enolate ensembles are based on an ensemble of hexamers composed of two enantiomers, R and S, which is archived in
Mathematical Descriptions of Ensembles ote: The following mathematical descriptions of enolate ensembles are based on an ensemble of hexamers composed of two enantiomers, R and S, which is archived in
Island-size distribution and capture numbers in three-dimensional nucleation: Comparison with mean-field behavior
 Island-size distribution and capture numbers in three-dimensional nucleation: Comparison with mean-field behavior Feng Shi,* Yunsic Shim, and Jacques G. Amar Department of Physics & Astronomy, University
Island-size distribution and capture numbers in three-dimensional nucleation: Comparison with mean-field behavior Feng Shi,* Yunsic Shim, and Jacques G. Amar Department of Physics & Astronomy, University
Radio Number for Square of Cycles
 Radio Number for Square of Cycles Daphne Der-Fen Liu Melanie Xie Department of Mathematics California State University, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 9003, USA August 30, 00 Abstract Let G be a connected
Radio Number for Square of Cycles Daphne Der-Fen Liu Melanie Xie Department of Mathematics California State University, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 9003, USA August 30, 00 Abstract Let G be a connected
Connectivity of Wireless Sensor Networks with Constant Density
 Connectivity of Wireless Sensor Networks with Constant Density Sarah Carruthers and Valerie King University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada Abstract. We consider a wireless sensor network in which each
Connectivity of Wireless Sensor Networks with Constant Density Sarah Carruthers and Valerie King University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada Abstract. We consider a wireless sensor network in which each
Atoms & Atomic Structure
 Atoms & Atomic Structure - An atom is the smallest piece of an element - are composed of three types of sub-atomic particles: protons, neutrons & electrons Nucleus = central portion of atom - small and
Atoms & Atomic Structure - An atom is the smallest piece of an element - are composed of three types of sub-atomic particles: protons, neutrons & electrons Nucleus = central portion of atom - small and
Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Big Ideas in Unit 6 How do atoms form chemical bonds? How does the type of a chemical bond influence a compounds physical and
Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Big Ideas in Unit 6 How do atoms form chemical bonds? How does the type of a chemical bond influence a compounds physical and
