ON THE GROWTH OF MINIMAL GRAPHS. Allen Weitsman
|
|
|
- Erin Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ON THE GROWTH OF MINIMAL GRAPHS Allen Weitsman Abstract. We consider minimal graphs u = u(, y > 0 over unbounded domains D R with D a piecewise smooth curve on which u = 0. We give some lower growth estimates for u in terms of the geometry of D. I. Introduction. Let D be an unbounded domain in R bounded by a piecewise differentiable arc, and 0 Θ(r π be the angular measure of the set D { z = r}. In the classical potential theory of harmonic functions, an important role is played by estimates involving Θ(r. For eample, if u(z is the harmonic measure of D { z <r} with respect to D { z = r}, then [T; p.6] we have Theorem A. If z D and z <κr/, then u(z 9 κ e π κr z dρ ρθ (ρ (0 <κ<, where Θ (r =Θ(r if D does not contain the entire circle z = r, andθ (r = otherwise. Theorem A is valid without topological assumptions on D, but with our current assumption that D is a piecewise differentiable arc, we have Θ (r =Θ(r forr>r 0. The proof of Theorem A for general domains is carried out by a method of Carleman. When the domain is simply connected, as in the current setting, we may use the methods of path families [F; p.0] or the Ahlfors distortion theorem [Ne; p.97]. In this work we shall rely on the method of path families. We define the asymptotic angle of D as (. β = lim sup Θ (r. r If u>0 is defined in D, then the order of u in D is given by log u(z (. α = lim sup z z D log z. 99 Mathematics Subject Classification. AMS Subject Classification: 35J60, 53A0. Key words and phrases. Minimal surfaces.
2 ALLEN WEITSMAN When u>0 is harmonic in D with u =0on D, it follows easily from Theorem A that (.3 α π/β. We are interested in lower bounds for growth rates for solutions to the minimal surface equation. Precisely, we consider solutions u to ( u (.4 Lu =div =0 u in D with (.5 u>0 in D, u =0 on D. In his paper [S], Spruck proved (.3 for β π, but under stringent side conditions on the behavior of u. These are i u(z as z, z D ii K(z, u(z C/( z asz, z D, where K is the Gauss curvature. The methods of [S] are nonparametric, and the conditions i and ii make the solutions resemble harmonic functions sufficiently closely so that Carleman s method can be applied. In the present work we shall use conformal parametric methods and remove the assumptions i and ii. However, here we assume that D is a single arc, whereas in [S] there are no topological constraints. We shall take advantage of the work of V. Mikljukov [M] on the moduli of path families on minimal surfaces. We shall prove Theorem.. Let D be an unbounded domain whose boundary D is a piecewise differentiable arc, and u satisfy (.4 and (.5. If β π, then (.3 holds. The case α>(β<π is ruled out for consideration in [S] by the assumption i. It is also not covered by our Theorem.. It seems reasonable in fact to conjecture that there are no nontrivial solutions u to (.4 and (.5 with β<π. This is reinforced by Nitsche s observation [Ni; p.56] that (.4 and (.5 have no nontrivial solutions if D is contained in a sector of opening less than π. I would like to thank Professor Spruck for interesting conversations and providing a preprint of his paper [S]. II. Modulus of a path family. Let D be a simply connected unbounded domain in R. Let F denote the surface given by u(z, z = i D with ds F =(u d u u d d (u d and dσ F = u d d
3 3 the respective length and area elements for F. For a family Γ of curves in D we define the modulus of Γ in the metric of F by mod F Γ=inf D ρ (zdσ F, the inf being taken over all nonnegative measurable functions ρ on D satisfying inf ρ(zds F. γ Γ γ The utility of the modulus comes from the elementary observation that it is a conformal invariant (cf. [M; p.65]. We shall use estimates on the modulus for path families of curves on a surface F given by solutions u(z to the minimal surface equation over domains D as in (. and (.. III. Isothermal coordinates. Let D be an unbounded domain, bounded by a simple piecewise differentiable arc and u satisfy (. and (. in D. We introduce a comple isothermal coordinate ζ for the surface F given by u over D so that the map ζ ( (ζ, (ζ,u( (ζ, (ζ is a conformal mapping onto F. We take the parameter space as the upper half plane H = {ζ : Imζ >0} with specified positively oriented points a, b D corresponding by ( (ζ, (ζ to (0, 0, (0, respectively, and.the mapping f(ζ = (ζi (ζ is then a univalent harmonic mapping of H onto D. Path families Γ in H correspond to path families on F which project to path families f(γ in D. y conformal invariance, the modulus may be computed either in H, or with the surface metric in D. When epressed in the coordinates of H, thenu = u(ζ is harmonic. With the special conditions here that u =0on H, u reflects to a harmonic function in the entire plane; since u>0inh, itmustbethatu is of the form c Imζ for some real constant c>0. IV. The modulus estimate. In this section D is an unbounded domain whose boundary is a simple piecewise differentiable curve, and D(r, R =D {r< z <R}. Fi a and b as in 3. For sufficiently large t>0 let S(t be the component of D {z : z = t} separating a from in D. Choosing r large enough so S(r separates b from in D, and R>r,letT be the subdomain of D between S(r and S(R. Let Γ = Γ(r, R be the family of curves in T that join S(r and S(R.
4 4 ALLEN WEITSMAN S(R T S(r Theorem 4.. With the above notations, suppose that u(z (4. lim sup z z D z Then (4. mod F Γ(r, R (log R D(r,R =0. ( o( d d π z (R. Proof. Following Mikljukov, we choose the density function ρ(z =( z u (z /, for z = T D(r, R andρ(z = 0 for all the remaining values z D. Hence ( z u (z dσ F (4.3 mod F Γ (. inf γ Γ γ ( z u (z / ds F For the denominator in (4.3, let γ be a curve in Γ, γ thecurveaboveitinf,andl( γ its length. Then d ρds F = γ γ. 3
5 5 Parametrizing γ with respect to arc length and using the fact that 3 d ds 3 (d /ds (d /ds (d 3 /ds, 3 we have γ d 3 = l( γ 0 (d /ds (d /ds (d 3 /ds ds 3 l( γ 0 d 3 /ds l( γ ds 3 0 dt t M log( R r M where M =ma S(r ( z u (z /.Thus, (4.4 γ ( ( z u (z / ds F log R r, M To obtain a bound for the numerator, we let η(z = z arctan δ(z, δ(z =u(z z, (4.5 z u (z = z ( δ (z. Tobeginwith,wenotethat η i = ( i ui arctan δ(z z 3 z δ (z z iu, z 3 and so (4.6 Also, i= u i z ( δ (z u = arctan δ(z z 3 i= u = i= η i u i u i u i δ(z u z 3 δ (z i= u i, u u i= i u i u.
6 6 ALLEN WEITSMAN and thus (4.7 i= u i z ( δ (z u = u z ( δ (z z ( δ (z u. Finally, by Green s Theorem (4.8 i= η i u i d d u = η u n u dz, η i= i u i u d d with n being the outer unit normal. The middle term vanishes because of the minimal surface equation. Using (4.5 (4.7 in (4.8 we then have dσ F z u (z = ( δ (z d d u z η u n dz u arctan δ(z δ(z δ (z i= i= i u i z d d u z i u i z d d u z Since this gives i= i u i z u u u, dσ F z u (z η u n dz u z u arctan δ(z u δ(z δ (z ( δ (z d d u z d d z u d d u z.
7 7 Since η u n dz u z η u dz u z π, and by (4. δ(z 0, we have dσ F z u (z ( o( d d π (R. z Combining this with (4.3 and (4.4 we obtain (4.. We now use the conformal invariance of the mapping H F as described in 3 together with the estimate of Theorem 4.. With a, b, f(ζ asin 3, continuing with [M; p.67] we take r>0sothats(r separates b and in D. For t r, lets (t =f (S(t so that S (t has endpoints on H in the ζ plane. Let l(t denote the Jordan curve formed by S (t along with its reflection across H and G the annular domain between l(r and l(r. Let Γ(r, R be the family of curves separating l(r andl(r ing. Then since l(r and l(r separate 0 (= f (a and (= f (b from, the modulus (in the Euclidean metric satisfies [LV; pp.3, 56 and 6 (.0] mod Γ(r, R log(6(p, π where P = min ζ l(r ζ. Now let Γ (r, R be the curves joining l(randl(ring. ThenmodΓ (r, R =/mod Γ(r, R. This follows from conformal invariance and the fact that this is the case for a true annulus [A; pp.,3]. Therefore, (4.9 mod Γ (r, R π log(6(m(r. Let m(t = min ζ(z. z =t z D Then by (4.9, the symmetry principle [A; p.6], and conformal invariance, (4.0 mod F Γ(r, R π log(6(m(r. Thus, (4.0 taken together with Theorem 4. yields
8 8 ALLEN WEITSMAN Theorem 4.. With the above notation and conventions,, ( log m(r lim inf ( o( d d π π. R (log R D(r,R z V. Proof of Theorem.. We assume for some β π that (.3 fails. Then (5. u(z =O( z π/β ɛ (ɛ>0,z,z D, so (4. holds and we may apply Theorem 4.. We have (5. ( log m(r π (log R ( o( dtdθ O( D(r,R t ( log m(r R β dt ( o( O( (log R r t ( log m(r β(log R ( o( (R y (5. we have (5.3 R m(r β/πo(. With s = m(r, (5.4 ma f(ζ R. ζ =s Putting together (5., (5.3, (5.4, and using the maimum principle, we obtain (5.5 ma u(f(ζ ma u(z ζ =s ζ H z =R z D O(R π/β ɛ =O(((m(R β/πo( π/β ɛ =o( s (s. Now, our hypothesis implies that u(f(ζ is harmonic and positive in H and 0 on H. As pointed out in 3, this implies that u(f(ζ = c Imζ. y (5.5 however, we have c =0, a contradiction. References [A] L. Ahlfors, Lectures on quasiconformal mappings, Van Nostrand, 966. [F] W. Fuchs, Topics in the theory of functions of one comple variable, Van Nostrand, 967. [LV] O. Lehto and K. Virtanen, Quasiconformal mappings in the plane, Springer-Verlag,, 973. [M] V. Mikljukov, Some singularities in the behavior of solutions of equations of minimal surface type in unbounded domains, Math. USSR Sbornik 44 (983, 6-73.
9 9 [Ne] R. Nevanlinna, Analytic functions, Springer-Verlag, 970. [Ni] J.C.C. Nitsche, On new results in the theory of minimal surfaces, ull. Amer. Math. Soc. 7 (965, [O] R. Osserman, A survey of minimal surfaces, Dover, 986. [S] J. Spruck, Two dimensional graphs over unbounded domains, J.Inst.Math.Jussien (00, [T] M. Tsuji, Potential theory in modern function theory, Maruzen Co. LTD., 959. Address: Department of Mathematics Purdue University West Lafayette, IN weitsman@purdue.edu
SPIRALING MINIMAL GRAPHS. Allen Weitsman
 SPIRALING MINIMAL GRAPHS Allen Weitsman Abstract. We consider minimal graphs u = u(x, y) > 0 over unbounded spiraling domains D with u = 0 on D. We show that such surfaces do exist, but only if the rate
SPIRALING MINIMAL GRAPHS Allen Weitsman Abstract. We consider minimal graphs u = u(x, y) > 0 over unbounded spiraling domains D with u = 0 on D. We show that such surfaces do exist, but only if the rate
MINIMAL GRAPHS OVER CONCAVE DOMAINS
 MINIMAL GRAPHS OVER CONCAVE DOMAINS ALLEN WEITSMAN Abstract. We consider minimal graphs u = u(x, y > 0 over concave unbounded domains D R 2 bounded by a Jordan arc γ on which u = 0. We prove that the sets
MINIMAL GRAPHS OVER CONCAVE DOMAINS ALLEN WEITSMAN Abstract. We consider minimal graphs u = u(x, y > 0 over concave unbounded domains D R 2 bounded by a Jordan arc γ on which u = 0. We prove that the sets
ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 5, 24 ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove some versions of the Schwarz
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 5, 24 ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove some versions of the Schwarz
ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS
 ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS Daoud Bshouty, Dept. of Mathematics, Technion Inst. of Technology, 3200 Haifa, Israel, and Allen Weitsman, Dept. of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, IN 47907
ON THE GAUSS MAP OF MINIMAL GRAPHS Daoud Bshouty, Dept. of Mathematics, Technion Inst. of Technology, 3200 Haifa, Israel, and Allen Weitsman, Dept. of Mathematics, Purdue University, W. Lafayette, IN 47907
ondary 31C05 Key words and phrases: Planar harmonic mappings, Quasiconformal mappings, Planar domains
 Novi Sad J. Math. Vol. 38, No. 3, 2008, 147-156 QUASICONFORMAL AND HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN SMOOTH JORDAN DOMAINS David Kalaj 1, Miodrag Mateljević 2 Abstract. We present some recent results on the topic
Novi Sad J. Math. Vol. 38, No. 3, 2008, 147-156 QUASICONFORMAL AND HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN SMOOTH JORDAN DOMAINS David Kalaj 1, Miodrag Mateljević 2 Abstract. We present some recent results on the topic
On the Poisson Integral of Step Functions and Minimal Surfaces. Allen Weitsman
 On the Poisson Integral of Step Functions and Minimal Surfaces Allen Weitsman Abstract. Applications of minimal surface methods are made to obtain information about univalent harmonic mappings. In the
On the Poisson Integral of Step Functions and Minimal Surfaces Allen Weitsman Abstract. Applications of minimal surface methods are made to obtain information about univalent harmonic mappings. In the
A Note on the Harmonic Quasiconformal Diffeomorphisms of the Unit Disc
 Filomat 29:2 (2015), 335 341 DOI 10.2298/FIL1502335K Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat A Note on the Harmonic Quasiconformal
Filomat 29:2 (2015), 335 341 DOI 10.2298/FIL1502335K Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat A Note on the Harmonic Quasiconformal
A SOLUTION TO SHEIL-SMALL S HARMONIC MAPPING PROBLEM FOR POLYGONS. 1. Introduction
 A SOLUTION TO SHEIL-SMALL S HARMONIC MAPPING PROLEM FOR POLYGONS DAOUD SHOUTY, ERIK LUNDERG, AND ALLEN WEITSMAN Abstract. The problem of mapping the interior of a Jordan polygon univalently by the Poisson
A SOLUTION TO SHEIL-SMALL S HARMONIC MAPPING PROLEM FOR POLYGONS DAOUD SHOUTY, ERIK LUNDERG, AND ALLEN WEITSMAN Abstract. The problem of mapping the interior of a Jordan polygon univalently by the Poisson
Norwegian University of Science and Technology N-7491 Trondheim, Norway
 QUASICONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 48 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1999 WHAT IS A DISK? KARI HAG Norwegian University of Science and
QUASICONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 48 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1999 WHAT IS A DISK? KARI HAG Norwegian University of Science and
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS
 A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
2 Simply connected domains
 RESEARCH A note on the Königs domain of compact composition operators on the Bloch space Matthew M Jones Open Access Correspondence: m.m.jones@mdx. ac.uk Department of Mathematics, Middlesex University,
RESEARCH A note on the Königs domain of compact composition operators on the Bloch space Matthew M Jones Open Access Correspondence: m.m.jones@mdx. ac.uk Department of Mathematics, Middlesex University,
Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the unit disk
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Approximation Theory 164 (2012) 815 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Approximation Theory 164 (2012) 815 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the
First fundamental Theorem of Nevanlinna Theory MAT 205B
 First fundamental Theorem of Nevanlinna Theory Ojesh Koul June 0, 208 The theory aims to describe the value distribution of meromorphic functions by looking at various formulae connecting the values of
First fundamental Theorem of Nevanlinna Theory Ojesh Koul June 0, 208 The theory aims to describe the value distribution of meromorphic functions by looking at various formulae connecting the values of
arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 28 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 28 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 28 Jun 2008](/thumbs/90/101198950.jpg) Limit Surfaces of Riemann Examples David Hoffman, Wayne Rossman arxiv:0806.467v [math.dg] 28 Jun 2008 Introduction The only connected minimal surfaces foliated by circles and lines are domains on one of
Limit Surfaces of Riemann Examples David Hoffman, Wayne Rossman arxiv:0806.467v [math.dg] 28 Jun 2008 Introduction The only connected minimal surfaces foliated by circles and lines are domains on one of
Bloch radius, normal families and quasiregular mappings
 Bloch radius, normal families and quasiregular mappings Alexandre Eremenko Abstract Bloch s Theorem is extended to K-quasiregular maps R n S n, where S n is the standard n-dimensional sphere. An example
Bloch radius, normal families and quasiregular mappings Alexandre Eremenko Abstract Bloch s Theorem is extended to K-quasiregular maps R n S n, where S n is the standard n-dimensional sphere. An example
On multiple points of meromorphic functions
 On multiple points of meromorphic functions Jim Langley and Dan Shea Abstract We establish lower bounds for the number of zeros of the logarithmic derivative of a meromorphic function of small growth with
On multiple points of meromorphic functions Jim Langley and Dan Shea Abstract We establish lower bounds for the number of zeros of the logarithmic derivative of a meromorphic function of small growth with
Bounded and integrable quadratic differentials: hyperbolic and extremal lengths on Riemann surfaces
 Geometric Complex Analysis edited by Junjiro Noguchi et al. World Scientific, Singapore, 1995 pp.443 450 Bounded and integrable quadratic differentials: hyperbolic and extremal lengths on Riemann surfaces
Geometric Complex Analysis edited by Junjiro Noguchi et al. World Scientific, Singapore, 1995 pp.443 450 Bounded and integrable quadratic differentials: hyperbolic and extremal lengths on Riemann surfaces
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
 VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
CHAPTER 1. Preliminaries
 CHAPTER 1 Preliminaries We collect here some definitions and properties of plane quasiconformal mappings. Two basic references for this material are the books by Ahlfors [7] andlehto and Virtanen [117],
CHAPTER 1 Preliminaries We collect here some definitions and properties of plane quasiconformal mappings. Two basic references for this material are the books by Ahlfors [7] andlehto and Virtanen [117],
Chapter 16. Manifolds and Geodesics Manifold Theory. Reading: Osserman [7] Pg , 55, 63-65, Do Carmo [2] Pg ,
![Chapter 16. Manifolds and Geodesics Manifold Theory. Reading: Osserman [7] Pg , 55, 63-65, Do Carmo [2] Pg , Chapter 16. Manifolds and Geodesics Manifold Theory. Reading: Osserman [7] Pg , 55, 63-65, Do Carmo [2] Pg ,](/thumbs/81/84541290.jpg) Chapter 16 Manifolds and Geodesics Reading: Osserman [7] Pg. 43-52, 55, 63-65, Do Carmo [2] Pg. 238-247, 325-335. 16.1 Manifold Theory Let us recall the definition of differentiable manifolds Definition
Chapter 16 Manifolds and Geodesics Reading: Osserman [7] Pg. 43-52, 55, 63-65, Do Carmo [2] Pg. 238-247, 325-335. 16.1 Manifold Theory Let us recall the definition of differentiable manifolds Definition
Singularities of inverse functions
 Singularities of inverse functions Alexandre Eremenko May 26, 2013 Abstract This is a lecture delivered at the workshop The role of complex analysis in complex dynamics in Edinburgh on May 22 2013. 1.
Singularities of inverse functions Alexandre Eremenko May 26, 2013 Abstract This is a lecture delivered at the workshop The role of complex analysis in complex dynamics in Edinburgh on May 22 2013. 1.
Phase Calculations for Planar Partition Polynomials
 Phase Calculations for Planar Partition Polynomials Robert Boyer and Daniel Parry Abstract. In the study of the asymptotic behavior of polynomials from partition theory, the determination of their leading
Phase Calculations for Planar Partition Polynomials Robert Boyer and Daniel Parry Abstract. In the study of the asymptotic behavior of polynomials from partition theory, the determination of their leading
HARMONIC MAPS BETWEEN ANNULI ON RIEMANN SURFACES
 HARMONIC MAPS BETWEEN ANNULI ON RIEMANN SURFACES DAVID KALAJ Abstract. Let ρ Σ = h z 2 be a metric in a Riemann surface Σ, where h is a positive real function. Let H r = {w = fz} be the family of univalent
HARMONIC MAPS BETWEEN ANNULI ON RIEMANN SURFACES DAVID KALAJ Abstract. Let ρ Σ = h z 2 be a metric in a Riemann surface Σ, where h is a positive real function. Let H r = {w = fz} be the family of univalent
A lower bound for the Bloch radius of K-quasiregular mappings
 A lower bound for the Bloch radius of K-quasiregular mappings Kai Rajala Abstract We give a quantitative proof to Eremenko s theorem [6], which extends the classical Bloch s theorem to the class of n-dimensional
A lower bound for the Bloch radius of K-quasiregular mappings Kai Rajala Abstract We give a quantitative proof to Eremenko s theorem [6], which extends the classical Bloch s theorem to the class of n-dimensional
COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS
 Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
UNIFORMLY PERFECT ANALYTIC AND CONFORMAL ATTRACTOR SETS. 1. Introduction and results
 UNIFORMLY PERFECT ANALYTIC AND CONFORMAL ATTRACTOR SETS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Conditions are given which imply that analytic iterated function systems (IFS s) in the complex plane C have uniformly
UNIFORMLY PERFECT ANALYTIC AND CONFORMAL ATTRACTOR SETS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Conditions are given which imply that analytic iterated function systems (IFS s) in the complex plane C have uniformly
GROWTH OF SOLUTIONS TO HIGHER ORDER LINEAR HOMOGENEOUS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS IN ANGULAR DOMAINS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol 200(200), No 64, pp 7 ISSN: 072-669 URL: http://ejdemathtxstateedu or http://ejdemathuntedu ftp ejdemathtxstateedu GROWTH OF SOLUTIONS TO HIGHER ORDER
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol 200(200), No 64, pp 7 ISSN: 072-669 URL: http://ejdemathtxstateedu or http://ejdemathuntedu ftp ejdemathtxstateedu GROWTH OF SOLUTIONS TO HIGHER ORDER
Interactions between Function Theory and Holomorphic Dynamics
 Interactions between Function Theory and Holomorphic Dynamics Alexandre Eremenko July 23, 2018 Dedicated to Walter Bergweiler on the occasion of his 60-th birthday It is not surprising that in the study
Interactions between Function Theory and Holomorphic Dynamics Alexandre Eremenko July 23, 2018 Dedicated to Walter Bergweiler on the occasion of his 60-th birthday It is not surprising that in the study
Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains
 Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains Ken-ichi Sakan (Osaka City Univ., Japan) Dariusz Partyka (The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Poland)
Quasiconformal and Lipschitz harmonic mappings of the unit disk onto bounded convex domains Ken-ichi Sakan (Osaka City Univ., Japan) Dariusz Partyka (The John Paul II Catholic University of Lublin, Poland)
ON A DISTANCE DEFINED BY THE LENGTH SPECTRUM ON TEICHMÜLLER SPACE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 28, 2003, 315 326 ON A DISTANCE DEFINED BY THE LENGTH SPECTRUM ON TEICHMÜLLER SPACE Hiroshige Shiga Tokyo Institute of Technology, Department of
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 28, 2003, 315 326 ON A DISTANCE DEFINED BY THE LENGTH SPECTRUM ON TEICHMÜLLER SPACE Hiroshige Shiga Tokyo Institute of Technology, Department of
Intrinsic Geometry. Andrejs Treibergs. Friday, March 7, 2008
 Early Research Directions: Geometric Analysis II Intrinsic Geometry Andrejs Treibergs University of Utah Friday, March 7, 2008 2. References Part of a series of thee lectures on geometric analysis. 1 Curvature
Early Research Directions: Geometric Analysis II Intrinsic Geometry Andrejs Treibergs University of Utah Friday, March 7, 2008 2. References Part of a series of thee lectures on geometric analysis. 1 Curvature
Propagation of Smallness and the Uniqueness of Solutions to Some Elliptic Equations in the Plane
 Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 267, 460 470 (2002) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7769, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Propagation of Smallness and the Uniqueness of Solutions
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 267, 460 470 (2002) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7769, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Propagation of Smallness and the Uniqueness of Solutions
VERTICAL LIMITS OF GRAPH DOMAINS
 VERTICAL LIMITS OF GRAPH DOMAINS HRANT HAKOBYAN AND DRAGOMIR ŠARIĆ Abstract. We consider the limiting behavior of Teichmüller geodesics in the universal Teichmüller space T (H). Our main result states
VERTICAL LIMITS OF GRAPH DOMAINS HRANT HAKOBYAN AND DRAGOMIR ŠARIĆ Abstract. We consider the limiting behavior of Teichmüller geodesics in the universal Teichmüller space T (H). Our main result states
Quasiconformal Maps and Circle Packings
 Quasiconformal Maps and Circle Packings Brett Leroux June 11, 2018 1 Introduction Recall the statement of the Riemann mapping theorem: Theorem 1 (Riemann Mapping). If R is a simply connected region in
Quasiconformal Maps and Circle Packings Brett Leroux June 11, 2018 1 Introduction Recall the statement of the Riemann mapping theorem: Theorem 1 (Riemann Mapping). If R is a simply connected region in
Mapping the disk to convex subregions
 Mapping the disk to convex subregions John A. Velling 11 March 1995 1. Introduction. Univalent maps f : D D have been much studied by many authors. See [1], [2], [5], for just a few references. A quick
Mapping the disk to convex subregions John A. Velling 11 March 1995 1. Introduction. Univalent maps f : D D have been much studied by many authors. See [1], [2], [5], for just a few references. A quick
ISOPERIMETRIC INEQUALITY FOR FLAT SURFACES
 Proceedings of The Thirteenth International Workshop on Diff. Geom. 3(9) 3-9 ISOPERIMETRIC INEQUALITY FOR FLAT SURFACES JAIGYOUNG CHOE Korea Institute for Advanced Study, Seoul, 3-7, Korea e-mail : choe@kias.re.kr
Proceedings of The Thirteenth International Workshop on Diff. Geom. 3(9) 3-9 ISOPERIMETRIC INEQUALITY FOR FLAT SURFACES JAIGYOUNG CHOE Korea Institute for Advanced Study, Seoul, 3-7, Korea e-mail : choe@kias.re.kr
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019](/thumbs/94/121818370.jpg) 1 SCHWARZ LEMMA FOR HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN RIEMANN SURFACES arxiv:1903.05163v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove a Schwarz type lemma for harmonic mappings between the unit and a
1 SCHWARZ LEMMA FOR HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN RIEMANN SURFACES arxiv:1903.05163v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove a Schwarz type lemma for harmonic mappings between the unit and a
7 The cigar soliton, the Rosenau solution, and moving frame calculations
 7 The cigar soliton, the Rosenau solution, and moving frame calculations When making local calculations of the connection and curvature, one has the choice of either using local coordinates or moving frames.
7 The cigar soliton, the Rosenau solution, and moving frame calculations When making local calculations of the connection and curvature, one has the choice of either using local coordinates or moving frames.
Random Conformal Welding
 Random Conformal Welding Antti Kupiainen joint work with K. Astala, P. Jones, E. Saksman Ascona 26.5.2010 Random Planar Curves 2d Statistical Mechanics: phase boundaries Closed curves or curves joining
Random Conformal Welding Antti Kupiainen joint work with K. Astala, P. Jones, E. Saksman Ascona 26.5.2010 Random Planar Curves 2d Statistical Mechanics: phase boundaries Closed curves or curves joining
Radially distributed values and normal families, II
 Radially distributed values and normal families, II Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko Dedicated to Larry Zalcman Abstract We consider the family of all functions holomorphic in the unit disk for
Radially distributed values and normal families, II Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko Dedicated to Larry Zalcman Abstract We consider the family of all functions holomorphic in the unit disk for
The Logarithmic Derivative for Minimal Surfaces in R 3. G. Rhoads and A. Weitsman. Dedicated to the memory of W alter Hengartner.
 The Logarithmic Derivative for Minimal Surfaces in R 3 G. Rhoads and A. Weitsman Abstract. E. F. Beckenbach and collaborators developed a value distribution theory for minimal surfaces which paralleled
The Logarithmic Derivative for Minimal Surfaces in R 3 G. Rhoads and A. Weitsman Abstract. E. F. Beckenbach and collaborators developed a value distribution theory for minimal surfaces which paralleled
SAMPLING SEQUENCES FOR BERGMAN SPACES FOR p < 1. Alexander P. Schuster and Dror Varolin
 SAMPLING SEQUENCES FOR BERGMAN SPACES FOR p < Alexander P. Schuster and ror Varolin Abstract. We provide a proof of the sufficiency direction of Seip s characterization of sampling sequences for Bergman
SAMPLING SEQUENCES FOR BERGMAN SPACES FOR p < Alexander P. Schuster and ror Varolin Abstract. We provide a proof of the sufficiency direction of Seip s characterization of sampling sequences for Bergman
David E. Barrett and Jeffrey Diller University of Michigan Indiana University
 A NEW CONSTRUCTION OF RIEMANN SURFACES WITH CORONA David E. Barrett and Jeffrey Diller University of Michigan Indiana University 1. Introduction An open Riemann surface X is said to satisfy the corona
A NEW CONSTRUCTION OF RIEMANN SURFACES WITH CORONA David E. Barrett and Jeffrey Diller University of Michigan Indiana University 1. Introduction An open Riemann surface X is said to satisfy the corona
Subharmonic functions
 Subharmonic functions N.A. 07 Upper semicontinuous functions. Let (X, d) be a metric space. A function f : X R { } is upper semicontinuous (u.s.c.) if lim inf f(y) f(x) x X. y x A function g is lower semicontinuous
Subharmonic functions N.A. 07 Upper semicontinuous functions. Let (X, d) be a metric space. A function f : X R { } is upper semicontinuous (u.s.c.) if lim inf f(y) f(x) x X. y x A function g is lower semicontinuous
Rigidity and Non-rigidity Results on the Sphere
 Rigidity and Non-rigidity Results on the Sphere Fengbo Hang Xiaodong Wang Department of Mathematics Michigan State University Oct., 00 1 Introduction It is a simple consequence of the maximum principle
Rigidity and Non-rigidity Results on the Sphere Fengbo Hang Xiaodong Wang Department of Mathematics Michigan State University Oct., 00 1 Introduction It is a simple consequence of the maximum principle
The result above is known as the Riemann mapping theorem. We will prove it using basic theory of normal families. We start this lecture with that.
 Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent functions with opening angle at infinity
 A SHARP BOUND FOR THE SCHWARZIAN DERIVATIVE OF CONCAVE FUNCTIONS BAPPADITYA BHOWMIK AND KARL-JOACHIM WIRTHS Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent
A SHARP BOUND FOR THE SCHWARZIAN DERIVATIVE OF CONCAVE FUNCTIONS BAPPADITYA BHOWMIK AND KARL-JOACHIM WIRTHS Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent
CORTONA SUMMER COURSE NOTES
 CORTONA SUMMER COURSE NOTES SUMMARY: These notes include 1) a list below of ancillary references, 2) a description of various proof techniques for the basic conjugation theorems, and 3) a page of miscellaneous
CORTONA SUMMER COURSE NOTES SUMMARY: These notes include 1) a list below of ancillary references, 2) a description of various proof techniques for the basic conjugation theorems, and 3) a page of miscellaneous
COMPOSITION SEMIGROUPS ON BMOA AND H AUSTIN ANDERSON, MIRJANA JOVOVIC, AND WAYNE SMITH
 COMPOSITION SEMIGROUPS ON BMOA AND H AUSTIN ANDERSON, MIRJANA JOVOVIC, AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. We study [ϕ t, X], the maximal space of strong continuity for a semigroup of composition operators induced
COMPOSITION SEMIGROUPS ON BMOA AND H AUSTIN ANDERSON, MIRJANA JOVOVIC, AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. We study [ϕ t, X], the maximal space of strong continuity for a semigroup of composition operators induced
CONFORMAL MODELS AND FINGERPRINTS OF PSEUDO-LEMNISCATES
 CONFORMAL MODELS AND FINGERPRINTS OF PSEUDO-LEMNISCATES TREVOR RICHARDS AND MALIK YOUNSI Abstract. We prove that every meromorphic function on the closure of an analytic Jordan domain which is sufficiently
CONFORMAL MODELS AND FINGERPRINTS OF PSEUDO-LEMNISCATES TREVOR RICHARDS AND MALIK YOUNSI Abstract. We prove that every meromorphic function on the closure of an analytic Jordan domain which is sufficiently
3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations
 Summer School Normal Families in Complex Analysis Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg May 22 29, 2015 3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations Aimo Hinkkanen University of Illinois at Urbana
Summer School Normal Families in Complex Analysis Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg May 22 29, 2015 3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations Aimo Hinkkanen University of Illinois at Urbana
HYPERBOLIC DERIVATIVES AND GENERALIZED SCHWARZ-PICK ESTIMATES
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 132, Number 11, Pages 339 3318 S 2-9939(4)7479-9 Article electronically published on May 12, 24 HYPERBOLIC DERIVATIVES AND GENERALIZED SCHWARZ-PICK
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 132, Number 11, Pages 339 3318 S 2-9939(4)7479-9 Article electronically published on May 12, 24 HYPERBOLIC DERIVATIVES AND GENERALIZED SCHWARZ-PICK
Differentiating Blaschke products
 Differentiating Blaschke products Oleg Ivrii April 14, 2017 Differentiating Blaschke Products Consider the following curious differentiation procedure: to a Blaschke product of degree d 1, F (z) = e iψ
Differentiating Blaschke products Oleg Ivrii April 14, 2017 Differentiating Blaschke Products Consider the following curious differentiation procedure: to a Blaschke product of degree d 1, F (z) = e iψ
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58
 CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
CHAPTER 2. CONFORMAL MAPPINGS 58 We prove that a strong form of converse of the above statement also holds. Please note we could apply the Theorem 1.11.3 to prove the theorem. But we prefer to apply the
Bounded domains which are universal for minimal surfaces
 Bounded domains which are universal for minimal surfaces Francisco Martín William H. Meeks, III Nicolai Nadirashvili August 16, 2005 Abstract We construct open domains in R 3 which do not admit complete
Bounded domains which are universal for minimal surfaces Francisco Martín William H. Meeks, III Nicolai Nadirashvili August 16, 2005 Abstract We construct open domains in R 3 which do not admit complete
SOME REMARKS ABOUT ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED ON AN ANNULUS. 1. Introduction. What else? Perimeter, eigenvalues of the Laplacian, etc...
 SOME REMARKS ABOUT ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED ON AN ANNULUS PIETRO POGGI-CORRADINI Abstract. We show that some recent reformulations of the classical Schwarz Lemma and results of Landau and Toeplitz can
SOME REMARKS ABOUT ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS DEFINED ON AN ANNULUS PIETRO POGGI-CORRADINI Abstract. We show that some recent reformulations of the classical Schwarz Lemma and results of Landau and Toeplitz can
Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary
 Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary David Chopp and John A. Velling December 1, 2003 Abstract Let γ be a Jordan curve in S 2, considered as the ideal
Foliations of hyperbolic space by constant mean curvature surfaces sharing ideal boundary David Chopp and John A. Velling December 1, 2003 Abstract Let γ be a Jordan curve in S 2, considered as the ideal
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007](/thumbs/95/125521566.jpg) A NOTE ON THE HAYMAN-WU THEOREM EDWARD CRANE arxiv:0707.1772v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 Abstract. The Hayman-Wu theorem states that the preimage of a line or circle L under a conformal mapping from the unit
A NOTE ON THE HAYMAN-WU THEOREM EDWARD CRANE arxiv:0707.1772v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 Abstract. The Hayman-Wu theorem states that the preimage of a line or circle L under a conformal mapping from the unit
Complex Variables and Elliptic Equations
 Estimate of hyperbolically partial derivatives of $\rho$harmonic quasiconformal mappings and its applications Journal: Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted by the Author:
Estimate of hyperbolically partial derivatives of $\rho$harmonic quasiconformal mappings and its applications Journal: Manuscript ID: Draft Manuscript Type: Research Paper Date Submitted by the Author:
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
THE L 2 -HODGE THEORY AND REPRESENTATION ON R n
 THE L 2 -HODGE THEORY AND REPRESENTATION ON R n BAISHENG YAN Abstract. We present an elementary L 2 -Hodge theory on whole R n based on the minimization principle of the calculus of variations and some
THE L 2 -HODGE THEORY AND REPRESENTATION ON R n BAISHENG YAN Abstract. We present an elementary L 2 -Hodge theory on whole R n based on the minimization principle of the calculus of variations and some
THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 26, 2001, 401 407 THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE A. F. Beardon University of Cambridge, DPMMS, Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 26, 2001, 401 407 THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE A. F. Beardon University of Cambridge, DPMMS, Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce
158 Robert Osserman As immediate corollaries, one has: Corollary 1 (Liouville's Theorem). A bounded analytic function in the entire plane is constant.
 Proceedings Ist International Meeting on Geometry and Topology Braga (Portugal) Public. Centro de Matematica da Universidade do Minho p. 157{168, 1998 A new variant of the Schwarz{Pick{Ahlfors Lemma Robert
Proceedings Ist International Meeting on Geometry and Topology Braga (Portugal) Public. Centro de Matematica da Universidade do Minho p. 157{168, 1998 A new variant of the Schwarz{Pick{Ahlfors Lemma Robert
Inequalities for sums of Green potentials and Blaschke products
 Submitted exclusively to the London Mathematical Society doi:10.1112/0000/000000 Inequalities for sums of reen potentials and Blaschke products Igor. Pritsker Abstract We study inequalities for the ima
Submitted exclusively to the London Mathematical Society doi:10.1112/0000/000000 Inequalities for sums of reen potentials and Blaschke products Igor. Pritsker Abstract We study inequalities for the ima
DAVID MAPS AND HAUSDORFF DIMENSION
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 9, 004, 38 DAVID MAPS AND HAUSDORFF DIMENSION Saeed Zakeri Stony Brook University, Institute for Mathematical Sciences Stony Brook, NY 794-365,
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 9, 004, 38 DAVID MAPS AND HAUSDORFF DIMENSION Saeed Zakeri Stony Brook University, Institute for Mathematical Sciences Stony Brook, NY 794-365,
RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATIONS AND DEGENERATE SUBDOMAINS OF THE UNIT DISK
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9939(XX)0000-0 RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATIONS AND DEGENERATE SUBDOMAINS OF THE UNIT DISK LINDA KEEN AND NIKOLA
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 00, Number 0, Pages 000 000 S 0002-9939(XX)0000-0 RANDOM HOLOMORPHIC ITERATIONS AND DEGENERATE SUBDOMAINS OF THE UNIT DISK LINDA KEEN AND NIKOLA
ON A MEASURE THEORETIC AREA FORMULA
 ON A MEASURE THEORETIC AREA FORMULA VALENTINO MAGNANI Abstract. We review some classical differentiation theorems for measures, showing how they can be turned into an integral representation of a Borel
ON A MEASURE THEORETIC AREA FORMULA VALENTINO MAGNANI Abstract. We review some classical differentiation theorems for measures, showing how they can be turned into an integral representation of a Borel
An alternative proof of Mañé s theorem on non-expanding Julia sets
 An alternative proof of Mañé s theorem on non-expanding Julia sets Mitsuhiro Shishikura and Tan Lei Abstract We give a proof of the following theorem of Mañé: A forward invariant compact set in the Julia
An alternative proof of Mañé s theorem on non-expanding Julia sets Mitsuhiro Shishikura and Tan Lei Abstract We give a proof of the following theorem of Mañé: A forward invariant compact set in the Julia
ON THE NIELSEN-THURSTON-BERS TYPE OF SOME SELF-MAPS OF RIEMANN SURFACES WITH TWO SPECIFIED POINTS
 Imayoshi, Y., Ito, M. and Yamamoto, H. Osaka J. Math. 40 (003), 659 685 ON THE NIELSEN-THURSTON-BERS TYPE OF SOME SELF-MAPS OF RIEMANN SURFACES WITH TWO SPECIFIED POINTS Dedicated to Professor Hiroki Sato
Imayoshi, Y., Ito, M. and Yamamoto, H. Osaka J. Math. 40 (003), 659 685 ON THE NIELSEN-THURSTON-BERS TYPE OF SOME SELF-MAPS OF RIEMANN SURFACES WITH TWO SPECIFIED POINTS Dedicated to Professor Hiroki Sato
Pacific Journal of Mathematics
 Pacific Journal of Mathematics LINES OF MINIMA ARE UNIFORMLY QUASIGEODESIC YOUNG-EUN CHOI, KASRA RAFI AND CAROLINE SERIES Volume 237 No. 1 September 2008 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. 237, No. 1,
Pacific Journal of Mathematics LINES OF MINIMA ARE UNIFORMLY QUASIGEODESIC YOUNG-EUN CHOI, KASRA RAFI AND CAROLINE SERIES Volume 237 No. 1 September 2008 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol. 237, No. 1,
UNIFORM DENSITIES OF REGULAR SEQUENCES IN THE UNIT DISK. Peter L. Duren, Alexander P. Schuster and Kristian Seip
 UNIFORM DENSITIES OF REGULAR SEQUENCES IN THE UNIT DISK Peter L. Duren, Alexander P. Schuster and Kristian Seip Abstract. The upper and lower uniform densities of some regular sequences are computed. These
UNIFORM DENSITIES OF REGULAR SEQUENCES IN THE UNIT DISK Peter L. Duren, Alexander P. Schuster and Kristian Seip Abstract. The upper and lower uniform densities of some regular sequences are computed. These
On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a Boundary Point
 Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 261, 649 664 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7564, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 261, 649 664 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2001.7564, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on On the Class of Functions Starlike with Respect to a
QUASI-METRIC AND METRIC SPACES
 CONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS An Electronic Journal of the American Mathematical Society Volume 10, Pages 355 360 (December 26, 2006) S 1088-4173(06)055-X QUASI-METRIC AND METRIC SPACES VIKTOR SCHROEDER
CONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS An Electronic Journal of the American Mathematical Society Volume 10, Pages 355 360 (December 26, 2006) S 1088-4173(06)055-X QUASI-METRIC AND METRIC SPACES VIKTOR SCHROEDER
SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS. Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S. L. Yadava. 1. Introduction
 Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
Growth of Solutions of Second Order Complex Linear Differential Equations with Entire Coefficients
 Filomat 32: (208), 275 284 https://doi.org/0.2298/fil80275l Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Growth of Solutions
Filomat 32: (208), 275 284 https://doi.org/0.2298/fil80275l Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Growth of Solutions
Quasisymmetric Embeddings of Slit Sierpiński Carpets into R 2
 Quasisymmetric Embeddings of Slit Sierpiński Carpets into R 2 Wenbo Li Graduate Center, CUNY CAFT, July 21, 2018 Wenbo Li 1 / 17 Sierpiński Carpet S 3 - the standard Sierpiński carpet in [0, 1] 2. Figure:
Quasisymmetric Embeddings of Slit Sierpiński Carpets into R 2 Wenbo Li Graduate Center, CUNY CAFT, July 21, 2018 Wenbo Li 1 / 17 Sierpiński Carpet S 3 - the standard Sierpiński carpet in [0, 1] 2. Figure:
An introduction to General Relativity and the positive mass theorem
 An introduction to General Relativity and the positive mass theorem National Center for Theoretical Sciences, Mathematics Division March 2 nd, 2007 Wen-ling Huang Department of Mathematics University of
An introduction to General Relativity and the positive mass theorem National Center for Theoretical Sciences, Mathematics Division March 2 nd, 2007 Wen-ling Huang Department of Mathematics University of
1 Introduction and statements of results
 CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE SURFACES WITH BOUNDARY IN EUCLIDEAN THREE-SPACE Rafael López 1 1 Introduction and statements of results The study of the structure of the space of constant mean curvature compact
CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE SURFACES WITH BOUNDARY IN EUCLIDEAN THREE-SPACE Rafael López 1 1 Introduction and statements of results The study of the structure of the space of constant mean curvature compact
arxiv: v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 2013 arxiv: v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 2013](/thumbs/86/93829905.jpg) SHAPES OF POLYNOMIAL JULIA SETS KATHRYN A. LINDSEY arxiv:209.043v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 203 Abstract. Any Jordan curve in the complex plane can be approximated arbitrarily well in the Hausdorff topology by
SHAPES OF POLYNOMIAL JULIA SETS KATHRYN A. LINDSEY arxiv:209.043v2 [math.ds] 9 Jun 203 Abstract. Any Jordan curve in the complex plane can be approximated arbitrarily well in the Hausdorff topology by
AN EFFECTIVE METRIC ON C(H, K) WITH NORMAL STRUCTURE. Mona Nabiei (Received 23 June, 2015)
 NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 46 (2016), 53-64 AN EFFECTIVE METRIC ON C(H, K) WITH NORMAL STRUCTURE Mona Nabiei (Received 23 June, 2015) Abstract. This study first defines a new metric with
NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 46 (2016), 53-64 AN EFFECTIVE METRIC ON C(H, K) WITH NORMAL STRUCTURE Mona Nabiei (Received 23 June, 2015) Abstract. This study first defines a new metric with
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 17 Apr 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 17 Apr 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 17 Apr 2008](/thumbs/94/121818340.jpg) ON CERTAIN NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC PDE AND QUASICONFOMAL MAPPS BETWEEN EUCLIDEAN SURFACES arxiv:0804.785v [math.cv] 7 Apr 008 DAVID KALAJ AND MIODRAG MATELJEVIĆ Abstract. It is proved that every q.c. C diffeomorphism
ON CERTAIN NONLINEAR ELLIPTIC PDE AND QUASICONFOMAL MAPPS BETWEEN EUCLIDEAN SURFACES arxiv:0804.785v [math.cv] 7 Apr 008 DAVID KALAJ AND MIODRAG MATELJEVIĆ Abstract. It is proved that every q.c. C diffeomorphism
On Bank-Laine functions
 Computational Methods and Function Theory Volume 00 0000), No. 0, 000 000 XXYYYZZ On Bank-Laine functions Alastair Fletcher Keywords. Bank-Laine functions, zeros. 2000 MSC. 30D35, 34M05. Abstract. In this
Computational Methods and Function Theory Volume 00 0000), No. 0, 000 000 XXYYYZZ On Bank-Laine functions Alastair Fletcher Keywords. Bank-Laine functions, zeros. 2000 MSC. 30D35, 34M05. Abstract. In this
On the Length of Lemniscates
 On the Length of Lemniscates Alexandre Eremenko & Walter Hayman For a monic polynomial p of degree d, we write E(p) := {z : p(z) =1}. A conjecture of Erdős, Herzog and Piranian [4], repeated by Erdős in
On the Length of Lemniscates Alexandre Eremenko & Walter Hayman For a monic polynomial p of degree d, we write E(p) := {z : p(z) =1}. A conjecture of Erdős, Herzog and Piranian [4], repeated by Erdős in
ERRATUM TO AFFINE MANIFOLDS, SYZ GEOMETRY AND THE Y VERTEX
 ERRATUM TO AFFINE MANIFOLDS, SYZ GEOMETRY AND THE Y VERTEX JOHN LOFTIN, SHING-TUNG YAU, AND ERIC ZASLOW 1. Main result The purpose of this erratum is to correct an error in the proof of the main result
ERRATUM TO AFFINE MANIFOLDS, SYZ GEOMETRY AND THE Y VERTEX JOHN LOFTIN, SHING-TUNG YAU, AND ERIC ZASLOW 1. Main result The purpose of this erratum is to correct an error in the proof of the main result
Complex Analysis Math 220C Spring 2008
 Complex Analysis Math 220C Spring 2008 Bernard Russo June 2, 2008 Contents 1 Monday March 31, 2008 class cancelled due to the Master s travel plans 1 2 Wednesday April 2, 2008 Course information; Riemann
Complex Analysis Math 220C Spring 2008 Bernard Russo June 2, 2008 Contents 1 Monday March 31, 2008 class cancelled due to the Master s travel plans 1 2 Wednesday April 2, 2008 Course information; Riemann
Describing Blaschke products by their critical points
 Describing Blaschke products by their critical points Oleg Ivrii July 2 6, 2018 Finite Blaschke Products A finite Blaschke product of degree d 1 is an analytic function from D D of the form F (z) = e iψ
Describing Blaschke products by their critical points Oleg Ivrii July 2 6, 2018 Finite Blaschke Products A finite Blaschke product of degree d 1 is an analytic function from D D of the form F (z) = e iψ
arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 19 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 19 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 19 Jun 2017](/thumbs/89/98745009.jpg) LIMITING BEHAVIOR OF SEQUENCES OF PROPERLY EMBEDDED MINIMAL DISKS arxiv:1706.06186v1 [math.dg] 19 Jun 2017 DAVID HOFFMAN AND BRIAN WHITE Abstract. We develop a theory of minimal θ-graphs and characterize
LIMITING BEHAVIOR OF SEQUENCES OF PROPERLY EMBEDDED MINIMAL DISKS arxiv:1706.06186v1 [math.dg] 19 Jun 2017 DAVID HOFFMAN AND BRIAN WHITE Abstract. We develop a theory of minimal θ-graphs and characterize
The Hilbert Transform and Fine Continuity
 Irish Math. Soc. Bulletin 58 (2006), 8 9 8 The Hilbert Transform and Fine Continuity J. B. TWOMEY Abstract. It is shown that the Hilbert transform of a function having bounded variation in a finite interval
Irish Math. Soc. Bulletin 58 (2006), 8 9 8 The Hilbert Transform and Fine Continuity J. B. TWOMEY Abstract. It is shown that the Hilbert transform of a function having bounded variation in a finite interval
A property of the derivative of an entire function
 A property of the derivative of an entire function Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko February 12, 2012 Abstract We prove that the derivative of a non-linear entire function is unbounded on the preimage
A property of the derivative of an entire function Walter Bergweiler and Alexandre Eremenko February 12, 2012 Abstract We prove that the derivative of a non-linear entire function is unbounded on the preimage
INVARIANT GRADIENT IN REFINEMENTS OF SCHWARZ AND HARNACK INEQUALITIES
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 43, 208, 39 399 INVARIANT GRADIENT IN REFINEMENTS OF SCHWARZ AND HARNACK INEQUALITIES Petar Melentijević University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mathematics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 43, 208, 39 399 INVARIANT GRADIENT IN REFINEMENTS OF SCHWARZ AND HARNACK INEQUALITIES Petar Melentijević University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mathematics
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 15 May 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 15 May 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 15 May 2008](/thumbs/88/117934523.jpg) Conformal Metrics Daniela Kraus and Oliver Roth University of Würzburg Department of Mathematics D 9774 Würzburg Germany May 6, 28 arxiv:85.2235v [math.cv] 5 May 28 Introduction Conformal metrics connect
Conformal Metrics Daniela Kraus and Oliver Roth University of Würzburg Department of Mathematics D 9774 Würzburg Germany May 6, 28 arxiv:85.2235v [math.cv] 5 May 28 Introduction Conformal metrics connect
arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 7 May 2012
![arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 7 May 2012 arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 7 May 2012](/thumbs/94/118748903.jpg) ON EXTREA FUNCTION OF A ODUUS OF A FOIATION. CISKA arxiv:125.1356v1 [math.dg] 7 ay 212 Abstract. We investigate the properties of a modulus of a foliation on a Riemannian manifold. We give necessary and
ON EXTREA FUNCTION OF A ODUUS OF A FOIATION. CISKA arxiv:125.1356v1 [math.dg] 7 ay 212 Abstract. We investigate the properties of a modulus of a foliation on a Riemannian manifold. We give necessary and
BOUNDARY CORRESPONDENCE UNDER QUASICONFORMAL HARMONIC DIFFEO- MORPHISMS OF A HALF-PLANE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 3, 25, 159 165 BOUNDARY CORRESPONDENCE UNDER QUASICONFORMAL HARMONIC DIFFEO- MORPHISMS OF A HALF-PLANE David Kalaj and Miroslav Pavlović Prirodno-matematički
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 3, 25, 159 165 BOUNDARY CORRESPONDENCE UNDER QUASICONFORMAL HARMONIC DIFFEO- MORPHISMS OF A HALF-PLANE David Kalaj and Miroslav Pavlović Prirodno-matematički
Minimal Surfaces: Nonparametric Theory. Andrejs Treibergs. January, 2016
 USAC Colloquium Minimal Surfaces: Nonparametric Theory Andrejs Treibergs University of Utah January, 2016 2. USAC Lecture: Minimal Surfaces The URL for these Beamer Slides: Minimal Surfaces: Nonparametric
USAC Colloquium Minimal Surfaces: Nonparametric Theory Andrejs Treibergs University of Utah January, 2016 2. USAC Lecture: Minimal Surfaces The URL for these Beamer Slides: Minimal Surfaces: Nonparametric
CONVEXITY OF INTEGRAL MEANS OF SUBHARMONIC FUNCTIONS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAIN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 60, October 1976 CONVEXITY OF INTEGRAL MEANS OF SUBHARMONIC FUNCTIONS JANG-MEI G. WU' Abstract. We study the convexity of integral means of subharmonic
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAIN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 60, October 1976 CONVEXITY OF INTEGRAL MEANS OF SUBHARMONIC FUNCTIONS JANG-MEI G. WU' Abstract. We study the convexity of integral means of subharmonic
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
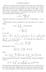 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
SZEGŐ KERNEL TRANSFORMATION LAW FOR PROPER HOLOMORPHIC MAPPINGS
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 3, 2014 SZEGŐ KERNEL TRANSFORMATION LAW FOR PROPER HOLOMORPHIC MAPPINGS MICHAEL BOLT ABSTRACT. Let Ω 1, Ω 2 be smoothly bounded doubly connected
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 3, 2014 SZEGŐ KERNEL TRANSFORMATION LAW FOR PROPER HOLOMORPHIC MAPPINGS MICHAEL BOLT ABSTRACT. Let Ω 1, Ω 2 be smoothly bounded doubly connected
SINGULAR INTEGRALS ON SIERPINSKI GASKETS
 SINGULAR INTEGRALS ON SIERPINSKI GASKETS VASILIS CHOUSIONIS Abstract. We construct a class of singular integral operators associated with homogeneous Calderón-Zygmund standard kernels on d-dimensional,
SINGULAR INTEGRALS ON SIERPINSKI GASKETS VASILIS CHOUSIONIS Abstract. We construct a class of singular integral operators associated with homogeneous Calderón-Zygmund standard kernels on d-dimensional,
MEAN CURVATURE FLOW OF ENTIRE GRAPHS EVOLVING AWAY FROM THE HEAT FLOW
 MEAN CURVATURE FLOW OF ENTIRE GRAPHS EVOLVING AWAY FROM THE HEAT FLOW GREGORY DRUGAN AND XUAN HIEN NGUYEN Abstract. We present two initial graphs over the entire R n, n 2 for which the mean curvature flow
MEAN CURVATURE FLOW OF ENTIRE GRAPHS EVOLVING AWAY FROM THE HEAT FLOW GREGORY DRUGAN AND XUAN HIEN NGUYEN Abstract. We present two initial graphs over the entire R n, n 2 for which the mean curvature flow
Bi-Lipschitz embeddings of Grushin spaces
 Bi-Lipschitz embeddings of Grushin spaces Matthew Romney University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 7 July 2016 The bi-lipschitz embedding problem Definition A map f : (X, d X ) (Y, d Y ) is bi-lipschitz
Bi-Lipschitz embeddings of Grushin spaces Matthew Romney University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 7 July 2016 The bi-lipschitz embedding problem Definition A map f : (X, d X ) (Y, d Y ) is bi-lipschitz
