Modeling face-to-face social interaction networks
|
|
|
- Kristina Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modeling face-to-face social interaction networks Romualdo Pastor-Satorras Dept. Fisica i Enginyería Nuclear Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Spain
2 Work done in collaboration with... Michele Starnini Andrea Baronchelli Northeastern University Alain Barrat
3 Dynamical social networks Networks have been used since long to characterize social systems (1934, J. Moreno) Many insights have been obtained, by looking at the topological properties of social networks! Small diameter, long tailed distributions, high clustering, community structure, etc Most previous considerations have focused on static social networks, in which vertices and edges do not change in time! Approximately correct in certain cases: citation networks Social interaction networks are however intrinsically dynamic, edges being a succession of contact or communication events, which are constantly created or terminated between pairs of individuals (actors)! Static networks being an integrated projection of dynamical ones The temporal dimension of social networks has important consequences! Epidemic spreading, usually considered on static networks
4 Effects of network dynamics on epidemics Key point: You are not in contact with all your friends simultaneously Imagine three individuals: Anne, Bob and Carol Anne has a contact with Bob and Bob has a contact with Carol A B C In a simple network interpretation, if Ann has a disease, she can pass it to Carol Adding a temporal dimension, the timing of the contacts matters t1 t2 A B C! If t2 < t1, then Carol cannot catch the disease!
5 Empirical analysis of dynamical social networks The empirical measurement of social interactions is a non-trivial task! Classically, it was performed by means of personal interviews and questionnaires " Expensive, time consuming, unreliable Recent technological advances have made possible the real-time tracking of social interactions in groups of individuals, at several temporal and spatial scales! exchanges! Mobile phone communications Here we focus on a cheap, largely scalable and high-resolution method:! The SocioPatterns project
6 The SocioPatterns Project Measure of the contact patterns of a group of interacting individuals in a spatially bounded setting, such as a set of offices or a conference. The participants are asked to carry small RFID tags (beacons). These beacons continuously broadcast small data packets which are received by a number of stations and relayed through a local network to a server Tags exchange low power messages in a peer-to-peer fashion to sense their neighborhood and assess directly contacts with nearby tags After the beacons detect a contact, they broadcast a report message at a higher power level. These reports are received by the stations and relayed to the monitoring infrastructure. The reports are stored with a time stamp, the id of the relaying station and the id of the tags which participate in the contact event Cattuto et al. PLoS ONE (2010)
7 Output of SocioPatterns deployments Cattuto et al. PLoS ONE (2010)
8 Representation of dynamical network s data Cattuto et al. PLoS ONE (2010) Holme et. al, Physics Reports (2011) & % $ # "! ( )! '( Contact Sequence Integrated (Weighted) Network T Instantaneous Temporal Networks
9 Statistical properties of dynamical networks Contact sequence:! Analysis of the patterns of interactions between agents & % $ " Length of conversations!t " Gap between conversations " # "! ( )! '( Holme et. al, Physics Reports (2011) Weighted integrated network:! Topological properties of the weight pattern " Weight # of edges (time conversing) " Strength s (total time conversing)
10 Contact sequence properties of face-to-face contacts Long-tailed distribution of conversation length and gaps Distribution of gap times between consecutive conversations hosp ht sfhh school P(!t) hosp ht sfhh school P(!) !t Distribution of the length of conversations !
11 General property: Burstiness of human activity b Oliveira et al., Nature (2005) c Barabasi, Nature (2005) P(τ) Darwin Response time τ (days) 10 2 α = 3/2 α = 3/ Einstein Response time τ (days) Distribution of time between consecutive s sent Distribution of response times between receiving a letter and answering it (Darwin-Einstein correspondence) 5 s 1 m 1 h 1 d 1 month Distribution of time between consecutive print requests -2 single user inter arrival times busiest single user -4 log 10 (P ind (t)) Distribution of times between consecutive HTML requests to the portal by the same user 4. a The distribution of t Dezso et al., PRE (2006) log 10 (t in seconds) Harder et al., Physica A (2006)
12 Weighted network topological properties Distribution of weights (total time of conversation between pairs of agents) hosp ht sfhh school P(w) 10-4 s(k) k Strength (total time of conversation) as a function of the number of different partners w
13 Modeling social interaction networks Think in what you do at a conference or meeting... [0] Bunch of scientists set free in a closed space... [1] The usually move (walk) from one place to another [3] The talking will last longer if they meet somebody interesting [2] They start interactions (talk) when they meet somebody [4] At some point, they get bored anyway and continue walking [5] From time to time, they leave the room (or stop altogether to interact) to go check , work etc. Eventually, they will return (or not...)
14 Model definition in mathematical terms N agents (individuals) in a square box of size L Two individuals at a distance less that d can interact ( talk ) Agents are characterized by an attractiveness a and and activity r! a interest of an agent as seen by others! r how active an agent is " Random variables with distributions $(a) and %(r) Agents perform a biased random walk, depending on its environment: At time t, agent i stays in place with probability q i (t) = max {a j}, j N i (t)!"# Otherwise, performs a step in a random direction With probability 1-r, the agent becomes inactive, and stops interacting If inactive, with probability r becomes active and interacts again!! pmove = 1 - q!"#$%!"$!"%!"&
15 Model Results: Statistics of contacts Heterogeneity and Burstiness of Human Dynamics P(!t) P(!t) " = 0.04 " =0.02 " = 0.01 "= !t hosp ht sfhh school model !t The bursty dynamics of human interactions is revealed by the power- law behavior of the distribution of the duration t of the contacts between pairs of agents, P ( t), and the distribution of gap times τ between two consecutive conversations involving a common individual, P (τ). P(!) P(!) ! "=0.04 "=0.02 "=0.01 "=0.005 hosp ht sfhh school model ! The distributions P ( t) and P (τ) of the various sets of em pirical data are in excellent agreement with the same dis tributions $(a) and obtained %(r) uniform by simulating distributions the attractiveness model Moreover, numerical results are robust with respect to vari ations of the agent density ρ, as shown in the insets.
16 f emdisodel. varitween the number of different contacts and the temporal duration of those contacts can be estimated by measuring the growth of the average strength of nodes of degree k, s(k), as a function of k. Model Results: Topology of the weighted connected network as k(t)/k tractivene of k(t). hosp ht sfhh school theory model 10 2 k(t)/k(t) 1 1 P(w) k(t) 10 1 s(k) k w
17 Conclusions Social networks are better characterized with an additional temporal dimension Recent advances allow the easy and cheap gathering of large-scale data on dynamical social networks! The SocioPatterns projects The statistical analysis of SocioPatterns data allows to obtain novel information about human behavior! Long-tailed interaction distributions, burstiness, etc We have developed a simple model that can explain the basic features of human social face-to-face interactions as represented by the SocioPatterns data Realistically inspired:! People walk and stop to talk! The more interesting the partner, the larger the tendency to keep talking Model with simple simple parameters and no tuning Results qualitatively independent of the functional parameters $(a) and %(r) Very good fitting between model results and empirical data Opens the door to a better understanding of social behavior and social interactions
18 Thanks for your attention and see you at the poster session!!
Modeling temporal networks using random itineraries
 Modeling temporal networks using random itineraries Alain Barrat CPT, Marseille, France & ISI, Turin, Italy j j i i G k k i j k i j me$ N k 2$ i j k 1$ 0$ A.B., B. Fernandez, K. Lin, L.-S. Young Phys.
Modeling temporal networks using random itineraries Alain Barrat CPT, Marseille, France & ISI, Turin, Italy j j i i G k k i j k i j me$ N k 2$ i j k 1$ 0$ A.B., B. Fernandez, K. Lin, L.-S. Young Phys.
Supplementary Information Activity driven modeling of time varying networks
 Supplementary Information Activity driven modeling of time varying networks. Perra, B. Gonçalves, R. Pastor-Satorras, A. Vespignani May 11, 2012 Contents 1 The Model 1 1.1 Integrated network......................................
Supplementary Information Activity driven modeling of time varying networks. Perra, B. Gonçalves, R. Pastor-Satorras, A. Vespignani May 11, 2012 Contents 1 The Model 1 1.1 Integrated network......................................
Reaction-diffusion processes and meta-population models in heterogeneous networks Supplementary information
 Reaction-diffusion processes and meta-population models in heterogeneous networs Supplementary information Vittoria Colizza 1,2, Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 3, Alessandro Vespignani 2,1 January 19, 2007 1
Reaction-diffusion processes and meta-population models in heterogeneous networs Supplementary information Vittoria Colizza 1,2, Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 3, Alessandro Vespignani 2,1 January 19, 2007 1
Plan of the lecture I. INTRODUCTION II. DYNAMICAL PROCESSES. I. Networks: definitions, statistical characterization II. Real world networks
 Plan of the lecture I. INTRODUCTION I. Networks: definitions, statistical characterization II. Real world networks II. DYNAMICAL PROCESSES I. Resilience, vulnerability II. Random walks III. Epidemic processes
Plan of the lecture I. INTRODUCTION I. Networks: definitions, statistical characterization II. Real world networks II. DYNAMICAL PROCESSES I. Resilience, vulnerability II. Random walks III. Epidemic processes
Temporal Networks aka time-varying networks, time-stamped graphs, dynamical networks...
 Temporal Networks aka time-varying networks, time-stamped graphs, dynamical networks... Network Theory and Applications ECS 253 / MAE 253 Spring 2016 Márton Pósfai (posfai@ucdavis.edu) Sources Reviews:
Temporal Networks aka time-varying networks, time-stamped graphs, dynamical networks... Network Theory and Applications ECS 253 / MAE 253 Spring 2016 Márton Pósfai (posfai@ucdavis.edu) Sources Reviews:
Complex networks: an introduction
 Alain Barrat Complex networks: an introduction CPT, Marseille, France ISI, Turin, Italy http://www.cpt.univ-mrs.fr/~barrat http://cxnets.googlepages.com Plan of the lecture I. INTRODUCTION II. I. Networks:
Alain Barrat Complex networks: an introduction CPT, Marseille, France ISI, Turin, Italy http://www.cpt.univ-mrs.fr/~barrat http://cxnets.googlepages.com Plan of the lecture I. INTRODUCTION II. I. Networks:
Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute
 Rethinking Network Structure Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute Università della Svizzera Italiana, December 16, 2011 Measuring network structure Central nodes Community structure Strength
Rethinking Network Structure Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute Università della Svizzera Italiana, December 16, 2011 Measuring network structure Central nodes Community structure Strength
Solar Open House Toolkit
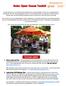 A Solar Open House is an informal meet and greet at a solar homeowner s home. It is an opportunity for homeowners who are considering going solar to see solar energy at work, ask questions about the process
A Solar Open House is an informal meet and greet at a solar homeowner s home. It is an opportunity for homeowners who are considering going solar to see solar energy at work, ask questions about the process
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c](/thumbs/89/100796430.jpg) Wealth Dynamics on Complex Networks arxiv:cond-mat/0402466v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c a Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Siena, Via Roma 56, 53100
Wealth Dynamics on Complex Networks arxiv:cond-mat/0402466v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 18 Feb 2004 Diego Garlaschelli a,b and Maria I. Loffredo b,c a Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Siena, Via Roma 56, 53100
A Tunable Mechanism for Identifying Trusted Nodes in Large Scale Distributed Networks
 A Tunable Mechanism for Identifying Trusted Nodes in Large Scale Distributed Networks Joydeep Chandra 1, Ingo Scholtes 2, Niloy Ganguly 1, Frank Schweitzer 2 1 - Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering,
A Tunable Mechanism for Identifying Trusted Nodes in Large Scale Distributed Networks Joydeep Chandra 1, Ingo Scholtes 2, Niloy Ganguly 1, Frank Schweitzer 2 1 - Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering,
Modeling Epidemic Risk Perception in Networks with Community Structure
 Modeling Epidemic Risk Perception in Networks with Community Structure Franco Bagnoli,,3, Daniel Borkmann 4, Andrea Guazzini 5,6, Emanuele Massaro 7, and Stefan Rudolph 8 Department of Energy, University
Modeling Epidemic Risk Perception in Networks with Community Structure Franco Bagnoli,,3, Daniel Borkmann 4, Andrea Guazzini 5,6, Emanuele Massaro 7, and Stefan Rudolph 8 Department of Energy, University
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research. Peer reviewed version. Link to published version (if available): /PhysRevE.93.
 Aoki, T., Rocha, L. E. C., & Gross, T. (2016). Temporal and structural heterogeneities emerging in adaptive temporal networks. Physical Review E, 93(4), [040301(R)]. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.93.040301 Peer
Aoki, T., Rocha, L. E. C., & Gross, T. (2016). Temporal and structural heterogeneities emerging in adaptive temporal networks. Physical Review E, 93(4), [040301(R)]. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.93.040301 Peer
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.pe] 3 May 2016
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.pe] 3 May 2016 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.pe] 3 May 2016](/thumbs/88/114889841.jpg) Temporal network structures controlling disease spreading Petter Holme, Department of Energy Science, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon 44-746, Korea We investigate disease spreading on eight empirical data
Temporal network structures controlling disease spreading Petter Holme, Department of Energy Science, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon 44-746, Korea We investigate disease spreading on eight empirical data
Oriented majority-vote model in social dynamics
 Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: M. Ángeles Serrano Mass events ruled by collective behaviour are present in our society every day. Some
Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: M. Ángeles Serrano Mass events ruled by collective behaviour are present in our society every day. Some
Preserving sparsity in dynamic network computations
 GoBack Preserving sparsity in dynamic network computations Francesca Arrigo and Desmond J. Higham Network Science meets Matrix Functions Oxford, Sept. 1, 2016 This work was funded by the Engineering and
GoBack Preserving sparsity in dynamic network computations Francesca Arrigo and Desmond J. Higham Network Science meets Matrix Functions Oxford, Sept. 1, 2016 This work was funded by the Engineering and
Epidemics and information spreading
 Epidemics and information spreading Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social Network
Epidemics and information spreading Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social Network
Temporal patterns in information and social systems
 Temporal patterns in information and social systems Matúš Medo University of Fribourg, Switzerland COST Workshop Quantifying scientific impact: networks, measures, insights? 12-13 February, 2015, Zurich
Temporal patterns in information and social systems Matúš Medo University of Fribourg, Switzerland COST Workshop Quantifying scientific impact: networks, measures, insights? 12-13 February, 2015, Zurich
Exploring Urban Areas of Interest. Yingjie Hu and Sathya Prasad
 Exploring Urban Areas of Interest Yingjie Hu and Sathya Prasad What is Urban Areas of Interest (AOIs)? What is Urban Areas of Interest (AOIs)? Urban AOIs exist in people s minds and defined by people s
Exploring Urban Areas of Interest Yingjie Hu and Sathya Prasad What is Urban Areas of Interest (AOIs)? What is Urban Areas of Interest (AOIs)? Urban AOIs exist in people s minds and defined by people s
ArcGIS Enterprise: What s New. Philip Heede Shannon Kalisky Melanie Summers Sam Williamson
 ArcGIS Enterprise: What s New Philip Heede Shannon Kalisky Melanie Summers Sam Williamson ArcGIS Enterprise is the new name for ArcGIS for Server What is ArcGIS Enterprise ArcGIS Enterprise is powerful
ArcGIS Enterprise: What s New Philip Heede Shannon Kalisky Melanie Summers Sam Williamson ArcGIS Enterprise is the new name for ArcGIS for Server What is ArcGIS Enterprise ArcGIS Enterprise is powerful
MSc Thesis. Modelling of communication dynamics. Szabolcs Vajna. Supervisor: Prof. János Kertész
 MSc Thesis Modelling of communication dynamics Szabolcs Vajna Supervisor: Prof. János Kertész Department of Theoretical Physics Institute of Physics Budapest University of Technology and Economics 202
MSc Thesis Modelling of communication dynamics Szabolcs Vajna Supervisor: Prof. János Kertész Department of Theoretical Physics Institute of Physics Budapest University of Technology and Economics 202
Location Determination Technologies for Sensor Networks
 Location Determination Technologies for Sensor Networks Moustafa Youssef University of Maryland at College Park UMBC Talk March, 2007 Motivation Location is important: Determining the location of an event
Location Determination Technologies for Sensor Networks Moustafa Youssef University of Maryland at College Park UMBC Talk March, 2007 Motivation Location is important: Determining the location of an event
Epidemics in Complex Networks and Phase Transitions
 Master M2 Sciences de la Matière ENS de Lyon 2015-2016 Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena Epidemics in Complex Networks and Phase Transitions Jordan Cambe January 13, 2016 Abstract Spreading phenomena
Master M2 Sciences de la Matière ENS de Lyon 2015-2016 Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena Epidemics in Complex Networks and Phase Transitions Jordan Cambe January 13, 2016 Abstract Spreading phenomena
Exploring Human Mobility with Multi-Source Data at Extremely Large Metropolitan Scales. ACM MobiCom 2014, Maui, HI
 Exploring Human Mobility with Multi-Source Data at Extremely Large Metropolitan Scales Desheng Zhang & Tian He University of Minnesota, USA Jun Huang, Ye Li, Fan Zhang, Chengzhong Xu Shenzhen Institute
Exploring Human Mobility with Multi-Source Data at Extremely Large Metropolitan Scales Desheng Zhang & Tian He University of Minnesota, USA Jun Huang, Ye Li, Fan Zhang, Chengzhong Xu Shenzhen Institute
Author(s) Alexei Vázquez, João Gama Oliveira, Zoltán Dezsö, Kwang-Il Goh, Imre Kondor, and Albert-László Barabási
 Author(s) Alexei Vázquez, João Gama Oliveira, Zoltán Dezsö, Kwang-Il Goh, Imre Kondor, and Albert-László Barabási This article is available at IRis: http://iris.lib.neu.edu/physics_fac_pubs/117 Modeling
Author(s) Alexei Vázquez, João Gama Oliveira, Zoltán Dezsö, Kwang-Il Goh, Imre Kondor, and Albert-László Barabási This article is available at IRis: http://iris.lib.neu.edu/physics_fac_pubs/117 Modeling
Stability and topology of scale-free networks under attack and defense strategies
 Stability and topology of scale-free networks under attack and defense strategies Lazaros K. Gallos, Reuven Cohen 2, Panos Argyrakis, Armin Bunde 3, and Shlomo Havlin 2 Department of Physics, University
Stability and topology of scale-free networks under attack and defense strategies Lazaros K. Gallos, Reuven Cohen 2, Panos Argyrakis, Armin Bunde 3, and Shlomo Havlin 2 Department of Physics, University
How Spatial Layout and Architecture Influence Everyday Work of Theoretical Physicists The Example of the mpipks
 How Spatial Layout and Architecture Influence Everyday Work of Theoretical Physicists The Example of the mpipks Dipl.-Ing. Kerstin Sailer Lehrstuhl Industriebau, TU Dresden Young Scientists Jam Session,
How Spatial Layout and Architecture Influence Everyday Work of Theoretical Physicists The Example of the mpipks Dipl.-Ing. Kerstin Sailer Lehrstuhl Industriebau, TU Dresden Young Scientists Jam Session,
Characterizing Large-scale Population s Indoor Spatiotemporal Interactive Behaviors
 Session 1 #4 ACM SIGKDD International Workshop on Urban Computing (UrbComp 2012) August 12, 2012 - Beijing, China Held in conjunction with the 18th ACM SIGKDD 2012 Characterizing Large-scale Population
Session 1 #4 ACM SIGKDD International Workshop on Urban Computing (UrbComp 2012) August 12, 2012 - Beijing, China Held in conjunction with the 18th ACM SIGKDD 2012 Characterizing Large-scale Population
Modelling data networks stochastic processes and Markov chains
 Modelling data networks stochastic processes and Markov chains a 1, 3 1, 2 2, 2 b 0, 3 2, 3 u 1, 3 α 1, 6 c 0, 3 v 2, 2 β 1, 1 Richard G. Clegg (richard@richardclegg.org) November 2016 Available online
Modelling data networks stochastic processes and Markov chains a 1, 3 1, 2 2, 2 b 0, 3 2, 3 u 1, 3 α 1, 6 c 0, 3 v 2, 2 β 1, 1 Richard G. Clegg (richard@richardclegg.org) November 2016 Available online
ArcGIS Enterprise: What s New. Philip Heede Shannon Kalisky Melanie Summers Shreyas Shinde
 ArcGIS Enterprise: What s New Philip Heede Shannon Kalisky Melanie Summers Shreyas Shinde ArcGIS Enterprise is the new name for ArcGIS for Server ArcGIS Enterprise Software Components ArcGIS Server Portal
ArcGIS Enterprise: What s New Philip Heede Shannon Kalisky Melanie Summers Shreyas Shinde ArcGIS Enterprise is the new name for ArcGIS for Server ArcGIS Enterprise Software Components ArcGIS Server Portal
Modelling data networks stochastic processes and Markov chains
 Modelling data networks stochastic processes and Markov chains a 1, 3 1, 2 2, 2 b 0, 3 2, 3 u 1, 3 α 1, 6 c 0, 3 v 2, 2 β 1, 1 Richard G. Clegg (richard@richardclegg.org) December 2011 Available online
Modelling data networks stochastic processes and Markov chains a 1, 3 1, 2 2, 2 b 0, 3 2, 3 u 1, 3 α 1, 6 c 0, 3 v 2, 2 β 1, 1 Richard G. Clegg (richard@richardclegg.org) December 2011 Available online
Preparing for Eruptions What will happen in future eruptions and how can we be prepared?
 Lesson Plan 12 Activities 1. Read or listen to Matt s Volcano Story from What s the Plan Stan Stories on: http://www.whatstheplanstan.govt.nz/teacher.html#disasters Discuss what Matt saw and did before,
Lesson Plan 12 Activities 1. Read or listen to Matt s Volcano Story from What s the Plan Stan Stories on: http://www.whatstheplanstan.govt.nz/teacher.html#disasters Discuss what Matt saw and did before,
Opinion Dynamics on Triad Scale Free Network
 Opinion Dynamics on Triad Scale Free Network Li Qianqian 1 Liu Yijun 1,* Tian Ruya 1,2 Ma Ning 1,2 1 Institute of Policy and Management, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China lqqcindy@gmail.com,
Opinion Dynamics on Triad Scale Free Network Li Qianqian 1 Liu Yijun 1,* Tian Ruya 1,2 Ma Ning 1,2 1 Institute of Policy and Management, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China lqqcindy@gmail.com,
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Dec 2010
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Dec 2010 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 9 Dec 2010](/thumbs/85/91333090.jpg) Thresholds for epidemic spreading in networks Claudio Castellano 1 and Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 2 1 Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi (CNR-ISC), UOS Sapienza and Dip. di Fisica, Sapienza Università di Roma,
Thresholds for epidemic spreading in networks Claudio Castellano 1 and Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 2 1 Istituto dei Sistemi Complessi (CNR-ISC), UOS Sapienza and Dip. di Fisica, Sapienza Università di Roma,
Lecture VI Introduction to complex networks. Santo Fortunato
 Lecture VI Introduction to complex networks Santo Fortunato Plan of the course I. Networks: definitions, characteristics, basic concepts in graph theory II. III. IV. Real world networks: basic properties
Lecture VI Introduction to complex networks Santo Fortunato Plan of the course I. Networks: definitions, characteristics, basic concepts in graph theory II. III. IV. Real world networks: basic properties
Network Science (overview, part 1)
 Network Science (overview, part 1) Ralucca Gera, Applied Mathematics Dept. Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California rgera@nps.edu Excellence Through Knowledge Overview Current research Section 1:
Network Science (overview, part 1) Ralucca Gera, Applied Mathematics Dept. Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, California rgera@nps.edu Excellence Through Knowledge Overview Current research Section 1:
arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 24 Mar 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 24 Mar 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 24 Mar 2013](/thumbs/77/75082356.jpg) The emergence and role of strong ties in time-varying communication networks Márton Karsai 1,2, Nicola Perra 1, and Alessandro Vespignani 1,3,4 1 Laboratory for the Modeling of Biological and Socio-technical
The emergence and role of strong ties in time-varying communication networks Márton Karsai 1,2, Nicola Perra 1, and Alessandro Vespignani 1,3,4 1 Laboratory for the Modeling of Biological and Socio-technical
Time varying networks and the weakness of strong ties
 Supplementary Materials Time varying networks and the weakness of strong ties M. Karsai, N. Perra and A. Vespignani 1 Measures of egocentric network evolutions by directed communications In the main text
Supplementary Materials Time varying networks and the weakness of strong ties M. Karsai, N. Perra and A. Vespignani 1 Measures of egocentric network evolutions by directed communications In the main text
3.6.1 Building Functions from Context. Warm Up
 Name: # Honors Coordinate Algebra: Period Ms. Pierre Date: 3.6.1 Building Functions from Context Warm Up 1. Willem buys 4 mangoes each week, and mango prices vary from week to week. Write an equation that
Name: # Honors Coordinate Algebra: Period Ms. Pierre Date: 3.6.1 Building Functions from Context Warm Up 1. Willem buys 4 mangoes each week, and mango prices vary from week to week. Write an equation that
Internal link prediction: a new approach for predicting links in bipartite graphs
 Internal link prediction: a new approach for predicting links in bipartite graphs Oussama llali, lémence Magnien and Matthieu Latapy LIP6 NRS and Université Pierre et Marie urie (UPM Paris 6) 4 place Jussieu
Internal link prediction: a new approach for predicting links in bipartite graphs Oussama llali, lémence Magnien and Matthieu Latapy LIP6 NRS and Université Pierre et Marie urie (UPM Paris 6) 4 place Jussieu
Non Member State Summer Student Program at ISOLDE
 Program at ISOLDE LabVIEW readout of a gauge pressure meter for the VITO beam line. Atomic local studies in Graphene. Diana Sofía Valverde Mendez Supervisors: Torben Esmann Mølholt
Program at ISOLDE LabVIEW readout of a gauge pressure meter for the VITO beam line. Atomic local studies in Graphene. Diana Sofía Valverde Mendez Supervisors: Torben Esmann Mølholt
Dating and Divorce. Li, Hao and Sergei Severinov Vancouver School of Economics University of British Columbia. August 9, 2018.
 Dating and Divorce Li, Hao and Sergei Severinov Vancouver School of Economics University of British Columbia August 9, 2018 Abstract We introduce private information in an otherwise standard search and
Dating and Divorce Li, Hao and Sergei Severinov Vancouver School of Economics University of British Columbia August 9, 2018 Abstract We introduce private information in an otherwise standard search and
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 May 2009
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 May 2009 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 1 May 2009](/thumbs/79/80119370.jpg) Glass transition and random walks on complex energy landscapes Andrea Baronchelli, 1 Alain Barrat,,3 and Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 1 1 Departament de Física i Enginyeria Nuclear, Universitat Politècnica
Glass transition and random walks on complex energy landscapes Andrea Baronchelli, 1 Alain Barrat,,3 and Romualdo Pastor-Satorras 1 1 Departament de Física i Enginyeria Nuclear, Universitat Politècnica
Modeling Dynamic Evolution of Online Friendship Network
 Commun. Theor. Phys. 58 (2012) 599 603 Vol. 58, No. 4, October 15, 2012 Modeling Dynamic Evolution of Online Friendship Network WU Lian-Ren ( ) 1,2, and YAN Qiang ( Ö) 1 1 School of Economics and Management,
Commun. Theor. Phys. 58 (2012) 599 603 Vol. 58, No. 4, October 15, 2012 Modeling Dynamic Evolution of Online Friendship Network WU Lian-Ren ( ) 1,2, and YAN Qiang ( Ö) 1 1 School of Economics and Management,
Path lengths, correlations, and centrality in temporal networks
 Path lengths, correlations, and centrality in temporal networks Raj Kumar Pan and Jari Saramäki BECS, School of Science and Technology, Aalto University, P.O. Box 100, FI-00076 (Dated: July 0, 011) A temporal
Path lengths, correlations, and centrality in temporal networks Raj Kumar Pan and Jari Saramäki BECS, School of Science and Technology, Aalto University, P.O. Box 100, FI-00076 (Dated: July 0, 011) A temporal
European Solar Days May Report Spain
 European Solar Days 2009 12-22 May Report Spain Support by: 1 Results of European Solar Days 2009 in Spain 1.1. Participation in European Solar Days 2009 The 2 nd Edition of the European Solar Days organised
European Solar Days 2009 12-22 May Report Spain Support by: 1 Results of European Solar Days 2009 in Spain 1.1. Participation in European Solar Days 2009 The 2 nd Edition of the European Solar Days organised
Self-organized scale-free networks
 Self-organized scale-free networks Kwangho Park and Ying-Cheng Lai Departments of Electrical Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona 85287, USA Nong Ye Department of Industrial Engineering,
Self-organized scale-free networks Kwangho Park and Ying-Cheng Lai Departments of Electrical Engineering, Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona 85287, USA Nong Ye Department of Industrial Engineering,
ROUNDTABLE ON SOCIAL IMPACTS OF TIME AND SPACE-BASED ROAD PRICING Luis Martinez (with Olga Petrik, Francisco Furtado and Jari Kaupilla)
 ROUNDTABLE ON SOCIAL IMPACTS OF TIME AND SPACE-BASED ROAD PRICING Luis Martinez (with Olga Petrik, Francisco Furtado and Jari Kaupilla) AUCKLAND, NOVEMBER, 2017 Objective and approach (I) Create a detailed
ROUNDTABLE ON SOCIAL IMPACTS OF TIME AND SPACE-BASED ROAD PRICING Luis Martinez (with Olga Petrik, Francisco Furtado and Jari Kaupilla) AUCKLAND, NOVEMBER, 2017 Objective and approach (I) Create a detailed
Towards the Understanding of Human Dynamics
 12 Towards the Understanding of Human Dynamics Tao Zhou, Xiao-Pu Han and Bing-Hong Wang Quantitative understanding of human behaviors provides elementary but important comprehension of the complexity of
12 Towards the Understanding of Human Dynamics Tao Zhou, Xiao-Pu Han and Bing-Hong Wang Quantitative understanding of human behaviors provides elementary but important comprehension of the complexity of
Relational Event Modeling: Basic Framework and Applications. Aaron Schecter & Noshir Contractor Northwestern University
 Relational Event Modeling: Basic Framework and Applications Aaron Schecter & Noshir Contractor Northwestern University Why Use Relational Events? Social network analysis has two main frames of reference;
Relational Event Modeling: Basic Framework and Applications Aaron Schecter & Noshir Contractor Northwestern University Why Use Relational Events? Social network analysis has two main frames of reference;
ECS 289 / MAE 298, Lecture 7 April 22, Percolation and Epidemiology on Networks, Part 2 Searching on networks
 ECS 289 / MAE 298, Lecture 7 April 22, 2014 Percolation and Epidemiology on Networks, Part 2 Searching on networks 28 project pitches turned in Announcements We are compiling them into one file to share
ECS 289 / MAE 298, Lecture 7 April 22, 2014 Percolation and Epidemiology on Networks, Part 2 Searching on networks 28 project pitches turned in Announcements We are compiling them into one file to share
Adaptive Rumor Spreading
 José Correa 1 Marcos Kiwi 1 Neil Olver 2 Alberto Vera 1 1 2 VU Amsterdam and CWI July 27, 2015 1/21 The situation 2/21 The situation 2/21 The situation 2/21 The situation 2/21 Introduction Rumors in social
José Correa 1 Marcos Kiwi 1 Neil Olver 2 Alberto Vera 1 1 2 VU Amsterdam and CWI July 27, 2015 1/21 The situation 2/21 The situation 2/21 The situation 2/21 The situation 2/21 Introduction Rumors in social
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models. Winter Midterm Exam Monday, Feb 10, 2014
 Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Monday, Feb 10, 2014 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Monday, Feb 10, 2014 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Motion II. Goals and Introduction
 Motion II Goals and Introduction As you have probably already seen in lecture or homework, and if you ve performed the experiment Motion I, it is important to develop a strong understanding of how to model
Motion II Goals and Introduction As you have probably already seen in lecture or homework, and if you ve performed the experiment Motion I, it is important to develop a strong understanding of how to model
TEMPORAL EXPONENTIAL- FAMILY RANDOM GRAPH MODELING (TERGMS) WITH STATNET
 1 TEMPORAL EXPONENTIAL- FAMILY RANDOM GRAPH MODELING (TERGMS) WITH STATNET Prof. Steven Goodreau Prof. Martina Morris Prof. Michal Bojanowski Prof. Mark S. Handcock Source for all things STERGM Pavel N.
1 TEMPORAL EXPONENTIAL- FAMILY RANDOM GRAPH MODELING (TERGMS) WITH STATNET Prof. Steven Goodreau Prof. Martina Morris Prof. Michal Bojanowski Prof. Mark S. Handcock Source for all things STERGM Pavel N.
Finite Markov Information-Exchange processes
 Finite Markov Information-Exchange processes David Aldous February 2, 2011 Course web site: Google Aldous STAT 260. Style of course Big Picture thousands of papers from different disciplines (statistical
Finite Markov Information-Exchange processes David Aldous February 2, 2011 Course web site: Google Aldous STAT 260. Style of course Big Picture thousands of papers from different disciplines (statistical
Spatial Epidemic Modelling in Social Networks
 Spatial Epidemic Modelling in Social Networks Joana Margarida Simoes Centre for Advanced Spatial Analysis, University College of London, UK Abstract. The spread of infectious diseases is highly influenced
Spatial Epidemic Modelling in Social Networks Joana Margarida Simoes Centre for Advanced Spatial Analysis, University College of London, UK Abstract. The spread of infectious diseases is highly influenced
Telecommunication Services Engineering (TSE) Lab. Chapter IX Presence Applications and Services.
 Chapter IX Presence Applications and Services http://users.encs.concordia.ca/~glitho/ Outline 1. Basics 2. Interoperability 3. Presence service in clouds Basics 1 - IETF abstract model 2 - An example of
Chapter IX Presence Applications and Services http://users.encs.concordia.ca/~glitho/ Outline 1. Basics 2. Interoperability 3. Presence service in clouds Basics 1 - IETF abstract model 2 - An example of
Decentralized Time Geography for Ad-Hoc Collaborative Planning
 Decentralized Time Geography for Ad-Hoc Collaborative Planning Martin Raubal 1, Stephan Winter 2, and Christopher Dorr 1 1 Department of Geography, University of California, Santa Barbara, USA raubal@geog.ucsb.edu;
Decentralized Time Geography for Ad-Hoc Collaborative Planning Martin Raubal 1, Stephan Winter 2, and Christopher Dorr 1 1 Department of Geography, University of California, Santa Barbara, USA raubal@geog.ucsb.edu;
Supporting Collaboration for the Gravitational Wave Astronomy Community with InCommon
 Supporting Collaboration for the Gravitational Wave Astronomy Community with InCommon Scott Koranda for LIGO LIGO and University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee August 20, 2014 LIGO-XXXXXXX-v1 1 / 28 LIGO Science
Supporting Collaboration for the Gravitational Wave Astronomy Community with InCommon Scott Koranda for LIGO LIGO and University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee August 20, 2014 LIGO-XXXXXXX-v1 1 / 28 LIGO Science
Research Article Effects of Resource Limitations and Cost Influences on Computer Virus Epidemic Dynamics and Tipping Points
 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 12, Article ID 473136, 15 pages doi:.1155/12/473136 Research Article Effects of Resource Limitations and Cost Influences on Computer Virus Epidemic Dynamics
Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 12, Article ID 473136, 15 pages doi:.1155/12/473136 Research Article Effects of Resource Limitations and Cost Influences on Computer Virus Epidemic Dynamics
Network Data: an overview
 Network Data: an overview Introduction to Graph Theory and Sociometric Notation Dante J. Salto & Taya L. Owens 6 February 2013 Rockefeller College RPAD 637 Works Summarized Wasserman, S. & Faust, K. (2009).
Network Data: an overview Introduction to Graph Theory and Sociometric Notation Dante J. Salto & Taya L. Owens 6 February 2013 Rockefeller College RPAD 637 Works Summarized Wasserman, S. & Faust, K. (2009).
Minimum spanning trees of weighted scale-free networks
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 October 2005 Europhys. Lett., 72 (2), pp. 308 314 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10232-x Minimum spanning trees of weighted scale-free networks P. J. Macdonald, E. Almaas and A.-L.
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 October 2005 Europhys. Lett., 72 (2), pp. 308 314 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10232-x Minimum spanning trees of weighted scale-free networks P. J. Macdonald, E. Almaas and A.-L.
Draft Proof - Do not copy, post, or distribute
 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between descriptive and inferential statistics. Introduction to Statistics 2. Explain how samples and populations,
1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between descriptive and inferential statistics. Introduction to Statistics 2. Explain how samples and populations,
Maanmittauspäivät 2018 Helsinki Maanmittauspäivät 2018 The Danish initiatives regarding open and free basic data including effect studies
 Maanmittauspäivät 2018 The Danish initiatives regarding open and free basic data including effect studies 22.03.2018 Agenda 1. Intro overall frame / selfie 2. Data Infrastructure 3. The Danish Digital
Maanmittauspäivät 2018 The Danish initiatives regarding open and free basic data including effect studies 22.03.2018 Agenda 1. Intro overall frame / selfie 2. Data Infrastructure 3. The Danish Digital
A route map to calibrate spatial interaction models from GPS movement data
 A route map to calibrate spatial interaction models from GPS movement data K. Sila-Nowicka 1, A.S. Fotheringham 2 1 Urban Big Data Centre School of Political and Social Sciences University of Glasgow Lilybank
A route map to calibrate spatial interaction models from GPS movement data K. Sila-Nowicka 1, A.S. Fotheringham 2 1 Urban Big Data Centre School of Political and Social Sciences University of Glasgow Lilybank
arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 24 Sep 2016
![arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 24 Sep 2016 arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 24 Sep 2016](/thumbs/90/101985331.jpg) Evolution of Cooperation on Temporal Networks Aming Li,2,3, Lei Zhou,4, Qi Su, Sean P. Cornelius 2,5, Yang-Yu Liu 5,6,, and Long Wang, Center for Systems and Control, College of Engineering, Peking University,
Evolution of Cooperation on Temporal Networks Aming Li,2,3, Lei Zhou,4, Qi Su, Sean P. Cornelius 2,5, Yang-Yu Liu 5,6,, and Long Wang, Center for Systems and Control, College of Engineering, Peking University,
Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks
 Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Virgili, Tarragona (Spain) Roma (Italy) Zaragoza, Zaragoza (Spain)
 Int.J.Complex Systems in Science vol. 1 (2011), pp. 47 54 Probabilistic framework for epidemic spreading in complex networks Sergio Gómez 1,, Alex Arenas 1, Javier Borge-Holthoefer 1, Sandro Meloni 2,3
Int.J.Complex Systems in Science vol. 1 (2011), pp. 47 54 Probabilistic framework for epidemic spreading in complex networks Sergio Gómez 1,, Alex Arenas 1, Javier Borge-Holthoefer 1, Sandro Meloni 2,3
Unit 5: NWS Hazardous Weather Products. Hazardous Weather and Flooding Preparedness
 Unit 5: NWS Hazardous Weather Products Objectives Describe the mission of the NWS Describe the basic organizational structure of the NWS Explain the purpose of various NWS products Explain how Probability
Unit 5: NWS Hazardous Weather Products Objectives Describe the mission of the NWS Describe the basic organizational structure of the NWS Explain the purpose of various NWS products Explain how Probability
L23: hidden Markov models
 L23: hidden Markov models Discrete Markov processes Hidden Markov models Forward and Backward procedures The Viterbi algorithm This lecture is based on [Rabiner and Juang, 1993] Introduction to Speech
L23: hidden Markov models Discrete Markov processes Hidden Markov models Forward and Backward procedures The Viterbi algorithm This lecture is based on [Rabiner and Juang, 1993] Introduction to Speech
Modeling, Analysis, and Control of Information Propagation in Multi-layer and Multiplex Networks. Osman Yağan
 Modeling, Analysis, and Control of Information Propagation in Multi-layer and Multiplex Networks Osman Yağan Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon University Joint work with Y. Zhuang and V. Gligor (CMU) Alex
Modeling, Analysis, and Control of Information Propagation in Multi-layer and Multiplex Networks Osman Yağan Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon University Joint work with Y. Zhuang and V. Gligor (CMU) Alex
Géza Ódor MTA-EK-MFA Budapest 16/01/2015 Rio de Janeiro
 Griffiths phases, localization and burstyness in network models Géza Ódor MTA-EK-MFA Budapest 16/01/2015 Rio de Janeiro Partners: R. Juhász M. A. Munoz C. Castellano R. Pastor-Satorras Infocommunication
Griffiths phases, localization and burstyness in network models Géza Ódor MTA-EK-MFA Budapest 16/01/2015 Rio de Janeiro Partners: R. Juhász M. A. Munoz C. Castellano R. Pastor-Satorras Infocommunication
Social Network Analysis. Daniela Lup
 Social Network Analysis Daniela Lup Outline Distinction ego-network vs. whole network Personal network how to analyse Whole network Cygna network Q & A / Brainstorming Cygna Ego Network The network that
Social Network Analysis Daniela Lup Outline Distinction ego-network vs. whole network Personal network how to analyse Whole network Cygna network Q & A / Brainstorming Cygna Ego Network The network that
MobiHoc 2014 MINIMUM-SIZED INFLUENTIAL NODE SET SELECTION FOR SOCIAL NETWORKS UNDER THE INDEPENDENT CASCADE MODEL
 MobiHoc 2014 MINIMUM-SIZED INFLUENTIAL NODE SET SELECTION FOR SOCIAL NETWORKS UNDER THE INDEPENDENT CASCADE MODEL Jing (Selena) He Department of Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Shouling Ji,
MobiHoc 2014 MINIMUM-SIZED INFLUENTIAL NODE SET SELECTION FOR SOCIAL NETWORKS UNDER THE INDEPENDENT CASCADE MODEL Jing (Selena) He Department of Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Shouling Ji,
Georgia Kayser, PhD. Module 4 Approaches to Sampling. Hello and Welcome to Monitoring Evaluation and Learning: Approaches to Sampling.
 Slide 1 Module 4 Approaches to Sampling Georgia Kayser, PhD Hello and Welcome to Monitoring Evaluation and Learning: Approaches to Sampling Slide 2 Objectives To understand the reasons for sampling populations
Slide 1 Module 4 Approaches to Sampling Georgia Kayser, PhD Hello and Welcome to Monitoring Evaluation and Learning: Approaches to Sampling Slide 2 Objectives To understand the reasons for sampling populations
Coordination. Failures and Consensus. Consensus. Consensus. Overview. Properties for Correct Consensus. Variant I: Consensus (C) P 1. v 1.
 Coordination Failures and Consensus If the solution to availability and scalability is to decentralize and replicate functions and data, how do we coordinate the nodes? data consistency update propagation
Coordination Failures and Consensus If the solution to availability and scalability is to decentralize and replicate functions and data, how do we coordinate the nodes? data consistency update propagation
Introduction to Social Network Analysis PSU Quantitative Methods Seminar, June 15
 Introduction to Social Network Analysis PSU Quantitative Methods Seminar, June 15 Jeffrey A. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln Department of Sociology Course Website https://sites.google.com/site/socjasmith/teaching2/psu_social_networks_seminar
Introduction to Social Network Analysis PSU Quantitative Methods Seminar, June 15 Jeffrey A. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln Department of Sociology Course Website https://sites.google.com/site/socjasmith/teaching2/psu_social_networks_seminar
Time in Distributed Systems: Clocks and Ordering of Events
 Time in Distributed Systems: Clocks and Ordering of Events Clocks in Distributed Systems Needed to Order two or more events happening at same or different nodes (Ex: Consistent ordering of updates at different
Time in Distributed Systems: Clocks and Ordering of Events Clocks in Distributed Systems Needed to Order two or more events happening at same or different nodes (Ex: Consistent ordering of updates at different
The Challenge of Geospatial Big Data Analysis
 288 POSTERS The Challenge of Geospatial Big Data Analysis Authors - Teerayut Horanont, University of Tokyo, Japan - Apichon Witayangkurn, University of Tokyo, Japan - Shibasaki Ryosuke, University of Tokyo,
288 POSTERS The Challenge of Geospatial Big Data Analysis Authors - Teerayut Horanont, University of Tokyo, Japan - Apichon Witayangkurn, University of Tokyo, Japan - Shibasaki Ryosuke, University of Tokyo,
Quarantine generated phase transition in epidemic spreading. Abstract
 Quarantine generated phase transition in epidemic spreading C. Lagorio, M. Dickison, 2 * F. Vazquez, 3 L. A. Braunstein,, 2 P. A. Macri, M. V. Migueles, S. Havlin, 4 and H. E. Stanley Instituto de Investigaciones
Quarantine generated phase transition in epidemic spreading C. Lagorio, M. Dickison, 2 * F. Vazquez, 3 L. A. Braunstein,, 2 P. A. Macri, M. V. Migueles, S. Havlin, 4 and H. E. Stanley Instituto de Investigaciones
Methodology for Computer Science Research Lecture 4: Mathematical Modeling
 Methodology for Computer Science Research Andrey Lukyanenko Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science and Technology andrey.lukyanenko@tkk.fi Definitions and Goals
Methodology for Computer Science Research Andrey Lukyanenko Department of Computer Science and Engineering Aalto University, School of Science and Technology andrey.lukyanenko@tkk.fi Definitions and Goals
Socio-spatial Properties of Online Location-based Social Networks
 Socio-spatial Properties of Online Location-based Social Networks Salvatore Scellato Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge salvatore.scellato@cam.ac.uk Renaud Lambiotte Deparment of Mathematics Imperial
Socio-spatial Properties of Online Location-based Social Networks Salvatore Scellato Computer Laboratory University of Cambridge salvatore.scellato@cam.ac.uk Renaud Lambiotte Deparment of Mathematics Imperial
These are special traffic patterns that create more stress on a switch
 Myths about Microbursts What are Microbursts? Microbursts are traffic patterns where traffic arrives in small bursts. While almost all network traffic is bursty to some extent, storage traffic usually
Myths about Microbursts What are Microbursts? Microbursts are traffic patterns where traffic arrives in small bursts. While almost all network traffic is bursty to some extent, storage traffic usually
Complex networks: an introduction Alain Barrat
 Complex networks: an introduction Alain Barrat CPT, Marseille, France ISI, Turin, Italy http://www.cpt.univ-mrs.fr/~barrat http://cxnets.googlepages.com Plan of the lecture I. INTRODUCTION I. Networks:
Complex networks: an introduction Alain Barrat CPT, Marseille, France ISI, Turin, Italy http://www.cpt.univ-mrs.fr/~barrat http://cxnets.googlepages.com Plan of the lecture I. INTRODUCTION I. Networks:
SDS developer guide. Develop distributed and parallel applications in Java. Nathanaël Cottin. version
 SDS developer guide Develop distributed and parallel applications in Java Nathanaël Cottin sds@ncottin.net http://sds.ncottin.net version 0.0.3 Copyright 2007 - Nathanaël Cottin Permission is granted to
SDS developer guide Develop distributed and parallel applications in Java Nathanaël Cottin sds@ncottin.net http://sds.ncottin.net version 0.0.3 Copyright 2007 - Nathanaël Cottin Permission is granted to
FCE 3900 EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH LECTURE 8 P O P U L A T I O N A N D S A M P L I N G T E C H N I Q U E
 FCE 3900 EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH LECTURE 8 P O P U L A T I O N A N D S A M P L I N G T E C H N I Q U E OBJECTIVE COURSE Understand the concept of population and sampling in the research. Identify the type
FCE 3900 EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH LECTURE 8 P O P U L A T I O N A N D S A M P L I N G T E C H N I Q U E OBJECTIVE COURSE Understand the concept of population and sampling in the research. Identify the type
Science Notebook Motion, Force, and Models
 5 th Science Notebook Motion, Force, and Models Investigation 1: Motion and Variables Name: Big Question: How does investigating a pendulum help you understand how scientists use math to do their work?
5 th Science Notebook Motion, Force, and Models Investigation 1: Motion and Variables Name: Big Question: How does investigating a pendulum help you understand how scientists use math to do their work?
Updated Precipitation Frequency Estimates for Minnesota
 1 Updated Precipitation Frequency Estimates for Minnesota Presenter: Authors: (alphabetical order) Sanja Perica, Director Hydrometeorological Design Studies Center (HDSC), Office of Hydrology, National
1 Updated Precipitation Frequency Estimates for Minnesota Presenter: Authors: (alphabetical order) Sanja Perica, Director Hydrometeorological Design Studies Center (HDSC), Office of Hydrology, National
Shared Memory vs Message Passing
 Shared Memory vs Message Passing Carole Delporte-Gallet Hugues Fauconnier Rachid Guerraoui Revised: 15 February 2004 Abstract This paper determines the computational strength of the shared memory abstraction
Shared Memory vs Message Passing Carole Delporte-Gallet Hugues Fauconnier Rachid Guerraoui Revised: 15 February 2004 Abstract This paper determines the computational strength of the shared memory abstraction
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 10 1 Roma Milano Napoli Torino Palermo Genova 0.3 0.25 (a) P(t) 10 1 (b) t (h) 0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 t (h) 0.15 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 Population Supplementary Figure 1: Variation
Supplementary Figures 10 1 Roma Milano Napoli Torino Palermo Genova 0.3 0.25 (a) P(t) 10 1 (b) t (h) 0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 t (h) 0.15 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 Population Supplementary Figure 1: Variation
Géza Ódor, MTA-EK-MFA Budapest Ronald Dickman, UFMG Brazil 08/04/2015
 Localization, Griffiths phases and burstyness in neural network models Géza Ódor, MTA-EK-MFA Budapest Ronald Dickman, UFMG Brazil 08/04/2015 Partners: Gergely Ódor R. Juhász Infocommunication technologies
Localization, Griffiths phases and burstyness in neural network models Géza Ódor, MTA-EK-MFA Budapest Ronald Dickman, UFMG Brazil 08/04/2015 Partners: Gergely Ódor R. Juhász Infocommunication technologies
Recommendation Systems
 Recommendation Systems Pawan Goyal CSE, IITKGP October 21, 2014 Pawan Goyal (IIT Kharagpur) Recommendation Systems October 21, 2014 1 / 52 Recommendation System? Pawan Goyal (IIT Kharagpur) Recommendation
Recommendation Systems Pawan Goyal CSE, IITKGP October 21, 2014 Pawan Goyal (IIT Kharagpur) Recommendation Systems October 21, 2014 1 / 52 Recommendation System? Pawan Goyal (IIT Kharagpur) Recommendation
Introduction to ArcGIS Server Development
 Introduction to ArcGIS Server Development Kevin Deege,, Rob Burke, Kelly Hutchins, and Sathya Prasad ESRI Developer Summit 2008 1 Schedule Introduction to ArcGIS Server Rob and Kevin Questions Break 2:15
Introduction to ArcGIS Server Development Kevin Deege,, Rob Burke, Kelly Hutchins, and Sathya Prasad ESRI Developer Summit 2008 1 Schedule Introduction to ArcGIS Server Rob and Kevin Questions Break 2:15
Market Connectivity. Anup Rao Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science University of Washington
 Market Connectivity Anup Rao Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science University of Washington Who am I? Not an economist A theoretical computer scientist (essentially ~ mathematician) I study communication
Market Connectivity Anup Rao Paul G. Allen School of Computer Science University of Washington Who am I? Not an economist A theoretical computer scientist (essentially ~ mathematician) I study communication
LAB 01 Electrostatic Charge
 LAB 01 Electrostatic Charge Group: (Lab section plus Group letter; for instance 01A for lab section 01, group A) Names: (Principle Coordinator) (Lab Partner) (Lab Partner) Directions: Everyone in your
LAB 01 Electrostatic Charge Group: (Lab section plus Group letter; for instance 01A for lab section 01, group A) Names: (Principle Coordinator) (Lab Partner) (Lab Partner) Directions: Everyone in your
Agency Vision and Decision- Maker Needs: A USGS Perspective
 Agency Vision and Decision- Maker Needs: A USGS Perspective Connecting Grassroots to Government for Disaster Management David Applegate USGS Associate Director for Natural Hazards September 13, 2012 U.S.
Agency Vision and Decision- Maker Needs: A USGS Perspective Connecting Grassroots to Government for Disaster Management David Applegate USGS Associate Director for Natural Hazards September 13, 2012 U.S.
Social Network Analysis. Mrigesh Kshatriya, CIFOR Sentinel Landscape Data Analysis workshop (3rd-7th March 2014) Venue: CATIE, Costa Rica.
 Social Network Analysis Mrigesh Kshatriya, CIFOR Sentinel Landscape Data Analysis workshop (3rd-7th March 2014) Venue: CATIE, Costa Rica. Talk outline What is a Social Network? Data collection Visualizing
Social Network Analysis Mrigesh Kshatriya, CIFOR Sentinel Landscape Data Analysis workshop (3rd-7th March 2014) Venue: CATIE, Costa Rica. Talk outline What is a Social Network? Data collection Visualizing
RFI Detectives Activity for Large Public Venues
 RFI Detectives Activity for Large Public Venues Adapted from the NRAO s Be An Interference Detective activity Background Most people living near big cities are familiar with light pollution and how it
RFI Detectives Activity for Large Public Venues Adapted from the NRAO s Be An Interference Detective activity Background Most people living near big cities are familiar with light pollution and how it
Reimaging GIS: Geographic Information Society. Clint Brown Linda Beale Mark Harrower Esri
 Reimaging GIS: Geographic Information Society Clint Brown Linda Beale Mark Harrower Esri 8 billion = Number of basemap requests per month on AGOL 14,000 = Unique requests per second 12,000 = New Items
Reimaging GIS: Geographic Information Society Clint Brown Linda Beale Mark Harrower Esri 8 billion = Number of basemap requests per month on AGOL 14,000 = Unique requests per second 12,000 = New Items
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS February 21, 2017
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS February 21, 2017 Content Questions How do you place a single arsenic atom with the ratio 1 in 100 million? Sounds difficult to get evenly spread throughout. Yes, techniques
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS February 21, 2017 Content Questions How do you place a single arsenic atom with the ratio 1 in 100 million? Sounds difficult to get evenly spread throughout. Yes, techniques
