HINT: Some of the solution methods involve highschool math as well as new methods from this class.
|
|
|
- Dennis Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOLUTIONS DISCRETE MATH 1 W3203 FINAL EXAM open book Your Name (2 pts for legibly PRINTING your name) Problem Points Score your name Total 200 SUGGESTION: Do the EASIEST problems first! HINT: Some of the solution methods involve highschool math as well as new methods from this class. 1 An example of the Reasonable Person Principle: A reasonable student expects to lose a lot of credit for neglecting to EXPLAIN an answer. Omit explanations at your own risk. W3203FXsol.F02 1 of 10 12/8/02
2 1 (23 pts). Consider the following recurrence system: a 0 = 0; a 1 = 1; a n = 4a n a (2). Calculate a 2, a 3, a 4, and a 5. SOL : a 2 = 4a = = 1 a 3 = 4a = = 5 a 4 = 4a = = 5 a 5 = 4a = = 21 1b (21). Find a closed form for a n. SOL 1 (by special forms): Homogenous a ˆ n 4a ˆ n 2 = 0 r 2 4 = 0 Particular a n 4a n 2 = 1 try a n = D a ˆ n = B 2 n + C D 4D = 1; D = 1 3 a 0 = 0 = B C( 2) a 1 = 1 = B 2 1 +C ( 2) B + C = 1 3 2B 2C = 4 3 B = 1 2 C = 1 6 a n = 2 n ( 2)n 1 3 SOL 2 by gen fcns on next page W3203FXsol.F02 2 of 10 12/8/02
3 SOL 2 by gen fcns: a n x n = 4 a n 2 x n + x n n = 2 n = 2 n =2 a n x n = 4x 2 a n 2 x n 2 + x 2 x n 2 n = 2 n =2 A( x ) a 1 x a 0 = 4x 2 A( x ) + x 2 1 x A( x ) x = 4x 2 A( x ) + x 2 1 x A( x )[ 1 4x 2 ] = x 2 1 x + x = x A( x ) = x ( 1 2x ) 1 + 2x 1 x n =2 ( )( 1 x ) = B 1 2x + C 1 + 2x + D 1 x solve with lin eq : B = 1 2, C = 1 6, D = 1 3 a n = 2 n ( 2)n 1 3 W3203FXsol.F02 3 of 10 12/8/02
4 2 (20 pts). Consider this binary relation on {1, 2, 3, 4}: R = ( 2,1), ( 2,3), ( 2, 4), ( 3,3), ( 4,3) 2a (5). Represent R as a matrix SOL : { } 2b (5). Represent R as a digraph. SOL: c (10). Calculate the relation R 2. { ( ) } SOL : R 2 = ( 2,3), ( 3,3), 4,3 W3203FXsol.F02 4 of 10 12/8/02
5 3a (10 pts). Give an example of a relation R on the set S = { a, b, c, d} such that R is both an equivalence relation and a partial ordering. SOL : R = ( a,a), ( b,b), ( c,c ), ( d,d ) { } 3b (15 pts). Prove that there is only one such relation R. Proof: Let Q be any eq rel on S that is also a p.o. Q Reflexive ( x S )[( x, x ) Q ]. R Q. Now suppose that x, y ( ) Q. Symmetry ( y, x ) Q. But then anti symmetry x = y. Q R. R = Q. W3203FXsol.F02 5 of 10 12/8/02
6 4a (10). The diameter of a graph is the maximum, taken over all vertex pairs u, v of the distance between u and v. Calculate the diameter of the Petersen graph. v u SOL: The two spanning trees both have height = 2. Thus vertices u and v are within distance 2 of every other vertex. By symmetry, no vertex has eccentricity 2. Thus, the diameter = 2. 4b (15). Calculate the chromatic number of the Petersen graph. w b w r r b b w w r SOL: A 3-coloring is shown at the right. Since there is a 5-cycle, no 2-coloring is possible. Thus, the chromatic number is 3. W3203FXsol.F02 6 of 10 12/8/02
7 5 (30 pts). Consider the following three graphs: G H J 5a (10). Decide whether G and H are isomorphic. Explain. SOL (many ways): NO. (1) diameter: diam (G) = 2; diam(j) = 3. (2) girth: girth (G) = 5; H has 4-cycles. (3) G is vertex-transitive; H is not. 5b (10). Decide whether G and J are isomorphic. Explain. SOL (many ways): NO. (1) diameter: diam (G) = 2; diam(j) = 3. (2) girth: girth (G) = 5; J has 4-cycles. (3) chromatic number: χ(g) = 3; χ(j) = 2 (bipartite). 5c (10). Decide whether H and J are isomorphic. Explain. SOL (many ways): NO. but NOT due to diameter or girth. (1) chromatic number: χ(h) = 3; χ(j) = 2 (bipartite). (2) In J, but not in H, every edge lies in a 4-cycle. (3) radius(h) = 2; radius(j) = 3. W3203FXsol.F02 7 of 10 12/8/02
8 6a (15). Mark two edges in the following graph such that it remains nonplanar after both are deleted. Prove your answer. SOL: Draw subdivided K 3,3 -subgraph as above, with two unused edges. 6b (15). Let G be the edge-complement of a 10-vertex, 3-regular simple graph. Prove that G is non-planar. PROOF: Graph G must be 6-regular. Thus, it has 30 edges. The Euler polyhedral equation V-E+F = 2 implies that F = 2. Thus, F = 22. However, the edge-face inequality 2E 3F implies that 60 = = 66, a contradiction! W3203FXsol.F02 8 of 10 12/8/02
9 7 (20). Consider the following recurrence: a 0 = 0; a n = n 2 na n 1 7a (3). Calculate a 1, a 2, and a 3. SOL : a 1 = a 0 = 1; a 2 = a 1 = 4 2 = 2; a 3 = a 2 = 9 6 = 3. 7c (17). Prove that a n = n. Proof by induction: Basis: a 0 = 0. Ind Hyp : Assume that a n 1 = n 1. Ind Step : a n = n 2 n a n 1 recursion = n 2 n ( n 1) by ind hyp ( ) = n = n 2 n 2 n W3203FXsol.F02 9 of 10 12/8/02
10 8 (25 pts). A bowl contains 50 fair coins {with p(h) = 0.5} and 50 standard loaded coins {with p(h) = 0.8}. A coin is drawn at random. 8a (10). The coin is tossed once. What is the probability of the outcome H? ( ) = pr ( H Fair ) + pr ( H Loaded ) SOL : pr H = pr ( H Fair ) pr(fair ) + pr ( H Loaded )pr(loaded) = = b (15). If the outcome of the toss is H, what is the probability that the coin selected was loaded? SOL : pr ( Loaded H ) = = or 8 13 ( ) pr ( H ) pr Loaded H W3203FXsol.F02 10 of 10 12/8/02
2 hours THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER. 6 June :45 11:45
 2 hours THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER DISCRETE MATHEMATICS 6 June 2016 9:45 11:45 Answer ALL THREE questions in Section A (30 marks in total) and TWO of the THREE questions in Section B (50 marks in total).
2 hours THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER DISCRETE MATHEMATICS 6 June 2016 9:45 11:45 Answer ALL THREE questions in Section A (30 marks in total) and TWO of the THREE questions in Section B (50 marks in total).
CMSC Discrete Mathematics FINAL EXAM Tuesday, December 5, 2017, 10:30-12:30
 CMSC-37110 Discrete Mathematics FINAL EXAM Tuesday, December 5, 2017, 10:30-12:30 Name (print): Email: This exam contributes 40% to your course grade. Do not use book, notes, scrap paper. NO ELECTRONIC
CMSC-37110 Discrete Mathematics FINAL EXAM Tuesday, December 5, 2017, 10:30-12:30 Name (print): Email: This exam contributes 40% to your course grade. Do not use book, notes, scrap paper. NO ELECTRONIC
6.042/18.062J Mathematics for Computer Science December 14, 2004 Tom Leighton and Eric Lehman. Final Exam
 6.04/18.06J Mathematics for Computer Science December 14, 004 Tom Leighton and Eric Lehman Final Exam YOUR NAME: : You may use two 8.5 11 sheets with notes in your own handwriting on both sides, but no
6.04/18.06J Mathematics for Computer Science December 14, 004 Tom Leighton and Eric Lehman Final Exam YOUR NAME: : You may use two 8.5 11 sheets with notes in your own handwriting on both sides, but no
CSE 321 Solutions to Practice Problems
 CSE 321 Solutions to Practice Problems Instructions: Feel free NOT to multiply out binomial coefficients, factorials, etc, and feel free to leave answers in the form of a sum. No calculators, books or
CSE 321 Solutions to Practice Problems Instructions: Feel free NOT to multiply out binomial coefficients, factorials, etc, and feel free to leave answers in the form of a sum. No calculators, books or
Planar Graphs (1) Planar Graphs (3) Planar Graphs (2) Planar Graphs (4)
 S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Planarity; Edges and Cycles 1 Planar Graphs (1) Topological graph theory, broadly conceived, is the study of graph layouts. Contemporary applications include circuit layouts on silicon
S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Planarity; Edges and Cycles 1 Planar Graphs (1) Topological graph theory, broadly conceived, is the study of graph layouts. Contemporary applications include circuit layouts on silicon
MATHEMATICS 105 Practice Final Exam, F Please answer the following questions (3 points each) 30 pt
 MATHEMATICS 105 Practice Final Exam, F2005 Print name Last name First name Here are some useful equations: Linear growth Recursive P N = P N 1 + d d is the common difference Exponential growth Recursive
MATHEMATICS 105 Practice Final Exam, F2005 Print name Last name First name Here are some useful equations: Linear growth Recursive P N = P N 1 + d d is the common difference Exponential growth Recursive
Discrete Math. Background Knowledge/Prior Skills Commutative and associative properties Solving systems of equations
 Discrete Math Numbers and Operations Standard: Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations. Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
Discrete Math Numbers and Operations Standard: Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations. Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
Name: Exam 2 Solutions. March 13, 2017
 Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 00 Finite Math Spring 07 Name: Instructors: Conant/Galvin Exam Solutions March, 07 This exam is in two parts on pages and contains problems worth
Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Math 00 Finite Math Spring 07 Name: Instructors: Conant/Galvin Exam Solutions March, 07 This exam is in two parts on pages and contains problems worth
DISCRETE STRUCTURES AMIN WITNO
 DISCRETE STRUCTURES AMIN WITNO p h i. w i t n o. c o m Discrete Structures Revision Notes and Problems Amin Witno Preface These notes were prepared for students as a revision workbook
DISCRETE STRUCTURES AMIN WITNO p h i. w i t n o. c o m Discrete Structures Revision Notes and Problems Amin Witno Preface These notes were prepared for students as a revision workbook
HOMEWORK #2 - MATH 3260
 HOMEWORK # - MATH 36 ASSIGNED: JANUARAY 3, 3 DUE: FEBRUARY 1, AT :3PM 1) a) Give by listing the sequence of vertices 4 Hamiltonian cycles in K 9 no two of which have an edge in common. Solution: Here is
HOMEWORK # - MATH 36 ASSIGNED: JANUARAY 3, 3 DUE: FEBRUARY 1, AT :3PM 1) a) Give by listing the sequence of vertices 4 Hamiltonian cycles in K 9 no two of which have an edge in common. Solution: Here is
12.1 Chromatic Number
 12.1 Chromatic Number History of Graph Colorings Theorem The Four Color Theorem: Any planar graph can be colored in at most four colors. But, it wasn t always the Four Color Theorem... Four Color Conjecture
12.1 Chromatic Number History of Graph Colorings Theorem The Four Color Theorem: Any planar graph can be colored in at most four colors. But, it wasn t always the Four Color Theorem... Four Color Conjecture
Math 430 Exam 1, Fall 2006
 c IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, October 21, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Exam 1, Fall 2006 These theorems may be cited at any time during the test by stating By
c IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, October 21, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Exam 1, Fall 2006 These theorems may be cited at any time during the test by stating By
Graph coloring, perfect graphs
 Lecture 5 (05.04.2013) Graph coloring, perfect graphs Scribe: Tomasz Kociumaka Lecturer: Marcin Pilipczuk 1 Introduction to graph coloring Definition 1. Let G be a simple undirected graph and k a positive
Lecture 5 (05.04.2013) Graph coloring, perfect graphs Scribe: Tomasz Kociumaka Lecturer: Marcin Pilipczuk 1 Introduction to graph coloring Definition 1. Let G be a simple undirected graph and k a positive
CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2016 Profs. Gold & Schnyder April 25, CS1800 Discrete Structures Final
 CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2016 Profs. Gold & Schnyder April 25, 2017 CS1800 Discrete Structures Final Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use a calculator or any
CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2016 Profs. Gold & Schnyder April 25, 2017 CS1800 Discrete Structures Final Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use a calculator or any
REVIEW QUESTIONS. Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms
 REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms 1. Why can t a Venn diagram be used to prove a statement about sets? 2. Suppose S is a set with n elements. Explain why the power set
REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms 1. Why can t a Venn diagram be used to prove a statement about sets? 2. Suppose S is a set with n elements. Explain why the power set
Sergey Norin Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University Montreal, Quebec H3A 2K6, Canada. and
 NON-PLANAR EXTENSIONS OF SUBDIVISIONS OF PLANAR GRAPHS Sergey Norin Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University Montreal, Quebec H3A 2K6, Canada and Robin Thomas 1 School of Mathematics
NON-PLANAR EXTENSIONS OF SUBDIVISIONS OF PLANAR GRAPHS Sergey Norin Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University Montreal, Quebec H3A 2K6, Canada and Robin Thomas 1 School of Mathematics
Graph Theory and Interconnection Networks
 Graph Theory and Interconnection Networks Lih-Hsing Hsu and Cheng-Kuan Lin @ CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa
Graph Theory and Interconnection Networks Lih-Hsing Hsu and Cheng-Kuan Lin @ CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa
Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009
 IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 13, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 13, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
Complexity of conditional colorability of graphs
 Complexity of conditional colorability of graphs Xueliang Li 1, Xiangmei Yao 1, Wenli Zhou 1 and Hajo Broersma 2 1 Center for Combinatorics and LPMC-TJKLC, Nankai University Tianjin 300071, P.R. China.
Complexity of conditional colorability of graphs Xueliang Li 1, Xiangmei Yao 1, Wenli Zhou 1 and Hajo Broersma 2 1 Center for Combinatorics and LPMC-TJKLC, Nankai University Tianjin 300071, P.R. China.
Notes on Graph Theory
 Notes on Graph Theory Maris Ozols June 8, 2010 Contents 0.1 Berge s Lemma............................................ 2 0.2 König s Theorem........................................... 3 0.3 Hall s Theorem............................................
Notes on Graph Theory Maris Ozols June 8, 2010 Contents 0.1 Berge s Lemma............................................ 2 0.2 König s Theorem........................................... 3 0.3 Hall s Theorem............................................
Problem Points Score Total 100
 Exam 2 A. Miller Spring 2002 Math 240 0 Show all work. Circle your answer. No notes, no books, no calculator, no cell phones, no pagers, no electronic devices at all. Solutions will be posted shortly after
Exam 2 A. Miller Spring 2002 Math 240 0 Show all work. Circle your answer. No notes, no books, no calculator, no cell phones, no pagers, no electronic devices at all. Solutions will be posted shortly after
McGill University Faculty of Science. Solutions to Practice Final Examination Math 240 Discrete Structures 1. Time: 3 hours Marked out of 60
 McGill University Faculty of Science Solutions to Practice Final Examination Math 40 Discrete Structures Time: hours Marked out of 60 Question. [6] Prove that the statement (p q) (q r) (p r) is a contradiction
McGill University Faculty of Science Solutions to Practice Final Examination Math 40 Discrete Structures Time: hours Marked out of 60 Question. [6] Prove that the statement (p q) (q r) (p r) is a contradiction
Practice Final Solutions. 1. Consider the following algorithm. Assume that n 1. line code 1 alg(n) { 2 j = 0 3 if (n = 0) { 4 return j
 Practice Final Solutions 1. Consider the following algorithm. Assume that n 1. line code 1 alg(n) 2 j = 0 3 if (n = 0) 4 return j } 5 else 6 j = 2n+ alg(n 1) 7 return j } } Set up a recurrence relation
Practice Final Solutions 1. Consider the following algorithm. Assume that n 1. line code 1 alg(n) 2 j = 0 3 if (n = 0) 4 return j } 5 else 6 j = 2n+ alg(n 1) 7 return j } } Set up a recurrence relation
Graph G = (V, E). V ={vertices}, E={edges}. V={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,k} E={(a,b),(a,g),( a,h),(a,k),(b,c),(b,k),...,(h,k)}
 Graph Theory Graph G = (V, E). V ={vertices}, E={edges}. a b c h k d g f e V={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,k} E={(a,b),(a,g),( a,h),(a,k),(b,c),(b,k),...,(h,k)} E =16. Digraph D = (V, A). V ={vertices}, E={edges}.
Graph Theory Graph G = (V, E). V ={vertices}, E={edges}. a b c h k d g f e V={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,k} E={(a,b),(a,g),( a,h),(a,k),(b,c),(b,k),...,(h,k)} E =16. Digraph D = (V, A). V ={vertices}, E={edges}.
MATH 2200 Final Review
 MATH 00 Final Review Thomas Goller December 7, 01 1 Exam Format The final exam will consist of 8-10 proofs It will take place on Tuesday, December 11, from 10:30 AM - 1:30 PM, in the usual room Topics
MATH 00 Final Review Thomas Goller December 7, 01 1 Exam Format The final exam will consist of 8-10 proofs It will take place on Tuesday, December 11, from 10:30 AM - 1:30 PM, in the usual room Topics
On (δ, χ)-bounded families of graphs
 On (δ, χ)-bounded families of graphs András Gyárfás Computer and Automation Research Institute Hungarian Academy of Sciences Budapest, P.O. Box 63 Budapest, Hungary, H-1518 gyarfas@sztaki.hu Manouchehr
On (δ, χ)-bounded families of graphs András Gyárfás Computer and Automation Research Institute Hungarian Academy of Sciences Budapest, P.O. Box 63 Budapest, Hungary, H-1518 gyarfas@sztaki.hu Manouchehr
Math 430 Final Exam, Fall 2008
 IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, December 9, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Final Exam, Fall 2008 Grades should be posted Friday 12/12. Have a good break, and don t forget
IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, December 9, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Final Exam, Fall 2008 Grades should be posted Friday 12/12. Have a good break, and don t forget
Exam 2 Solutions. x 1 x. x 4 The generating function for the problem is the fourth power of this, (1 x). 4
 Math 5366 Fall 015 Exam Solutions 1. (0 points) Find the appropriate generating function (in closed form) for each of the following problems. Do not find the coefficient of x n. (a) In how many ways can
Math 5366 Fall 015 Exam Solutions 1. (0 points) Find the appropriate generating function (in closed form) for each of the following problems. Do not find the coefficient of x n. (a) In how many ways can
Final Examination. Your name: Circle the name of your Tutorial Instructor: David Hanson Jelani Sayan
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.042J/18.062J, Fall 05: Mathematics for Computer Science December 21 Prof. Albert R. Meyer and Prof. Ronitt Rubinfeld revised December 22, 2005, 1118 minutes Circle
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.042J/18.062J, Fall 05: Mathematics for Computer Science December 21 Prof. Albert R. Meyer and Prof. Ronitt Rubinfeld revised December 22, 2005, 1118 minutes Circle
2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work that explains how you obtained your answer or you must explain how you obtained your answer.
 Math 50, Fall 2011 Test 3 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Directions 1. Time limit: 1 hour 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work that explains how you obtained your
Math 50, Fall 2011 Test 3 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Directions 1. Time limit: 1 hour 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work that explains how you obtained your
CS1800 Discrete Structures Final Version A
 CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2017 Profs. Aslam, Gold, & Pavlu December 11, 2017 CS1800 Discrete Structures Final Version A Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use
CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2017 Profs. Aslam, Gold, & Pavlu December 11, 2017 CS1800 Discrete Structures Final Version A Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use
MATH1240 Definitions and Theorems
 MATH1240 Definitions and Theorems 1 Fundamental Principles of Counting For an integer n 0, n factorial (denoted n!) is defined by 0! = 1, n! = (n)(n 1)(n 2) (3)(2)(1), for n 1. Given a collection of n
MATH1240 Definitions and Theorems 1 Fundamental Principles of Counting For an integer n 0, n factorial (denoted n!) is defined by 0! = 1, n! = (n)(n 1)(n 2) (3)(2)(1), for n 1. Given a collection of n
Note on Highly Connected Monochromatic Subgraphs in 2-Colored Complete Graphs
 Georgia Southern University From the SelectedWorks of Colton Magnant 2011 Note on Highly Connected Monochromatic Subgraphs in 2-Colored Complete Graphs Shinya Fujita, Gunma National College of Technology
Georgia Southern University From the SelectedWorks of Colton Magnant 2011 Note on Highly Connected Monochromatic Subgraphs in 2-Colored Complete Graphs Shinya Fujita, Gunma National College of Technology
MATH c UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS Examination for the Module MATH2210 (May/June 2004) INTRODUCTION TO DISCRETE MATHEMATICS. Time allowed : 2 hours
 This question paper consists of 5 printed pages, each of which is identified by the reference MATH221001 MATH221001 No calculators allowed c UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS Examination for the Module MATH2210 (May/June
This question paper consists of 5 printed pages, each of which is identified by the reference MATH221001 MATH221001 No calculators allowed c UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS Examination for the Module MATH2210 (May/June
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.042J/18.062J, Fall 02: Mathematics for Computer Science Professor Albert Meyer and Dr.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.042J/18.062J, Fall 02: Mathematics for Computer Science Professor Albert Meyer and Dr. Radhika Nagpal Quiz 1 Appendix Appendix Contents 1 Induction 2 2 Relations
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.042J/18.062J, Fall 02: Mathematics for Computer Science Professor Albert Meyer and Dr. Radhika Nagpal Quiz 1 Appendix Appendix Contents 1 Induction 2 2 Relations
Tribhuvan University Institute of Science and Technology Micro Syllabus
 Tribhuvan University Institute of Science and Technology Micro Syllabus Course Title: Discrete Structure Course no: CSC-152 Full Marks: 80+20 Credit hours: 3 Pass Marks: 32+8 Nature of course: Theory (3
Tribhuvan University Institute of Science and Technology Micro Syllabus Course Title: Discrete Structure Course no: CSC-152 Full Marks: 80+20 Credit hours: 3 Pass Marks: 32+8 Nature of course: Theory (3
(a) How many pairs (A, B) are there with A, B [n] and A B? (The inclusion is required to be strict.)
![(a) How many pairs (A, B) are there with A, B [n] and A B? (The inclusion is required to be strict.) (a) How many pairs (A, B) are there with A, B [n] and A B? (The inclusion is required to be strict.)](/thumbs/89/99851024.jpg) 1 Enumeration 11 Basic counting principles 1 June 2008, Question 1: (a) How many pairs (A, B) are there with A, B [n] and A B? (The inclusion is required to be strict) n/2 ( ) n (b) Find a closed form
1 Enumeration 11 Basic counting principles 1 June 2008, Question 1: (a) How many pairs (A, B) are there with A, B [n] and A B? (The inclusion is required to be strict) n/2 ( ) n (b) Find a closed form
Perfect matchings in highly cyclically connected regular graphs
 Perfect matchings in highly cyclically connected regular graphs arxiv:1709.08891v1 [math.co] 6 Sep 017 Robert Lukot ka Comenius University, Bratislava lukotka@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Edita Rollová University
Perfect matchings in highly cyclically connected regular graphs arxiv:1709.08891v1 [math.co] 6 Sep 017 Robert Lukot ka Comenius University, Bratislava lukotka@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Edita Rollová University
Preliminaries. Graphs. E : set of edges (arcs) (Undirected) Graph : (i, j) = (j, i) (edges) V = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, E = {(1, 3), (3, 2), (2, 4)}
 Preliminaries Graphs G = (V, E), V : set of vertices E : set of edges (arcs) (Undirected) Graph : (i, j) = (j, i) (edges) 1 2 3 5 4 V = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, E = {(1, 3), (3, 2), (2, 4)} 1 Directed Graph (Digraph)
Preliminaries Graphs G = (V, E), V : set of vertices E : set of edges (arcs) (Undirected) Graph : (i, j) = (j, i) (edges) 1 2 3 5 4 V = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, E = {(1, 3), (3, 2), (2, 4)} 1 Directed Graph (Digraph)
Planar Ramsey Numbers for Small Graphs
 Planar Ramsey Numbers for Small Graphs Andrzej Dudek Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Emory University Atlanta, GA 30322, USA Andrzej Ruciński Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science
Planar Ramsey Numbers for Small Graphs Andrzej Dudek Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Emory University Atlanta, GA 30322, USA Andrzej Ruciński Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science
1.3 Vertex Degrees. Vertex Degree for Undirected Graphs: Let G be an undirected. Vertex Degree for Digraphs: Let D be a digraph and y V (D).
 1.3. VERTEX DEGREES 11 1.3 Vertex Degrees Vertex Degree for Undirected Graphs: Let G be an undirected graph and x V (G). The degree d G (x) of x in G: the number of edges incident with x, each loop counting
1.3. VERTEX DEGREES 11 1.3 Vertex Degrees Vertex Degree for Undirected Graphs: Let G be an undirected graph and x V (G). The degree d G (x) of x in G: the number of edges incident with x, each loop counting
Math 430 Exam 2, Fall 2008
 Do not distribute. IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, February 16, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Exam 2, Fall 2008 These theorems may be cited at any time during the test
Do not distribute. IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, February 16, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 430 Exam 2, Fall 2008 These theorems may be cited at any time during the test
An approximate version of Hadwiger s conjecture for claw-free graphs
 An approximate version of Hadwiger s conjecture for claw-free graphs Maria Chudnovsky Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA and Alexandra Ovetsky Fradkin Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544,
An approximate version of Hadwiger s conjecture for claw-free graphs Maria Chudnovsky Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA and Alexandra Ovetsky Fradkin Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544,
CSE 311: Foundations of Computing I Autumn 2014 Practice Final: Section X. Closed book, closed notes, no cell phones, no calculators.
 CSE 311: Foundations of Computing I Autumn 014 Practice Final: Section X YY ZZ Name: UW ID: Instructions: Closed book, closed notes, no cell phones, no calculators. You have 110 minutes to complete the
CSE 311: Foundations of Computing I Autumn 014 Practice Final: Section X YY ZZ Name: UW ID: Instructions: Closed book, closed notes, no cell phones, no calculators. You have 110 minutes to complete the
R(p, k) = the near regular complete k-partite graph of order p. Let p = sk+r, where s and r are positive integers such that 0 r < k.
 MATH3301 EXTREMAL GRAPH THEORY Definition: A near regular complete multipartite graph is a complete multipartite graph with orders of its partite sets differing by at most 1. R(p, k) = the near regular
MATH3301 EXTREMAL GRAPH THEORY Definition: A near regular complete multipartite graph is a complete multipartite graph with orders of its partite sets differing by at most 1. R(p, k) = the near regular
Integrity in Graphs: Bounds and Basics
 Integrity in Graphs: Bounds and Basics Wayne Goddard 1 Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 USA and Henda C. Swart Department of Mathematics, University of
Integrity in Graphs: Bounds and Basics Wayne Goddard 1 Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 USA and Henda C. Swart Department of Mathematics, University of
Solutions. CS 2800 Fall 2017 Final exam Friday, December 8. NetID: 1. Modular arithmetic [9 pts]
![Solutions. CS 2800 Fall 2017 Final exam Friday, December 8. NetID: 1. Modular arithmetic [9 pts] Solutions. CS 2800 Fall 2017 Final exam Friday, December 8. NetID: 1. Modular arithmetic [9 pts]](/thumbs/92/108353251.jpg) S 28 Fall 27 Final exam Friday, December 8. Modular arithmetic [9 pts] Solutions (a) [5 pts] Let d j d j... d 2 d d be the base representation of n. Use equivalence classes to prove that if n is a multiple
S 28 Fall 27 Final exam Friday, December 8. Modular arithmetic [9 pts] Solutions (a) [5 pts] Let d j d j... d 2 d d be the base representation of n. Use equivalence classes to prove that if n is a multiple
On Dominator Colorings in Graphs
 On Dominator Colorings in Graphs Ralucca Michelle Gera Department of Applied Mathematics Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 994, USA ABSTRACT Given a graph G, the dominator coloring problem seeks a
On Dominator Colorings in Graphs Ralucca Michelle Gera Department of Applied Mathematics Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 994, USA ABSTRACT Given a graph G, the dominator coloring problem seeks a
Upper Bounds of Dynamic Chromatic Number
 Upper Bounds of Dynamic Chromatic Number Hong-Jian Lai, Bruce Montgomery and Hoifung Poon Department of Mathematics West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26506-6310 June 22, 2000 Abstract A proper vertex
Upper Bounds of Dynamic Chromatic Number Hong-Jian Lai, Bruce Montgomery and Hoifung Poon Department of Mathematics West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26506-6310 June 22, 2000 Abstract A proper vertex
GRAPHS & DIGRAPHS 5th Edition. Preface to the fifth edition
 GRAPHS & DIGRAPHS 5th Edition Gary Chartrand Western Michigan University Linda Lesniak Drew University Ping Zhang Western Michigan University Preface to the fifth edition Since graph theory was considered
GRAPHS & DIGRAPHS 5th Edition Gary Chartrand Western Michigan University Linda Lesniak Drew University Ping Zhang Western Michigan University Preface to the fifth edition Since graph theory was considered
Graph homomorphisms. Peter J. Cameron. Combinatorics Study Group Notes, September 2006
 Graph homomorphisms Peter J. Cameron Combinatorics Study Group Notes, September 2006 Abstract This is a brief introduction to graph homomorphisms, hopefully a prelude to a study of the paper [1]. 1 Homomorphisms
Graph homomorphisms Peter J. Cameron Combinatorics Study Group Notes, September 2006 Abstract This is a brief introduction to graph homomorphisms, hopefully a prelude to a study of the paper [1]. 1 Homomorphisms
ACO Comprehensive Exam October 18 and 19, Analysis of Algorithms
 Consider the following two graph problems: 1. Analysis of Algorithms Graph coloring: Given a graph G = (V,E) and an integer c 0, a c-coloring is a function f : V {1,,...,c} such that f(u) f(v) for all
Consider the following two graph problems: 1. Analysis of Algorithms Graph coloring: Given a graph G = (V,E) and an integer c 0, a c-coloring is a function f : V {1,,...,c} such that f(u) f(v) for all
Advanced Topics in Discrete Math: Graph Theory Fall 2010
 21-801 Advanced Topics in Discrete Math: Graph Theory Fall 2010 Prof. Andrzej Dudek notes by Brendan Sullivan October 18, 2010 Contents 0 Introduction 1 1 Matchings 1 1.1 Matchings in Bipartite Graphs...................................
21-801 Advanced Topics in Discrete Math: Graph Theory Fall 2010 Prof. Andrzej Dudek notes by Brendan Sullivan October 18, 2010 Contents 0 Introduction 1 1 Matchings 1 1.1 Matchings in Bipartite Graphs...................................
Applications of Chromatic Polynomials Involving Stirling Numbers
 Applications of Chromatic Polynomials Involving Stirling Numbers A. Mohr and T.D. Porter Department of Mathematics Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 6290 tporter@math.siu.edu June 23, 2008 The
Applications of Chromatic Polynomials Involving Stirling Numbers A. Mohr and T.D. Porter Department of Mathematics Southern Illinois University Carbondale, IL 6290 tporter@math.siu.edu June 23, 2008 The
IVA S STUDY GUIDE FOR THE DISCRETE FINAL EXAM - SELECTED SOLUTIONS. 1. Combinatorics
 IVA S STUDY GUIDE FOR THE DISCRETE FINAL EXAM - SELECTED SOLUTIONS Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text Review all the combinatorics problems from homewor Do at least a couple of extra
IVA S STUDY GUIDE FOR THE DISCRETE FINAL EXAM - SELECTED SOLUTIONS Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text Review all the combinatorics problems from homewor Do at least a couple of extra
Midterm. You may use a calculator, but not any device that can access the Internet or store large amounts of data.
 INST 737 April 1, 2013 Midterm Name: }{{} by writing my name I swear by the honor code Read all of the following information before starting the exam: For free response questions, show all work, clearly
INST 737 April 1, 2013 Midterm Name: }{{} by writing my name I swear by the honor code Read all of the following information before starting the exam: For free response questions, show all work, clearly
Recurrence Relations
 Recurrence Relations Recurrence Relations Reading (Epp s textbook) 5.6 5.8 1 Recurrence Relations A recurrence relation for a sequence aa 0, aa 1, aa 2, ({a n }) is a formula that relates each term a k
Recurrence Relations Recurrence Relations Reading (Epp s textbook) 5.6 5.8 1 Recurrence Relations A recurrence relation for a sequence aa 0, aa 1, aa 2, ({a n }) is a formula that relates each term a k
Essential Learning Outcomes for Algebra 2
 ALGEBRA 2 ELOs 1 Essential Learning Outcomes for Algebra 2 The following essential learning outcomes (ELOs) represent the 12 skills that students should be able to demonstrate knowledge of upon completion
ALGEBRA 2 ELOs 1 Essential Learning Outcomes for Algebra 2 The following essential learning outcomes (ELOs) represent the 12 skills that students should be able to demonstrate knowledge of upon completion
COM S 330 Homework 08 Solutions. Type your answers to the following questions and submit a PDF file to Blackboard. One page per problem.
 COM S 0 Homework 08 Solutions Type your answers to the following questions and submit a PDF file to Blackboard. One page per problem. Problem 1. [10pts] Let M = (S, T, s 0 ) be the state machine where
COM S 0 Homework 08 Solutions Type your answers to the following questions and submit a PDF file to Blackboard. One page per problem. Problem 1. [10pts] Let M = (S, T, s 0 ) be the state machine where
GIRTH SIX CUBIC GRAPHS HAVE PETERSEN MINORS
 GIRTH SIX CUBIC GRAPHS HAVE PETERSEN MINORS Neil Robertson 1 Department of Mathematics Ohio State University 231 W. 18th Ave. Columbus, Ohio 43210, USA P. D. Seymour Bellcore 445 South St. Morristown,
GIRTH SIX CUBIC GRAPHS HAVE PETERSEN MINORS Neil Robertson 1 Department of Mathematics Ohio State University 231 W. 18th Ave. Columbus, Ohio 43210, USA P. D. Seymour Bellcore 445 South St. Morristown,
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/77/75937586.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Final Exam Review Session Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Notes 140608 Review Things to Know has
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Final Exam Review Session Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Notes 140608 Review Things to Know has
Midterm 1. Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on Your Left: Name of Person Sitting on Your Right: Name of Person Sitting in Front of You:
 CS70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory, Fall 2018 Midterm 1 8:00-10:00pm, 24 September Your First Name: SIGN Your Name: Your Last Name: Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on Your Left: Name
CS70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory, Fall 2018 Midterm 1 8:00-10:00pm, 24 September Your First Name: SIGN Your Name: Your Last Name: Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on Your Left: Name
THE EXTREMAL FUNCTIONS FOR TRIANGLE-FREE GRAPHS WITH EXCLUDED MINORS 1
 THE EXTREMAL FUNCTIONS FOR TRIANGLE-FREE GRAPHS WITH EXCLUDED MINORS 1 Robin Thomas and Youngho Yoo School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 0-0160, USA We prove two results:
THE EXTREMAL FUNCTIONS FOR TRIANGLE-FREE GRAPHS WITH EXCLUDED MINORS 1 Robin Thomas and Youngho Yoo School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 0-0160, USA We prove two results:
Ramsey Unsaturated and Saturated Graphs
 Ramsey Unsaturated and Saturated Graphs P Balister J Lehel RH Schelp March 20, 2005 Abstract A graph is Ramsey unsaturated if there exists a proper supergraph of the same order with the same Ramsey number,
Ramsey Unsaturated and Saturated Graphs P Balister J Lehel RH Schelp March 20, 2005 Abstract A graph is Ramsey unsaturated if there exists a proper supergraph of the same order with the same Ramsey number,
CSCE 750 Final Exam Answer Key Wednesday December 7, 2005
 CSCE 750 Final Exam Answer Key Wednesday December 7, 2005 Do all problems. Put your answers on blank paper or in a test booklet. There are 00 points total in the exam. You have 80 minutes. Please note
CSCE 750 Final Exam Answer Key Wednesday December 7, 2005 Do all problems. Put your answers on blank paper or in a test booklet. There are 00 points total in the exam. You have 80 minutes. Please note
Math 414, Fall 2016, Test I
 Math 414, Fall 2016, Test I Dr. Holmes September 23, 2016 The test begins at 10:30 am and ends officially at 11:45 am: what will actually happen at 11:45 is that I will give a five minute warning. The
Math 414, Fall 2016, Test I Dr. Holmes September 23, 2016 The test begins at 10:30 am and ends officially at 11:45 am: what will actually happen at 11:45 is that I will give a five minute warning. The
Discrete Structures: Sample Questions, Exam 2, SOLUTIONS
 Discrete Structures: Sample Questions, Exam 2, SOLUTIONS (This is longer than the actual test.) 1. Show that any postage of 8 cents or more can be achieved by using only -cent and 5-cent stamps. We proceed
Discrete Structures: Sample Questions, Exam 2, SOLUTIONS (This is longer than the actual test.) 1. Show that any postage of 8 cents or more can be achieved by using only -cent and 5-cent stamps. We proceed
Painting Squares in 2 1 Shades
 Painting Squares in 1 Shades Daniel W. Cranston Landon Rabern May 1, 014 Abstract Cranston and Kim conjectured that if G is a connected graph with maximum degree and G is not a Moore Graph, then χ l (G
Painting Squares in 1 Shades Daniel W. Cranston Landon Rabern May 1, 014 Abstract Cranston and Kim conjectured that if G is a connected graph with maximum degree and G is not a Moore Graph, then χ l (G
Induced Cycles of Fixed Length
 Induced Cycles of Fixed Length Terry McKee Wright State University Dayton, Ohio USA terry.mckee@wright.edu Cycles in Graphs Vanderbilt University 31 May 2012 Overview 1. Investigating the fine structure
Induced Cycles of Fixed Length Terry McKee Wright State University Dayton, Ohio USA terry.mckee@wright.edu Cycles in Graphs Vanderbilt University 31 May 2012 Overview 1. Investigating the fine structure
Problem Point Value Points
 Math 70 TUFTS UNIVERSITY October 12, 2015 Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics Sections 1 and 2 Exam I Instructions: No notes or books are allowed. All calculators, cell phones, or other electronic
Math 70 TUFTS UNIVERSITY October 12, 2015 Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics Sections 1 and 2 Exam I Instructions: No notes or books are allowed. All calculators, cell phones, or other electronic
Algebra 2 CP Semester 1 PRACTICE Exam
 Algebra 2 CP Semester 1 PRACTICE Exam NAME DATE HR You may use a calculator. Please show all work directly on this test. You may write on the test. GOOD LUCK! THIS IS JUST PRACTICE GIVE YOURSELF 45 MINUTES
Algebra 2 CP Semester 1 PRACTICE Exam NAME DATE HR You may use a calculator. Please show all work directly on this test. You may write on the test. GOOD LUCK! THIS IS JUST PRACTICE GIVE YOURSELF 45 MINUTES
Discrete Structures: Sample Questions, Exam 2, SOLUTIONS
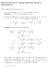 Discrete Structures: Sample Questions, Exam, SOLUTIONS This is longer than the actual test.) 1. List all the strings over X = {a, b, c} of length or less. λ, a, b, c, aa, ab, ac, ba, bb, bc, ca, cb, cc..
Discrete Structures: Sample Questions, Exam, SOLUTIONS This is longer than the actual test.) 1. List all the strings over X = {a, b, c} of length or less. λ, a, b, c, aa, ab, ac, ba, bb, bc, ca, cb, cc..
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 27 MARCH 28, 2010
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 27 MARCH 28, 200 Instructions. Write on the front of your blue book your student ID number. Do not write your name anywhere on your blue book. Each
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN UNDERGRADUATE MATH COMPETITION 27 MARCH 28, 200 Instructions. Write on the front of your blue book your student ID number. Do not write your name anywhere on your blue book. Each
Discrete Mathematics
 Discrete Mathematics Workshop Organized by: ACM Unit, ISI Tutorial-1 Date: 05.07.2017 (Q1) Given seven points in a triangle of unit area, prove that three of them form a triangle of area not exceeding
Discrete Mathematics Workshop Organized by: ACM Unit, ISI Tutorial-1 Date: 05.07.2017 (Q1) Given seven points in a triangle of unit area, prove that three of them form a triangle of area not exceeding
(1) Which of the following are propositions? If it is a proposition, determine its truth value: A propositional function, but not a proposition.
 Math 231 Exam Practice Problem Solutions WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the
Math 231 Exam Practice Problem Solutions WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the
INDUCED CYCLES AND CHROMATIC NUMBER
 INDUCED CYCLES AND CHROMATIC NUMBER A.D. SCOTT DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, GOWER STREET, LONDON WC1E 6BT Abstract. We prove that, for any pair of integers k, l 1, there exists an integer
INDUCED CYCLES AND CHROMATIC NUMBER A.D. SCOTT DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, GOWER STREET, LONDON WC1E 6BT Abstract. We prove that, for any pair of integers k, l 1, there exists an integer
UC Berkeley, CS 174: Combinatorics and Discrete Probability (Fall 2008) Midterm 1. October 7, 2008
 UC Berkeley, CS 74: Combinatorics and Discrete Probability (Fall 2008) Midterm Instructor: Prof. Yun S. Song October 7, 2008 Your Name : Student ID# : Read these instructions carefully:. This is a closed-book
UC Berkeley, CS 74: Combinatorics and Discrete Probability (Fall 2008) Midterm Instructor: Prof. Yun S. Song October 7, 2008 Your Name : Student ID# : Read these instructions carefully:. This is a closed-book
Spring 2017 Midterm 1 04/26/2017
 Math 2B Spring 2017 Midterm 1 04/26/2017 Time Limit: 50 Minutes Name (Print): Student ID This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter
Math 2B Spring 2017 Midterm 1 04/26/2017 Time Limit: 50 Minutes Name (Print): Student ID This exam contains 10 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are missing. Enter
2 β 0 -excellent graphs
 β 0 -excellent graphs A. P. Pushpalatha, G. Jothilakshmi Thiagarajar College of Engineering Madurai - 65 015 India Email: gjlmat@tce.edu, appmat@tce.edu S. Suganthi, V. Swaminathan Ramanujan Research Centre
β 0 -excellent graphs A. P. Pushpalatha, G. Jothilakshmi Thiagarajar College of Engineering Madurai - 65 015 India Email: gjlmat@tce.edu, appmat@tce.edu S. Suganthi, V. Swaminathan Ramanujan Research Centre
IE 4521 Midterm #1. Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson. March 2, 2010
 IE 4521 Midterm #1 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson March 2, 2010 Before you begin: This exam has 9 pages (including the normal distribution table) and a total of 8 problems. Make sure that all pages are present.
IE 4521 Midterm #1 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson March 2, 2010 Before you begin: This exam has 9 pages (including the normal distribution table) and a total of 8 problems. Make sure that all pages are present.
INDEPENDENT TRANSVERSAL DOMINATION IN GRAPHS
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 32 (2012) 5 17 INDEPENDENT TRANSVERSAL DOMINATION IN GRAPHS Ismail Sahul Hamid Department of Mathematics The Madura College Madurai, India e-mail: sahulmat@yahoo.co.in
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 32 (2012) 5 17 INDEPENDENT TRANSVERSAL DOMINATION IN GRAPHS Ismail Sahul Hamid Department of Mathematics The Madura College Madurai, India e-mail: sahulmat@yahoo.co.in
FORBIDDEN MINORS AND MINOR-CLOSED GRAPH PROPERTIES
 FORBIDDEN MINORS AND MINOR-CLOSED GRAPH PROPERTIES DAN WEINER Abstract. Kuratowski s Theorem gives necessary and sufficient conditions for graph planarity that is, embeddability in R 2. This motivates
FORBIDDEN MINORS AND MINOR-CLOSED GRAPH PROPERTIES DAN WEINER Abstract. Kuratowski s Theorem gives necessary and sufficient conditions for graph planarity that is, embeddability in R 2. This motivates
BASIC GRAPH THEORY. SUB CODE: 09MAT01 Total hours 52
 SYLLABUS For the course work syllabus recommended by the Guide for doing Ph.D in the Department of Mathematics, Sri Siddhartha Institute of Technology under SSU, Tumkur. BASIC GRAPH THEORY SUB CODE: 09MAT01
SYLLABUS For the course work syllabus recommended by the Guide for doing Ph.D in the Department of Mathematics, Sri Siddhartha Institute of Technology under SSU, Tumkur. BASIC GRAPH THEORY SUB CODE: 09MAT01
Chapter 01: Probability Theory (Cont d)
 Chapter 01: Probability Theory (Cont d) Section 1.5: Probabilities of Event Intersections Problem (01): When a company receives an order, there is a probability of 0.42 that its value is over $1000. If
Chapter 01: Probability Theory (Cont d) Section 1.5: Probabilities of Event Intersections Problem (01): When a company receives an order, there is a probability of 0.42 that its value is over $1000. If
MATH 363: Discrete Mathematics
 MATH 363: Discrete Mathematics Learning Objectives by topic The levels of learning for this class are classified as follows. 1. Basic Knowledge: To recall and memorize - Assess by direct questions. The
MATH 363: Discrete Mathematics Learning Objectives by topic The levels of learning for this class are classified as follows. 1. Basic Knowledge: To recall and memorize - Assess by direct questions. The
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2016 Seshia and Walrand Midterm 1 Solutions
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2016 Seshia and Walrand Midterm 1 Solutions PRINT Your Name: Answer: Oski Bear SIGN Your Name: PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: Dwinelle
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2016 Seshia and Walrand Midterm 1 Solutions PRINT Your Name: Answer: Oski Bear SIGN Your Name: PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: Dwinelle
Exam in Discrete Mathematics
 Exam in Discrete Mathematics First Year at the Faculty of Engineering and Science and the Technical Faculty of IT and Design June 4th, 018, 9.00-1.00 This exam consists of 11 numbered pages with 14 problems.
Exam in Discrete Mathematics First Year at the Faculty of Engineering and Science and the Technical Faculty of IT and Design June 4th, 018, 9.00-1.00 This exam consists of 11 numbered pages with 14 problems.
are the q-versions of n, n! and . The falling factorial is (x) k = x(x 1)(x 2)... (x k + 1).
 Lecture A jacques@ucsd.edu Notation: N, R, Z, F, C naturals, reals, integers, a field, complex numbers. p(n), S n,, b(n), s n, partition numbers, Stirling of the second ind, Bell numbers, Stirling of the
Lecture A jacques@ucsd.edu Notation: N, R, Z, F, C naturals, reals, integers, a field, complex numbers. p(n), S n,, b(n), s n, partition numbers, Stirling of the second ind, Bell numbers, Stirling of the
STUDY GUIDE FOR THE WRECKONING. 1. Combinatorics. (1) How many (positive integer) divisors does 2940 have? What about 3150?
 STUDY GUIDE FOR THE WRECKONING. Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text. Review all the combinatorics problems from homework. Do at least a couple of extra problems given below. () How
STUDY GUIDE FOR THE WRECKONING. Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text. Review all the combinatorics problems from homework. Do at least a couple of extra problems given below. () How
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
CMSC Discrete Mathematics SOLUTIONS TO SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November, 2005
 CMSC-37110 Discrete Mathematics SOLUTIONS TO SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November, 2005 Instructor: László Babai Ryerson 164 e-mail: laci@cs This exam contributes 20% to your course grade. 1. (6 points) Let a
CMSC-37110 Discrete Mathematics SOLUTIONS TO SECOND MIDTERM EXAM November, 2005 Instructor: László Babai Ryerson 164 e-mail: laci@cs This exam contributes 20% to your course grade. 1. (6 points) Let a
Prelim 1 (10 8)!8! = 10 9 = 45. (b) How many ways can it be done if the first three questions are required? 2 = 21
 Math 1105 Fall 010 J.T. Gene Hwang, Instructor Robyn Miller, T.A. Prelim 1 Instructions This is a closed book exam. Graphing calculators are not permitted. Solutions should be written in your blue book
Math 1105 Fall 010 J.T. Gene Hwang, Instructor Robyn Miller, T.A. Prelim 1 Instructions This is a closed book exam. Graphing calculators are not permitted. Solutions should be written in your blue book
A taste of perfect graphs
 A taste of perfect graphs Remark Determining the chromatic number of a graph is a hard problem, in general, and it is even hard to get good lower bounds on χ(g). An obvious lower bound we have seen before
A taste of perfect graphs Remark Determining the chromatic number of a graph is a hard problem, in general, and it is even hard to get good lower bounds on χ(g). An obvious lower bound we have seen before
A counter-example to Voloshin s hypergraph co-perfectness conjecture
 A counter-example to Voloshin s hypergraph co-perfectness conjecture Daniel Král Department of Applied Mathematics and Institute for Theoretical Computer Science (ITI) Charles University Malostranské náměstí
A counter-example to Voloshin s hypergraph co-perfectness conjecture Daniel Král Department of Applied Mathematics and Institute for Theoretical Computer Science (ITI) Charles University Malostranské náměstí
arxiv: v3 [math.co] 25 Feb 2019
![arxiv: v3 [math.co] 25 Feb 2019 arxiv: v3 [math.co] 25 Feb 2019](/thumbs/94/122041178.jpg) Extremal Theta-free planar graphs arxiv:111.01614v3 [math.co] 25 Feb 2019 Yongxin Lan and Yongtang Shi Center for Combinatorics and LPMC Nankai University, Tianjin 30001, China and Zi-Xia Song Department
Extremal Theta-free planar graphs arxiv:111.01614v3 [math.co] 25 Feb 2019 Yongxin Lan and Yongtang Shi Center for Combinatorics and LPMC Nankai University, Tianjin 30001, China and Zi-Xia Song Department
CS1800 Discrete Structures Spring 2018 February CS1800 Discrete Structures Midterm Version A
 CS1800 Discrete Structures Spring 2018 February 2018 CS1800 Discrete Structures Midterm Version A Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use a calculator or any other electronic
CS1800 Discrete Structures Spring 2018 February 2018 CS1800 Discrete Structures Midterm Version A Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use a calculator or any other electronic
Introductory Probability
 Introductory Probability Bernoulli Trials and Binomial Probability Distributions Dr. Nguyen nicholas.nguyen@uky.edu Department of Mathematics UK February 04, 2019 Agenda Bernoulli Trials and Probability
Introductory Probability Bernoulli Trials and Binomial Probability Distributions Dr. Nguyen nicholas.nguyen@uky.edu Department of Mathematics UK February 04, 2019 Agenda Bernoulli Trials and Probability
Tree-chromatic number
 Tree-chromatic number Paul Seymour 1 Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 November 2, 2014; revised June 25, 2015 1 Supported by ONR grant N00014-10-1-0680 and NSF grant DMS-1265563. Abstract Let
Tree-chromatic number Paul Seymour 1 Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 November 2, 2014; revised June 25, 2015 1 Supported by ONR grant N00014-10-1-0680 and NSF grant DMS-1265563. Abstract Let
Exam Practice Problems
 Math 231 Exam Practice Problems WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the topics.
Math 231 Exam Practice Problems WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the topics.
Each question has equal weight. The maximum possible mark is 75/75.
 PRIFYSGOL CYMRU ABERTAWE UNIVERSITY OF WALES SWANSEA DEGREE EXAMINATIONS 007 MODULE MAP363 Combinatorics: SPECIMEN PAPER Time Allowed hours There are SIX questions on the paper. A candidate s best THREE
PRIFYSGOL CYMRU ABERTAWE UNIVERSITY OF WALES SWANSEA DEGREE EXAMINATIONS 007 MODULE MAP363 Combinatorics: SPECIMEN PAPER Time Allowed hours There are SIX questions on the paper. A candidate s best THREE
