CONVERGENCE TO FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION AND LOSS PROBABILITY. Jin-Chun Kim and Hee-Choon Lee
|
|
|
- Herbert Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kangweon-Kyungki Math. Jour. (2003), No., pp CONVERGENCE TO FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION AND LOSS PROBABILITY Jin-Chun Kim and Hee-Choon Lee Abstract. We study the weak convergence to Fractional Brownian motion and some examples with applications to traffic modeling. Finally, we get loss probability for queue-length distribution related to self-similar process.. Introduction Traditional traffic models based on the Poisson process or, more generally, on short range dependent processes, cannot describe the behavior of actual LAN traffic. Because of tremendous burstiness of LAN traffic at any time scale, many researchers have studied long range dependent process and self-similar process. Kelly ([4]) has considered the notion of effective bandwidth in the context of stochastic models for the statistical sharing of resources to figure out the loss probability. Chang and Zajic ([2]) apply the result on the effective bandwidth of stationary departure process to intree networks with time varying capacities and priority tandem queues. Recently, several researchers ([],[4],[6],[0]) have proposed and developed the theory of effective bandwidth and loss probability as a tentative solution for various problems that arise in high speed digital networks, in particular ATM networks. On the other hand, there has been a recent flood of literature and discussion on the tail behavior of queue-length distribution, motivated by potential applications to the design and control by high-speed telecommunication networks([3],[5]). Received January 0, Mathematics Subject Classification: 60B0, 60K30. Key words and phrases: Limit Theorem, FBM, Loss Probability.
2 36 J.C. Kim and H.C. Lee In section 2, we define the effective bandwidth with a stationary source and introduce the effective bandwidth of Brownian motion and Fractional Brownian motion. In section 3, we study the weak convergence to Fractional Brownian motion and give some examples with applications to traffic modeling. In section 4, we obtain the loss probability, i.e. tail behavior of queue-length distribution, of self-similar process. 2. Definition and Preinary In this section we first define the effective bandwidth with a stationary source X i which is the number of arrivals in the ith time unit. Definition 2.. The effective bandwidth of X() = i= X i is defined as eb X (θ, ) = θ If X i are independent, then P log E[eθ i= X i ], 0 < θ <. eb X (θ, ) = i eb Xi (θ, ). Furthermore, for any fixed value of, eb X (θ, ) is increasing in θ and EX[0, ] eb X (θ, ) X[0, ], where X[0, ] is the essential supremum. Definition 2.2. A stochastic process {X(t)} is said to be a Brownian motion if. X(t) has stationary and independent increments 2. for t > 0, X(t) N(µ, σ 2 t) 3. X(0) = 0 a.s. The effective bandwidth of a Browian motion is eb(θ, ) = µ + θσ2 2, where µ is the mean arrival rate and σ 2 is the variance of the arrival. A critical point of a Brownian Motion stream inf sup 0 θ 0 {θ(b + C) θ(µ + θσ2 2 )}
3 Convergence to FBM and loss probability 37 = B C µ, 2(C µ) θ =. σ 2 Let ρ X (k) be the covariance of stationary stochastic process X(t). Then we define the followings. Definition 2.3. A stationary stochastic process exhibits short range dependence if ρ X (k) < k= Definition 2.4. A stationary stochastic process exhibits long range dependence if ρ X (k) = k= Definition 2.5. A stochastic process {B H (t)} is said to be a Fractional Brownian motion(f BM) with Hurst parameter H if. B H (t) has stationary increments 2. for t > 0, B H (t) is normally distributed with mean 0 3. B H (0) = 0 a.s. 4. The increments of B H (t), Z(j) = B H (j + ) B H (j) satisfy ρ Z (k) = 2 { k + 2H + k 2H 2k 2H } A standard example of a long range dependent process is fractional Brownian motion, Hurst parameter H > /2. If H < /2, then this fractional Brownian motion exhibits short range dependence. On the other hand, the effective bandwidth of a FBM is eb(θ, ) = µ + θσ2 2 2H, and the critical points are = B H C µ H, θ = B + (C µ) σ 2 ( ) 2H. Definition 2.6. A continuous process X(t) is self-similar with selfsimilarity parameter H 0 if it satisfies the condition: X(t) d = c H X(ct), t 0, c > 0, where the equality is in the sense of finite-dimensional distributions.
4 38 J.C. Kim and H.C. Lee Brownian motion and Fractional Brownian motion are two important examples of self-similar process. 3. Convergence to Fractional Brownian motion Let Y i (j) be the number of arrivals in the jth time unit of ith source. Let M Y M (j) = (Y i (j) E(Y i (j)), i= and (k) denote the covariance of Y (j). Lemma 3.. [8] The stationary sequence M /2 Y M(j) converges in the sense of finite dimensional distributions to G H (j), where G H (j) represents a stationary Gaussian process with covariance function of the same form as (k), as M. Theorem 3.. T H M /2 [T t] Y M (j) converges in the sense of finite dimensional distributions to {σ 0 B H (t) 0 t }. Furthermore, as M and T, (a) (Long Range dependence) If ρ(k) ck 2H 2, c > 0 and /2 < H <, then σ0 2 c = H(2H ). (b) If ρ(k) < and ρ(k) = c > 0, k= then σ 2 0 = c. (c) (Short Range dependence) k= ρ(k) ck 2H 2, c < 0 and 0 < H < /2,
5 then σ0 2 c = H(2H ). Convergence to FBM and loss probability 39 Proof. Set Z j = /M /2 Y M (j). By Lemma 3., Z j converges in the sense of finite dimensional distributions to G H (j) as M goes to infinity. By Theorem 7.2. of [9], the finite dimensional distributions of N H [Nt] j= G H(j) converges to those of {σ 0 B H (t), 0 t }. Theorem 3.2. Let X t be the autoregressive process of order one, i.e. X t = φ X t + a t, where a t N(0, ) for each t. Then i.e. Proof. [T t] Y M (j) = φ φ B(t). ( φ B)X t = a t, X t = φ j a t j. Therefore, for large M. Since Cov Xt (k) = φ k, k, φ <. ρ(k) = φ k, Then, from theorem 3., we get ρ(k) = φ k = φ φ <. [T t] Y M (j) = φ φ B /2 (t) = φ φ B(t). Example 3. (FARIMA(p,d,q)). Let Y i (j) = b i ( d)a j i. Then ρ(k) ck 2d as k where H = d + /2, /2 < d < /2 and c = Γ( 2d) sin(πd). π
6 40 J.C. Kim and H.C. Lee By Theorem 3., T H M /2 [T t] M (Y i c (j)) = H(2H ) B H(t). i= Example 3.2 (Binary sequence). Let Y i (j) denote the increment process for the ith stationary binary sequence W i (t) that it generates, where W i (t) = means that there is a packet at time t and W i (t) = 0 means that there is no packet. We get ρ(k) ck 2H 2, as k and E[Y i (j)] = µ µ +µ 2 if E[Onperiod] = µ and E[Offperiod] = µ 2. By Theorem 3., T H M /2 [T t] M (Y i (j)) i= c = H(2H ) B H(t). M i= µ t µ + µ 2 4. Loss Probability of Stochastic Process Let A be the amount of work that arrives to be processed in [0, ] and S be the amount of work that can be processed in the same time interval. Then the workload process is and queue-length is defined Theorem 4.. [2] where and Q = A S. Q = sup Q. logp (Q > b) = δ, b δ = sup{θ : λ(θ) 0} λ(θ) = log EeθQ.
7 Convergence to FBM and loss probability 4 Note that for long range dependent data, where γ = 2( H). Theorem 4.2 ([7], Prop. 9). sup N logp (Q > b) δb γ, N log P (Q > Nb) {θ (b + c ) θ eb(θ, )}. From now on, we study the property and loss probability of selfsimilar process. Self-similar processes are of interest in probability theory because they are connected with it theorems. Namely, every it process with scaling is self-similar as the following lemma states. Theorem 4.3 ([9]). Suppose X(t) is continuous in probability of t = 0 and the distribution of X(t) is nondegenerate for each t > 0. If there exist a stochastic process Y (t) and real {K(T ); T 0} with K(T ) > 0, T K(T ) = such that as T, Y (T t) X(t), K(T ) where means the convergence of finite-dimensional distributions, then for some H > 0, X(t) is self-similar process. Furthermore, K(T ) is of the form K(T ) = T H L(T ), where L(T ) is a slowly varying function. Let A = µ + X H (), where X H () is a self-similar process. Theorem 4.4. For any a > 0, where c a,h,µ = µ(a a H ). Proof. A a = c a,h,µ () + a H A, A a = µa + X H (a) = µ(a a H ) + a H (µ + X H ()) = µ(a a H ) + a H A.
8 42 J.C. Kim and H.C. Lee Let c be a service rate and Q be a waiting length at. Then and queueing length is defined. Theorem 4.5. For any b > 0, Proof. P (sup P (Q > b) > sup P Q = A c Q = sup Q ( X H () > b (µ c) H ). ((A() c) > b) = P (sup(x H () + µ c > b) > sup = sup = sup P P (X H () + (µ c) > b) P (X H () > b (µ c)) ( X H () > b (µ c) H ). If X H () S α (σ, β, µ) with 0 < α < 2, then left hand side of Theorem 4.5 equals ( ) α + β b (µ c) C α σ α, 2 H where ( C α = x α sin xdx). 0 References [] D.D. Botvich and N.G. Duffield, Large deviations, the shape of the loss curve and economies of scale in large multipleers, Queueing Systems, 20(995), [2] C.S. Chang and T. Zajic, Effective Bandwidths of departure processes from Queues Time Varying Capacities, IEEE INFOCOM 95(995), Boston. [3] N.G. Duffield and N. O Connell, Large daviations and overflow probabilities for the general single-server queue with applications, Math. Proc. Com. Phil. Soc., 8(995), [4] F. Kelly, Notes on effective bandwidths, Stochastic networks, Theory and applications, 996, 4-68.
9 Convergence to FBM and loss probability 43 [5] N. Laskin, I. Lambadaris, F. Harmantzis and M. Devetsikiotis, Fractional Levy Motions and its application to Network Traffic Modeling, Submitted. [6] I. Norros, On the use of Fractional Brownian in the Theory of Connectionless Networks, IEEE Journal on selected areas In Communications, Vol. 3(995), [7] P. Rabinovitch, Statistical estimation of effective bandwidth, Information and System Sciences, [8] B. Sikdar and K.S. Vastola, On the Convergence of MMPP and Fractional ARIMA processes with long-range dependence to Fractional Brownian motion, Proc. of the 34th CISS, Prinston, NJ, [9] G. Samorodnitsky and M. S. Taqqu, Stable non-gaussian processes: Stochastic models with Infinite Variance, Chapman and Hall, New York, London, 994. [0] D. Wischik, Sample path large deviations for queues with many inputs, Ann. of Applied Probability, 2000 Jin-Chun Kim Dept. of Computer Aided Mathematical Information Science Semyung University Jecheon 390-7, Korea Hee-Choon Lee Dept. of Applied Statistics Sangji University Wonju , Korea
ON THE CONVERGENCE OF FARIMA SEQUENCE TO FRACTIONAL GAUSSIAN NOISE. Joo-Mok Kim* 1. Introduction
 JOURNAL OF THE CHUNGCHEONG MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 26, No. 2, May 2013 ON THE CONVERGENCE OF FARIMA SEQUENCE TO FRACTIONAL GAUSSIAN NOISE Joo-Mok Kim* Abstract. We consider fractional Gussian noise
JOURNAL OF THE CHUNGCHEONG MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 26, No. 2, May 2013 ON THE CONVERGENCE OF FARIMA SEQUENCE TO FRACTIONAL GAUSSIAN NOISE Joo-Mok Kim* Abstract. We consider fractional Gussian noise
Asymptotic Delay Distribution and Burst Size Impact on a Network Node Driven by Self-similar Traffic
 Èíôîðìàöèîííûå ïðîöåññû, Òîì 5, 1, 2005, ñòð. 4046. c 2004 D'Apice, Manzo. INFORMATION THEORY AND INFORMATION PROCESSING Asymptotic Delay Distribution and Burst Size Impact on a Network Node Driven by
Èíôîðìàöèîííûå ïðîöåññû, Òîì 5, 1, 2005, ñòð. 4046. c 2004 D'Apice, Manzo. INFORMATION THEORY AND INFORMATION PROCESSING Asymptotic Delay Distribution and Burst Size Impact on a Network Node Driven by
Stochastic Network Calculus
 Stochastic Network Calculus Assessing the Performance of the Future Internet Markus Fidler joint work with Amr Rizk Institute of Communications Technology Leibniz Universität Hannover April 22, 2010 c
Stochastic Network Calculus Assessing the Performance of the Future Internet Markus Fidler joint work with Amr Rizk Institute of Communications Technology Leibniz Universität Hannover April 22, 2010 c
Network Traffic Characteristic
 Network Traffic Characteristic Hojun Lee hlee02@purros.poly.edu 5/24/2002 EL938-Project 1 Outline Motivation What is self-similarity? Behavior of Ethernet traffic Behavior of WAN traffic Behavior of WWW
Network Traffic Characteristic Hojun Lee hlee02@purros.poly.edu 5/24/2002 EL938-Project 1 Outline Motivation What is self-similarity? Behavior of Ethernet traffic Behavior of WAN traffic Behavior of WWW
A NOVEL APPROACH TO THE ESTIMATION OF THE HURST PARAMETER IN SELF-SIMILAR TRAFFIC
 Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Tampa, Florida, November 2002 A NOVEL APPROACH TO THE ESTIMATION OF THE HURST PARAMETER IN SELF-SIMILAR TRAFFIC Houssain Kettani and John A. Gubner
Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Tampa, Florida, November 2002 A NOVEL APPROACH TO THE ESTIMATION OF THE HURST PARAMETER IN SELF-SIMILAR TRAFFIC Houssain Kettani and John A. Gubner
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION WITH H < 1/2 AS A LIMIT OF SCHEDULED TRAFFIC
 Applied Probability Trust ( April 20) FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION WITH H < /2 AS A LIMIT OF SCHEDULED TRAFFIC VICTOR F. ARAMAN, American University of Beirut PETER W. GLYNN, Stanford University Keywords:
Applied Probability Trust ( April 20) FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION WITH H < /2 AS A LIMIT OF SCHEDULED TRAFFIC VICTOR F. ARAMAN, American University of Beirut PETER W. GLYNN, Stanford University Keywords:
Effect of the Traffic Bursts in the Network Queue
 RICE UNIVERSITY Effect of the Traffic Bursts in the Network Queue by Alireza KeshavarzHaddad A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science Approved, Thesis
RICE UNIVERSITY Effect of the Traffic Bursts in the Network Queue by Alireza KeshavarzHaddad A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science Approved, Thesis
Convexity Properties of Loss and Overflow Functions
 Convexity Properties of Loss and Overflow Functions Krishnan Kumaran?, Michel Mandjes y, and Alexander Stolyar? email: kumaran@lucent.com, michel@cwi.nl, stolyar@lucent.com? Bell Labs/Lucent Technologies,
Convexity Properties of Loss and Overflow Functions Krishnan Kumaran?, Michel Mandjes y, and Alexander Stolyar? email: kumaran@lucent.com, michel@cwi.nl, stolyar@lucent.com? Bell Labs/Lucent Technologies,
Performance Evaluation and Service Rate Provisioning for a Queue with Fractional Brownian Input
 Performance Evaluation and Service Rate Provisioning for a Queue with Fractional Brownian Input Jiongze Chen 1, Ronald G. Addie 2, Moshe Zukerman 1 Abstract The Fractional Brownian motion (fbm) traffic
Performance Evaluation and Service Rate Provisioning for a Queue with Fractional Brownian Input Jiongze Chen 1, Ronald G. Addie 2, Moshe Zukerman 1 Abstract The Fractional Brownian motion (fbm) traffic
On the relevance of long-tailed durations for the statistical multiplexing of large aggregations.
 On the relevance of long-tailed durations for the statistical multiplexing of large aggregations. N. G. Duffield AT&T Laboratories Room 2C-323, 600 Mountain Avenue, Murray Hill, NJ 07974, USA duffield@research.att.com
On the relevance of long-tailed durations for the statistical multiplexing of large aggregations. N. G. Duffield AT&T Laboratories Room 2C-323, 600 Mountain Avenue, Murray Hill, NJ 07974, USA duffield@research.att.com
The Burstiness Behavior of Regulated Flows in Networks
 The Burstiness Behavior of Regulated Flows in Networks Yu Ying 1, Ravi Mazumdar 2, Catherine Rosenberg 2 and Fabrice Guillemin 3 1 Dept. of ECE, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 47906, U.S.A. yingy@ecn.purdue.edu
The Burstiness Behavior of Regulated Flows in Networks Yu Ying 1, Ravi Mazumdar 2, Catherine Rosenberg 2 and Fabrice Guillemin 3 1 Dept. of ECE, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 47906, U.S.A. yingy@ecn.purdue.edu
Estimation of the long Memory parameter using an Infinite Source Poisson model applied to transmission rate measurements
 of the long Memory parameter using an Infinite Source Poisson model applied to transmission rate measurements François Roueff Ecole Nat. Sup. des Télécommunications 46 rue Barrault, 75634 Paris cedex 13,
of the long Memory parameter using an Infinite Source Poisson model applied to transmission rate measurements François Roueff Ecole Nat. Sup. des Télécommunications 46 rue Barrault, 75634 Paris cedex 13,
Sample path large deviations of a Gaussian process with stationary increments and regularily varying variance
 Sample path large deviations of a Gaussian process with stationary increments and regularily varying variance Tommi Sottinen Department of Mathematics P. O. Box 4 FIN-0004 University of Helsinki Finland
Sample path large deviations of a Gaussian process with stationary increments and regularily varying variance Tommi Sottinen Department of Mathematics P. O. Box 4 FIN-0004 University of Helsinki Finland
On the Impact of Traffic Characteristics on Radio Resource Fluctuation in Multi-Service Cellular CDMA Networks
 On the Impact of Traffic Characteristics on Radio Resource Fluctuation in Multi-Service Cellular CDMA Networks Keivan Navaie Sys. and Comp. Department Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada keivan@sce.carleton.ca
On the Impact of Traffic Characteristics on Radio Resource Fluctuation in Multi-Service Cellular CDMA Networks Keivan Navaie Sys. and Comp. Department Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada keivan@sce.carleton.ca
A Measurement-Analytic Approach for QoS Estimation in a Network Based on the Dominant Time Scale
 222 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL. 11, NO. 2, APRIL 2003 A Measurement-Analytic Approach for QoS Estimation in a Network Based on the Dominant Time Scale Do Young Eun and Ness B. Shroff, Senior
222 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL. 11, NO. 2, APRIL 2003 A Measurement-Analytic Approach for QoS Estimation in a Network Based on the Dominant Time Scale Do Young Eun and Ness B. Shroff, Senior
Long range dependent Markov chains with applications
 Long range dependent Markov chains with applications Barlas Oğuz, Venkat Anantharam Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Email: {barlas, ananth}@eecs.berkeley.edu
Long range dependent Markov chains with applications Barlas Oğuz, Venkat Anantharam Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Email: {barlas, ananth}@eecs.berkeley.edu
Resource Allocation for Video Streaming in Wireless Environment
 Resource Allocation for Video Streaming in Wireless Environment Shahrokh Valaee and Jean-Charles Gregoire Abstract This paper focuses on the development of a new resource allocation scheme for video streaming
Resource Allocation for Video Streaming in Wireless Environment Shahrokh Valaee and Jean-Charles Gregoire Abstract This paper focuses on the development of a new resource allocation scheme for video streaming
NEW FRONTIERS IN APPLIED PROBABILITY
 J. Appl. Prob. Spec. Vol. 48A, 209 213 (2011) Applied Probability Trust 2011 NEW FRONTIERS IN APPLIED PROBABILITY A Festschrift for SØREN ASMUSSEN Edited by P. GLYNN, T. MIKOSCH and T. ROLSKI Part 4. Simulation
J. Appl. Prob. Spec. Vol. 48A, 209 213 (2011) Applied Probability Trust 2011 NEW FRONTIERS IN APPLIED PROBABILITY A Festschrift for SØREN ASMUSSEN Edited by P. GLYNN, T. MIKOSCH and T. ROLSKI Part 4. Simulation
Loss Probability Calculations and Asymptotic Analysis for Finite Buffer Multiplexers
 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL. 9, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2001 755 Loss Probability Calculations Asymptotic Analysis for Finite Buffer Multiplexers Han S. Kim Ness B. Shroff, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL. 9, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2001 755 Loss Probability Calculations Asymptotic Analysis for Finite Buffer Multiplexers Han S. Kim Ness B. Shroff, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
HEAVY-TRAFFIC EXTREME-VALUE LIMITS FOR QUEUES
 HEAVY-TRAFFIC EXTREME-VALUE LIMITS FOR QUEUES by Peter W. Glynn Department of Operations Research Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4022 and Ward Whitt AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974-0636
HEAVY-TRAFFIC EXTREME-VALUE LIMITS FOR QUEUES by Peter W. Glynn Department of Operations Research Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4022 and Ward Whitt AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974-0636
Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales. Rolf Riedi
 Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales Rolf Riedi Dept of Statistics Stochastic Systems and Modelling in Networking and Finance Part II Dependable Adaptive Systems and Mathematical Modeling Kaiserslautern,
Capturing Network Traffic Dynamics Small Scales Rolf Riedi Dept of Statistics Stochastic Systems and Modelling in Networking and Finance Part II Dependable Adaptive Systems and Mathematical Modeling Kaiserslautern,
Tighter Effective Bandwidth Estimation for Multifractal Network Traffic
 Tighter Effective Bandwidth Estimation for Multifractal Network Traffic Jeferson Wilian de Godoy Stênico and Lee Luan Ling School of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of Campinas - Unicamp
Tighter Effective Bandwidth Estimation for Multifractal Network Traffic Jeferson Wilian de Godoy Stênico and Lee Luan Ling School of Electrical and Computer Engineering State University of Campinas - Unicamp
Documents de Travail du Centre d Economie de la Sorbonne
 Documents de Travail du Centre d Economie de la Sorbonne A note on self-similarity for discrete time series Dominique GUEGAN, Zhiping LU 2007.55 Maison des Sciences Économiques, 106-112 boulevard de L'Hôpital,
Documents de Travail du Centre d Economie de la Sorbonne A note on self-similarity for discrete time series Dominique GUEGAN, Zhiping LU 2007.55 Maison des Sciences Économiques, 106-112 boulevard de L'Hôpital,
Delay Bounds in Communication Networks with Heavy-Tailed and Self-Similar Traffic
 Delay Bounds in Communication Networks with Heavy-Tailed and Self-Similar Traffic Jörg Liebeherr, Almut Burchard, Florin Ciucu 1 Abstract Traffic with self-similar and heavy-tailed characteristics has
Delay Bounds in Communication Networks with Heavy-Tailed and Self-Similar Traffic Jörg Liebeherr, Almut Burchard, Florin Ciucu 1 Abstract Traffic with self-similar and heavy-tailed characteristics has
A GENERALIZED MARKOVIAN QUEUE TO MODEL AN OPTICAL PACKET SWITCHING MULTIPLEXER
 A GENERALIZED MARKOVIAN QUEUE TO MODEL AN OPTICAL PACKET SWITCHING MULTIPLEXER RAM CHAKKA Department of Computer Science Norfolk State University, USA TIEN VAN DO, ZSOLT PÁNDI Department of Telecommunications
A GENERALIZED MARKOVIAN QUEUE TO MODEL AN OPTICAL PACKET SWITCHING MULTIPLEXER RAM CHAKKA Department of Computer Science Norfolk State University, USA TIEN VAN DO, ZSOLT PÁNDI Department of Telecommunications
Evaluation of Effective Bandwidth Schemes for Self-Similar Traffic
 Proceedings of the 3th ITC Specialist Seminar on IP Measurement, Modeling and Management, Monterey, CA, September 2000, pp. 2--2-0 Evaluation of Effective Bandwidth Schemes for Self-Similar Traffic Stefan
Proceedings of the 3th ITC Specialist Seminar on IP Measurement, Modeling and Management, Monterey, CA, September 2000, pp. 2--2-0 Evaluation of Effective Bandwidth Schemes for Self-Similar Traffic Stefan
Tales of Time Scales. Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ
 Tales of Time Scales Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ New Book Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues Springer 2001 I won t
Tales of Time Scales Ward Whitt AT&T Labs Research Florham Park, NJ New Book Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues Springer 2001 I won t
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
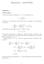 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
End-to-End Quality of Service-based Admission Control Using the Fictitious Network Analysis
 End-to-End Quality of Service-based Admission Control Using the Fictitious Network Analysis Pablo Belzarena, Paola Bermolen, Pedro Casas, Maria Simon a Julio Herrera y Reissig 565, CP 300, Montevideo,
End-to-End Quality of Service-based Admission Control Using the Fictitious Network Analysis Pablo Belzarena, Paola Bermolen, Pedro Casas, Maria Simon a Julio Herrera y Reissig 565, CP 300, Montevideo,
Integral representations in models with long memory
 Integral representations in models with long memory Georgiy Shevchenko, Yuliya Mishura, Esko Valkeila, Lauri Viitasaari, Taras Shalaiko Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv 29 September 215, Ulm
Integral representations in models with long memory Georgiy Shevchenko, Yuliya Mishura, Esko Valkeila, Lauri Viitasaari, Taras Shalaiko Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv 29 September 215, Ulm
Sensitivity of ABR Congestion Control Algorithms to Hurst Parameter Estimates
 Sensitivity of ABR Congestion Control Algorithms to Hurst Parameter Estimates Sven A. M. Östring 1, Harsha Sirisena 1, and Irene Hudson 2 1 Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering 2 Department
Sensitivity of ABR Congestion Control Algorithms to Hurst Parameter Estimates Sven A. M. Östring 1, Harsha Sirisena 1, and Irene Hudson 2 1 Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering 2 Department
Tail probabilities of low-priority waiting times and queue lengths in MAP/GI/1 queues
 Queueing Systems 34 (2) 215 236 215 Tail probabilities of low-priority waiting times and queue lengths in MAP/GI/1 queues Vijay Subramanian a, and R. Srikant b a Mathematics of Communication Networks,
Queueing Systems 34 (2) 215 236 215 Tail probabilities of low-priority waiting times and queue lengths in MAP/GI/1 queues Vijay Subramanian a, and R. Srikant b a Mathematics of Communication Networks,
ON THE MAXIMUM WORKLOAD OF A QUEUE FED BY FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION. By Assaf J. Zeevi 1 and Peter W. Glynn 2 Stanford University
 The Annals of Applied Probability 2000, Vol. 10, No. 4, 1084 1099 ON THE MAXIMUM WORKLOAD OF A QUEUE FED BY FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION By Assaf J. Zeevi 1 and Peter W. Glynn 2 Stanford University Consider
The Annals of Applied Probability 2000, Vol. 10, No. 4, 1084 1099 ON THE MAXIMUM WORKLOAD OF A QUEUE FED BY FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION By Assaf J. Zeevi 1 and Peter W. Glynn 2 Stanford University Consider
Exploring regularities and self-similarity in Internet traffic
 Exploring regularities and self-similarity in Internet traffic FRANCESCO PALMIERI and UGO FIORE Centro Servizi Didattico Scientifico Università degli studi di Napoli Federico II Complesso Universitario
Exploring regularities and self-similarity in Internet traffic FRANCESCO PALMIERI and UGO FIORE Centro Servizi Didattico Scientifico Università degli studi di Napoli Federico II Complesso Universitario
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Minimum L 1 -norm Estimation for Fractional Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Type Process
 isid/ms/23/25 September 11, 23 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/eprints Minimum L 1 -norm Estimation for Fractional Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Type Process B. L. S. Prakasa Rao Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi
isid/ms/23/25 September 11, 23 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/eprints Minimum L 1 -norm Estimation for Fractional Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Type Process B. L. S. Prakasa Rao Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi
Inequality Comparisons and Traffic Smoothing in Multi-Stage ATM Multiplexers
 IEEE Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications, 2000 Inequality Comparisons and raffic Smoothing in Multi-Stage AM Multiplexers Michael J. Neely MI -- LIDS mjneely@mit.edu Abstract
IEEE Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications, 2000 Inequality Comparisons and raffic Smoothing in Multi-Stage AM Multiplexers Michael J. Neely MI -- LIDS mjneely@mit.edu Abstract
Beyond the color of the noise: what is memory in random phenomena?
 Beyond the color of the noise: what is memory in random phenomena? Gennady Samorodnitsky Cornell University September 19, 2014 Randomness means lack of pattern or predictability in events according to
Beyond the color of the noise: what is memory in random phenomena? Gennady Samorodnitsky Cornell University September 19, 2014 Randomness means lack of pattern or predictability in events according to
TOWARDS BETTER MULTI-CLASS PARAMETRIC-DECOMPOSITION APPROXIMATIONS FOR OPEN QUEUEING NETWORKS
 TOWARDS BETTER MULTI-CLASS PARAMETRIC-DECOMPOSITION APPROXIMATIONS FOR OPEN QUEUEING NETWORKS by Ward Whitt AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974-0636 March 31, 199 Revision: November 9, 199 ABSTRACT
TOWARDS BETTER MULTI-CLASS PARAMETRIC-DECOMPOSITION APPROXIMATIONS FOR OPEN QUEUEING NETWORKS by Ward Whitt AT&T Bell Laboratories Murray Hill, NJ 07974-0636 March 31, 199 Revision: November 9, 199 ABSTRACT
Chapter 2: Random Variables
 ECE54: Stochastic Signals and Systems Fall 28 Lecture 2 - September 3, 28 Dr. Salim El Rouayheb Scribe: Peiwen Tian, Lu Liu, Ghadir Ayache Chapter 2: Random Variables Example. Tossing a fair coin twice:
ECE54: Stochastic Signals and Systems Fall 28 Lecture 2 - September 3, 28 Dr. Salim El Rouayheb Scribe: Peiwen Tian, Lu Liu, Ghadir Ayache Chapter 2: Random Variables Example. Tossing a fair coin twice:
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains
 Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
ON THE NON-EXISTENCE OF PRODUCT-FORM SOLUTIONS FOR QUEUEING NETWORKS WITH RETRIALS
 ON THE NON-EXISTENCE OF PRODUCT-FORM SOLUTIONS FOR QUEUEING NETWORKS WITH RETRIALS J.R. ARTALEJO, Department of Statistics and Operations Research, Faculty of Mathematics, Complutense University of Madrid,
ON THE NON-EXISTENCE OF PRODUCT-FORM SOLUTIONS FOR QUEUEING NETWORKS WITH RETRIALS J.R. ARTALEJO, Department of Statistics and Operations Research, Faculty of Mathematics, Complutense University of Madrid,
Measured Effective Bandwidths
 Measured Effective Bandwidths S. Giordano, G. Procissi and S. Tartarelli Department of Information Engineering University of Pisa, Italy fgiordano,procissi,tartarellig@iet.unipi.it Abstract This paper
Measured Effective Bandwidths S. Giordano, G. Procissi and S. Tartarelli Department of Information Engineering University of Pisa, Italy fgiordano,procissi,tartarellig@iet.unipi.it Abstract This paper
Convergence of the long memory Markov switching model to Brownian motion
 Convergence of the long memory Marov switching model to Brownian motion Changryong Bae Sungyunwan University Natércia Fortuna CEF.UP, Universidade do Porto Vladas Pipiras University of North Carolina February
Convergence of the long memory Marov switching model to Brownian motion Changryong Bae Sungyunwan University Natércia Fortuna CEF.UP, Universidade do Porto Vladas Pipiras University of North Carolina February
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H 2 b /s queue
 An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation
 A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation Guoqiang Hu, Yuming Jiang, Anne Nevin Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Systems Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation Guoqiang Hu, Yuming Jiang, Anne Nevin Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Systems Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks
 A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks by Doo Il Choi, Charles Knessl and Charles Tier University of Illinois at Chicago 85 South
A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks by Doo Il Choi, Charles Knessl and Charles Tier University of Illinois at Chicago 85 South
Scaling Properties in the Stochastic Network Calculus
 Scaling Properties in the Stochastic Network Calculus A Dissertation Presented to the faculty of the School of Engineering and Applied Science University of Virginia In Partial Fulfillment of the requirements
Scaling Properties in the Stochastic Network Calculus A Dissertation Presented to the faculty of the School of Engineering and Applied Science University of Virginia In Partial Fulfillment of the requirements
ECE353: Probability and Random Processes. Lecture 18 - Stochastic Processes
 ECE353: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 18 - Stochastic Processes Xiao Fu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University E-mail: xiao.fu@oregonstate.edu From RV
ECE353: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 18 - Stochastic Processes Xiao Fu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University E-mail: xiao.fu@oregonstate.edu From RV
A New Technique for Link Utilization Estimation
 A New Technique for Link Utilization Estimation in Packet Data Networks using SNMP Variables S. Amarnath and Anurag Kumar* Dept. of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A New Technique for Link Utilization Estimation in Packet Data Networks using SNMP Variables S. Amarnath and Anurag Kumar* Dept. of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Robust Queueing Network Analyzer Based on Indices of Dispersion
 A Robust Queueing Network Analyzer Based on Indices of Dispersion Wei You (joint work with Ward Whitt) Columbia University INFORMS 2018, Phoenix November 6, 2018 1/20 Motivation Many complex service systems
A Robust Queueing Network Analyzer Based on Indices of Dispersion Wei You (joint work with Ward Whitt) Columbia University INFORMS 2018, Phoenix November 6, 2018 1/20 Motivation Many complex service systems
Delay Bounds for Networks with Heavy-Tailed and Self-Similar Traffic
 Delay Bounds for Networks with Heavy-Tailed and Self-Similar Traffic Jörg Liebeherr, Almut Burchard, Florin Ciucu Abstract 1 arxiv:0911.3856v1 [cs.ni] 19 Nov 2009 We provide upper bounds on the end-to-end
Delay Bounds for Networks with Heavy-Tailed and Self-Similar Traffic Jörg Liebeherr, Almut Burchard, Florin Ciucu Abstract 1 arxiv:0911.3856v1 [cs.ni] 19 Nov 2009 We provide upper bounds on the end-to-end
Jae Gil Choi and Young Seo Park
 Kangweon-Kyungki Math. Jour. 11 (23), No. 1, pp. 17 3 TRANSLATION THEOREM ON FUNCTION SPACE Jae Gil Choi and Young Seo Park Abstract. In this paper, we use a generalized Brownian motion process to define
Kangweon-Kyungki Math. Jour. 11 (23), No. 1, pp. 17 3 TRANSLATION THEOREM ON FUNCTION SPACE Jae Gil Choi and Young Seo Park Abstract. In this paper, we use a generalized Brownian motion process to define
LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS. Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ Murray Hill, NJ 07974
 LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS by Daniel P. Heyman Ward Whitt Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ 07701 Murray Hill, NJ 07974 May 11, 1988 ABSTRACT We study the
LIMITS FOR QUEUES AS THE WAITING ROOM GROWS by Daniel P. Heyman Ward Whitt Bell Communications Research AT&T Bell Laboratories Red Bank, NJ 07701 Murray Hill, NJ 07974 May 11, 1988 ABSTRACT We study the
A Network Calculus with Effective Bandwidth
 A Network Calculus with Effective Bandwidth Technical Report: University of Virginia, CS-2003-20, November 2003 Chengzhi Li Almut Burchard Jörg Liebeherr Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics
A Network Calculus with Effective Bandwidth Technical Report: University of Virginia, CS-2003-20, November 2003 Chengzhi Li Almut Burchard Jörg Liebeherr Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics
queue KTH, Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology
 Analysis of the Packet oss Process in an MMPP+M/M/1/K queue György Dán, Viktória Fodor KTH, Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology {gyuri,viktoria}@imit.kth.se
Analysis of the Packet oss Process in an MMPP+M/M/1/K queue György Dán, Viktória Fodor KTH, Royal Institute of Technology, Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology {gyuri,viktoria}@imit.kth.se
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial
 Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
PACKING-DIMENSION PROFILES AND FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION
 PACKING-DIMENSION PROFILES AND FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION DAVAR KHOSHNEVISAN AND YIMIN XIAO Abstract. In order to compute the packing dimension of orthogonal projections Falconer and Howroyd 997) introduced
PACKING-DIMENSION PROFILES AND FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTION DAVAR KHOSHNEVISAN AND YIMIN XIAO Abstract. In order to compute the packing dimension of orthogonal projections Falconer and Howroyd 997) introduced
Stability and Rare Events in Stochastic Models Sergey Foss Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh and Institute of Mathematics, Novosibirsk
 Stability and Rare Events in Stochastic Models Sergey Foss Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh and Institute of Mathematics, Novosibirsk ANSAPW University of Queensland 8-11 July, 2013 1 Outline (I) Fluid
Stability and Rare Events in Stochastic Models Sergey Foss Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh and Institute of Mathematics, Novosibirsk ANSAPW University of Queensland 8-11 July, 2013 1 Outline (I) Fluid
In Memory of Wenbo V Li s Contributions
 In Memory of Wenbo V Li s Contributions Qi-Man Shao The Chinese University of Hong Kong qmshao@cuhk.edu.hk The research is partially supported by Hong Kong RGC GRF 403513 Outline Lower tail probabilities
In Memory of Wenbo V Li s Contributions Qi-Man Shao The Chinese University of Hong Kong qmshao@cuhk.edu.hk The research is partially supported by Hong Kong RGC GRF 403513 Outline Lower tail probabilities
Some Background Information on Long-Range Dependence and Self-Similarity On the Variability of Internet Traffic Outline Introduction and Motivation Ch
 On the Variability of Internet Traffic Georgios Y Lazarou Information and Telecommunication Technology Center Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science The University of Kansas, Lawrence
On the Variability of Internet Traffic Georgios Y Lazarou Information and Telecommunication Technology Center Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science The University of Kansas, Lawrence
Brownian motion. Samy Tindel. Purdue University. Probability Theory 2 - MA 539
 Brownian motion Samy Tindel Purdue University Probability Theory 2 - MA 539 Mostly taken from Brownian Motion and Stochastic Calculus by I. Karatzas and S. Shreve Samy T. Brownian motion Probability Theory
Brownian motion Samy Tindel Purdue University Probability Theory 2 - MA 539 Mostly taken from Brownian Motion and Stochastic Calculus by I. Karatzas and S. Shreve Samy T. Brownian motion Probability Theory
Extremes and ruin of Gaussian processes
 International Conference on Mathematical and Statistical Modeling in Honor of Enrique Castillo. June 28-30, 2006 Extremes and ruin of Gaussian processes Jürg Hüsler Department of Math. Statistics, University
International Conference on Mathematical and Statistical Modeling in Honor of Enrique Castillo. June 28-30, 2006 Extremes and ruin of Gaussian processes Jürg Hüsler Department of Math. Statistics, University
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models
 Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
From Fractional Brownian Motion to Multifractional Brownian Motion
 From Fractional Brownian Motion to Multifractional Brownian Motion Antoine Ayache USTL (Lille) Antoine.Ayache@math.univ-lille1.fr Cassino December 2010 A.Ayache (USTL) From FBM to MBM Cassino December
From Fractional Brownian Motion to Multifractional Brownian Motion Antoine Ayache USTL (Lille) Antoine.Ayache@math.univ-lille1.fr Cassino December 2010 A.Ayache (USTL) From FBM to MBM Cassino December
CS418 Operating Systems
 CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
One important issue in the study of queueing systems is to characterize departure processes. Study on departure processes was rst initiated by Burke (
 The Departure Process of the GI/G/ Queue and Its MacLaurin Series Jian-Qiang Hu Department of Manufacturing Engineering Boston University 5 St. Mary's Street Brookline, MA 2446 Email: hqiang@bu.edu June
The Departure Process of the GI/G/ Queue and Its MacLaurin Series Jian-Qiang Hu Department of Manufacturing Engineering Boston University 5 St. Mary's Street Brookline, MA 2446 Email: hqiang@bu.edu June
Poisson Cluster process as a model for teletraffic arrivals and its extremes
 Poisson Cluster process as a model for teletraffic arrivals and its extremes Barbara González-Arévalo, University of Louisiana Thomas Mikosch, University of Copenhagen Gennady Samorodnitsky, Cornell University
Poisson Cluster process as a model for teletraffic arrivals and its extremes Barbara González-Arévalo, University of Louisiana Thomas Mikosch, University of Copenhagen Gennady Samorodnitsky, Cornell University
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.070J Fall 2013 Lecture 22 12/09/2013. Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.7J Fall 213 Lecture 22 12/9/213 Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion Content. 1. G/G/1 queueing system 2. One dimensional reflection mapping
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.265/15.7J Fall 213 Lecture 22 12/9/213 Skorokhod Mapping Theorem. Reflected Brownian Motion Content. 1. G/G/1 queueing system 2. One dimensional reflection mapping
Other properties of M M 1
 Other properties of M M 1 Přemysl Bejda premyslbejda@gmail.com 2012 Contents 1 Reflected Lévy Process 2 Time dependent properties of M M 1 3 Waiting times and queue disciplines in M M 1 Contents 1 Reflected
Other properties of M M 1 Přemysl Bejda premyslbejda@gmail.com 2012 Contents 1 Reflected Lévy Process 2 Time dependent properties of M M 1 3 Waiting times and queue disciplines in M M 1 Contents 1 Reflected
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
A Generator of Pseudo-Random Self-Similar Sequences Based on SRA
 A Generator of Pseudo-Random Self-Similar Sequences Based on SRA H.-D. J. Jeong,D.McNickle and K. Pawlikowski Department of Computer Science and Management University of Canterbury Christchurch, New Zealand
A Generator of Pseudo-Random Self-Similar Sequences Based on SRA H.-D. J. Jeong,D.McNickle and K. Pawlikowski Department of Computer Science and Management University of Canterbury Christchurch, New Zealand
M/M/1 Queueing System with Delayed Controlled Vacation
 M/M/1 Queueing System with Delayed Controlled Vacation Yonglu Deng, Zhongshan University W. John Braun, University of Winnipeg Yiqiang Q. Zhao, University of Winnipeg Abstract An M/M/1 queue with delayed
M/M/1 Queueing System with Delayed Controlled Vacation Yonglu Deng, Zhongshan University W. John Braun, University of Winnipeg Yiqiang Q. Zhao, University of Winnipeg Abstract An M/M/1 queue with delayed
Survey of Source Modeling Techniques for ATM Networks
 Survey of Source Modeling Techniques for ATM Networks Sponsor: Sprint Yong-Qing Lu David W. Petr Victor S. Frost Technical Report TISL-10230-1 Telecommunications and Information Sciences Laboratory Department
Survey of Source Modeling Techniques for ATM Networks Sponsor: Sprint Yong-Qing Lu David W. Petr Victor S. Frost Technical Report TISL-10230-1 Telecommunications and Information Sciences Laboratory Department
LARGE DEVIATION PROBABILITIES FOR SUMS OF HEAVY-TAILED DEPENDENT RANDOM VECTORS*
 LARGE EVIATION PROBABILITIES FOR SUMS OF HEAVY-TAILE EPENENT RANOM VECTORS* Adam Jakubowski Alexander V. Nagaev Alexander Zaigraev Nicholas Copernicus University Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science
LARGE EVIATION PROBABILITIES FOR SUMS OF HEAVY-TAILE EPENENT RANOM VECTORS* Adam Jakubowski Alexander V. Nagaev Alexander Zaigraev Nicholas Copernicus University Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science
Computer Science, Informatik 4 Communication and Distributed Systems. Simulation. Discrete-Event System Simulation. Dr.
 Simulation Discrete-Event System Simulation Chapter 0 Output Analysis for a Single Model Purpose Objective: Estimate system performance via simulation If θ is the system performance, the precision of the
Simulation Discrete-Event System Simulation Chapter 0 Output Analysis for a Single Model Purpose Objective: Estimate system performance via simulation If θ is the system performance, the precision of the
Packing-Dimension Profiles and Fractional Brownian Motion
 Under consideration for publication in Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1 Packing-Dimension Profiles and Fractional Brownian Motion By DAVAR KHOSHNEVISAN Department of Mathematics, 155 S. 1400 E., JWB 233,
Under consideration for publication in Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1 Packing-Dimension Profiles and Fractional Brownian Motion By DAVAR KHOSHNEVISAN Department of Mathematics, 155 S. 1400 E., JWB 233,
Estimating Loynes exponent
 Estimating Loynes exponent Ken R. Duffy Sean P. Meyn 28 th October 2009; revised 7 th January 20 Abstract Loynes distribution, which characterizes the one dimensional marginal of the stationary solution
Estimating Loynes exponent Ken R. Duffy Sean P. Meyn 28 th October 2009; revised 7 th January 20 Abstract Loynes distribution, which characterizes the one dimensional marginal of the stationary solution
Network Traffic Modeling using a Multifractal Wavelet Model
 5-th International Symposium on Digital Signal Processing for Communication Systems, DSPCS 99, Perth, 1999 Network Traffic Modeling using a Multifractal Wavelet Model Matthew S. Crouse, Rudolf H. Riedi,
5-th International Symposium on Digital Signal Processing for Communication Systems, DSPCS 99, Perth, 1999 Network Traffic Modeling using a Multifractal Wavelet Model Matthew S. Crouse, Rudolf H. Riedi,
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on on Parallel and Distributed Computing Systems (PDCS-97), pages , October 1997
 In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on on Parallel and Distributed Computing Systems (PDCS-97), pages 322-327, October 1997 Consequences of Ignoring Self-Similar Data Trac in Telecommunications
In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on on Parallel and Distributed Computing Systems (PDCS-97), pages 322-327, October 1997 Consequences of Ignoring Self-Similar Data Trac in Telecommunications
HSC Research Report. The Lamperti transformation for self-similar processes HSC/97/02. Krzysztof Burnecki* Makoto Maejima** Aleksander Weron*, ***
 HSC Research Report HSC/97/02 The Lamperti transformation for self-similar processes Krzysztof Burnecki* Makoto Maeima** Aleksander Weron*, *** * Hugo Steinhaus Center, Wrocław University of Technology,
HSC Research Report HSC/97/02 The Lamperti transformation for self-similar processes Krzysztof Burnecki* Makoto Maeima** Aleksander Weron*, *** * Hugo Steinhaus Center, Wrocław University of Technology,
Stochastic-Process Limits
 Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
Probability and Statistics Concepts
 University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems
 Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems Mung Chiang, Arak Sutivong, and Stephen Boyd Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University, CA 9435 Abstract We present a systematic treatment
Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems Mung Chiang, Arak Sutivong, and Stephen Boyd Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University, CA 9435 Abstract We present a systematic treatment
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 43, NO. 3, MARCH
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 43, NO. 3, MARCH 1998 315 Asymptotic Buffer Overflow Probabilities in Multiclass Multiplexers: An Optimal Control Approach Dimitris Bertsimas, Ioannis Ch. Paschalidis,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 43, NO. 3, MARCH 1998 315 Asymptotic Buffer Overflow Probabilities in Multiclass Multiplexers: An Optimal Control Approach Dimitris Bertsimas, Ioannis Ch. Paschalidis,
Continuous-Time Markov Chain
 Continuous-Time Markov Chain Consider the process {X(t),t 0} with state space {0, 1, 2,...}. The process {X(t),t 0} is a continuous-time Markov chain if for all s, t 0 and nonnegative integers i, j, x(u),
Continuous-Time Markov Chain Consider the process {X(t),t 0} with state space {0, 1, 2,...}. The process {X(t),t 0} is a continuous-time Markov chain if for all s, t 0 and nonnegative integers i, j, x(u),
Accurate and Fast Replication on the Generation of Fractal Network Traffic Using Alternative Probability Models
 Accurate and Fast Replication on the Generation of Fractal Network Traffic Using Alternative Probability Models Stenio Fernandes, Carlos Kamienski & Djamel Sadok Computer Science Center, Federal University
Accurate and Fast Replication on the Generation of Fractal Network Traffic Using Alternative Probability Models Stenio Fernandes, Carlos Kamienski & Djamel Sadok Computer Science Center, Federal University
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits. IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015
 Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
In Proceedings of the 13th U.K. Workshop on Performance Engineering of Computer. and Telecommunication Systems (UKPEW'97), July 1997, Ilkley, U.K.
 In Proceedings of the 13th U.K. Workshop on Performance Engineering of Computer and Telecommunication Systems (UKPEW'97), July 1997, Ilkley, U.K. Investigation of Cell Scale and Burst Scale Eects on the
In Proceedings of the 13th U.K. Workshop on Performance Engineering of Computer and Telecommunication Systems (UKPEW'97), July 1997, Ilkley, U.K. Investigation of Cell Scale and Burst Scale Eects on the
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
MODELS FOR COMPUTER NETWORK TRAFFIC
 MODELS FOR COMPUTER NETWORK TRAFFIC Murad S. Taqqu Boston University Joint work with Walter Willinger, Joshua Levy and Vladas Pipiras,... Web Site http://math.bu.edu/people/murad OUTLINE Background: 1)
MODELS FOR COMPUTER NETWORK TRAFFIC Murad S. Taqqu Boston University Joint work with Walter Willinger, Joshua Levy and Vladas Pipiras,... Web Site http://math.bu.edu/people/murad OUTLINE Background: 1)
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
A Direct Approach to Transient Queue-Size Distribution in a Finite-Buffer Queue with AQM
 Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 7, No. 3, 99-915 (213) 99 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal A Direct Approach to Transient Queue-Size Distribution in a Finite-Buffer Queue with
Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 7, No. 3, 99-915 (213) 99 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal A Direct Approach to Transient Queue-Size Distribution in a Finite-Buffer Queue with
Little s result. T = average sojourn time (time spent) in the system N = average number of customers in the system. Little s result says that
 J. Virtamo 38.143 Queueing Theory / Little s result 1 Little s result The result Little s result or Little s theorem is a very simple (but fundamental) relation between the arrival rate of customers, average
J. Virtamo 38.143 Queueing Theory / Little s result 1 Little s result The result Little s result or Little s theorem is a very simple (but fundamental) relation between the arrival rate of customers, average
An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling
 F An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling Fourth Edition Mark A. Pinsky Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois Samuel Karlin Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford,
F An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling Fourth Edition Mark A. Pinsky Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois Samuel Karlin Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford,
Chapter 11. Output Analysis for a Single Model Prof. Dr. Mesut Güneş Ch. 11 Output Analysis for a Single Model
 Chapter Output Analysis for a Single Model. Contents Types of Simulation Stochastic Nature of Output Data Measures of Performance Output Analysis for Terminating Simulations Output Analysis for Steady-state
Chapter Output Analysis for a Single Model. Contents Types of Simulation Stochastic Nature of Output Data Measures of Performance Output Analysis for Terminating Simulations Output Analysis for Steady-state
Large number of queues in tandem: Scaling properties under back-pressure algorithm
 Queueing Syst (2011) 67: 111 126 DOI 10.1007/s11134-010-9203-0 Large number of queues in tandem: Scaling properties under back-pressure algorithm Alexander L. Stolyar Received: 30 October 2009 / Revised:
Queueing Syst (2011) 67: 111 126 DOI 10.1007/s11134-010-9203-0 Large number of queues in tandem: Scaling properties under back-pressure algorithm Alexander L. Stolyar Received: 30 October 2009 / Revised:
Supermodular ordering of Poisson arrays
 Supermodular ordering of Poisson arrays Bünyamin Kızıldemir Nicolas Privault Division of Mathematical Sciences School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Nanyang Technological University 637371 Singapore
Supermodular ordering of Poisson arrays Bünyamin Kızıldemir Nicolas Privault Division of Mathematical Sciences School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Nanyang Technological University 637371 Singapore
