Discussion Global Dynamics at the Zero Lower Bound
|
|
|
- Egbert Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Discussion Global Dynamics at the Zero Lower Bound Brent Bundick Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City April 4 The opinions expressed in this discussion are those of the author and do not reflect the views of the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City or the Federal Reserve System.
2 Global Dynamics at the Zero Lower Bound Very interesting and well-executed paper Contribution: Rigorous modeling of a zero lower bound economy Effects of recent downturn lasting longer than expected Rigorous modeling is key first step to explaining recent outcomes
3 Why can technological improvements be contractionary? Aggregate demand curve has positive slope at zero lower bound Use linearized AS-AD model to build intuition π t = βe t π t+ + ψ y y t ( η) ψz t ψa t ( ) y t = E t y t+ (r t r) E t π t+ + ( ρ a ) a t ) r t = max (, r + φ π π t + φ y y t
4 Aggregate Demand Away From Zero Lower Bound ( + φ y + ψ ) ( y y t = E t y t+ φ π ) ( ) π t + Shocks β β! AD AS Declines in π t offset with lower real rates which raises Y t Y
5 Technology Shock Away From Zero Lower Bound ( + φ y + ψ ) ( y y t = E t y t+ φ π ) ( ) π t + Shocks β β! AD AS Higher technology lowers π t & raises Y t with policy accommodation Y
6 Aggregate Demand At Zero Lower Bound ( + ψ ) y y t = E t y t+ + ( ) β β π t + Shocks! AD AS Declines in π t cannot be initially offset which raises real rates Y
7 Technology Shock At Zero Lower Bound ( + ψ ) y y t = E t y t+ + ( ) β β π t + Shocks! AD AS Higher technology can cause larger disinflation & output losses Y
8 Discussion: Focus on Expectations About Future ( + ψ ) y y t = E t y t+ + ( ) β β π t + Shocks! AD AD(Y t+ ) AS Expectations about future crucial in determining effects of shocks Y
9 in high technology states. Higher labor demand raises equilibrium hours, which mitigates the decline in the real wage. In short, a tension exists at the ZLB between the supply-side effects of technology and the demand-side effects of the real interest rate. When the central bank responds less aggressively to the steady-state output gap when the ZLB does not bind (i.e., a lower φ y ), the demand-side effects at the ZLB are weaker and both real and nominal variables are less volatile. Assumptions About Zero Lower Bound Duration.75.5 Adjusted Output (ŷ adj ) Inflation Rate (ˆπ) 5 5 Labor Hours (ˆn).6.4. Real Interest Rate ( r/e[π]) 5 5 Nominal Interest Rate (ˆr) Assume preference shock is constant in impulse responses.75.5 Steady State Scenario Real Wage Rate (ŵ).8.4 ZLB Scenario Agents expect zero lower bound exit within - periods Economy surprised by zero lower bound duration every period Comment: What is the right zero lower bound scenario?
10 Unexpected Long Zero Lower Bound Episode.6 Output Inflation 3 Nominal Interest Rate Real Interest Rate Preference Shock Technology Gavin et al (4) Unexpected ZLB Length
11 Expected Long Zero Lower Bound Episode Output Inflation 3 Nominal Interest Rate Real Interest Rate..4 Preference Shock Technology Gavin et al (4) Unexpected ZLB Length Large AR() Shock Expected ZLB Length
12 Central Bank Responds to Output Gap.7 Output Inflation 4 Nominal Interest Rate Real Interest Rate.. Preference Shock Technology Output Gap
13 Central Bank Responds to Steady State Output Output Inflation 4 Nominal Interest Rate Real Interest Rate Preference Shock Technology Output Gap Steady State Output
14 Output Gap Response - Longer Zero Lower Bound Episode Output Inflation 4 Nominal Interest Rate Real Interest Rate..4 Preference Shock Technology Output Gap Steady State Output Output Gap Longer ZLB Episode
15 Expectations About Current Zero Lower Bound Duration Figure 8: The Expected Path of Nominal Interest Rates Gust, Lopez-Saĺıdo, and Smith (3) Model-implied (Red) & Futures Markets (Gray) Financial Market Federal Funds Rate Expectations % confidence bands median Expectations as of 9:Q 3 4 Expectations as of :Q Expected duration Blue Chip increased 3 month markedly Treasury with Bill late-4 Expectations language 6 6
16 Comments Use an alternative zero lower bound scenario. Use expectations from data at a given point. Use average scenario from model simulations 3. Show robustness under variety of scenarios Decomposing differences between linear & nonlinear model. Role of quadratic adjustment costs. Precautionary labor supply Away from zero lower bound Additional downside risk implied by the zero lower bound Solve linear with nonlinear costs or nonlinear with quadratic utility Very nice and well-executed paper
17 Additional Details
18 Precautionary Labor Supply W t L S (λ t ) L D (K t, Z t ) N t
19 Precautionary Labor Supply Without Capital W t L S (! t ) L D ( ) L D (µ t ) N t
Queen s University Department of Economics Instructor: Kevin Andrew
 Queen s University Department of Economics Instructor: Kevin Andrew Econ 320: Assignment 4 Section A (100%): Long Answer Due: April 2nd 2014 3pm All questions of Equal Value 1. Consider the following version
Queen s University Department of Economics Instructor: Kevin Andrew Econ 320: Assignment 4 Section A (100%): Long Answer Due: April 2nd 2014 3pm All questions of Equal Value 1. Consider the following version
Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions
 Monetary Economics Problem Set #4 Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions This problem set is marked out of 100 points. The weight given to each part is indicated below. Please contact me asap if
Monetary Economics Problem Set #4 Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions This problem set is marked out of 100 points. The weight given to each part is indicated below. Please contact me asap if
Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy
 Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy Leonardo Melosi London Business School 24 May 2012 Motivation Disperse information about aggregate fundamentals Morris and Shin (2003), Sims (2003), and Woodford (2002)
Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy Leonardo Melosi London Business School 24 May 2012 Motivation Disperse information about aggregate fundamentals Morris and Shin (2003), Sims (2003), and Woodford (2002)
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle. June 7, 2018
 Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin June 7, 218 Motivation Key observations during the Great Recession: Extraordinary contraction
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin June 7, 218 Motivation Key observations during the Great Recession: Extraordinary contraction
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4
 Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks
 Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
APPENDIX TO RESERVE REQUIREMENTS AND OPTIMAL CHINESE STABILIZATION POLICY
 APPENDIX TO RESERVE REQUIREMENTS AND OPTIMAL CHINESE STABILIZATION POLICY CHUN CHANG ZHENG LIU MARK M. SPIEGEL JINGYI ZHANG Abstract. This appendix shows some additional details of the model and equilibrium
APPENDIX TO RESERVE REQUIREMENTS AND OPTIMAL CHINESE STABILIZATION POLICY CHUN CHANG ZHENG LIU MARK M. SPIEGEL JINGYI ZHANG Abstract. This appendix shows some additional details of the model and equilibrium
Stagnation Traps. Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro
 Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
THE ZERO LOWER BOUND: FREQUENCY, DURATION,
 THE ZERO LOWER BOUND: FREQUENCY, DURATION, AND NUMERICAL CONVERGENCE Alexander W. Richter Auburn University Nathaniel A. Throckmorton DePauw University INTRODUCTION Popular monetary policy rule due to
THE ZERO LOWER BOUND: FREQUENCY, DURATION, AND NUMERICAL CONVERGENCE Alexander W. Richter Auburn University Nathaniel A. Throckmorton DePauw University INTRODUCTION Popular monetary policy rule due to
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World
 Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé and Mathias Trabandt ECB-EABCN-Atlanta Nonlinearities Conference, December 15-16, 2014 Sveriges Riksbank and Federal Reserve Board December 16, 2014
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé and Mathias Trabandt ECB-EABCN-Atlanta Nonlinearities Conference, December 15-16, 2014 Sveriges Riksbank and Federal Reserve Board December 16, 2014
A Discussion of Arouba, Cuba-Borda and Schorfheide: Macroeconomic Dynamics Near the ZLB: A Tale of Two Countries"
 A Discussion of Arouba, Cuba-Borda and Schorfheide: Macroeconomic Dynamics Near the ZLB: A Tale of Two Countries" Morten O. Ravn, University College London, Centre for Macroeconomics and CEPR M.O. Ravn
A Discussion of Arouba, Cuba-Borda and Schorfheide: Macroeconomic Dynamics Near the ZLB: A Tale of Two Countries" Morten O. Ravn, University College London, Centre for Macroeconomics and CEPR M.O. Ravn
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World
 Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin November 28, 2016 Lindé and Trabandt Multipliers () in Nonlinear Models November 28, 2016
Fiscal Multipliers in a Nonlinear World Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin November 28, 2016 Lindé and Trabandt Multipliers () in Nonlinear Models November 28, 2016
Assessing the Fed s Performance through the Effect of Technology Shocks: New Evidence
 through the Effect of Technology Shocks: New Evidence Carlo Coen Castellino September 2010 Abstract In this work I revisit the paper by Galí et al. (2003), which explains how the changes over time in the
through the Effect of Technology Shocks: New Evidence Carlo Coen Castellino September 2010 Abstract In this work I revisit the paper by Galí et al. (2003), which explains how the changes over time in the
Escaping the Great Recession 1
 Escaping the Great Recession 1 Francesco Bianchi Duke University University of Pennsylvania CEPR and NBER Leonardo Melosi FRB of Chicago ESSIM - Tarragona 1 The views in this paper are solely the responsibility
Escaping the Great Recession 1 Francesco Bianchi Duke University University of Pennsylvania CEPR and NBER Leonardo Melosi FRB of Chicago ESSIM - Tarragona 1 The views in this paper are solely the responsibility
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest
 Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest Gianni Amisano and Oreste Tristani European Central Bank IRF 28 Frankfurt, 26 June Amisano-Tristani (European Central Bank) Productivity and the
Perceived productivity and the natural rate of interest Gianni Amisano and Oreste Tristani European Central Bank IRF 28 Frankfurt, 26 June Amisano-Tristani (European Central Bank) Productivity and the
New Keynesian Model Walsh Chapter 8
 New Keynesian Model Walsh Chapter 8 1 General Assumptions Ignore variations in the capital stock There are differentiated goods with Calvo price stickiness Wages are not sticky Monetary policy is a choice
New Keynesian Model Walsh Chapter 8 1 General Assumptions Ignore variations in the capital stock There are differentiated goods with Calvo price stickiness Wages are not sticky Monetary policy is a choice
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market
 The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
The Dark Corners of the Labor Market Vincent Sterk Conference on Persistent Output Gaps: Causes and Policy Remedies EABCN / University of Cambridge / INET University College London September 2015 Sterk
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle
 Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin 49th Konstanz Seminar on Monetary Theory and Monetary Policy May 16, 2018 Lindé and Trabandt
Resolving the Missing Deflation Puzzle Jesper Lindé Sveriges Riksbank Mathias Trabandt Freie Universität Berlin 49th Konstanz Seminar on Monetary Theory and Monetary Policy May 16, 2018 Lindé and Trabandt
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective
 Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE April 215 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment April 215 1 / 16
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE April 215 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment April 215 1 / 16
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Bayesian Estimation of DSGE Models: Lessons from Second-order Approximations
 Bayesian Estimation of DSGE Models: Lessons from Second-order Approximations Sungbae An Singapore Management University Bank Indonesia/BIS Workshop: STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC MACROECONOMIC MODELS IN ASIA-PACIFIC
Bayesian Estimation of DSGE Models: Lessons from Second-order Approximations Sungbae An Singapore Management University Bank Indonesia/BIS Workshop: STRUCTURAL DYNAMIC MACROECONOMIC MODELS IN ASIA-PACIFIC
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions
 Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999)
 Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty
 1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty Sofarwehaveassumedawayaggregatefluctuations (i.e., business cycles) in our description of the incomplete-markets economies with uninsurable idiosyncratic risk
1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty Sofarwehaveassumedawayaggregatefluctuations (i.e., business cycles) in our description of the incomplete-markets economies with uninsurable idiosyncratic risk
Variance Decomposition Analysis for Nonlinear DSGE Models: An Application with ZLB
 Variance Decomposition Analysis for Nonlinear DSGE Models: An Application with ZLB Phuong V. Ngo Maksim Isakin Francois Gourio January 5, 2018 Abstract In this paper, we first proposes two new methods
Variance Decomposition Analysis for Nonlinear DSGE Models: An Application with ZLB Phuong V. Ngo Maksim Isakin Francois Gourio January 5, 2018 Abstract In this paper, we first proposes two new methods
The Zero Lower Bound
 The Zero Lower Bound Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 7 Introduction In the standard New Keynesian model, monetary policy is often described by an interest rate rule (e.g. a Taylor rule) that
The Zero Lower Bound Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 7 Introduction In the standard New Keynesian model, monetary policy is often described by an interest rate rule (e.g. a Taylor rule) that
Solution Methods. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde. University of Pennsylvania. March 16, 2016
 Solution Methods Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania March 16, 2016 Jesús Fernández-Villaverde (PENN) Solution Methods March 16, 2016 1 / 36 Functional equations A large class of problems
Solution Methods Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania March 16, 2016 Jesús Fernández-Villaverde (PENN) Solution Methods March 16, 2016 1 / 36 Functional equations A large class of problems
New Keynesian Macroeconomics
 New Keynesian Macroeconomics Chapter 4: The New Keynesian Baseline Model (continued) Prof. Dr. Kai Carstensen Ifo Institute for Economic Research and LMU Munich May 21, 212 Prof. Dr. Kai Carstensen (LMU
New Keynesian Macroeconomics Chapter 4: The New Keynesian Baseline Model (continued) Prof. Dr. Kai Carstensen Ifo Institute for Economic Research and LMU Munich May 21, 212 Prof. Dr. Kai Carstensen (LMU
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models. December 4, 2007
 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models December 4, 2007 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models Random shocks to generate trajectories that look like the observed national accounts. Rational
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models December 4, 2007 Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models Random shocks to generate trajectories that look like the observed national accounts. Rational
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE
 THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 ECB Forum on Central Banking Macroeconomics of Price- and Wage-Setting June 19, 2018 Sintra, Portugal Any opinions expressed
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 ECB Forum on Central Banking Macroeconomics of Price- and Wage-Setting June 19, 2018 Sintra, Portugal Any opinions expressed
Optimal Inflation Stabilization in a Medium-Scale Macroeconomic Model
 Optimal Inflation Stabilization in a Medium-Scale Macroeconomic Model Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University 1 Objective of the Paper: Within a mediumscale estimated model of the macroeconomy
Optimal Inflation Stabilization in a Medium-Scale Macroeconomic Model Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University 1 Objective of the Paper: Within a mediumscale estimated model of the macroeconomy
Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model.
 Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, UiO 22 September 2009 Lecture notes on closed economy macro dynamics AD-AS model Inflation targeting regime.
Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, UiO 22 September 2009 Lecture notes on closed economy macro dynamics AD-AS model Inflation targeting regime.
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
The New Keynesian Model
 The New Keynesian Model Basic Issues Roberto Chang Rutgers January 2013 R. Chang (Rutgers) New Keynesian Model January 2013 1 / 22 Basic Ingredients of the New Keynesian Paradigm Representative agent paradigm
The New Keynesian Model Basic Issues Roberto Chang Rutgers January 2013 R. Chang (Rutgers) New Keynesian Model January 2013 1 / 22 Basic Ingredients of the New Keynesian Paradigm Representative agent paradigm
GCOE Discussion Paper Series
 GCOE Discussion Paper Series Global COE Program Human Behavior and Socioeconomic Dynamics Discussion Paper No.34 Inflation Inertia and Optimal Delegation of Monetary Policy Keiichi Morimoto February 2009
GCOE Discussion Paper Series Global COE Program Human Behavior and Socioeconomic Dynamics Discussion Paper No.34 Inflation Inertia and Optimal Delegation of Monetary Policy Keiichi Morimoto February 2009
The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap
 The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé and Martín Uribe Columbia University European Central Bank Conference on Monetary Policy Frankfurt am Main, October 29-3, 218
The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé and Martín Uribe Columbia University European Central Bank Conference on Monetary Policy Frankfurt am Main, October 29-3, 218
DSGE Model Forecasting
 University of Pennsylvania EABCN Training School May 1, 216 Introduction The use of DSGE models at central banks has triggered a strong interest in their forecast performance. The subsequent material draws
University of Pennsylvania EABCN Training School May 1, 216 Introduction The use of DSGE models at central banks has triggered a strong interest in their forecast performance. The subsequent material draws
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
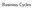 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction
 The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Models
 Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Models Dr. Andrea Beccarini M.Sc. Willi Mutschler Summer 2014 A. Beccarini () Advanced Macroeconomics DSGE Summer 2014 1 / 33 The log-linearization procedure: One
Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Models Dr. Andrea Beccarini M.Sc. Willi Mutschler Summer 2014 A. Beccarini () Advanced Macroeconomics DSGE Summer 2014 1 / 33 The log-linearization procedure: One
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
The Correlation of Oil and Equity Prices: The Role of the Zero Lower Bound
 The Correlation of Oil and Equity Prices: The Role of the Zero Lower Bound Deepa Datta, Benjamin Johannsen, Hannah Kwon, and Robert J. Vigfusson Federal Reserve Board August 18, 2016 The views in this
The Correlation of Oil and Equity Prices: The Role of the Zero Lower Bound Deepa Datta, Benjamin Johannsen, Hannah Kwon, and Robert J. Vigfusson Federal Reserve Board August 18, 2016 The views in this
Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion
 14.05 Lecture Notes Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion A large number of private agents play against a government. Government objective. The government objective is given by the following loss function:
14.05 Lecture Notes Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion A large number of private agents play against a government. Government objective. The government objective is given by the following loss function:
Citation Working Paper Series, F-39:
 Equilibrium Indeterminacy under F Title Interest Rate Rules Author(s) NAKAGAWA, Ryuichi Citation Working Paper Series, F-39: 1-14 Issue Date 2009-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10112/2641 Rights Type Technical
Equilibrium Indeterminacy under F Title Interest Rate Rules Author(s) NAKAGAWA, Ryuichi Citation Working Paper Series, F-39: 1-14 Issue Date 2009-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10112/2641 Rights Type Technical
Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy
 Class handout Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy Giovanni Di Bartolomeo University of Teramo 1. The Phillips menu In the 190s, econometricians estimated a negative relationship
Class handout Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy Giovanni Di Bartolomeo University of Teramo 1. The Phillips menu In the 190s, econometricians estimated a negative relationship
The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks.
 The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks. Ida Wolden Bache Norges Bank Kai Leitemo Norwegian School of Management BI September 2, 2008 Abstract We argue that the correct
The Price Puzzle: Mixing the Temporary and Permanent Monetary Policy Shocks. Ida Wolden Bache Norges Bank Kai Leitemo Norwegian School of Management BI September 2, 2008 Abstract We argue that the correct
Incomplete Markets, Heterogeneity and Macroeconomic Dynamics
 Incomplete Markets, Heterogeneity and Macroeconomic Dynamics Bruce Preston and Mauro Roca Presented by Yuki Ikeda February 2009 Preston and Roca (presenter: Yuki Ikeda) 02/03 1 / 20 Introduction Stochastic
Incomplete Markets, Heterogeneity and Macroeconomic Dynamics Bruce Preston and Mauro Roca Presented by Yuki Ikeda February 2009 Preston and Roca (presenter: Yuki Ikeda) 02/03 1 / 20 Introduction Stochastic
Does Calvo Meet Rotemberg at the Zero Lower Bound?
 Does Calvo Meet Rotemberg at the Zero Lower Bound? Jianjun Miao Phuong V. Ngo January 27, 2016 Abstract This paper compares the Calvo and Rotemberg price adjustments in a fully nonlinear framework with
Does Calvo Meet Rotemberg at the Zero Lower Bound? Jianjun Miao Phuong V. Ngo January 27, 2016 Abstract This paper compares the Calvo and Rotemberg price adjustments in a fully nonlinear framework with
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE
 THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 BOJ-IMES Conference Central Banking in a Changing World May 31, 2018 Tokyo, Japan Any opinions expressed here are my own
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 BOJ-IMES Conference Central Banking in a Changing World May 31, 2018 Tokyo, Japan Any opinions expressed here are my own
The Making Of A Great Contraction. With A Liquidity Trap And A Jobless Recovery. Columbia University
 The Making Of A Great Contraction With A Liquidity Trap And A Jobless Recovery Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Columbia University November 5, 2013 A jobless recovery is a situation in which: Output
The Making Of A Great Contraction With A Liquidity Trap And A Jobless Recovery Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Columbia University November 5, 2013 A jobless recovery is a situation in which: Output
Learning and Global Dynamics
 Learning and Global Dynamics James Bullard 10 February 2007 Learning and global dynamics The paper for this lecture is Liquidity Traps, Learning and Stagnation, by George Evans, Eran Guse, and Seppo Honkapohja.
Learning and Global Dynamics James Bullard 10 February 2007 Learning and global dynamics The paper for this lecture is Liquidity Traps, Learning and Stagnation, by George Evans, Eran Guse, and Seppo Honkapohja.
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8
 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Is the Macroeconomy Locally Unstable and Why should we care?
 Is the Macroeconomy Locally Unstable and Why should we care? Paul Beaudry, Dana Galizia & Franck Portier NBER macroannual April 2016 1 / 22 Introduction In most macro-models, BC fluctuation arises as the
Is the Macroeconomy Locally Unstable and Why should we care? Paul Beaudry, Dana Galizia & Franck Portier NBER macroannual April 2016 1 / 22 Introduction In most macro-models, BC fluctuation arises as the
Extracting Rational Expectations Model Structural Matrices from Dynare
 Extracting Rational Expectations Model Structural Matrices from Dynare Callum Jones New York University In these notes I discuss how to extract the structural matrices of a model from its Dynare implementation.
Extracting Rational Expectations Model Structural Matrices from Dynare Callum Jones New York University In these notes I discuss how to extract the structural matrices of a model from its Dynare implementation.
The Return of the Wage Phillips Curve
 The Return of the Wage Phillips Curve Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE March 2010 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) The Return of the Wage Phillips Curve March 2010 1 / 15 Introduction Two
The Return of the Wage Phillips Curve Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE March 2010 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) The Return of the Wage Phillips Curve March 2010 1 / 15 Introduction Two
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Discussion of Contagious Malady? Global Dimensions of Secular Stagnation
 Discussion of Contagious Malady? Global Dimensions of Secular Stagnation Jaume Ventura CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE 18 June, 2015 Jaume Ventura (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Florence workshop 18 June, 2015
Discussion of Contagious Malady? Global Dimensions of Secular Stagnation Jaume Ventura CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE 18 June, 2015 Jaume Ventura (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Florence workshop 18 June, 2015
Estimating Macroeconomic Models: A Likelihood Approach
 Estimating Macroeconomic Models: A Likelihood Approach Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania, NBER, and CEPR Juan Rubio-Ramírez Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Estimating Dynamic Macroeconomic
Estimating Macroeconomic Models: A Likelihood Approach Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania, NBER, and CEPR Juan Rubio-Ramírez Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Estimating Dynamic Macroeconomic
Determinacy in the New Keynesian Model with Market Segmentation
 Determinacy in the New Keynesian Model with Market Segmentation Seung Moon Lee Korea Energy Economics Institute November, 212 Abstract This paper introduces the asset market segmentation into an otherwise
Determinacy in the New Keynesian Model with Market Segmentation Seung Moon Lee Korea Energy Economics Institute November, 212 Abstract This paper introduces the asset market segmentation into an otherwise
DSGE-Models. Calibration and Introduction to Dynare. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics
 DSGE-Models Calibration and Introduction to Dynare Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de Summer 2012 Willi Mutschler
DSGE-Models Calibration and Introduction to Dynare Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de Summer 2012 Willi Mutschler
Introduction to Macroeconomics
 Introduction to Macroeconomics Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 39 Macroeconomics is Dynamic Decisions are taken over
Introduction to Macroeconomics Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 39 Macroeconomics is Dynamic Decisions are taken over
Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations?
 Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations? A Bayesian DSGE Approach Ippei Fujiwara 1 Yasuo Hirose 1 Mototsugu 2 1 Bank of Japan 2 Vanderbilt University August 4, 2009 Contributions of this paper
Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations? A Bayesian DSGE Approach Ippei Fujiwara 1 Yasuo Hirose 1 Mototsugu 2 1 Bank of Japan 2 Vanderbilt University August 4, 2009 Contributions of this paper
1 The Basic RBC Model
 IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
WORKING PAPER NO INTEREST RATE VERSUS MONEY SUPPLY INSTRUMENTS: ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF MARKOV-PERFECT OPTIMAL MONETARY POLICY
 WORKING PAPER NO. 07-27 INTEREST RATE VERSUS MONEY SUPPLY INSTRUMENTS: ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF MARKOV-PERFECT OPTIMAL MONETARY POLICY Michael Dotsey Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Andreas Hornstein
WORKING PAPER NO. 07-27 INTEREST RATE VERSUS MONEY SUPPLY INSTRUMENTS: ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF MARKOV-PERFECT OPTIMAL MONETARY POLICY Michael Dotsey Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Andreas Hornstein
The transmission mechanism How the monetary-policy instrument affects the economy and the target variables
 Eco 200, part 3, Fall 2004 200L2.tex Lars Svensson 11/18/04 The transmission mechanism How the monetary-policy instrument affects the economy and the target variables Variables t =..., 1, 0, 1,... denotes
Eco 200, part 3, Fall 2004 200L2.tex Lars Svensson 11/18/04 The transmission mechanism How the monetary-policy instrument affects the economy and the target variables Variables t =..., 1, 0, 1,... denotes
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective
 Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE May 218 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment May 218 1 / 18 Introducing
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE May 218 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment May 218 1 / 18 Introducing
Forecast combination based on multiple encompassing tests in a macroeconomic DSGE-VAR system
 Forecast combination based on multiple encompassing tests in a macroeconomic DSGE-VAR system Mauro Costantini 1, Ulrich Gunter 2, and Robert M. Kunst 3 Presented at the CFE-ERCIM 2011, London, December
Forecast combination based on multiple encompassing tests in a macroeconomic DSGE-VAR system Mauro Costantini 1, Ulrich Gunter 2, and Robert M. Kunst 3 Presented at the CFE-ERCIM 2011, London, December
Redistributive Taxation in a Partial-Insurance Economy
 Redistributive Taxation in a Partial-Insurance Economy Jonathan Heathcote Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Kjetil Storesletten Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Gianluca Violante
Redistributive Taxation in a Partial-Insurance Economy Jonathan Heathcote Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Kjetil Storesletten Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and CEPR Gianluca Violante
ASYMMETRIC EXPECTATION EFFECTS OF REGIME SHIFTS IN MONETARY POLICY
 FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF SAN FRANCISCO WORKING PAPER SERIES ASYMMETRIC EXPECTATION EFFECTS OF REGIME SHIFTS IN MONETARY POLICY Zheng Liu Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco and Emory University Daniel
FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF SAN FRANCISCO WORKING PAPER SERIES ASYMMETRIC EXPECTATION EFFECTS OF REGIME SHIFTS IN MONETARY POLICY Zheng Liu Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco and Emory University Daniel
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations. Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno
 Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
Precautionary Demand for Money in a Monetary Business Cycle Model
 Discussion of Precautionary Demand for Money in a Monetary Business Cycle Model by I. Telyukova and L. Visschers Makoto Nakajima FRB Philadelphia March 27, 2009 Makoto Nakajima (FRB Philadelphia) Discussion
Discussion of Precautionary Demand for Money in a Monetary Business Cycle Model by I. Telyukova and L. Visschers Makoto Nakajima FRB Philadelphia March 27, 2009 Makoto Nakajima (FRB Philadelphia) Discussion
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case.
 Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Demand Shocks, Monetary Policy, and the Optimal Use of Dispersed Information
 Demand Shocks, Monetary Policy, and the Optimal Use of Dispersed Information Guido Lorenzoni (MIT) WEL-MIT-Central Banks, December 2006 Motivation Central bank observes an increase in spending Is it driven
Demand Shocks, Monetary Policy, and the Optimal Use of Dispersed Information Guido Lorenzoni (MIT) WEL-MIT-Central Banks, December 2006 Motivation Central bank observes an increase in spending Is it driven
Rising Wage Inequality and the Effectiveness of Tuition Subsidy Policies:
 Rising Wage Inequality and the Effectiveness of Tuition Subsidy Policies: Explorations with a Dynamic General Equilibrium Model of Labor Earnings based on Heckman, Lochner and Taber, Review of Economic
Rising Wage Inequality and the Effectiveness of Tuition Subsidy Policies: Explorations with a Dynamic General Equilibrium Model of Labor Earnings based on Heckman, Lochner and Taber, Review of Economic
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 10
 UNIVERSIT OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 10 THE ZERO LOWER BOUND IN THE IS-MP-IA FRAMEWORK FEBRUAR 21, 2018 I. INTRODUCTION II. THE IS-MP-IA
UNIVERSIT OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 10 THE ZERO LOWER BOUND IN THE IS-MP-IA FRAMEWORK FEBRUAR 21, 2018 I. INTRODUCTION II. THE IS-MP-IA
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
What You Match Does Matter: The Effects of Data on DSGE Estimation
 Discussion of What You Match Does Matter: The Effects of Data on DSGE Estimation by Pablo Guerron-Quintana Marc Giannoni Columbia University, NBER and CEPR Workshop on Methods and Applications for DSGE
Discussion of What You Match Does Matter: The Effects of Data on DSGE Estimation by Pablo Guerron-Quintana Marc Giannoni Columbia University, NBER and CEPR Workshop on Methods and Applications for DSGE
Global Value Chain Participation and Current Account Imbalances
 Global Value Chain Participation and Current Account Imbalances Johannes Brumm University of Zurich Georgios Georgiadis European Central Bank Johannes Gräb European Central Bank Fabian Trottner Princeton
Global Value Chain Participation and Current Account Imbalances Johannes Brumm University of Zurich Georgios Georgiadis European Central Bank Johannes Gräb European Central Bank Fabian Trottner Princeton
New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks
 New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks Satya P. Das @ NIPFP Satya P. Das (@ NIPFP) New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks 1 / 20 1 Blanchard-Kiyotaki Model 2 New Keynesian Phillips Curve 3 Utility
New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks Satya P. Das @ NIPFP Satya P. Das (@ NIPFP) New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks 1 / 20 1 Blanchard-Kiyotaki Model 2 New Keynesian Phillips Curve 3 Utility
Getting to page 31 in Galí (2008)
 Getting to page 31 in Galí 2008) H J Department of Economics University of Copenhagen December 4 2012 Abstract This note shows in detail how to compute the solutions for output inflation and the nominal
Getting to page 31 in Galí 2008) H J Department of Economics University of Copenhagen December 4 2012 Abstract This note shows in detail how to compute the solutions for output inflation and the nominal
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model
 Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes.
 14.452. Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes. Olivier Blanchard May 12, 2007 Nr. 1 Look at three issues: Time consistency. The inflation bias. The trade-off between inflation and activity. Implementation and
14.452. Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes. Olivier Blanchard May 12, 2007 Nr. 1 Look at three issues: Time consistency. The inflation bias. The trade-off between inflation and activity. Implementation and
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions
 Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
The Basic New Keynesian Model, the Labor Market and Sticky Wages
 The Basic New Keynesian Model, the Labor Market and Sticky Wages Lawrence J. Christiano August 25, 203 Baseline NK model with no capital and with a competitive labor market. private sector equilibrium
The Basic New Keynesian Model, the Labor Market and Sticky Wages Lawrence J. Christiano August 25, 203 Baseline NK model with no capital and with a competitive labor market. private sector equilibrium
The Natural Rate of Interest and its Usefulness for Monetary Policy
 The Natural Rate of Interest and its Usefulness for Monetary Policy Robert Barsky, Alejandro Justiniano, and Leonardo Melosi Online Appendix 1 1 Introduction This appendix describes the extended DSGE model
The Natural Rate of Interest and its Usefulness for Monetary Policy Robert Barsky, Alejandro Justiniano, and Leonardo Melosi Online Appendix 1 1 Introduction This appendix describes the extended DSGE model
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital
 Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B. Lecture 2
 ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B Lecture 2 Giulio Fella c Giulio Fella, 2014 ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B - Lecture 2 40/197 Aim of consumption theory Consumption theory aims at explaining consumption/saving decisions
ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B Lecture 2 Giulio Fella c Giulio Fella, 2014 ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B - Lecture 2 40/197 Aim of consumption theory Consumption theory aims at explaining consumption/saving decisions
Expectations, Learning and Macroeconomic Policy
 Expectations, Learning and Macroeconomic Policy George W. Evans (Univ. of Oregon and Univ. of St. Andrews) Lecture 4 Liquidity traps, learning and stagnation Evans, Guse & Honkapohja (EER, 2008), Evans
Expectations, Learning and Macroeconomic Policy George W. Evans (Univ. of Oregon and Univ. of St. Andrews) Lecture 4 Liquidity traps, learning and stagnation Evans, Guse & Honkapohja (EER, 2008), Evans
General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 2013
 HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory SPRING 203 You have FOUR hours. Answer all questions Part A (Prof. Laibson): 48 minutes Part B (Prof. Aghion): 48
Analysis of the Government Expenditure Multiplier under Zero Lower Bound: the Role of Public Investment 1
 Analysis of the Government Expenditure Multiplier under Zero Lower Bound: the Role of Public Investment 1 Mariam Mamedli 2 Abstract In times of economic downturn fiscal authorities face the need to stimulate
Analysis of the Government Expenditure Multiplier under Zero Lower Bound: the Role of Public Investment 1 Mariam Mamedli 2 Abstract In times of economic downturn fiscal authorities face the need to stimulate
Fiscal Expansions in Secular Stagnation: What if it isn t Secular?
 Fiscal Expansions in Secular Stagnation: What if it isn t Secular? Vaishali Garga This version: November 7, 208 Latest version: Click here Abstract Low natural real interest rates limit the power of monetary
Fiscal Expansions in Secular Stagnation: What if it isn t Secular? Vaishali Garga This version: November 7, 208 Latest version: Click here Abstract Low natural real interest rates limit the power of monetary
Problem 1 (30 points)
 Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT: THE PHILLIPS CURVE. Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University
 INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT: THE PHILLIPS CURVE Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University ROADMAP INCOME EXPENDITURE LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE IS CURVE LM CURVE SHORT-RUN IS-LM MODEL AGGREGATE
INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT: THE PHILLIPS CURVE Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University ROADMAP INCOME EXPENDITURE LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE IS CURVE LM CURVE SHORT-RUN IS-LM MODEL AGGREGATE
Lars Svensson 10/2/05. Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation
 Eco 00, part, Fall 005 00L5_F05.tex Lars Svensson 0//05 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation Japan: recession, low growth since early 90s, deflation in GDP deflator and
Eco 00, part, Fall 005 00L5_F05.tex Lars Svensson 0//05 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation Japan: recession, low growth since early 90s, deflation in GDP deflator and
A Modern Equilibrium Model. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
Monetary Economics. Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one. Chris Edmond. 2nd Semester 2014
 Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
