Generic Aubry sets on surfaces
|
|
|
- Peregrine McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France Nanjing University (June 10th, 2013)
2 Setting Let M be a smooth compact manifold of dimension n 2 be fixed. Let H : T M R be a Hamiltonian of class C k, with k 2, satisfying the following properties: (H1) Superlinear growth: For every K 0, there is C (K) R such that H(x, p) K p + C (K) (x, p) T M. (H2) Uniform convexity: For every (x, p) T M, 2 H p 2 (x, p) is positive definite.
3 Critical value of H Definition We call critical value of H the constant c = c[h] defined as { { ( )} } c[h] := H x, du(x). inf u C 1 (M;R) max x M In other terms, c[h] is the infimum of numbers c R such that there is a C 1 function u : M R satisfying H ( x, du(x) ) c x M.
4 Critical value of H Definition We call critical value of H the constant c = c[h] defined as { { ( )} } c[h] := H x, du(x). inf u C 1 (M;R) max x M In other terms, c[h] is the infimum of numbers c R such that there is a C 1 function u : M R satisfying Note that min x M H ( x, du(x) ) c x M. {H(x, 0)} c[h] max {H(x, 0)}. x M
5 Critical subsolutions Definition We call critical subsolution any Lipschitz function u : M R such that H ( x, du(x) ) c[h] for a.e. x M.
6 Critical subsolutions Definition We call critical subsolution any Lipschitz function u : M R such that H ( x, du(x) ) c[h] for a.e. x M. Let L : TM R be the Tonelli Lagrangian associated with H by Legendre-Fenchel duality, that is { } L(x, v) := max p Tx M p v H(x, p) (x, v) TM. Proposition A Lipschitz function u : M R is a critical subsolution if and only if for every Lipschitz curve γ : [a, b] M, u ( γ(b) ) u ( γ(a) ) b a L ( γ(t), γ(t) ) ds + c[h] (b a).
7 The weak KAM Theorem Definition Given u : M R and t 0, T t u : M R is defined by with T t u(x) := min y M {u(y) + A t(y, x)}, { t A t (z, z ) := inf 0 L ( γ(s), γ(s) ) } ds + c[h] t, where the infimum is taken over the Lipschitz curves γ : [0, t] M such that γ(0) = z and γ(t) = z.
8 The weak KAM Theorem Definition Given u : M R and t 0, T t u : M R is defined by with T t u(x) := min y M {u(y) + A t(y, x)}, { t A t (z, z ) := inf 0 L ( γ(s), γ(s) ) } ds + c[h] t, where the infimum is taken over the Lipschitz curves γ : [0, t] M such that γ(0) = z and γ(t) = z. Theorem (Fathi, 1997) There is a critical subsolution u : M R such that T t u = u t 0. It is called a critical or a weak KAM solution of H.
9 More on critical solutions Given a critical solution u : M R, for every x M, there is a curve γ : (, 0] M with γ(0) = x such that, for any a < b 0, u ( γ(b) ) u ( γ(a) ) = b a L ( γ(s), γ(s) ) ds + c(b a). Therefore, any restriction of γ minimizes the action between its end-points. Then, it satisfies the Euler-Lagrange equations.
10 Projected Aubry set and Aubry set Definition and Proposition The projected Aubry set of H defined as A(H) = {x M A t (x, x) = 0}. is compact and nonempty.
11 Projected Aubry set and Aubry set Definition and Proposition The projected Aubry set of H defined as A(H) = {x M A t (x, x) = 0}. is compact and nonempty. Any critical subsolution u is C 1 at any point of A(H) and satisfies H ( x, du(x) ) = c[h], x A(H).
12 Projected Aubry set and Aubry set Definition and Proposition The projected Aubry set of H defined as A(H) = {x M A t (x, x) = 0}. is compact and nonempty. Any critical subsolution u is C 1 at any point of A(H) and satisfies H ( x, du(x) ) = c[h], x A(H). For every x A(H), the differential of a critical subsolution at x does not depend on u.
13 Projected Aubry set and Aubry set Definition and Proposition The projected Aubry set of H defined as A(H) = {x M A t (x, x) = 0}. is compact and nonempty. Any critical subsolution u is C 1 at any point of A(H) and satisfies H ( x, du(x) ) = c[h], x A(H). For every x A(H), the differential of a critical subsolution at x does not depend on u. The Aubry set of H defined by Ã(H) := {( x, du(x) ) x A(H), u crit. subsol. } T M is compact, invariant by φ H t, and is a Lipschitz graph over A(H).
14 Questions Uniqueness (up to constants) of critical solutions? Regularity of critical solutions? Structure of the Aubry sets? Size of the (quotiented) Aubry set? Dynamics of the Aubry set?
15 The Mañé Conjecture Conjecture (Mañé, 96) For every Tonelli Hamiltonian H : T M R of class C k (with k 2), there is a residual subset (i.e., a countable intersection of open and dense subsets) G of C k (M) such that, for every V G, the Aubry set of the Hamiltonian H V := H + V is either an equilibrium point or a periodic orbit.
16 The Mañé Conjecture Conjecture (Mañé, 96) For every Tonelli Hamiltonian H : T M R of class C k (with k 2), there is a residual subset (i.e., a countable intersection of open and dense subsets) G of C k (M) such that, for every V G, the Aubry set of the Hamiltonian H V := H + V is either an equilibrium point or a periodic orbit. Strategy of proof: Density result. Stability result.
17 Partial results Theorem (Figalli-LR, 2011) Let H : T M R be a Tonelli Hamiltonian of class C 2. If there is a critical subsolution sufficiently regular on a neighborhood of A(H), then for every ɛ > 0, there exists V C 2 (M),with V C 2 < ɛ such that the Aubry set of H + V is a hyperbolic periodic orbit.
18 Partial results Theorem (Figalli-LR, 2011) Let H : T M R be a Tonelli Hamiltonian of class C 2. If there is a critical subsolution sufficiently regular on a neighborhood of A(H), then for every ɛ > 0, there exists V C 2 (M),with V C 2 < ɛ such that the Aubry set of H + V is a hyperbolic periodic orbit. Theorem (Contreras-Figalli-LR, 2013) Let H : T M R be a Tonelli Hamiltonian of class C 2, and assume that dim M = 2. Then there is an open dense set of potentials V C 2 (M) such that, for every V V, the Aubry set of H + V is hyperbolic in its energy level.
19 Key ingredients of the proof Green bundles Nonsmooth analysis Techniques from closing lemmas Geometric control theory Geometric measure theory
20 Green bundles I D φ H t (θ)φ H t θ V θ V φ H t (θ) For every θ T M and every t R, we define the Lagrangian subspace Gθ t T θt M by Gθ t := ( ) ( ) φ H t V φ H t (θ).
21 Green bundles II Definition For every θ Ã(H), we define the positive and negative Green bundles at θ as G + θ := lim t + G t θ and G θ := lim t G t θ G θ θ G + θ V θ
22 A dichotomy Two cases may appear: For every θ Ã(H) the Green bundles G θ and G + θ are transverse There is θ Ã(H) such that G θ = G + θ
23 A dichotomy Two cases may appear: For every θ Ã(H) the Green bundles G θ and G + θ are transverse hyperbolicity of Ã(H) There is θ Ã(H) such that G θ = G + θ
24 A dichotomy Two cases may appear: For every θ Ã(H) the Green bundles G θ and G + θ are transverse hyperbolicity of Ã(H) There is θ Ã(H) such that G θ = G + θ further regularity for critical solutions
25 Further regularity (after Arnaud) Definition Let S R k be a compact set which has the origin as a cluster point. The paratingent cone to S at 0 is the cone defined as { } x i y i C 0 (S) := λ lim i x i y i λ R, x S i y i 0.
26 Further regularity (after Arnaud) Definition Let S R k be a compact set which has the origin as a cluster point. The paratingent cone to S at 0 is the cone defined as { } x i y i C 0 (S) := λ lim i x i y i λ R, x S i y i 0. Proposition For every θ Ã(H), there holds G θ C θ (Ã(H) ) G + θ.
27 Further regularity (after Arnaud) Definition Let S R k be a compact set which has the origin as a cluster point. The paratingent cone to S at 0 is the cone defined as { } x i y i C 0 (S) := λ lim i x i y i λ R, x S i y i 0. Proposition For every θ Ã(H), there holds G θ C θ (Ã(H) ) G + θ. As a consequence, if G θ = G + θ for some θ Ã(H), then Ã(H) is locally contained in the graph of a Lipschitz 1-form which is C 1 at θ.
28 Closing the Aubry set Under this additional regularity, given ɛ > 0, we are able to a C 2 potential V : M R with V C 2 < ɛ, a periodic orbit γ : [0, T ] M (γ(0) = γ(t )), a Lipschitz function v : M R, in such a way that the following properties are satisfied: H ( x, dv(x) ) + V (x) 0 for a.e. x M, T 0 L( γ(t), γ(t) ) V (γ(t)) dt = 0.
29 Closing the Aubry set Under this additional regularity, given ɛ > 0, we are able to a C 2 potential V : M R with V C 2 < ɛ, a periodic orbit γ : [0, T ] M (γ(0) = γ(t )), a Lipschitz function v : M R, in such a way that the following properties are satisfied: H ( x, dv(x) ) + V (x) 0 for a.e. x M, T 0 L( γ(t), γ(t) ) V (γ(t)) dt = 0. This shows that the Aubry set of H + V contains a periodic orbit.
30 Thank you for your attention!!
Mañé s Conjecture from the control viewpoint
 Mañé s Conjecture from the control viewpoint Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis Setting Let M be a smooth compact manifold of dimension n 2 be fixed. Let H : T M R be a Hamiltonian of class C k, with
Mañé s Conjecture from the control viewpoint Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis Setting Let M be a smooth compact manifold of dimension n 2 be fixed. Let H : T M R be a Hamiltonian of class C k, with
Regularity of solutions to Hamilton-Jacobi equations for Tonelli Hamiltonians
 Regularity of solutions to Hamilton-Jacobi equations for Tonelli Hamiltonians Université Nice Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France Nonlinear Analysis and Optimization Royal Society, London,
Regularity of solutions to Hamilton-Jacobi equations for Tonelli Hamiltonians Université Nice Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France Nonlinear Analysis and Optimization Royal Society, London,
Geometric control and dynamical systems
 Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France 9th AIMS International Conference on Dynamical Systems, Differential Equations and Applications Control of an inverted pendulum
Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France 9th AIMS International Conference on Dynamical Systems, Differential Equations and Applications Control of an inverted pendulum
On the Hausdorff Dimension of the Mather Quotient
 On the Hausdorff Dimension of the Mather Quotient Albert Fathi, Alessio Figalli, Ludovic Rifford February 29, 2008 Abstract Under appropriate assumptions on the dimension of the ambient manifold and the
On the Hausdorff Dimension of the Mather Quotient Albert Fathi, Alessio Figalli, Ludovic Rifford February 29, 2008 Abstract Under appropriate assumptions on the dimension of the ambient manifold and the
A Kupka-Smale Theorem for Hamiltonian systems. systems from Mañé s viewpoint, a control approach. Ludovic Rifford PICOF 12
 A Kupka-Smale Theorem for Hamiltonian systems from Mañé s viewpoint, a control approach Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France PICOF 12 The Kupka-Smale Theorem for vector
A Kupka-Smale Theorem for Hamiltonian systems from Mañé s viewpoint, a control approach Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France PICOF 12 The Kupka-Smale Theorem for vector
Closing Aubry sets II
 Closing Aubry sets II A. Figalli L. Rifford July 1, 1 Abstract Given a Tonelli Hamiltonian H : T M R of class C k, with k 4, we prove the following results: 1 Assume there is a critical viscosity subsolution
Closing Aubry sets II A. Figalli L. Rifford July 1, 1 Abstract Given a Tonelli Hamiltonian H : T M R of class C k, with k 4, we prove the following results: 1 Assume there is a critical viscosity subsolution
A generic property of families of Lagrangian systems
 Annals of Mathematics, 167 (2008), 1099 1108 A generic property of families of Lagrangian systems By Patrick Bernard and Gonzalo Contreras * Abstract We prove that a generic Lagrangian has finitely many
Annals of Mathematics, 167 (2008), 1099 1108 A generic property of families of Lagrangian systems By Patrick Bernard and Gonzalo Contreras * Abstract We prove that a generic Lagrangian has finitely many
MATHER THEORY, WEAK KAM, AND VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI PDE S
 MATHER THEORY, WEAK KAM, AND VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI PDE S VADIM YU. KALOSHIN 1. Motivation Consider a C 2 smooth Hamiltonian H : T n R n R, where T n is the standard n-dimensional torus
MATHER THEORY, WEAK KAM, AND VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI PDE S VADIM YU. KALOSHIN 1. Motivation Consider a C 2 smooth Hamiltonian H : T n R n R, where T n is the standard n-dimensional torus
Generic hyperbolicity of Aubry sets on surfaces
 Generic hyperbolicity of Aubry sets on surfaces G. Contreras A. Figalli L. Rifford May 26, 214 Abstract Given a Tonelli Hamiltonian of class C 2 on the cotangent bundle of a compact surface, we show that
Generic hyperbolicity of Aubry sets on surfaces G. Contreras A. Figalli L. Rifford May 26, 214 Abstract Given a Tonelli Hamiltonian of class C 2 on the cotangent bundle of a compact surface, we show that
Green bundles : a dynamical study
 Green bundles : a dynamical study Marie-Claude Arnaud December 2007 1 CONTENT 1) Hamiltonian and Lagrangian formalism 2) Lipschitz Lagrangian submanifolds, images of such manifolds and minimization properties
Green bundles : a dynamical study Marie-Claude Arnaud December 2007 1 CONTENT 1) Hamiltonian and Lagrangian formalism 2) Lipschitz Lagrangian submanifolds, images of such manifolds and minimization properties
Lecture 3. Topology of the set of singularities of a solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation
 Lecture 3. Topology of the set of singularities of a solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Albert Fathi Padova, 14 February 2018 We will present results which are a joint work with Piermarco Cannarsa
Lecture 3. Topology of the set of singularities of a solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Albert Fathi Padova, 14 February 2018 We will present results which are a joint work with Piermarco Cannarsa
WEAK KAM THEORETIC ASPECTS FOR NONREGULAR COMMUTING HAMILTONIANS
 WEAK KAM THEORETIC ASPECTS FOR NONREGULAR COMMUTING HAMILTONIANS ANDREA DAVINI AND MAXIME ZAVIDOVIQUE Abstract. In this paper we introduce the notion of commutation for a pair of continuous and convex
WEAK KAM THEORETIC ASPECTS FOR NONREGULAR COMMUTING HAMILTONIANS ANDREA DAVINI AND MAXIME ZAVIDOVIQUE Abstract. In this paper we introduce the notion of commutation for a pair of continuous and convex
Local semiconvexity of Kantorovich potentials on non-compact manifolds
 Local semiconvexity of Kantorovich potentials on non-compact manifolds Alessio Figalli, Nicola Gigli Abstract We prove that any Kantorovich potential for the cost function c = d / on a Riemannian manifold
Local semiconvexity of Kantorovich potentials on non-compact manifolds Alessio Figalli, Nicola Gigli Abstract We prove that any Kantorovich potential for the cost function c = d / on a Riemannian manifold
Topology of the set of singularities of a solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation
 Topology of the set of singularities of a solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Albert Fathi IAS Princeton March 15, 2016 In this lecture, a singularity for a locally Lipschitz real valued function
Topology of the set of singularities of a solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Albert Fathi IAS Princeton March 15, 2016 In this lecture, a singularity for a locally Lipschitz real valued function
Optimal transportation on non-compact manifolds
 Optimal transportation on non-compact manifolds Albert Fathi, Alessio Figalli 07 November 2007 Abstract In this work, we show how to obtain for non-compact manifolds the results that have already been
Optimal transportation on non-compact manifolds Albert Fathi, Alessio Figalli 07 November 2007 Abstract In this work, we show how to obtain for non-compact manifolds the results that have already been
arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 2 Nov 2010
![arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 2 Nov 2010 arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 2 Nov 2010](/thumbs/94/121306739.jpg) LECTURE NOTES ON MATHER S THEORY FOR LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS ALFONSO SORRENTINO arxiv:111.59v1 [math.ds] 2 Nov 21 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Tonelli Lagrangians and Hamiltonians on compact manifolds 3 3.
LECTURE NOTES ON MATHER S THEORY FOR LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS ALFONSO SORRENTINO arxiv:111.59v1 [math.ds] 2 Nov 21 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Tonelli Lagrangians and Hamiltonians on compact manifolds 3 3.
Journal of Differential Equations
 J. Differential Equations 25 211) 2389 241 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Differential Equations www.elsevier.com/locate/jde A particular minimization property implies C -integrability
J. Differential Equations 25 211) 2389 241 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Differential Equations www.elsevier.com/locate/jde A particular minimization property implies C -integrability
Hyperbolic periodic orbits and Mather sets in certain symmetric cases
 Hyperbolic periodic orbits and Mather sets in certain symmetric cases M.-. ARNAUD July 12, 2006 Abstract We consider a Lagrangian function L : T M R which is superlinear and convex in the fibers and has
Hyperbolic periodic orbits and Mather sets in certain symmetric cases M.-. ARNAUD July 12, 2006 Abstract We consider a Lagrangian function L : T M R which is superlinear and convex in the fibers and has
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS, AND ASYMPTOTICS FOR HAMILTONIAN SYSTEMS
 VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS, AND ASYMPTOTICS FOR HAMILTONIAN SYSTEMS DIOGO AGUIAR GOMES U.C. Berkeley - CA, US and I.S.T. - Lisbon, Portugal email:dgomes@math.ist.utl.pt Abstract.
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS, AND ASYMPTOTICS FOR HAMILTONIAN SYSTEMS DIOGO AGUIAR GOMES U.C. Berkeley - CA, US and I.S.T. - Lisbon, Portugal email:dgomes@math.ist.utl.pt Abstract.
LECTURE NOTES ON MATHER S THEORY FOR LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS
 LECTURE NOTES ON MATHER S THEORY FOR LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS ALFONSO SORRENTINO Abstract. These notes are based on a series of lectures that the author gave at the CIMPA Research School Hamiltonian and Lagrangian
LECTURE NOTES ON MATHER S THEORY FOR LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS ALFONSO SORRENTINO Abstract. These notes are based on a series of lectures that the author gave at the CIMPA Research School Hamiltonian and Lagrangian
Weak KAM pairs and Monge-Kantorovich duality
 Advanced Studies in Pure Mathematics 47-2, 2007 Asymptotic Analysis and Singularities pp. 397 420 Weak KAM pairs and Monge-Kantorovich duality Abstract. Patrick Bernard and Boris Buffoni The dynamics of
Advanced Studies in Pure Mathematics 47-2, 2007 Asymptotic Analysis and Singularities pp. 397 420 Weak KAM pairs and Monge-Kantorovich duality Abstract. Patrick Bernard and Boris Buffoni The dynamics of
Chain recurrence, chain transitivity, Lyapunov functions and rigidity of Lagrangian submanifolds of optical hypersurfaces
 arxiv:1510.04491v1 [math.ds] 15 Oct 2015 Chain recurrence, chain transitivity, Lyapunov functions and rigidity of Lagrangian submanifolds of optical hypersurfaces Alberto Abbondandolo 1 Olga Bernardi 2
arxiv:1510.04491v1 [math.ds] 15 Oct 2015 Chain recurrence, chain transitivity, Lyapunov functions and rigidity of Lagrangian submanifolds of optical hypersurfaces Alberto Abbondandolo 1 Olga Bernardi 2
Transport Continuity Property
 On Riemannian manifolds satisfying the Transport Continuity Property Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis (Joint work with A. Figalli and C. Villani) I. Statement of the problem Optimal transport on Riemannian
On Riemannian manifolds satisfying the Transport Continuity Property Université de Nice - Sophia Antipolis (Joint work with A. Figalli and C. Villani) I. Statement of the problem Optimal transport on Riemannian
The Monge problem on non-compact manifolds
 The Monge problem on non-compact manifolds Alessio Figalli Scuola Normale Superiore Pisa Abstract In this paper we prove the existence of an optimal transport map on non-compact manifolds for a large class
The Monge problem on non-compact manifolds Alessio Figalli Scuola Normale Superiore Pisa Abstract In this paper we prove the existence of an optimal transport map on non-compact manifolds for a large class
A few words about the MTW tensor
 A few words about the Ma-Trudinger-Wang tensor Université Nice - Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France Salah Baouendi Memorial Conference (Tunis, March 2014) The Ma-Trudinger-Wang tensor
A few words about the Ma-Trudinger-Wang tensor Université Nice - Sophia Antipolis & Institut Universitaire de France Salah Baouendi Memorial Conference (Tunis, March 2014) The Ma-Trudinger-Wang tensor
Periodic Orbits of Weakly Exact Magnetic Flows
 Nonl. Analysis and Differential Equations, Vol. 1, 213, no. 2, 93-1 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Periodic Orbits of Weakly Exact Magnetic Flows Osvaldo Osuna Instituto de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad
Nonl. Analysis and Differential Equations, Vol. 1, 213, no. 2, 93-1 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Periodic Orbits of Weakly Exact Magnetic Flows Osvaldo Osuna Instituto de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad
CAUCHY PROBLEMS FOR STATIONARY HAMILTON JACOBI EQUATIONS UNDER MILD REGULARITY ASSUMPTIONS. Olga Bernardi and Franco Cardin.
 JOURNAL OF GEOMETRIC MECHANICS doi:10.3934/jgm.2009.1.271 c American Institute of Mathematical Sciences Volume 1, Number 3, September 2009 pp. 271 294 CAUCHY PROBLEMS FOR STATIONARY HAMILTON JACOBI EQUATIONS
JOURNAL OF GEOMETRIC MECHANICS doi:10.3934/jgm.2009.1.271 c American Institute of Mathematical Sciences Volume 1, Number 3, September 2009 pp. 271 294 CAUCHY PROBLEMS FOR STATIONARY HAMILTON JACOBI EQUATIONS
Weak KAM Theorem in Lagrangian Dynamics Preliminary Version Number 10. Albert FATHI
 Weak KAM Theorem in Lagrangian Dynamics Preliminary Version Number 10 Albert FATHI Lyon, Version 15 June 2008 ii Contents Preface vii Introduction ix 0.1 The Hamilton-Jacobi Method............ xi 1 Convex
Weak KAM Theorem in Lagrangian Dynamics Preliminary Version Number 10 Albert FATHI Lyon, Version 15 June 2008 ii Contents Preface vii Introduction ix 0.1 The Hamilton-Jacobi Method............ xi 1 Convex
HAMILTONIAN ELLIPTIC DYNAMICS ON SYMPLECTIC 4-MANIFOLDS
 HAMILTONIAN ELLIPTIC DYNAMICS ON SYMPLECTIC 4-MANIFOLDS MÁRIO BESSA AND JOÃO LOPES DIAS Abstract. We consider C 2 Hamiltonian functions on compact 4-dimensional symplectic manifolds to study elliptic dynamics
HAMILTONIAN ELLIPTIC DYNAMICS ON SYMPLECTIC 4-MANIFOLDS MÁRIO BESSA AND JOÃO LOPES DIAS Abstract. We consider C 2 Hamiltonian functions on compact 4-dimensional symplectic manifolds to study elliptic dynamics
Geometry of generating function and Lagrangian spectral invariants
 Geometry of generating function and Lagrangian spectral invariants Yong-Geun Oh IBS Center for Geometry and Physics & POSTECH & University of Wisconsin-Madsion Paris, Alanfest, July 18, 2012 Yong-Geun
Geometry of generating function and Lagrangian spectral invariants Yong-Geun Oh IBS Center for Geometry and Physics & POSTECH & University of Wisconsin-Madsion Paris, Alanfest, July 18, 2012 Yong-Geun
On the number of Mather measures of Lagrangian systems
 On the number of Mather measures of Lagrangian systems Patrick Bernard November 2009 Patrick Bernard 1 CEREMADE, CNRS Pl. du Maréchal de Lattre de Tassigny 75775 Paris Cedex 16 France patrick.bernard@ceremade.dauphine.fr
On the number of Mather measures of Lagrangian systems Patrick Bernard November 2009 Patrick Bernard 1 CEREMADE, CNRS Pl. du Maréchal de Lattre de Tassigny 75775 Paris Cedex 16 France patrick.bernard@ceremade.dauphine.fr
Invariant measures of Hamiltonian systems with prescribed asymptotic Maslov index
 Invariant measures of Hamiltonian systems with prescribed asymptotic Maslov index Alberto Abbondandolo and Alessio Figalli September 29, 27 Dedicated to Vladimir Igorevich Arnold Abstract We study the
Invariant measures of Hamiltonian systems with prescribed asymptotic Maslov index Alberto Abbondandolo and Alessio Figalli September 29, 27 Dedicated to Vladimir Igorevich Arnold Abstract We study the
REGULARITY THEORY FOR HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS
 REGULARITY THEORY FOR HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS DIOGO AGUIAR GOMES Abstract. The objective of this paper is to discuss the regularity of viscosity solutions of time independent Hamilton-Jacobi Equations.
REGULARITY THEORY FOR HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS DIOGO AGUIAR GOMES Abstract. The objective of this paper is to discuss the regularity of viscosity solutions of time independent Hamilton-Jacobi Equations.
THE PALAIS-SMALE CONDITION ON CONTACT TYPE ENERGY LEVELS FOR CONVEX LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS
 THE PALAIS-SMALE CONDITION ON CONTACT TYPE ENERGY LEVELS FOR CONVEX LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS Gonzalo Contreras Comunicación Técnica No I-3-1/25-4-23 (MB/CIMAT) THE PALAIS-SMALE CONDITION AND MAÑÉ S CRITICAL
THE PALAIS-SMALE CONDITION ON CONTACT TYPE ENERGY LEVELS FOR CONVEX LAGRANGIAN SYSTEMS Gonzalo Contreras Comunicación Técnica No I-3-1/25-4-23 (MB/CIMAT) THE PALAIS-SMALE CONDITION AND MAÑÉ S CRITICAL
Optimality Conditions for Nonsmooth Convex Optimization
 Optimality Conditions for Nonsmooth Convex Optimization Sangkyun Lee Oct 22, 2014 Let us consider a convex function f : R n R, where R is the extended real field, R := R {, + }, which is proper (f never
Optimality Conditions for Nonsmooth Convex Optimization Sangkyun Lee Oct 22, 2014 Let us consider a convex function f : R n R, where R is the extended real field, R := R {, + }, which is proper (f never
Optimal transportation and action-minimizing measures
 Scuola Normale Superiore of Pisa and École Normale Supérieure of Lyon Phd thesis 24th October 27 Optimal transportation and action-minimizing measures Alessio Figalli a.figalli@sns.it Advisor Prof. Luigi
Scuola Normale Superiore of Pisa and École Normale Supérieure of Lyon Phd thesis 24th October 27 Optimal transportation and action-minimizing measures Alessio Figalli a.figalli@sns.it Advisor Prof. Luigi
arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 1 May 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 1 May 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 1 May 2016](/thumbs/71/65571911.jpg) LECTURE NOTES ON CLOSED ORBITS FOR TWISTED AUTONOMOUS TONELLI LAGRANGIAN FLOWS GABRIELE BENEDETTI arxiv:165.258v1 [math.ds] 1 May 216 Abstract. These notes were prepared in occasion of a mini-course given
LECTURE NOTES ON CLOSED ORBITS FOR TWISTED AUTONOMOUS TONELLI LAGRANGIAN FLOWS GABRIELE BENEDETTI arxiv:165.258v1 [math.ds] 1 May 216 Abstract. These notes were prepared in occasion of a mini-course given
ON JOHN MATHER S SEMINAL CONTRIBUTIONS IN HAMILTONIAN DYNAMICS
 ON JOHN MATHER S SEMINAL CONTRIBUTIONS IN HAMILTONIAN DYNAMICS ALFONSO SORRENTINO To the memory of John N. Mather, a remarkable man and mathematician. (1942 2017) John N. Mather was undoubtedly one of
ON JOHN MATHER S SEMINAL CONTRIBUTIONS IN HAMILTONIAN DYNAMICS ALFONSO SORRENTINO To the memory of John N. Mather, a remarkable man and mathematician. (1942 2017) John N. Mather was undoubtedly one of
SOME REMARKS ON THE TOPOLOGY OF HYPERBOLIC ACTIONS OF R n ON n-manifolds
 SOME REMARKS ON THE TOPOLOGY OF HYPERBOLIC ACTIONS OF R n ON n-manifolds DAMIEN BOULOC Abstract. This paper contains some more results on the topology of a nondegenerate action of R n on a compact connected
SOME REMARKS ON THE TOPOLOGY OF HYPERBOLIC ACTIONS OF R n ON n-manifolds DAMIEN BOULOC Abstract. This paper contains some more results on the topology of a nondegenerate action of R n on a compact connected
Variational Analysis and Tame Optimization
 Variational Analysis and Tame Optimization Aris Daniilidis http://mat.uab.cat/~arisd Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona April 15 17, 2010 PLAN OF THE TALK Nonsmooth analysis Genericity of pathological situations
Variational Analysis and Tame Optimization Aris Daniilidis http://mat.uab.cat/~arisd Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona April 15 17, 2010 PLAN OF THE TALK Nonsmooth analysis Genericity of pathological situations
Vadim Kaloshin & Maria Saprykina
 An Example of a Nearly Integrable Hamiltonian System with a Trajectory Dense in a Set of Maximal Hausdorff Dimension Vadim Kaloshin & Maria Saprykina Communications in Mathematical Physics ISSN 1-3616
An Example of a Nearly Integrable Hamiltonian System with a Trajectory Dense in a Set of Maximal Hausdorff Dimension Vadim Kaloshin & Maria Saprykina Communications in Mathematical Physics ISSN 1-3616
NOTES AND ERRATA FOR RECURRENCE AND TOPOLOGY. (τ + arg z) + 1
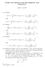 NOTES AND ERRATA FOR RECURRENCE AND TOPOLOGY JOHN M. ALONGI p.11 Replace ρ(t, z) = ρ(t, z) = p.11 Replace sin 2 z e τ ] 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 1 + z (e τ dτ. sin 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 z 2 z e τ ] 2 1 + z (e τ dτ.
NOTES AND ERRATA FOR RECURRENCE AND TOPOLOGY JOHN M. ALONGI p.11 Replace ρ(t, z) = ρ(t, z) = p.11 Replace sin 2 z e τ ] 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 1 + z (e τ dτ. sin 2 (τ + arg z) + 1 z 2 z e τ ] 2 1 + z (e τ dτ.
Whitney topology and spaces of preference relations. Abstract
 Whitney topology and spaces of preference relations Oleksandra Hubal Lviv National University Michael Zarichnyi University of Rzeszow, Lviv National University Abstract The strong Whitney topology on the
Whitney topology and spaces of preference relations Oleksandra Hubal Lviv National University Michael Zarichnyi University of Rzeszow, Lviv National University Abstract The strong Whitney topology on the
The Monge problem for supercritical Mañé potentials on compact manifolds
 Advances in Mathematics 27 (26) 691 76 www.elsevier.com/locate/aim The Monge problem for supercritical Mañé potentials on compact manifolds Patrick Bernard a,, Boris Buffoni b a Institut Fourier, Grenoble,
Advances in Mathematics 27 (26) 691 76 www.elsevier.com/locate/aim The Monge problem for supercritical Mañé potentials on compact manifolds Patrick Bernard a,, Boris Buffoni b a Institut Fourier, Grenoble,
1 )(y 0) {1}. Thus, the total count of points in (F 1 (y)) is equal to deg y0
 1. Classification of 1-manifolds Theorem 1.1. Let M be a connected 1 manifold. Then M is diffeomorphic either to [0, 1], [0, 1), (0, 1), or S 1. We know that none of these four manifolds are not diffeomorphic
1. Classification of 1-manifolds Theorem 1.1. Let M be a connected 1 manifold. Then M is diffeomorphic either to [0, 1], [0, 1), (0, 1), or S 1. We know that none of these four manifolds are not diffeomorphic
REGULAR DEPENDENCE OF THE PEIERLS BARRIERS ON PERTURBATIONS
 REGULAR DEPENDENCE OF THE PEIERLS BARRIERS ON PERTURBATIONS QINBO CHEN AND CHONG-QING CHENG Abstract. Let f be an exact area-preserving monotone twist diffeomorphism of the infinite cylinder and P ω,f
REGULAR DEPENDENCE OF THE PEIERLS BARRIERS ON PERTURBATIONS QINBO CHEN AND CHONG-QING CHENG Abstract. Let f be an exact area-preserving monotone twist diffeomorphism of the infinite cylinder and P ω,f
TOPOLOGY TAKE-HOME CLAY SHONKWILER
 TOPOLOGY TAKE-HOME CLAY SHONKWILER 1. The Discrete Topology Let Y = {0, 1} have the discrete topology. Show that for any topological space X the following are equivalent. (a) X has the discrete topology.
TOPOLOGY TAKE-HOME CLAY SHONKWILER 1. The Discrete Topology Let Y = {0, 1} have the discrete topology. Show that for any topological space X the following are equivalent. (a) X has the discrete topology.
An introduction to the Aubry-Mather theory
 São Paulo Journal of Mathematical Sciences 4, 1 (2010), 17 63 An introduction to the Aubry-Mather theory Andrey Biryuk and Diogo A. Gomes Departamento de Matemática and Center for Mathematical Analysis,
São Paulo Journal of Mathematical Sciences 4, 1 (2010), 17 63 An introduction to the Aubry-Mather theory Andrey Biryuk and Diogo A. Gomes Departamento de Matemática and Center for Mathematical Analysis,
ELAM XIV, Montevideo december 2005 Conservative dynamics and the calculus of variations
 ELAM XIV, Montevideo december 2005 Conservative dynamics and the calculus of variations Alain Chenciner Université Paris 7 & IMCCE chenciner@imcce.fr October 28, 2005 Abstract Starting with elementary
ELAM XIV, Montevideo december 2005 Conservative dynamics and the calculus of variations Alain Chenciner Université Paris 7 & IMCCE chenciner@imcce.fr October 28, 2005 Abstract Starting with elementary
LECTURE 15: COMPLETENESS AND CONVEXITY
 LECTURE 15: COMPLETENESS AND CONVEXITY 1. The Hopf-Rinow Theorem Recall that a Riemannian manifold (M, g) is called geodesically complete if the maximal defining interval of any geodesic is R. On the other
LECTURE 15: COMPLETENESS AND CONVEXITY 1. The Hopf-Rinow Theorem Recall that a Riemannian manifold (M, g) is called geodesically complete if the maximal defining interval of any geodesic is R. On the other
UTILITY OPTIMIZATION IN A FINITE SCENARIO SETTING
 UTILITY OPTIMIZATION IN A FINITE SCENARIO SETTING J. TEICHMANN Abstract. We introduce the main concepts of duality theory for utility optimization in a setting of finitely many economic scenarios. 1. Utility
UTILITY OPTIMIZATION IN A FINITE SCENARIO SETTING J. TEICHMANN Abstract. We introduce the main concepts of duality theory for utility optimization in a setting of finitely many economic scenarios. 1. Utility
Lecture 3: Lagrangian duality and algorithms for the Lagrangian dual problem
 Lecture 3: Lagrangian duality and algorithms for the Lagrangian dual problem Michael Patriksson 0-0 The Relaxation Theorem 1 Problem: find f := infimum f(x), x subject to x S, (1a) (1b) where f : R n R
Lecture 3: Lagrangian duality and algorithms for the Lagrangian dual problem Michael Patriksson 0-0 The Relaxation Theorem 1 Problem: find f := infimum f(x), x subject to x S, (1a) (1b) where f : R n R
Necessary conditions in optimal control and in the calculus of variations
 Necessary conditions in optimal control and in the calculus of variations Francis Clarke Institut universitaire de France et Institut Camille Jordan Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 69622 Villeurbanne,
Necessary conditions in optimal control and in the calculus of variations Francis Clarke Institut universitaire de France et Institut Camille Jordan Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1 69622 Villeurbanne,
Lipschitz shadowing implies structural stability
 Lipschitz shadowing implies structural stability Sergei Yu. Pilyugin Sergei B. Tihomirov Abstract We show that the Lipschitz shadowing property of a diffeomorphism is equivalent to structural stability.
Lipschitz shadowing implies structural stability Sergei Yu. Pilyugin Sergei B. Tihomirov Abstract We show that the Lipschitz shadowing property of a diffeomorphism is equivalent to structural stability.
Unique equilibrium states for geodesic flows in nonpositive curvature
 Unique equilibrium states for geodesic flows in nonpositive curvature Todd Fisher Department of Mathematics Brigham Young University Fractal Geometry, Hyperbolic Dynamics and Thermodynamical Formalism
Unique equilibrium states for geodesic flows in nonpositive curvature Todd Fisher Department of Mathematics Brigham Young University Fractal Geometry, Hyperbolic Dynamics and Thermodynamical Formalism
g 2 (x) (1/3)M 1 = (1/3)(2/3)M.
 COMPACTNESS If C R n is closed and bounded, then by B-W it is sequentially compact: any sequence of points in C has a subsequence converging to a point in C Conversely, any sequentially compact C R n is
COMPACTNESS If C R n is closed and bounded, then by B-W it is sequentially compact: any sequence of points in C has a subsequence converging to a point in C Conversely, any sequentially compact C R n is
Franks Lemma for C 2 Mane Perturbations of Riemannian Metrics and Applications to Persistence
 Franks Lemma for C Mane Perturbations of Riemannian Metrics and Applications to Persistence A Lazrag, Ludovic Rifford, Rafael Ruggiero To cite this version: A Lazrag, Ludovic Rifford, Rafael Ruggiero.
Franks Lemma for C Mane Perturbations of Riemannian Metrics and Applications to Persistence A Lazrag, Ludovic Rifford, Rafael Ruggiero To cite this version: A Lazrag, Ludovic Rifford, Rafael Ruggiero.
On fine differentiability properties of horizons and applications to Riemannian geometry
 On fine differentiability properties of horizons and applications to Riemannian geometry Piotr T. Chruściel Département de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences Parc de Grandmont F37200 Tours, France Joseph
On fine differentiability properties of horizons and applications to Riemannian geometry Piotr T. Chruściel Département de Mathématiques Faculté des Sciences Parc de Grandmont F37200 Tours, France Joseph
Hamiltonian Systems of Negative Curvature are Hyperbolic
 Hamiltonian Systems of Negative Curvature are Hyperbolic A. A. Agrachev N. N. Chtcherbakova Abstract The curvature and the reduced curvature are basic differential invariants of the pair: Hamiltonian system,
Hamiltonian Systems of Negative Curvature are Hyperbolic A. A. Agrachev N. N. Chtcherbakova Abstract The curvature and the reduced curvature are basic differential invariants of the pair: Hamiltonian system,
Symbolic extensions for partially hyperbolic diffeomorphisms
 for partially hyperbolic diffeomorphisms Todd Fisher tfisher@math.byu.edu Department of Mathematics Brigham Young University Workshop on Partial Hyperbolicity Entropy Topological entropy measures the exponential
for partially hyperbolic diffeomorphisms Todd Fisher tfisher@math.byu.edu Department of Mathematics Brigham Young University Workshop on Partial Hyperbolicity Entropy Topological entropy measures the exponential
A strong form of Arnold diffusion for two and a half degrees of freedom
 A strong form of Arnold diffusion for two and a half degrees of freedom arxiv:1212.1150v1 [math.ds] 5 Dec 2012 V. Kaloshin, K. Zhang February 7, 2014 Abstract In the present paper we prove a strong form
A strong form of Arnold diffusion for two and a half degrees of freedom arxiv:1212.1150v1 [math.ds] 5 Dec 2012 V. Kaloshin, K. Zhang February 7, 2014 Abstract In the present paper we prove a strong form
1. Let A R be a nonempty set that is bounded from above, and let a be the least upper bound of A. Show that there exists a sequence {a n } n N
 Applied Analysis prelim July 15, 216, with solutions Solve 4 of the problems 1-5 and 2 of the problems 6-8. We will only grade the first 4 problems attempted from1-5 and the first 2 attempted from problems
Applied Analysis prelim July 15, 216, with solutions Solve 4 of the problems 1-5 and 2 of the problems 6-8. We will only grade the first 4 problems attempted from1-5 and the first 2 attempted from problems
Duality and dynamics in Hamilton-Jacobi theory for fully convex problems of control
 Duality and dynamics in Hamilton-Jacobi theory for fully convex problems of control RTyrrell Rockafellar and Peter R Wolenski Abstract This paper describes some recent results in Hamilton- Jacobi theory
Duality and dynamics in Hamilton-Jacobi theory for fully convex problems of control RTyrrell Rockafellar and Peter R Wolenski Abstract This paper describes some recent results in Hamilton- Jacobi theory
A FRANKS LEMMA FOR CONVEX PLANAR BILLIARDS
 A FRANKS LEMMA FOR CONVEX PLANAR BILLIARDS DANIEL VISSCHER Abstract Let γ be an orbit of the billiard flow on a convex planar billiard table; then the perpendicular part of the derivative of the billiard
A FRANKS LEMMA FOR CONVEX PLANAR BILLIARDS DANIEL VISSCHER Abstract Let γ be an orbit of the billiard flow on a convex planar billiard table; then the perpendicular part of the derivative of the billiard
Equilibria with a nontrivial nodal set and the dynamics of parabolic equations on symmetric domains
 Equilibria with a nontrivial nodal set and the dynamics of parabolic equations on symmetric domains J. Földes Department of Mathematics, Univerité Libre de Bruxelles 1050 Brussels, Belgium P. Poláčik School
Equilibria with a nontrivial nodal set and the dynamics of parabolic equations on symmetric domains J. Földes Department of Mathematics, Univerité Libre de Bruxelles 1050 Brussels, Belgium P. Poláčik School
Action minimizing properties and distances on the group of Hamiltonian diffeomorphisms
 Action minimizing properties and distances on the group of Hamiltonian diffeomorphisms Alfonso Sorrentino Claude Viterbo 2 CEREMADE, UMR du CNRS 7534 Université Paris-Dauphine 75775 Paris Cedex 6, France
Action minimizing properties and distances on the group of Hamiltonian diffeomorphisms Alfonso Sorrentino Claude Viterbo 2 CEREMADE, UMR du CNRS 7534 Université Paris-Dauphine 75775 Paris Cedex 6, France
Convergence of discrete Aubry Mather model in the continuous limit
 Nonlinearity PAPER Convergence of discrete Aubry Mather model in the continuous limit To cite this article: Xifeng Su and Philippe Thieullen 2018 Nonlinearity 31 2126 Related content - Minimizing orbits
Nonlinearity PAPER Convergence of discrete Aubry Mather model in the continuous limit To cite this article: Xifeng Su and Philippe Thieullen 2018 Nonlinearity 31 2126 Related content - Minimizing orbits
BOLZA PROBLEMS WITH GENERAL TIME CONSTRAINTS P. D. LOEWEN AND R. T. ROCKAFELLAR
 PREPRINT, Prepared on 5 February 1996 c 1996 P. D. LOEWEN AND R. T. ROCKAFELLAR BOLZA PROBLEMS WITH GENERAL TIME CONSTRAINTS P. D. LOEWEN AND R. T. ROCKAFELLAR Abstract. This work provides necessary conditions
PREPRINT, Prepared on 5 February 1996 c 1996 P. D. LOEWEN AND R. T. ROCKAFELLAR BOLZA PROBLEMS WITH GENERAL TIME CONSTRAINTS P. D. LOEWEN AND R. T. ROCKAFELLAR Abstract. This work provides necessary conditions
LECTURE 10: THE PARALLEL TRANSPORT
 LECTURE 10: THE PARALLEL TRANSPORT 1. The parallel transport We shall start with the geometric meaning of linear connections. Suppose M is a smooth manifold with a linear connection. Let γ : [a, b] M be
LECTURE 10: THE PARALLEL TRANSPORT 1. The parallel transport We shall start with the geometric meaning of linear connections. Suppose M is a smooth manifold with a linear connection. Let γ : [a, b] M be
Asymptotic behavior of infinity harmonic functions near an isolated singularity
 Asymptotic behavior of infinity harmonic functions near an isolated singularity Ovidiu Savin, Changyou Wang, Yifeng Yu Abstract In this paper, we prove if n 2 x 0 is an isolated singularity of a nonegative
Asymptotic behavior of infinity harmonic functions near an isolated singularity Ovidiu Savin, Changyou Wang, Yifeng Yu Abstract In this paper, we prove if n 2 x 0 is an isolated singularity of a nonegative
CONSUMER DEMAND. Consumer Demand
 CONSUMER DEMAND KENNETH R. DRIESSEL Consumer Demand The most basic unit in microeconomics is the consumer. In this section we discuss the consumer optimization problem: The consumer has limited wealth
CONSUMER DEMAND KENNETH R. DRIESSEL Consumer Demand The most basic unit in microeconomics is the consumer. In this section we discuss the consumer optimization problem: The consumer has limited wealth
PARTIAL REGULARITY OF BRENIER SOLUTIONS OF THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION
 PARTIAL REGULARITY OF BRENIER SOLUTIONS OF THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION ALESSIO FIGALLI AND YOUNG-HEON KIM Abstract. Given Ω, Λ R n two bounded open sets, and f and g two probability densities concentrated
PARTIAL REGULARITY OF BRENIER SOLUTIONS OF THE MONGE-AMPÈRE EQUATION ALESSIO FIGALLI AND YOUNG-HEON KIM Abstract. Given Ω, Λ R n two bounded open sets, and f and g two probability densities concentrated
1.4 The Jacobian of a map
 1.4 The Jacobian of a map Derivative of a differentiable map Let F : M n N m be a differentiable map between two C 1 manifolds. Given a point p M we define the derivative of F at p by df p df (p) : T p
1.4 The Jacobian of a map Derivative of a differentiable map Let F : M n N m be a differentiable map between two C 1 manifolds. Given a point p M we define the derivative of F at p by df p df (p) : T p
LECTURE: KOBORDISMENTHEORIE, WINTER TERM 2011/12; SUMMARY AND LITERATURE
 LECTURE: KOBORDISMENTHEORIE, WINTER TERM 2011/12; SUMMARY AND LITERATURE JOHANNES EBERT 1.1. October 11th. 1. Recapitulation from differential topology Definition 1.1. Let M m, N n, be two smooth manifolds
LECTURE: KOBORDISMENTHEORIE, WINTER TERM 2011/12; SUMMARY AND LITERATURE JOHANNES EBERT 1.1. October 11th. 1. Recapitulation from differential topology Definition 1.1. Let M m, N n, be two smooth manifolds
The quasi-periodic Frenkel-Kontorova model
 The quasi-periodic Frenkel-Kontorova model Philippe Thieullen (Bordeaux) joint work with E. Garibaldi (Campinas) et S. Petite (Amiens) Korean-French Conference in Mathematics Pohang, August 24-28,2015
The quasi-periodic Frenkel-Kontorova model Philippe Thieullen (Bordeaux) joint work with E. Garibaldi (Campinas) et S. Petite (Amiens) Korean-French Conference in Mathematics Pohang, August 24-28,2015
Mathematical Appendix
 Ichiro Obara UCLA September 27, 2012 Obara (UCLA) Mathematical Appendix September 27, 2012 1 / 31 Miscellaneous Results 1. Miscellaneous Results This first section lists some mathematical facts that were
Ichiro Obara UCLA September 27, 2012 Obara (UCLA) Mathematical Appendix September 27, 2012 1 / 31 Miscellaneous Results 1. Miscellaneous Results This first section lists some mathematical facts that were
Maximal monotone operators are selfdual vector fields and vice-versa
 Maximal monotone operators are selfdual vector fields and vice-versa Nassif Ghoussoub Department of Mathematics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver BC Canada V6T 1Z2 nassif@math.ubc.ca February
Maximal monotone operators are selfdual vector fields and vice-versa Nassif Ghoussoub Department of Mathematics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver BC Canada V6T 1Z2 nassif@math.ubc.ca February
Aubry-Mather theory for homeomorphisms
 Aubry-Mather theory for homeomorphisms Albert Fathi & Pierre Pageault Abstract In this paper, we develop a variational approach to study the dynamic of a homeomorphism on a compact metric space. In particular,
Aubry-Mather theory for homeomorphisms Albert Fathi & Pierre Pageault Abstract In this paper, we develop a variational approach to study the dynamic of a homeomorphism on a compact metric space. In particular,
MIN-MAX REPRESENTATIONS OF VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS AND APPLICATIONS IN RARE-EVENT SIMULATION
 MIN-MAX REPRESENTATIONS OF VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS AND APPLICATIONS IN RARE-EVENT SIMULATION BOUALEM DJEHICHE, HENRIK HULT, AND PIERRE NYQUIST Abstract. In this paper a duality
MIN-MAX REPRESENTATIONS OF VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS OF HAMILTON-JACOBI EQUATIONS AND APPLICATIONS IN RARE-EVENT SIMULATION BOUALEM DJEHICHE, HENRIK HULT, AND PIERRE NYQUIST Abstract. In this paper a duality
An Eulerian Approach to Optimal Transport with Applications to the Otto Calculus. Benjamin Schachter
 An Eulerian Approach to Optimal Transport with Applications to the Otto Calculus by Benjamin Schachter A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Graduate
An Eulerian Approach to Optimal Transport with Applications to the Otto Calculus by Benjamin Schachter A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Graduate
ON A CLASS OF NONSMOOTH COMPOSITE FUNCTIONS
 MATHEMATICS OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 28, No. 4, November 2003, pp. 677 692 Printed in U.S.A. ON A CLASS OF NONSMOOTH COMPOSITE FUNCTIONS ALEXANDER SHAPIRO We discuss in this paper a class of nonsmooth
MATHEMATICS OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 28, No. 4, November 2003, pp. 677 692 Printed in U.S.A. ON A CLASS OF NONSMOOTH COMPOSITE FUNCTIONS ALEXANDER SHAPIRO We discuss in this paper a class of nonsmooth
1. Introduction Boundary estimates for the second derivatives of the solution to the Dirichlet problem for the Monge-Ampere equation
 POINTWISE C 2,α ESTIMATES AT THE BOUNDARY FOR THE MONGE-AMPERE EQUATION O. SAVIN Abstract. We prove a localization property of boundary sections for solutions to the Monge-Ampere equation. As a consequence
POINTWISE C 2,α ESTIMATES AT THE BOUNDARY FOR THE MONGE-AMPERE EQUATION O. SAVIN Abstract. We prove a localization property of boundary sections for solutions to the Monge-Ampere equation. As a consequence
The optimal partial transport problem
 The optimal partial transport problem Alessio Figalli Abstract Given two densities f and g, we consider the problem of transporting a fraction m [0, min{ f L 1, g L 1}] of the mass of f onto g minimizing
The optimal partial transport problem Alessio Figalli Abstract Given two densities f and g, we consider the problem of transporting a fraction m [0, min{ f L 1, g L 1}] of the mass of f onto g minimizing
Functional Analysis
 The Hahn Banach Theorem : Functional Analysis 1-9-06 Extensions of Linear Forms and Separation of Convex Sets Let E be a vector space over R and F E be a subspace. A function f : F R is linear if f(αx
The Hahn Banach Theorem : Functional Analysis 1-9-06 Extensions of Linear Forms and Separation of Convex Sets Let E be a vector space over R and F E be a subspace. A function f : F R is linear if f(αx
Lagrange duality. The Lagrangian. We consider an optimization program of the form
 Lagrange duality Another way to arrive at the KKT conditions, and one which gives us some insight on solving constrained optimization problems, is through the Lagrange dual. The dual is a maximization
Lagrange duality Another way to arrive at the KKT conditions, and one which gives us some insight on solving constrained optimization problems, is through the Lagrange dual. The dual is a maximization
arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 24 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 24 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.ds] 24 Jan 2019](/thumbs/94/121840007.jpg) Weak KAM theory in higher-dimensional holonomic measure flows Rodolfo Ríos-Zertuche arxiv:191.8181v1 [math.ds] 24 Jan 219 Abstract We construct a weak kam theory for higher-dimensional holonomic measures.
Weak KAM theory in higher-dimensional holonomic measure flows Rodolfo Ríos-Zertuche arxiv:191.8181v1 [math.ds] 24 Jan 219 Abstract We construct a weak kam theory for higher-dimensional holonomic measures.
MULTIFRACTAL ANALYSIS OF CONFORMAL AXIOM A FLOWS
 MULTIFRACTAL ANALYSIS OF CONFORMAL AXIOM A FLOWS YA. B. PESIN, V. SADOVSKAYA Abstract. We develop the multifractal analysis of conformal axiom A flows. This includes the study of the Hausdorff dimension
MULTIFRACTAL ANALYSIS OF CONFORMAL AXIOM A FLOWS YA. B. PESIN, V. SADOVSKAYA Abstract. We develop the multifractal analysis of conformal axiom A flows. This includes the study of the Hausdorff dimension
Donaldson Invariants and Moduli of Yang-Mills Instantons
 Donaldson Invariants and Moduli of Yang-Mills Instantons Lincoln College Oxford University (slides posted at users.ox.ac.uk/ linc4221) The ASD Equation in Low Dimensions, 17 November 2017 Moduli and Invariants
Donaldson Invariants and Moduli of Yang-Mills Instantons Lincoln College Oxford University (slides posted at users.ox.ac.uk/ linc4221) The ASD Equation in Low Dimensions, 17 November 2017 Moduli and Invariants
Intersections and translative integral formulas for boundaries of convex bodies
 to appear in Math. Nachr. (199?), Intersections translative integral formulas for boundaries of convex bodies By Daniel Hug Reiner Schätzle of Freiburg (Received November 06, 1998) Abstract. Let K, L IR
to appear in Math. Nachr. (199?), Intersections translative integral formulas for boundaries of convex bodies By Daniel Hug Reiner Schätzle of Freiburg (Received November 06, 1998) Abstract. Let K, L IR
1. Supremum and Infimum Remark: In this sections, all the subsets of R are assumed to be nonempty.
 1. Supremum and Infimum Remark: In this sections, all the subsets of R are assumed to be nonempty. Let E be a subset of R. We say that E is bounded above if there exists a real number U such that x U for
1. Supremum and Infimum Remark: In this sections, all the subsets of R are assumed to be nonempty. Let E be a subset of R. We say that E is bounded above if there exists a real number U such that x U for
Introduction to Continuous Dynamical Systems
 Lecture Notes on Introduction to Continuous Dynamical Systems Fall, 2012 Lee, Keonhee Department of Mathematics Chungnam National Univeristy - 1 - Chap 0. Introduction What is a dynamical system? A dynamical
Lecture Notes on Introduction to Continuous Dynamical Systems Fall, 2012 Lee, Keonhee Department of Mathematics Chungnam National Univeristy - 1 - Chap 0. Introduction What is a dynamical system? A dynamical
Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 2014
 Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
Equivariant self-similar wave maps from Minkowski spacetime into 3-sphere
 Equivariant self-similar wave maps from Minkowski spacetime into 3-sphere arxiv:math-ph/99126v1 17 Oct 1999 Piotr Bizoń Institute of Physics, Jagellonian University, Kraków, Poland March 26, 28 Abstract
Equivariant self-similar wave maps from Minkowski spacetime into 3-sphere arxiv:math-ph/99126v1 17 Oct 1999 Piotr Bizoń Institute of Physics, Jagellonian University, Kraków, Poland March 26, 28 Abstract
FOURTH ORDER CONSERVATIVE TWIST SYSTEMS: SIMPLE CLOSED CHARACTERISTICS
 FOURTH ORDER CONSERVATIVE TWIST SYSTEMS: SIMPLE CLOSED CHARACTERISTICS J.B. VAN DEN BERG AND R.C.A.M. VANDERVORST ABSTRACT. On the energy manifolds of fourth order conservative systems closed characteristics
FOURTH ORDER CONSERVATIVE TWIST SYSTEMS: SIMPLE CLOSED CHARACTERISTICS J.B. VAN DEN BERG AND R.C.A.M. VANDERVORST ABSTRACT. On the energy manifolds of fourth order conservative systems closed characteristics
Joint work with Nguyen Hoang (Univ. Concepción, Chile) Padova, Italy, May 2018
 EXTENDED EULER-LAGRANGE AND HAMILTONIAN CONDITIONS IN OPTIMAL CONTROL OF SWEEPING PROCESSES WITH CONTROLLED MOVING SETS BORIS MORDUKHOVICH Wayne State University Talk given at the conference Optimization,
EXTENDED EULER-LAGRANGE AND HAMILTONIAN CONDITIONS IN OPTIMAL CONTROL OF SWEEPING PROCESSES WITH CONTROLLED MOVING SETS BORIS MORDUKHOVICH Wayne State University Talk given at the conference Optimization,
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS. We follow Han and Lin, Elliptic Partial Differential Equations, 5.
 VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS PETER HINTZ We follow Han and Lin, Elliptic Partial Differential Equations, 5. 1. Motivation Throughout, we will assume that Ω R n is a bounded and connected domain and that a ij C(Ω)
VISCOSITY SOLUTIONS PETER HINTZ We follow Han and Lin, Elliptic Partial Differential Equations, 5. 1. Motivation Throughout, we will assume that Ω R n is a bounded and connected domain and that a ij C(Ω)
A CONSTRUCTION OF TRANSVERSE SUBMANIFOLDS
 UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA, FASCICULUS XLI 2003 A CONSTRUCTION OF TRANSVERSE SUBMANIFOLDS by J. Szenthe Abstract. In case of Riemannian manifolds isometric actions admitting submanifolds
UNIVERSITATIS IAGELLONICAE ACTA MATHEMATICA, FASCICULUS XLI 2003 A CONSTRUCTION OF TRANSVERSE SUBMANIFOLDS by J. Szenthe Abstract. In case of Riemannian manifolds isometric actions admitting submanifolds
NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination. Answer Key
 NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination Answer Key 1 1. [25 points] Let X be a set with 2 or more elements. Show that there are topologies U and V on X such that the identity map J : (X, U)
NAME: Mathematics 205A, Fall 2008, Final Examination Answer Key 1 1. [25 points] Let X be a set with 2 or more elements. Show that there are topologies U and V on X such that the identity map J : (X, U)
CHAPTER 7. Connectedness
 CHAPTER 7 Connectedness 7.1. Connected topological spaces Definition 7.1. A topological space (X, T X ) is said to be connected if there is no continuous surjection f : X {0, 1} where the two point set
CHAPTER 7 Connectedness 7.1. Connected topological spaces Definition 7.1. A topological space (X, T X ) is said to be connected if there is no continuous surjection f : X {0, 1} where the two point set
TRANSITIVITY OF FINSLER GEODESIC FLOWS IN COMPACT SURFACES WITHOUT CONJUGATE POINTS AND HIGHER GENUS
 TRANSITIVITY OF FINSLER GEODESIC FLOWS IN COMPACT SURFACES WITHOUT CONJUGATE POINTS AND HIGHER GENUS JOSÉ BARBOSA GOMES AND RAFAEL O. RUGGIERO Abstract. We show that the geodesic flow of a compact, C 4,
TRANSITIVITY OF FINSLER GEODESIC FLOWS IN COMPACT SURFACES WITHOUT CONJUGATE POINTS AND HIGHER GENUS JOSÉ BARBOSA GOMES AND RAFAEL O. RUGGIERO Abstract. We show that the geodesic flow of a compact, C 4,
