A NOTE ON THE LOCATION OF CRITICAL POINTS OF POLYNOMIALS
|
|
|
- Andra Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL Volume 27, No. 2, February 1971 SOCIETY A NOTE ON THE LOCATION OF CRITICAL POINTS OF POLYNOMIALS E. B. SAFF AND J. B. TWOMEY Abstract. Let(P(a, 3) denote the set of cubic polynomials which have all of their zeros in z SI and at least one zero at z=a ( a\ â 1). In this paper we describe a minimal region 2D(a, 3) with the property that every polynomial in (?(a, 3) has at least one critical point in 2D(o, 3). The location of the zeros of the logarithmic derivative of the function (z a)m(z z )mi(z gj)"2 is also discussed. 1. Introduction. Let p(z) be a polynomial of degree n (5; 2) having all its zeros in the closed disk 7: \z\ 1. Ilieff has conjectured [l, p. 25] that if a is a zero of p(z), then at least one critical point of p(z) (i.e., zero of p'(z)) lies in the disk 12 a :S 1. A more difficult problem related to this conjecture is stated in [2] as follows: Let <P(a, n) be the set of all nth degree polynomials which have all of their zeros in 7 and at least one zero at the point 2=a. Describe a region SD(o, n) such that (i) 2D(a, n) contains at least one critical point of every p(z)e(?(a, n) and such that (ii) no proper subset of )(a, n) has property (i). It is the aim of the present note to describe sets 2)(a, 3), a 1, and thereby improve the results of Schmeisser [3] and others [4], [5] concerning the location of critical points of cubic polynomials. We shall define only those sets 2D(a, 3) for which O^a^l, since the remaining sets can then be obtained by rotation. Our main result is Theorem 1. Letp(z) = (z o)(z 21) (2 z2), where O^a^l, 2i 1, and \z2\ 1. Let A (a) denote the closed disk A(a): I 2 - a/2 I <, ((4 - a2)/l2yi2, and C(a) denote Us circumference. Then p'(z) has at least one zero in the set >(a, 3) defined by SD(a, 3) = A(a)\[C(a)n{z:Im2 > 0}], a > 0, 0(0, 3) - A(0). Presented to the Society, March 28, 1970 under the title Critical points of polynomials; received by the editors March 16,1970. AMS 1969 subject classifications. Primary Key words and phrases. Critical points of polynomials, zeros of the derivative Ilieff conjecture, cubic polynomials, logarithmic derivatives of polynomials. Copyright 1971, American Mathematical Society 303
2 304 E. B. SAFF AND J. B. TWOMEY [February Furthermore if SD(a, 3) ts replaced by any proper subset of SD(a, 3), then the assertion is false. The proof of Theorem 1 is given in 2. In 3 we consider the location of the zeros of the logarithmic derivative of the function (z a)m(z zi)mi(z z2)m%, and in 4 we mention an open problem that is suggested by our results. 2. Proof of Theorem 1. The proof is based upon the following simple lemma: Lemma 1. ///(f) =b2ç2+biç+b0is nonzero in f <1, then (1) I *o = 5iii- Soil I Proof. The case 02=0 is trivial. The case 02^0 is at once reduced to 02=1. Let a, ß be the roots of f2+*if+&o = 0, \a\ 1, \ß\ èl. Then ( a -1)( /S -1)^0, and so a/3 +l^ a +\ß\. Multiplying both sides of the last inequality by a/3 1 = \bo\ 1 (^0) there follows ôo 2-l= «2 /3 + «j /? 2- \a\ - /81 which proves Lemma 1. We can now prove = (\a\2-l)\ß\ + (\ß\2-l)\a\ è ( a 2-l)/3 + ( /3 2-l)a = \h-hbil, Lemma 2. Let p(z) = (z a)(z Zi)(z z2), where 0<a^l, zi =1, and \Zi\ ál. // p'(z) has no zero inside C(a), then Zi=zi or a=zi = l or a=z2 = l. Furthermore, if pa(z)=(z a) (z eia) (z e~ia) and /a + 6A\ /a-6a\ 0 ± ai = cos-1 (-j S a S cos-11-1 = a2 S x, where A = ((4 a2)/12)1/2, then p'a(z) has a pair of conjugate zeros and as a varies from ai to a these zeros describe C(a). If, however, 0 Sa <«i or a2<a^x, then p'a(z) has a zero inside C(a). Proof. Let zi = exp [idi ] and z2 = r exp [id2] (0 S r S 1 ). To prove the first part of the lemma we note initially that since p'(z) is nonzero inside C(a), the polynomial P( )» P'(Aï + a/2) = 3^2f2 + A(a-2zi- 2zt)t + ZiZa - a2/4 is nonzero in f <1. Hence as a consequence (2) l*o 2- o2 2= Re(5!*a 5o&0, of (1) we have
3 1971] THE LOCATION OF CRITICAL POINTS OF POLYNOMIALS 305 where bk denotes the coefficient of f* in the expansion of P(Ç). Since Re(5,02 - hb!) = A[a(l - r 005(0! + 02)) - 2(1 - r2) cos 0,] and A ^a/2, we deduce from (2) that a2(l - r 005(0! + 02))/2 - (1 - r2) ^ a2(l - r cos(0i + 02))/2 - a cos 0,(1 - r2), that is (1 r2)(a cos0, 1) ^0. Hence either r = 1 or 1 =a=cos 0i = 2i. If r = l, then (2) implies that (a/2 - A)(\ - cos(0, + 02)) ê 0, and so either a/2=a, i.e., a = \, or cos(0i+02) =1, i.e., 22 = 21. Finally, if r = 1 and a = 1, we have equality in (2) and it follows from (1) that Im(5i >2 bobi) sin(0i + 02) sin 61 sin 02 = 0. This last equation implies that 01 = 0 or02= Oor0i+02 = O (mod 27r), i.e., 21 = 1 or 22 = 1 or z2=zi. The proof of the first part of Lemma 2 is now complete. To prove the second part we note that p'a(aç +a/2) has the zeros - (a - 4 cos a) ± [(a - 4 cos a)2-36a2]1'2 and that the quantity under the radical is nonpositive if ai ^0:^0:2. Furthermore, it is easily verified that as a varies from «i to a2 the points ft, 2 describe the boundary of the unit disk. Finally, if 0^a<o!i or a2<a^tt, then ft and f2 are real and unequal and, since their product is unity, it follows that one of them lies in f < 1. This implies the second part of Lemma 2 and concludes the proof. We next establish Lemma 3. Let p(z) = (z a)(z zi)(z z2), where Oga^l, zi <l, and \z2\ < 1. Then p'(z) has at least one zero inside C(a). Proof. Since zi <l and z2 <1, there exists a number p (0 <p < 1) such that q(w) = p(pw + (1 p)a) = p3(w a)(w wi)(w w2), where wi =1 and \w2\ ^1. By Lemma 2, q'(w) has a zero in w a/21 ^A and hence p'(z) has a zero (f^i) in the disk y(p, a): 2 - a/2 - (1 - p)a/2 ^ pa. Since A ^a/2 with equality only for a = 1, it is readily verified that
4 306 E. b. saff and J. B. TWOMEY [February every point of y(p, a), except z = 1 in the case a = 1, lies inside C(a). This proves the lemma. Combining Lemmas 2 and 3 we clearly obtain the first part of Theorem 1 for a>0. For a=0 the required result is an immediate consequence of the fact that the modulus of the product of the zeros of p'(z) is less than or equal to 1/3. To prove the second part of Theorem 1 for the case a>0 it suffices to show that for any point z0 inside C(a) there exists p(z)e (a, 3) such that p'(zo) =0 and p'(z)^0 for all z (^Zo) in D(o, 3). Consider first the polynomial p(z, t) = (z - a)(z - e«)(z - ß(t)), where ß(t) = (l-t)a+teis (O^í^l). For t = 0 we have p(z, 0) = (z-a)2(z-ei») so that p'(z, 0) has a zero at a and at (a+2e")/3. It is easy to see that the second zero lies outside C(a) except for the trivial case a =e's = 1. As t varies continuously from 0 to 1, each root of p'(z, t) varies continuously on the line segment [a, e**], one from a to (2a+eie)/3, the other from (a + 2e*)/3 to eie (compare [6, p. 24]). It follows, therefore, that no point Zo of the closed disk s 2a/31 iïl/3 can be omitted from 2D(a, 3). Suppose next that z0 is a point inside C(a) for which z0 2a/3 >l/3, and choose z0 ( z >1) such that the derivative of -Po(z) = (z a)(z z'0)2 has a zero at z0. We note that Pi («o) 1 2 (3) - =-+- = 0. -Po(zo) zo a Zo So Now consider the mapping /(z) = l/(z0 z). Under w = l(z) the unit circumference is mapped onto a circle V and z0 is mapped to a point w'0 inside T. Choose w{, w2 on V such that w'0 = (w[+w2)/2, and let z[, z'2 be the points on \z\ =1 that satisfy w[=l(z[), w'2=l(z2). It follows that (4) -r =-r +-r, Zo Zo Zo Zi Zo Z2 and, combining (3) and (4), we deduce that the derivative of po(z) ^(z a)(z z'i)(z zq has a zero at z = z0. Since \z[\ = z =1 implies that zízá a2/4 ^3^42, it is easily seen by considering the polynomial pó(ac+a/2) that the second zero of p'0(z) lies outside C(a). This proves Theorem 1 for a>0. For the case a = 0 we observe that the derivative of z(z - reia)(z - re"-"^'1), 0gag2x, 0 g r g 1,
5 1971] THE LOCATION OF CRITICAL POINTS OF POLYNOMIALS 307 has a double zero at 2 = re'ca+*'6>/v3, and hence no point may be omitted from SD(0, 3). This completes the proof of Theorem The logarithmic derivative. By applying the methods of 2 it is possible to prove Theorem 2. Let m, mi, and m2 be nonnegative real numbers with n=m-r-mi+m2>0, and suppose m mi m2 F(z) =-h-h-> z a z Zi z z where OiSa^l, zi I, and \z2\ 1. Set a(m, n) = (n m)a/(n + m), A(m, n) = (m(\ a(m, n)2)/n)112. Then F(z) has at least one zero in the disk (5) 2 a(m, n) ^ A(m, n). We note that if p(z) is a polynomial of the form p(z) = (z a)m(z Zi)mi(z 22)m2, where O^o^l, zi ^1, and z2 1, then Theorem 2 implies that p(z) has at least one critical point distinct from a in the disk (5). It follows easily from this that Ilieff's conjecture is true for such p(z). 4. Conjecture. The equation m * mk F(z) =-+ -= 0 z a k=i z zk (m^0,mk^0,n=m+mi+ +m,>0,0^a^l, \zk\ ^1 (l^k^s)) has a root f satisfying,. ( (m a(s l)m\) lh where a = (n m)a/(n + (s l)rw). Support for the conjecture comes from Theorem 2 (the case s = 2). It is also easy to verify that the conjecture is true for a =0. Its truth for a = 1 follows from a modification of the proof in [2 ]. We remark that for the case where w = l, mk = l (i^k^s), the conjecture is due to J. S. Ratti and is sharper than Ilieff's. The authors wish to thank the referee for suggesting an elementary proof of Lemma 1.
6 308 E. B. SAFF AND J. B. TWOMEY References 1. W. K. Hayman, Research problems in function theory, Athlone Press, London, MR 36 # A. W. Goodman, Q. I. Rahman and J. S. Ratti, On the zeros of a polynomial and its derivative, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 21 (1969), MR 39 # G. Schmeisser, Bermerkungen zu einer Vermutung von Ilieff, Math. Z. 111 (1969), D. A. Brannan, On a conjecture of Ilieff, Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 64 (1968), MR 36 # A. Joyal, On the zeros of a polynomial and its derivative, J. Math. Anal. Appl. 26 (1969), MR 39 # J. L. Walsh, The location of critical points of analytical and harmonic functions, Amer. Math. Soc. Colloq. Publ., vol. 34, Amer. Math. Soc, Providence, R. I., MR 12, 249. University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida 33620
p'(z) = nl[(z-cj), \Cj\<l (1 <;<"-!). 7 = 1
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 3, Number 4, December 99 ON THE SENDOV CONJECTURE FOR SIXTH DEGREE POLYNOMIALS JOHNNY E. BROWN (Communicated by Clifford J. Earle, Jr.) Abstract.
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 3, Number 4, December 99 ON THE SENDOV CONJECTURE FOR SIXTH DEGREE POLYNOMIALS JOHNNY E. BROWN (Communicated by Clifford J. Earle, Jr.) Abstract.
SOME PROPERTIES OF SELF-INVERSIVE POLYNOMIALS
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 44, Number 2, June 1974 SOME PROPERTIES OF SELF-INVERSIVE POLYNOMIALS P. J. O'HARA AND R. S. RODRIGUEZ Abstract. A complex polynomial is called self-inversive
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 44, Number 2, June 1974 SOME PROPERTIES OF SELF-INVERSIVE POLYNOMIALS P. J. O'HARA AND R. S. RODRIGUEZ Abstract. A complex polynomial is called self-inversive
1. Partial Fraction Expansion All the polynomials in this note are assumed to be complex polynomials.
 Partial Fraction Expansion All the polynomials in this note are assumed to be complex polynomials A rational function / is a quotient of two polynomials P, Q with 0 By Fundamental Theorem of algebra, =
Partial Fraction Expansion All the polynomials in this note are assumed to be complex polynomials A rational function / is a quotient of two polynomials P, Q with 0 By Fundamental Theorem of algebra, =
Polynomial expansions in the Borel region
 Polynomial expansions in the Borel region By J. T. HURT and L. R. FORD, Rice Institute, Houston, Texas. (Received 22nd August, 1936. Read 6th November, 1936.) This paper deals with certain expansions of
Polynomial expansions in the Borel region By J. T. HURT and L. R. FORD, Rice Institute, Houston, Texas. (Received 22nd August, 1936. Read 6th November, 1936.) This paper deals with certain expansions of
ON CONSTRUCTING NEARLY DECOMPOSABLE MATRICES D. J. HARTFIEL
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 27, No. 2, February 1971 ON CONSTRUCTING NEARLY DECOMPOSABLE MATRICES D. J. HARTFIEL Abstract. In this paper we consider the construction of nearly
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 27, No. 2, February 1971 ON CONSTRUCTING NEARLY DECOMPOSABLE MATRICES D. J. HARTFIEL Abstract. In this paper we consider the construction of nearly
A NOTE ON A BASIS PROBLEM
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 51, Number 2, September 1975 A NOTE ON A BASIS PROBLEM J. M. ANDERSON ABSTRACT. It is shown that the functions {exp xvx\v_. form a basis for the
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 51, Number 2, September 1975 A NOTE ON A BASIS PROBLEM J. M. ANDERSON ABSTRACT. It is shown that the functions {exp xvx\v_. form a basis for the
GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR THE JACOBI POLYNOMIAL M. E. COHEN
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 57, Number 2, June 1976 GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR THE JACOBI POLYNOMIAL M. E. COHEN Abstract. Two theorems are proved with the aid of operator and
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 57, Number 2, June 1976 GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR THE JACOBI POLYNOMIAL M. E. COHEN Abstract. Two theorems are proved with the aid of operator and
GROWTH NEAR THE BOUNDARY IN H2( i) SPACES1
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 62, Number 1, January 1977 GROWTH NEAR THE BOUNDARY IN H2( i) SPACES1 THOMAS KRIETE AND TAVAN TRENT Abstract. Let H\p.) be the closure in L\n) of
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 62, Number 1, January 1977 GROWTH NEAR THE BOUNDARY IN H2( i) SPACES1 THOMAS KRIETE AND TAVAN TRENT Abstract. Let H\p.) be the closure in L\n) of
SOME COUNTEREXAMPLES IN DYNAMICS OF RATIONAL SEMIGROUPS. 1. Introduction
 SOME COUNTEREXAMPLES IN DYNAMICS OF RATIONAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ, TOSHIYUKI SUGAWA, AND HIROKI SUMI Abstract. We give an example of two rational functions with non-equal Julia sets that generate
SOME COUNTEREXAMPLES IN DYNAMICS OF RATIONAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ, TOSHIYUKI SUGAWA, AND HIROKI SUMI Abstract. We give an example of two rational functions with non-equal Julia sets that generate
ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES OF OPERATOR ROOTS OF POLYNOMIALS
 ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES OF OPERATOR ROOTS OF POLYNOMIALS TRIEU LE Abstract. Properties of m-selfadjoint and m-isometric operators have been investigated by several researchers. Particularly interesting to
ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES OF OPERATOR ROOTS OF POLYNOMIALS TRIEU LE Abstract. Properties of m-selfadjoint and m-isometric operators have been investigated by several researchers. Particularly interesting to
POLYNOMIALS WITH A SHARP CAUCHY BOUND AND THEIR ZEROS OF MAXIMAL MODULUS
 M athematical Inequalities & Applications Volume 18, Number 4 (2015), 1387 1392 doi:10.7153/mia-18-108 POLYNOMIALS WITH A SHARP CAUCHY BOUND AND THEIR ZEROS OF MAXIMAL MODULUS HARALD K. WIMMER (Communicated
M athematical Inequalities & Applications Volume 18, Number 4 (2015), 1387 1392 doi:10.7153/mia-18-108 POLYNOMIALS WITH A SHARP CAUCHY BOUND AND THEIR ZEROS OF MAXIMAL MODULUS HARALD K. WIMMER (Communicated
Section 5.8. (i) ( 3 + i)(14 2i) = ( 3)(14 2i) + i(14 2i) = {( 3)14 ( 3)(2i)} + i(14) i(2i) = ( i) + (14i + 2) = i.
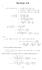 1. Section 5.8 (i) ( 3 + i)(14 i) ( 3)(14 i) + i(14 i) {( 3)14 ( 3)(i)} + i(14) i(i) ( 4 + 6i) + (14i + ) 40 + 0i. (ii) + 3i 1 4i ( + 3i)(1 + 4i) (1 4i)(1 + 4i) (( + 3i) + ( + 3i)(4i) 1 + 4 10 + 11i 10
1. Section 5.8 (i) ( 3 + i)(14 i) ( 3)(14 i) + i(14 i) {( 3)14 ( 3)(i)} + i(14) i(i) ( 4 + 6i) + (14i + ) 40 + 0i. (ii) + 3i 1 4i ( + 3i)(1 + 4i) (1 4i)(1 + 4i) (( + 3i) + ( + 3i)(4i) 1 + 4 10 + 11i 10
NOTE ON THE BESSEL POLYNOMIALS
 NOTE ON THE BESSEL POLYNOMIALS BY M. NASSIF 1. This note can be considered as an addendum to the comprehensive study of the class of Bessel polynomials carried on by H. L. Krall and O. Frink [l ]. In fact
NOTE ON THE BESSEL POLYNOMIALS BY M. NASSIF 1. This note can be considered as an addendum to the comprehensive study of the class of Bessel polynomials carried on by H. L. Krall and O. Frink [l ]. In fact
CHAINS IN PARTIALLY ORDERED SETS
 CHAINS IN PARTIALLY ORDERED SETS OYSTEIN ORE 1. Introduction. Dedekind [l] in his remarkable paper on Dualgruppen was the first to analyze the axiomatic basis for the theorem of Jordan-Holder in groups.
CHAINS IN PARTIALLY ORDERED SETS OYSTEIN ORE 1. Introduction. Dedekind [l] in his remarkable paper on Dualgruppen was the first to analyze the axiomatic basis for the theorem of Jordan-Holder in groups.
THE NORM OF A HERMITIAN ELEMENT IN A BANACH ALGEBRA
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY ' Volume 28, Number 2, May 1971 THE NORM OF A HERMITIAN ELEMENT IN A BANACH ALGEBRA A. M. SINCLAIR Abstract. We prove that the norm of a hermitian element
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY ' Volume 28, Number 2, May 1971 THE NORM OF A HERMITIAN ELEMENT IN A BANACH ALGEBRA A. M. SINCLAIR Abstract. We prove that the norm of a hermitian element
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 998 Comments to the author at krm@mathsuqeduau All contents copyright c 99 Keith
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 998 Comments to the author at krm@mathsuqeduau All contents copyright c 99 Keith
LENGTH AND AREA ESTIMATES OF THE DERIVATIVES OF BOUNDED HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume KK, Number I. May 1983 LENGTH AND AREA ESTIMATES OF THE DERIVATIVES OF BOUNDED HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS SHINJI YAMASHITA Abstract. MacGregor [1] and
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume KK, Number I. May 1983 LENGTH AND AREA ESTIMATES OF THE DERIVATIVES OF BOUNDED HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS SHINJI YAMASHITA Abstract. MacGregor [1] and
ON TOPOLOGISING THE FIELD C(t)
 ON TOPOLOGISING THE FIELD C(t) J. H. WILLIAMSON In many questions concerning the existence of fields over the complex field, with topologies satisfying given compatibility axioms, it is sufficient to restrict
ON TOPOLOGISING THE FIELD C(t) J. H. WILLIAMSON In many questions concerning the existence of fields over the complex field, with topologies satisfying given compatibility axioms, it is sufficient to restrict
ON ANALYTIC CONTINUATION TO A SCHLICHT FUNCTION1 CARL H. FITZGERALD
 ON ANALYTIC CONTINUATION TO A SCHLICHT FUNCTION1 CARL H. FITZGERALD This paper presents a characterization of the real functions on an interval of the real axis which can be analytically continued to be
ON ANALYTIC CONTINUATION TO A SCHLICHT FUNCTION1 CARL H. FITZGERALD This paper presents a characterization of the real functions on an interval of the real axis which can be analytically continued to be
MAXIMAL SUBALGEBRAS AND CHIEF FACTORS OF LIE ALGEBRAS DAVID A. TOWERS
 MAXIMAL SUBALGEBRAS AND CHIEF FACTORS OF LIE ALGEBRAS DAVID A. TOWERS Department of Mathematics and Statistics Lancaster University Lancaster LA1 4YF England d.towers@lancaster.ac.uk Abstract This paper
MAXIMAL SUBALGEBRAS AND CHIEF FACTORS OF LIE ALGEBRAS DAVID A. TOWERS Department of Mathematics and Statistics Lancaster University Lancaster LA1 4YF England d.towers@lancaster.ac.uk Abstract This paper
ON A SINE POLYNOMIAL OF TURÁN
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 48, Number 1, 18 ON A SINE POLYNOMIAL OF TURÁN HORST ALZER AND MAN KAM KWONG ABSTRACT. In 1935, Turán proved that ( n + a j ) S n,a() = sin(j) >, n j n, a N,
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 48, Number 1, 18 ON A SINE POLYNOMIAL OF TURÁN HORST ALZER AND MAN KAM KWONG ABSTRACT. In 1935, Turán proved that ( n + a j ) S n,a() = sin(j) >, n j n, a N,
(2) ^max^lpm g M/?"[l - ^-(l - /T1)2}
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 56, April 1976 SOME INEQUALITIES FOR POLYNOMIALS Q. I. RAHMAN Abstract. Let pn(z) be a polynomial of degree n. Given that pn(z) has a zero on the
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 56, April 1976 SOME INEQUALITIES FOR POLYNOMIALS Q. I. RAHMAN Abstract. Let pn(z) be a polynomial of degree n. Given that pn(z) has a zero on the
On the Bank Laine conjecture
 J. Eur. Math. Soc. 19, 1899 199 c European Mathematical Society 217 DOI 1.4171/JEMS/78 Walter Bergweiler Alexandre Eremenko On the Bank Laine conjecture Received August 11, 214 and in revised form March
J. Eur. Math. Soc. 19, 1899 199 c European Mathematical Society 217 DOI 1.4171/JEMS/78 Walter Bergweiler Alexandre Eremenko On the Bank Laine conjecture Received August 11, 214 and in revised form March
ON PERMUTATION POLYNOMIALS OF PRESCRIBED SHAPE
 ON PERMUTATION POLYNOMIALS OF PRESCRIBED SHAPE AMIR AKBARY, DRAGOS GHIOCA, AND QIANG WANG Abstract. We count permutation polynomials of F q which are sums of m + 2 monomials of prescribed degrees. This
ON PERMUTATION POLYNOMIALS OF PRESCRIBED SHAPE AMIR AKBARY, DRAGOS GHIOCA, AND QIANG WANG Abstract. We count permutation polynomials of F q which are sums of m + 2 monomials of prescribed degrees. This
SMOOTHNESS OF FUNCTIONS GENERATED BY RIESZ PRODUCTS
 SMOOTHNESS OF FUNCTIONS GENERATED BY RIESZ PRODUCTS PETER L. DUREN Riesz products are a useful apparatus for constructing singular functions with special properties. They have been an important source
SMOOTHNESS OF FUNCTIONS GENERATED BY RIESZ PRODUCTS PETER L. DUREN Riesz products are a useful apparatus for constructing singular functions with special properties. They have been an important source
Analog of Hayman Conjecture for linear difference polynomials
 Analog of Hayman Conjecture for linear difference polynomials RAJ SHREE DHAR Higher Education Department, J and K Government Jammu and Kashmir,INDIA dhar.rajshree@jk.gov.in September 9, 2018 Abstract We
Analog of Hayman Conjecture for linear difference polynomials RAJ SHREE DHAR Higher Education Department, J and K Government Jammu and Kashmir,INDIA dhar.rajshree@jk.gov.in September 9, 2018 Abstract We
SOME HILBERT SPACE EXTREMAL PROBLEMS
 SOME HILBERT SPACE EXTREMAL PROBLEMS MARVIN ROSENBLUM1 In this note we shall generalize in several ways the following theorem of Philip Davis: Let I2 be a real or complex sequential Hubert space. Fix \hj\o
SOME HILBERT SPACE EXTREMAL PROBLEMS MARVIN ROSENBLUM1 In this note we shall generalize in several ways the following theorem of Philip Davis: Let I2 be a real or complex sequential Hubert space. Fix \hj\o
Some theorems on the explicit evaluations of singular moduli 1
 General Mathematics Vol 17 No 1 009) 71 87 Some theorems on the explicit evaluations of singular moduli 1 K Sushan Bairy Abstract At scattered places in his notebooks Ramanujan recorded some theorems for
General Mathematics Vol 17 No 1 009) 71 87 Some theorems on the explicit evaluations of singular moduli 1 K Sushan Bairy Abstract At scattered places in his notebooks Ramanujan recorded some theorems for
Z(J5L_ + J«L+...+_«_
 ON THE LOCATION OF THE ROOTS OF THE JACOBIAN OF TWO BINARY FORMS, AND OF THE DERIVATIVE OF A RATIONAL FUNCTION* By J. L. WALSH Introduction Professor Bôcher has shown how the roots of certain algebraic
ON THE LOCATION OF THE ROOTS OF THE JACOBIAN OF TWO BINARY FORMS, AND OF THE DERIVATIVE OF A RATIONAL FUNCTION* By J. L. WALSH Introduction Professor Bôcher has shown how the roots of certain algebraic
du+ z f 2(u) , which generalized the result corresponding to the class of analytic functions given by Nash.
 Korean J. Math. 24 (2016), No. 3, pp. 36 374 http://dx.doi.org/10.11568/kjm.2016.24.3.36 SHARP HEREDITARY CONVEX RADIUS OF CONVEX HARMONIC MAPPINGS UNDER AN INTEGRAL OPERATOR Xingdi Chen and Jingjing Mu
Korean J. Math. 24 (2016), No. 3, pp. 36 374 http://dx.doi.org/10.11568/kjm.2016.24.3.36 SHARP HEREDITARY CONVEX RADIUS OF CONVEX HARMONIC MAPPINGS UNDER AN INTEGRAL OPERATOR Xingdi Chen and Jingjing Mu
On Strongly Prime Semiring
 BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://math.usm.my/bulletin Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. (2) 30(2) (2007), 135 141 On Strongly Prime Semiring T.K. Dutta and M.L. Das Department
BULLETIN of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society http://math.usm.my/bulletin Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. (2) 30(2) (2007), 135 141 On Strongly Prime Semiring T.K. Dutta and M.L. Das Department
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
Bounds for the Eventual Positivity of Difference Functions of Partitions into Prime Powers
 3 47 6 3 Journal of Integer Seuences, Vol. (7), rticle 7..3 ounds for the Eventual Positivity of Difference Functions of Partitions into Prime Powers Roger Woodford Department of Mathematics University
3 47 6 3 Journal of Integer Seuences, Vol. (7), rticle 7..3 ounds for the Eventual Positivity of Difference Functions of Partitions into Prime Powers Roger Woodford Department of Mathematics University
NIL DERIVATIONS AND CHAIN CONDITIONS IN PRIME RINGS
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 94, Number 2, June 1985 NIL DERIVATIONS AND CHAIN CONDITIONS IN PRIME RINGS L. O. CHUNG AND Y. OBAYASHI Abstract. It is known that in a prime ring,
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 94, Number 2, June 1985 NIL DERIVATIONS AND CHAIN CONDITIONS IN PRIME RINGS L. O. CHUNG AND Y. OBAYASHI Abstract. It is known that in a prime ring,
SEMIRINGS SATISFYING PROPERTIES OF DISTRIBUTIVE TYPE
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 82, Number 3, July 1981 SEMIRINGS SATISFYING PROPERTIES OF DISTRIBUTIVE TYPE ARIF KAYA AND M. SATYANARAYANA Abstract. Any distributive lattice admits
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 82, Number 3, July 1981 SEMIRINGS SATISFYING PROPERTIES OF DISTRIBUTIVE TYPE ARIF KAYA AND M. SATYANARAYANA Abstract. Any distributive lattice admits
ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES OF WEAK PERRON NUMBERS. 1. Introduction
 t m Mathematical Publications DOI: 10.2478/tmmp-2013-0023 Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 56 (2013), 27 33 ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES OF WEAK PERRON NUMBERS Horst Brunotte ABSTRACT. We study algebraic properties of real
t m Mathematical Publications DOI: 10.2478/tmmp-2013-0023 Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 56 (2013), 27 33 ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES OF WEAK PERRON NUMBERS Horst Brunotte ABSTRACT. We study algebraic properties of real
A SIMPLIFIED FORM FOR NEARLY REDUCIBLE AND NEARLY DECOMPOSABLE MATRICES D. J. HARTFIEL
 A SIMPLIFIED FORM FOR NEARLY REDUCIBLE AND NEARLY DECOMPOSABLE MATRICES D. J. HARTFIEL Introduction and definitions. Nearly reducible and nearly decomposable matrices have been discussed in [4], [5], and
A SIMPLIFIED FORM FOR NEARLY REDUCIBLE AND NEARLY DECOMPOSABLE MATRICES D. J. HARTFIEL Introduction and definitions. Nearly reducible and nearly decomposable matrices have been discussed in [4], [5], and
SOME EXAMPLES OF ALGEBRAIC DEGENERACY AND HYPERBOLIC MANIFOLDS
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 10, Number 3, Summer 1980 SOME EXAMPLES OF ALGEBRAIC DEGENERACY AND HYPERBOLIC MANIFOLDS KAZUO AZUKAWA AND MASAAKI SUZUKI 1. Introduction. Let D be an algebraic
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 10, Number 3, Summer 1980 SOME EXAMPLES OF ALGEBRAIC DEGENERACY AND HYPERBOLIC MANIFOLDS KAZUO AZUKAWA AND MASAAKI SUZUKI 1. Introduction. Let D be an algebraic
Pade approximants and noise: rational functions
 Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 105 (1999) 285 297 Pade approximants and noise: rational functions Jacek Gilewicz a; a; b;1, Maciej Pindor a Centre de Physique Theorique, Unite Propre
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 105 (1999) 285 297 Pade approximants and noise: rational functions Jacek Gilewicz a; a; b;1, Maciej Pindor a Centre de Physique Theorique, Unite Propre
CHARACTERIZATIONS OF LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEMS WITH A REGULAR SINGULAR POINT
 CHARACTERIZATIONS OF LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEMS WITH A REGULAR SINGULAR POINT The linear differential system by W. A. HARRIS, Jr. (Received 25th July 1971) -T = Az)w (1) where w is a vector with n components
CHARACTERIZATIONS OF LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEMS WITH A REGULAR SINGULAR POINT The linear differential system by W. A. HARRIS, Jr. (Received 25th July 1971) -T = Az)w (1) where w is a vector with n components
BANK-LAINE FUNCTIONS WITH SPARSE ZEROS
 BANK-LAINE FUNCTIONS WITH SPARSE ZEROS J.K. LANGLEY Abstract. A Bank-Laine function is an entire function E satisfying E (z) = ± at every zero of E. We construct a Bank-Laine function of finite order with
BANK-LAINE FUNCTIONS WITH SPARSE ZEROS J.K. LANGLEY Abstract. A Bank-Laine function is an entire function E satisfying E (z) = ± at every zero of E. We construct a Bank-Laine function of finite order with
ADVANCED PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
 Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 17745. This department especially welcomes problems
Edited by RAYMOND E. WHITNEY Please send all communications concerning to RAYMOND E. WHITNEY, MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT, LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY, LOCK HAVEN, PA 17745. This department especially welcomes problems
On Bank-Laine functions
 Computational Methods and Function Theory Volume 00 0000), No. 0, 000 000 XXYYYZZ On Bank-Laine functions Alastair Fletcher Keywords. Bank-Laine functions, zeros. 2000 MSC. 30D35, 34M05. Abstract. In this
Computational Methods and Function Theory Volume 00 0000), No. 0, 000 000 XXYYYZZ On Bank-Laine functions Alastair Fletcher Keywords. Bank-Laine functions, zeros. 2000 MSC. 30D35, 34M05. Abstract. In this
(1) 0 á per(a) Í f[ U, <=i
 ON LOWER BOUNDS FOR PERMANENTS OF (, 1) MATRICES1 HENRYK MINC 1. Introduction. The permanent of an «-square matrix A = (a^) is defined by veria) = cesn n II «"( j. If A is a (, 1) matrix, i.e. a matrix
ON LOWER BOUNDS FOR PERMANENTS OF (, 1) MATRICES1 HENRYK MINC 1. Introduction. The permanent of an «-square matrix A = (a^) is defined by veria) = cesn n II «"( j. If A is a (, 1) matrix, i.e. a matrix
UNIFORM BOUNDS FOR BESSEL FUNCTIONS
 Journal of Applied Analysis Vol. 1, No. 1 (006), pp. 83 91 UNIFORM BOUNDS FOR BESSEL FUNCTIONS I. KRASIKOV Received October 8, 001 and, in revised form, July 6, 004 Abstract. For ν > 1/ and x real we shall
Journal of Applied Analysis Vol. 1, No. 1 (006), pp. 83 91 UNIFORM BOUNDS FOR BESSEL FUNCTIONS I. KRASIKOV Received October 8, 001 and, in revised form, July 6, 004 Abstract. For ν > 1/ and x real we shall
POLYNOMIALS WITH COEFFICIENTS FROM A FINITE SET
 ao DOI: 1.478/s1175-14-8-y Math. Slovaca 64 (14), No. 6, 1397 148 POLYNOMIALS WITH COEFFICIENTS FROM A FINITE SET Javad Baradaran* Mohsen Taghavi** (Communicated by Stanis lawa Kanas ) ABSTRACT. This paper
ao DOI: 1.478/s1175-14-8-y Math. Slovaca 64 (14), No. 6, 1397 148 POLYNOMIALS WITH COEFFICIENTS FROM A FINITE SET Javad Baradaran* Mohsen Taghavi** (Communicated by Stanis lawa Kanas ) ABSTRACT. This paper
THE ZERO-DISTRIBUTION AND THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF A FOURIER INTEGRAL. Haseo Ki and Young One Kim
 THE ZERO-DISTRIBUTION AND THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF A FOURIER INTEGRAL Haseo Ki Young One Kim Abstract. The zero-distribution of the Fourier integral Q(u)eP (u)+izu du, where P is a polynomial with leading
THE ZERO-DISTRIBUTION AND THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR OF A FOURIER INTEGRAL Haseo Ki Young One Kim Abstract. The zero-distribution of the Fourier integral Q(u)eP (u)+izu du, where P is a polynomial with leading
Uniformly convex functions II
 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LVIII. (199 Uniformly convex functions II by Wancang Ma and David Minda (Cincinnati, Ohio Abstract. Recently, A. W. Goodman introduced the class UCV of normalized uniformly
ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LVIII. (199 Uniformly convex functions II by Wancang Ma and David Minda (Cincinnati, Ohio Abstract. Recently, A. W. Goodman introduced the class UCV of normalized uniformly
A CHARACTERIZATION OF INNER PRODUCT SPACES
 A CHARACTERIZATION OF INNER PRODUCT SPACES DAVID ALBERT SENECHALLE The well-known parallelogram law of Jordan and von Neumann [l] has been generalized in two different ways by M. M. Day [2] and E. R. Lorch
A CHARACTERIZATION OF INNER PRODUCT SPACES DAVID ALBERT SENECHALLE The well-known parallelogram law of Jordan and von Neumann [l] has been generalized in two different ways by M. M. Day [2] and E. R. Lorch
Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing , People s Republic of China
 J. Number Theory 16(016), 190 11. A RESULT SIMILAR TO LAGRANGE S THEOREM Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 10093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
J. Number Theory 16(016), 190 11. A RESULT SIMILAR TO LAGRANGE S THEOREM Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 10093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
BERGMAN OPERATORS FOR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS IN THREE INDEPENDENT VARIABLES
 BULLETIN OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 77, Number 5, September 1971 BERGMAN OPERATORS FOR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS IN THREE INDEPENDENT VARIABLES BY DAVID COLTON Communicated by Fred Brauer, March
BULLETIN OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 77, Number 5, September 1971 BERGMAN OPERATORS FOR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS IN THREE INDEPENDENT VARIABLES BY DAVID COLTON Communicated by Fred Brauer, March
and A", where (1) p- 8/+ 1 = X2 + Y2 = C2 + 2D2, C = X=\ (mod4).
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 87, Number 3. March 1983 THE Odie PERIOD POLYNOMIAL RONALD J. EVANS1 Abstract. The coefficients and the discriminant of the octic period polynomial
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 87, Number 3. March 1983 THE Odie PERIOD POLYNOMIAL RONALD J. EVANS1 Abstract. The coefficients and the discriminant of the octic period polynomial
IMPROVED RESULTS ON THE OSCILLATION OF THE MODULUS OF THE RUDIN-SHAPIRO POLYNOMIALS ON THE UNIT CIRCLE. September 12, 2018
 IMPROVED RESULTS ON THE OSCILLATION OF THE MODULUS OF THE RUDIN-SHAPIRO POLYNOMIALS ON THE UNIT CIRCLE Tamás Erdélyi September 12, 2018 Dedicated to Paul Nevai on the occasion of his 70th birthday Abstract.
IMPROVED RESULTS ON THE OSCILLATION OF THE MODULUS OF THE RUDIN-SHAPIRO POLYNOMIALS ON THE UNIT CIRCLE Tamás Erdélyi September 12, 2018 Dedicated to Paul Nevai on the occasion of his 70th birthday Abstract.
A NOTE ON THE DEGREE OF POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION*
 1936.] DEGREE OF POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION 873 am = #121 = #212= 1 The trilinear form associated with this matrix is x 1 yiz2+xiy2zi+x2yizi, which is equivalent to L under the transformations Xi = xi, X2
1936.] DEGREE OF POLYNOMIAL APPROXIMATION 873 am = #121 = #212= 1 The trilinear form associated with this matrix is x 1 yiz2+xiy2zi+x2yizi, which is equivalent to L under the transformations Xi = xi, X2
On Riemann Boundary Value Problem in Hardy Classes with Variable Summability Exponent
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 15, 743-751 On Riemann Boundary Value Problem in Hardy Classes with Variable Summability Exponent Muradov T.R. Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics of
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 15, 743-751 On Riemann Boundary Value Problem in Hardy Classes with Variable Summability Exponent Muradov T.R. Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics of
TOPOLOGICAL ENTROPY FOR DIFFERENTIABLE MAPS OF INTERVALS
 Chung, Y-.M. Osaka J. Math. 38 (200), 2 TOPOLOGICAL ENTROPY FOR DIFFERENTIABLE MAPS OF INTERVALS YONG MOO CHUNG (Received February 9, 998) Let Á be a compact interval of the real line. For a continuous
Chung, Y-.M. Osaka J. Math. 38 (200), 2 TOPOLOGICAL ENTROPY FOR DIFFERENTIABLE MAPS OF INTERVALS YONG MOO CHUNG (Received February 9, 998) Let Á be a compact interval of the real line. For a continuous
Numerical Range in C*-Algebras
 Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 6, No. 2, (2012), 91-98 Numerical Range in C*-Algebras M. T. Heydari Yasouj University Abstract. Let A be a C*-algebra with unit 1 and let S be the state space of
Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 6, No. 2, (2012), 91-98 Numerical Range in C*-Algebras M. T. Heydari Yasouj University Abstract. Let A be a C*-algebra with unit 1 and let S be the state space of
PILLAI S CONJECTURE REVISITED
 PILLAI S COJECTURE REVISITED MICHAEL A. BEETT Abstract. We prove a generalization of an old conjecture of Pillai now a theorem of Stroeker and Tijdeman) to the effect that the Diophantine equation 3 x
PILLAI S COJECTURE REVISITED MICHAEL A. BEETT Abstract. We prove a generalization of an old conjecture of Pillai now a theorem of Stroeker and Tijdeman) to the effect that the Diophantine equation 3 x
Abstract. For the Briot-Bouquet differential equations of the form given in [1] zu (z) u(z) = h(z),
![Abstract. For the Briot-Bouquet differential equations of the form given in [1] zu (z) u(z) = h(z), Abstract. For the Briot-Bouquet differential equations of the form given in [1] zu (z) u(z) = h(z),](/thumbs/92/109673972.jpg) J. Korean Math. Soc. 43 (2006), No. 2, pp. 311 322 STRONG DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION AND APPLICATIONS TO UNIVALENCY CONDITIONS José A. Antonino Astract. For the Briot-Bouquet differential equations of
J. Korean Math. Soc. 43 (2006), No. 2, pp. 311 322 STRONG DIFFERENTIAL SUBORDINATION AND APPLICATIONS TO UNIVALENCY CONDITIONS José A. Antonino Astract. For the Briot-Bouquet differential equations of
Mapping the disk to convex subregions
 Mapping the disk to convex subregions John A. Velling 11 March 1995 1. Introduction. Univalent maps f : D D have been much studied by many authors. See [1], [2], [5], for just a few references. A quick
Mapping the disk to convex subregions John A. Velling 11 March 1995 1. Introduction. Univalent maps f : D D have been much studied by many authors. See [1], [2], [5], for just a few references. A quick
FORMAL TAYLOR SERIES AND COMPLEMENTARY INVARIANT SUBSPACES
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCITEY Volume 45, Number 1, July 1974 FORMAL TAYLOR SERIES AND COMPLEMENTARY INVARIANT SUBSPACES DOMINGO A. HERRERO X ABSTRACT. A class of operators (which includes
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCITEY Volume 45, Number 1, July 1974 FORMAL TAYLOR SERIES AND COMPLEMENTARY INVARIANT SUBSPACES DOMINGO A. HERRERO X ABSTRACT. A class of operators (which includes
FIXED POINTS OF MEROMORPHIC SOLUTIONS OF HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 3, 2006, 9 2 FIXED POINTS OF MEROMORPHIC SOLUTIONS OF HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Liu Ming-Sheng and Zhang Xiao-Mei South China Normal
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 3, 2006, 9 2 FIXED POINTS OF MEROMORPHIC SOLUTIONS OF HIGHER ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Liu Ming-Sheng and Zhang Xiao-Mei South China Normal
ON THE DENSITY OF SOME SEQUENCES OF INTEGERS P. ERDOS
 ON THE DENSITY OF SOME SEQUENCES OF INTEGERS P. ERDOS Let ai
ON THE DENSITY OF SOME SEQUENCES OF INTEGERS P. ERDOS Let ai
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CONSECUTIVE PRIME NUMBERS. IV. / = lim inf ^11-tl.
 THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CONSECUTIVE PRIME NUMBERS. IV r. a. ran kin 1. Introduction. Let pn denote the nth prime, and let 0 be the lower bound of all positive numbers
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CONSECUTIVE PRIME NUMBERS. IV r. a. ran kin 1. Introduction. Let pn denote the nth prime, and let 0 be the lower bound of all positive numbers
ON THE NUMBER OF POSITIVE SUMS OF INDEPENDENT RANDOM VARIABLES
 ON THE NUMBER OF POSITIVE SUMS OF INDEPENDENT RANDOM VARIABLES P. ERDÖS AND M. KAC 1 1. Introduction. In a recent paper 2 the authors have introduced a method for proving certain limit theorems of the
ON THE NUMBER OF POSITIVE SUMS OF INDEPENDENT RANDOM VARIABLES P. ERDÖS AND M. KAC 1 1. Introduction. In a recent paper 2 the authors have introduced a method for proving certain limit theorems of the
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk 1
 The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk Michael Dorff and Ted Suffridge Abstract The class S H consists of univalent, harmonic, and sense-preserving functions f in the unit disk,,
The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk Michael Dorff and Ted Suffridge Abstract The class S H consists of univalent, harmonic, and sense-preserving functions f in the unit disk,,
An operator preserving inequalities between polynomials
 An operator preserving inequalities between polynomials NISAR A. RATHER Kashmir University P.G. Department of Mathematics Hazratbal-190006, Srinagar INDIA dr.narather@gmail.com MUSHTAQ A. SHAH Kashmir
An operator preserving inequalities between polynomials NISAR A. RATHER Kashmir University P.G. Department of Mathematics Hazratbal-190006, Srinagar INDIA dr.narather@gmail.com MUSHTAQ A. SHAH Kashmir
ARTIN S CONJECTURE AND SYSTEMS OF DIAGONAL EQUATIONS
 ARTIN S CONJECTURE AND SYSTEMS OF DIAGONAL EQUATIONS TREVOR D. WOOLEY Abstract. We show that Artin s conjecture concerning p-adic solubility of Diophantine equations fails for infinitely many systems of
ARTIN S CONJECTURE AND SYSTEMS OF DIAGONAL EQUATIONS TREVOR D. WOOLEY Abstract. We show that Artin s conjecture concerning p-adic solubility of Diophantine equations fails for infinitely many systems of
AN IMPROVED ESTIMATE IN THE METHOD OF FREEZING ROBERT E. VINOGRAD
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 89, Number I, September 1983 AN IMPROVED ESTIMATE IN THE METHOD OF FREEZING ROBERT E. VINOGRAD Abstract. Let x = A{t)x and \k(t) be the eigenvalues
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 89, Number I, September 1983 AN IMPROVED ESTIMATE IN THE METHOD OF FREEZING ROBERT E. VINOGRAD Abstract. Let x = A{t)x and \k(t) be the eigenvalues
SUPPORT POINTS AND DOUBLE POLES
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 122, Number 2, October 1994 SUPPORT POINTS AND DOUBLE POLES SAY SONG GOH (Communicated by Albert Baemstein II) Abstract. This paper gives some sufficient
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 122, Number 2, October 1994 SUPPORT POINTS AND DOUBLE POLES SAY SONG GOH (Communicated by Albert Baemstein II) Abstract. This paper gives some sufficient
The Hilbert Transform and Fine Continuity
 Irish Math. Soc. Bulletin 58 (2006), 8 9 8 The Hilbert Transform and Fine Continuity J. B. TWOMEY Abstract. It is shown that the Hilbert transform of a function having bounded variation in a finite interval
Irish Math. Soc. Bulletin 58 (2006), 8 9 8 The Hilbert Transform and Fine Continuity J. B. TWOMEY Abstract. It is shown that the Hilbert transform of a function having bounded variation in a finite interval
SOME VARIANTS OF LAGRANGE S FOUR SQUARES THEOREM
 Acta Arith. 183(018), no. 4, 339 36. SOME VARIANTS OF LAGRANGE S FOUR SQUARES THEOREM YU-CHEN SUN AND ZHI-WEI SUN Abstract. Lagrange s four squares theorem is a classical theorem in number theory. Recently,
Acta Arith. 183(018), no. 4, 339 36. SOME VARIANTS OF LAGRANGE S FOUR SQUARES THEOREM YU-CHEN SUN AND ZHI-WEI SUN Abstract. Lagrange s four squares theorem is a classical theorem in number theory. Recently,
STRONGLY EXTREME POINTS IN LPfa X)
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 16, Number 1, Winter 1986 STRONGLY EXTREME POINTS IN LPfa X) MARK A. SMITH ABSTRACT. A natural characterization of strongly extreme points in the unit ball
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 16, Number 1, Winter 1986 STRONGLY EXTREME POINTS IN LPfa X) MARK A. SMITH ABSTRACT. A natural characterization of strongly extreme points in the unit ball
Guanlong Bao, Zengjian Lou, Ruishen Qian, and Hasi Wulan
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 53 (2016, No. 2, pp. 561 568 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2016.53.2.561 ON ABSOLUTE VALUES OF Q K FUNCTIONS Guanlong Bao, Zengjian Lou, Ruishen Qian, and Hasi Wulan Abstract.
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 53 (2016, No. 2, pp. 561 568 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2016.53.2.561 ON ABSOLUTE VALUES OF Q K FUNCTIONS Guanlong Bao, Zengjian Lou, Ruishen Qian, and Hasi Wulan Abstract.
DICKSON INVARIANTS HIT BY THE STEENROD SQUARES
 DICKSON INVARIANTS HIT BY THE STEENROD SQUARES K F TAN AND KAI XU Abstract Let D 3 be the Dickson invariant ring of F 2 [X 1,X 2,X 3 ]bygl(3, F 2 ) In this paper, we prove each element in D 3 is hit by
DICKSON INVARIANTS HIT BY THE STEENROD SQUARES K F TAN AND KAI XU Abstract Let D 3 be the Dickson invariant ring of F 2 [X 1,X 2,X 3 ]bygl(3, F 2 ) In this paper, we prove each element in D 3 is hit by
NONLINEAR EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS FOR HIGHER ORDER LIDSTONE BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS
 NONLINEAR EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS FOR HIGHER ORDER LIDSTONE BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS PAUL W. ELOE Abstract. In this paper, we consider the Lidstone boundary value problem y (2m) (t) = λa(t)f(y(t),..., y (2j)
NONLINEAR EIGENVALUE PROBLEMS FOR HIGHER ORDER LIDSTONE BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS PAUL W. ELOE Abstract. In this paper, we consider the Lidstone boundary value problem y (2m) (t) = λa(t)f(y(t),..., y (2j)
Multidimensional Riemann derivatives
 STUDIA MATHEMATICA 235 (1) (2016) Multidimensional Riemann derivatives by J. Marshall Ash and Stefan Catoiu (Chicago, IL) Abstract. The well-known concepts of nth Peano, Lipschitz, Riemann, Riemann Lipschitz,
STUDIA MATHEMATICA 235 (1) (2016) Multidimensional Riemann derivatives by J. Marshall Ash and Stefan Catoiu (Chicago, IL) Abstract. The well-known concepts of nth Peano, Lipschitz, Riemann, Riemann Lipschitz,
How to sharpen a tridiagonal pair
 How to sharpen a tridiagonal pair Tatsuro Ito and Paul Terwilliger arxiv:0807.3990v1 [math.ra] 25 Jul 2008 Abstract Let F denote a field and let V denote a vector space over F with finite positive dimension.
How to sharpen a tridiagonal pair Tatsuro Ito and Paul Terwilliger arxiv:0807.3990v1 [math.ra] 25 Jul 2008 Abstract Let F denote a field and let V denote a vector space over F with finite positive dimension.
b jσ(j), Keywords: Decomposable numerical range, principal character AMS Subject Classification: 15A60
 On the Hu-Hurley-Tam Conjecture Concerning The Generalized Numerical Range Che-Man Cheng Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Macau, Macau. E-mail: fstcmc@umac.mo and Chi-Kwong Li Department
On the Hu-Hurley-Tam Conjecture Concerning The Generalized Numerical Range Che-Man Cheng Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Macau, Macau. E-mail: fstcmc@umac.mo and Chi-Kwong Li Department
Proof of a conjecture by Ðoković on the Poincaré series of the invariants of a binary form
 Proof of a conjecture by Ðoković on the Poincaré series of the invariants of a binary form A. Blokhuis, A. E. Brouwer, T. Szőnyi Abstract Ðoković [3] gave an algorithm for the computation of the Poincaré
Proof of a conjecture by Ðoković on the Poincaré series of the invariants of a binary form A. Blokhuis, A. E. Brouwer, T. Szőnyi Abstract Ðoković [3] gave an algorithm for the computation of the Poincaré
a 11 x 1 + a 12 x a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x a 2n x n = b 2.
 Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the unit disk
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Approximation Theory 164 (2012) 815 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Approximation Theory 164 (2012) 815 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the
FIBONACCI DIOPHANTINE TRIPLES. Florian Luca and László Szalay Universidad Nacional Autonoma de México, Mexico and University of West Hungary, Hungary
 GLASNIK MATEMATIČKI Vol. 436300, 53 64 FIBONACCI DIOPHANTINE TRIPLES Florian Luca and László Szalay Universidad Nacional Autonoma de México, Mexico and University of West Hungary, Hungary Abstract. In
GLASNIK MATEMATIČKI Vol. 436300, 53 64 FIBONACCI DIOPHANTINE TRIPLES Florian Luca and László Szalay Universidad Nacional Autonoma de México, Mexico and University of West Hungary, Hungary Abstract. In
IV. Conformal Maps. 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability. 2. Automorphisms of the Riemann sphere: Möbius transformations
 MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
arxiv: v1 [math.mg] 15 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.mg] 15 Jul 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.mg] 15 Jul 2013](/thumbs/71/65850401.jpg) INVERSE BERNSTEIN INEQUALITIES AND MIN-MAX-MIN PROBLEMS ON THE UNIT CIRCLE arxiv:1307.4056v1 [math.mg] 15 Jul 013 TAMÁS ERDÉLYI, DOUGLAS P. HARDIN, AND EDWARD B. SAFF Abstract. We give a short and elementary
INVERSE BERNSTEIN INEQUALITIES AND MIN-MAX-MIN PROBLEMS ON THE UNIT CIRCLE arxiv:1307.4056v1 [math.mg] 15 Jul 013 TAMÁS ERDÉLYI, DOUGLAS P. HARDIN, AND EDWARD B. SAFF Abstract. We give a short and elementary
COMBINATORIAL DIMENSION OF FRACTIONAL CARTESIAN PRODUCTS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 120, Number 1, January 1994 COMBINATORIAL DIMENSION OF FRACTIONAL CARTESIAN PRODUCTS RON C. BLEI AND JAMES H. SCHMERL (Communicated by Jeffry N.
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 120, Number 1, January 1994 COMBINATORIAL DIMENSION OF FRACTIONAL CARTESIAN PRODUCTS RON C. BLEI AND JAMES H. SCHMERL (Communicated by Jeffry N.
ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS IN CYCLES OF QUADRATIC POLYNOMIALS
 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS IN CYCLES OF QUADRATIC POLYNOMIALS TIMO ERKAMA It is an open question whether n-cycles of complex quadratic polynomials can be contained in the field Q(i) of complex rational numbers
ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS IN CYCLES OF QUADRATIC POLYNOMIALS TIMO ERKAMA It is an open question whether n-cycles of complex quadratic polynomials can be contained in the field Q(i) of complex rational numbers
238 H. S. WILF [April
 238 H. S. WILF [April 2. V. Garten, Über Tauber'she Konstanten bei Cesaro'sehen Mittlebildung, Comment. Math. Helv. 25 (1951), 311-335. 3. P. Hartman, Tauber's theorem and absolute constants, Amer. J.
238 H. S. WILF [April 2. V. Garten, Über Tauber'she Konstanten bei Cesaro'sehen Mittlebildung, Comment. Math. Helv. 25 (1951), 311-335. 3. P. Hartman, Tauber's theorem and absolute constants, Amer. J.
ON THE SET OF ALL CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS WITH UNIFORMLY CONVERGENT FOURIER SERIES
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 24, Number, November 996 ON THE SET OF ALL CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS WITH UNIFORMLY CONVERGENT FOURIER SERIES HASEO KI Communicated by Andreas R. Blass)
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 24, Number, November 996 ON THE SET OF ALL CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS WITH UNIFORMLY CONVERGENT FOURIER SERIES HASEO KI Communicated by Andreas R. Blass)
its weaknesses. The ASG consists of three subgenerators K,fl,
 ALTERNATING STEP GENERATORS CONTROLLED BY DE BRUIJN SEQUENCES C.G. Giinther Brown Boveri Research Center 5405 Baden, Switzerland ABSTRACT The alternating step generator (ASG) is a new generator of pseudo-
ALTERNATING STEP GENERATORS CONTROLLED BY DE BRUIJN SEQUENCES C.G. Giinther Brown Boveri Research Center 5405 Baden, Switzerland ABSTRACT The alternating step generator (ASG) is a new generator of pseudo-
ON WEIGHTED PARTIAL ORDERINGS ON THE SET OF RECTANGULAR COMPLEX MATRICES
 olume 10 2009, Issue 2, Article 41, 10 pp. ON WEIGHTED PARTIAL ORDERINGS ON THE SET OF RECTANGULAR COMPLEX MATRICES HANYU LI, HU YANG, AND HUA SHAO COLLEGE OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICS CHONGQING UNIERSITY
olume 10 2009, Issue 2, Article 41, 10 pp. ON WEIGHTED PARTIAL ORDERINGS ON THE SET OF RECTANGULAR COMPLEX MATRICES HANYU LI, HU YANG, AND HUA SHAO COLLEGE OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICS CHONGQING UNIERSITY
ON FACTORIZATIONS OF ENTIRE FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED TYPE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 29, 2004, 345 356 ON FACTORIZATIONS OF ENTIRE FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED TYPE Liang-Wen Liao and Chung-Chun Yang Nanjing University, Department of Mathematics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 29, 2004, 345 356 ON FACTORIZATIONS OF ENTIRE FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED TYPE Liang-Wen Liao and Chung-Chun Yang Nanjing University, Department of Mathematics
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs
 Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs Functions of genus zero for which the fast escaping set has Hausdorff dimension two Journal Item
Open Research Online The Open University s repository of research publications and other research outputs Functions of genus zero for which the fast escaping set has Hausdorff dimension two Journal Item
MINIMAL NORMAL AND COMMUTING COMPLETIONS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFORMATION AND SYSTEMS SCIENCES Volume 4, Number 1, Pages 5 59 c 8 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information MINIMAL NORMAL AND COMMUTING COMPLETIONS DAVID P KIMSEY AND
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFORMATION AND SYSTEMS SCIENCES Volume 4, Number 1, Pages 5 59 c 8 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information MINIMAL NORMAL AND COMMUTING COMPLETIONS DAVID P KIMSEY AND
THE ZECKENDORF ARRAY EQUALS THE WYTHOFF ARRAY
 Clark Kimberllng University of Evansville, Evansville, IN 47722 (Submitted February 1993) 1. INTRODUCTION It is well known that every n in the set N of positive integers is uniquely a sum of nonconsecutive
Clark Kimberllng University of Evansville, Evansville, IN 47722 (Submitted February 1993) 1. INTRODUCTION It is well known that every n in the set N of positive integers is uniquely a sum of nonconsecutive
On m-ary Overpartitions
 On m-ary Overpartitions Øystein J. Rødseth Department of Mathematics, University of Bergen, Johs. Brunsgt. 1, N 5008 Bergen, Norway E-mail: rodseth@mi.uib.no James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics,
On m-ary Overpartitions Øystein J. Rødseth Department of Mathematics, University of Bergen, Johs. Brunsgt. 1, N 5008 Bergen, Norway E-mail: rodseth@mi.uib.no James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics,
Weak Subordination for Convex Univalent Harmonic Functions
 Weak Subordination for Convex Univalent Harmonic Functions Stacey Muir Abstract For two complex-valued harmonic functions f and F defined in the open unit disk with f() = F () =, we say f is weakly subordinate
Weak Subordination for Convex Univalent Harmonic Functions Stacey Muir Abstract For two complex-valued harmonic functions f and F defined in the open unit disk with f() = F () =, we say f is weakly subordinate
THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 26, 2001, 401 407 THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE A. F. Beardon University of Cambridge, DPMMS, Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 26, 2001, 401 407 THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC OF A RECTANGLE A. F. Beardon University of Cambridge, DPMMS, Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce
