LENGTH AND AREA ESTIMATES OF THE DERIVATIVES OF BOUNDED HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
|
|
|
- Kristopher Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume KK, Number I. May 1983 LENGTH AND AREA ESTIMATES OF THE DERIVATIVES OF BOUNDED HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS SHINJI YAMASHITA Abstract. MacGregor [1] and Yamashita [5] proved the estimates of the coefficient a of the Taylor expansion/(z) = a() + a z" + of / nonconstant and holomorphic in z < 1 in terms of the area of the image of z < r < 1 by / and the length of its outer or exact outer boundary. We shall consider some analogous estimates in terms of the non-euclidean geometry for / bounded, / < 1, in z < 1. For example, 2nr" \ an /(1 aa \2) is strictly less than the non-euclidean length of the boundary of the image of z < r, the multiplicity not being counted. 1. Introduction. Unless otherwise specified, by / we always mean a function nonconstant, holomorphic, and bounded, / < 1, in the disk (7= { z < 1}. The non-euclidean metric in U is expressed by the differential form p(z)\dz\, p(z) = (1 - z 2)-', z EU. Then A(z, r) = {w G ÍT; w - z\/\ 1 - zw\<r) is the non- Euclidean disk of the non-euclidean center z E U and the non-euclidean radius (l/2)log[(l + r)/(\ -r)](0<r<\). By the image g(g) of a domain G by a function g holomorphic in G we mean the set of w in the w-plane such that w g(z) for at least one z EG; simply, g(g) is the projection of the Riemannian image of G by g. The exact outer boundary Ci(r, z) of D(r, z) = D(r, z, f) =/(A(z, r)) is the boundary of the unbounded component of the complement of the closure of D(r, z) in the plane; see [5], Roughly, C*(r, z) is the boundary dd(r, z) of D(r, z) minus the "shorelines" of the "bays" and the "lakes" of the "island" D(r, z). Furthermore, C*(/% z) is a Jordan curve consisting of a finite number of analytic arcs. Let X(r, z) = j JC*(r,z) p(w) \dw\ be the non-euclidean length of Ctt(r, z). The non-euclidean length of dd(r, z) is thus not smaller than X(r, z) > 0. A non-euclidean version of S. Yamashita's estimate [5, Theorem 2] is Theorem 1. Let f be nonconstant, holomorphic, and bounded, \f\< 1, in U. Let «= n(z) be the first number such that /(n)(z) =0, n > \, z E U. Then, for each r, 0<r< 1, (1.1) 2Wr"(l- z 2)" /""(z) /[«!(l- /(z) 2)] where, for 0 < x < + oo, $(x) <*(X(r,z))<X(r,z), > 0 and (x)2 = 2tr(-n2 + x2)1/2-2tt2. Received by the editors March 24, Mathematics Subject Classification. Primary 30C99; Secondary 30C50, 30C American Mathematical Society /82/ /S02.00
2 30 SHINJI YAMASHITA We note that (0 <) $(x) < x for x > 0, so that the second inequality in (1.1) is immediate. In particular, (1.1) for z = 0, together with (1.2) f(z) = a0 + a z" +.-- (an + 0), yields that 27rr" a /(l - a0 2) ^i>(a(r,0)) <A(r,0); this is a non-euclidean counterpart of [5, Theorem 1]. For the proof of Theorem 1 we shall make use of the following Theorem 2; unfortunately, the formulation appears to be complicated. Let E be the unbounded component of the complement of D( r, z ), not that of the closure of D(r, z). Let D (r, z) be the complement of E. Then D (r, z) consists of the "island" D(r, z) plus its reclaimed "lakes". As is pointed out by T. H. MacGregor [l,p. 319; 2, Lemma 2], the domain D (r, z) is simply connected whose boundary is called the outer boundary of D(r, z). Thus, for/(z) = (z + 1/ j3)3/&, D(r,0) is a proper subset of D~(r,0) if 1/2 < r < 1, while D(r,0) = >"(/-,0) if 0<r< 1/2. Returning to our general/we let ot(r, z) = a(r, z, /) = / / p{w) dx dy (w x + iy) J JD\r.z) be the non-euclidean area of D (r, z) (0 < r < 1, z G (7). Theorem 2. Let f and n(z) be as in Theorem 1. Then, for each r,0 < r < 1, (1.3) ^2"(l- z 2)2" /(",(^)/[«!(l- /(^) 2)] 2<«('-^). Specifically, ( 1.3) for z = 0 with ( 1.2) reads (1.4) r2»[\a \/{l-\a0\2)]2^a(r,0), for all r, 0 < r < 1. This is a non-euclidean counterpart of MacGregor's estimate [1, Theorem 1]: (1.5) trr2"\a \2<a(r,0), where a(r, 0) is the Euclidean area of D(r, 0), not that of D (r,0) for/of (1.2) not necessarily bounded in U. Since a(r,0) < a(r,0) for / < 1, (1.4) yields a better estimate than (1.5) if a0 is so near 1 that {\-\a0\2)2a(r,0)^a(r,0). 2. Proofs. In the proof of his theorem [1, Theorem 1] MacGregor makes use of the following improvement of [3, Theorem 4.7, p. 80]. MacGregor's Lemma. Let g(z) = bq + b z"+--- (b 0,n>\) be holomorphic in U, and let rx be the inner radius [3, p. 79] ofg(u) (2-1) \b \^rx. at b0. Then
3 LENGTH AND AREA ESTIMATES 31 Proof of Theorem 2. First we prove (1.4), then (1.3). For the proof of (1.4) welet g(z)=f(rz) = a0 + a r"z" in U, and let rx be the inner radius of g(u) D(r,0) at a0. Then the estimate (2.1), together with b = a r", yields (2.2) KI'"<»V Let r2 be the inner radius of D (r,0) at a0. Then rx < r2 because D(r,0) C D (r,0); see [3, p. 80]. Let D* be the circular symmetrization [3, p. 69] of D (r,0) with respect to the half-line {ta0; 0 < t < +00} (= {'; 0 < t < +00}, if aq - 0). Then D* is simply connected because the same is true of D (r,q). Let h(z) a0 + cxz + be a univalent holomorphic function in U with h(u) = D*. Then the inner radius r, of D* at a0 satisfies r3 = c, [3, p. 79], and by [3,Theorem 4.8, p. 81], r2 «s r3, so that, by (2.2), whence follows a k"*='3= ci = Ä'(0)], (2.3) r2"[\ a \/{\-\a0 \2)]2 <\ h'(0) 2/ (l - *<0) 2)2, because «(0) = a0. Since I «' 2/(1 I «2)2 is subharmonic in U, and since the non-euclidean area of D* is the same as that of D (r, 0), or, a(r, 0), it follows that \h'(0)\2/(l-\h(0)\2)2^(l/v)ffjh'(z)\2/{l-\h(z)\2)2dxdy = a(r,0)/it, which, together with (2.3), yields (1.4). To prove (1.3) we consider the composed function F(w) = f((w + z)/(\ + zw)) of a variable w E U. Since F<">(0)/«!= (l -\z\2)"f{n)(z)/n\, F@) = f(z)y and since «(r> 0, F) = a(r, z, f), (1.3) is a consequence of (1.4) applied tof. Proof of Theorem 1. The Gauss curvature 7i(z) of the non-euclidean space U endowed with the metric u(z) dz \ is given by K(z) = -4«x(z)"2(32/3z3z)logjLi(z) =-A inu. Let D*(r, z) be the domain bounded by the Jordan curve C*(r, z). Then D(r, z) C D (r,z)e D*(r, z). Let A be the non-euclidean area of D\r, z). Then a(r,z)<a and AmA + 4A2 < X(r, z)2;
4 32 SHINJI YAMASHITA the latter is a consequence of [4,(4.25), p. 1206], together with K = -4. Consequently, 2a(r,z)=s(7T2 + A2)1/2-7r. The estimate (1.1) now follows from (1.3) after a short computation. 3. Schwarz-Pick's lemma. As applications of Theorems 1 and 2 we obtain improvements of Schwarz-Pick's lemma: For example, let (l- z 2) /'(z) /(l- /(z) 2)<l, M(r, z) - min(l,0(a(/\ z))/(2trr)), for 0 < r < 1, z G U. Iff'(z) = 0, then we obtain by (1.1) that (1 -\z 2) /'(z) /(1 -\f(z) 2) <M(r,z), ZEU. while if /'(z) = 0, then the estimate is trivial. The estimate in terms of a(r, z) is similar, and is left as an exercise. 4. Concluding remarks. As to the sharpness of (1.4) on which (1.3) depends we have poor information: (1.4) is sharp in the limiting case, r -» 0. More precisely, let us be given «> 1 and a0 E D. We set and T(z) = (z + a0)/ {\ + c7~0z) = a0 + bz + ---, f(z) = T(z")=a0 + a z"+-.., where a = b. Then, a(r,0) = a(r,0, /) is the non-euclidean area of A(a0, r") which is the same as that of A(0, r"), or a(r, 0) = irr2"/(\ r2"). Since (1.4) now reads K, /(i-ki2)= z>l/(i- ao 2)=i, nr2" = TTr2"[\a \/(\ - \ a0 2)]2 < irr2"/ (1 - r2"), whence, the fact that 1 r2" -* 1 as r -> 0 yields the sharpness in the limit. Now, the situation explained at the end of 1 is obvious for the present/. given 0 < r < 1, we choose a real a0 so that For, A calculation shows that 0<a0<l and (l - a r2")2 < 1 - r2". a(r,0) = nr2"(\ - a2)2/(\ - a2r2")2, so that ( 1 - a\ )2«( r, 0) < a( r, 0). Conversely, given a complex number a0 with 1//2 < a0 < 1' insn f r each r with 0<r< ao <l and (l - \a0\2r2")2 < \ - r2",
5 the same argument as above again shows that LENGTH AND AREA ESTIMATES 33 (\-\ao\2)2a(r,0)<a(r,0). References 1. T. H. MacGregor. Length and area estimates for analytic functions, Michigan Math. J. 11 (1964), _, Translations of the image domains of analytic functions, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 16 (1965), W. K. Hayman, Mullivalent functions, Cambridge Univ. Press, London, R. Osserman. The isoperimetric inequality. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 84 ( 1978), S. Yamashita, Length estimates for holomorphic functions, Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 81 (1981), Tokyo Metropolitan University, Fukazawa, Setagaya-Ku, Tokyo (158), Japan
ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 5, 24 ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove some versions of the Schwarz
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 44, Number 5, 24 ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS ON SURFACES WITH POSITIVE GAUSS CURVATURE AND THE SCHWARZ LEMMA DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove some versions of the Schwarz
6.2 Mean value theorem and maximum principles
 Hence g = u x iu y is analytic. Since is simply connected, R g(z) dz =forany closed path =) g has an integral function, G = g in. Call G = U + iv. For analytic functions d G = d G. Hence dz dx g = d dz
Hence g = u x iu y is analytic. Since is simply connected, R g(z) dz =forany closed path =) g has an integral function, G = g in. Call G = U + iv. For analytic functions d G = d G. Hence dz dx g = d dz
3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations
 Summer School Normal Families in Complex Analysis Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg May 22 29, 2015 3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations Aimo Hinkkanen University of Illinois at Urbana
Summer School Normal Families in Complex Analysis Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg May 22 29, 2015 3. 4. Uniformly normal families and generalisations Aimo Hinkkanen University of Illinois at Urbana
158 Robert Osserman As immediate corollaries, one has: Corollary 1 (Liouville's Theorem). A bounded analytic function in the entire plane is constant.
 Proceedings Ist International Meeting on Geometry and Topology Braga (Portugal) Public. Centro de Matematica da Universidade do Minho p. 157{168, 1998 A new variant of the Schwarz{Pick{Ahlfors Lemma Robert
Proceedings Ist International Meeting on Geometry and Topology Braga (Portugal) Public. Centro de Matematica da Universidade do Minho p. 157{168, 1998 A new variant of the Schwarz{Pick{Ahlfors Lemma Robert
SOLUTIONS OF NONHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH EXCEPTIONALLY FEW ZEROS
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 23, 1998, 429 452 SOLUTIONS OF NONHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH EXCEPTIONALLY FEW ZEROS Gary G. Gundersen, Enid M. Steinbart, and
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 23, 1998, 429 452 SOLUTIONS OF NONHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH EXCEPTIONALLY FEW ZEROS Gary G. Gundersen, Enid M. Steinbart, and
DIMENSIONS OF JULIA SETS OF HYPERBOLIC ENTIRE FUNCTIONS
 Bull. London Math. Soc. 36 2004 263 270 C 2004 London Mathematical Society DOI: 10.1112/S0024609303002698 DIMENSIONS OF JULIA SETS OF HYPERBOLIC ENTIRE FUNCTIONS GWYNETH M. STALLARD Abstract It is known
Bull. London Math. Soc. 36 2004 263 270 C 2004 London Mathematical Society DOI: 10.1112/S0024609303002698 DIMENSIONS OF JULIA SETS OF HYPERBOLIC ENTIRE FUNCTIONS GWYNETH M. STALLARD Abstract It is known
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
5.3 The Upper Half Plane
 Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
BLOCH SPACE AND THE NORM OF THE BERGMAN PROJECTION
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 38, 2013, 849 853 BLOCH SPACE AN THE NORM OF THE BERGMAN PROJECTION Antti Perälä University of Helsinki, epartment of Mathematics and Statistics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 38, 2013, 849 853 BLOCH SPACE AN THE NORM OF THE BERGMAN PROJECTION Antti Perälä University of Helsinki, epartment of Mathematics and Statistics
SUPPORT POINTS AND DOUBLE POLES
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 122, Number 2, October 1994 SUPPORT POINTS AND DOUBLE POLES SAY SONG GOH (Communicated by Albert Baemstein II) Abstract. This paper gives some sufficient
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 122, Number 2, October 1994 SUPPORT POINTS AND DOUBLE POLES SAY SONG GOH (Communicated by Albert Baemstein II) Abstract. This paper gives some sufficient
Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett/
 (February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
(February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS
 Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
Series Logo Volume 00, Number 00, Xxxx 19xx COMPLETELY INVARIANT JULIA SETS OF POLYNOMIAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ Abstract. Let G be a semigroup of rational functions of degree at least two, under composition
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS
 A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
A TALE OF TWO CONFORMALLY INVARIANT METRICS H. S. BEAR AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. The Harnack metric is a conformally invariant metric defined in quite general domains that coincides with the hyperbolic
Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the unit disk
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Approximation Theory 164 (2012) 815 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Journal of Approximation Theory 164 (2012) 815 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat Full length article Stolz angle limit of a certain class of self-mappings of the
arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014 arxiv: v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014](/thumbs/94/121818359.jpg) ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS AND THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC arxiv:1307.4006v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014 MARIJAN MARKOVIĆ Abstract. Motivated by some recent results of Kalaj and Vuorinen (Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 2012),
ON HARMONIC FUNCTIONS AND THE HYPERBOLIC METRIC arxiv:1307.4006v3 [math.cv] 4 Mar 2014 MARIJAN MARKOVIĆ Abstract. Motivated by some recent results of Kalaj and Vuorinen (Proc. Amer. Math. Soc., 2012),
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
CONVEXITY OF INTEGRAL MEANS OF SUBHARMONIC FUNCTIONS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAIN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 60, October 1976 CONVEXITY OF INTEGRAL MEANS OF SUBHARMONIC FUNCTIONS JANG-MEI G. WU' Abstract. We study the convexity of integral means of subharmonic
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAIN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 60, October 1976 CONVEXITY OF INTEGRAL MEANS OF SUBHARMONIC FUNCTIONS JANG-MEI G. WU' Abstract. We study the convexity of integral means of subharmonic
FIXED POINTS OF MULTIVALUED MAPPINGS IN CERTAIN CONVEX METRIC SPACES. Tomoo Shimizu Wataru Takahashi. 1. Introduction
 Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 8, 1996, 197 203 FIXED POINTS OF MULTIVALUED MAPPINGS IN CERTAIN CONVEX METRIC SPACES Tomoo Shimizu Wataru Takahashi
Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 8, 1996, 197 203 FIXED POINTS OF MULTIVALUED MAPPINGS IN CERTAIN CONVEX METRIC SPACES Tomoo Shimizu Wataru Takahashi
NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR WEIGHTED POINTWISE HARDY INEQUALITIES
 NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR WEIGHTED POINTWISE HARDY INEQUALITIES JUHA LEHRBÄCK Abstract. We establish necessary conditions for domains Ω R n which admit the pointwise (p, β)-hardy inequality u(x) Cd Ω(x)
NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR WEIGHTED POINTWISE HARDY INEQUALITIES JUHA LEHRBÄCK Abstract. We establish necessary conditions for domains Ω R n which admit the pointwise (p, β)-hardy inequality u(x) Cd Ω(x)
A Class of Univalent Harmonic Mappings
 Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 6, 016, no. 5, 675-680 A Class of Univalent Harmonic Mappings Jinjing Qiao Department of Mathematics, Hebei University, Baoding, Hebei 07100, People s Republic of China Qiannan
Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 6, 016, no. 5, 675-680 A Class of Univalent Harmonic Mappings Jinjing Qiao Department of Mathematics, Hebei University, Baoding, Hebei 07100, People s Republic of China Qiannan
BOHR S POWER SERIES THEOREM IN SEVERAL VARIABLES
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 125, Number 10, October 1997, Pages 2975 2979 S 0002-9939(97)04270-6 BOHR S POWER SERIES THEOREM IN SEVERAL VARIABLES HAROLD P. BOAS AND DMITRY KHAVINSON
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 125, Number 10, October 1997, Pages 2975 2979 S 0002-9939(97)04270-6 BOHR S POWER SERIES THEOREM IN SEVERAL VARIABLES HAROLD P. BOAS AND DMITRY KHAVINSON
Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 2012 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file)
 Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 212 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file) February 9, 212 16. Prove: If u is a complex-valued harmonic function, then the real and the imaginary parts
Key to Complex Analysis Homework 1 Spring 212 (Thanks to Da Zheng for providing the tex-file) February 9, 212 16. Prove: If u is a complex-valued harmonic function, then the real and the imaginary parts
Harmonic Mappings for which Second Dilatation is Janowski Functions
 Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 3, 2013, no. 8, 617-624 Harmonic Mappings for which Second Dilatation is Janowski Functions Emel Yavuz Duman İstanbul Kültür University Department of Mathematics and Computer
Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 3, 2013, no. 8, 617-624 Harmonic Mappings for which Second Dilatation is Janowski Functions Emel Yavuz Duman İstanbul Kültür University Department of Mathematics and Computer
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
 VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
VOLUME INTEGRAL MEANS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS JIE XIAO AND KEHE ZHU ABSTRACT. The classical integral means of a holomorphic function f in the unit disk are defined by [ 1/p 1 2π f(re iθ ) dθ] p, r < 1.
Norwegian University of Science and Technology N-7491 Trondheim, Norway
 QUASICONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 48 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1999 WHAT IS A DISK? KARI HAG Norwegian University of Science and
QUASICONFORMAL GEOMETRY AND DYNAMICS BANACH CENTER PUBLICATIONS, VOLUME 48 INSTITUTE OF MATHEMATICS POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES WARSZAWA 1999 WHAT IS A DISK? KARI HAG Norwegian University of Science and
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019](/thumbs/94/121818370.jpg) 1 SCHWARZ LEMMA FOR HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN RIEMANN SURFACES arxiv:1903.05163v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove a Schwarz type lemma for harmonic mappings between the unit and a
1 SCHWARZ LEMMA FOR HARMONIC MAPPINGS BETWEEN RIEMANN SURFACES arxiv:1903.05163v1 [math.cv] 12 Mar 2019 DAVID KALAJ ABSTRACT. We prove a Schwarz type lemma for harmonic mappings between the unit and a
Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15)
 Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
A note on a construction of J. F. Feinstein
 STUDIA MATHEMATICA 169 (1) (2005) A note on a construction of J. F. Feinstein by M. J. Heath (Nottingham) Abstract. In [6] J. F. Feinstein constructed a compact plane set X such that R(X), the uniform
STUDIA MATHEMATICA 169 (1) (2005) A note on a construction of J. F. Feinstein by M. J. Heath (Nottingham) Abstract. In [6] J. F. Feinstein constructed a compact plane set X such that R(X), the uniform
ON SOME LENGTH PROBLEMS FOR ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS
 Nunokawa, M. and Sokół, J. Osaka J. Math. 5 (4), 695 77 ON SOME LENGTH PROBLEMS FOR ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS MAMORU NUNOKAWA and JANUSZ SOKÓŁ (Received December 6, ) Let A be the class of functions Abstract
Nunokawa, M. and Sokół, J. Osaka J. Math. 5 (4), 695 77 ON SOME LENGTH PROBLEMS FOR ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS MAMORU NUNOKAWA and JANUSZ SOKÓŁ (Received December 6, ) Let A be the class of functions Abstract
7.2 Conformal mappings
 7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
An Investigation on Minimal Surfaces of Multivalent Harmonic Functions 1
 General Mathematics Vol. 19, No. 1 (2011), 99 107 An Investigation on Minimal Surfaces of Multivalent Harmonic Functions 1 Hakan Mete Taştan, Yaşar Polato glu Abstract The projection on the base plane
General Mathematics Vol. 19, No. 1 (2011), 99 107 An Investigation on Minimal Surfaces of Multivalent Harmonic Functions 1 Hakan Mete Taştan, Yaşar Polato glu Abstract The projection on the base plane
Subclass of Meromorphic Functions with Positive Coefficients Defined by Frasin and Darus Operator
 Int. J. Open Problems Complex Analysis, Vol. 8, No. 1, March 2016 ISSN 2074-2827; Copyright c ICSRS Publication, 2016 www.i-csrs.org Subclass of Meromorphic Functions with Positive Coefficients Defined
Int. J. Open Problems Complex Analysis, Vol. 8, No. 1, March 2016 ISSN 2074-2827; Copyright c ICSRS Publication, 2016 www.i-csrs.org Subclass of Meromorphic Functions with Positive Coefficients Defined
Complex Analysis Problems
 Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
FORMAL TAYLOR SERIES AND COMPLEMENTARY INVARIANT SUBSPACES
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCITEY Volume 45, Number 1, July 1974 FORMAL TAYLOR SERIES AND COMPLEMENTARY INVARIANT SUBSPACES DOMINGO A. HERRERO X ABSTRACT. A class of operators (which includes
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCITEY Volume 45, Number 1, July 1974 FORMAL TAYLOR SERIES AND COMPLEMENTARY INVARIANT SUBSPACES DOMINGO A. HERRERO X ABSTRACT. A class of operators (which includes
Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature
 Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Abstract We give optimal bounds of the height, curvature, area and enclosed volume of K-surfaces in R 3 bounding a
Estimates in surfaces with positive constant Gauss curvature J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Abstract We give optimal bounds of the height, curvature, area and enclosed volume of K-surfaces in R 3 bounding a
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD
 MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
On the mean values of an analytic function
 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LVII.2 (1992) On the mean values of an analytic function by G. S. Srivastava and Sunita Rani (Roorkee) Abstract. Let f(z), z = re iθ, be analytic in the finite disc z < R.
ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LVII.2 (1992) On the mean values of an analytic function by G. S. Srivastava and Sunita Rani (Roorkee) Abstract. Let f(z), z = re iθ, be analytic in the finite disc z < R.
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
A HARDY LITTLEWOOD THEOREM FOR BERGMAN SPACES
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 43, 2018, 807 821 A HARY LITTLEWOO THEOREM FOR BERGMAN SPACES Guanlong Bao, Hasi Wulan and Kehe Zhu Shantou University, epartment of Mathematics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 43, 2018, 807 821 A HARY LITTLEWOO THEOREM FOR BERGMAN SPACES Guanlong Bao, Hasi Wulan and Kehe Zhu Shantou University, epartment of Mathematics
A RAPID INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX ANALYSIS
 A RAPID INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX ANALYSIS AKHIL MATHEW ABSTRACT. These notes give a rapid introduction to some of the basic results in complex analysis, assuming familiarity from the reader with Stokes
A RAPID INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX ANALYSIS AKHIL MATHEW ABSTRACT. These notes give a rapid introduction to some of the basic results in complex analysis, assuming familiarity from the reader with Stokes
Solutions to Exercises 6.1
 34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
34 Chapter 6 Conformal Mappings Solutions to Exercises 6.. An analytic function fz is conformal where f z. If fz = z + e z, then f z =e z z + z. We have f z = z z += z =. Thus f is conformal at all z.
Mapping the disk to convex subregions
 Mapping the disk to convex subregions John A. Velling 11 March 1995 1. Introduction. Univalent maps f : D D have been much studied by many authors. See [1], [2], [5], for just a few references. A quick
Mapping the disk to convex subregions John A. Velling 11 March 1995 1. Introduction. Univalent maps f : D D have been much studied by many authors. See [1], [2], [5], for just a few references. A quick
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007](/thumbs/95/125521566.jpg) A NOTE ON THE HAYMAN-WU THEOREM EDWARD CRANE arxiv:0707.1772v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 Abstract. The Hayman-Wu theorem states that the preimage of a line or circle L under a conformal mapping from the unit
A NOTE ON THE HAYMAN-WU THEOREM EDWARD CRANE arxiv:0707.1772v1 [math.cv] 12 Jul 2007 Abstract. The Hayman-Wu theorem states that the preimage of a line or circle L under a conformal mapping from the unit
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010
 An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
1. The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions.
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
ON FACTORIZATIONS OF ENTIRE FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED TYPE
 Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 29, 2004, 345 356 ON FACTORIZATIONS OF ENTIRE FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED TYPE Liang-Wen Liao and Chung-Chun Yang Nanjing University, Department of Mathematics
Annales Academiæ Scientiarum Fennicæ Mathematica Volumen 29, 2004, 345 356 ON FACTORIZATIONS OF ENTIRE FUNCTIONS OF BOUNDED TYPE Liang-Wen Liao and Chung-Chun Yang Nanjing University, Department of Mathematics
Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent functions with opening angle at infinity
 A SHARP BOUND FOR THE SCHWARZIAN DERIVATIVE OF CONCAVE FUNCTIONS BAPPADITYA BHOWMIK AND KARL-JOACHIM WIRTHS Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent
A SHARP BOUND FOR THE SCHWARZIAN DERIVATIVE OF CONCAVE FUNCTIONS BAPPADITYA BHOWMIK AND KARL-JOACHIM WIRTHS Abstract. We derive a sharp bound for the modulus of the Schwarzian derivative of concave univalent
Invertible Composition Operators: The product of a composition operator with the adjoint of a composition operator.
 Invertible Composition Operators: The product of a composition operator with the adjoint of a composition operator. John H. Clifford, Trieu Le and Alan Wiggins Abstract. In this paper, we study the product
Invertible Composition Operators: The product of a composition operator with the adjoint of a composition operator. John H. Clifford, Trieu Le and Alan Wiggins Abstract. In this paper, we study the product
The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk 1
 The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk Michael Dorff and Ted Suffridge Abstract The class S H consists of univalent, harmonic, and sense-preserving functions f in the unit disk,,
The Inner Mapping Radius of Harmonic Mappings of the Unit Disk Michael Dorff and Ted Suffridge Abstract The class S H consists of univalent, harmonic, and sense-preserving functions f in the unit disk,,
COMPOSITION SEMIGROUPS ON BMOA AND H AUSTIN ANDERSON, MIRJANA JOVOVIC, AND WAYNE SMITH
 COMPOSITION SEMIGROUPS ON BMOA AND H AUSTIN ANDERSON, MIRJANA JOVOVIC, AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. We study [ϕ t, X], the maximal space of strong continuity for a semigroup of composition operators induced
COMPOSITION SEMIGROUPS ON BMOA AND H AUSTIN ANDERSON, MIRJANA JOVOVIC, AND WAYNE SMITH Abstract. We study [ϕ t, X], the maximal space of strong continuity for a semigroup of composition operators induced
A PROOF OF THE UNIFORMIZATION THEOREM FOR ARBITRARY PLANE DOMAINS
 PROCEEDINGS of the AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 104, Number 2, October 1988 A PROOF OF THE UNIFORMIZATION THEOREM FOR ARBITRARY PLANE DOMAINS YUVAL FISHER, JOHN H. HUBBARD AND BEN S. WITTNER (Communicated
PROCEEDINGS of the AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 104, Number 2, October 1988 A PROOF OF THE UNIFORMIZATION THEOREM FOR ARBITRARY PLANE DOMAINS YUVAL FISHER, JOHN H. HUBBARD AND BEN S. WITTNER (Communicated
Coecient bounds for certain subclasses of analytic functions of complex order
 Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 45 (4) (2016), 1015 1022 Coecient bounds for certain subclasses of analytic functions of complex order Serap Bulut Abstract In this paper, we introduce
Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 45 (4) (2016), 1015 1022 Coecient bounds for certain subclasses of analytic functions of complex order Serap Bulut Abstract In this paper, we introduce
Topology of Quadrature Domains
 Topology of Quadrature Domains Seung-Yeop Lee (University of South Florida) August 12, 2014 1 / 23 Joint work with Nikolai Makarov Topology of quadrature domains (arxiv:1307.0487) Sharpness of connectivity
Topology of Quadrature Domains Seung-Yeop Lee (University of South Florida) August 12, 2014 1 / 23 Joint work with Nikolai Makarov Topology of quadrature domains (arxiv:1307.0487) Sharpness of connectivity
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 5
 DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 5 CLAY SHONKWILER 1 Check the calculations above that the Gaussian curvature of the upper half-plane and Poincaré disk models of the hyperbolic plane is 1. Proof. The calculations
DIFFERENTIAL GEOMETRY HW 5 CLAY SHONKWILER 1 Check the calculations above that the Gaussian curvature of the upper half-plane and Poincaré disk models of the hyperbolic plane is 1. Proof. The calculations
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL
 PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
(1.2) Jjexp/(z) 2 \dz\ < expj i \f'(z)\2 do(z) J (q = 1).
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 83, Number 2, October 1981 A DIRICHLET NORM INEQUALITY AND SOME INEQUALITIES FOR REPRODUCING KERNEL SPACES JACOB BURBEA Abstract. Let / be analytic
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 83, Number 2, October 1981 A DIRICHLET NORM INEQUALITY AND SOME INEQUALITIES FOR REPRODUCING KERNEL SPACES JACOB BURBEA Abstract. Let / be analytic
An operator preserving inequalities between polynomials
 An operator preserving inequalities between polynomials NISAR A. RATHER Kashmir University P.G. Department of Mathematics Hazratbal-190006, Srinagar INDIA dr.narather@gmail.com MUSHTAQ A. SHAH Kashmir
An operator preserving inequalities between polynomials NISAR A. RATHER Kashmir University P.G. Department of Mathematics Hazratbal-190006, Srinagar INDIA dr.narather@gmail.com MUSHTAQ A. SHAH Kashmir
The Gauss map and second fundamental form of surfaces in R 3
 The Gauss map and second fundamental form of surfaces in R 3 J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Departamento de Geometría y Topoloía, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Granada, 18071 GRANADA. SPAIN. e-mail: jaalvez@oliat.ur.es;
The Gauss map and second fundamental form of surfaces in R 3 J. A. Gálvez A. Martínez Departamento de Geometría y Topoloía, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Granada, 18071 GRANADA. SPAIN. e-mail: jaalvez@oliat.ur.es;
Non-real zeroes of real entire functions and their derivatives
 Non-real zeroes of real entire functions and their derivatives Daniel A. Nicks Abstract A real entire function belongs to the Laguerre-Pólya class LP if it is the limit of a sequence of real polynomials
Non-real zeroes of real entire functions and their derivatives Daniel A. Nicks Abstract A real entire function belongs to the Laguerre-Pólya class LP if it is the limit of a sequence of real polynomials
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 19 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 19 Jul 2012 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 19 Jul 2012](/thumbs/93/112110727.jpg) arxiv:1207.4529v1 [math.cv] 19 Jul 2012 On the Radius Constants for Classes of Analytic Functions 1 ROSIHAN M. ALI, 2 NAVEEN KUMAR JAIN AND 3 V. RAVICHANDRAN 1,3 School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti
arxiv:1207.4529v1 [math.cv] 19 Jul 2012 On the Radius Constants for Classes of Analytic Functions 1 ROSIHAN M. ALI, 2 NAVEEN KUMAR JAIN AND 3 V. RAVICHANDRAN 1,3 School of Mathematical Sciences, Universiti
COMPUTING POLYNOMIAL CONFORMAL MODELS FOR LOW-DEGREE BLASCHKE PRODUCTS
 COMPUTING POLYNOMIAL CONFORMAL MODELS FOR LOW-DEGREE BLASCHKE PRODUCTS TREVOR RICHARDS AND MALIK YOUNSI Abstract. For any finite Blaschke product B, there is an injective analytic map ϕ : D C and a polynomial
COMPUTING POLYNOMIAL CONFORMAL MODELS FOR LOW-DEGREE BLASCHKE PRODUCTS TREVOR RICHARDS AND MALIK YOUNSI Abstract. For any finite Blaschke product B, there is an injective analytic map ϕ : D C and a polynomial
Free Boundary Value Problems for Analytic Functions in the Closed Unit Disk
 Free Boundary Value Problems for Analytic Functions in the Closed Unit Disk Richard Fournier Stephan Ruscheweyh CRM-2558 January 1998 Centre de recherches de mathématiques, Université de Montréal, Montréal
Free Boundary Value Problems for Analytic Functions in the Closed Unit Disk Richard Fournier Stephan Ruscheweyh CRM-2558 January 1998 Centre de recherches de mathématiques, Université de Montréal, Montréal
QUASINORMAL FAMILIES AND PERIODIC POINTS
 QUASINORMAL FAMILIES AND PERIODIC POINTS WALTER BERGWEILER Dedicated to Larry Zalcman on his 60th Birthday Abstract. Let n 2 be an integer and K > 1. By f n we denote the n-th iterate of a function f.
QUASINORMAL FAMILIES AND PERIODIC POINTS WALTER BERGWEILER Dedicated to Larry Zalcman on his 60th Birthday Abstract. Let n 2 be an integer and K > 1. By f n we denote the n-th iterate of a function f.
j(z) > + FZ f(z) z + oz f(z) 1-.F < 1-.F zf (z) } 1 E (z 6 U,F 1). (1.3) >/(z e u) ANGULAR ESTIMATIONS OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS
 Internat. J. Math. & Math. Sci. VOL. 1 NO. (1998) 369374 369 ANGULAR ESTIMATIONS OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS NAK EUN CHO, IN HWA KIM JI A KIM Department of Applied Mathematics Pukyong National University
Internat. J. Math. & Math. Sci. VOL. 1 NO. (1998) 369374 369 ANGULAR ESTIMATIONS OF CERTAIN INTEGRAL OPERATORS NAK EUN CHO, IN HWA KIM JI A KIM Department of Applied Mathematics Pukyong National University
n(t,f) n(0,f) dt+n(0,f)logr t log + f(re iθ ) dθ.
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 53 (2016), No. 1, pp. 29 38 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2016.53.1.029 VALUE DISTRIBUTION OF SOME q-difference POLYNOMIALS Na Xu and Chun-Ping Zhong Abstract. For a transcendental
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 53 (2016), No. 1, pp. 29 38 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2016.53.1.029 VALUE DISTRIBUTION OF SOME q-difference POLYNOMIALS Na Xu and Chun-Ping Zhong Abstract. For a transcendental
SOME COUNTEREXAMPLES IN DYNAMICS OF RATIONAL SEMIGROUPS. 1. Introduction
 SOME COUNTEREXAMPLES IN DYNAMICS OF RATIONAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ, TOSHIYUKI SUGAWA, AND HIROKI SUMI Abstract. We give an example of two rational functions with non-equal Julia sets that generate
SOME COUNTEREXAMPLES IN DYNAMICS OF RATIONAL SEMIGROUPS RICH STANKEWITZ, TOSHIYUKI SUGAWA, AND HIROKI SUMI Abstract. We give an example of two rational functions with non-equal Julia sets that generate
Uniformly convex functions II
 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LVIII. (199 Uniformly convex functions II by Wancang Ma and David Minda (Cincinnati, Ohio Abstract. Recently, A. W. Goodman introduced the class UCV of normalized uniformly
ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LVIII. (199 Uniformly convex functions II by Wancang Ma and David Minda (Cincinnati, Ohio Abstract. Recently, A. W. Goodman introduced the class UCV of normalized uniformly
MATH COMPLEX ANALYSIS. Contents
 MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
CONSIDERATION OF COMPACT MINIMAL SURFACES IN 4-DIMENSIONAL FLAT TORI IN TERMS OF DEGENERATE GAUSS MAP
 CONSIDERATION OF COMPACT MINIMAL SURFACES IN 4-DIMENSIONAL FLAT TORI IN TERMS OF DEGENERATE GAUSS MAP TOSHIHIRO SHODA Abstract. In this paper, we study a compact minimal surface in a 4-dimensional flat
CONSIDERATION OF COMPACT MINIMAL SURFACES IN 4-DIMENSIONAL FLAT TORI IN TERMS OF DEGENERATE GAUSS MAP TOSHIHIRO SHODA Abstract. In this paper, we study a compact minimal surface in a 4-dimensional flat
9 Conformal Types of Riemann Surfaces
 9 Conformal Types of Riemann Surfaces We will discuss complete minimal surfaces of finite topological type and their annular ends. We need first consider a little of the conformal type of such surfaces.
9 Conformal Types of Riemann Surfaces We will discuss complete minimal surfaces of finite topological type and their annular ends. We need first consider a little of the conformal type of such surfaces.
A Note on Coefficient Inequalities for (j, i)-symmetrical Functions with Conic Regions
 BULLETIN OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4874 ISSN (o) 2303-4955 wwwimviblorg /JOURNALS / BULLETIN Vol 6(2016) 77-87 Former BULLETIN OF THE SOCIETY OF MATHEMATICIANS BANJA
BULLETIN OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4874 ISSN (o) 2303-4955 wwwimviblorg /JOURNALS / BULLETIN Vol 6(2016) 77-87 Former BULLETIN OF THE SOCIETY OF MATHEMATICIANS BANJA
Chapter 6: The metric space M(G) and normal families
 Chapter 6: The metric space MG) and normal families Course 414, 003 04 March 9, 004 Remark 6.1 For G C open, we recall the notation MG) for the set algebra) of all meromorphic functions on G. We now consider
Chapter 6: The metric space MG) and normal families Course 414, 003 04 March 9, 004 Remark 6.1 For G C open, we recall the notation MG) for the set algebra) of all meromorphic functions on G. We now consider
Plane hyperbolic geometry
 2 Plane hyperbolic geometry In this chapter we will see that the unit disc D has a natural geometry, known as plane hyperbolic geometry or plane Lobachevski geometry. It is the local model for the hyperbolic
2 Plane hyperbolic geometry In this chapter we will see that the unit disc D has a natural geometry, known as plane hyperbolic geometry or plane Lobachevski geometry. It is the local model for the hyperbolic
Math 320-2: Midterm 2 Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 2015
 Math 30-: Midterm Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 015 1. Give an example of each of the following. No justification is needed. (a) A metric on R with respect to which R is bounded. (b)
Math 30-: Midterm Practice Solutions Northwestern University, Winter 015 1. Give an example of each of the following. No justification is needed. (a) A metric on R with respect to which R is bounded. (b)
MORE NOTES FOR MATH 823, FALL 2007
 MORE NOTES FOR MATH 83, FALL 007 Prop 1.1 Prop 1. Lemma 1.3 1. The Siegel upper half space 1.1. The Siegel upper half space and its Bergman kernel. The Siegel upper half space is the domain { U n+1 z C
MORE NOTES FOR MATH 83, FALL 007 Prop 1.1 Prop 1. Lemma 1.3 1. The Siegel upper half space 1.1. The Siegel upper half space and its Bergman kernel. The Siegel upper half space is the domain { U n+1 z C
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
November 27 Lecturer Dmitri Zaitsev Michaelmas Term Course S h e e t 2. Due: after the lecture. + O(4)) (z 3! + O(5)) = c z3 + O(4),
 November 7 Lecturer Dmitri Zaitsev Michaelmas Term 017 Course 343 017 S h e e t Due: after the lecture Exercise 1 Determine the zero order of f at 0: (i) f(z) = z cosz sinz; Solution Use power series expansion
November 7 Lecturer Dmitri Zaitsev Michaelmas Term 017 Course 343 017 S h e e t Due: after the lecture Exercise 1 Determine the zero order of f at 0: (i) f(z) = z cosz sinz; Solution Use power series expansion
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
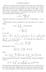 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
THE RESIDUE THEOREM. f(z) dz = 2πi res z=z0 f(z). C
 THE RESIDUE THEOREM ontents 1. The Residue Formula 1 2. Applications and corollaries of the residue formula 2 3. ontour integration over more general curves 5 4. Defining the logarithm 7 Now that we have
THE RESIDUE THEOREM ontents 1. The Residue Formula 1 2. Applications and corollaries of the residue formula 2 3. ontour integration over more general curves 5 4. Defining the logarithm 7 Now that we have
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE. Department of Mathematics. MA4247 Complex Analysis II. Lecture Notes Part IV
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part IV Chapter 2. Further properties of analytic/holomorphic functions (continued) 2.4. The Open mapping
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part IV Chapter 2. Further properties of analytic/holomorphic functions (continued) 2.4. The Open mapping
A NOTE ON THE LOCATION OF CRITICAL POINTS OF POLYNOMIALS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL Volume 27, No. 2, February 1971 SOCIETY A NOTE ON THE LOCATION OF CRITICAL POINTS OF POLYNOMIALS E. B. SAFF AND J. B. TWOMEY Abstract. Let(P(a, 3) denote the set
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL Volume 27, No. 2, February 1971 SOCIETY A NOTE ON THE LOCATION OF CRITICAL POINTS OF POLYNOMIALS E. B. SAFF AND J. B. TWOMEY Abstract. Let(P(a, 3) denote the set
On a new class of (j, i)-symmetric function on conic regions
 Available online at wwwisr-publicationscom/jnsa J Nonlinear Sci Appl 10 (2017) 4628 4637 Research Article Journal Homepage: wwwtjnsacom - wwwisr-publicationscom/jnsa On a new class of (j i)-symmetric function
Available online at wwwisr-publicationscom/jnsa J Nonlinear Sci Appl 10 (2017) 4628 4637 Research Article Journal Homepage: wwwtjnsacom - wwwisr-publicationscom/jnsa On a new class of (j i)-symmetric function
(7) Suppose α, β, γ are nonzero complex numbers such that α = β = γ.
 January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
January 22, 2011 COMPLEX ANALYSIS: PROBLEMS SHEET -1 M.THAMBAN NAIR (1) Show that C is a field under the addition and multiplication defined for complex numbers. (2) Show that the map f : R C defined by
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall Anton R. Schep
 Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Math 341: Convex Geometry. Xi Chen
 Math 341: Convex Geometry Xi Chen 479 Central Academic Building, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta T6G 2G1, CANADA E-mail address: xichen@math.ualberta.ca CHAPTER 1 Basics 1. Euclidean Geometry
Math 341: Convex Geometry Xi Chen 479 Central Academic Building, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta T6G 2G1, CANADA E-mail address: xichen@math.ualberta.ca CHAPTER 1 Basics 1. Euclidean Geometry
IV. Conformal Maps. 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability. 2. Automorphisms of the Riemann sphere: Möbius transformations
 MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
MTH6111 Complex Analysis 2009-10 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 IV. Conformal Maps 1. Geometric interpretation of differentiability We saw from the definition of complex differentiability that if f
Course 212: Academic Year Section 1: Metric Spaces
 Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Course 212: Academic Year 1991-2 Section 1: Metric Spaces D. R. Wilkins Contents 1 Metric Spaces 3 1.1 Distance Functions and Metric Spaces............. 3 1.2 Convergence and Continuity in Metric Spaces.........
Möbius Transformation
 Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
Möbius Transformation 1 1 June 15th, 2010 Mathematics Science Center Tsinghua University Philosophy Rigidity Conformal mappings have rigidity. The diffeomorphism group is of infinite dimension in general.
ON THE DEFORMATION WITH CONSTANT MILNOR NUMBER AND NEWTON POLYHEDRON
 ON THE DEFORMATION WITH CONSTANT MILNOR NUMBER AND NEWTON POLYHEDRON OULD M ABDERRAHMANE Abstract- We show that every µ-constant family of isolated hypersurface singularities satisfying a nondegeneracy
ON THE DEFORMATION WITH CONSTANT MILNOR NUMBER AND NEWTON POLYHEDRON OULD M ABDERRAHMANE Abstract- We show that every µ-constant family of isolated hypersurface singularities satisfying a nondegeneracy
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008
 Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
LINEAR FRACTIONAL COMPOSITION OPERATORS ON H 2
 J Integral Equations and Operator Theory (988, 5 60 LINEAR FRACTIONAL COMPOSITION OPERATORS ON H 2 CARL C COWEN Abstract If ϕ is an analytic function mapping the unit disk D into itself, the composition
J Integral Equations and Operator Theory (988, 5 60 LINEAR FRACTIONAL COMPOSITION OPERATORS ON H 2 CARL C COWEN Abstract If ϕ is an analytic function mapping the unit disk D into itself, the composition
Complex Analysis Important Concepts
 Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM. 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces
 8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
2 Complex Functions and the Cauchy-Riemann Equations
 2 Complex Functions and the Cauchy-Riemann Equations 2.1 Complex functions In one-variable calculus, we study functions f(x) of a real variable x. Likewise, in complex analysis, we study functions f(z)
2 Complex Functions and the Cauchy-Riemann Equations 2.1 Complex functions In one-variable calculus, we study functions f(x) of a real variable x. Likewise, in complex analysis, we study functions f(z)
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
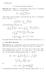 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Complex Analysis review notes for weeks 1-6
 Complex Analysis review notes for weeks -6 Peter Milley Semester 2, 2007 In what follows, unless stated otherwise a domain is a connected open set. Generally we do not include the boundary of the set,
Complex Analysis review notes for weeks -6 Peter Milley Semester 2, 2007 In what follows, unless stated otherwise a domain is a connected open set. Generally we do not include the boundary of the set,
Hermitian forms and rational maps of hyperquadrics
 Hermitian forms and rational maps of hyperquadrics Jiří Lebl Department of Mathematics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign March 13th 2010 Jiří Lebl (UIUC) Hermitian forms and hyperquadrics March
Hermitian forms and rational maps of hyperquadrics Jiří Lebl Department of Mathematics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign March 13th 2010 Jiří Lebl (UIUC) Hermitian forms and hyperquadrics March
