Two-scale Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners for boundary refinements
|
|
|
- Leon White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Two-scale Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners for boundary refinements Patrice Hauret 1 and Patrick Le Tallec 2 1 Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories, MS 25-45, California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91125, USA 2 Laboratoire de Mécanique des Solides, CNRS UMR 7649, Département de Mécanique, Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau Cedex, FRANCE Summary. The present work introduces simple Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners for the resolution of elasticity problems in presence of numerous small disjoint geometric refinements on the boundary of the domain, situation which typically occurs in tire industry. Moreover, the condition number of the preconditioned system is proved to be independent of the number and the size of the small details on the boundary. Finally, as an enhancement, the second proposed preconditioner makes use of a coarse space counterbalancing the effect of essential boundary conditions on the small details, and a simple numerical academic test illustrates the increased efficiency. Further details on the motivation as well as complete proofs can be found in [4, 5]. 1 Introduction Let Ω R d be the reference configuration of a body, partitioned into a coarse region Ω where the properties of the material are rather smooth and where a coarse approximation should be sufficient, and into small disjoint boundary regions denoted by (Ω k ) 1 k K where a fine discretization is required (e.g. geometrical refinements, fine behavior of the material). Such a situation typically occurs for tires, the internal structure and the surface sculptures playing the role of the coarse and fine zones, respectively. Let us denote by Γ D a part of the boundary of Ω where displacements are prescribed and by Γ N = Ω \ Γ D its complementary part. Denoting by H 1(Ω) := {v H 1 (Ω) d, v ΓD Ω = } the space of admissible displacements, our model elastostatic problem consists in finding u H 1 (Ω) such that: a(u, v) := E ijkl ε(u) kl ε(v) ij = f v + g v =: l(v), v H 1 (Ω). Γ N Ω Ω
2 2 Patrice Hauret and Patrick Le Tallec Here E denotes the fourth order elasticity tensor, f L 2 (Ω) d and g L 2 (Γ N ) d the loading forces, and ɛ(v) = 1 2 ( v + ( v)t ) is the linearized strain tensor. Considering that the solution must be computed with a multi-scale approach in order to respect the characteristics of the problem, the strategy proposed in this paper consists in using: 1. mortar formulations [2, 13] on the interfaces Γ k = Ω Ω k enabling to use independent approximations in the coarse and fine regions respectively, 2. efficient Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners [9], which we adapt so that the computational cost of the full algebraic problem remains independent (or at least weakly dependent) of the number and the size of the fine subdomains (Ω k ) 1 k K. The sequel is organized as follows. After the introduction of a mortar formulation (section 2), we propose two possible Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners and state their two-scale properties (section 3). In particular, the second enhanced preconditioner makes use of a coarse space counterbalancing the effect of essential boundary conditions imposed on the boundary sculptures. A simple numerical test shows its increased efficiency for a simple academic problem. A broader perspective on the subject as well as complete proofs are given in [4, 5]. 2 Non-conforming formulation For every k K, let (T k;hk ) hk > be a sequence of meshes of the substructure Ω k, h k denoting the maximal diameter of its elements. The corresponding finite-element spaces of order q are denoted by (V k;hk ) hk > H (Ω 1 k ). As in [3, 7], for stability purpose when using a discontinuous mortar formulation, interface bubbles can be added on the fine subdomains. As a consequence, we introduce the potentially enriched spaces of displacements X k;hk = V k;hk B k;hk for every 1 k K and X ;h = V ;h. For each interface Γ k, W k;hk will stand for the trace of the local space X k;hk on this interface. In order to impose a weak displacement continuity between Ω and Ω k, a space of Lagrange multipliers M k;hk is introduced on the mesh T k;hk over Γ k. Actually, various choices of continuous or of discontinuous polynomial functions of degree r can be used [2, 1, 12, 8, 6, 7] but in any case, they must satisfy the following fundamental assumptions: Assumption 1 [Coercivity]. Let u H 1 (Ω ) d and u k H 1 (Ω k ) d be rigid motions, i.e. ε(u ) = in L 2 (Ω ) d d and ε(u k ) = in L 2 (Ω k ) d d, satisfying the weak continuity requirement Γ k (u u k ) µ = for every µ M k;hk. Then u = u k almost everywhere on Γ k. Assumption 2 [Inf-sup condition]. There exists a mapping π k : L 2 (Γ k ) W k;hk such that for all v L 2 (Γ k ),
3 Two-scale Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners for boundary refinements 3 (π k v) µ = v µ, µ M k;hk, Γ k Γ k satisfying π k v k, 1 C v 2 k, 1. The mesh dependent norm 2 k, 1 introduced 2 above is defined as in [1, 11] by v 2 k, = diam(k Γ 1 k ) 1 v 2. 2 K T K Γ k k;hk Assumption 3 [Accuracy]. The total degree r of Lagrange multipliers is bounded from below by r q 1, q being the total degree of the displacement shape functions. Then, the mortar formulation of the problem of interest can be written as finding u = (u, u 1,..., u K ) K k= X k;h k and λ = (λ 1,..., λ K ) K k=1 M k;h k satisfying for every v K k= X k;h k and µ K k=1 M k;h k, a (u, v ) + K k=1 b k(v, λ k ) = l (v ) a k (u k, v k ) b k (v k, λ k ) = l k (v k ), 1 k K b k (u, µ k ) b k (u k, µ k ) =, 1 k K. (1) The above problem uses the obvious notation a k (u k, v k ) = Ω k E ijmn ε(u k ) mn ε(v k ) ij, l k (v k ) = Ω k f v k + Γ N Ω k g v k, b k (v, µ k ) = Γ k v µ k and b k (v k, µ k ) = Γ k v k µ k. 3 Two-scale preconditioners In matrix notation, after elimination of the Lagrange multipliers λ k in the first equation of (1), the system becomes S U ( = L ), ( ) U k L k K k =, 1 k K, B k U Λ k where S = A K k=1 Bt k R kk 1 k Rt k B k is the Schur complement matrix, K ( ) and L = L B t kr k K 1 Lk k the corresponding right hand side. In k=1 these definitions, the local stiffness matrix K k and restriction operator R k are given by ( ) ( ) Ak B K k = t k Uk, R B k k = Λ Λ k. k (2)
4 4 Patrice Hauret and Patrick Le Tallec An iterative solver can be efficiently used to solve (2) if one is able to define a preconditioner S of the exact Schur complement S which is spectrally equivalent to S, with constants independent of the number and the size of the small subdomains. When L,.., L K are given, the application of such a preconditioner consists in the following operations: 1. Compute L by solving Dirichlet problems on the small subdomains prescribing zero displacements on the interfaces (Γ k ) 1 k K, 2. Solve the extended Neumann problem S Ũ = L, 3. Compute (Ũk, Λ k ) over each Ω k by solving the Dirichlet problem: ( ) ( ) Ũk Lk K k =. Λ k B k Ũ The most natural -and rather efficient- preconditioner consists in simply using S = A. This is a standard Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioner for which we prove [5]: Proposition 1. Assuming that A is invertible, i.e. Γ D Ω has a positive measure, the following spectral equivalence holds for all U : with: W 1,h S U, U A U, U S U, U, ( ) 1 C k C k L = 1 + C max + max, W 1,h k I 1 c k I 2 α L k where I 1 (resp. I 2 ) is the set of indices k 1 such that Ω k is not fixed on its boundary (resp. is fixed on a part of its boundary), the positive constants c k and C k are such that c k ξ 2 E ijmn ξ mn ξ ij C k ξ 2 over Ω k for every symmetric matrix ξ R d d, α is the coercivity constant of the bilinear form a and L k = diam(ω k ). The constant C > is independent of the number K and the size of the subdomains. This simple choice will lack of efficiency in two simple situations: 1. a fine subdomain Ω k (k 1) has a small size L k << L and is fixed on a part of its boundary (k I 2 ); in this situation, because of its size, the substructure will have a rather large stiffness to interface rigid body displacements, 2. a fine subdomain Ω k (k 1) has several stiff modes involving interface motions (rigid links, incompressibility). Assuming that these directions of localized interface stiffness be in very small number N k (this is indeed the case for interface rigid body motions), we then propose a modification of the previous preconditioner enabling to correct such a lack of efficiency.
5 Two-scale Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners for boundary refinements 5 For all k 1 such that Ω k is fixed on a part of its boundary, we denote by (e i k ) 1 i N k (with N k = 6 in general) the interface rigid motions of Γ k or rigid links and introduce W k = span{e i k, i = 1,.., N k}. To each interface rigid body motion e i k, we associate its local a k-harmonic extension (u i k, λi k ) X k;h k M k;δk solution of a k (v, u i k ) v λ Γ i k =, v X k;h k, k (3) u i k µ = e i k µ, µ M k;δk. Γ k Γ k These solutions span two small local spaces X k = span{u i k, i = 1,.., N k} X k;hk, M k = span{λ i k, i = 1,.., N k} M k;δk. If k 1 is such that Ω k is not fixed on its boundary, we adopt W k = M k = {}. Then, instead of finding U such that S U = L, we propose to compute u X ;h, (u k ) ( X k ) 1 k K, (λ k ) ( M k ) 1 k K solution of the coupled problem K a (u, v ) + v λ k = l (v ), v X ;h, k=1 Γ k a k (u k, v k ) v k λ k =, v k X k, 1 k K, (4) Γ k u k µ k = u µ k, µ k M k, 1 k K. Γ k Γ k This amounts to reduce the local substructure response to the harmonic extension of its stiff interface modes, which belongs to X k. We introduce the ] t matrix I k = Λ t k B k where Λ t k [Λ = 1 k,.., ΛN k k is the matrix built with the multipliers computed in (3), and the restriction Åk of the displacement stiffness matrix A k to the local space X k ) (Åk = (U k) i t A k U j k = a k(u j k, ij ui k) = u j k λi k, (5) Γ k where (3) has been used. Exploiting (5) to reformulate (4)-2,(4)-3, the system (4) can be rewritten after some algebraic elimination as S U = L, (6)
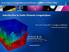
6 6 Patrice Hauret and Patrick Le Tallec with a new approximate Schur complement given by S = A + = A + K k=1 K k=1 I t kå t k I k (7) B t kλ k Å t k Λt kb k. The complexity of its inversion is much smaller than solving S U = L because each local problem (3) used in the construction of S only involves a subspace of displacements of dimension N k. Moreover, we prove in [5] that: Proposition 2. For all U, the following spectral equivalence holds W 1,h S U, U S U, U S U, U, with ( 1 = C 1 + max W 1,h 1 k K ) C k. c The constant C > is independent of the number K and the size of the subdomains. 4 Numerical illustration Let us consider here a two-scale beam (as represented on figure 1) whose both tips are clamped. The material is elastic, isotropic, homogeneous in each substructure, and the displacements under loading are computed by a preconditioned conjugate gradient method. Figure 2 illustrates the advantage of the enhanced Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioner when two small substructures are clamped. In conformity with the announced results, the gain in efficiency is independent of the ratio of Young moduli between the fine and coarse zones. Moreover, a factor 3 improvement is achieved in the number of iterations, and roughly speaking in the time of computation. Finally, it is shown in [5] that such a preconditioner can be used as an efficient quasi-tangent operator in the nonlinear framework as soon as boundary geometrical details are sufficiently soft. 5 Conclusion The domain-decomposition based preconditioners proposed here achieve scaleindependent performances. They should be extended to cases where the details overlap the coarse region in the line of the fictitious domains approach, and also to cases where the details are not disjoint but constitute a continuous belt along the boundary.
7 Xd3d 8..3b (25/9/23) Two-scale Dirichlet-Neumann preconditioners for boundary refinements Fig. 1. Maximal stress distribution on a deformed configuration of our two-scale model problem where two of the details are clamped on their lower face. r = 1 r = 1 1 Enhanced Simple 1 Enhanced Simple L^2 norm of error L^2 norm of error # iterations # iterations r = r = 1.E6 1 Enhanced Simple 1 Enhanced Simple L^2 norm of error L^2 norm of error # iterations # iterations Fig. 2. Convergence of the simple and enhanced Dirichlet-Neumann algorithms for different values of the ratio r of Young moduli between the fine and coarse subdomains. Acknowledgement. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Michelin Tire Company during the completion of this work at the Center of Applied Mathematics (CMAP), Ecole Polytechnique, and Professor François Jouve for providing his finite element code in which the presented ideas have been implemented.
8 8 Patrice Hauret and Patrick Le Tallec References 1. A. Agouzal and J.M. Thomas. Une méthode d éléments finis hybrides en décomposition de domaines. RAIRO M2AN, 29: , C. Bernardi, Y. Maday, and A.T. Patera. Domain decomposition by the mortar element method. In H.G. Kaper ans M. Garbey, editor, Asymptotic and Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations with Critical Parameters, pages N.A.T.O. ASI, Kluwer Academic Publishers, F. Brezzi and D. Marini. Error estimates for the three-field formulation with bubble stabilization. Math. Comp., 7: , P. Hauret. Méthodes numériques pour la dynamique des structures non-linéaires incompressibles à deux échelles (Numerical methods for the dynamic analysis of two-scale incompressible nonlinear structures). PhD thesis, Ecole Polytechnique, P. Hauret and P. Le Tallec. Dirichlet-neumann preconditioners for elliptic problems with small disjoint geometric refinements on the boundary. Technical Report 552, CMAP - Ecole Polytechnique, september P. Hauret and P. Le Tallec. A stabilized discontinuous mortar formulation for elastostatics and elastodynamics problems, part i: abstract framework. Technical Report 553, CMAP - Ecole Polytechnique, september P. Hauret and P. Le Tallec. A stabilized discontinuous mortar formulation for elastostatics and elastodynamics problems, part ii: discontinuous Lagrange multipliers. Technical Report 554, CMAP - Ecole Polytechnique, september C. Kim, R.D. Lazarov, J.E. Pasciak, and P.S. Vassilevski. Multiplier spaces for the mortar finite element method in three dimensions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 39: , A. Quarteroni and A. Valli. Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations. Oxford University Press, P. Seshaiyer. Non-conforming hp finite element methods. PhD thesis, University of Maryland, B.I. Wohlmuth. Hierarchical a posteriori error estimators for mortar finite element methods with Lagrange multipliers. SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 36: , B.I. Wohlmuth. A mortar finite element method using dual spaces for the Lagrange multiplier. SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 38: , B.I. Wohlmuth. Discretization methods and iterative solvers based on domain decomposition. Springer, 21.
Non-Conforming Finite Element Methods for Nonmatching Grids in Three Dimensions
 Non-Conforming Finite Element Methods for Nonmatching Grids in Three Dimensions Wayne McGee and Padmanabhan Seshaiyer Texas Tech University, Mathematics and Statistics (padhu@math.ttu.edu) Summary. In
Non-Conforming Finite Element Methods for Nonmatching Grids in Three Dimensions Wayne McGee and Padmanabhan Seshaiyer Texas Tech University, Mathematics and Statistics (padhu@math.ttu.edu) Summary. In
Construction of a New Domain Decomposition Method for the Stokes Equations
 Construction of a New Domain Decomposition Method for the Stokes Equations Frédéric Nataf 1 and Gerd Rapin 2 1 CMAP, CNRS; UMR7641, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau Cedex, France 2 Math. Dep., NAM,
Construction of a New Domain Decomposition Method for the Stokes Equations Frédéric Nataf 1 and Gerd Rapin 2 1 CMAP, CNRS; UMR7641, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau Cedex, France 2 Math. Dep., NAM,
New constructions of domain decomposition methods for systems of PDEs
 New constructions of domain decomposition methods for systems of PDEs Nouvelles constructions de méthodes de décomposition de domaine pour des systèmes d équations aux dérivées partielles V. Dolean?? F.
New constructions of domain decomposition methods for systems of PDEs Nouvelles constructions de méthodes de décomposition de domaine pour des systèmes d équations aux dérivées partielles V. Dolean?? F.
Overlapping Schwarz preconditioners for Fekete spectral elements
 Overlapping Schwarz preconditioners for Fekete spectral elements R. Pasquetti 1, L. F. Pavarino 2, F. Rapetti 1, and E. Zampieri 2 1 Laboratoire J.-A. Dieudonné, CNRS & Université de Nice et Sophia-Antipolis,
Overlapping Schwarz preconditioners for Fekete spectral elements R. Pasquetti 1, L. F. Pavarino 2, F. Rapetti 1, and E. Zampieri 2 1 Laboratoire J.-A. Dieudonné, CNRS & Université de Nice et Sophia-Antipolis,
A Balancing Algorithm for Mortar Methods
 A Balancing Algorithm for Mortar Methods Dan Stefanica Baruch College, City University of New York, NY 11, USA Dan Stefanica@baruch.cuny.edu Summary. The balancing methods are hybrid nonoverlapping Schwarz
A Balancing Algorithm for Mortar Methods Dan Stefanica Baruch College, City University of New York, NY 11, USA Dan Stefanica@baruch.cuny.edu Summary. The balancing methods are hybrid nonoverlapping Schwarz
A stabilized discontinuous mortar formulation for elastostatics and elastodynamics problems Part II: discontinuous Lagrange multipliers
 ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE CENTRE DE MATHÉMATIQUES APPLIQUÉES UMR CNRS 7641 9118 PALAISEAU CEDEX (FRANCE). Tél: 01 69 33 41 50. Fax: 01 69 33 30 11 http://www.cmap.polytechnique.fr/ A stabilized discontinuous
ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE CENTRE DE MATHÉMATIQUES APPLIQUÉES UMR CNRS 7641 9118 PALAISEAU CEDEX (FRANCE). Tél: 01 69 33 41 50. Fax: 01 69 33 30 11 http://www.cmap.polytechnique.fr/ A stabilized discontinuous
18. Balancing Neumann-Neumann for (In)Compressible Linear Elasticity and (Generalized) Stokes Parallel Implementation
 Fourteenth nternational Conference on Domain Decomposition Methods Editors: smael Herrera, David E Keyes, Olof B Widlund, Robert Yates c 23 DDMorg 18 Balancing Neumann-Neumann for (n)compressible Linear
Fourteenth nternational Conference on Domain Decomposition Methods Editors: smael Herrera, David E Keyes, Olof B Widlund, Robert Yates c 23 DDMorg 18 Balancing Neumann-Neumann for (n)compressible Linear
PARTITION OF UNITY FOR THE STOKES PROBLEM ON NONMATCHING GRIDS
 PARTITION OF UNITY FOR THE STOES PROBLEM ON NONMATCHING GRIDS CONSTANTIN BACUTA AND JINCHAO XU Abstract. We consider the Stokes Problem on a plane polygonal domain Ω R 2. We propose a finite element method
PARTITION OF UNITY FOR THE STOES PROBLEM ON NONMATCHING GRIDS CONSTANTIN BACUTA AND JINCHAO XU Abstract. We consider the Stokes Problem on a plane polygonal domain Ω R 2. We propose a finite element method
Lecture Note III: Least-Squares Method
 Lecture Note III: Least-Squares Method Zhiqiang Cai October 4, 004 In this chapter, we shall present least-squares methods for second-order scalar partial differential equations, elastic equations of solids,
Lecture Note III: Least-Squares Method Zhiqiang Cai October 4, 004 In this chapter, we shall present least-squares methods for second-order scalar partial differential equations, elastic equations of solids,
PhD dissertation defense
 Isogeometric mortar methods with applications in contact mechanics PhD dissertation defense Brivadis Ericka Supervisor: Annalisa Buffa Doctor of Philosophy in Computational Mechanics and Advanced Materials,
Isogeometric mortar methods with applications in contact mechanics PhD dissertation defense Brivadis Ericka Supervisor: Annalisa Buffa Doctor of Philosophy in Computational Mechanics and Advanced Materials,
On Mixed Methods for Signorini Problems
 Annals of University of Craiova, Math. Comp. Sci. Ser. Volume 30, 2003, Pages 45 52 ISS: 1223-6934 On Mixed Methods for Signorini Problems Faker Ben Belgacem, Yves Renard, and Leila Slimane Abstract. We
Annals of University of Craiova, Math. Comp. Sci. Ser. Volume 30, 2003, Pages 45 52 ISS: 1223-6934 On Mixed Methods for Signorini Problems Faker Ben Belgacem, Yves Renard, and Leila Slimane Abstract. We
An Iterative Substructuring Method for Mortar Nonconforming Discretization of a Fourth-Order Elliptic Problem in two dimensions
 An Iterative Substructuring Method for Mortar Nonconforming Discretization of a Fourth-Order Elliptic Problem in two dimensions Leszek Marcinkowski Department of Mathematics, Warsaw University, Banacha
An Iterative Substructuring Method for Mortar Nonconforming Discretization of a Fourth-Order Elliptic Problem in two dimensions Leszek Marcinkowski Department of Mathematics, Warsaw University, Banacha
Acceleration of a Domain Decomposition Method for Advection-Diffusion Problems
 Acceleration of a Domain Decomposition Method for Advection-Diffusion Problems Gert Lube 1, Tobias Knopp 2, and Gerd Rapin 2 1 University of Göttingen, Institute of Numerical and Applied Mathematics (http://www.num.math.uni-goettingen.de/lube/)
Acceleration of a Domain Decomposition Method for Advection-Diffusion Problems Gert Lube 1, Tobias Knopp 2, and Gerd Rapin 2 1 University of Göttingen, Institute of Numerical and Applied Mathematics (http://www.num.math.uni-goettingen.de/lube/)
A discontinuous stabilized mortar method for general 3D elastic problems
 A discontinuous stabilized mortar method for general 3D elastic problems Patrice Hauret a, and Patrick Le Tallec b a Manufacture Française des Pneumatiques Michelin, Centre de Technologies Ladoux, 63040
A discontinuous stabilized mortar method for general 3D elastic problems Patrice Hauret a, and Patrick Le Tallec b a Manufacture Française des Pneumatiques Michelin, Centre de Technologies Ladoux, 63040
Domain Decomposition Preconditioners for Spectral Nédélec Elements in Two and Three Dimensions
 Domain Decomposition Preconditioners for Spectral Nédélec Elements in Two and Three Dimensions Bernhard Hientzsch Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, 51 Mercer Street, New
Domain Decomposition Preconditioners for Spectral Nédélec Elements in Two and Three Dimensions Bernhard Hientzsch Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, 51 Mercer Street, New
Multilevel Preconditioning of Graph-Laplacians: Polynomial Approximation of the Pivot Blocks Inverses
 Multilevel Preconditioning of Graph-Laplacians: Polynomial Approximation of the Pivot Blocks Inverses P. Boyanova 1, I. Georgiev 34, S. Margenov, L. Zikatanov 5 1 Uppsala University, Box 337, 751 05 Uppsala,
Multilevel Preconditioning of Graph-Laplacians: Polynomial Approximation of the Pivot Blocks Inverses P. Boyanova 1, I. Georgiev 34, S. Margenov, L. Zikatanov 5 1 Uppsala University, Box 337, 751 05 Uppsala,
The Mortar Wavelet Method Silvia Bertoluzza Valerie Perrier y October 29, 1999 Abstract This paper deals with the construction of wavelet approximatio
 The Mortar Wavelet Method Silvia Bertoluzza Valerie Perrier y October 9, 1999 Abstract This paper deals with the construction of wavelet approximation spaces, in the framework of the Mortar method. We
The Mortar Wavelet Method Silvia Bertoluzza Valerie Perrier y October 9, 1999 Abstract This paper deals with the construction of wavelet approximation spaces, in the framework of the Mortar method. We
On Nonlinear Dirichlet Neumann Algorithms for Jumping Nonlinearities
 On Nonlinear Dirichlet Neumann Algorithms for Jumping Nonlinearities Heiko Berninger, Ralf Kornhuber, and Oliver Sander FU Berlin, FB Mathematik und Informatik (http://www.math.fu-berlin.de/rd/we-02/numerik/)
On Nonlinear Dirichlet Neumann Algorithms for Jumping Nonlinearities Heiko Berninger, Ralf Kornhuber, and Oliver Sander FU Berlin, FB Mathematik und Informatik (http://www.math.fu-berlin.de/rd/we-02/numerik/)
20. A Dual-Primal FETI Method for solving Stokes/Navier-Stokes Equations
 Fourteenth International Conference on Domain Decomposition Methods Editors: Ismael Herrera, David E. Keyes, Olof B. Widlund, Robert Yates c 23 DDM.org 2. A Dual-Primal FEI Method for solving Stokes/Navier-Stokes
Fourteenth International Conference on Domain Decomposition Methods Editors: Ismael Herrera, David E. Keyes, Olof B. Widlund, Robert Yates c 23 DDM.org 2. A Dual-Primal FEI Method for solving Stokes/Navier-Stokes
Short title: Total FETI. Corresponding author: Zdenek Dostal, VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava, 17 listopadu 15, CZ Ostrava, Czech Republic
 Short title: Total FETI Corresponding author: Zdenek Dostal, VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava, 17 listopadu 15, CZ-70833 Ostrava, Czech Republic mail: zdenek.dostal@vsb.cz fax +420 596 919 597 phone
Short title: Total FETI Corresponding author: Zdenek Dostal, VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava, 17 listopadu 15, CZ-70833 Ostrava, Czech Republic mail: zdenek.dostal@vsb.cz fax +420 596 919 597 phone
A LAGRANGE MULTIPLIER METHOD FOR ELLIPTIC INTERFACE PROBLEMS USING NON-MATCHING MESHES
 A LAGRANGE MULTIPLIER METHOD FOR ELLIPTIC INTERFACE PROBLEMS USING NON-MATCHING MESHES P. HANSBO Department of Applied Mechanics, Chalmers University of Technology, S-4 96 Göteborg, Sweden E-mail: hansbo@solid.chalmers.se
A LAGRANGE MULTIPLIER METHOD FOR ELLIPTIC INTERFACE PROBLEMS USING NON-MATCHING MESHES P. HANSBO Department of Applied Mechanics, Chalmers University of Technology, S-4 96 Göteborg, Sweden E-mail: hansbo@solid.chalmers.se
Checkerboard instabilities in topological shape optimization algorithms
 Checkerboard instabilities in topological shape optimization algorithms Eric Bonnetier, François Jouve Abstract Checkerboards instabilities for an algorithm of topological design are studied on a simple
Checkerboard instabilities in topological shape optimization algorithms Eric Bonnetier, François Jouve Abstract Checkerboards instabilities for an algorithm of topological design are studied on a simple
ETNA Kent State University
 Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 11, pp. 1-24, 2000. Copyright 2000,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA NEUMANN NEUMANN METHODS FOR VECTOR FIELD PROBLEMS ANDREA TOSELLI Abstract. In this paper,
Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 11, pp. 1-24, 2000. Copyright 2000,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA NEUMANN NEUMANN METHODS FOR VECTOR FIELD PROBLEMS ANDREA TOSELLI Abstract. In this paper,
ON THE MULTIPOINT MIXED FINITE VOLUME METHODS ON QUADRILATERAL GRIDS
 ON THE MULTIPOINT MIXED FINITE VOLUME METHODS ON QUADRILATERAL GRIDS VINCENT FONTAINE 1,2 AND ANIS YOUNES 2 1 Laboratoire de Physique des Bâtiments et des Systèmes, Université de La Réunion, 15 avenue
ON THE MULTIPOINT MIXED FINITE VOLUME METHODS ON QUADRILATERAL GRIDS VINCENT FONTAINE 1,2 AND ANIS YOUNES 2 1 Laboratoire de Physique des Bâtiments et des Systèmes, Université de La Réunion, 15 avenue
An example of nonuniqueness for the continuous static unilateral contact model with Coulomb friction
 An example of nonuniqueness for the continuous static unilateral contact model with Coulomb friction Un exemple de non-unicité pour le modèle continu statique de contact unilatéral avec frottement de Coulomb
An example of nonuniqueness for the continuous static unilateral contact model with Coulomb friction Un exemple de non-unicité pour le modèle continu statique de contact unilatéral avec frottement de Coulomb
A Balancing Algorithm for Mortar Methods
 A Balancing Algorithm for Mortar Methods Dan Stefanica Baruch College, City University of New York, NY, USA. Dan_Stefanica@baruch.cuny.edu Summary. The balancing methods are hybrid nonoverlapping Schwarz
A Balancing Algorithm for Mortar Methods Dan Stefanica Baruch College, City University of New York, NY, USA. Dan_Stefanica@baruch.cuny.edu Summary. The balancing methods are hybrid nonoverlapping Schwarz
ETNA Kent State University
 Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 37, pp. 166-172, 2010. Copyright 2010,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA A GRADIENT RECOVERY OPERATOR BASED ON AN OBLIQUE PROJECTION BISHNU P. LAMICHHANE Abstract.
Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis. Volume 37, pp. 166-172, 2010. Copyright 2010,. ISSN 1068-9613. ETNA A GRADIENT RECOVERY OPERATOR BASED ON AN OBLIQUE PROJECTION BISHNU P. LAMICHHANE Abstract.
ITERATIVE SOLUTION OF A COMBINED MIXED AND STANDARD GALERKIN DISCRETIZATION METHOD FOR ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS
 ITERATIVE SOLUTION OF A COMBINED MIXED AND STANDARD GALERKIN DISCRETIZATION METHOD FOR ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS RAYTCHO D. LAZAROV, JOSEPH E. PASCIAK, AND PANAYOT S. VASSILEVSKI Abstract. In this paper, we consider
ITERATIVE SOLUTION OF A COMBINED MIXED AND STANDARD GALERKIN DISCRETIZATION METHOD FOR ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS RAYTCHO D. LAZAROV, JOSEPH E. PASCIAK, AND PANAYOT S. VASSILEVSKI Abstract. In this paper, we consider
A Domain Decomposition Method for Quasilinear Elliptic PDEs Using Mortar Finite Elements
 W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T A Domain Decomposition Method for Quasilinear Elliptic PDEs Using Mortar Finite Elements Matthias Gsell and Olaf Steinbach Institute of Computational Mathematics
W I S S E N T E C H N I K L E I D E N S C H A F T A Domain Decomposition Method for Quasilinear Elliptic PDEs Using Mortar Finite Elements Matthias Gsell and Olaf Steinbach Institute of Computational Mathematics
The Mortar Finite Element Method for Contact Problems
 The Mortar Finite Element Method for Contact Problems F. Ben Belgacem, P. Hild, P. Laborde Mathématiques pour l Industrie et la Physique, Unité Mixte de Recherche CNRS UPS INSAT (UMR 5640), Université
The Mortar Finite Element Method for Contact Problems F. Ben Belgacem, P. Hild, P. Laborde Mathématiques pour l Industrie et la Physique, Unité Mixte de Recherche CNRS UPS INSAT (UMR 5640), Université
LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES)
 LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES) RAYTCHO LAZAROV 1 Notations and Basic Functional Spaces Scalar function in R d, d 1 will be denoted by u,
LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES) RAYTCHO LAZAROV 1 Notations and Basic Functional Spaces Scalar function in R d, d 1 will be denoted by u,
A domain decomposition algorithm for contact problems with Coulomb s friction
 A domain decomposition algorithm for contact problems with Coulomb s friction J. Haslinger 1,R.Kučera 2, and T. Sassi 1 1 Introduction Contact problems of elasticity are used in many fields of science
A domain decomposition algorithm for contact problems with Coulomb s friction J. Haslinger 1,R.Kučera 2, and T. Sassi 1 1 Introduction Contact problems of elasticity are used in many fields of science
Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems
 Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert To cite this version: Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert. Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems. Proceedings
Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert To cite this version: Franck Boyer, Florence Hubert. Finite volume method for nonlinear transmission problems. Proceedings
ASM-BDDC Preconditioners with variable polynomial degree for CG- and DG-SEM
 ASM-BDDC Preconditioners with variable polynomial degree for CG- and DG-SEM C. Canuto 1, L. F. Pavarino 2, and A. B. Pieri 3 1 Introduction Discontinuous Galerkin (DG) methods for partial differential
ASM-BDDC Preconditioners with variable polynomial degree for CG- and DG-SEM C. Canuto 1, L. F. Pavarino 2, and A. B. Pieri 3 1 Introduction Discontinuous Galerkin (DG) methods for partial differential
Hybridized Discontinuous Galerkin Methods
 Hybridized Discontinuous Galerkin Methods Theory and Christian Waluga Joint work with Herbert Egger (Uni Graz) 1st DUNE User Meeting, Stuttgart Christian Waluga (AICES) HDG Methods October 6-8, 2010 1
Hybridized Discontinuous Galerkin Methods Theory and Christian Waluga Joint work with Herbert Egger (Uni Graz) 1st DUNE User Meeting, Stuttgart Christian Waluga (AICES) HDG Methods October 6-8, 2010 1
AND BARBARA I. WOHLMUTH
 A QUASI-DUAL LAGRANGE MULTIPLIER SPACE FOR SERENDIPITY MORTAR FINITE ELEMENTS IN 3D BISHNU P. LAMICHHANE AND BARBARA I. WOHLMUTH Abstract. Domain decomposition techniques provide a flexible tool for the
A QUASI-DUAL LAGRANGE MULTIPLIER SPACE FOR SERENDIPITY MORTAR FINITE ELEMENTS IN 3D BISHNU P. LAMICHHANE AND BARBARA I. WOHLMUTH Abstract. Domain decomposition techniques provide a flexible tool for the
Discontinuous Galerkin Method for interface problem of coupling different order elliptic equations
 Discontinuous Galerkin Method for interface problem of coupling different order elliptic equations Igor Mozolevski, Endre Süli Federal University of Santa Catarina, Brazil Oxford University Computing Laboratory,
Discontinuous Galerkin Method for interface problem of coupling different order elliptic equations Igor Mozolevski, Endre Süli Federal University of Santa Catarina, Brazil Oxford University Computing Laboratory,
Comparative Analysis of Mesh Generators and MIC(0) Preconditioning of FEM Elasticity Systems
 Comparative Analysis of Mesh Generators and MIC(0) Preconditioning of FEM Elasticity Systems Nikola Kosturski and Svetozar Margenov Institute for Parallel Processing, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Abstract.
Comparative Analysis of Mesh Generators and MIC(0) Preconditioning of FEM Elasticity Systems Nikola Kosturski and Svetozar Margenov Institute for Parallel Processing, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Abstract.
Domain Decomposition Algorithms for an Indefinite Hypersingular Integral Equation in Three Dimensions
 Domain Decomposition Algorithms for an Indefinite Hypersingular Integral Equation in Three Dimensions Ernst P. Stephan 1, Matthias Maischak 2, and Thanh Tran 3 1 Institut für Angewandte Mathematik, Leibniz
Domain Decomposition Algorithms for an Indefinite Hypersingular Integral Equation in Three Dimensions Ernst P. Stephan 1, Matthias Maischak 2, and Thanh Tran 3 1 Institut für Angewandte Mathematik, Leibniz
Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs
 Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs Junping Wang Computational Mathematics Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Arlington, VA 22230 Polytopal Element
Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs Junping Wang Computational Mathematics Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Arlington, VA 22230 Polytopal Element
Two new enriched multiscale coarse spaces for the Additive Average Schwarz method
 346 Two new enriched multiscale coarse spaces for the Additive Average Schwarz method Leszek Marcinkowski 1 and Talal Rahman 2 1 Introduction We propose additive Schwarz methods with spectrally enriched
346 Two new enriched multiscale coarse spaces for the Additive Average Schwarz method Leszek Marcinkowski 1 and Talal Rahman 2 1 Introduction We propose additive Schwarz methods with spectrally enriched
A Two-grid Method for Coupled Free Flow with Porous Media Flow
 A Two-grid Method for Coupled Free Flow with Porous Media Flow Prince Chidyagwai a and Béatrice Rivière a, a Department of Computational and Applied Mathematics, Rice University, 600 Main Street, Houston,
A Two-grid Method for Coupled Free Flow with Porous Media Flow Prince Chidyagwai a and Béatrice Rivière a, a Department of Computational and Applied Mathematics, Rice University, 600 Main Street, Houston,
Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components
 Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components Håkan Jakobsson Research Assistant hakan.jakobsson@math.umu.se Mats G. Larson Professor Applied Mathematics mats.larson@math.umu.se Department
Reduction of Finite Element Models of Complex Mechanical Components Håkan Jakobsson Research Assistant hakan.jakobsson@math.umu.se Mats G. Larson Professor Applied Mathematics mats.larson@math.umu.se Department
Locking phenomena in Computational Mechanics: nearly incompressible materials and plate problems
 Locking phenomena in Computational Mechanics: nearly incompressible materials and plate problems C. Lovadina Dipartimento di Matematica Univ. di Pavia IMATI-CNR, Pavia Bologna, September, the 18th 2006
Locking phenomena in Computational Mechanics: nearly incompressible materials and plate problems C. Lovadina Dipartimento di Matematica Univ. di Pavia IMATI-CNR, Pavia Bologna, September, the 18th 2006
Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains
 Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains E. Chahine 1, P. Laborde 2, J. Pommier 1, Y. Renard 3 and M. Salaün 4 (1) INSA Toulouse, laboratoire MIP, CNRS UMR 5640, Complexe scientifique de Rangueil,
Some improvements of Xfem for cracked domains E. Chahine 1, P. Laborde 2, J. Pommier 1, Y. Renard 3 and M. Salaün 4 (1) INSA Toulouse, laboratoire MIP, CNRS UMR 5640, Complexe scientifique de Rangueil,
A Mixed Nonconforming Finite Element for Linear Elasticity
 A Mixed Nonconforming Finite Element for Linear Elasticity Zhiqiang Cai, 1 Xiu Ye 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907-1395 2 Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
A Mixed Nonconforming Finite Element for Linear Elasticity Zhiqiang Cai, 1 Xiu Ye 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907-1395 2 Department of Mathematics and Statistics,
Some New Elements for the Reissner Mindlin Plate Model
 Boundary Value Problems for Partial Differential Equations and Applications, J.-L. Lions and C. Baiocchi, eds., Masson, 1993, pp. 287 292. Some New Elements for the Reissner Mindlin Plate Model Douglas
Boundary Value Problems for Partial Differential Equations and Applications, J.-L. Lions and C. Baiocchi, eds., Masson, 1993, pp. 287 292. Some New Elements for the Reissner Mindlin Plate Model Douglas
Local Mesh Refinement with the PCD Method
 Advances in Dynamical Systems and Applications ISSN 0973-5321, Volume 8, Number 1, pp. 125 136 (2013) http://campus.mst.edu/adsa Local Mesh Refinement with the PCD Method Ahmed Tahiri Université Med Premier
Advances in Dynamical Systems and Applications ISSN 0973-5321, Volume 8, Number 1, pp. 125 136 (2013) http://campus.mst.edu/adsa Local Mesh Refinement with the PCD Method Ahmed Tahiri Université Med Premier
arxiv: v1 [math.na] 29 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.na] 29 Feb 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.na] 29 Feb 2016](/thumbs/92/110614295.jpg) EFFECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE WEAK GALERKIN FINITE ELEMENT METHODS FOR THE BIHARMONIC EQUATION LIN MU, JUNPING WANG, AND XIU YE Abstract. arxiv:1602.08817v1 [math.na] 29 Feb 2016 The weak Galerkin (WG)
EFFECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE WEAK GALERKIN FINITE ELEMENT METHODS FOR THE BIHARMONIC EQUATION LIN MU, JUNPING WANG, AND XIU YE Abstract. arxiv:1602.08817v1 [math.na] 29 Feb 2016 The weak Galerkin (WG)
ADAPTIVE MIXED HYBRID AND MACRO HYBRID FINITE ELEMENT METHODS. 1. Introduction
 Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXVII, 1(1998), pp. 159 179 159 ADAPTIVE MIXED HYBRID AND MACRO HYBRID FINITE ELEMENT METHODS R. H. W. HOPPE and B. I. WOHLMUTH Abstract. In this paper, we consider efficient
Acta Math. Univ. Comenianae Vol. LXVII, 1(1998), pp. 159 179 159 ADAPTIVE MIXED HYBRID AND MACRO HYBRID FINITE ELEMENT METHODS R. H. W. HOPPE and B. I. WOHLMUTH Abstract. In this paper, we consider efficient
A FETI-DP Method for Mortar Finite Element Discretization of a Fourth Order Problem
 A FETI-DP Method for Mortar Finite Element Discretization of a Fourth Order Problem Leszek Marcinkowski 1 and Nina Dokeva 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Warsaw University, Banacha 2, 02 097 Warszawa, Poland,
A FETI-DP Method for Mortar Finite Element Discretization of a Fourth Order Problem Leszek Marcinkowski 1 and Nina Dokeva 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Warsaw University, Banacha 2, 02 097 Warszawa, Poland,
BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS
 Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol.., No. 1., (2005), pp. 83 94 BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS Vladimír Kutiš and Justín Murín Department
Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol.., No. 1., (2005), pp. 83 94 BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS Vladimír Kutiš and Justín Murín Department
Convergence Behavior of a Two-Level Optimized Schwarz Preconditioner
 Convergence Behavior of a Two-Level Optimized Schwarz Preconditioner Olivier Dubois 1 and Martin J. Gander 2 1 IMA, University of Minnesota, 207 Church St. SE, Minneapolis, MN 55455 dubois@ima.umn.edu
Convergence Behavior of a Two-Level Optimized Schwarz Preconditioner Olivier Dubois 1 and Martin J. Gander 2 1 IMA, University of Minnesota, 207 Church St. SE, Minneapolis, MN 55455 dubois@ima.umn.edu
Introduction to Finite Element computations
 Non Linear Computational Mechanics Athens MP06/2012 Introduction to Finite Element computations Vincent Chiaruttini, Georges Cailletaud vincent.chiaruttini@onera.fr Outline Continuous to discrete problem
Non Linear Computational Mechanics Athens MP06/2012 Introduction to Finite Element computations Vincent Chiaruttini, Georges Cailletaud vincent.chiaruttini@onera.fr Outline Continuous to discrete problem
Optimal multilevel preconditioning of strongly anisotropic problems.part II: non-conforming FEM. p. 1/36
 Optimal multilevel preconditioning of strongly anisotropic problems. Part II: non-conforming FEM. Svetozar Margenov margenov@parallel.bas.bg Institute for Parallel Processing, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
Optimal multilevel preconditioning of strongly anisotropic problems. Part II: non-conforming FEM. Svetozar Margenov margenov@parallel.bas.bg Institute for Parallel Processing, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences,
MORTAR MULTISCALE FINITE ELEMENT METHODS FOR STOKES-DARCY FLOWS
 MORTAR MULTISCALE FINITE ELEMENT METHODS FOR STOKES-DARCY FLOWS VIVETTE GIRAULT, DANAIL VASSILEV, AND IVAN YOTOV Abstract. We investigate mortar multiscale numerical methods for coupled Stokes and Darcy
MORTAR MULTISCALE FINITE ELEMENT METHODS FOR STOKES-DARCY FLOWS VIVETTE GIRAULT, DANAIL VASSILEV, AND IVAN YOTOV Abstract. We investigate mortar multiscale numerical methods for coupled Stokes and Darcy
The mortar element method for quasilinear elliptic boundary value problems
 The mortar element method for quasilinear elliptic boundary value problems Leszek Marcinkowski 1 Abstract We consider a discretization of quasilinear elliptic boundary value problems by the mortar version
The mortar element method for quasilinear elliptic boundary value problems Leszek Marcinkowski 1 Abstract We consider a discretization of quasilinear elliptic boundary value problems by the mortar version
From Direct to Iterative Substructuring: some Parallel Experiences in 2 and 3D
 From Direct to Iterative Substructuring: some Parallel Experiences in 2 and 3D Luc Giraud N7-IRIT, Toulouse MUMPS Day October 24, 2006, ENS-INRIA, Lyon, France Outline 1 General Framework 2 The direct
From Direct to Iterative Substructuring: some Parallel Experiences in 2 and 3D Luc Giraud N7-IRIT, Toulouse MUMPS Day October 24, 2006, ENS-INRIA, Lyon, France Outline 1 General Framework 2 The direct
Asymptotic expansions and domain decomposition
 Asymptotic expansions and domain decomposition Giuseppe Geymonat, Sofiane Hendili, Françoise Krasucki, Michèle Serpilli, Marina Vidrascu To cite this version: Giuseppe Geymonat, Sofiane Hendili, Françoise
Asymptotic expansions and domain decomposition Giuseppe Geymonat, Sofiane Hendili, Françoise Krasucki, Michèle Serpilli, Marina Vidrascu To cite this version: Giuseppe Geymonat, Sofiane Hendili, Françoise
Interior superconvergence in mortar and non-mortar mixed finite element methods on non-matching grids
 Interior superconvergence in mortar and non-mortar mixed finite element methods on non-matching grids Gergina Pencheva a,, Ivan Yotov b a Center for Subsurface Modeling, Institute for Computational Engineering
Interior superconvergence in mortar and non-mortar mixed finite element methods on non-matching grids Gergina Pencheva a,, Ivan Yotov b a Center for Subsurface Modeling, Institute for Computational Engineering
A Robust Preconditioner for the Hessian System in Elliptic Optimal Control Problems
 A Robust Preconditioner for the Hessian System in Elliptic Optimal Control Problems Etereldes Gonçalves 1, Tarek P. Mathew 1, Markus Sarkis 1,2, and Christian E. Schaerer 1 1 Instituto de Matemática Pura
A Robust Preconditioner for the Hessian System in Elliptic Optimal Control Problems Etereldes Gonçalves 1, Tarek P. Mathew 1, Markus Sarkis 1,2, and Christian E. Schaerer 1 1 Instituto de Matemática Pura
FINITE ELEMENT APPROXIMATION OF STOKES-LIKE SYSTEMS WITH IMPLICIT CONSTITUTIVE RELATION
 Proceedings of ALGORITMY pp. 9 3 FINITE ELEMENT APPROXIMATION OF STOKES-LIKE SYSTEMS WITH IMPLICIT CONSTITUTIVE RELATION JAN STEBEL Abstract. The paper deals with the numerical simulations of steady flows
Proceedings of ALGORITMY pp. 9 3 FINITE ELEMENT APPROXIMATION OF STOKES-LIKE SYSTEMS WITH IMPLICIT CONSTITUTIVE RELATION JAN STEBEL Abstract. The paper deals with the numerical simulations of steady flows
b i (x) u + c(x)u = f in Ω,
 SIAM J. NUMER. ANAL. Vol. 39, No. 6, pp. 1938 1953 c 2002 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics SUBOPTIMAL AND OPTIMAL CONVERGENCE IN MIXED FINITE ELEMENT METHODS ALAN DEMLOW Abstract. An elliptic
SIAM J. NUMER. ANAL. Vol. 39, No. 6, pp. 1938 1953 c 2002 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics SUBOPTIMAL AND OPTIMAL CONVERGENCE IN MIXED FINITE ELEMENT METHODS ALAN DEMLOW Abstract. An elliptic
A Nonoverlapping Subdomain Algorithm with Lagrange Multipliers and its Object Oriented Implementation for Interface Problems
 Contemporary Mathematics Volume 8, 998 B 0-88-0988--03030- A Nonoverlapping Subdomain Algorithm with Lagrange Multipliers and its Object Oriented Implementation for Interface Problems Daoqi Yang. Introduction
Contemporary Mathematics Volume 8, 998 B 0-88-0988--03030- A Nonoverlapping Subdomain Algorithm with Lagrange Multipliers and its Object Oriented Implementation for Interface Problems Daoqi Yang. Introduction
Dirichlet-Neumann and Neumann-Neumann Methods
 Dirichlet-Neumann and Neumann-Neumann Methods Felix Kwok Hong Kong Baptist University Introductory Domain Decomposition Short Course DD25, Memorial University of Newfoundland July 22, 2018 Outline Methods
Dirichlet-Neumann and Neumann-Neumann Methods Felix Kwok Hong Kong Baptist University Introductory Domain Decomposition Short Course DD25, Memorial University of Newfoundland July 22, 2018 Outline Methods
Domain Decomposition Methods for Mortar Finite Elements
 Domain Decomposition Methods for Mortar Finite Elements Dan Stefanica Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University September 1999 A dissertation in the Department of Mathematics Submitted
Domain Decomposition Methods for Mortar Finite Elements Dan Stefanica Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University September 1999 A dissertation in the Department of Mathematics Submitted
OVERLAPPING SCHWARZ ALGORITHMS FOR ALMOST INCOMPRESSIBLE LINEAR ELASTICITY TR
 OVERLAPPING SCHWARZ ALGORITHMS FOR ALMOST INCOMPRESSIBLE LINEAR ELASTICITY MINGCHAO CAI, LUCA F. PAVARINO, AND OLOF B. WIDLUND TR2014-969 Abstract. Low order finite element discretizations of the linear
OVERLAPPING SCHWARZ ALGORITHMS FOR ALMOST INCOMPRESSIBLE LINEAR ELASTICITY MINGCHAO CAI, LUCA F. PAVARINO, AND OLOF B. WIDLUND TR2014-969 Abstract. Low order finite element discretizations of the linear
PSEUDO-COMPRESSIBILITY METHODS FOR THE UNSTEADY INCOMPRESSIBLE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS
 PSEUDO-COMPRESSIBILITY METHODS FOR THE UNSTEADY INCOMPRESSIBLE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS Jie Shen Department of Mathematics, Penn State University University Par, PA 1680, USA Abstract. We present in this
PSEUDO-COMPRESSIBILITY METHODS FOR THE UNSTEADY INCOMPRESSIBLE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS Jie Shen Department of Mathematics, Penn State University University Par, PA 1680, USA Abstract. We present in this
Stochastic multiscale modeling of subsurface and surface flows. Part III: Multiscale mortar finite elements for coupled Stokes-Darcy flows
 Stochastic multiscale modeling of subsurface and surface flows. Part III: Multiscale mortar finite elements for coupled Stokes-Darcy flows Ivan otov Department of Mathematics, University of Pittsburgh
Stochastic multiscale modeling of subsurface and surface flows. Part III: Multiscale mortar finite elements for coupled Stokes-Darcy flows Ivan otov Department of Mathematics, University of Pittsburgh
ENERGY NORM A POSTERIORI ERROR ESTIMATES FOR MIXED FINITE ELEMENT METHODS
 ENERGY NORM A POSTERIORI ERROR ESTIMATES FOR MIXED FINITE ELEMENT METHODS CARLO LOVADINA AND ROLF STENBERG Abstract The paper deals with the a-posteriori error analysis of mixed finite element methods
ENERGY NORM A POSTERIORI ERROR ESTIMATES FOR MIXED FINITE ELEMENT METHODS CARLO LOVADINA AND ROLF STENBERG Abstract The paper deals with the a-posteriori error analysis of mixed finite element methods
PREPRINT 2010:23. A nonconforming rotated Q 1 approximation on tetrahedra PETER HANSBO
 PREPRINT 2010:23 A nonconforming rotated Q 1 approximation on tetrahedra PETER HANSBO Department of Mathematical Sciences Division of Mathematics CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG
PREPRINT 2010:23 A nonconforming rotated Q 1 approximation on tetrahedra PETER HANSBO Department of Mathematical Sciences Division of Mathematics CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG
Hybridized DG methods
 Hybridized DG methods University of Florida (Banff International Research Station, November 2007.) Collaborators: Bernardo Cockburn University of Minnesota Raytcho Lazarov Texas A&M University Thanks:
Hybridized DG methods University of Florida (Banff International Research Station, November 2007.) Collaborators: Bernardo Cockburn University of Minnesota Raytcho Lazarov Texas A&M University Thanks:
Multispace and Multilevel BDDC. Jan Mandel University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center
 Multispace and Multilevel BDDC Jan Mandel University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center Based on joint work with Bedřich Sousedík, UCDHSC and Czech Technical University, and Clark R. Dohrmann,
Multispace and Multilevel BDDC Jan Mandel University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center Based on joint work with Bedřich Sousedík, UCDHSC and Czech Technical University, and Clark R. Dohrmann,
Domain decomposition methods via boundary integral equations
 Domain decomposition methods via boundary integral equations G. C. Hsiao a O. Steinbach b W. L. Wendland b a Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA. E
Domain decomposition methods via boundary integral equations G. C. Hsiao a O. Steinbach b W. L. Wendland b a Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA. E
Multipréconditionnement adaptatif pour les méthodes de décomposition de domaine. Nicole Spillane (CNRS, CMAP, École Polytechnique)
 Multipréconditionnement adaptatif pour les méthodes de décomposition de domaine Nicole Spillane (CNRS, CMAP, École Polytechnique) C. Bovet (ONERA), P. Gosselet (ENS Cachan), A. Parret Fréaud (SafranTech),
Multipréconditionnement adaptatif pour les méthodes de décomposition de domaine Nicole Spillane (CNRS, CMAP, École Polytechnique) C. Bovet (ONERA), P. Gosselet (ENS Cachan), A. Parret Fréaud (SafranTech),
A MULTIGRID ALGORITHM FOR. Richard E. Ewing and Jian Shen. Institute for Scientic Computation. Texas A&M University. College Station, Texas SUMMARY
 A MULTIGRID ALGORITHM FOR THE CELL-CENTERED FINITE DIFFERENCE SCHEME Richard E. Ewing and Jian Shen Institute for Scientic Computation Texas A&M University College Station, Texas SUMMARY In this article,
A MULTIGRID ALGORITHM FOR THE CELL-CENTERED FINITE DIFFERENCE SCHEME Richard E. Ewing and Jian Shen Institute for Scientic Computation Texas A&M University College Station, Texas SUMMARY In this article,
A Locking-Free MHM Method for Elasticity
 Trabalho apresentado no CNMAC, Gramado - RS, 2016. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics A Locking-Free MHM Method for Elasticity Weslley S. Pereira 1 Frédéric
Trabalho apresentado no CNMAC, Gramado - RS, 2016. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics A Locking-Free MHM Method for Elasticity Weslley S. Pereira 1 Frédéric
Selecting Constraints in Dual-Primal FETI Methods for Elasticity in Three Dimensions
 Selecting Constraints in Dual-Primal FETI Methods for Elasticity in Three Dimensions Axel Klawonn 1 and Olof B. Widlund 2 1 Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen, Fachbereich Mathematik, (http://www.uni-essen.de/ingmath/axel.klawonn/)
Selecting Constraints in Dual-Primal FETI Methods for Elasticity in Three Dimensions Axel Klawonn 1 and Olof B. Widlund 2 1 Universität Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen, Fachbereich Mathematik, (http://www.uni-essen.de/ingmath/axel.klawonn/)
Spectral element agglomerate AMGe
 Spectral element agglomerate AMGe T. Chartier 1, R. Falgout 2, V. E. Henson 2, J. E. Jones 4, T. A. Manteuffel 3, S. F. McCormick 3, J. W. Ruge 3, and P. S. Vassilevski 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Davidson
Spectral element agglomerate AMGe T. Chartier 1, R. Falgout 2, V. E. Henson 2, J. E. Jones 4, T. A. Manteuffel 3, S. F. McCormick 3, J. W. Ruge 3, and P. S. Vassilevski 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Davidson
Schur Complements on Hilbert Spaces and Saddle Point Systems
 Schur Complements on Hilbert Spaces and Saddle Point Systems Constantin Bacuta Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, 5 Ewing Hall 976 Abstract For any continuous bilinear form defined on a pair
Schur Complements on Hilbert Spaces and Saddle Point Systems Constantin Bacuta Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, 5 Ewing Hall 976 Abstract For any continuous bilinear form defined on a pair
Yongdeok Kim and Seki Kim
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 39 (00), No. 3, pp. 363 376 STABLE LOW ORDER NONCONFORMING QUADRILATERAL FINITE ELEMENTS FOR THE STOKES PROBLEM Yongdeok Kim and Seki Kim Abstract. Stability result is obtained for
J. Korean Math. Soc. 39 (00), No. 3, pp. 363 376 STABLE LOW ORDER NONCONFORMING QUADRILATERAL FINITE ELEMENTS FOR THE STOKES PROBLEM Yongdeok Kim and Seki Kim Abstract. Stability result is obtained for
A u + b u + cu = f in Ω, (1.1)
 A WEIGHTED H(div) LEAST-SQUARES METHOD FOR SECOND-ORDER ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS Z. CAI AND C. R. WESTPHAL Abstract. This paper presents analysis of a weighted-norm least squares finite element method for elliptic
A WEIGHTED H(div) LEAST-SQUARES METHOD FOR SECOND-ORDER ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS Z. CAI AND C. R. WESTPHAL Abstract. This paper presents analysis of a weighted-norm least squares finite element method for elliptic
Discrete Analysis for Plate Bending Problems by Using Hybrid-type Penalty Method
 131 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 21 (2008) Published online (http://hdl.handle.net/10114/1532) Discrete Analysis for Plate Bending Problems by Using
131 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 21 (2008) Published online (http://hdl.handle.net/10114/1532) Discrete Analysis for Plate Bending Problems by Using
Dual-Primal Isogeometric Tearing and Interconnecting Solvers for Continuous and Discontinuous Galerkin IgA Equations
 Dual-Primal Isogeometric Tearing and Interconnecting Solvers for Continuous and Discontinuous Galerkin IgA Equations Christoph Hofer and Ulrich Langer Doctoral Program Computational Mathematics Numerical
Dual-Primal Isogeometric Tearing and Interconnecting Solvers for Continuous and Discontinuous Galerkin IgA Equations Christoph Hofer and Ulrich Langer Doctoral Program Computational Mathematics Numerical
1.The anisotropic plate model
 Pré-Publicações do Departamento de Matemática Universidade de Coimbra Preprint Number 6 OPTIMAL CONTROL OF PIEZOELECTRIC ANISOTROPIC PLATES ISABEL NARRA FIGUEIREDO AND GEORG STADLER ABSTRACT: This paper
Pré-Publicações do Departamento de Matemática Universidade de Coimbra Preprint Number 6 OPTIMAL CONTROL OF PIEZOELECTRIC ANISOTROPIC PLATES ISABEL NARRA FIGUEIREDO AND GEORG STADLER ABSTRACT: This paper
Local discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic problems
 COMMUNICATIONS IN NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Commun. Numer. Meth. Engng 2002; 18:69 75 [Version: 2000/03/22 v1.0] Local discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic problems P. Castillo 1 B. Cockburn
COMMUNICATIONS IN NUMERICAL METHODS IN ENGINEERING Commun. Numer. Meth. Engng 2002; 18:69 75 [Version: 2000/03/22 v1.0] Local discontinuous Galerkin methods for elliptic problems P. Castillo 1 B. Cockburn
Adaptive Coarse Space Selection in BDDC and FETI-DP Iterative Substructuring Methods: Towards Fast and Robust Solvers
 Adaptive Coarse Space Selection in BDDC and FETI-DP Iterative Substructuring Methods: Towards Fast and Robust Solvers Jan Mandel University of Colorado at Denver Bedřich Sousedík Czech Technical University
Adaptive Coarse Space Selection in BDDC and FETI-DP Iterative Substructuring Methods: Towards Fast and Robust Solvers Jan Mandel University of Colorado at Denver Bedřich Sousedík Czech Technical University
Optimal Interface Conditions for an Arbitrary Decomposition into Subdomains
 Optimal Interface Conditions for an Arbitrary Decomposition into Subdomains Martin J. Gander and Felix Kwok Section de mathématiques, Université de Genève, Geneva CH-1211, Switzerland, Martin.Gander@unige.ch;
Optimal Interface Conditions for an Arbitrary Decomposition into Subdomains Martin J. Gander and Felix Kwok Section de mathématiques, Université de Genève, Geneva CH-1211, Switzerland, Martin.Gander@unige.ch;
A FAST SOLVER FOR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS WITH HARMONIC COEFFICIENT APPROXIMATIONS
 Proceedings of ALGORITMY 2005 pp. 222 229 A FAST SOLVER FOR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS WITH HARMONIC COEFFICIENT APPROXIMATIONS ELENA BRAVERMAN, MOSHE ISRAELI, AND ALEXANDER SHERMAN Abstract. Based on a fast subtractional
Proceedings of ALGORITMY 2005 pp. 222 229 A FAST SOLVER FOR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS WITH HARMONIC COEFFICIENT APPROXIMATIONS ELENA BRAVERMAN, MOSHE ISRAELI, AND ALEXANDER SHERMAN Abstract. Based on a fast subtractional
The Mortar Boundary Element Method
 The Mortar Boundary Element Method A Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Martin Healey School of Information Systems, Computing and Mathematics Brunel University March 2010 Abstract
The Mortar Boundary Element Method A Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Martin Healey School of Information Systems, Computing and Mathematics Brunel University March 2010 Abstract
An optimal control problem governed by implicit evolution quasi-variational inequalities
 Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (213), 157 166 An optimal control problem governed by implicit evolution quasi-variational inequalities Anca Capatina and Claudia Timofte
Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (213), 157 166 An optimal control problem governed by implicit evolution quasi-variational inequalities Anca Capatina and Claudia Timofte
FETI domain decomposition method to solution of contact problems with large displacements
 FETI domain decomposition method to solution of contact problems with large displacements Vít Vondrák 1, Zdeněk Dostál 1, Jiří Dobiáš 2, and Svatopluk Pták 2 1 Dept. of Appl. Math., Technical University
FETI domain decomposition method to solution of contact problems with large displacements Vít Vondrák 1, Zdeněk Dostál 1, Jiří Dobiáš 2, and Svatopluk Pták 2 1 Dept. of Appl. Math., Technical University
A mixed finite element approximation of the Stokes equations with the boundary condition of type (D+N)
 wwwijmercom Vol2, Issue1, Jan-Feb 2012 pp-464-472 ISSN: 2249-6645 A mixed finite element approximation of the Stokes equations with the boundary condition of type (D+N) Jaouad El-Mekkaoui 1, Abdeslam Elakkad
wwwijmercom Vol2, Issue1, Jan-Feb 2012 pp-464-472 ISSN: 2249-6645 A mixed finite element approximation of the Stokes equations with the boundary condition of type (D+N) Jaouad El-Mekkaoui 1, Abdeslam Elakkad
Additive Average Schwarz Method for a Crouzeix-Raviart Finite Volume Element Discretization of Elliptic Problems
 Additive Average Schwarz Method for a Crouzeix-Raviart Finite Volume Element Discretization of Elliptic Problems Atle Loneland 1, Leszek Marcinkowski 2, and Talal Rahman 3 1 Introduction In this paper
Additive Average Schwarz Method for a Crouzeix-Raviart Finite Volume Element Discretization of Elliptic Problems Atle Loneland 1, Leszek Marcinkowski 2, and Talal Rahman 3 1 Introduction In this paper
16.21 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2003 Unit #5 - Constitutive Equations
 6.2 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2003 Unit #5 - Constitutive quations Constitutive quations For elastic materials: If the relation is linear: Û σ ij = σ ij (ɛ) = ρ () ɛ ij σ ij =
6.2 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2003 Unit #5 - Constitutive quations Constitutive quations For elastic materials: If the relation is linear: Û σ ij = σ ij (ɛ) = ρ () ɛ ij σ ij =
arxiv: v1 [math.na] 28 Feb 2008
![arxiv: v1 [math.na] 28 Feb 2008 arxiv: v1 [math.na] 28 Feb 2008](/thumbs/74/71359553.jpg) BDDC by a frontal solver and the stress computation in a hip joint replacement arxiv:0802.4295v1 [math.na] 28 Feb 2008 Jakub Šístek a, Jaroslav Novotný b, Jan Mandel c, Marta Čertíková a, Pavel Burda a
BDDC by a frontal solver and the stress computation in a hip joint replacement arxiv:0802.4295v1 [math.na] 28 Feb 2008 Jakub Šístek a, Jaroslav Novotný b, Jan Mandel c, Marta Čertíková a, Pavel Burda a
STOKES PROBLEM WITH SEVERAL TYPES OF BOUNDARY CONDITIONS IN AN EXTERIOR DOMAIN
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2013 2013, No. 196, pp. 1 28. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu STOKES PROBLEM
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2013 2013, No. 196, pp. 1 28. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu STOKES PROBLEM
Isogeometric mortaring
 Isogeometric mortaring E. Brivadis, A. Buffa, B. Wohlmuth, L. Wunderlich IMATI E. Magenes - Pavia Technical University of Munich A. Buffa (IMATI-CNR Italy) IGA mortaring 1 / 29 1 Introduction Splines Approximation
Isogeometric mortaring E. Brivadis, A. Buffa, B. Wohlmuth, L. Wunderlich IMATI E. Magenes - Pavia Technical University of Munich A. Buffa (IMATI-CNR Italy) IGA mortaring 1 / 29 1 Introduction Splines Approximation
Basic Concepts of Adaptive Finite Element Methods for Elliptic Boundary Value Problems
 Basic Concepts of Adaptive Finite lement Methods for lliptic Boundary Value Problems Ronald H.W. Hoppe 1,2 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Houston 2 Institute of Mathematics, University of Augsburg
Basic Concepts of Adaptive Finite lement Methods for lliptic Boundary Value Problems Ronald H.W. Hoppe 1,2 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Houston 2 Institute of Mathematics, University of Augsburg
c 2008 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
 SIAM J. NUMER. ANAL. Vol. 46, No. 3, pp. 640 65 c 2008 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics A WEIGHTED H(div) LEAST-SQUARES METHOD FOR SECOND-ORDER ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS Z. CAI AND C. R. WESTPHAL
SIAM J. NUMER. ANAL. Vol. 46, No. 3, pp. 640 65 c 2008 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics A WEIGHTED H(div) LEAST-SQUARES METHOD FOR SECOND-ORDER ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS Z. CAI AND C. R. WESTPHAL
