QUIZ 1 September 4, NAME: ACETONE Score: /10
|
|
|
- Brett Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUIZ 1 September 4, 2015 NAME: AETONE Score: /10 Be sure to show proper units in every case.] 1. (5 points) Draw structures for the following molecules to the right of each name. 2 N O O 2S p-aminobenzoic acid ydrogen sulfide Methane Naphthalene trans-butadiene 2. (5 points) In the table, indicate the proper best definition of each word or phrase in column A by inserting the proper number from column B: 9 Equilibrium Gas constant olumn A olumn B 1. A property proportional to the size of the system 2. A property independent of the size of the system 2 Intensive property 6 Surroundings 8 eat capacity. Fundamental constant of the universe, given as J K -1 mol -1 in SI units 4. Describing a macroscopic system in which the parts are observed to exchange energy over time 5. Statement of the zeroth law of thermodynamics 6. Everything in the universe except the system under study 7. Describing a multi-part system in which the parts exchange thermal energy through their boundaries 8. Measure of the amount of energy required to change the temperature of a substance by a given amount 9. The condition of a system for which no macroscopic change is observed
2 QUIZ 1 September 4, 2015 NAME: AETONE Score: /10. (10 points) For each entry on the left, given the derivative with respect to the independent variable indicated. (A, B,, and n are constants.) Function Derivative ff(tt) ee AA/TT2 dddd dddd 2AA TT ee AA/TT2 gg(ee) AA + BBEE 2 + EE dddd dddd 2BB EE EE 2 PPPP nnnnnn PP TT VV nnnn VV dd AA/TT2 ff(tt) ee llllll 2AA dddd TT h(xx) AA BB ddh dddd AAAA (BB ) 2
3 Fall, 2015(15F) QUIZ 2 September 11, 2015 NAME: BIPENYL Score: /20 [Show all work clearly. Be sure to show proper units and correct number of significant figures.] 1. (5 points) In Table 4.1 in the andbook, the van der Waals parameter, a, for 2O is about 150 times larger than the value of a for e. In one complete sentence, explain what this means about these two molecules. The intermolecular attraction between water molecules is much stronger than the intermolecular interaction between helium atoms. 2. (5 points) In the box, indicate the correct definition (from column B) of the words or phrases in column A. olumn A olumn B e Elastic collision a. Absolute temperature f Mole fraction of substance i b. Boltzmann s constant d Pressure c. elsius a Thermodynamic temperature scale d. Force per unit area g Zeroth Law e. No change in translational energy f. Pi/Ptotal g. Two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system at temperature T are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.. (10 points) An athlete at high performance may inhale.75 liters of air at 1.00 atm and K. The inhaled air contains 0.5% water by volume and the exhaled air contains 6.2% by volume. For a respiration rate of 2 breaths per minute, how many moles of water are exhaled per minute through the lungs? V total L 6.84 L m This volume corresponds to a specific number of moles: P Vtotal ( Pa)( m ) n 0.280mole 1 RT J K K First, calculate the volume expelled per breath: V ( )(.75 L) L In 2 breaths, the expelled volume is: ( ) ( )( )
4 QUIZ September 18, 2015 NAME: ARBON TETRALORIDE Score: /20 1. (6 points) Using van der Waals constants, estimate the radius of a methane molecule, assuming that the molecule is a sphere. The van der Waals b for methane is m /mol. The excluded volume per molecule is therefore VV mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm bb mm /mmmmmm mm /mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm. This is the NN mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm/mmmmmm point where two molecules just touch, so VV mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm (2rr), where r is the radius of the molecule. Solving for the radius gives the size of the methane molecule: rr VV mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm 8 ( mm ) 8 One may also use this equation, which is in the book: mm σσ bb (4/ mm /mmmmmm) 2ππNN 0 2ππ( mmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm/mmmmmm) 10 mm From this, one finds rr mm. Either method is counted correct. 2. (4 points) The one-dimensional speed distribution function is ff(vv xx ) 2mm eeeeee mmvv 2 xx, where the ππππππ 2kkkk symbols have their usual meaning. Derive an equation for the average speed, < vv xx > in one dimension. One merely does the integral: < vv xx > 0 ff(vv xx )vv xx ddvv xx 2mm ππππππ 0 vv xxexp mmvv 2 xx ddvv 2kkkk xx 2kkkk ππππ. (10 points) In the following, indicate which statements match the word or phrase in column A the best by putting the letter of it in the blank next to the answer. [There is only one best answer for each.] olumn A c Boyle temperature a. AAexp ( EE kkkk ) olumn B e ompression factor d ritical temperature b Gaussian a Boltzmann factor b. BBexp ( xx2 2σσ 2) c. For a van der Waals gas, aa RRRR d. ondition at which 0 and VV mm TT 2 PP 0 VV mm 2 TT e. PPVV mm RRRR
5 Fall, 2015(15F) QUIZ 4 September 25, 2015 NAME: DIOXANE Score: /20 1. (6 points) Suppose you draw a single card from a standard 52-card deck. (a) What is the probability of drawing an ace of any suit? There are four aces out of 52 cards, so the probability is PP (b) What is the probability of drawing the ace of hearts from a standard deck? There is only one ace of hearts, so the probability is PP (6 points) Determine the rms speed of Kr at K. uu kkkk mm RRRR MM ( JJ KK 1 mmmmmm 1 )( KK) kkkk mmmmmm mm ss 1. (4 points) For a particular system, the internal energy is given by the following equation: UU(TT, VV) UU 0 + AAAA + BBBB, where UU 0, AA, aaaaaa BB are constants independent of temperature and volume. Show that this is a mathematically acceptable form for U as a state function. [Show all work; explain.] One has to show the Maxwell relation: AA and TT (UU 0 + AAAA + BBBB) TT BB. But vv VV TT TT vv (UU 0 + AAAA + BBBB) vv 0. Similarly TT VV VV 0. These two crossed partial derivatives are equal, which is the requirement for an acceptable state function. 4. (4 points) elium gas is expanded from a molar volume of 22.4 liters to a molar volume of 44.8 liters against a constant external pressure of bar. ow much work does the amount of gas do in this process? The work done by the gas is ww PP eeeeee (VV 2 VV 1 ) PPPP ( mm mm ) 1.12 kkjj
6 QUIZ 5 October 9, 2015 NAME: FURAN Score: /20 1. (12 points) alculate the change in enthalpy of water when it is heated from room temperature ( K) to its normal boiling point (7.15 K), as accurately as you can KK mm PPPP dddd KK 7.17 KK TT TT TT KK TT 2 dddd JJ TT KK TT TT TT JJ KK ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ) JJ , JJ + 8,46.92 JJ 27, JJ + 7,105.9 JJ + 2, JJ 5, JJ But this is on a molar basis. The molar mass of water is gm, so one can find this on a weight basis by division: 5, JJ JJ gggg gggg TT 4 2. (8 points) For a gas that obeys the van der Waals equation of state, determine function of T, Vm, and the van der Waals constants. VV mm as a RRRR aa VV mm bb For a van der Waals gas, PP VV mm 2. Taking the derivative of this function gives VV mm RRRR VV mm bb aa VV2 RR mm VV VV VV mm mm bb 0 RR VV mm bb mm
7 QUIZ 6 October 16, 2015 NAME: GLYOSIDE Score: /20 1. (10 points) Assume that you have an ideal gas with a temperature-independent heat capacity, VVVV 5 RR. (a) Suppose that you carry 2.60 moles of this gas through a reversible expansion that 2 doubles the volume at constant temperature. What is the change in entropy? VV 2 VV 2 SS SS VV ddvv PP VV 1 TT TT ddvv nnnn 1 VV 1 VV VV dddd nnnn llll 2VV 1 VV 1 VV 1 2VV 1 (2.60)( JJ KK 1 ) ln(2) JJ KK 1 (b) Suppose that you carry the same amount of this gas through a process in which the temperature goes from the starting temperature of K to K, while holding the volume constant. What is the entropy change during that process? TT SS SS TT ddtt VV TT KK VV TT dddd KK nn 5RR 2 llll KK KK JJ KK 1 (2.60) ln(1.540) JJ KK 1 2. (10 points) Which of the following equations is/are correct, and which is/are incorrect? Mark an X in the appropriate box. (Graded right 0.5wrong; do not guess.) EQUATION orrect Incorrect θ θ P T P X θ θ S V P T T P X θ θ S V T T P X ds S S dt + dv T P V T X ( T, P) P θ V ( T ) + V T dp θ T P X P
8 Fall, 2015(15F) QUIZ 7 October 2, 2015 NAME: YDRAZINE Score: /20 1. (8 points) Using information in the andbook, calculate the molar entropy of fusion of water at its normal melting point. θθ From the andbook s Table 6.1, the information is: TT ff KK and ff,mm 6.01 kkkk mmmmmm 1 θθ By definition SS ff,mm θθ ff,mm TT ff JJ mmmmmm KK 22.0 JJ KK 1 mmmmmm 1 2. (8 points) onsider a reversible arnot engine using an ideal gas that operates between room temperature ( K) and K. (a) If one extracts exactly 1 kj of heat at K, how much work can the engine do? First calculate the ideal efficiency: εε TT hoooo TT cccccccc TT hoooo KK KK KK That determines how much of the heat is used as work: ww εε qq ( )(1 kkkk) JJ (b) Secondly, consider a arnot engine working between the same temperatures as in (a), except that it uses a van der Waals gas as the working fluid. What is the maximum work one can achieve from this engine for an input of exactly 1 kj? The ideal efficiency gives maximum work, so the maximum work is the same: J. (4 points) In each case, give the simplest requirement for spontaneity in terms of an inequality. onstant temperature and constant volume ( AA) TT,VV 0 onstant temperature and constant pressure ( GG) TT,PP 0
9 QUIZ 8 October 0, 2015 NAME: INDIGO Score: /20 1.(10 points) (a) Using data in your handbook, calculate the enthalpy of the dissociation of bromine at K by the reaction BBBB 2 (gg) 2 BBBB (gg) This is done using data for the various formation enthalpies in Table 5.8. θθ 2 ff mm θθ (BBBB) ff mm θθ (BBBB 2 ) 2(111.9 kkkk) 0.9 kkkk 19.8 kkkk (b) Also using data from your handbook, calculate the Gibbs free energy change for the same reaction at K. From the same data table, one can find the Gibbs energy change in an analogous manner: GG θθ 2 ff GG mm θθ (BBBB) ff GG mm θθ (BBBB 2 ) 2(82.4 kkkk).1 kkkk kkkk 2. (10 points) alculate the change in entropy when one mole of water is heated from K to K at a constant pressure of 1 bar. This calculation involves only a change in temperature so the change is calculated as follows: KK θθ SS mm SS mm θθ dddd KK PP 08.5 KK KK θθ PPPP (TT) TT dddd Substitution from Table 5.6 for the temperature-dependent heat capacity gives: SS mm θθ 08.5 KK KK cc 1 + cc 2 TT + cc TT 2 + cc 4 TT + cc 5 TT 2 dddd TT TT 2 cc 1 TT + cc 2 + cc TT + cc 4 TT 2 + TT 1 cc 5 TT dddd cc 1 llll TT 2 + cc TT 2 (TT 2 TT 1 ) + cc 1 2 (TT 2 2 TT 2 1 ) + cc 4 (TT 2 TT 1 ) cc TT TT 1 ( )llll ( ) ( ) + ( ) JJ KK(mmmmmm) JJ [ ] KK(mmmmmm) JJ KK(mmmmmm) Note that using a temperature-independent Pm in the simple equation gives a similar value, but the correct way of working the problem is to include all temperature-dependent terms. Using a temperature-independent heat capacity without explicitly saying why you assume temperature independence (in this case, because the temperature range is small) shows a lack of knowledge of the general usage of these equations.
10 QUIZ 9 November 1, 2015 NAME: KERATIN Score: /20 1. (10 points) A commonly studied reaction is the dimerization of NO2 to dinitrogen tetroxide in the gas phase: 2 NNNN 2 (gg) NN 2 OO 4 (gg) (a) Predict, by calculation, the equilibrium constant for this reaction at K. [Show all work.] First method from free energies of formation: GG θθ 99.8 kkkk 2(51. kkkk) 2.8 kkkk 2800 JJ KK aa ( KK) eeeeee JJ.09 KK ( KK) Second method from enthalpies of formation and Third-Law entropies: GG θθ θθ TT SS θθ 11.1 kkkk 2(.2 kkkk) ( KK) 04.4 JJ JJ 55. kkkk kkkk KK KK 2.9 kkkk KK aa ( KK) eeeepp Either method is considered correct JJ JJ KK ( KK).22, essentially the same number. (b) Assume that the pressures are sufficiently low that each component can be considered an ideal gas. Write a correct expression for Ka in terms of the partial pressure of each gas, Pi, and any other necessary parameters. [Define any symbols you use.] PP NN2 OO 4 KK aa 2 PP θθ PP NNNN2 where PP θθ is the standard pressure (in the case of data from Table 5.8, that is 1 bar). 2. (10 points) onsider the dimerization of NO2, as discussed in question 1. Assume that for practical purposes, both θ and S θ are temperature-independent. [This is an approximation, of course, and will lead to some errors, but may not be too bad.] Predict Ka for this reaction at 7.15 K, considering that approximation to be correct. [Show all work, including derivation of any intermediate quantities.] In this case, one may use the second method, as in question 1, because the enthalpy and entropy changes are independent of temperature: And GG θθ θθ TT SS θθ 55. kkkk (7.15 KK) JJ 10.0 kkkk KK KK aa (TT) eeeeee GGθθ RRRR KK aa(7.15 KK) eeeeee 1000 JJ JJ KK (7.15 KK)
11 QUIZ 10 November 20, 2015 NAME: LYSERGI AID Score: /20 1. (10 points) Ratcliffe and hao (anad. J. hem. Eng. 1969, 47, 148.) measured the properties of solutions of isopropanol (PP tttttttt) and n-decane (PP tttttttt). For a particular solution, the liquid had a mole fraction, XX 2, of and the total pressure over the solution, PP tttttttttt, was torr. They condensed the gas phase and measured that in gas, the n-decane gas-phase mole fraction was From these data, find the activities, aa ii, and activity coefficients, γγ ii, of isopropanol and n-decane, assuming a Raoult s law standard state. First calculate the partial pressures of the two components: PP 1 YY 1 PP tttttttttt (909.6 tttttttt) 882. tttttttt and PP 2 YY 2 PP tttttttttt 0.000(909.6 tttttttt) 27. tttttttt. The activity on the Raoult s Law scale is aa ii PP ii PP ii. Using the values in the problem, this formula gives: aa iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii and aa dddddddddddd At equilibrium, the activity of a component in the gas phase is equal to the activity in the liquid. So, we can calculate the activity coefficients from aa ii γγ ii XX ii. When one does that, the results are γγ iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii aa iiiiiiiirrrrrrrrrrrrrr XX iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii and γγ dddddddddddd aa dddddddddddd XX dddddddddddd (10 points) Below is a boiling point diagram for a solution of two materials, A and B. The abscissa is the mole fraction of component B. Insert the appropriate letter(s) in the blank space(s) next to phrases to indicate the appropriate region(s) or point(s) which those phrases describe. _(f) Boiling temperature of B _(e) Boiling temperature of A _(g) Azeotrope _(b) Liquid (c)(d)_ Liquid + vapor _(a) Vapor
12 QUIZ 11 December 4, 2015 NAME: MALEI ANYDRIDE Score: /20 1. (10 points) An aqueous solution containing calcium chloride freezes at -4. If you were to heat this solution until it boils, what would the temperature be? From Tables 7.5 and 7.6 in the andbook, one finds KK bb KK kkkk/mmmmmm and KK ff KK kkkk/mmmmmm. Since the molality is constant in the two processes: θθ bb mm θθ ff KK bb KK ff KK ence, θθ bb bb θθ KK ff (4 KK) KK. ff Normally, water boils at 100, so this solution boils at (10 points) The enry s Law constant for N2 in water is bar at K, on the mole fraction scale. At equilibrium at this temperature, how many moles of N2 are dissolved in 1 kg of water with a nitrogen overpressure of 0.79 bar? Because the solution is in the dilute limit, one may assume the activity coefficient is 1. Therefore, PP NN bbaaaa XX NN2 kk bbbbbb The molar mass of water is MM 2( gg) gg gg In one kilogram of water, there are 1000 gg nn 2 OO mmmmmm gg Then, from the definition of mole fraction in a binary solution XX NN nn NN2 nn 1 XX 2 OO NN ( mmmmmm) mmmmmm
NAME: NITROMETHANE CHEMISTRY 443, Fall, 2015(15F) Section Number: 10 Final Examination, December 18, 2015
 NAME: NITROMETHANE CHEMISTRY 443, Fall, 015(15F) Section Number: 10 Final Examination, December 18, 015 Answer each question in the space provided; use back of page if extra space is needed. Answer questions
NAME: NITROMETHANE CHEMISTRY 443, Fall, 015(15F) Section Number: 10 Final Examination, December 18, 015 Answer each question in the space provided; use back of page if extra space is needed. Answer questions
2018 Fall Semester Quiz 4 For General Chemistry I (CH101)
 2018 Fa Semester Quiz 4 For General Chemistry I (CH101) Date: November 5 (Mon), Time: 19:00 ~ 19:45 Professor Name Class Student I.D. Number Name Solution Avogadro constant (N A): 6.022 x 10 23 mol -1
2018 Fa Semester Quiz 4 For General Chemistry I (CH101) Date: November 5 (Mon), Time: 19:00 ~ 19:45 Professor Name Class Student I.D. Number Name Solution Avogadro constant (N A): 6.022 x 10 23 mol -1
Answers to Practice Test Questions 8 Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium. gas gas
 Answers to Practice Test Questions 8 Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium. (a)-(c) solid liquid solid critical point liquid gas gas triple point xenon neon (d) The normal boiling point of the noble gas
Answers to Practice Test Questions 8 Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium. (a)-(c) solid liquid solid critical point liquid gas gas triple point xenon neon (d) The normal boiling point of the noble gas
Revision : Thermodynamics
 Revision : Thermodynamics Formula sheet Formula sheet Formula sheet Thermodynamics key facts (1/9) Heat is an energy [measured in JJ] which flows from high to low temperature When two bodies are in thermal
Revision : Thermodynamics Formula sheet Formula sheet Formula sheet Thermodynamics key facts (1/9) Heat is an energy [measured in JJ] which flows from high to low temperature When two bodies are in thermal
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
Heat, Work, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 18 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 Different ways to increase the internal energy of system: 2 Joule s apparatus
Last Name: First Name: Purdue ID: Please write your name in BLOCK letters. Otherwise Gradescope may not recognize your name.
 Solution Key Last Name: First Name: Purdue ID: Please write your name in BLOCK letters. Otherwise Gradescope may not recognize your name. CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: MWF 10:30 am MWF 3:30 pm TR 8:30 am
Solution Key Last Name: First Name: Purdue ID: Please write your name in BLOCK letters. Otherwise Gradescope may not recognize your name. CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: MWF 10:30 am MWF 3:30 pm TR 8:30 am
Name: Discussion Section:
 CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
CBE 141: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Spring 2018, UC Berkeley Midterm 2 March 22, 2018 Time: 80 minutes, closed-book and closed-notes, one-sided 8 ½ x 11 equation sheet allowed Please show all
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics. Algebraic Expressions. Mr Black 's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9. Algebra
 Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Algebraic Expressions Mr Black 's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9 Algebra Algebraic Expressions Worksheets Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Algebraic Expressions Mr Black 's Maths Resources for Teachers GCSE 1-9 Algebra Algebraic Expressions Worksheets Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets
Free energy dependence along the coexistence curve
 Free energy dependence along the coexistence curve In a system where two phases (e.g. liquid and gas) are in equilibrium the Gibbs energy is G = GG l + GG gg, where GG l and GG gg are the Gibbs energies
Free energy dependence along the coexistence curve In a system where two phases (e.g. liquid and gas) are in equilibrium the Gibbs energy is G = GG l + GG gg, where GG l and GG gg are the Gibbs energies
Chapter 6. Heat capacity, enthalpy, & entropy
 Chapter 6 Heat capacity, enthalpy, & entropy 1 6.1 Introduction In this lecture, we examine the heat capacity as a function of temperature, compute the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy, as functions
Chapter 6 Heat capacity, enthalpy, & entropy 1 6.1 Introduction In this lecture, we examine the heat capacity as a function of temperature, compute the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy, as functions
Gravitation. Chapter 8 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Gravitation Chapter 8 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 What you are about to learn: Newton's law of universal gravitation About motion in circular and other orbits How to
Gravitation Chapter 8 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 What you are about to learn: Newton's law of universal gravitation About motion in circular and other orbits How to
Sodium, Na. Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 9.2 to 9.7.
 Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 9.2 to 9.7 Forms of Carbon Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter The kinetic-molecular theory
Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 9.2 to 9.7 Forms of Carbon Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter The kinetic-molecular theory
Worksheet Week 4 Solutions
 adapted from Rickey Kellow by ADH Chemisty 124 Fall 2018 Problem 1: Worksheet Week 4 Solutions (a) The reaction quotient QQ (written in terms of the partial pressures) for the given reaction is QQ = PP
adapted from Rickey Kellow by ADH Chemisty 124 Fall 2018 Problem 1: Worksheet Week 4 Solutions (a) The reaction quotient QQ (written in terms of the partial pressures) for the given reaction is QQ = PP
L.2 Formulas and Applications
 43 L. Formulas and Applications In the previous section, we studied how to solve linear equations. Those skills are often helpful in problem solving. However, the process of solving an application problem
43 L. Formulas and Applications In the previous section, we studied how to solve linear equations. Those skills are often helpful in problem solving. However, the process of solving an application problem
CHEMISTRY Spring, 2018 QUIZ 1 February 16, NAME: HANS ZIMMER Score /20
 QUIZ 1 February 16, 018 NAME: HANS ZIMMER Score /0 [Numbers without decimal points are to be considered infinitely precise. Show reasonable significant figures and proper units. In particular, use generally
QUIZ 1 February 16, 018 NAME: HANS ZIMMER Score /0 [Numbers without decimal points are to be considered infinitely precise. Show reasonable significant figures and proper units. In particular, use generally
Mathematics Ext 2. HSC 2014 Solutions. Suite 403, 410 Elizabeth St, Surry Hills NSW 2010 keystoneeducation.com.
 Mathematics Ext HSC 4 Solutions Suite 43, 4 Elizabeth St, Surry Hills NSW info@keystoneeducation.com.au keystoneeducation.com.au Mathematics Extension : HSC 4 Solutions Contents Multiple Choice... 3 Question...
Mathematics Ext HSC 4 Solutions Suite 43, 4 Elizabeth St, Surry Hills NSW info@keystoneeducation.com.au keystoneeducation.com.au Mathematics Extension : HSC 4 Solutions Contents Multiple Choice... 3 Question...
Answers to Practice Test Questions 12 Organic Acids and Bases
 Answers to Practice Test Questions 12 rganic Acids and Bases 1. (a) (b) pppp aa = llllll(kk aa ) KK aa = 10 pppp aa KK aa = 10 4.20 KK aa = 6.3 10 5 (c) Benzoic acid is a weak acid. We know this because
Answers to Practice Test Questions 12 rganic Acids and Bases 1. (a) (b) pppp aa = llllll(kk aa ) KK aa = 10 pppp aa KK aa = 10 4.20 KK aa = 6.3 10 5 (c) Benzoic acid is a weak acid. We know this because
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
CHAPTER 2 Special Theory of Relativity
 CHAPTER 2 Special Theory of Relativity Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 Topics 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 Inertial Frames of Reference Conceptual and Experimental
CHAPTER 2 Special Theory of Relativity Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 Topics 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 Inertial Frames of Reference Conceptual and Experimental
RETA Book 1 Chapter 1 Fundamental Items
 RETA Book 1 Chapter 1 Fundamental Items Peter Thomas, P.E. Resource Compliance RETA Certification Levels CARO Certified Assistant Refrigeration Operator CARO is an entry-level credential that is designed
RETA Book 1 Chapter 1 Fundamental Items Peter Thomas, P.E. Resource Compliance RETA Certification Levels CARO Certified Assistant Refrigeration Operator CARO is an entry-level credential that is designed
Thornton & Rex, 4th ed. Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1
 Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers Thornton & Rex, 4th ed. Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 CHAPTER 1 The Birth of Modern Physics Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 2 Topics 1) Classical Physics
Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers Thornton & Rex, 4th ed. Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 CHAPTER 1 The Birth of Modern Physics Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 2 Topics 1) Classical Physics
Physics 111. Lecture 34 (Walker 17.2,17.4-5) Kinetic Theory of Gases Phases of Matter Latent Heat
 Physics 111 Lecture 34 (Walker 17.2,17.4-5) Kinetic Theory of Gases Phases of Matter Latent Heat Dec. 7, 2009 Kinetic Theory Pressure is the result of collisions between gas molecules and walls of container.
Physics 111 Lecture 34 (Walker 17.2,17.4-5) Kinetic Theory of Gases Phases of Matter Latent Heat Dec. 7, 2009 Kinetic Theory Pressure is the result of collisions between gas molecules and walls of container.
(1) Correspondence of the density matrix to traditional method
 (1) Correspondence of the density matrix to traditional method New method (with the density matrix) Traditional method (from thermal physics courses) ZZ = TTTT ρρ = EE ρρ EE = dddd xx ρρ xx ii FF = UU
(1) Correspondence of the density matrix to traditional method New method (with the density matrix) Traditional method (from thermal physics courses) ZZ = TTTT ρρ = EE ρρ EE = dddd xx ρρ xx ii FF = UU
Math 171 Spring 2017 Final Exam. Problem Worth
 Math 171 Spring 2017 Final Exam Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Worth 9 6 6 5 9 8 5 8 8 8 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Total 8 5 5 6 6 8 6 6 6 6 6 150 Last Name: First Name: Student ID: Section:
Math 171 Spring 2017 Final Exam Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Worth 9 6 6 5 9 8 5 8 8 8 10 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Total 8 5 5 6 6 8 6 6 6 6 6 150 Last Name: First Name: Student ID: Section:
Physics 371 Spring 2017 Prof. Anlage Review
 Physics 71 Spring 2017 Prof. Anlage Review Special Relativity Inertial vs. non-inertial reference frames Galilean relativity: Galilean transformation for relative motion along the xx xx direction: xx =
Physics 71 Spring 2017 Prof. Anlage Review Special Relativity Inertial vs. non-inertial reference frames Galilean relativity: Galilean transformation for relative motion along the xx xx direction: xx =
P(N,V,T) = NRT V. = P(N,V,T) dv
 CHEM-443, Fall 2016, Section 010 Student Name Quiz 1 09/09/2016 Directions: Please answer each question to the best of your ability. Make sure your response is legible, precise, includes relevant dimensional
CHEM-443, Fall 2016, Section 010 Student Name Quiz 1 09/09/2016 Directions: Please answer each question to the best of your ability. Make sure your response is legible, precise, includes relevant dimensional
dg = V dp - S dt (1.1) 2) There are two T ds equations that are useful in the analysis of thermodynamic systems. The first of these
 CHM 3410 Problem Set 5 Due date: Wednesday, October 7 th Do all of the following problems. Show your work. "Entropy never sleeps." - Anonymous 1) Starting with the relationship dg = V dp - S dt (1.1) derive
CHM 3410 Problem Set 5 Due date: Wednesday, October 7 th Do all of the following problems. Show your work. "Entropy never sleeps." - Anonymous 1) Starting with the relationship dg = V dp - S dt (1.1) derive
Chapter 22 : Electric potential
 Chapter 22 : Electric potential What is electric potential? How does it relate to potential energy? How does it relate to electric field? Some simple applications What does it mean when it says 1.5 Volts
Chapter 22 : Electric potential What is electric potential? How does it relate to potential energy? How does it relate to electric field? Some simple applications What does it mean when it says 1.5 Volts
Secondary 3H Unit = 1 = 7. Lesson 3.3 Worksheet. Simplify: Lesson 3.6 Worksheet
 Secondary H Unit Lesson Worksheet Simplify: mm + 2 mm 2 4 mm+6 mm + 2 mm 2 mm 20 mm+4 5 2 9+20 2 0+25 4 +2 2 + 2 8 2 6 5. 2 yy 2 + yy 6. +2 + 5 2 2 2 0 Lesson 6 Worksheet List all asymptotes, holes and
Secondary H Unit Lesson Worksheet Simplify: mm + 2 mm 2 4 mm+6 mm + 2 mm 2 mm 20 mm+4 5 2 9+20 2 0+25 4 +2 2 + 2 8 2 6 5. 2 yy 2 + yy 6. +2 + 5 2 2 2 0 Lesson 6 Worksheet List all asymptotes, holes and
Work, Energy, and Power. Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Work, Energy, and Power Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 With the knowledge we got so far, we can handle the situation on the left but not the one on the right.
Work, Energy, and Power Chapter 6 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 With the knowledge we got so far, we can handle the situation on the left but not the one on the right.
Review for Exam Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering University of Iowa
 57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 1 Review for Exam3 12. 11. 2013 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering University of Iowa 57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 2 Chapter
57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 1 Review for Exam3 12. 11. 2013 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering University of Iowa 57:020 Fluids Mechanics Fall2013 2 Chapter
Review for Exam Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa
 Review for Exam2 11. 13. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
Review for Exam2 11. 13. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
Chem 75 February, 2017 Practice Exam 2
 As before, here is last year s Exam 2 in two forms: just the questions, and then the questions followed by their solutions. 1. (2 + 6 + 8 points) At high temperature, aluminum nitride, AlN(s), decomposes
As before, here is last year s Exam 2 in two forms: just the questions, and then the questions followed by their solutions. 1. (2 + 6 + 8 points) At high temperature, aluminum nitride, AlN(s), decomposes
Soluble: A solute that dissolves in a specific solvent. Insoluble: A solute that will not dissolve in a specific solvent. "Like Dissolves Like"
 Solutions Homogeneous Mixtures Solutions: Mixtures that contain two or more substances called the solute and the solvent where the solute dissolves in the solvent so the solute and solvent are not distinguishable
Solutions Homogeneous Mixtures Solutions: Mixtures that contain two or more substances called the solute and the solvent where the solute dissolves in the solvent so the solute and solvent are not distinguishable
Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS
 Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS SOLUTIONS single phase homogeneous mixture of two or more components NONELECTROLYTES do not contain ionic species. CONCENTRATION UNITS percent
Lecture 6. NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTONS NONELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS SOLUTIONS single phase homogeneous mixture of two or more components NONELECTROLYTES do not contain ionic species. CONCENTRATION UNITS percent
Name: First three letters of last name
 Name: First three letters of last name Chemistry 342 Third Exam April 22, 2005 2:00 PM in C6 Lecture Center Write all work you want graded in the spaces provided. Both the logical solution to the problem
Name: First three letters of last name Chemistry 342 Third Exam April 22, 2005 2:00 PM in C6 Lecture Center Write all work you want graded in the spaces provided. Both the logical solution to the problem
Interaction with matter
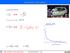 Interaction with matter accelerated motion: ss = bb 2 tt2 tt = 2 ss bb vv = vv 0 bb tt = vv 0 2 ss bb EE = 1 2 mmvv2 dddd dddd = mm vv 0 2 ss bb 1 bb eeeeeeeeeeee llllllll bbbbbbbbbbbbbb dddddddddddddddd
Interaction with matter accelerated motion: ss = bb 2 tt2 tt = 2 ss bb vv = vv 0 bb tt = vv 0 2 ss bb EE = 1 2 mmvv2 dddd dddd = mm vv 0 2 ss bb 1 bb eeeeeeeeeeee llllllll bbbbbbbbbbbbbb dddddddddddddddd
Temperature C. Heat Added (Joules)
 Now let s apply the heat stuff to real-world stuff like phase changes and the energy or cost it takes to carry it out. A heating curve...a plot of temperature of a substance vs heat added to a substance.
Now let s apply the heat stuff to real-world stuff like phase changes and the energy or cost it takes to carry it out. A heating curve...a plot of temperature of a substance vs heat added to a substance.
Thermodynamic condition for equilibrium between two phases a and b is G a = G b, so that during an equilibrium phase change, G ab = G a G b = 0.
 CHAPTER 5 LECTURE NOTES Phases and Solutions Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between
CHAPTER 5 LECTURE NOTES Phases and Solutions Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between
Final Examination. Multiple Choice Questions. 1. The Virial expansion of the Compressibility Factor for a van der Waals gas is:
 CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry I Fall 2013 Name: Final Examination Multiple Choice Questions 1. The Virial expansion of the Compressibility Factor for a van der Waals gas is: Z = 1 + + The Boyle Temperature
CHEM 331 Physical Chemistry I Fall 2013 Name: Final Examination Multiple Choice Questions 1. The Virial expansion of the Compressibility Factor for a van der Waals gas is: Z = 1 + + The Boyle Temperature
PHY103A: Lecture # 9
 Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
Semester II, 2017-18 Department of Physics, IIT Kanpur PHY103A: Lecture # 9 (Text Book: Intro to Electrodynamics by Griffiths, 3 rd Ed.) Anand Kumar Jha 20-Jan-2018 Summary of Lecture # 8: Force per unit
Classical RSA algorithm
 Classical RSA algorithm We need to discuss some mathematics (number theory) first Modulo-NN arithmetic (modular arithmetic, clock arithmetic) 9 (mod 7) 4 3 5 (mod 7) congruent (I will also use = instead
Classical RSA algorithm We need to discuss some mathematics (number theory) first Modulo-NN arithmetic (modular arithmetic, clock arithmetic) 9 (mod 7) 4 3 5 (mod 7) congruent (I will also use = instead
Chapter 11 Spontaneous Change and Equilibrium
 Chapter 11 Spontaneous Change and Equilibrium 11-1 Enthalpy and Spontaneous Change 11-2 Entropy 11-3 Absolute Entropies and Chemical Reactions 11-4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics 11-5 The Gibbs Function
Chapter 11 Spontaneous Change and Equilibrium 11-1 Enthalpy and Spontaneous Change 11-2 Entropy 11-3 Absolute Entropies and Chemical Reactions 11-4 The Second Law of Thermodynamics 11-5 The Gibbs Function
(1) Introduction: a new basis set
 () Introduction: a new basis set In scattering, we are solving the S eq. for arbitrary VV in integral form We look for solutions to unbound states: certain boundary conditions (EE > 0, plane and spherical
() Introduction: a new basis set In scattering, we are solving the S eq. for arbitrary VV in integral form We look for solutions to unbound states: certain boundary conditions (EE > 0, plane and spherical
BHASVIC MαTHS. Skills 1
 PART A: Integrate the following functions with respect to x: (a) cos 2 2xx (b) tan 2 xx (c) (d) 2 PART B: Find: (a) (b) (c) xx 1 2 cosec 2 2xx 2 cot 2xx (d) 2cccccccccc2 2xx 2 ccccccccc 5 dddd Skills 1
PART A: Integrate the following functions with respect to x: (a) cos 2 2xx (b) tan 2 xx (c) (d) 2 PART B: Find: (a) (b) (c) xx 1 2 cosec 2 2xx 2 cot 2xx (d) 2cccccccccc2 2xx 2 ccccccccc 5 dddd Skills 1
A) sublimation. B) liquefaction. C) evaporation. D) condensation. E) freezing. 11. Below is a phase diagram for a substance.
 PX0411-1112 1. Which of the following statements concerning liquids is incorrect? A) The volume of a liquid changes very little with pressure. B) Liquids are relatively incompressible. C) Liquid molecules
PX0411-1112 1. Which of the following statements concerning liquids is incorrect? A) The volume of a liquid changes very little with pressure. B) Liquids are relatively incompressible. C) Liquid molecules
PX-III Chem 1411 Chaps 11 & 12 Ebbing
 PX-III Chem 1411 Chaps 11 & 12 Ebbing 1. What is the name for the following phase change? I 2 (s) I 2 (g) A) melting B) condensation C) sublimation D) freezing E) vaporization 2. Which of the following
PX-III Chem 1411 Chaps 11 & 12 Ebbing 1. What is the name for the following phase change? I 2 (s) I 2 (g) A) melting B) condensation C) sublimation D) freezing E) vaporization 2. Which of the following
**VII-1 C NC I-3 C NC II-2 C NC *VII-2 C NC I-4 C NC. CHEMISTRY 131 Quiz 5 Fall 2010 Form B
 **VII-1 N I-3 N II-2 N *VII-2 N I-4 N EMISTRY 131 Quiz 5 Fall 2010 Form B NAME: Key hapter 11: States of Matter A. (2 pts) onsider the structures of the compounds shown below, and determine which intermolecular
**VII-1 N I-3 N II-2 N *VII-2 N I-4 N EMISTRY 131 Quiz 5 Fall 2010 Form B NAME: Key hapter 11: States of Matter A. (2 pts) onsider the structures of the compounds shown below, and determine which intermolecular
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics. Quadratics. mr-mathematics.com Maths Resources for Teachers. Algebra
 Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Quadratics mr-mathematics.com Maths Resources for Teachers Algebra Quadratics Worksheets Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets Solving x + bx + c by factorisation
Worksheets for GCSE Mathematics Quadratics mr-mathematics.com Maths Resources for Teachers Algebra Quadratics Worksheets Contents Differentiated Independent Learning Worksheets Solving x + bx + c by factorisation
Thermodynamics, Design, Simulation and Benchmarking of Biofuel Processes
 Thermodynamics, Design, Simulation and Benchmarking of Biofuel Processes Mauro Torli Philip Loldrup Fosbøl Georgios Kontogeorgis SYNFERON project work packages Commercial syngas fermentation technologies:
Thermodynamics, Design, Simulation and Benchmarking of Biofuel Processes Mauro Torli Philip Loldrup Fosbøl Georgios Kontogeorgis SYNFERON project work packages Commercial syngas fermentation technologies:
School of Chemical & Biological Engineering, Konkuk University
 School of Chemical & iological Engineering, Konkuk University Lecture 7 Ch. 5 Simple Mixtures Colligative properties Prof. Yo-Sep Min Physical Chemistry I, Spring 2009 Ch. 5-2 he presence of a solute in
School of Chemical & iological Engineering, Konkuk University Lecture 7 Ch. 5 Simple Mixtures Colligative properties Prof. Yo-Sep Min Physical Chemistry I, Spring 2009 Ch. 5-2 he presence of a solute in
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 1 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Topics 5.7
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 1 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles 5.6 Uncertainty Principle Topics 5.7
Lecture Outline Chapter 17. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 17 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 17 Phases and Phase Changes Ideal Gases Kinetic Theory Units of Chapter 17 Solids and Elastic Deformation Phase Equilibrium and
Lecture Outline Chapter 17 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 17 Phases and Phase Changes Ideal Gases Kinetic Theory Units of Chapter 17 Solids and Elastic Deformation Phase Equilibrium and
Introduction into thermodynamics
 Introduction into thermodynamics Solid-state thermodynamics, J. Majzlan Chemical thermodynamics deals with reactions between substances and species. Mechanical thermodynamics, on the other hand, works
Introduction into thermodynamics Solid-state thermodynamics, J. Majzlan Chemical thermodynamics deals with reactions between substances and species. Mechanical thermodynamics, on the other hand, works
Answers to Practice Test Questions 6 Entropy and Free Energy
 Answers to Practice Test Questions 6 Entropy and Free Energy 1. Enthalpy of formation (and free energy of formation) is the enthalpy change (and free energy change) involved in producing a compound from
Answers to Practice Test Questions 6 Entropy and Free Energy 1. Enthalpy of formation (and free energy of formation) is the enthalpy change (and free energy change) involved in producing a compound from
Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
 CHAPTER 8 GASES Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases The density of gases is much less than that of solids or liquids. Densities (g/ml) Solid Liquid Gas H O 0.97 0.998 0.000588 CCl 4.70.59 0.00503
CHAPTER 8 GASES Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases The density of gases is much less than that of solids or liquids. Densities (g/ml) Solid Liquid Gas H O 0.97 0.998 0.000588 CCl 4.70.59 0.00503
Mathematics Paper 2 Grade 12 Preliminary Examination 2017
 Mathematics Paper 2 Grade 12 Preliminary Examination 2017 DURATION: 180 min EXAMINER: R. Obermeyer MARKS: 150 MODERATOR: A. Janisch Date: 15 September 2017 External Moderator: I. Atteridge INSTRUCTIONS:
Mathematics Paper 2 Grade 12 Preliminary Examination 2017 DURATION: 180 min EXAMINER: R. Obermeyer MARKS: 150 MODERATOR: A. Janisch Date: 15 September 2017 External Moderator: I. Atteridge INSTRUCTIONS:
Chapter 17: Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energy
 Chapter 17: Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energy Review of Chemical Thermodynamics System: the matter of interest Surroundings: everything in the universe which is not part of the system Closed System:
Chapter 17: Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free Energy Review of Chemical Thermodynamics System: the matter of interest Surroundings: everything in the universe which is not part of the system Closed System:
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 9: Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics
 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 9: Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics Marc R. Roussel January 23, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Entropy and the second law January 23, 2018 1 / 29 States in thermodynamics The thermodynamic
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 9: Entropy and the second law of thermodynamics Marc R. Roussel January 23, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Entropy and the second law January 23, 2018 1 / 29 States in thermodynamics The thermodynamic
FACULTY OF SCIENCE MID-TERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 120 GENERAL CHEMISTRY MIDTERM 1. Examiners: Prof. B. Siwick Prof. I. Butler Dr. A.
 FACULTY OF SCIENCE MID-TERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 120 GENERAL CHEMISTRY MIDTERM 1 Examiners: Prof. B. Siwick Prof. I. Butler Dr. A. Fenster Name: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Enter your student number and name on the
FACULTY OF SCIENCE MID-TERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 120 GENERAL CHEMISTRY MIDTERM 1 Examiners: Prof. B. Siwick Prof. I. Butler Dr. A. Fenster Name: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Enter your student number and name on the
Chem 260 Quiz - Chapter 4 (11/19/99)
 Chem 260 Quiz - Chapter 4 (11/19/99) Name (print) Signature Terms in bold: phase transitions transition temperature phase diagram phase boundaries vapor pressure thermal analysis dynamic equilibrium boiling
Chem 260 Quiz - Chapter 4 (11/19/99) Name (print) Signature Terms in bold: phase transitions transition temperature phase diagram phase boundaries vapor pressure thermal analysis dynamic equilibrium boiling
DATA THAT YOU MAY USE UNITS Conventional Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 10-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr = Pa CONSTANTS
 DATA THAT YOU MAY USE UNITS Conventional S.I. Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 0-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr =.03 0 5 Pa torr = 33.3 Pa Temperature C 0 C = 73.5 K PV L-atm =.03 0 5 dm 3
DATA THAT YOU MAY USE UNITS Conventional S.I. Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 0-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr =.03 0 5 Pa torr = 33.3 Pa Temperature C 0 C = 73.5 K PV L-atm =.03 0 5 dm 3
Rotational Motion. Chapter 10 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition
 Rotational Motion Chapter 10 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 We ll look for a way to describe the combined (rotational) motion 2 Angle Measurements θθ ss rr rrrrrrrrrrrrrr
Rotational Motion Chapter 10 of Essential University Physics, Richard Wolfson, 3 rd Edition 1 We ll look for a way to describe the combined (rotational) motion 2 Angle Measurements θθ ss rr rrrrrrrrrrrrrr
where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = atm L mol R = atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit)
 Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
Ideal Gas Behavior. NC State University
 Chemistry 331 Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Behavior NC State University Macroscopic variables P, T Pressure is a force per unit area (P= F/A) The force arises from the change in momentum as particles hit an object
Chemistry 331 Lecture 6 Ideal Gas Behavior NC State University Macroscopic variables P, T Pressure is a force per unit area (P= F/A) The force arises from the change in momentum as particles hit an object
SOLUTIONS. General Chemistry I CHAPTER
 11 CHAPTER SOLUTIONS 11.1 Composition of Solutions 11.2 Nature of Dissolved Species 11.3 Reaction Stoichiometry in Solutions: Acid-Base Titrations 11.4 Reaction Stoichiometry in Solutions: Oxidation-Reduction
11 CHAPTER SOLUTIONS 11.1 Composition of Solutions 11.2 Nature of Dissolved Species 11.3 Reaction Stoichiometry in Solutions: Acid-Base Titrations 11.4 Reaction Stoichiometry in Solutions: Oxidation-Reduction
17-1 Ideal Gases. Gases are the easiest state of matter to describe - All ideal gases exhibit similar behavior.
 17-1 Ideal Gases Gases are the easiest state of matter to describe - All ideal gases exhibit similar behavior. An ideal gas is one that is thin enough, that the interactions between molecules can be ignored.
17-1 Ideal Gases Gases are the easiest state of matter to describe - All ideal gases exhibit similar behavior. An ideal gas is one that is thin enough, that the interactions between molecules can be ignored.
Entropy Changes & Processes
 Entropy Changes & Processes Chapter 4 of Atkins: he Second Law: he Concepts Section 4.3 Entropy of Phase ransition at the ransition emperature Expansion of the Perfect Gas Variation of Entropy with emperature
Entropy Changes & Processes Chapter 4 of Atkins: he Second Law: he Concepts Section 4.3 Entropy of Phase ransition at the ransition emperature Expansion of the Perfect Gas Variation of Entropy with emperature
National 5 Mathematics. Practice Paper E. Worked Solutions
 National 5 Mathematics Practice Paper E Worked Solutions Paper One: Non-Calculator Copyright www.national5maths.co.uk 2015. All rights reserved. SQA Past Papers & Specimen Papers Working through SQA Past
National 5 Mathematics Practice Paper E Worked Solutions Paper One: Non-Calculator Copyright www.national5maths.co.uk 2015. All rights reserved. SQA Past Papers & Specimen Papers Working through SQA Past
Chemistry 122 (Tyvoll) ANSWERS TO PRACTICE EXAMINATION I Fall 2005
 hemistry 122 (Tyvoll) ANSWERS T PRATIE EXAMINATIN I Fall 2005 1. Which statement is not correct? 1) A volatile liquid has a high boiling point. 2. Which of the following compounds is predicted to have
hemistry 122 (Tyvoll) ANSWERS T PRATIE EXAMINATIN I Fall 2005 1. Which statement is not correct? 1) A volatile liquid has a high boiling point. 2. Which of the following compounds is predicted to have
Review of differential and integral calculus and introduction to multivariate differential calculus.
 Chemistry 2301 Introduction: Review of terminology used in thermodynamics Review of differential and integral calculus and introduction to multivariate differential calculus. The properties of real gases:
Chemistry 2301 Introduction: Review of terminology used in thermodynamics Review of differential and integral calculus and introduction to multivariate differential calculus. The properties of real gases:
m m 3 mol Pa = Pa or bar At this pressure the system must also be at approximately 1000 K.
 5. PHASES AND SOLUTIONS n Thermodynamics of Vapor Pressure 5.. At equilibrium, G(graphite) G(diamond); i.e., G 2 0. We are given G 2900 J mol. ( G/ P) T V V 2.0 g mol.95 0 6 m 3 mol Holding T constant
5. PHASES AND SOLUTIONS n Thermodynamics of Vapor Pressure 5.. At equilibrium, G(graphite) G(diamond); i.e., G 2 0. We are given G 2900 J mol. ( G/ P) T V V 2.0 g mol.95 0 6 m 3 mol Holding T constant
Unit WorkBook 2 Level 4 ENG U13 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines UniCourse LTD. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Plant Equipment Page
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 13: Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Engines Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Plant Equipment Page
Review for Exam Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa
 Review for Exam3 12. 9. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
Review for Exam3 12. 9. 2015 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Adjunct Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Iowa Assistant Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering, University
**VII-1 C NC *VII-2 C NC I-2 C NC I-3 C NC I-4 C NC II-1 C NC II-2 C NC II-3 C NC IV-1 C NC IV-2 C NC VIII-1 C NC
 **VII-1 N *VII-2 N I-2 N I-3 N I-4 N II-1 N II-2 N II-3 N IV-1 N IV-2 N VIII-1 N EMISTRY 131-01 Quiz 5 Summer 2013 Form B NAME: Key hapter 11: States of Matter A. (2 pts) onsider the structures of the
**VII-1 N *VII-2 N I-2 N I-3 N I-4 N II-1 N II-2 N II-3 N IV-1 N IV-2 N VIII-1 N EMISTRY 131-01 Quiz 5 Summer 2013 Form B NAME: Key hapter 11: States of Matter A. (2 pts) onsider the structures of the
10.1 Three Dimensional Space
 Math 172 Chapter 10A notes Page 1 of 12 10.1 Three Dimensional Space 2D space 0 xx.. xx-, 0 yy yy-, PP(xx, yy) [Fig. 1] Point PP represented by (xx, yy), an ordered pair of real nos. Set of all ordered
Math 172 Chapter 10A notes Page 1 of 12 10.1 Three Dimensional Space 2D space 0 xx.. xx-, 0 yy yy-, PP(xx, yy) [Fig. 1] Point PP represented by (xx, yy), an ordered pair of real nos. Set of all ordered
Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries
 Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between two phases.
Phase Equilibrium: Preliminaries Phase diagrams for two one component systems, CO 2 and H 2 O, are shown below. The main items to note are the following: The lines represent equilibria between two phases.
Multiple Choice 2 POINTS EACH Select the choice that best answers the question. Mark it clearly on your answer sheet.
 Chemistry 45.5 100 Points Take Home Exam 1 2009-10 Name: Student ID: Form A Multiple Choice 2 POINTS EACH Select the choice that best answers the question. Mark it clearly on your answer sheet. 1. Likes
Chemistry 45.5 100 Points Take Home Exam 1 2009-10 Name: Student ID: Form A Multiple Choice 2 POINTS EACH Select the choice that best answers the question. Mark it clearly on your answer sheet. 1. Likes
10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
Quantum Mechanics. An essential theory to understand properties of matter and light. Chemical Electronic Magnetic Thermal Optical Etc.
 Quantum Mechanics An essential theory to understand properties of matter and light. Chemical Electronic Magnetic Thermal Optical Etc. Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 CHAPTER 3 Experimental Basis of
Quantum Mechanics An essential theory to understand properties of matter and light. Chemical Electronic Magnetic Thermal Optical Etc. Fall 2018 Prof. Sergio B. Mendes 1 CHAPTER 3 Experimental Basis of
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II. Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition
 MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
MME 2010 METALLURGICAL THERMODYNAMICS II Fundamentals of Thermodynamics for Systems of Constant Composition Thermodynamics addresses two types of problems: 1- Computation of energy difference between two
Prof. Dr. Rishi Raj Design of an Impulse Turbine Blades Hasan-1
 Prof. Dr. Rishi Raj Design of an Impulse Turbine Blades Hasan-1 The main purpose of this project, design of an impulse turbine is to understand the concept of turbine blades by defining and designing the
Prof. Dr. Rishi Raj Design of an Impulse Turbine Blades Hasan-1 The main purpose of this project, design of an impulse turbine is to understand the concept of turbine blades by defining and designing the
Information Booklet of Formulae and Constants
 Pearson BTEC Level 3 Nationals Engineering Information Booklet of Formulae and Constants Unit 1: Engineering Principles Extended Certificate, Foundation Diploma, Diploma, Extended Diploma in Engineering
Pearson BTEC Level 3 Nationals Engineering Information Booklet of Formulae and Constants Unit 1: Engineering Principles Extended Certificate, Foundation Diploma, Diploma, Extended Diploma in Engineering
Problem Set #10 Assigned November 8, 2013 Due Friday, November 15, 2013 Please show all work for credit To Hand in
 Problem Set #10 Assigned November 8, 2013 Due Friday, November 15, 2013 Please show all work for credit To Hand in 1. 2. 1 3. 4. The vapor pressure of an unknown solid is approximately given by ln(p/torr)
Problem Set #10 Assigned November 8, 2013 Due Friday, November 15, 2013 Please show all work for credit To Hand in 1. 2. 1 3. 4. The vapor pressure of an unknown solid is approximately given by ln(p/torr)
Representative Questions Exam 3
 Representative Questions Exam 3 1. The kinetic-molecular theory of gases assumes which of the following? a. gas samples are mostly empty space b. the average kinetic energy is proportional to the Kelvin
Representative Questions Exam 3 1. The kinetic-molecular theory of gases assumes which of the following? a. gas samples are mostly empty space b. the average kinetic energy is proportional to the Kelvin
OFB Chapter 6 Condensed Phases and Phase Transitions
 OFB Chapter 6 Condensed Phases and Phase Transitions 6-1 Intermolecular Forces: Why Condensed Phases Exist 6- The Kinetic Theory of Liquids and Solids 6-3 Phase Equilibrium 6-4 Phase Transitions 6-5 Phase
OFB Chapter 6 Condensed Phases and Phase Transitions 6-1 Intermolecular Forces: Why Condensed Phases Exist 6- The Kinetic Theory of Liquids and Solids 6-3 Phase Equilibrium 6-4 Phase Transitions 6-5 Phase
CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances.
 I. Generalities. CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances. A. Definitions: 1. A phase of a substance is a form of matter that is uniform throughout in chemical composition and physical state.
I. Generalities. CHAPTER 4 Physical Transformations of Pure Substances. A. Definitions: 1. A phase of a substance is a form of matter that is uniform throughout in chemical composition and physical state.
CHEM 231. Physical Chemistry I NJIT Fall Semester, Prerequisites: Chem 126 or 123, Phys 111 Co requisite: Math 211
 CHEM 231 Physical Chemistry I NJIT Fall Semester, 2017 Prerequisites: Chem 126 or 123, Phys 111 Co requisite: Math 211 Textbook: Chapters to be covered: Instructor: Goals: Prerequisites: Course Outline:
CHEM 231 Physical Chemistry I NJIT Fall Semester, 2017 Prerequisites: Chem 126 or 123, Phys 111 Co requisite: Math 211 Textbook: Chapters to be covered: Instructor: Goals: Prerequisites: Course Outline:
Chemical Thermodynamics. Chapter 18
 Chemical Thermodynamics Chapter 18 Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy Changes Gibbs Free Energy Free Energy and Temperature Free Energy and Equilibrium
Chemical Thermodynamics Chapter 18 Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy Changes Gibbs Free Energy Free Energy and Temperature Free Energy and Equilibrium
General Strong Polarization
 General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) May 1, 018 G.Tech:
General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) May 1, 018 G.Tech:
General Strong Polarization
 General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) December 4, 2017 IAS:
General Strong Polarization Madhu Sudan Harvard University Joint work with Jaroslaw Blasiok (Harvard), Venkatesan Gurswami (CMU), Preetum Nakkiran (Harvard) and Atri Rudra (Buffalo) December 4, 2017 IAS:
10.4 The Cross Product
 Math 172 Chapter 10B notes Page 1 of 9 10.4 The Cross Product The cross product, or vector product, is defined in 3 dimensions only. Let aa = aa 1, aa 2, aa 3 bb = bb 1, bb 2, bb 3 then aa bb = aa 2 bb
Math 172 Chapter 10B notes Page 1 of 9 10.4 The Cross Product The cross product, or vector product, is defined in 3 dimensions only. Let aa = aa 1, aa 2, aa 3 bb = bb 1, bb 2, bb 3 then aa bb = aa 2 bb
Practice Final Exam CH 201
 Practice Final Exam CH 201 Name: (please print) Student I D : Instructions - Read Carefully 1. Please show your work, and put your final answers in the spaces provided. 2. Point values for each question
Practice Final Exam CH 201 Name: (please print) Student I D : Instructions - Read Carefully 1. Please show your work, and put your final answers in the spaces provided. 2. Point values for each question
Physical Chemistry I Exam points
 Chemistry 360 Fall 2018 Dr. Jean M. tandard October 17, 2018 Name Physical Chemistry I Exam 2 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must
Chemistry 360 Fall 2018 Dr. Jean M. tandard October 17, 2018 Name Physical Chemistry I Exam 2 100 points Note: You must show your work on problems in order to receive full credit for any answers. You must
ME5286 Robotics Spring 2017 Quiz 2
 Page 1 of 5 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2017 Quiz 2 Total Points: 30 You are responsible for following these instructions. Please take a minute and read them completely. 1. Put your name on this page, any other
Page 1 of 5 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2017 Quiz 2 Total Points: 30 You are responsible for following these instructions. Please take a minute and read them completely. 1. Put your name on this page, any other
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics Sample Exercise 19.2 (p. 819) Elemental mercury is a silver liquid at room temperature. Its normal freezing point is -38.9 o C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is H
Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics Sample Exercise 19.2 (p. 819) Elemental mercury is a silver liquid at room temperature. Its normal freezing point is -38.9 o C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is H
Eureka Math. Geometry, Module 5. Student File_B. Contains Exit Ticket and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Functions Eureka Math Geometry, Module 5 Student File_B Contains and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may be reproduced,
A Story of Functions Eureka Math Geometry, Module 5 Student File_B Contains and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may be reproduced,
(b) The measurement of pressure
 (b) The measurement of pressure The pressure of the atmosphere is measured with a barometer. The original version of a barometer was invented by Torricelli, a student of Galileo. The barometer was an inverted
(b) The measurement of pressure The pressure of the atmosphere is measured with a barometer. The original version of a barometer was invented by Torricelli, a student of Galileo. The barometer was an inverted
F.1 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
 section F1 214 is the reverse process of multiplication. polynomials in algebra has similar role as factoring numbers in arithmetic. Any number can be expressed as a product of prime numbers. For example,
section F1 214 is the reverse process of multiplication. polynomials in algebra has similar role as factoring numbers in arithmetic. Any number can be expressed as a product of prime numbers. For example,
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
