Master s in NANOSCIENCE
|
|
|
- Clement Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CÓDE NAME OF MODULE TYPE MATHEMATICAL METHODS FOR NANOSCIENCE M M = mandatory E = elective Learning goals of the module. (List the specific learning goals that the current module should provide to the student; goals can focus on content, skills, or attitudes) The goal of this module is to provide the students with the required fundamental mathematical methods for the theoretical developments of the degree Methodology: learning activities and credit value of the module (ECTS) Learning activities. (Time required to teach the module; links to other modules included in the MSc Program and suggested chronological sequence with the latter) The program will consist of lectures up to 46 hours which are to be distributed among theoretical ones, seminars and problems. The instrumental character of the subject requires the dedication of a considerable number of seminars and practical exercises in order to apply the theoretical mathematical methods to real problems. Since this module is aimed to provide the student with basic knowledge, the subject will be held in the first term (four month period) of the first year of the degree ECTS credit value (and time) 1 ECTS credit = 25 hours UPV/EHU TYPE OF LECTURE Theory Practice M (2) S PA PL PO TA TAI PCL PCC Periodic Evaluation Final Classroom lectures Personal work (3) TOTAL (1) M (standard lecture); S (seminar); PA (practical exercises in classroom); PL (practical exercises in laboratory); PO (practical exercises with computers); TA (non-industrial workshops); TAI (industrial workshops); PCL (clinical practice); PCC (field practice); the acronyms are taken from the Spanish wording. (2) M = maximum allowed is 60% of the full classroom lectures. (3) Personal work = time that the student would use to prepare and develop individual and group assignments. 1
2 Module Program. (Lectures) Lecture 1 THEORY OF FUNCTIONS OF A COMPLEX VARIABLE Lecture 2 INTEGRATION IN THE COMPLEX PLANE Lecture 3 FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS. HILBERT SPACES Lecture 4 THEORY OF LINEAR OPERATORS. APPLICATIONS TO DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS. Lecture 5 GROUP THEORY Bibliography. (Basic and specialized bibliographies, journal references, internet addresses, etc.) - COMPLEX ANALYSIS: FOR MATHEMATICS AND ENGINEERING. FIFTH EDITION, JOHN H. MATHEWS AND RUSSELL W. HOWELL - GRADUATE MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS. KELLY, JAMES J. - ANALISIS REAL Y COMPLEJO. W. RUDIN. MC GRAW HILL. - ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS. ERWING KREYZIG. JOHN WILEY&SONS - MATHEMATHICS METHODS FOR PHYSICS&ENGINEERING. RILEY ET AL. CAMBRIDGE - GROUP THEORY IN PHYSICS. J.F. CORNWELL Criteria and methods for evaluation and grading (Analysis of the methodology that will be used to evaluate the learning process of the student) The evaluation of the knowledge of the fundamentals obtained by the student will be deduced by means of individual tasks which might include the resolution of practical problems and their presentation as a short lecture 2
3 Learning resources The student should be given open access to the bibliographical material of the libraries of the Faculty of Chemistry of the UPV/EHU, the Unit of Physics of Materials and also to that of the Donostia International Physics Center. Moreover, within the aim of performing computer practices and tasks the computer science resources of the Donostia International Physics Center will be also available Language and number of groups attending the module 1 NUMBER OF GROUPS x LANGUAGE: ENGLISH Fields of science and technology to which the module is related CODE FIELD PHYSICS OF CONDENSED MATTER APPLIED PHYSICS Department in charge of the Program CODE DEPARTMENT (1) DEPARTMENT OF MATERIALS PHYSICS Teachers in charge of the module DNI Teacher UPV/EHU Number of credits C Rivacoba Ochoa, Alberto M Alvarez González, Fernando 1 3
4 CÓDE NAME OF MODULE TYPE FUNDAMENTALS OF QUANTUM MECHANICS M M = mandatory E = elective Learning goals of the module. (List the specific learning goals that the current module should provide to the student; goals can focus on content, skills, or attitudes.) The laws of Quantum Mechanics are the laws that describe the phenomenon taking place at the nanoscale. This module is thought to address the fundamentals of quantum mechanics, i.e., the formalism from which quantum theory was built, as well as the basic physical problems that are only understood within this theory. The student will learn crucial concepts and tools, such as the probabilistic meaning of the wave function, the idea of operators and observables, the Schrödinger equation that describes the evolution of a system, and approximation methods that allow to solve the Schrödinger equation when the exact solution is not possible Methodology: learning activities and credit value of the module (ECTS) Learning activities. (Time required to teach the module; links to other modules included in the MSc Program and suggested chronological sequence with the latter) The course consists of 45 hours of lectures and seminars. The course is offered for the first term and first year in Master program. The schedule takes into account that the central concepts and ideas given in this course are the basic background to other courses in the Master: Fundamentals in Solid State Physics Low dimensional systems and nanostructures Fundamentals of nanoscale characterization Nanostructural properties ECTS credit value (and time) 1 ECTS credit = 25 hours UPV/EHU 4
5 TYPE OF LECTURE Theory Practice M (2) S PA PL PO TA TAI PCL PCC Periodic Evaluation Final Classroom lectures Personal work (3) TOTAL (4) M (standard lecture); S (seminar); PA (practical exercises in classroom); PL (practical exercises in laboratory); PO (practical exercises with computers); TA (non-industrial workshops); TAI (industrial workshops); PCL (clinical practice); PCC (field practice); the acronyms are taken from the Spanish wording. (5) M = maximum allowed is 60% of the full classroom lectures. (6) Personal work = time that the student would use to prepare and develop individual and group assignments Module Program. (Lectures) Lecture 1 THE ORIGINS OF QUANTUM THEORY Lecture 2 THE POSTULATES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS Lecture 3 OBSERVABLES: OPERATORS IN QUANTUM MECHANICS Lecture 4 POSITION AND MOMENTUM OPERATORS. UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE Lecture 5 SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION. STATIONARY STATES. TIME EVOLUTION OF QUANTUM SYSTEM Lecture 6 ONE-DIMENSIONAL PROBLEMS Lecture 7 THE ONE-DIMENSIONAL HARMONIC OSCILLATOR Lecture 8 GENERAL THEORY OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM 5
6 Lecture 9 ORBITAL ANGULAR MOMENTUM Lecture 10 SPIN ANGULAR MOMENTUM Lecture 11 PARTICLE IN A CENTRAL POTENTIAL. THE HYDROGEN ATOM Lecture 12 APPROXIMATION METHODS FOR STATIONARY AND TIME- DEPENDENT PROBLEMS Lecture 13 IDENTICAL PARTICLES: FERMIONS AND BOSONS Lecture 14 SCATTERING THEORY Bibliography. (Basic and specialized bibliographies, journal references, internet addresses, etc.) - QUANTUM MECHANICS, C. COHEN TANNOUDJI, B. DIU, AND F. LALOË,, ED. JOHN WILEY AND SONS - MECÁNICA CUÁNTICA, F.J YNDURAIN ARIEL CIENCIA - QUANTUM MECHANICS, B.H. BRANSDEN AND C.J.JOACHAIN PEARSON EDUCATION - QUANTUM MECHANICS L. I. SCHIFF,, ED. MCGRAW-HILL - QUANTUM MECHANICS, A. MESSIAH, ED. DOVER - QUANTUM PHYSICS, R. EISBERG AND R. RESNICK, ED. JOHN WILEY AND SONS - QUANTUM MECHANICS (NON RELATIVISTIC THEORY), L. D. LANDAU AND E. M. LIFSHITZ, ED. BUTTERWORTH-HEINEMANN 6
7 Criteria and methods for evaluation and grading (Analysis of the methodology that will be used to evaluate the learning process of the student) The concepts of quantum mechanics are crucial to follow most of the modules given in this Master. For this reason, the method used to evaluate the learning process of the student will be a final exam that will represent 75% of the final grade. In this final exam the student will have the opportunity to show his/her familiarity with the basic concepts of quantum mechanics. The 25% of the grade left will evaluate the student s personal work. In particular, the student will be asked to solve a few problems related with the concepts explained during the lectures Learning resources The student will have access to the bibliographical resources available in the University of the Basque Country, Centro de Física de Materiales, and Donostia International Physics Center Language and number of groups attending the module 1 NUMBER OF GROUPS x LANGUAGE: ENGLISH Fields of science and technology to which the module is related CODE FIELD PHYSICS OF CONDENSED MATTER APPLIED PHYSICS Department in charge of the Program CODE DEPARTMENT (1) DEPARTMENT OF MATERIALS PHYSICS 7
8 Teachers in charge of the module DNI Teacher UPV/EHU Number of credits X Andrés Arnau Pino 2.25 DNI Teacher other institutions Number of credits F Maite Alducin Ochoa
9 CÓDE NAME OF MODULE TYPE FUNDAMENTALS OF SOLID STATE PHYSICS M M = mandatory E = elective Learning goals of the module. (List the specific learning goals that the current module should provide to the student; goals can focus on content, skills, or attitudes.) The gole of the module is to develop a generale picture of solid state physics that can be used by students to understand the classification of materials in terms of their properties: metals, semiconductors, and insulators. This includes general properties of crystal symmetry: crystal lattice translational symmetry and point group operations, reciprocal lattice, one particle properties and classification of one particle states in terms of wave vectors. It also includes band structure of metals, semiconductors, and insulators; vibrations in solids; experimental and theoretical methods of study of electronic and vibrational properties of solids. Magnetism of solids why some materials are magnetic? Methodology: learning activities and credit value of the module (ECTS) Learning activities. (Time required to teach the module; links to other modules included in the MSc Program and suggested chronological sequence with the latter) The course of the fundamentals of solid state physics will be given in the first four-month period of a master in nanoscience. This is because a knowledge of basic notions and properties of solids is fundamentals for understanding of other disciplines of a master in nanoscience. The themes of the course form a bridge that connects phenomena of Extended materials and Nano size metallic. Semiconductor and insulator systems. in particular, information obtained is necessary for study of other courses ECTS credit value (and time) 1 ECTS credit = 25 hours UPV/EHU TYPE OF LECTURE Theory Practice M (2) S PA PL PO TA TAI PCL PCC Periodic Evaluation Final Classroom lectures Personal work (3) TOTAL (7) M (standard lecture); S (seminar); PA (practical exercises in classroom); PL (practical exercises in laboratory); PO (practical exercises with computers); TA (non-industrial workshops); TAI 9
10 (industrial workshops); PCL (clinical practice); PCC (field practice); the acronyms are taken from the Spanish wording. (8) M = maximum allowed is 60% of the full classroom lectures. (9) Personal work = time that the student would use to prepare and develop individual and group assignments Module Program. (Lectures) Lecture 1 GEOMETRICAL DESCRIPTION OF CRYSTALS: DIRECT AND RECIPROCAL LATTICES. Lecture 2 VIBRATIONS IN SOLIDS: PHONONS Lecture 3 FREE ELECTRONS IN SOLIDS. Lecture 4 THE ELECTRONIC BANDSTRUCTURE OF SOLIDS: BLOCH THEOREM, THE NEARLY FREE-ELECTRON APPROXIMATION, THE THIGHT-BINDING APPROXIMATION. Lecture 5 BAND STRUCTURE OF SELECTED METALS Lecture 5 COHESION OF SOLIDS. Lecture 6 MAGNETISM IN SOLIDS: WHY SOME MATRERIOALS ARE MAGNETIC Language and number of groups attending the module 1 x NUMBER OF GROUPS LANGUAGE: ENGLISH 10
11 Fields of science and technology to which the module is related CODE FIELD PHYSICS OF CONDENSED MATTER APPLIED PHYSICS Department in charge of the Program CODE DEPARTMENT (1) DEPARTMENT OF MATERIALS PHYSICS Teachers in charge of the module DNI Teacher UPV/EHU Number of credits Pedro Miguel Echenique Landiribar Eugene V. Tchulcov 11
12 CÓDE NAME OF MODULE TYPE CLASSICAL ELECTRODYNAMICS M M = mandatory E = elective Learning goals of the module. (List the specific learning goals that the current module should provide to the student; goals can focus on content, skills, or attitudes.) The interaction among charges is the one that determines the structure of matter from the atomic level up to the formation of macroscopic structures. Furthermore, the interaction of the electromagnetic field with matter is the basis of a great number of techniques devoted to the analysis of the structure of the materials. In many problems classical electrodynamics provides an adequate description of the interactions in nanostructures. The aim of this subject is to familiarize the student with the basic concepts of electric and magnetic fields, the response of macroscopic systems to external fields, and the relation of this response with the microscopic structure of the medium. Moreover, based on the Maxwell equations the fundamental concepts of optics will be presented, and the propagation, reflexion and refraction of electromagnetic waves will be studied Methodology: learning activities and credit value of the module (ECTS) Learning activities. (Time required to teach the module; links to other modules included in the MSc Program and suggested chronological sequence with the latter) The subject will consist in 45 hours of theoretical lectures and seminars. Since the aim of this subject is that the student adquires basic knowledges, the subject will be taught during the first quadrimester of the first year of the master. in this way the student will be able to apply in a sistematic way the adquired knowledge in the development of many subjects of the master, such as: Fundamental of solid state physics Low dimensional systems and nanostructures Fundamentals of nanoscale characterization Nanostructural properties 12
13 ECTS credit value (and time) 1 ECTS credit = 25 hours UPV/EHU TYPE OF LECTURE Theory Practice M (2) S PA PL PO TA TAI PCL PCC Periodic Evaluation Final Classroom lectures Personal work (3) TOTAL (10) M (standard lecture); S (seminar); PA (practical exercises in classroom); PL (practical exercises in laboratory); PO (practical exercises with computers); TA (non-industrial workshops); TAI (industrial workshops); PCL (clinical practice); PCC (field practice); the acronyms are taken from the Spanish wording. (11) M = maximum allowed is 60% of the full classroom lectures. (12) Personal work = time that the student would use to prepare and develop individual and group assignments Module Program. (Lectures) Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTROSTATICS. PROBLEMS OF ELECTROSTATICS WITH CONDUCTORS. Lecture 2 DIELECTRIC MEDIA. POLARIZATION. BOUNDARY CONDITIONS IN THE PRESENCE OF CONDUCTORS. ELECTROSTATIC ENERGY. Lecture 3 MAGNETOSTATICS. MAGNETIZATION. BOUNDARY PROBLEMS IN THE PRESENCE OF MAGNETIZABLE MEDIA. Lecture 4 FARADAY LAW. MAXWELL EQUATIONS. ENERGY OF THE ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD. Lecture 5 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES. PROPAGATION. REFLEXION. REFRACTION. Lecture 6 RETARDED POTENTIALS. RADIATIVE SYSTEMS. RADIATION OF AN OSCILLATING DIPOLE. POTENTIALS CREATED BY A MOVING CHARGE. 13
14 Bibliography. (Basic and specialized bibliographies, journal references, internet addresses, etc.) - CLASSICAL ELECTRODYNAMICS, J. D. JACKSON, JOHN WILEY AND SONS, CLASSICAL FIELD THEORY, F.E. LOW, JOHN WILEY AND SONS, CLASSICAL THEORY OF ELECTROMAGNETISM, B. DI BARTOLO, WORLD SCIENTIFIC, CLASSICAL ELECTRODYNAMICS, W. GRENIER, SPRINGER VERLAG, PROPAGATION, SCATTERING AND DISSIPATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES, A. S. ILYNSKI, G. YA. SLEPYAN, A. YA. SLEPYAN, PETER PETEGRINUS, , THE FEYNMAN LECTURES ON PHYSICS: VOL. 2, R. P. FEYNMAN, R. B. LEIGHTON, AND M. SANDS, ADDISON-WESLEY, Language and number of groups attending the module 1 NUMBER OF GROUPS x LANGUAGE: ENGLISH Fields of science and technology to which the module is related CODE FIELD PHYSICS OF CONDENSED MATTER APPLIED PHYSICS Department in charge of the Program CODE DEPARTMENT (1) DEPARTMENT OF MATERIALS PHYSICS Teachers in charge of the module DNI Teacher UPV/EHU Number of credits Joseba Iñaki Juaristi Oliden Alberto Rivacoba Ochoa 14
15 CÓDE NAME OF MODULE TYPE INTRODUCTION TO MATERIAL SCIENCE M M = mandatory E = elective Learning goals of the module. (List the specific learning goals that the current module should provide to the student; goals can focus on content, skills, or attitudes.) In this module we want the student to acquire a basic knowledge in materials science: a classification of materials depending on their structure and an overview and a description of thermal, mechanical optical, electric and magnetic properties of materials. The student must learn the importance of the different types of defects which change the properties of materials, like doping of semiconductors, and the structural changes appearing when submitting the materials to pressure, temperature or composition changes. Under the recent research results in materials science, a revision of the new methods for the design of new materials will be presented Methodology: learning activities and credit value of the module (ECTS) Learning activities. (Time required to teach the module; links to other modules included in the MSc Program and suggested chronological sequence with the latter) The module will take 45 hours of lectures divided into theoretical ones and others more practical or applied like seminars. As it is a module where the student must acquire basic knowledge, it will be developed in the first half of the first course of the master. By this way the student will be capable to systematicallyapply these concepts on the development other modules in the master like: Fundamentals of solid state physics Low dimensional systems, and nanostructures Fundamentals of nanoscale characterization Nanostructural properties ECTS credit value (and time) 1 ECTS credit = 25 hours UPV/EHU TYPE OF LECTURE Theory Practice M (2) S PA PL PO TA TAI PCL PCC Periodic Evaluation Final Classroom lectures Personal work (3) TOTAL 15
16 (13) M (standard lecture); S (seminar); PA (practical exercises in classroom); PL (practical exercises in laboratory); PO (practical exercises with computers); TA (non-industrial workshops); TAI (industrial workshops); PCL (clinical practice); PCC (field practice); the acronyms are taken from the Spanish wording. (14) M = maximum allowed is 60% of the full classroom lectures. (15) Personal work = time that the student would use to prepare and develop individual and group assignments Module Program. (Lectures) Lecture 1 CLASSIFICATION OF MATERIALS :STRUCTURE AND FUNDAMENTAL PROPERTIES Lecture 2 IMPERFECTIONS: DEFECTS, DISLOCATION, IMPURITIES Lecture 3 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES Lecture 4 THERMAL PROPERTIES Lecture 5 OPTICAL PROPERTIES Lectura 6 ELECTRIC PROPERTIES Lectura 7 MAGNETIC PROPERTIES Lectura 8 DIFFERENT TYPE OF MATERIALS: POLYMERS, CERAMICS, ALLOYS, NEW MATERIALS. PREPARATION TECHNIQUES Bibliography. (Basic and specialized bibliographies, journal references, internet addresses, etc.) - MATERIAL SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING: AN INTRODUCTION, WILLIAM D. CALLISTER, JR., ISBN (WILEY). - PHYSICAL FOUNDATIONS OF MATERIALS SCIENCE, G. GOTTSTEIN ISBN (SPRINGER) 16
17 Criteria and methods for evaluation and grading (Analysis of the methodology that will be used to evaluate the learning process of the student) As it is a module of fundamental and basic character for the development of the master, it will be necessary to evaluate the acquired knowledge by means of an examination which will correspond to a 50% of the final qualification. The resting 50% will be marked by the exposure of a subject related to the matter and the corresponding exposition of it Learning resources The student will have free access to the libraries of the Facultad de Química of the UPV/EHU, the Unidad de Física de Materiales (Centro Mixto CSIC-UPV/EHU) and to the existing computer resources Language and number of groups attending the module 1 NUMBER OF GROUPS x LANGUAGE: ENGLISH Fields of science and technology to which the module is related CODE FIELD PHYSICS OF CONDENSED MATTER APPLIED PHYSICS Department in charge of the Program CODE DEPARTMENT (1) DEPARTMENT OF MATERIALS PHYSICS Teachers in charge of the module DNI Teacher UPV/EHU Number of credits M Juan José del Val Altunas 2.5 Julián María González Estévez 2 17
Master s in NANOSCIENCE
 CÓDE NAME OF MODULE TYPE MODELLING AND MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS AT THE NANOSCALE M M = mandatory E = elective 3.3.1. Learning goals of the module. (List the specific learning goals that the current
CÓDE NAME OF MODULE TYPE MODELLING AND MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS AT THE NANOSCALE M M = mandatory E = elective 3.3.1. Learning goals of the module. (List the specific learning goals that the current
FISQ - Quantum Physics
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
ES - Solid State
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN PHYSICS
 MASTER OF SCIENCE IN PHYSICS The Master of Science in Physics program aims to develop competent manpower to fill the demands of industry and academe. At the end of the program, the students should have
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN PHYSICS The Master of Science in Physics program aims to develop competent manpower to fill the demands of industry and academe. At the end of the program, the students should have
Code: ECTS Credits: 6. Degree Type Year Semester
 Quantum Optics 2016/2017 Code: 100180 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500097 Physics OT 4 0 Contact Name: Verónica Ahufinger Breto Email: Veronica.Ahufinger@uab.cat Teachers Use of languages
Quantum Optics 2016/2017 Code: 100180 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500097 Physics OT 4 0 Contact Name: Verónica Ahufinger Breto Email: Veronica.Ahufinger@uab.cat Teachers Use of languages
FYSA01, Physics 1: General Physics, 30 credits Fysik 1: Allmän fysik, 30 högskolepoäng First Cycle / Grundnivå
 Faculty of Science FYSA01, Physics 1: General Physics, 30 credits Fysik 1: Allmän fysik, 30 högskolepoäng First Cycle / Grundnivå Details of approval The syllabus was approved by Study programmes board,
Faculty of Science FYSA01, Physics 1: General Physics, 30 credits Fysik 1: Allmän fysik, 30 högskolepoäng First Cycle / Grundnivå Details of approval The syllabus was approved by Study programmes board,
EMAG - Electromagnetism
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics 739 - TSC - Department of
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics 739 - TSC - Department of
Materials Chemistry
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering
Course Syllabus. offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2015/16. Introduction to Solid State Physics
 Course Syllabus offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2015/16 Part I Course Overview Course Title: Introduction to Solid State Physics Course Code: AP3272 Course
Course Syllabus offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2015/16 Part I Course Overview Course Title: Introduction to Solid State Physics Course Code: AP3272 Course
Uniqueness theorems, Separation of variables for Poisson's equation
 NPTEL Syllabus Electrodynamics - Web course COURSE OUTLINE The course is a one semester advanced course on Electrodynamics at the M.Sc. Level. It will start by revising the behaviour of electric and magnetic
NPTEL Syllabus Electrodynamics - Web course COURSE OUTLINE The course is a one semester advanced course on Electrodynamics at the M.Sc. Level. It will start by revising the behaviour of electric and magnetic
Physics (PHYS) Courses. Physics (PHYS) 1
 Physics (PHYS) 1 Physics (PHYS) Courses PHYS 5001. Introduction to Quantum Computing. 3 Credit Hours. This course will give an elementary introduction to some basics of quantum information and quantum
Physics (PHYS) 1 Physics (PHYS) Courses PHYS 5001. Introduction to Quantum Computing. 3 Credit Hours. This course will give an elementary introduction to some basics of quantum information and quantum
M.Sc. Physics
 --------------------------------------- M.Sc. Physics Curriculum & Brief Syllabi (2012) --------------------------------------- DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CALICUT CURRICULUM
--------------------------------------- M.Sc. Physics Curriculum & Brief Syllabi (2012) --------------------------------------- DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CALICUT CURRICULUM
Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II --
 Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II -- Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small Hall (new wing), tel: 1-3532 e-mail: saaubi@wm.edu web: http://www.physics.wm.edu/~saubin/index.html
Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II -- Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small Hall (new wing), tel: 1-3532 e-mail: saaubi@wm.edu web: http://www.physics.wm.edu/~saubin/index.html
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES
 PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
ENGINEERING PHYSICS II. Earth Science Engineering MSc / Geophysical Engineering specialization
 ENGINEERING PHYSICS II. Earth Science Engineering MSc / Geophysical Engineering specialization 2017/2018 2. Semester COURSE COMMUNICATION FOLDER University of Miskolc Faculty of Earth Science and Engineering
ENGINEERING PHYSICS II. Earth Science Engineering MSc / Geophysical Engineering specialization 2017/2018 2. Semester COURSE COMMUNICATION FOLDER University of Miskolc Faculty of Earth Science and Engineering
FDM - Physics of Memory Devices
 Coordinating unit: 270 - FIB - Barcelona School of Informatics Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2016 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN INFORMATICS ENGINEERING (Syllabus 2010).
Coordinating unit: 270 - FIB - Barcelona School of Informatics Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2016 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN INFORMATICS ENGINEERING (Syllabus 2010).
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
 Department of Physics 1 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Roy F. Mitte Building Room 3240 T: 512.245.2131 F: 512.245.8233 www.txstate.edu/physics/ (http://www.txstate.edu/physics) Physics, the study of matter and
Department of Physics 1 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Roy F. Mitte Building Room 3240 T: 512.245.2131 F: 512.245.8233 www.txstate.edu/physics/ (http://www.txstate.edu/physics) Physics, the study of matter and
FIS - Physics
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 200 - FME - School of Mathematics and Statistics 751 - DECA - Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 749 - MAT - Department
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 200 - FME - School of Mathematics and Statistics 751 - DECA - Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 749 - MAT - Department
Physics 4322 Spring Section Introduction to Classical Electrodynamics - Part 2
 Physics 4322 Spring 2018 - Section 13301 Introduction to Classical Electrodynamics - Part 2 Text - Introduction to Electrodynamics; - David Griffiths Publisher - Pretice-Hall Supplementary Material - Feynman
Physics 4322 Spring 2018 - Section 13301 Introduction to Classical Electrodynamics - Part 2 Text - Introduction to Electrodynamics; - David Griffiths Publisher - Pretice-Hall Supplementary Material - Feynman
City University of Hong Kong. Course Syllabus. offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2016/17
 City University of Hong Kong offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2016/17 Part I Course Overview Course Title: Electromagnetism Course Code: AP3205 Course
City University of Hong Kong offered by Department of Physics and Materials Science with effect from Semester A 2016/17 Part I Course Overview Course Title: Electromagnetism Course Code: AP3205 Course
CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY
 CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM by WOLFGANG K. H. PANOFSKY Stanford University and MELBA PHILLIPS Washington University SECOND EDITION ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo
CLASSICAL ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM by WOLFGANG K. H. PANOFSKY Stanford University and MELBA PHILLIPS Washington University SECOND EDITION ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo
FÍSICA - Physics
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 250 - ETSECCPB - Barcelona School of Civil Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 250 - ETSECCPB - Barcelona School of Civil Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN CIVIL ENGINEERING
EC 577 / MS 577: Electrical Optical and Magnetic Properties of Materials Professor Theodore. D. Moustakas Fall Semester 2012
 EC 577 / MS 577: Electrical Optical and Magnetic Properties of Materials Professor Theodore. D. Moustakas Fall Semester 2012 Office: 8 St. Mary s Street, Room no: 835 Phone: 353-5431 e-mail: tdm@bu.edu
EC 577 / MS 577: Electrical Optical and Magnetic Properties of Materials Professor Theodore. D. Moustakas Fall Semester 2012 Office: 8 St. Mary s Street, Room no: 835 Phone: 353-5431 e-mail: tdm@bu.edu
PHYSICS (PHY) Kent State University Catalog
 Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 PHYSICS (PHY) PHY 11030 SEVEN IDEAS THAT SHOOK THE UNIVERSE (KBS) 3 Credit Description of major revolutionary physical concepts and their implications for understanding
Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 PHYSICS (PHY) PHY 11030 SEVEN IDEAS THAT SHOOK THE UNIVERSE (KBS) 3 Credit Description of major revolutionary physical concepts and their implications for understanding
FISES - Statistical Physics
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
SIMCON - Computer Simulation of Condensed Matter
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 748 - FIS - Department of Physics Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
300 - EETAC - Castelldefels School of Telecommunications and Aerospace Engineering FIS - Department of Physics
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 300 - EETAC - Castelldefels School of Telecommunications and Aerospace Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 300 - EETAC - Castelldefels School of Telecommunications and Aerospace Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S
PHYSICS-PH (PH) Courses. Physics-PH (PH) 1
 Physics-PH (PH) 1 PHYSICS-PH (PH) Courses PH 110 Physics of Everyday Phenomena (GT-SC2) Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Fundamental concepts of physics and elementary quantitative reasoning applied to phenomena in
Physics-PH (PH) 1 PHYSICS-PH (PH) Courses PH 110 Physics of Everyday Phenomena (GT-SC2) Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Fundamental concepts of physics and elementary quantitative reasoning applied to phenomena in
Computational Engineering
 Coordinating unit: 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering Teaching unit: 220 - ETSEIAT - Terrassa School of Industrial and Aeronautical Engineering Academic
Coordinating unit: 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering Teaching unit: 220 - ETSEIAT - Terrassa School of Industrial and Aeronautical Engineering Academic
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
 Department of Physics 1 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Office in Engineering Building, Room 124 (970) 491-6206 physics.colostate.edu (http://www.physics.colostate.edu) Professor Jacob Roberts, Chair Undergraduate
Department of Physics 1 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Office in Engineering Building, Room 124 (970) 491-6206 physics.colostate.edu (http://www.physics.colostate.edu) Professor Jacob Roberts, Chair Undergraduate
Modified Physics Course Descriptions Old
 Modified Physics Course Descriptions Old New PHYS 122, General Physics II, 4 cr, 3 cl hrs, 2 recitation hrs Prerequisite: PHYS 121 Corequisites: MATH 132; PHYS 122L Continuation of PHYS 121 including electricity
Modified Physics Course Descriptions Old New PHYS 122, General Physics II, 4 cr, 3 cl hrs, 2 recitation hrs Prerequisite: PHYS 121 Corequisites: MATH 132; PHYS 122L Continuation of PHYS 121 including electricity
Superconductivity. Introduction. Final project. Statistical Mechanics Fall Mehr Un Nisa Shahid
 1 Final project Statistical Mechanics Fall 2010 Mehr Un Nisa Shahid 12100120 Superconductivity Introduction Superconductivity refers to the phenomenon of near-zero electric resistance exhibited by conductors
1 Final project Statistical Mechanics Fall 2010 Mehr Un Nisa Shahid 12100120 Superconductivity Introduction Superconductivity refers to the phenomenon of near-zero electric resistance exhibited by conductors
CM - Computational Mechanics
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 200 - FME - School of Mathematics and Statistics 751 - DECA - Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 749 - MAT - Department
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 200 - FME - School of Mathematics and Statistics 751 - DECA - Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 749 - MAT - Department
A. F. J. Levi 1 EE539: Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017.
 A. F. J. Levi 1 Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017. TTh 9.00 a.m. 10.50 a.m., VHE 210. Web site: http://alevi.usc.edu Web site: http://classes.usc.edu/term-20173/classes/ee EE539: Abstract and Prerequisites
A. F. J. Levi 1 Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017. TTh 9.00 a.m. 10.50 a.m., VHE 210. Web site: http://alevi.usc.edu Web site: http://classes.usc.edu/term-20173/classes/ee EE539: Abstract and Prerequisites
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF PUNE PUNE SYLLABUS for the M.Phil. (Physics ) Course
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF PUNE PUNE - 411007 SYLLABUS for the M.Phil. (Physics ) Course Each Student will be required to do 3 courses, out of which two are common courses. The third course syllabus
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNIVERSITY OF PUNE PUNE - 411007 SYLLABUS for the M.Phil. (Physics ) Course Each Student will be required to do 3 courses, out of which two are common courses. The third course syllabus
SUBJECT: ADVANCED ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 Page 1 of 8 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS * Type: DESCRIPTION Basic training, Compulsory Optional Final Project Work, External Practices Duration: Semester Semester / s: 1 Number of ECTS credits: 5 Language:
Page 1 of 8 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS * Type: DESCRIPTION Basic training, Compulsory Optional Final Project Work, External Practices Duration: Semester Semester / s: 1 Number of ECTS credits: 5 Language:
PHYS304 Quantum Physics II (2005) Unit Outline
 MACQUARIE UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Division of ICS PHYS304 Quantum Physics II (2005) Unit Outline This is a three credit point unit intended to further develop the study of quantum mechanics. The
MACQUARIE UNIVERSITY Department of Physics Division of ICS PHYS304 Quantum Physics II (2005) Unit Outline This is a three credit point unit intended to further develop the study of quantum mechanics. The
QUI - Chemistry
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 300 - EETAC - Castelldefels School of Telecommunications and Aerospace Engineering 745 - EAB - Department of Agri-Food Engineering
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 300 - EETAC - Castelldefels School of Telecommunications and Aerospace Engineering 745 - EAB - Department of Agri-Food Engineering
AP Physics C Syllabus
 Course Overview AP Physics C Syllabus AP Physics C will meet for 90 minutes on block scheduling and for 45 minutes on regular scheduling. Class activities will include lecture, demonstration, problem solving
Course Overview AP Physics C Syllabus AP Physics C will meet for 90 minutes on block scheduling and for 45 minutes on regular scheduling. Class activities will include lecture, demonstration, problem solving
TITLE OF COURSE: INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS* Type: DESCRIPTION Basic training, Compulsory elective, Optional Final degree project, Practicum Duration: Annual Semester/s: 3 rd and 4 th Number of credits ECTS: 12 Language/s:
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS* Type: DESCRIPTION Basic training, Compulsory elective, Optional Final degree project, Practicum Duration: Annual Semester/s: 3 rd and 4 th Number of credits ECTS: 12 Language/s:
Topic B. Spectral Analysis and the Classical Description of Absorption Susceptibility. Topic C. Basic Quantum Mechanical Models Spectroscopic Systems
 Chem 249: Syllabus Experimental Spectroscopy Winter Quarter 2018 Lecture: TuTh 1100a-1220p Room TBA Web Page: http://unicorn.ps.uci.edu/249/ Instructor: Prof. Robert M. Corn Overview Chemistry 249 is a
Chem 249: Syllabus Experimental Spectroscopy Winter Quarter 2018 Lecture: TuTh 1100a-1220p Room TBA Web Page: http://unicorn.ps.uci.edu/249/ Instructor: Prof. Robert M. Corn Overview Chemistry 249 is a
F1FM - Physics I: Fundamentals of Mechanics
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 295 - EEBE - Barcelona East School of Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 295 - EEBE - Barcelona East School of Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
CAL2 - Calculus 2
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 749 - MAT - Department of Mathematics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 749 - MAT - Department of Mathematics Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ENGINEERING PHYSICS
Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II --
 Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II -- Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small Hall (new wing), tel: 1-3532 e-mail: saaubi@wm.edu web: http://www.physics.wm.edu/~saubin/index.html
Physics 622: Quantum Mechanics -- Part II -- Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small Hall (new wing), tel: 1-3532 e-mail: saaubi@wm.edu web: http://www.physics.wm.edu/~saubin/index.html
ONEMAG - Electromagnetic Waves
 Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE
Coordinating unit: 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering Teaching unit: 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S DEGREE
Physics and Physical Chemistry applied to the Pharmacy
 SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2015-2016 Physics and Physical Chemistry applied to the Pharmacy MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Physics and Mathematics LECTURER(S) Physiscs and Physical Chemistry applied
SUBJECT GUIDE Academic year 2015-2016 Physics and Physical Chemistry applied to the Pharmacy MODULE CONTENT YEAR TERM CREDITS TYPE Physics and Mathematics LECTURER(S) Physiscs and Physical Chemistry applied
Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II
 Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II (i.e. time-dependent electromagnetism) [image from weapons.technology.youngester.com] Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small
Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II (i.e. time-dependent electromagnetism) [image from weapons.technology.youngester.com] Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255, Small Hall, tel: 1-3545 Lab: room 069, Small
Nonlinear Systems, Chaos and Control in Engineering
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S
Degree Type Year Semester
 Spectroscopy 2015/2016 Code: 102531 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2502444 Chemistry OB 2 2 Contact Name: Ricard Gelabert Peiri Email: Ricard.Gelabert@uab.cat Teachers Use of languages Principal
Spectroscopy 2015/2016 Code: 102531 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2502444 Chemistry OB 2 2 Contact Name: Ricard Gelabert Peiri Email: Ricard.Gelabert@uab.cat Teachers Use of languages Principal
Subject Guide. 1. Information about the subject. 2. Context. 3. Requirements. 4. Competencies and learning results
 Subject Guide 1. Information about the subject SUBJECT Experimentation in Physical Chemistry II CODE GQUIMI01-4-002 EDUCATIONAL OFFER Bachelor s Degree in Chemistry CENTER Facultad de Química TYPE Compulsory
Subject Guide 1. Information about the subject SUBJECT Experimentation in Physical Chemistry II CODE GQUIMI01-4-002 EDUCATIONAL OFFER Bachelor s Degree in Chemistry CENTER Facultad de Química TYPE Compulsory
ESSEX COUNTY COLLEGE Mathematics and Physics Division PHY 203 General Physics III Course Outline
 ESSEX COUNTY COLLEGE Mathematics and Physics Division PHY 203 General Physics III Course Outline Course Number & Name: PHY 203 General Physics III Credit Hours: 5.0 Contact Hours: 7.0 Lecture/Lab: 7.0
ESSEX COUNTY COLLEGE Mathematics and Physics Division PHY 203 General Physics III Course Outline Course Number & Name: PHY 203 General Physics III Credit Hours: 5.0 Contact Hours: 7.0 Lecture/Lab: 7.0
AQ - Chemical Analysis
 Coordinating unit: 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering Teaching unit: 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S
Coordinating unit: 205 - ESEIAAT - Terrassa School of Industrial, Aerospace and Audiovisual Engineering Teaching unit: 713 - EQ - Department of Chemical Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2018 BACHELOR'S
Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory
 Philippe A. Martin Francois Rothen Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory An Introduction Translated by Steven Goldfarb, Andrew Jordan and Samuel Leach Second Edition With 102 Figures, 7 Tables and
Philippe A. Martin Francois Rothen Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory An Introduction Translated by Steven Goldfarb, Andrew Jordan and Samuel Leach Second Edition With 102 Figures, 7 Tables and
4 credits, 3-hrs. lecture/2-hrs. lab/2-hrs. recitation Lecture:
 PHY 220 HOSTOS COMMUNITY COLLEGE GENERAL PHYSICS II 4 credits, 3-hrs. lecture/2-hrs. lab/2-hrs. recitation Lecture: Schedule Laboratory: Recitation: Instructor: E-mail: Office: Phone: Office Hours: Required
PHY 220 HOSTOS COMMUNITY COLLEGE GENERAL PHYSICS II 4 credits, 3-hrs. lecture/2-hrs. lab/2-hrs. recitation Lecture: Schedule Laboratory: Recitation: Instructor: E-mail: Office: Phone: Office Hours: Required
Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II
 Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II (i.e. time-dependent electromagnetism) [image from www.apdconsumo.pt] [image from weapons.technology.youngester.com] Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255,
Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II (i.e. time-dependent electromagnetism) [image from www.apdconsumo.pt] [image from weapons.technology.youngester.com] Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255,
PHYSICS (PHYS) Physics (PHYS) 1. PHYS 5880 Astrophysics Laboratory
 Physics (PHYS) 1 PHYSICS (PHYS) PHYS 5210 Theoretical Mechanics Kinematics and dynamics of particles and rigid bodies. Lagrangian and Hamiltonian equations of motion. PHYS 5230 Classical Electricity And
Physics (PHYS) 1 PHYSICS (PHYS) PHYS 5210 Theoretical Mechanics Kinematics and dynamics of particles and rigid bodies. Lagrangian and Hamiltonian equations of motion. PHYS 5230 Classical Electricity And
PHYSICS. For Senior Comprehensives. Requirements for a Major. Physics 1
 Physics 1 PHYSICS Physics is the study of the fundamental laws that govern our universe. Our curriculum is designed to give our students a solid foundation for understanding these laws and how they were
Physics 1 PHYSICS Physics is the study of the fundamental laws that govern our universe. Our curriculum is designed to give our students a solid foundation for understanding these laws and how they were
COURSE: ADVANCED ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS * Type: Basic training, Compulsory Optional Final Project Work, External Practices Duration: Semester Semester / s: 1 Number of ECTS credits: 5 Language: Spanish, Catalán and English
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS * Type: Basic training, Compulsory Optional Final Project Work, External Practices Duration: Semester Semester / s: 1 Number of ECTS credits: 5 Language: Spanish, Catalán and English
SYLLABUS. MSc./Solid State Physics/Biophysics and Medical Physics/Computational Physics
 SYLLABUS 1. Information regarding the programme 1.1 Higher education Babes-Bolyai University institution 1.2 Faculty Physics 1.3 Department Department of solid state physics and advanced technologies 1.4
SYLLABUS 1. Information regarding the programme 1.1 Higher education Babes-Bolyai University institution 1.2 Faculty Physics 1.3 Department Department of solid state physics and advanced technologies 1.4
MSE8210 Advanced Topics in Theoretical Surface and Interface Science
 MSE8210 Advanced Topics in Theoretical Surface and Interface Science Aloysius Soon 알로이시우스손 aloysius.soon@yonsei.ac.kr Course outline An introduction to fundamental concepts in theoretical surface science
MSE8210 Advanced Topics in Theoretical Surface and Interface Science Aloysius Soon 알로이시우스손 aloysius.soon@yonsei.ac.kr Course outline An introduction to fundamental concepts in theoretical surface science
Titulación Grado en Ingeniería de Materiales Ficha de Asignatura: Properties of Materials II
 Department (Faculty) FISICA APLICADA (ETSI de Telecomunicacion) Name of the Subject Code Magnetic and thermal properties of materials 45000121 Credits ECTS Type Year/Semester Duration Language 6 OB 3/1
Department (Faculty) FISICA APLICADA (ETSI de Telecomunicacion) Name of the Subject Code Magnetic and thermal properties of materials 45000121 Credits ECTS Type Year/Semester Duration Language 6 OB 3/1
Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II
 Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II (i.e. time-dependent electromagnetism) [image from www.apdconsumo.pt] [image from weapons.technology.youngester.com] Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255,
Physics 402: Electricity & Magnetism II (i.e. time-dependent electromagnetism) [image from www.apdconsumo.pt] [image from weapons.technology.youngester.com] Instructors Prof. Seth Aubin Office: room 255,
ELAS - Elasticity
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 295 - EEBE - Barcelona East School of Engineering 737 - RMEE - Department of Strength of Materials and Structural Engineering
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 295 - EEBE - Barcelona East School of Engineering 737 - RMEE - Department of Strength of Materials and Structural Engineering
F2FE - Physics II: Fundamentals of Electromagnetism
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 295 - EEBE - Barcelona East School of Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 295 - EEBE - Barcelona East School of Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
QOT - Quantum Optical Technologies
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 230 - ETSETB - Barcelona School of Telecommunications Engineering 739 - TSC - Department of Signal Theory and Communications
Co-requisite: University Physics Lab I (PHYS 3013) Requisite: Calculus (MATH 3051 or equivalent)
 UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO RIO PIEDRAS CAMPUS COLLEGE OF NATURAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM Title: University Physics I Code: PHYS 3011 Number of Credits: 3 Co-requisite: University
UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO RIO PIEDRAS CAMPUS COLLEGE OF NATURAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM Title: University Physics I Code: PHYS 3011 Number of Credits: 3 Co-requisite: University
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record PHYS 143
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record PHYS 143 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2011-2012 catalog PHYS 143 Electricity, Magnetism, Optics, Atomic and Nuclear Structure
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record PHYS 143 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2011-2012 catalog PHYS 143 Electricity, Magnetism, Optics, Atomic and Nuclear Structure
PHYSICS. Course Syllabus. Section 1: Mathematical Physics. Subject Code: PH. Course Structure. Electromagnetic Theory
 PHYSICS Subject Code: PH Course Structure Sections/Units Topics Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Mathematical Physics Classical Mechanics Electromagnetic
PHYSICS Subject Code: PH Course Structure Sections/Units Topics Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Section 6 Section 7 Section 8 Mathematical Physics Classical Mechanics Electromagnetic
Electromagnetism
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN MATERIALS ENGINEERING
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2017 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN MATERIALS ENGINEERING
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR ENGINEERING PHYSICS II PHS4561 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in the freshman
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR ENGINEERING PHYSICS II PHS4561 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in the freshman
Title (of the subject): QUÍMICA BIOORGÁNICA Code: Degree/Master: GRADO DE BIOQUÍMICA Name of the module to which it belongs:
 217/ Year DETAILS OF THE SUBJECT Title (of the subject): Code: 1 Degree/Master: GRADO DE BIOQUÍMICA Year: Name of the module to which it belongs: Field: Character: OPTATIVA ECTS Credits: Face-to-face classroom
217/ Year DETAILS OF THE SUBJECT Title (of the subject): Code: 1 Degree/Master: GRADO DE BIOQUÍMICA Year: Name of the module to which it belongs: Field: Character: OPTATIVA ECTS Credits: Face-to-face classroom
ANMODCONQ - Basin Analysis and Modelling
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2015 250 - ETSECCPB - Barcelona School of Civil Engineering 1004 - UB - (ENG)Universitat de Barcelona MASTER'S DEGREE IN GEOLOGICAL
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2015 250 - ETSECCPB - Barcelona School of Civil Engineering 1004 - UB - (ENG)Universitat de Barcelona MASTER'S DEGREE IN GEOLOGICAL
ENV level elective. ENV 200 Intro to Environmental Science 4 credits ENV 330 Ecosystems and Ecological Design 4 credits
 PHYSICS Andrew Dawes, Chair; James Butler, Stephen Hall The program in physics is designed to prepare students for a variety of career paths including (but not limited to) physics and engineering graduate
PHYSICS Andrew Dawes, Chair; James Butler, Stephen Hall The program in physics is designed to prepare students for a variety of career paths including (but not limited to) physics and engineering graduate
Physics 112 for class and recitation WF 10:10 a.m. - 10:40 a.m. or by appointment
 SYLLABUS (Subject to Modification) PHYS. 4310 Quantum Mechanics Dr. Sandra Quintanilla Office: Physics 309 Spring 2016 email: squintanilla@unt.edu Lecture: MWF 9:00 9:50 a.m. Phone: 565-4739 Recitation:
SYLLABUS (Subject to Modification) PHYS. 4310 Quantum Mechanics Dr. Sandra Quintanilla Office: Physics 309 Spring 2016 email: squintanilla@unt.edu Lecture: MWF 9:00 9:50 a.m. Phone: 565-4739 Recitation:
SYLLABUS ELEC 261: ELECTRONIC MATERIALS AND QUANTUM DEVICES SUMMER 2018
 SYLLABUS ELEC 261: ELECTRONIC MATERIALS AND QUANTUM DEVICES SUMMER 2018 Credit Hours: 3 Time and Place: Online Course Summer Session II: May 29 June 29, 2018 Instructors: Junichiro Kono, Professor of Electrical
SYLLABUS ELEC 261: ELECTRONIC MATERIALS AND QUANTUM DEVICES SUMMER 2018 Credit Hours: 3 Time and Place: Online Course Summer Session II: May 29 June 29, 2018 Instructors: Junichiro Kono, Professor of Electrical
Anexa nr. 2. Subject Content
 Anexa nr. 2 Subject Content 1. Program information 1.1 University West University of Timișoara 1.2 Faculty Physics 1.3 Department Physics 1.4 Field of study Physics 1.5 Study cycle Master 1.6 Study programme
Anexa nr. 2 Subject Content 1. Program information 1.1 University West University of Timișoara 1.2 Faculty Physics 1.3 Department Physics 1.4 Field of study Physics 1.5 Study cycle Master 1.6 Study programme
Study Plan for Ph.D in Physics (2011/2012)
 Plan Study Plan for Ph.D in Physics (2011/2012) Offered Degree: Ph.D in Physics 1. General Rules and Conditions:- This plan conforms to the regulations of the general frame of the higher graduate studies
Plan Study Plan for Ph.D in Physics (2011/2012) Offered Degree: Ph.D in Physics 1. General Rules and Conditions:- This plan conforms to the regulations of the general frame of the higher graduate studies
Physics 610: Electricity & Magnetism I
 Physics 610: Electricity & Magnetism I [i.e. relativistic EM, electro/magneto-(quasi)statics] [lin12.triumph.ca] [J-lab accelerator] [ixnovi.people.wm.edu] [Thywissen group, U. of Toronto] [nanotechetc.com]
Physics 610: Electricity & Magnetism I [i.e. relativistic EM, electro/magneto-(quasi)statics] [lin12.triumph.ca] [J-lab accelerator] [ixnovi.people.wm.edu] [Thywissen group, U. of Toronto] [nanotechetc.com]
Curriculum for the Bachelor s Programme in Physics at the Faculty of Mathematics, Computer Science and Physics of the University of Innsbruck
 Note: The following curriculum is a consolidated version. It is legally non-binding and for informational purposes only. The legally binding versions are found in the University of Innsbruck Bulletins
Note: The following curriculum is a consolidated version. It is legally non-binding and for informational purposes only. The legally binding versions are found in the University of Innsbruck Bulletins
Syllabus for MATHEMATICS FOR INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
 Syllabus for MATHEMATICS FOR INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS Lecturers: Kirill Bukin, Nadezhda Shilova Class teachers: Pavel Zhukov, Nadezhda Shilova Course description Mathematics for international relations
Syllabus for MATHEMATICS FOR INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS Lecturers: Kirill Bukin, Nadezhda Shilova Class teachers: Pavel Zhukov, Nadezhda Shilova Course description Mathematics for international relations
Subject Guide. Facultad de Química
 Bachelor s Degree in Chemistry Subject Guide 1. Information about the subject SUBJECT Chemical Engineering CODE GQUIMI01-2-008 EDUCATIONAL OFFER Bachelor s Degree in Chemistry CENTER Facultad de Química
Bachelor s Degree in Chemistry Subject Guide 1. Information about the subject SUBJECT Chemical Engineering CODE GQUIMI01-2-008 EDUCATIONAL OFFER Bachelor s Degree in Chemistry CENTER Facultad de Química
MODERN PHYSICS Frank J. Blatt Professor of Physics, University of Vermont
 MODERN PHYSICS Frank J. Blatt Professor of Physics, University of Vermont McGRAW-HILL, INC. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal New Delhi
MODERN PHYSICS Frank J. Blatt Professor of Physics, University of Vermont McGRAW-HILL, INC. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal New Delhi
Course level: First-cycle studies Number of hours per week: 2L E, 2C, 1Lab, 0, 0 GUIDE TO SUBJECT
 Subject (course) name: Physics Programme: Electrical Engineering Specialty: Subject code: W Title graduate: Engineer Type of course: obligatory Form of classes: Lectures, Classes, Labs, Seminar, Project
Subject (course) name: Physics Programme: Electrical Engineering Specialty: Subject code: W Title graduate: Engineer Type of course: obligatory Form of classes: Lectures, Classes, Labs, Seminar, Project
B.S. PHYSICS DEGREE PROGRAM
 B.S. PHYSICS DEGREE PROGRAM Students can obtain a Bachelor of Science degree in Physics by completing 74 credit hours in Physics, Math, Computer Science and Chemistry as indicate below. Additionally, 52
B.S. PHYSICS DEGREE PROGRAM Students can obtain a Bachelor of Science degree in Physics by completing 74 credit hours in Physics, Math, Computer Science and Chemistry as indicate below. Additionally, 52
Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics
 Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics 1 Introduction Syllabus for Fall 2009 This is essentially a standard first-year course in quantum mechanics, the basic language for describing physics at the atomic and subatomic
Physics 162a Quantum Mechanics 1 Introduction Syllabus for Fall 2009 This is essentially a standard first-year course in quantum mechanics, the basic language for describing physics at the atomic and subatomic
Classical Electrodynamics
 Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics
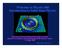 Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscope image of atoms placed on a surface, and confined quantum electron waves D. Eigler IBM Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 1
Welcome to Physics 460 Introduction to Solid State Physics Scanning Tunneling Microscope image of atoms placed on a surface, and confined quantum electron waves D. Eigler IBM Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 1
QAU - Car's Chemistry
 Coordinating unit: 330 - EPSEM - Manresa School of Engineering Teaching unit: 750 - EMIT - Department of Mining, Industrial and ICT Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN AUTOMOTIVE
Coordinating unit: 330 - EPSEM - Manresa School of Engineering Teaching unit: 750 - EMIT - Department of Mining, Industrial and ICT Engineering Academic year: Degree: 2017 BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN AUTOMOTIVE
College of Arts and Sciences
 Note: It is assumed that all prerequisites include, in addition to any specific course listed, the phrase or equivalent, or consent of instructor. 105 SICS AND ASTRONOMY TODAY. (1) This course is intended
Note: It is assumed that all prerequisites include, in addition to any specific course listed, the phrase or equivalent, or consent of instructor. 105 SICS AND ASTRONOMY TODAY. (1) This course is intended
Syllabus and Topics Statistical Mechanics Thermal Physics II Spring 2009
 Syllabus and Topics 33-765 Statistical Mechanics 33-342 Thermal Physics II Spring 2009 Robert F. Sekerka 6416 Wean Hall, Phone 412-268-2362 rs07@andrew.cmu.edu http://sekerkaweb.phys.cmu.edu January 12,
Syllabus and Topics 33-765 Statistical Mechanics 33-342 Thermal Physics II Spring 2009 Robert F. Sekerka 6416 Wean Hall, Phone 412-268-2362 rs07@andrew.cmu.edu http://sekerkaweb.phys.cmu.edu January 12,
TEACHERS OF SCIENCE: Physics 9-12 FORM I-D GRID
 8710.4750 TEACHERS OF SCIENCE: sics 9-12 FORM I-D GRID Professional Education Program Evaluation Report (PEPER II) 8710.4750 Teachers of Science: sics 9-12 Subp. 7. Subject matter standards for teachers
8710.4750 TEACHERS OF SCIENCE: sics 9-12 FORM I-D GRID Professional Education Program Evaluation Report (PEPER II) 8710.4750 Teachers of Science: sics 9-12 Subp. 7. Subject matter standards for teachers
AP PHYSICS (B) SYLLABUS. Text: Physics, Sixth Edition by Cutnell and Johnson ISBN , Wiley and Sons, 2004 COURSE OVERVIEW
 AP PHYSICS (B) SYLLABUS Text: Physics, Sixth Edition by Cutnell and Johnson ISBN 0471-15183-1, Wiley and Sons, 2004 COURSE OVERVIEW Advanced Placement Physics is an intensive and rigorous college level
AP PHYSICS (B) SYLLABUS Text: Physics, Sixth Edition by Cutnell and Johnson ISBN 0471-15183-1, Wiley and Sons, 2004 COURSE OVERVIEW Advanced Placement Physics is an intensive and rigorous college level
The Oxford Solid State Basics
 The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
Physics & Astronomy & 2000 Level /9 - August Physics (PH) modules PH1011 Physics 1A
 Physics (PH) modules PH1011 Physics 1A SCOTCAT Credits: 20 SCQF Level 7 Semester 1 Planned timetable: 12.00 noon lectures, one afternoon from five each week, 2.00 pm - 3.00 pm tutorial and 3.00 pm -5.30
Physics (PH) modules PH1011 Physics 1A SCOTCAT Credits: 20 SCQF Level 7 Semester 1 Planned timetable: 12.00 noon lectures, one afternoon from five each week, 2.00 pm - 3.00 pm tutorial and 3.00 pm -5.30
Physics & Engineering
 Faculty Steve Waters, chair; Vola Andrianarijaona, Raulton Haye, James Robertson Departmental Office: 238 Chan Shun Hall; (707) 965-7269 Degrees and Programs Physics, B.S....163 Biophysics, B.S....164
Faculty Steve Waters, chair; Vola Andrianarijaona, Raulton Haye, James Robertson Departmental Office: 238 Chan Shun Hall; (707) 965-7269 Degrees and Programs Physics, B.S....163 Biophysics, B.S....164
Chemistry with Spanish for Science
 Programme Specification (Undergraduate) Chemistry with Spanish for Science This document provides a definitive record of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student
Programme Specification (Undergraduate) Chemistry with Spanish for Science This document provides a definitive record of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student
Algebra and Geometry (250101)
 Algebra and Geometry (250101) General information School: ETSECCPB Departments: 751 - Departament d'enginyeria Civil i Ambiental Credits: 6.0 ECTS Programs: 1305 - GRAU EN ENGINYERIA CIVIL (2017), 790
Algebra and Geometry (250101) General information School: ETSECCPB Departments: 751 - Departament d'enginyeria Civil i Ambiental Credits: 6.0 ECTS Programs: 1305 - GRAU EN ENGINYERIA CIVIL (2017), 790
QUANTUM WELLS, WIRES AND DOTS
 QUANTUM WELLS, WIRES AND DOTS Theoretical and Computational Physics of Semiconductor Nanostructures Second Edition Paul Harrison The University of Leeds, UK /Cf}\WILEY~ ^INTERSCIENCE JOHN WILEY & SONS,
QUANTUM WELLS, WIRES AND DOTS Theoretical and Computational Physics of Semiconductor Nanostructures Second Edition Paul Harrison The University of Leeds, UK /Cf}\WILEY~ ^INTERSCIENCE JOHN WILEY & SONS,
MSE640: Advances in Investigation of Intermolecular & Surface Forces
 MSE640: Advances in Investigation of Forces Course Title Advances in investigation of Intermolecular & surface forces Course Code MSE640 Credit Hours 3 Pre-requisites (if any) MSE507, MSE508 or equivalent
MSE640: Advances in Investigation of Forces Course Title Advances in investigation of Intermolecular & surface forces Course Code MSE640 Credit Hours 3 Pre-requisites (if any) MSE507, MSE508 or equivalent
Basic Thermodynamics
 Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN MATERIALS ENGINEERING
Coordinating unit: Teaching unit: Academic year: Degree: ECTS credits: 2018 240 - ETSEIB - Barcelona School of Industrial Engineering 748 - FIS - Department of Physics BACHELOR'S DEGREE IN MATERIALS ENGINEERING
