MST Topics in History of Mathematics
|
|
|
- Antony Page
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MST Topics in History of Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 017 8: rchimedes Measurement of a Circle
2 The works of rchimedes Recipient Propositions n the Sphere and Cylinder, ook I Dosithesus 44 n the Sphere and Cylinder, ook II Dosithesus 9 Measurement of a Circle 3 n Conoids and Spheroids Dosithesus 3 n Spirals Dosithesus 8 n the Equilibrium of Planes, ook I 15 n the Equilibrium of Planes, ook II 10 The Sand-Reckoner King Gelon Quadrature of the Parabola Dosithesus 4 n Floating odies, ook I 9 n Floating odies, ook II 10 ook of Lemmas 15 The Cattle Problem The Method Eratosthenes 15 1
3 rchimedes: Measurement of a Circle Proposition 1. The area of any circle is equal to a right-angled triangle in which one of the sides about the right angle is equal to the radius, and the other to the circumference, of the circle. rea of circle= 1 radius circumference = π(radius). Proposition. The area of a circle is to the square on its diameter as 11 to 14. rea of circle= (diameter) = 7 (radius). Proposition 3. The circumference of any circle is less than3 1 7 but greater than of its diameter < π < 7.
4 rchimedes calculation ofπ: upper bound Consider a circle of unit diameter. Let Z n be the length of a side of a regular n gon circumscribing the circle. C If is a tangent to the circle, and if = 1 Z n, andc bisects, then C = 1 Z n. rchimedes showed that Z n = Z n Zn 3
5 rchimedes calculation ofπ: upper bound Consider a circle of unit diameter. Let Z n be the length of a side of a regular n gon circumscribing the circle. C If is a tangent to the circle, and if = 1 Z n, andc bisects, then C = 1 Z n. rchimedes showed that Z n = Z n Zn Since C bisects angle, C : C = : ; C : = : +; Z n : Z n = 1 : 1 + (1 ) + ( Zn ) = 1 : 1+ 1+Z n. 4
6 Upper bound ofπ (continued) eginning with the simple fact Z 6 = 3 1 3, and the inequality , rchimedes used the relation Z 6 Z n = Z n 1+ 1+Z n 30 4 times and obtained Thus, 1 Z 96 > circumference < 96Z 96 < = < =
7 rchimedes calculation ofπ: lower bound Consider again a circle of unit diameter. Let be a side of a regularn gon C inscribed in a circle, with lengthz n. IfK is a diameter andkc bisects K, then C is a side of a regularn gon inscribed in the circle. Suppose C has lengthz n respectively. K rchimedes showed that 1 = 1 (1+ 1 z z n z n), z 6 = 1 n. 6
8 rchimedes calculation ofπ: lower bound Let andkc intersect at H. Since KH bisects anglek, KC = HC, and the triangleskc, HC are similar. C H KC : C = C : CH = K : H = K : H = K+K : H +H = K+K :. K 7
9 rchimedes calculation ofπ: lower bound Let andkc intersect at H. Since KH bisects anglek, KC = HC, and the triangleskc, HC are similar. KC : C =... = K+K :. Therefore, KC : C = (K+K) : C H K d z n : z n = (d+ d z n) : z n d : z n = z n +(d+ d z n) : z n. From this, d zn +(d+ d zn) d(d+ d zn) = = z n z n z n With d = 1, this explains rchimedes 1 = 1 (1+ 1 z z n z n). n 8
10 Lower bound of π (continued) eginning with z 6 = 1, and an inequality , rchimedes iterated this relation four times, and obtained Consequently, 1 z 96 < D E F circumference > 96z 96 > C > K 9
11 ncient records ofπ (1) In his commentary of the Nine Chapters of Mathematical rt, LIU Hui (3rd century D) gave the approximation π by approximating a circle by circumscribed and inscribed regular polygons of96 sides. () ZU Chongzhi (49-500) gave the estimates forπ: He also gave the crude approximation 7 and the fine approximation forπ < π <
12 Reformulation of rchimedes method Leta n andb n respectively denote the perimeters of a circumscribing regular6 n gon and an inscribed regular6 n gon of a circle of diameter 1. Then a 0 = 3,b 0 = 3, and a n+1 = a nb n a n +b n, b n+1 = a n+1 b n. This was the basis of practically all calculations of π before the 16th century. Correct to the first 34 decimal places, π =
History of Mathematics
 History of Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Spring 2014 4: rchimedes Quadrature of the Parabola onsider the parabola y = x 2. Let 1, 1 be two points on the x axis,
History of Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Spring 2014 4: rchimedes Quadrature of the Parabola onsider the parabola y = x 2. Let 1, 1 be two points on the x axis,
I.31 Now given a circular field, the circumference is 30 bu and the diameter 10 bu. Question: What is the area? Answer:
 Chapter 9 Areas of circular regions 9.1 Problems I31 38 1 I.31 Now given a circular field, the circumference is 30 bu and the diameter 10 bu. I.3 Given another circular field, the circumference is 181
Chapter 9 Areas of circular regions 9.1 Problems I31 38 1 I.31 Now given a circular field, the circumference is 30 bu and the diameter 10 bu. I.3 Given another circular field, the circumference is 181
A Presentation By: Charlotte Lenz
 A Presentation By: Charlotte Lenz http://www.math.nyu.edu/~crorres/archimedes/pictures/ ArchimedesPictures.html Born: 287 BC to an Astronomer named Phidias Grew up in Syracuse, Sicily Only left Sicily
A Presentation By: Charlotte Lenz http://www.math.nyu.edu/~crorres/archimedes/pictures/ ArchimedesPictures.html Born: 287 BC to an Astronomer named Phidias Grew up in Syracuse, Sicily Only left Sicily
History of Mathematics
 istory of Mathematics Paul Yiu epartment of Mathematics lorida tlantic University Spring 2014 4: Volumes and surface areas uclid XII.2: Ratio of circle area to square on diameter ircles are to one another
istory of Mathematics Paul Yiu epartment of Mathematics lorida tlantic University Spring 2014 4: Volumes and surface areas uclid XII.2: Ratio of circle area to square on diameter ircles are to one another
Example 1: Finding angle measures: I ll do one: We ll do one together: You try one: ML and MN are tangent to circle O. Find the value of x
 Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
Exhaustion: From Eudoxus to Archimedes
 Exhaustion: From Eudoxus to Archimedes Franz Lemmermeyer April 22, 2005 Abstract Disclaimer: Eventually, I plan to polish this and use my own diagrams; so far, most of it is lifted from the web. Exhaustion
Exhaustion: From Eudoxus to Archimedes Franz Lemmermeyer April 22, 2005 Abstract Disclaimer: Eventually, I plan to polish this and use my own diagrams; so far, most of it is lifted from the web. Exhaustion
Circles. II. Radius - a segment with one endpoint the center of a circle and the other endpoint on the circle.
 Circles Circles and Basic Terminology I. Circle - the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point (called the center) in the plane. Circles are named by their center. II.
Circles Circles and Basic Terminology I. Circle - the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point (called the center) in the plane. Circles are named by their center. II.
Archimedes Quadrature of the Parabola
 Archimedes and the Quadrature of the Parabola MATH 110 Topics in Mathematics Mathematics Through Time November 1, 2013 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction 2 3 Who was Archimedes? Lived ca. 287-212 BCE,
Archimedes and the Quadrature of the Parabola MATH 110 Topics in Mathematics Mathematics Through Time November 1, 2013 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction 2 3 Who was Archimedes? Lived ca. 287-212 BCE,
Chapter-wise questions
 hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
Page 1
 Pacing Chart Unit Week Day CCSS Standards Objective I Can Statements 121 CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.1 Prove that all circles are similar. Prove that all circles are similar. I can prove that all circles
Pacing Chart Unit Week Day CCSS Standards Objective I Can Statements 121 CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.HSG.C.A.1 Prove that all circles are similar. Prove that all circles are similar. I can prove that all circles
Credited with formulating the method of exhaustion for approximating a circle by polygons
 MATH 300 History of Mathematics Figures in Greek Mathematics Sixth Century BCE Thales of Miletus May have formulated earliest theorems in geometry (e.g., ASA) Predicted an eclipse in 585 BCE Pythagoras
MATH 300 History of Mathematics Figures in Greek Mathematics Sixth Century BCE Thales of Miletus May have formulated earliest theorems in geometry (e.g., ASA) Predicted an eclipse in 585 BCE Pythagoras
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles
 Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
Mu Alpha Theta State 2007 Euclidean Circles 1. Joe had a bet with Mr. Federer saying that if Federer can solve the following problem in one minute, Joe would be his slave for a whole month. The problem
Geometry Teachers Weekly Assessment Package Unit 8. Created by: Jeanette Stein
 Geometry Teachers Weekly Assessment Package Unit 8 reated by: Jeanette Stein 2018HighSchoolMathTeachers 1 Semester 2 Skills Geometry Weekly Assessments 2018HighSchoolMathTeachers SEMESTER 2 SKILLS 3 UNIT
Geometry Teachers Weekly Assessment Package Unit 8 reated by: Jeanette Stein 2018HighSchoolMathTeachers 1 Semester 2 Skills Geometry Weekly Assessments 2018HighSchoolMathTeachers SEMESTER 2 SKILLS 3 UNIT
Geometry. Class Examples (July 3) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 3) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 Example 11(a): Fermat point. Given triangle, construct externally similar isosceles triangles
Geometry lass Examples (July 3) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 Example 11(a): Fermat point. Given triangle, construct externally similar isosceles triangles
Unit 10 Geometry Circles. NAME Period
 Unit 10 Geometry Circles NAME Period 1 Geometry Chapter 10 Circles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (10-1) Circles and Circumference
Unit 10 Geometry Circles NAME Period 1 Geometry Chapter 10 Circles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (10-1) Circles and Circumference
Geometry Honors Homework
 Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
Geometry Honors Homework pg. 1 12-1 Practice Form G Tangent Lines Algebra Assume that lines that appear to be tangent are tangent. O is the center of each circle. What is the value of x? 1. 2. 3. The circle
C=2πr C=πd. Chapter 10 Circles Circles and Circumference. Circumference: the distance around the circle
 10.1 Circles and Circumference Chapter 10 Circles Circle the locus or set of all points in a plane that are A equidistant from a given point, called the center When naming a circle you always name it by
10.1 Circles and Circumference Chapter 10 Circles Circle the locus or set of all points in a plane that are A equidistant from a given point, called the center When naming a circle you always name it by
Integrated Math II. IM2.1.2 Interpret given situations as functions in graphs, formulas, and words.
 Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Geometry Final Exam Review
 Name: Date: Period: Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Fill in the flow chart below with the properties that belong to each polygon. 2. Find the measure of each numbered angle: 3. Find the value of x 4. Calculate
Name: Date: Period: Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Fill in the flow chart below with the properties that belong to each polygon. 2. Find the measure of each numbered angle: 3. Find the value of x 4. Calculate
GALOIS THEORY : LECTURE 11
 GLOIS THORY : LTUR 11 LO GOLMKHR 1. LGRI IL XTNSIONS Given α L/K, the degree of α over K is defined to be deg m α, where m α is the minimal polynomial of α over K; recall that this, in turn, is equal to
GLOIS THORY : LTUR 11 LO GOLMKHR 1. LGRI IL XTNSIONS Given α L/K, the degree of α over K is defined to be deg m α, where m α is the minimal polynomial of α over K; recall that this, in turn, is equal to
GEOMETRICAL DEFINITION OF π AND ITS APPROXIMATIONS BY NESTED RADICALS. Milan Janjić. 1. Introduction
 THE TECHING OF THETICS 008, Vol. XI,, pp. 5 34 GEOETRICL DEFINITION OF π ND ITS PPROXITIONS Y NESTED RDICLS ilan Janjić bstract. In this paper the length of the arc of a circle and the area of a circular
THE TECHING OF THETICS 008, Vol. XI,, pp. 5 34 GEOETRICL DEFINITION OF π ND ITS PPROXITIONS Y NESTED RDICLS ilan Janjić bstract. In this paper the length of the arc of a circle and the area of a circular
NOTE. The Surface Area of the Bicylinder and Archimedes Method
 Historia Mathematica 29 (2002), 199 203 doi:10.1006/hmat.2002.2349, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on NOTE The Surface Area of the Bicylinder and Archimedes Method Jan P. Hogendijk Department
Historia Mathematica 29 (2002), 199 203 doi:10.1006/hmat.2002.2349, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on NOTE The Surface Area of the Bicylinder and Archimedes Method Jan P. Hogendijk Department
History of Mathematics Workbook
 History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
Geometry A is a prerequisite for Geometry B. Before beginning this course, you should be able to do the following:
 Syllabus Geometry B Overview Geometry is a branch of mathematics that uses logic and formal thinking to establish mathematical relationships between points, lines, surfaces, and solids. In Geometry B,
Syllabus Geometry B Overview Geometry is a branch of mathematics that uses logic and formal thinking to establish mathematical relationships between points, lines, surfaces, and solids. In Geometry B,
Geometry. A. Right Triangle. Legs of a right triangle : a, b. Hypotenuse : c. Altitude : h. Medians : m a, m b, m c. Angles :,
 Geometry A. Right Triangle Legs of a right triangle : a, b Hypotenuse : c Altitude : h Medians : m a, m b, m c Angles :, Radius of circumscribed circle : R Radius of inscribed circle : r Area : S 1. +
Geometry A. Right Triangle Legs of a right triangle : a, b Hypotenuse : c Altitude : h Medians : m a, m b, m c Angles :, Radius of circumscribed circle : R Radius of inscribed circle : r Area : S 1. +
Syllabus for Grade 7. More details on each of the topics is covered in the following pages.
 Syllabus for Grade 7 Chapter 1 Algebraic Reasoning Chapter 2 Integers and rational numbers Chapter 3 Number Theory Chapter 4 Rational number Chapter 5 Patterns and functions Chapter 6 Proportional Relationships
Syllabus for Grade 7 Chapter 1 Algebraic Reasoning Chapter 2 Integers and rational numbers Chapter 3 Number Theory Chapter 4 Rational number Chapter 5 Patterns and functions Chapter 6 Proportional Relationships
MATH Spring 2010 Topics per Section
 MATH 101 - Spring 2010 Topics per Section Chapter 1 : These are the topics in ALEKS covered by each Section of the book. Section 1.1 : Section 1.2 : Ordering integers Plotting integers on a number line
MATH 101 - Spring 2010 Topics per Section Chapter 1 : These are the topics in ALEKS covered by each Section of the book. Section 1.1 : Section 1.2 : Ordering integers Plotting integers on a number line
Secondary 1 - Secondary 3 CCSS Vocabulary Word List Revised Vocabulary Word Sec 1 Sec 2 Sec 3 absolute value equation
 Vocabulary Word Sec 1 Sec 2 Sec 3 absolute value equation (optional) absolute value function absolute value inequality (optional) acute angle addition rule algebraic representation alternate exterior angles
Vocabulary Word Sec 1 Sec 2 Sec 3 absolute value equation (optional) absolute value function absolute value inequality (optional) acute angle addition rule algebraic representation alternate exterior angles
Arkansas Council of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State Competition Geometry Exam. B. 28 (5x-41) 3 m (2x+25)
 rkansas ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State ompetition Geometry Exam For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. (Figures may not be drawn to scale.) fter
rkansas ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State ompetition Geometry Exam For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. (Figures may not be drawn to scale.) fter
1. For any integer a, a 0, 1 a and a a. 4. If a b and b c then a c. 5. If a b and b a then a = ±b.
 4. Euclidean Number Theory Books VII, VIII and IX of the Elements were on Number Theory. Two major results are: Proposition 14 which says that every integer greater or equal 2 can be factored as a product
4. Euclidean Number Theory Books VII, VIII and IX of the Elements were on Number Theory. Two major results are: Proposition 14 which says that every integer greater or equal 2 can be factored as a product
Archimedes of Syracuse
 Table of contents 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 The Punic Wars The Punic Wars The Punic 1 Wars were a series of wars between Carthage and Rome, occurring between 264 BCE and 146 BCE The First Punic War: 264 BCE
Table of contents 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 The Punic Wars The Punic Wars The Punic 1 Wars were a series of wars between Carthage and Rome, occurring between 264 BCE and 146 BCE The First Punic War: 264 BCE
Circles in Neutral Geometry
 Everything we do in this set of notes is Neutral. Definitions: 10.1 - Circles in Neutral Geometry circle is the set of points in a plane which lie at a positive, fixed distance r from some fixed point.
Everything we do in this set of notes is Neutral. Definitions: 10.1 - Circles in Neutral Geometry circle is the set of points in a plane which lie at a positive, fixed distance r from some fixed point.
Integrated Mathematics I, II, III 2016 Scope and Sequence
 Mathematics I, II, III 2016 Scope and Sequence I Big Ideas Math 2016 Mathematics I, II, and III Scope and Sequence Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Properties of exponents to rational
Mathematics I, II, III 2016 Scope and Sequence I Big Ideas Math 2016 Mathematics I, II, and III Scope and Sequence Number and Quantity The Real Number System (N-RN) Properties of exponents to rational
Definitions. (V.1). A magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures
 hapter 8 Euclid s Elements ooks V 8.1 V.1-3 efinitions. (V.1). magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures the greater. (V.2). The greater is a multiple of the less when
hapter 8 Euclid s Elements ooks V 8.1 V.1-3 efinitions. (V.1). magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures the greater. (V.2). The greater is a multiple of the less when
a) 3 cm b) 3 cm c) cm d) cm
 (1) Choose the correct answer: 1) =. a) b) ] - [ c) ] - ] d) ] [ 2) The opposite figure represents the interval. a) [-3, 5 ] b) ] -3, 5 [ c) [ -3, 5 [ d) ] -3, 5 ] -3 5 3) If the volume of the sphere is
(1) Choose the correct answer: 1) =. a) b) ] - [ c) ] - ] d) ] [ 2) The opposite figure represents the interval. a) [-3, 5 ] b) ] -3, 5 [ c) [ -3, 5 [ d) ] -3, 5 ] -3 5 3) If the volume of the sphere is
Prep for College Algebra
 Prep for College Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (219 topics + 85 additional topics)
Prep for College Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (219 topics + 85 additional topics)
Limits and the derivative function. Limits and the derivative function
 The Velocity Problem A particle is moving in a straight line. t is the time that has passed from the start of motion (which corresponds to t = 0) s(t) is the distance from the particle to the initial position
The Velocity Problem A particle is moving in a straight line. t is the time that has passed from the start of motion (which corresponds to t = 0) s(t) is the distance from the particle to the initial position
For math conventions used on the GRE, refer to this link:
 GRE Review ISU Student Success Center Quantitative Workshop One Quantitative Section: Overview Your test will include either two or three 35-minute quantitative sections. There will be 20 questions in
GRE Review ISU Student Success Center Quantitative Workshop One Quantitative Section: Overview Your test will include either two or three 35-minute quantitative sections. There will be 20 questions in
Prep for College Algebra with Trigonometry
 Prep for College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (246 topics +
Prep for College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (246 topics +
Copyright 2018 UC Regents and ALEKS Corporation. ALEKS is a registered trademark of ALEKS Corporation. 2/10
 Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
NEW YORK ALGEBRA TABLE OF CONTENTS
 NEW YORK ALGEBRA TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS TOPIC A: Number Theory: Properties of Real Numbers {A.N.1} PART 1: Closure...1 PART 2: Commutative Property...2 PART 3: Associative
NEW YORK ALGEBRA TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 NUMBER SENSE & OPERATIONS TOPIC A: Number Theory: Properties of Real Numbers {A.N.1} PART 1: Closure...1 PART 2: Commutative Property...2 PART 3: Associative
MAP 2302 MAP 4103 MAE 3920 MAE 4360 MAS 4301 MAS Introduction to Abstract Algebra I. Introduction to Abstract Algebra
 B.S. In Mathematics Florida A&M University MAC 2311 MAD 2120 MAC 2312 MAE 1920 MAC 2313 STA 2023 MHF 4202 MAE 2920 MAS 3105 MAP 2302 MAP 4103 MAS 4301 MAE 3920 MAE 4360 MTG 4212 MAS 4203 FTCE Skills &
B.S. In Mathematics Florida A&M University MAC 2311 MAD 2120 MAC 2312 MAE 1920 MAC 2313 STA 2023 MHF 4202 MAE 2920 MAS 3105 MAP 2302 MAP 4103 MAS 4301 MAE 3920 MAE 4360 MTG 4212 MAS 4203 FTCE Skills &
Anticipations of Calculus - Archimedes
 Anticipations of Calculus - Archimedes Let ABC be a segment of a parabola bounded by the straight line AC and the parabola ABC, and let D be the middle point of AC. Draw the straight line DBE parallel
Anticipations of Calculus - Archimedes Let ABC be a segment of a parabola bounded by the straight line AC and the parabola ABC, and let D be the middle point of AC. Draw the straight line DBE parallel
The Edge-Tangent Sphere of a Circumscriptible Tetrahedron
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 19 24 FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 The Edge-Tangent Sphere of a Circumscriptible Tetrahedron Yu-Dong Wu and Zhi-Hua Zhang Abstract A tetrahedron is circumscriptible if
Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 19 24 FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 The Edge-Tangent Sphere of a Circumscriptible Tetrahedron Yu-Dong Wu and Zhi-Hua Zhang Abstract A tetrahedron is circumscriptible if
Archimedes and Pi. Burton Rosenberg. September 7, 2003
 Archimedes and Pi Burton Rosenberg September 7, 2003 Introduction Proposition 3 of Archimedes Measurement of a Circle states that π is less than 22/7 and greater than 223/71. The approximation π a 22/7
Archimedes and Pi Burton Rosenberg September 7, 2003 Introduction Proposition 3 of Archimedes Measurement of a Circle states that π is less than 22/7 and greater than 223/71. The approximation π a 22/7
Chapter 0. Introduction. An Overview of the Course
 Chapter 0 Introduction An Overview of the Course In the first part of these notes we consider the problem of calculating the areas of various plane figures. The technique we use for finding the area of
Chapter 0 Introduction An Overview of the Course In the first part of these notes we consider the problem of calculating the areas of various plane figures. The technique we use for finding the area of
The radius of a circle is increasing at a constant rate of the rate of increase in the area of the circle at the instant when the circumference is?
 Unit #11: Related Rates Topic: More Related Rates Problems Objective: SWBAT apply derivatives to real life applications. Warm Up #5: The radius of a circle is increasing at a constant rate of. What is
Unit #11: Related Rates Topic: More Related Rates Problems Objective: SWBAT apply derivatives to real life applications. Warm Up #5: The radius of a circle is increasing at a constant rate of. What is
M1 for a complete method with relative place value correct. Condone 1 multiplication error, addition not necessary.
 . 54 4 6 080 96 5 4 0 8 0 6 9 6 50 4 0 000 80 4 00 6 000 + 00 + 80 + 6 = 96 4.96 M for a complete method with relative place value correct. Condone multiplication error, addition not necessary. M for a
. 54 4 6 080 96 5 4 0 8 0 6 9 6 50 4 0 000 80 4 00 6 000 + 00 + 80 + 6 = 96 4.96 M for a complete method with relative place value correct. Condone multiplication error, addition not necessary. M for a
T a b l e o f C o n t e n t s
 T a b l e o f C o n t e n t s C O M P E T E N C Y 1 KNOWLEDGE OF ALGEBRA... 1 SKILL 1.1: Apply the properties of real numbers: closure, commutative, associative, distributive, transitive, identities, and
T a b l e o f C o n t e n t s C O M P E T E N C Y 1 KNOWLEDGE OF ALGEBRA... 1 SKILL 1.1: Apply the properties of real numbers: closure, commutative, associative, distributive, transitive, identities, and
UNC Charlotte Super Competition - Comprehensive test March 2, 2015
 March 2, 2015 1. triangle is inscribed in a semi-circle of radius r as shown in the figure: θ The area of the triangle is () r 2 sin 2θ () πr 2 sin θ () r sin θ cos θ () πr 2 /4 (E) πr 2 /2 2. triangle
March 2, 2015 1. triangle is inscribed in a semi-circle of radius r as shown in the figure: θ The area of the triangle is () r 2 sin 2θ () πr 2 sin θ () r sin θ cos θ () πr 2 /4 (E) πr 2 /2 2. triangle
ENGI Parametric Vector Functions Page 5-01
 ENGI 3425 5. Parametric Vector Functions Page 5-01 5. Parametric Vector Functions Contents: 5.1 Arc Length (Cartesian parametric and plane polar) 5.2 Surfaces of Revolution 5.3 Area under a Parametric
ENGI 3425 5. Parametric Vector Functions Page 5-01 5. Parametric Vector Functions Contents: 5.1 Arc Length (Cartesian parametric and plane polar) 5.2 Surfaces of Revolution 5.3 Area under a Parametric
r=1 Our discussion will not apply to negative values of r, since we make frequent use of the fact that for all non-negative numbers x and t
 Chapter 2 Some Area Calculations 2.1 The Area Under a Power Function Let a be a positive number, let r be a positive number, and let S r a be the set of points (x, y) in R 2 such that 0 x a and 0 y x r.
Chapter 2 Some Area Calculations 2.1 The Area Under a Power Function Let a be a positive number, let r be a positive number, and let S r a be the set of points (x, y) in R 2 such that 0 x a and 0 y x r.
Math Review for AP Calculus
 Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Math Prep for Statics
 Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Circles. Exercise 9.1
 9 uestion. Exercise 9. How many tangents can a circle have? Solution For every point of a circle, we can draw a tangent. Therefore, infinite tangents can be drawn. uestion. Fill in the blanks. (i) tangent
9 uestion. Exercise 9. How many tangents can a circle have? Solution For every point of a circle, we can draw a tangent. Therefore, infinite tangents can be drawn. uestion. Fill in the blanks. (i) tangent
College Algebra with Trigonometry
 College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (556 topics + 614 additional
College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (556 topics + 614 additional
Math Requirements for applicants by Innopolis University
 Math Requirements for applicants by Innopolis University Contents 1: Algebra... 2 1.1 Numbers, roots and exponents... 2 1.2 Basics of trigonometry... 2 1.3 Logarithms... 2 1.4 Transformations of expressions...
Math Requirements for applicants by Innopolis University Contents 1: Algebra... 2 1.1 Numbers, roots and exponents... 2 1.2 Basics of trigonometry... 2 1.3 Logarithms... 2 1.4 Transformations of expressions...
Appendix C: Event Topics per Meet
 Appendix C: Event Topics per Meet Meet 1 1A Pre-algebra Topics Fractions to add and express as the quotient of two relatively prime integers Complex fractions and continued fractions Decimals, repeating
Appendix C: Event Topics per Meet Meet 1 1A Pre-algebra Topics Fractions to add and express as the quotient of two relatively prime integers Complex fractions and continued fractions Decimals, repeating
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry
 Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
Chapter 10. Properties of Circles
 Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
Explain any relationship you see between the length of the diameter and the circumference.
 Level A π Problem of the Month Circular Reasoning π Janet and Lydia want to learn more about circles. They decide to measure different size circles that they can find. They measure the circles in two ways.
Level A π Problem of the Month Circular Reasoning π Janet and Lydia want to learn more about circles. They decide to measure different size circles that they can find. They measure the circles in two ways.
Objective Mathematics
 . In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
. In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
Grade 7 9 Outcomes Continuum Strand Grade 7 Grade 8 Grade 9
 Number Sense and Number Concepts GCO A: Students will demonstrate number sense and apply number theory concepts A1 model and use power, base, and exponent to represent repeated multiplication A2 rename
Number Sense and Number Concepts GCO A: Students will demonstrate number sense and apply number theory concepts A1 model and use power, base, and exponent to represent repeated multiplication A2 rename
8 th Grade Math Connects
 8 th Grade Math Connects Chapter 1: Rational Numbers and Percent Multi-Part Lesson 1: Rational Numbers A: Rational Numbers B: Add and Subtract Rational Numbers C: Multiply Rational Numbers D: Divide Rational
8 th Grade Math Connects Chapter 1: Rational Numbers and Percent Multi-Part Lesson 1: Rational Numbers A: Rational Numbers B: Add and Subtract Rational Numbers C: Multiply Rational Numbers D: Divide Rational
Chapter 1. Solving Algebraic Equations for a Variable
 www.ck1.org CHAPTER 1 Solving Algebraic Equations for a Variable Here you ll learn how to isolate the variable in an equation or formula. Problem: You are planning a trip to Spain in the summer. In the
www.ck1.org CHAPTER 1 Solving Algebraic Equations for a Variable Here you ll learn how to isolate the variable in an equation or formula. Problem: You are planning a trip to Spain in the summer. In the
π is a mathematical constant that symbolizes the ratio of a circle s circumference to its
 Ziya Chen Math 4388 Shanyu Ji Origin of π π is a mathematical constant that symbolizes the ratio of a circle s circumference to its diameter, which is approximately 3.14159265 We have been using this symbol
Ziya Chen Math 4388 Shanyu Ji Origin of π π is a mathematical constant that symbolizes the ratio of a circle s circumference to its diameter, which is approximately 3.14159265 We have been using this symbol
West Haven Public Schools Unit Planning Organizer
 West Haven Public Schools Unit Planning Organizer Subject: Circles and Other Conic Sections Grade 10 Unit: Five Pacing: 4 weeks + 1 week Essential Question(s): 1. What is the relationship between angles
West Haven Public Schools Unit Planning Organizer Subject: Circles and Other Conic Sections Grade 10 Unit: Five Pacing: 4 weeks + 1 week Essential Question(s): 1. What is the relationship between angles
Key competencies (student abilities)
 Year 9 Mathematics Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics is accepted by universities and employers as proof of mathematical knowledge and understanding. Successful Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics candidates gain lifelong
Year 9 Mathematics Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics is accepted by universities and employers as proof of mathematical knowledge and understanding. Successful Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics candidates gain lifelong
The Arbelos and Nine-Point Circles
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 115 120. FORU GEO ISSN 1534-1178 The rbelos and Nine-Point Circles uang Tuan ui bstract. We construct some new rchimedean circles in an arbelos in connection with the
Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 (2007) 115 120. FORU GEO ISSN 1534-1178 The rbelos and Nine-Point Circles uang Tuan ui bstract. We construct some new rchimedean circles in an arbelos in connection with the
Proof of the Equivalent Area of a Circle and a Right Triangle with Leg Lengths of the Radius and Circumference
 Proof of the Equivalent Area of a ircle and a Right Triangle with Leg Lengths of the Radius and ircumference Brennan ain July 22, 2018 Abstract In this paper I seek to prove Archimedes Theorem that a circle
Proof of the Equivalent Area of a ircle and a Right Triangle with Leg Lengths of the Radius and ircumference Brennan ain July 22, 2018 Abstract In this paper I seek to prove Archimedes Theorem that a circle
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet
 1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
1998 Harvard/MIT Math Tournament GEOMETRY Answer Sheet Name: School: Grade: 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10a 5 10b 6 10c TOTAL: GEOMETRY Question One. [3 points] Quadrilateral ALEX, pictured below (but not necessarily
PRACTICE TEST 1 Math Level IC
 SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
SOLID VOLUME OTHER REFERENCE DATA Right circular cone L = cl V = volume L = lateral area r = radius c = circumference of base h = height l = slant height Sphere S = 4 r 2 V = volume r = radius S = surface
UNIT 6. BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle. The Circle
 UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
UNIT 6 BELL WORK: Draw 3 different sized circles, 1 must be at LEAST 15cm across! Cut out each circle The Circle 1 Questions How are perimeter and area related? How are the areas of polygons and circles
Mathematics 6 12 Section 26
 Mathematics 6 12 Section 26 1 Knowledge of algebra 1. Identify graphs of linear inequalities on a number line. 2. Identify graphs of linear equations and inequalities in the coordinate plane. 3. Identify
Mathematics 6 12 Section 26 1 Knowledge of algebra 1. Identify graphs of linear inequalities on a number line. 2. Identify graphs of linear equations and inequalities in the coordinate plane. 3. Identify
Circles and Volume. Circle Theorems. Essential Questions. Module Minute. Key Words. What To Expect. Analytical Geometry Circles and Volume
 Analytical Geometry Circles and Volume Circles and Volume There is something so special about a circle. It is a very efficient shape. There is no beginning, no end. Every point on the edge is the same
Analytical Geometry Circles and Volume Circles and Volume There is something so special about a circle. It is a very efficient shape. There is no beginning, no end. Every point on the edge is the same
TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION CLASS-X SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Course Structure
 TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION--19 CLASS-X SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Course Structure Units Unit Name Marks I NUMBER SYSTEMS 06 II ALGEBRA 20 III COORDINATE GEOMETRY 06 IV GEOMETRY 15 V TRIGONOMETRY 12 VI MENSURATION
TERMWISE SYLLABUS SESSION--19 CLASS-X SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS Course Structure Units Unit Name Marks I NUMBER SYSTEMS 06 II ALGEBRA 20 III COORDINATE GEOMETRY 06 IV GEOMETRY 15 V TRIGONOMETRY 12 VI MENSURATION
Honors Day 2015 Archimedes Balancing Calculus
 Honors Day 2015 Department of Mathematics Florida State University Honors Day Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL April 10, 2015 Historical Time Line 1906 Palimpsest discovered Rigorous development
Honors Day 2015 Department of Mathematics Florida State University Honors Day Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL April 10, 2015 Historical Time Line 1906 Palimpsest discovered Rigorous development
Chapter 10 Worksheet 1 Name: Honors Accelerated Geometry Hour:
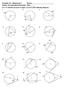 hapter 10 Worksheet 1 Name: Honors ccelerated Geometry Hour: For 1-15, find the measure of angle in each of the following diagrams. 1. 2.. 258 84 140 40 4. 5. 6. 2 y 80 y 72 7. 8. 9. 50 X 40 140 4 y 10.
hapter 10 Worksheet 1 Name: Honors ccelerated Geometry Hour: For 1-15, find the measure of angle in each of the following diagrams. 1. 2.. 258 84 140 40 4. 5. 6. 2 y 80 y 72 7. 8. 9. 50 X 40 140 4 y 10.
Content Guidelines Overview
 Content Guidelines Overview The Pearson Video Challenge is open to all students, but all video submissions must relate to set of predetermined curriculum areas and topics. In the following pages the selected
Content Guidelines Overview The Pearson Video Challenge is open to all students, but all video submissions must relate to set of predetermined curriculum areas and topics. In the following pages the selected
Geometry. Class Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 Example 1(a). Given a triangle, the intersection P of the perpendicular bisector of and
Geometry lass Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 Example 1(a). Given a triangle, the intersection P of the perpendicular bisector of and
SAT Subject Test Practice Test II: Math Level I Time 60 minutes, 50 Questions
 SAT Subject Test Practice Test II: Math Level I Time 60 minutes, 50 Questions All questions in the Math Level 1 and Math Level Tests are multiple-choice questions in which you are asked to choose the BEST
SAT Subject Test Practice Test II: Math Level I Time 60 minutes, 50 Questions All questions in the Math Level 1 and Math Level Tests are multiple-choice questions in which you are asked to choose the BEST
arxiv: v1 [math.ho] 23 May 2007
![arxiv: v1 [math.ho] 23 May 2007 arxiv: v1 [math.ho] 23 May 2007](/thumbs/96/128000906.jpg) arxiv:0705.343v [math.ho] 3 May 007 Annotations to a certain passage of Descartes for finding the quadrature of the circle Leonhard Euler In excerpts from the Manuscripts of Descartes, a few words are
arxiv:0705.343v [math.ho] 3 May 007 Annotations to a certain passage of Descartes for finding the quadrature of the circle Leonhard Euler In excerpts from the Manuscripts of Descartes, a few words are
Review Topics. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review Topics MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. On the real number line, label the points with the given coordinates. 1) 11,- 11 1)
Review Topics MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. On the real number line, label the points with the given coordinates. 1) 11,- 11 1)
Affine Transformations
 Solutions to hapter Problems 435 Then, using α + β + γ = 360, we obtain: ( ) x a = (/2) bc sin α a + ac sin β b + ab sin γ c a ( ) = (/2) bc sin α a 2 + (ac sin β)(ab cos γ ) + (ab sin γ )(ac cos β) =
Solutions to hapter Problems 435 Then, using α + β + γ = 360, we obtain: ( ) x a = (/2) bc sin α a + ac sin β b + ab sin γ c a ( ) = (/2) bc sin α a 2 + (ac sin β)(ab cos γ ) + (ab sin γ )(ac cos β) =
Brunswick School Department Honors Geometry Unit 6: Right Triangles and Trigonometry
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Right triangles have many real-world applications. What is a right triangle? How to find the geometric mean of two numbers? What is the Pythagorean
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Right triangles have many real-world applications. What is a right triangle? How to find the geometric mean of two numbers? What is the Pythagorean
Generalized Archimedean Arbelos Twins
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 4 (204) 409 48 FORUM GEOM ISSN 534-78 Generalized rchimedean rbelos Twins Nikolaos Dergiades bstract We generalize the well known rchimedean arbelos twins by extending the notion
Forum Geometricorum Volume 4 (204) 409 48 FORUM GEOM ISSN 534-78 Generalized rchimedean rbelos Twins Nikolaos Dergiades bstract We generalize the well known rchimedean arbelos twins by extending the notion
Practice SAC. Unit 4 Further Mathematics: Geometry and Trigonometry Module
 Practice SAC Unit 4 Further Mathematics: Geometry and Trigonometry Module Student Name: Subject Teacher s Name: Equipment Permitted: Writing materials, 1 bound reference, CAS- Calculator Structure of book
Practice SAC Unit 4 Further Mathematics: Geometry and Trigonometry Module Student Name: Subject Teacher s Name: Equipment Permitted: Writing materials, 1 bound reference, CAS- Calculator Structure of book
Prentice Hall Mathematics, Pre-Algebra 2007 Correlated to: Michigan Grade Level Content Expectations (Grades 8)
 NUMBER AND OPERATIONS Understand real number concepts N.ME.08.01 Understand the meaning SE/TE: Direct Instruction: 189 (Ex. 48), 588-591, of a square root of a number and its 593-596, 598-599, 603, 608,
NUMBER AND OPERATIONS Understand real number concepts N.ME.08.01 Understand the meaning SE/TE: Direct Instruction: 189 (Ex. 48), 588-591, of a square root of a number and its 593-596, 598-599, 603, 608,
Integrated Math II Performance Level Descriptors
 Limited Integrated Math II Performance Level Descriptors A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Integrated Math II. A student at this
Limited Integrated Math II Performance Level Descriptors A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Integrated Math II. A student at this
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Mathematics Grades Adopted Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
 , VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 2, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 3,, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 5 Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 State: Georgia Common Core Standards Subject: Mathematics
, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 2, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 3,, VersaTiles (R), High School Level, Book 5 Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 State: Georgia Common Core Standards Subject: Mathematics
Check boxes of Edited Copy of Sp Topics (was 145 for pilot) Beginning Algebra, 3rd Ed. [open all close all] Course Readiness and
![Check boxes of Edited Copy of Sp Topics (was 145 for pilot) Beginning Algebra, 3rd Ed. [open all close all] Course Readiness and Check boxes of Edited Copy of Sp Topics (was 145 for pilot) Beginning Algebra, 3rd Ed. [open all close all] Course Readiness and](/thumbs/81/82758218.jpg) Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10021 Sp 11 152 Topics (was 145 for pilot) Beginning Algebra, 3rd Ed. [open all close all] Course Readiness and Additional Topics Appendix Course Readiness Multiplication
Check boxes of Edited Copy of 10021 Sp 11 152 Topics (was 145 for pilot) Beginning Algebra, 3rd Ed. [open all close all] Course Readiness and Additional Topics Appendix Course Readiness Multiplication
Mathematics Precalculus: Academic Unit 7: Conics
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Conics are models of real-life situations. Conics have many reflective properties that are used in every day situations Conics work can be simplified
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Conics are models of real-life situations. Conics have many reflective properties that are used in every day situations Conics work can be simplified
Rising 7th Grade Math. Pre-Algebra Summer Review Packet
 Rising 7th Grade Math Pre-Algebra Summer Review Packet Operations with Integers Adding Integers Negative + Negative: Add the absolute values of the two numbers and make the answer negative. ex: -5 + (-9)
Rising 7th Grade Math Pre-Algebra Summer Review Packet Operations with Integers Adding Integers Negative + Negative: Add the absolute values of the two numbers and make the answer negative. ex: -5 + (-9)
Geometry. Class Examples (July 8) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 8) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 The incircle The internal angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent at the incenter
Geometry lass Examples (July 8) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 The incircle The internal angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent at the incenter
THE SAND-RECKONER. number could be expressed which exceeded the multitude of. up to a height equal to that of the highest of the mountains,
 THE SAND-RECKONER. " THERE are some, king Gelon, who think that the number of the sand is infinite in multitude ; and I mean by the sand not only that which exists about Syracuse and the rest of Sicily
THE SAND-RECKONER. " THERE are some, king Gelon, who think that the number of the sand is infinite in multitude ; and I mean by the sand not only that which exists about Syracuse and the rest of Sicily
The Pythagorean Theorem
 The Pythagorean Theorem Geometry y now, you know the Pythagorean Theorem and how to use it for basic problems. The onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem states that: If the lengths of the sides of a triangle
The Pythagorean Theorem Geometry y now, you know the Pythagorean Theorem and how to use it for basic problems. The onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem states that: If the lengths of the sides of a triangle
02)
 GRE / GMATmath,! abscissa, scalene, intercept, markup, such that, break even. abscissa. (4, 2) 4abscissa, 2ordinate absolute value acre add adjacent angles altitude ; angle () acute angle (90 ) right angle
GRE / GMATmath,! abscissa, scalene, intercept, markup, such that, break even. abscissa. (4, 2) 4abscissa, 2ordinate absolute value acre add adjacent angles altitude ; angle () acute angle (90 ) right angle
Circles Print Activity. Use the Explore It mode to answer the following questions. 1. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions:
 Name: Circles Print Activity Use the Explore It mode to answer the following questions. 1. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions: a. A is a/an angle. (central/inscribed) b. A is subtended
Name: Circles Print Activity Use the Explore It mode to answer the following questions. 1. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions: a. A is a/an angle. (central/inscribed) b. A is subtended
Integrated Mathematics II
 Integrated Mathematics II This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Integrated Mathematics II This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Chapter 3. Coaxial circles. 3.1 The radical axis of two circles. A quadratic equation of the form
 Chapter 3 Coaxial circles 3.1 The radical axis of two circles A quadratic equation of the form x 2 +y 2 +2gx+2fy +c = 0 represents a circle, center( g, f) and radius the square root ofg 2 +f 2 c. It is
Chapter 3 Coaxial circles 3.1 The radical axis of two circles A quadratic equation of the form x 2 +y 2 +2gx+2fy +c = 0 represents a circle, center( g, f) and radius the square root ofg 2 +f 2 c. It is
