CBSE Solved 2017 Paper (Physics)
|
|
|
- Maurice Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) CTON Q. Nichome and coppe wies of same lengh and same adius ae conneced in seies. Cuen is passed hough hem. Which wie ges heaed up moe? Jusify you soluion. ae of hea poducion is given as P. Fo seies connecion, cuen is same hough boh nichome and coppe wie. Theefoe fo consan, P. Fo a given lengh and adius, nichome wie offes moe esisance han coppe wie. Theefoe, ae of hea poducion fo nichome wie is moe han ae of hea poducion in coppe. Q. Do elecomagneic waves cay enegy and momenum? lecomagneic waves cay boh enegy and momenum. n a egion of fee space having elecic field of magniude and magneic field of magniude, he enegy densiy will be given as U e + m is divided equally beween elecic field and magneic field. The magniude of he momenum change, Δp of he objec is elaed o he enegy change, ΔU by, U p c Q3. How does he angle of minimum deviaion of glass pism vay, if he inciden viole ligh is eplaced by ed ligh? Give eason. ngle of minimum deviaion (d ) is given by d ( n ) d is diecly popoional o efacive index n. nd, efacive index in invesely popoional o he wavelengh of inciden ligh, ha is, n / l. Wavelengh of ed ligh is moe han he wavelengh of viole ligh which implies efacive index of glass fo ed ligh will be less han efacive index of glass fo viole ligh. Theefoe, angle of minimum deviaion of glass pism will decease if viole ligh would be eplaced by ed ligh. Q4. Name he phenomenon which shows he quanum naue of elecomagneic adiaion. lbe insein, in 95, explained phooelecic effec on he basis of Planck s quanum heoy accoding o which ligh is consideed o be made up of small packes (o paicles) of enegy known as quana of enegy o adiaion. insein explained he phooelecic effec hus: n elecon absobs a quanum of enegy (hn) fom ligh and if he enegy absobed is geae han he minimum enegy equied by an elecon o escape fom he meal suface (known as wok funcion f ), hen he elecon is ejeced fom he meal suface wih some kineic enegy. Q5. Pedic he polaiy of he capacio in he siuaion descibed below: N The appoach of he magne (noh pole) inceases he magneic flux hough he loop, heeby inducing a cuen in he loop. The loop sas acing as a magneic dipole wih a souh pole and a noh pole, and is magneic dipole momen is dieced fom souh o noh opposie o ha of magne. To oppose he incease in magneic flux caused by he appoaching magne, he loop s noh pole mus face he appoaching noh pole so as o epel i. Thus, accoding o he igh-hand humb ule, he cuen induced in he loop mus be couneclockwise when seen hough he igh side. imilaly, when magne (souh pole) appoaches owad he coil, i will geneae inceasing magne field owads lef and cuen will be couneclockwise. n view fom igh side: Field is owads you. y applying Thumb ule cuen will be aniclockwise. Thus, cuen will flow fom plae of capacio o plae. Theefoe, is a highe poenial and is a lowe poenial. N C 7 Physics soluion.indd 4/8/7 :7:6 PM
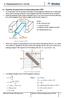
2 P- C olved 7 Pape (Physics) CTON Q6. Daw he inensiy paen fo single sli diffacion and double sli inefeence. Hence, sae wo diffeences beween inefeence and diffacion paen. (a) f he wo slis ae open, inefeence paen appea on he sceen as shown in Fig. a. (b) f he only one sli is open, diffacion paen appeas on he sceen as shown in Fig. b. passing hough P. Daw a plo showing vaiaion of inensiy when p vaies fom o o. uppose he inciden unpolaized beam has inensiy. Unpolaized ligh P Plane P polaized ligh q p p p p f (a) When unpolaized ligh passes hough polaoid P, he ligh becomes plane polaized. We know ha, if he ligh fom an odinay souce passes hough a polaoid he inensiy is educed by half. Theefoe, he inensiy of polaized beam is /. This polaized ligh hen passes hough polaoid P. is given ha angle beween he pass axes of polaoids P and P is q. Thus, accoding o Law of Malus, he esulan inensiy of ligh would be diecly popoional o he squae of cosine of he angle q beween planes of ansmission of he polaoids P and P. cos q p p p p f (b) Diffeence beween inefeence and diffacion paen nefeence nefeence akes place beween wo sepaae wavefons aising fom wo sepaae coheen souces. ll bigh finges have equal inensiy. ll dak finges have zeo inensiy. Widh of finges obained hough inefeence of monochomaic ligh has equal widh. Diffacion n he phenomenon of diffacion, he ineacion akes place beween he seconday waveles oiginaing fom diffeen poins of he exposed pas of he same wavefon. Only he fis maximum has maximum inensiy and he inensiy deceases as he ode of maxima inceases. nensiy of dak finges is no zeo. Finges obained hough diffacion of monochomaic ligh do no have equal widh. O Unpolaized ligh is passed hough a Polaoid P. When his polaized beam passes hough anohe Polaoid P and if he pass axis of P makes angle p wih he pass axis of P, hen wie he expession fo he polaized beam Vaiaion of inensiy wih q : q, cos q , cos q 45 45, cos q 6, cos 6 4 q 9, cos 9 q 8, cos 8 q 7, cos 7 q 36, cos Gaphical plo showing vaiaion of inensiy wih q : nensiy l o l o q C 7 Physics soluion.indd 4/8/7 :7: PM
3 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P-3 Q7. denify he elecomagneic waves whose wavelengh vay as (a) m < k < 8 m (b) 3 m < k < m Wie one use fo each. (a) X-ays. Wavelengh of X-ays vay in ange m < l < 8 m. Uses: X-ays ae used in sugey fo he deecion of diseased ogans, facues and sones in body. is also used fo he deecion of explosives, silve and gold in he body of smuggles. (b) Micowaves. Wavelengh of micowaves vay in ange 3 m < l < m. Uses: Micowaves ae used in sudy of aomic and molecula sucues and in ada sysems fo navigaion. Q8. Find he condiion unde which he chaged paicles moving wih diffeen speeds in he pesence of elecic and magneic field vecos can be used o selec chaged paicles of a paicula speed. Foce expeienced by a chaged paicle q moving wih velociy v in he pesence of elecic and magneic fields is given by, F F + F whee, F q and F q( v ) F q( + v ) Conside elecic and magneic fields ae pependicula o each ohe and also pependicula o he velociy of moving chaged paicle. z F Then, F qj and F q vi ( k ) qvj Theefoe, F q v ( ) j y F yä Now, conside he magniude of foce due o elecic field be equal o he foce due o magneic field, v q qv v This is he condiion used o selec chaged paicles of a paicula speed. Q9..5 ev elecon beam is used o excie a gaseous hydogen aom a oom empeaue. Deemine he wavelengh and coesponding seies of lines emied. x Given, enegy of elecon beam.5 ev. negy of gound sae of hydogen aom a oom empeaue 3.6 ev. negy of excied gaseous hydogen aom.5 ev + ( 3.6 ev). ev. negy of n h obial of hydogen aom is given by, 3. 6 ev n n ev n Thus, gaseous hydogen aom has jumped fom gound sae o n 3 level. Possible ansiions duing de-exciaion ae 3, 3 and. n 3 Lyman n n alme nm.5 nm Lyman.55 nm (a) 3 ansiion: Tansiion o n level coesponds o Lyman eies. Wavelengh of Lyman seies is given as, whee n 3 l H n l l nm 7. (b) 3 ansiion: Tansiion o n level coesponds o alme eies. Wavelengh of alme seies is given as, whee n 3 l H n l l nm 7. (c) ansiion: Tansiion o n level coesponds o Lyman eies. Wavelengh of Lyman seies is given as, whee n l H n l C 7 Physics soluion.indd 3 4/8/7 :7: PM
4 P-4 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) 4 l nm 7. Thus, wo lines of wavelengh.5 nm and.5 nm ae emied in Lyman eies. One line of wavelengh nm is emied in alme eies. Q. Wie wo popeies of a maeial suiable fo making (a) pemanen magne, and (b) an elecomagne. (a) Popeies suiable fo making pemanen magne ae: (i) High eeniviy (ii) High coeciviy (iii) High hyseesis loss (b) Popeies suiable fo making elecomagne ae: (i) Low eeniviy (ii) Low coeciviy (iii) Low hyseesis loss CTON C Q. (a) The poenial diffeence applied acoss a given esiso is aleed so ha he hea poduced pe second inceases by a faco of 9. y wha faco does he applied poenial diffeence change? (b) n he figue shown, an ammee and a esiso of 4 Ω ae conneced o he eminal of he souce. The emf of he souce is V having an inenal esisance of Ω. Calculae he volmee and ammee eadings. V H V O, 9H V V 9V V 3V Thus, poenial diffeence would incease by a faco of 3. (b) quivalen cicui diagam of given figue is shown in he figue given below, V V Ω a V Ω b 4 Ω c d (a) ccoding o Joule s law of heaing, hea poduced when cuen flows hough a conduco of esisance fo ime is given by H V Using V o, we have H V H V () uppose iniially hea poduced pe second is H and poenial diffeence is V. When poenial diffeence is aleed o V, hea poduced pe sec becomes H which is 9 imes of hea poduced iniially i.e., 9H. H V () On aking aio of eqs. () and (), we ge H V H V 4 Ω Consideing ammee and volmee o be ideal, heefoe volmee has infinie esisance and ammee has zeo esisance. Using Ohm s law, cuen passing hough cicui is V whee, T is oal esisance in he cicui +. V mmee shows. Now, volage dop acoss ab is V ab V ( ) 4 8 V T Volmee shows 8 V. Q. (a) How is ampliude modulaion achieved? (b) The fequencies of wo side bands in an M wave ae 64 khz and 66 khz, especively. Find he fequencies of caie and modulaing signal. Wha is he bandwidh equied fo ampliude modulaion? C 7 Physics soluion.indd 4 4/8/7 :7:5 PM
5 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P-5 (a) mpliude modulaion is achieved by supeimposing low fequency modulaing wave on a high fequency caie wave in such a way ha he fequency of he modulaed wave is same as he caie wave bu he ampliude of caie wave vaies in accodance wih he ampliude of he audio fequency modulaing wave o volage. Modulaing signal mpliude Modulao Caie Wave mpliude Modulaed Wave (b) Given fequency of lowe side band w L 64 khz Fequency of uppe side band w U 66 khz We know ha wl wc w m and wu wc + w m whee, w c is fequency of caie and w m is fequency of modulaing signal. w L w m c w m U w c w m w c w c + w m Theefoe, fequency of caie wave is c wl + wu khz imilaly, fequency of modulaing signal is wu wl w m khz andwidh of ampliude modulaed wave is ac inpu p-side of diode is conneced o negaive eminal of baey and n-side of diode is conneced o posiive eminal of baey. Theefoe, he given juncion diode is evese biased. (b) Cicui diagam: The ac volage o be ecified is conneced o pimay P P of sep down ansfome. is seconday of sep-down ansfome. is conneced o p-side of p-n juncion diode D. is conneced o p-side of p-n juncion diode D. Oupu is aken acoss load esisance. P Cene-ap ansfome Cene Tap P (a) D D Ldc oupu Woking: Duing posiive half cycle of inpu ac volage, suppose P is negaive and P is posiive. y inducion, is posiive and is negaive. Theefoe, diode D is fowad biased and diode D is evese biased. Fowad cuen flows hough diode D in he diecion shown in Fig. (a) and oupu is aken acoss load esisance L. Duing negaive half cycle of inpu ac volage, suppose P is posiive and P is negaive. y inducion, is negaive and is posiive. Theefoe, diode D is fowad biased and diode D is evese biased. Fowad cuen flows hough diode D in he diecion shown in Fig. (a) and oupu is aken acoss load esisance L. The ecified oupu of he posiive and he negaive half cycle of inpu ac signal is shown in Fig. (b). Duing boh half cycles, cuen flows hough L and oupu is coninuous as shown in Fig. (c). Tha is why i is called full wave ecifie. X Y andwidh w w khz U Q3. (a) n he following diagam, is he juncion diode fowad biased o evese biased? L +5V Wavefom a (i) (b) Daw he cicui diagam of full wave ecifie and sae how i woks. (a) quivalen cicui of above diagam is, Wavefom a (ii) (b) p n + 5V Oupu wavefom (acoss L) D conducs D D D conducs conducs conducs (c) C 7 Physics soluion.indd 5 4/8/7 :7:8 PM
6 P-6 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) Q4. Using phoon picue of ligh, show how insein s phooelecic equaion can be esablished. Wie wo feaues of phooelecic effec which canno be explained by wave heoy. lbe insein explained phooelecic effec on he basis of Planck s quanum heoy accoding o which ligh is consideed o be made up of small packes of enegy known as quana of enegy o adiaion. ach quana has enegy equal o hn, whee h is Planck s consan having value J s and n is he fequency of ligh. n elecon absobs a quanum of enegy (hn ) fom ligh and if he enegy absobed is geae han he minimum enegy equied by an elecon o escape fom he meal suface (known as wok funcion f ), hen he elecon is ejeced fom he meal suface wih some kineic enegy (K). insein summed up he esuls of he phooelecic expeimens in he given equaion: hn K + f max () insein assumed ha enegy equal o he phoon s enegy hn is ansfeed o a single elecon in he maeial of he age. f he elecon is o escape fom he age, i mus pick up enegy a leas equal o f. ny addiional enegy ha he elecon acquies fom he phoon appeas as kineic enegy (K) of he elecon. f a phoon of mass m and velociy v is ejeced he kineic enegy of phooelecon is given by, Puing his in eq. () K max mv hn f + m v mv hn f () q. () is insein s phooelecic equaion. f he inciden phoon has heshold fequency n, which is sufficien o ejec phooelecon wihou any kineic enegy, hen hn Puing his in eq. (), we have f mv hn hn Kmax h( n n ) Feaues of phooelecic effec which canno be explained by wave heoy: (i) nsananeous ejecion of phooelecons. (ii) xisence of heshold fequency fo a meal suface. (iii) Kineic enegy of ejeced elecons is independen of he inensiy of ligh bu depends on fequency of inciden adiaion. Q5. (a) Monochomaic ligh of wavelengh 589 nm is inciden fom ai on a wae suface. f n fo wae is.33, find he wavelengh, fequency and speed of he efaced ligh. (b) double convex lens is made of a glass of efacive index.55, wih boh faces of he same adius of cuvaue. Find he adius of cuvaue equied, if he focal lengh is cm. (a) Given, wavelengh of inciden ligh, l 589 nm m peed of ligh in ai, c 3 8 m/s, efacive index of wae, n.33. Fequency is given by 8 c 3 4 n 59. Hz 9 l 589 peed of ligh in wae is given by, v 8 c m/s n 33. Wavelengh of ligh is given by, v 6. l n m (b) Given, efacive index of glass n.55, focal lengh f cm Le adius of cuvaue of one face of lens adius of cuvaue of ohe face of lens Using lens make s fomula, f n ( ) f is adius of cuvaue of double convex lens, hen and n f ( ) ubsiuing given values, we ge 55 (. ) cm Q6. Define muual inducance beween a pai of coils. Deive an expession fo he muual inducance of wo long coaxial solenoids of same lengh wound one ove he ohe. Muual inducance is he popey of a pai of coils due o which each coil opposes any change in cuen flowing hough ohe by developing an induced emf. Le us deive muual inducance of wo long coaxial solenoids of same lengh wound ove one anohe. Le and be wo long solenoids of same lengh l such ha suounds Le numbe of uns pe uni lengh of solenoid n l C 7 Physics soluion.indd 6 4/8/7 :7:34 PM
7 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P-7 Numbe of uns pe uni lengh of solenoid n Conside a ime vaying cuen passing hough solenoid ime vaying magneic flux Φ is induced in solenoid, is given by Φ Φ M () whee, M is he coefficien of muual inducance of solenoid wih espec o. Magneic field in solenoid due o cuen is given by, m n Thus, magneic flux hough solenoid is Φ N () whee, N (oal numbe of uns in solenoid ) n l (aea of solenoid) p ubsiuing values of,, N in () we ge, Φ m p Compaing eqs. () and (3), we ge ( n )( )( nl ) (3) M m nnp l (4) Consideing opposie case whee ime vaying cuen passes hough solenoid, due o his a magneic flux Φ develops in solenoid. This is given by, Φ Φ M (5) whee, M is he coefficien of muual inducance of solenoid wih espec o. Le us assume solenoids o be vey long. Magneic flux due o is confined inside and hee is no magneic flux ouside. Magneic flux linked wih is Φ N (6) whee, N (oal numbe of uns in solenoid ) n l nd magneic field in solenoid due o cuen is given by, m nl ubsiuing values of,, N in (6) we ge, Φ m p Compaing eqs. (5) and (7) we ge, ( n )( )( n l ) (7) M m nnp l (8) Fom, eqs. (4) and (8) M M m nnp l Theefoe, his is he equied expession of muual inducance fo wo long coaxial solenoids wound ove one ohe. O Define self-inducance of a coil. Obain he expession fo he enegy soed in an induco L conneced acoss a souce of emf. elf-inducance is he popey of a coil due o which i opposes any change in he cuen flowing hough i by inducing an emf in iself. negy soed in an induco L: uppose an alenaing cuen is applied o an induco L. Cuen flows hough he induco and gows fom o maximum value. Due o change in cuen, an emf develops in he induco which opposes his change in cuen. any insan of ime, emf induced is given by e L d d To mainain maximum value of cuen, powe is supplied. any insan of ime, powe applied is given by, dw d () e () f we ignoe he esisive losses and conside only he inducive effec, hen on subsiuing value of ε fom () ino he () we ge, dw d L d d dw L d d d Ld Toal wok done by exenal souce in esablishing he cuen is W Ld L L Q7. (a) Wie he pinciple of woking of a mee bidge. (b) n a mee bidge, he balance poin is found a a disance l wih esisance and as shown in figue. l G n unknown esisance X is now conneced in paallel o he esisance and he balance poin is found a a disance l. Obain a fomula fo X in ems of l, l and. (a) Mee bidge is based on he pinciple of wheasone bidge and i is used o find he esisance of an unknown conduco o o compae wo unknown esisance. Cicui diagam of mee bidge: P J K D G Q l l + C 7 Physics soluion.indd 7 4/8/7 :7:43 PM
8 P-8 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) is m long wie made of consanan o manganin wih unifom aea of coss secion. is esisance box. is unknown esisance. P is esisance of wie of lengh l l. Q is esisance of wie of lengh l l ( l ). One eminal of galvanomee is conneced o poin D and ohe eminal is conneced o jockey. y adjusing suiable value o esisance and sliding he jockey along he wie, a balance poin is obained a poin J whee galvanomee shows no deflecion. The cicui is now same as a wheasone bidge, so accoding o balanced wheasone bidge condiion, P Q ubsiuing he values of P and Q in he above equaion, we ge l ( l ) f l and ae known, can be deemined. (b) Fom he given figue in quesion, balance poin is found a disance l wih esisance and. Using he condiion of balanced wheasone bidge, P Q Use, P l and Q ( l ) v l + l ( l ) l ( l ) K G X () When an unknown esisance X is conneced in paallel o he esisance, he balance poin is found a l. quivalen esisance of X and in paallel X X + pplying condiion of balanced wheasone bidge, l X ( l ) X + ( l ) X l X + ubsiuing he value of fom equaion () X X + ( l ) l l ( l ) X l X + ( l ) l ( l ) X + l ( l) X l ( l ) + l X ( l ) l ( l ) l ( l) X l ( l ) l( l) l( l) ( l l) X l ( l ) l ( l ) l( l) X ( l l ) This is he equied fomula fo X in ems of l, l and. Q8. Daw he block diagam of a genealized communicaion sysem. Wie he funcions of each of he following: (a) Tansmie (b) Channel (c) ecevie lock diagam of genealized communicaion sysem is as shown Communicaion sysem nfomaion souce Message signal Tansmie Tansmied signal Communicaion channel eceived signal eceive Message signal Use of infomaion Noise C 7 Physics soluion.indd 8 4/8/7 :7:5 PM
9 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P-9 (a) Tansmie: compises of message signal souce, modulao and ansmiing anenna. Tansmie makes signal compaible fo communicaion channel via modulao and anenna. Tansmie ansmis infomaion afe modifying i ino a fom ha is suiable fo ansmission. (b) Channel: The physical pah beween ansmie and eceive is called channel. Funcion of channel is o cay modulaed wave fom he ansmie o he eceive. (c) eceive: compises of pickup anenna, demodulao, amplifie and ansduce. Main funcion of eceive is o decode oiginal signal. involves picking up he signals, demodulaing and displaces he oiginal message. Q9. (a) Wie he funcions of he hee segmens of a ansiso. (b) The figue shows he inpu wavefoms and fo ND gae. Daw he oupu wave foms and wie he uh able fo his logic gae npu Oupu Oupu of ND gae is high only when boh he inpus ae high. Oupu wavefom fo he given inpu is, (npu) (a) The hee segmens of a ansiso ae: (i) mie: The funcion of emie is o emi he majoiy caies. (ii) ase: The funcion of base is o povide pope ineacion beween emie and colleco. (iii) Colleco: The funcion of colleco is o collec he majoiy caies. mie ase Colleco (b) Le oupu of ND gae is Y Tuh able fo ND gae is npu Oupu Y can be obseved ha Duing ime o, inpu and inpu, heefoe, oupu Y. Duing ime o 3, inpu and inpu, heefoe, oupu Y. Duing ime 3 o 4, inpu and inpu, heefoe, oupu Y. Duing ime 4 o 5, inpu and inpu, heefoe, oupu Y. Duing ime 5 o 6, inpu and inpu, heefoe, oupu Y. Duing ime 6 o 7, inpu and inpu, heefoe, oupu Y. Duing ime 7 o 8, inpu and inpu, heefoe, oupu Y. Q. (a) Daw he ay diagam depicing he fomaion of he image by an asonomical elescope in nomal adjusmen. (b) You ae given he following hee lenses. Which wo lenses will you use as an eyepiece and as an objecive o consuc an asonomical elescope? Give eason. Lenses Powe (D) peue (cm) L 3 8 L 6 L 3 (a) When he final image is fomed a infiniy, such an adjusmen of a elescope is known as nomal adjusmen. Figue below shows ay diagam of asonomical elescope. C 7 Physics soluion.indd 9 4/8/7 :7:5 PM
10 P- C olved 7 Pape (Physics) fo fe d d l lsinq a C a Fo, Fe b C d k ldlsinq O mage a infiniy (b) Fo he consucion of an asonomical elescope, objecive lens should have maximum diamee and eye piece should have maximum powe. Fom he given lis of lenses, lens L has maximum diamee i.e., lens L has maximum apeue of 8 cm. Lens L 3 has maximum powe of D. Theefoe, lens L can be used as objecive and L 3 can be used as he eyepiece o consuc an asonomical elescope. Q. (a) ae io ava law and expess his law in he veco fom. (b) Two idenical cicula coils, P and Q each of adius, caying cuens and 3, especively, ae placed concenically and pependicula o each ohe lying in he XY and YZ planes. Find he magniude and diecion of he ne magneic field a he cene of he coils. whee, k is popoionaliy consan, k m n veco fom, 4p d k d l l 3 (b) Magneic field a he cene of a ing of adius caying cuen is given by, Q Z m Z P X X (a) io ava law deals wih magneic field inducion a a poin due o small cuen caying elemen. P q d l olde segmen Le be small cuen elemen. Lengh of cuen elemen dl. Cuen in elemen. Le P be a poin whee magneic field inducion is o be deduced. Disance beween P and cuen elemen dl ngle beween dl and q Magneic field inducion a poin P d io ava law saes ha he magneic field inducion a poin P depends on, d dl d d d sinq Combining all elaions, we ge (i) Fo he coil caying cuen and lying in XY plane, magneic field is along Z axis. Magneic field is given by, m m z ( ) m z (ii) Fo he coil caying cuen 3 and lying in YZ plane, magneic field is along X axis. Magneic field is given by m x m 3 m x 3 Ne magneic field is given by + Diecion of ne field will be along Y axis. + m 3 m m + ( + ) m ( 3) m m x z ( 4) Q. Two idenical paallel plae capacios and ae conneced o a baey of V vols wih a swich closed. The swich is now opened and he fee space beween he C 7 Physics soluion.indd 4/8/7 :8: PM
11 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P- plaes of he capacio is filled wih a dielecic of dielecic consan K. Find he aio of he oal elecosaic enegy soed in boh capacios befoe and afe he inoducion of he dielecic. is given ha he capacios ae idenical. Le he capaciance of wo capacios be C. (i) When swich is closed, capacios and ae a same poenial V. negy soed in capacio U U CV negy soed in capacio U U CV Toal enegy in he sysem U U + U U CV + CV CV (ii) Now swich is open and a dielecic consan K is inoduced. The capaciance of wo capacios changes o C KC Now capacio is conneced o volage souce wheeas, is no conneced o he souce. Theefoe, poenial of capacio emains same V and poenial of capacio changes o V q q V V C KC K negy soed in capacio afe inoducion of dielecic U U C V KCV negy soed in capacio afe inoducion of dielecic U V U C V KC K CV K Toal enegy of he sysem afe inoducion of dielecic is U U + U CV U KCV + CV + K K K aio of he oal elecosaic enegy soed in boh capacios befoe and afe he inoducion of he dielecic consan is U CV K U K + CV K + K K + K CTON D Q3. sha s mohe ead an aicle in he newspape abou a disase ha ook place a Chenobyl. he could no undesand much fom he aicle and asked a few quesions fom sha egading he aicle. sha ied o answe he mohe s quesions based on wha she lean in class X Physics. (a) Wha was he insallaion a Chenobyl whee he disase ook place? Wha, accoding o you, was he cause of his disase? (b) xplain he pocess of elease of enegy in he insallaion a Chenobyl. (c) Wha, accoding o you, wee he values displayed by sha and he mohe? (a) majo acciden occued a a uni of ligh wae gaphie modeaed eaco in he nuclea powe saion a Chenobyl, Ukaine. The acciden occued duing an expeimen o es a way of cooling he coe of he eaco in an emegency siuaion. The main causes of he disase was: (i) Human eo: Thee was no good communicaion beween he uses. was lagely because of he opeaos. (ii) ad design: The eacos wee unsable a low powe. (b) The pocess of elease of enegy is as follows: (i) Fissionable maeial geneally pue Uanium 35 9 U is used. Uanium is loaded ino he eaco. (ii) low neuons cause fission of uanium, aoms spli and elease enegy poducing neuon and spliing ohe aoms in a conolled manne. (iii) Conol ods made of cadmium ae inseed in he eaco o absob neuons and slow down he chain eacion. To speed up he eacion ods ae emoved fom he eaco. The eacion is given as, 35 9 U+ n a + K + 3( n)+ Q Mass of uanium u; Mass of neuon.87 u Mass of baium u; Mass of kypon u Theefoe, mass of eacans u Mass of poducs (3.87) u Mass defec ( M) Mass of eacans Mass of poducs u C 7 Physics soluion.indd 4/8/7 :8:5 PM
12 P- C olved 7 Pape (Physics) negy eleased, Q Mc (. 53u)( 93. 5MeV / u). 443MeV (c) sha s mohe is sensiive and a well awae lady. he is concened abou he envionmen and is cuious o lean abou i. sha is a billian suden well vesed wih he knowledge of nuclea powe plans. he explained he mohe he woking of nuclea powe plans and abou he disase ha occued in Chebonyl. CTON Q4. (a) Deive an expession fo he elecic field due o a dipole of lengh a a a poin disance fom he cene of he dipole on he axial line. (b) Daw a gaph of vesus fo > > a (c) f his dipole wee kep in a unifom exenal elecic field, diagammaically epesen he posiion of he dipole in sable and unsable equilibium and wie he expessions fo he oque acing on he dipole in boh he cases. (a) Conside an elecic dipole consising of wo poin chages +q and q sepaaed by disance a. Le P be a poin a a disance fom he cene of he dipole on he axial line whee he elecic field is o be calculaed. a p P + q O q Le be he elecic field inensiy a poin P due o chage +q a poin, q q a p 4pe P 4pe ( ) Diecion of is along P. Le be he elecic field inensiy a P due o chage q a poin, q q a p 4pe P 4pe ( + ) Diecion of is along P. The ne elecic field a poin P due o boh he chages (o dipole) accoding o he pinciple of supeposiion will be P q q p a + a pe ( ) ( ) 4 q 4a p qa p 4pe ( a ) 4pe ( a ) Now, we know ha p q a and k / 4pe. ubsiuing hese values in his equaion, we ge kp ( a ) (b) Fo > > a kp kp 3 ( ) 3 Clealy is invesely popoional o 3. Gaphical epesenaion of he elaion is (c) Le an elecic dipole consising of chages + q and q and of lengh a placed in a unifom elecic field, making an angle θ. Dipole momen, p q a Foce exeed on chage +q, F q. The diecion of foce is along. Foce exeed on chage q, F q. The diecion of foce is opposie o. The wo foces acing on a dipole ae equal and opposie in diecion. Theefoe, hey fom a couple which exes a oque. Toque F Pependicula disance beween he foces F C F sinq q asin q ( aq ) sinq p sinq n veco fom, p F q a p n case of sable equilibium, he oque ends o align he dipole o he diecion of elecic field, ha is, q.theefoe, q p sinq p sin a + q C +q F C 7 Physics soluion.indd 4/8/7 :8:6 PM
13 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P-3 n case of unsable equilibium, he dipole is opposie o he diecion of elecic field and he oque will un he dipole hough 8. Theefoe, p sinq p sin8 pplying Gauss law, we ge oal elecic flux ove suface Toal chage enclosed in he suface/ε d d s e [Fom () and ()] +q 8 a O (a) Use Gauss s heoem o find he elecic field due o a unifomly chaged infinie lage plane hin shee wih suface chage densiy. (b) n infinie lage hin plane shee has a unifom suface chage densiy +. Obain he expession fo he amoun of wok done in binging a poin chage q fom infiniy o a poin, disan, in fon of he chaged plane shee. (a) Gauss s heoem saes ha oal elecic flux ove a closed suface is / e imes he oal chage enclosed in he suface. Conside a Gaussian suface, a cylinde aound poin P passing hough he hin shee. n P n n Le he elecic field is o be obained a poin P. Disance of poin P fom he shee. Coss secional aea of cylinde d. Lengh of cylinde he edges of he cylinde, he elecic field veco and veco nomal o aea elemen n ae paallel; heefoe elecic flux ove he edges is f nd ncos d d On he cuved suface of cylinde, he elecic field veco and veco nomal o aea elemen n ae pependicula o each ohe. Theefoe, elecic flux ove he edges is f nd ncos9 d Theefoe, oal elecic flux ove enie suface of cylinde is f d () is given ha he suface chage densiy of hin shee is σ, heefoe, oal chage enclosed in he cylinde σd () n n q Q n s e (b) To calculae he amoun of wok done in binging a poin chage q fom infiniy o a poin a disance in fon of he chaged plane shee having chage densiy +σ. We need o calculae he poenial nea he chaged shee. ince Wok Done Poenial Chage Poenial nea chaged shee: Magniude of elecic field due o hin shee is given by, s () e Diecion of elecic field is away fom he shee. Poenial gadien is given by dv d dv d negaing he above equaion we ge dv d V d V s [Fom ()] e Theefoe, wok done in binging a poin chage q fom infiniy o a poin a disance, s W V q q e Q5. device X is conneced o an ac souce VV sinv. The vaiaion of volage, cuen and powe in one cycle is shown in he following gaph: Y p C π w (a) denify he device X. (b) Which of he cuve,, and C epesen he volage, cuen and powe consumed in he cicui? Jusify you answe. (c) How does is impedance vay wih fequency of he ac souce? how gaphically. C 7 Physics soluion.indd 3 4/8/7 :8: PM
14 P-4 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) (d) Obain an expession fo he cuen in he cicui and is phase elaion wih ac volage. (a) ince in an ac cicui conaining capaciance only, alenaing cuen leads he alenaing emf by phase angle of 9. o, in he given figue cuve C leads cuve by phase angle of 9. Hence device X is a capacio. (b) ince volage V V sinw is popoional o sine funcion. Theefoe, he cuve epesening volage should be a sine wave. We know ha cuen leads volage V by a phase angle of 9. sin + w p cos( w ) Thus, cuen being popoional o cosine funcion should be epesened by he cuve having cosine wave. When w, V V sin and cos When w p /, p p V Vsin V and cos When w p, V V sinp and cosp Thus, cuve epesens volage, C epesens cuen and epesens powe. (c) Cuen in cicui, CV w cosw V + C ( / ) sin w p w When sin w + p, cuen will be maximum, Theefoe, V ( / w C ) On compaing wih Ohm s law, V, we have, w C as he impedance offeed by he capacio denoed by X C X C C w pn C Whee, n is he fequency of ac supply. mpedance is invesely popoional o fequency of ac supply. mpedance Fequency (d) n alenaing emf is applied V V sinw, he cuen flowing hough he cicui ansfes chage o he capacio which poduces poenial diffeence beween plaes. f q is chage on he capacio wih capaciance C, hen, poenial diffeence acoss plaes is equal o applied emf, q C V V sinw q CV sinw Cuen in he cicui a any insan is given by, dq d d d CV sinw CV w cosw ( ) V + C ( / ) sin w p w When sin w + p, cuen will be maximum, Theefoe, V ( / w C ) sin + w p On compaing above equaion wih V V sinw, we find ha cuen leads volage V by a phase angle of 9. Phase diagam elaion beween cuen and volage is shown below V 9 w O (a) Daw he labelled diagam of an ac geneao. Obain he expession fo he emf induced in he oaing coil of N uns each of coss-secional aea in he pesence of magneic field. (b) hoizonal conducing od m long exending fom eas o wes is falling wih speed 5. m/s a igh angles o he hoizonal componen of he ah s magneic field,.3 4 Wb/m. Find he insananeous value of he emf induced in he od. (a) The ac geneao is a machine which poduces alenaing cuen enegy fom mechanical enegy. V o C 7 Physics soluion.indd 4 4/8/7 :8:3 PM
15 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P-5 Consucion: CD is ecangula amaue coil having lage numbe of uns. N and ae song magneic poles in which amaue CD oaes. and ae hollow meallic slip ings. The wo ends of he ings ae conneced o amaue and he ings also oae as coil oaes. and ae flexible meal plaes o ods called bushes conneced wih and especively. passes cuen fom amaue coil o load esisance. s amaue coil oaes in magneic field, he angle q beween nomal of coil and magneic field changes coninuously. The magneic flux linked wih he coil changes. nd heefoe an emf is induced in he coil. Le numbe of uns in coil N. Coss-secional aea of each un of coil. engh of magneic field. ngle ha nomal of coil makes wih field a any insan q. C D N C D N Wes ouh l m.3 x 4 v 5. m/s Noh as Q6. (a) Define wavefon. Use Huygens Pinciple o veify he laws of efacion. (b) How is linealy polaized ligh obained by he pocess of scaeing of ligh? Find he ewse angle fo ai-glass ineface, when he efacive index of glass.5. (a) When a ligh souce emis ligh, all he paicles aound he ligh begin o vibae. wavefon is coninuous locus of all such paicles which ae vibaing in he same phase. Huygens Pinciple saes ha: (i) ach poin on pimay wavefon acs as a fesh souce of new disubance called seconday waveles, which sends disubance in all he diecions wih velociy of ligh. (ii) any insan, a suface ouching hese seconday waveles in fowad diecion gives he new posiion of he wavefon a ha insan called he seconday wavefon. N coil q nomal X i i D P ae N Y Magneic flux linked wih coil is Φ N( ) Ncosq Ncosw D dense whee, w is angula velociy of he oaing coil. When coil oaes,q changes and hence he magneic flux linked wih he coil changes due o which an emf is induced in he coil. any insan, emf induced in he coil is e d Φ d d e ( N w) Nw w d cos sin (b) Given ha, lengh of wie, l m, speed of wie, v 5. m/s, magneic field sengh,.3 x 4 Wb/m. Theefoe, emf induced in wie is given by 4 3 e lv V n he above figue; XY is he ineface beween ae medium and dense medium. is plane wavefon inciden on XY a angle of incidence i. Le v be velociy of ligh in ae medium and v be velociy of ligh in dense medium. ccoding o Huygens Pinciple, evey poin on is a souce of seconday waveles. uppose waveles fom eaches poin on XY in seconds. Waveles fom will each poin in he dense medium in seconds. nd in he same ime waveles a poin D will each poin D in he dense medium. Theefoe, epesens he efaced wavefon a XY plane a an angle of efacion. Time aken by ligh o avel a poin on inciden wavefon o a coesponding poin in efaced wavefon should be equal. Time aken by ligh o go fom D o D will be C 7 Physics soluion.indd 5 4/8/7 :8:36 PM
16 P-6 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) DP PD + v v Now ime aken by seconday wavele o avel disance DP in ae medium and PD in dense medium is equal o ime aken by seconday waveles o avel disance in ae medium. Theefoe, v Now, N + N DP + N, hus, DP N + v v Using eqs. () and (), we ge, DP PD DP N + + v v v v PD N v v n igh angled iangle, DP, DP, so, PD P sin Now, in igh angled iangle NP, NP i, heefoe, N P sin i P sin P sin i v v y definiion, n v v P sin i v P sin v, we have / sin i n sin This is nell s law of efacion of ligh. (b) When whie ligh beam is passed hough a medium consising of paicles of ode of wavelengh of inciden ligh hen he beam ges scaeed. When he scaeed beam is seen in diecion pependicula o he diecion of incidence, i is plane o linealy polaized. inciden beam z () () O Objec n unpolaized ligh is inciden along z-axis on scaee. n obseve along x-axis will see vibaions of elecic veco ha ae paallel o y-axis. imilaly, an obseve on y-axis will see vibaion of elecic veco ha ae paallel o x-axis. Theefoe, ligh scaeed in diecion pependicula o inciden ligh is always linealy polaized. This phenomenon is called polaizaion by scaeing. ccoding o ewse s law, n an i p whee, n is he efacive index of medium, i p is he polaizing angle o ewse s angle. n quesion, i is given ha n.5 and we have o find i p. Thus, using ewse s law, we ge 5. an i p i p an 5. i p O (a) Daw a ay diagam o show he image fomaion by a combinaion of wo hin convex lenses in conac. Obain he expession fo he powe of his combinaion in ems of he focal lengh of he lenses. (b) ay of ligh passing fom ai hough an equilaeal glass pism undegoes minimum deviaion when angle of incidence is 3/4 h of he angle of he pism. Calculae he speed of ligh in he pism. (a) ay diagam showing image fomaion by combinaion of wo hin convex lenses in conac is given below. Hee, C and C ae opical cenes of wo hin convex lenses L and L especively. O is he objec placed a pinciple axis of he combinaion of lenses. is he image fomed by lens L alone. is he final image fomed by he combinaion of lenses L and L. u C C v image xpession fo powe: Powe of lens is measued as he ecipocal of focal lengh of he lens v P F caee Obseve y whee, F is he equivalen focal lengh of he combinaion of wo lenses. To find he equivalen focal lengh, le OC u x Obseve C v C v C 7 Physics soluion.indd 6 4/8/7 :8:48 PM
17 C olved 7 Pape (Physics) P-7 Focal lengh of lens L f ; focal lengh of lens L f. f hee was a single lens L, image will be fomed a. o by lens fomula, we have v u f mage will seve as a viual objec o lens L, heefoe C u. pplying lens fomula on lens L, we have dding eqs. () and (), we ge () () v v f v u + v v f + f + (3) v u f f Now le wo lenses be eplaced by a single lens of focal lengh F, which foms image a disance v fom he opical cene of an objec ha is placed a disance u fom opical cene of he lens. pplying lens fomula on his lens, we ge (4) v u F On compaing eqs. (3) and (4), we ge + F f f ff F f + f Theefoe, powe of his combinaion of lenses in ems of focal lengh of lenses is, P F f f P + ff (b) Given, angle of pism ngle of incidence i i i 6 Fo angle of minimum deviaion, i i i and We know ha, +, 3 ccoding o nell s law, efacive index of pism is given by i n sin sin ubsiuing he value of i and, we ge sin45 n / sin / peed of ligh in pism is given by v c n whee, c is he speed of ligh in ai and n is efacive index of pism. ubsiuing values of c and n we ge v m/s.. 44 C 7 Physics soluion.indd 7 4/8/7 :8:55 PM
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) , PART A PHYSICS
 Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
Lecture 5. Chapter 3. Electromagnetic Theory, Photons, and Light
 Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
Lecue 5 Chape 3 lecomagneic Theo, Phoons, and Ligh Gauss s Gauss s Faada s Ampèe- Mawell s + Loen foce: S C ds ds S C F dl dl q Mawell equaions d d qv A q A J ds ds In mae fields ae defined hough ineacion
r r r r r EE334 Electromagnetic Theory I Todd Kaiser
 334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
KINEMATICS OF RIGID BODIES
 KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
KINEMTICS OF RIGID ODIES In igid body kinemaics, we use he elaionships govening he displacemen, velociy and acceleaion, bu mus also accoun fo he oaional moion of he body. Descipion of he moion of igid
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
Two-dimensional Effects on the CSR Interaction Forces for an Energy-Chirped Bunch. Rui Li, J. Bisognano, R. Legg, and R. Bosch
 Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
2. v = 3 4 c. 3. v = 4c. 5. v = 2 3 c. 6. v = 9. v = 4 3 c
 Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Vesion 074 Exam Final Daf swinney (55185) 1 This pin-ou should have 30 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions may coninue on he nex column o page find all choices befoe answeing. 001 10.0 poins AballofmassM
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (K.C.S.E.)
 Name: Index No.. Candidae s Sign.... Dae:... Kenya Ceificae of Seconday Educaion (K.C.S.E.) 232/2 PHYSICS JULY/AUGUST 2014 TIME: 2 HOURS 232/2 Phycs 2 2 hou INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES: Wie you name
Name: Index No.. Candidae s Sign.... Dae:... Kenya Ceificae of Seconday Educaion (K.C.S.E.) 232/2 PHYSICS JULY/AUGUST 2014 TIME: 2 HOURS 232/2 Phycs 2 2 hou INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES: Wie you name
THERMAL PHYSICS. E nc T. W PdV. degrees of freedom. 32 m N V. P mv. Q c. AeT (emitted energy rate) E Ae T Tsurroundings. Q nc p
 HRMA PHYSICS PHY 8 Final es: Compehensie Concep and Fomula Shee NB: Do no add anyhing o he fomula shee excep in he space specially assigned. hemodynamic Paamees: Volume V of mass m wih densiy ρ: V m empeaue
HRMA PHYSICS PHY 8 Final es: Compehensie Concep and Fomula Shee NB: Do no add anyhing o he fomula shee excep in he space specially assigned. hemodynamic Paamees: Volume V of mass m wih densiy ρ: V m empeaue
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
P h y s i c s F a c t s h e e t
 P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
P h y s i c s F a c s h e e Sepembe 2001 Numbe 20 Simple Hamonic Moion Basic Conceps This Facshee will:! eplain wha is mean by simple hamonic moion! eplain how o use he equaions fo simple hamonic moion!
Relative and Circular Motion
 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Circuits 24/08/2010. Question. Question. Practice Questions QV CV. Review Formula s RC R R R V IR ... Charging P IV I R ... E Pt.
 4/08/00 eview Fomul s icuis cice s BL B A B I I I I E...... s n n hging Q Q 0 e... n... Q Q n 0 e Q I I0e Dischging Q U Q A wie mde of bss nd nohe wie mde of silve hve he sme lengh, bu he dimee of he bss
4/08/00 eview Fomul s icuis cice s BL B A B I I I I E...... s n n hging Q Q 0 e... n... Q Q n 0 e Q I I0e Dischging Q U Q A wie mde of bss nd nohe wie mde of silve hve he sme lengh, bu he dimee of he bss
Low-complexity Algorithms for MIMO Multiplexing Systems
 Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Low-complexiy Algoihms fo MIMO Muliplexing Sysems Ouline Inoducion QRD-M M algoihm Algoihm I: : o educe he numbe of suviving pahs. Algoihm II: : o educe he numbe of candidaes fo each ansmied signal. :
Computer Propagation Analysis Tools
 Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools. Compue Popagaion Analysis Tools Inoducion By now you ae pobably geing he idea ha pedicing eceived signal sengh is a eally impoan as in he design of a wieless communicaion
The sudden release of a large amount of energy E into a background fluid of density
 10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
10 Poin explosion The sudden elease of a lage amoun of enegy E ino a backgound fluid of densiy ceaes a song explosion, chaaceized by a song shock wave (a blas wave ) emanaing fom he poin whee he enegy
Non-sinusoidal Signal Generators
 Non-sinusoidal Signal Geneaos ecangle, iangle, saw ooh, pulse, ec. Muliibao cicuis: asable no sable saes (wo quasi-sable saes; i emains in each sae fo pedeemined imes) monosable one sable sae, one unsable
Non-sinusoidal Signal Geneaos ecangle, iangle, saw ooh, pulse, ec. Muliibao cicuis: asable no sable saes (wo quasi-sable saes; i emains in each sae fo pedeemined imes) monosable one sable sae, one unsable
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
Ferent equation of the Universe
 Feen equaion of he Univese I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize - Discoveies Feen equaion of he Univese: i + ia = = (... N... N M m i= i ) i a M m j=
Feen equaion of he Univese I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize - Discoveies Feen equaion of he Univese: i + ia = = (... N... N M m i= i ) i a M m j=
Lecture-V Stochastic Processes and the Basic Term-Structure Equation 1 Stochastic Processes Any variable whose value changes over time in an uncertain
 Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
Lecue-V Sochasic Pocesses and he Basic Tem-Sucue Equaion 1 Sochasic Pocesses Any vaiable whose value changes ove ime in an unceain way is called a Sochasic Pocess. Sochasic Pocesses can be classied as
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Poisson s Ratio
 Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
Fouh diion MCHANICS OF MATRIALS Poisson s Raio Bee Johnson DeWolf Fo a slende ba subjeced o aial loading: 0 The elongaion in he -diecion is accompanied b a conacion in he ohe diecions. Assuming ha he maeial
Pressure Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Stress Analysis
 Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
Pessue Vessels Thin and Thick-Walled Sess Analysis y James Doane, PhD, PE Conens 1.0 Couse Oveview... 3.0 Thin-Walled Pessue Vessels... 3.1 Inoducion... 3. Sesses in Cylindical Conaines... 4..1 Hoop Sess...
r P + '% 2 r v(r) End pressures P 1 (high) and P 2 (low) P 1 , which must be independent of z, so # dz dz = P 2 " P 1 = " #P L L,
 Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
Lecue 36 Pipe Flow and Low-eynolds numbe hydodynamics 36.1 eading fo Lecues 34-35: PKT Chape 12. Will y fo Monday?: new daa shee and daf fomula shee fo final exam. Ou saing poin fo hydodynamics ae wo equaions:
General Non-Arbitrage Model. I. Partial Differential Equation for Pricing A. Traded Underlying Security
 1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
1 Geneal Non-Abiage Model I. Paial Diffeenial Equaion fo Picing A. aded Undelying Secuiy 1. Dynamics of he Asse Given by: a. ds = µ (S, )d + σ (S, )dz b. he asse can be eihe a sock, o a cuency, an index,
Chapter 2 Wave Motion
 Lecue 4 Chape Wae Moion Plane waes 3D Diffeenial wae equaion Spheical waes Clindical waes 3-D waes: plane waes (simples 3-D waes) ll he sufaces of consan phase of disubance fom paallel planes ha ae pependicula
Lecue 4 Chape Wae Moion Plane waes 3D Diffeenial wae equaion Spheical waes Clindical waes 3-D waes: plane waes (simples 3-D waes) ll he sufaces of consan phase of disubance fom paallel planes ha ae pependicula
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lecture 1 bis. Photo courtesy of Malene Thyssen,
 3.012 Fund of Ma Sci: Bonding Lecue 1 bis WAVE MECHANICS Phoo couesy of Malene Thyssen, www.mfoo.dk/malene/ 3.012 Fundamenals of Maeials Science: Bonding - Nicola Mazai (MIT, Fall 2005) Las Time 1. Playes:
3.012 Fund of Ma Sci: Bonding Lecue 1 bis WAVE MECHANICS Phoo couesy of Malene Thyssen, www.mfoo.dk/malene/ 3.012 Fundamenals of Maeials Science: Bonding - Nicola Mazai (MIT, Fall 2005) Las Time 1. Playes:
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
SAMPLE PAPER I. Time Allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70
 SAMPL PAPR I Time Allowed : 3 hous Maximum Maks : 70 Note : Attempt All questions. Maks allotted to each question ae indicated against it. 1. The magnetic field lines fom closed cuves. Why? 1 2. What is
SAMPL PAPR I Time Allowed : 3 hous Maximum Maks : 70 Note : Attempt All questions. Maks allotted to each question ae indicated against it. 1. The magnetic field lines fom closed cuves. Why? 1 2. What is
MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH
 Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
Fundamenal Jounal of Mahemaical Phsics Vol 3 Issue 013 Pages 55-6 Published online a hp://wwwfdincom/ MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR APPROXIMATING PARTICLE BEHAVIOUR AT RADIUS OF THE PLANCK LENGTH Univesias
MEEN 617 Handout #11 MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Systems with VISCOUS DAMPING
 MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
MEEN 67 Handou # MODAL ANALYSIS OF MDOF Sysems wih VISCOS DAMPING ^ Symmeic Moion of a n-dof linea sysem is descibed by he second ode diffeenial equaions M+C+K=F whee () and F () ae n ows vecos of displacemens
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
On Control Problem Described by Infinite System of First-Order Differential Equations
 Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
Ausalian Jounal of Basic and Applied Sciences 5(): 736-74 ISS 99-878 On Conol Poblem Descibed by Infinie Sysem of Fis-Ode Diffeenial Equaions Gafujan Ibagimov and Abbas Badaaya J'afau Insiue fo Mahemaical
7 Wave Equation in Higher Dimensions
 7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
7 Wave Equaion in Highe Dimensions We now conside he iniial-value poblem fo he wave equaion in n dimensions, u c u x R n u(x, φ(x u (x, ψ(x whee u n i u x i x i. (7. 7. Mehod of Spheical Means Ref: Evans,
ELECTROSTATICS::BHSEC MCQ 1. A. B. C. D.
 ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
The Great Wave Hokusai. LO: Recognize physical principles associated with terms in sonar equation.
 Sona Equaion: The Wave Equaion The Gea Wave Hokusai LO: Recognize hysical inciles associaed wih ems in sona equaion. he Punchline If densiy oo high o esolve individual oganisms, hen: E[enegy fom volume]
Sona Equaion: The Wave Equaion The Gea Wave Hokusai LO: Recognize hysical inciles associaed wih ems in sona equaion. he Punchline If densiy oo high o esolve individual oganisms, hen: E[enegy fom volume]
156 There are 9 books stacked on a shelf. The thickness of each book is either 1 inch or 2
 156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
156 Thee ae 9 books sacked on a shelf. The hickness of each book is eihe 1 inch o 2 F inches. The heigh of he sack of 9 books is 14 inches. Which sysem of equaions can be used o deemine x, he numbe of
Fig. 1S. The antenna construction: (a) main geometrical parameters, (b) the wire support pillar and (c) the console link between wire and coaxial
 a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
New method to explain and calculate the gyroscopic torque and its possible relation to the spin of electron
 Laes Tends in Applied and Theoeical Mechanics New mehod o explain and calculae he gyoscopic oque and is possible elaion o he o elecon BOJIDAR DJORDJEV Independen Reseache 968 4- Dobudja see, Ezeovo, Vana
Laes Tends in Applied and Theoeical Mechanics New mehod o explain and calculae he gyoscopic oque and is possible elaion o he o elecon BOJIDAR DJORDJEV Independen Reseache 968 4- Dobudja see, Ezeovo, Vana
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Orthotropic Materials
 Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
Kapiel 2 Ohoopic Maeials 2. Elasic Sain maix Elasic sains ae elaed o sesses by Hooke's law, as saed below. The sesssain elaionship is in each maeial poin fomulaed in he local caesian coodinae sysem. ε
EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY
 Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
Mahemaics Today Vol7(Dec-)54-6 ISSN 976-38 EVENT HORIZONS IN COSMOLOGY K Punachanda Rao Depamen of Mahemaics Chiala Engineeing College Chiala 53 57 Andha Padesh, INDIA E-mail: dkpaocecc@yahoocoin ABSTRACT
The Wrong EHT Black Holes image and money; the Ferent image. Einstein and all the scientists did not understand Gravitation
 The Wong EHT Black Holes image and money; he Feen image. Einsein and all he scieniss did no undesand Gaviaion I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize -
The Wong EHT Black Holes image and money; he Feen image. Einsein and all he scieniss did no undesand Gaviaion I discoveed a new Gaviaion heoy which beaks he wall of Planck scale! Absac My Nobel Pize -
An Open cycle and Closed cycle Gas Turbine Engines. Methods to improve the performance of simple gas turbine plants
 An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
An Open cycle and losed cycle Gas ubine Engines Mehods o impove he pefomance of simple gas ubine plans I egeneaive Gas ubine ycle: he empeaue of he exhaus gases in a simple gas ubine is highe han he empeaue
( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba
![( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba ( ) exp i ω b ( ) [ III-1 ] exp( i ω ab. exp( i ω ba](/thumbs/83/87856399.jpg) THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
THE INTEACTION OF ADIATION AND MATTE: SEMICLASSICAL THEOY PAGE 26 III. EVIEW OF BASIC QUANTUM MECHANICS : TWO -LEVEL QUANTUM SYSTEMS : The lieaue of quanum opics and lase specoscop abounds wih discussions
An Automatic Door Sensor Using Image Processing
 An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
An Auomaic Doo Senso Using Image Pocessing Depamen o Elecical and Eleconic Engineeing Faculy o Engineeing Tooi Univesiy MENDEL 2004 -Insiue o Auomaion and Compue Science- in BRNO CZECH REPUBLIC 1. Inoducion
PAPER-I I.E.S-(OBJ) of 15
 I.E.S-(OBJ) 00 of 5 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER-I. Digial daa acquisiion sysems ae used. Only when he oupu of he ansduces is in digial fom. When physical pocess being monioed is slowly vaying (naow bandwidh)
I.E.S-(OBJ) 00 of 5 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER-I. Digial daa acquisiion sysems ae used. Only when he oupu of he ansduces is in digial fom. When physical pocess being monioed is slowly vaying (naow bandwidh)
Basic Circuit Elements Professor J R Lucas November 2001
 Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Reinforcement learning
 Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Lecue 3 Reinfocemen leaning Milos Hauskech milos@cs.pi.edu 539 Senno Squae Reinfocemen leaning We wan o lean he conol policy: : X A We see examples of x (bu oupus a ae no given) Insead of a we ge a feedback
Physics 2001/2051 Moments of Inertia Experiment 1
 Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
AST00 Lecue Noes 5 6: Geneal Relaiviy Basic pinciples Schwazschild geomey The geneal heoy of elaiviy may be summaized in one equaion, he Einsein equaion G µν 8πT µν, whee G µν is he Einsein enso and T
Calculate the electric potential at B d2=4 m Calculate the electric potential at A d1=3 m 3 m 3 m
 MTE : Ch 13 5:3-7pm on Oct 31 ltenate Exams: Wed Ch 13 6:3pm-8:pm (people attending the altenate exam will not be allowed to go out of the oom while othes fom pevious exam ae still aound) Thu @ 9:-1:3
MTE : Ch 13 5:3-7pm on Oct 31 ltenate Exams: Wed Ch 13 6:3pm-8:pm (people attending the altenate exam will not be allowed to go out of the oom while othes fom pevious exam ae still aound) Thu @ 9:-1:3
Combinatorial Approach to M/M/1 Queues. Using Hypergeometric Functions
 Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
Inenaional Mahemaical Foum, Vol 8, 03, no 0, 463-47 HIKARI Ld, wwwm-hikaicom Combinaoial Appoach o M/M/ Queues Using Hypegeomeic Funcions Jagdish Saan and Kamal Nain Depamen of Saisics, Univesiy of Delhi,
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam)
 (Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
PY208 Matter & Interactions Final Exam S2005
 PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
LawsoftheElectroElectricalInduction
 Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing: F Elecical and Eleconics Engineeing Volume 15 Issue 9 Vesion 1. Yea 15 Type: Double Blind Pee Reviewed Inenaional Reseach Jounal Publishe: Global Jounals Inc.
Global Jounal of Reseaches in Engineeing: F Elecical and Eleconics Engineeing Volume 15 Issue 9 Vesion 1. Yea 15 Type: Double Blind Pee Reviewed Inenaional Reseach Jounal Publishe: Global Jounals Inc.
4. Electric field lines with respect to equipotential surfaces are
 Pre-es Quasi-saic elecromagneism. The field produced by primary charge Q and by an uncharged conducing plane disanced from Q by disance d is equal o he field produced wihou conducing plane by wo following
Pre-es Quasi-saic elecromagneism. The field produced by primary charge Q and by an uncharged conducing plane disanced from Q by disance d is equal o he field produced wihou conducing plane by wo following
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read sections 25.4 & 25.5, the introduction to chapter 26 and sections 26.1 to 26.2 & 26.4.
 PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
Energy dispersion relation for negative refraction (NR) materials
 Enegy dispesion elaion fo negaive efacion (NR) maeials Y.Ben-Ayeh Physics Depamen, Technion Isael of Technology, Haifa 3, Isael E-mail addess: ph65yb@physics.echnion,ac.il; Fax:97 4 895755 Keywods: Negaive-efacion,
Enegy dispesion elaion fo negaive efacion (NR) maeials Y.Ben-Ayeh Physics Depamen, Technion Isael of Technology, Haifa 3, Isael E-mail addess: ph65yb@physics.echnion,ac.il; Fax:97 4 895755 Keywods: Negaive-efacion,
FARADAY'S LAW. dates : No. of lectures allocated. Actual No. of lectures 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09
 FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
Chapter 3 Optical Systems with Annular Pupils
 Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law
 Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
 Pepaed by: M. S. KumaSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - - ELECTROSTATICS MARKS WEIGHTAGE 8 maks QUICK REVISION (Impotant Concepts & Fomulas) Chage Quantization: Chage is always in the fom of an integal multiple
Pepaed by: M. S. KumaSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - - ELECTROSTATICS MARKS WEIGHTAGE 8 maks QUICK REVISION (Impotant Concepts & Fomulas) Chage Quantization: Chage is always in the fom of an integal multiple
Chapter 10 INDUCTANCE Recommended Problems:
 Chaper 0 NDUCTANCE Recommended Problems: 3,5,7,9,5,6,7,8,9,,,3,6,7,9,3,35,47,48,5,5,69, 7,7. Self nducance Consider he circui shown in he Figure. When he swich is closed, he curren, and so he magneic field,
Chaper 0 NDUCTANCE Recommended Problems: 3,5,7,9,5,6,7,8,9,,,3,6,7,9,3,35,47,48,5,5,69, 7,7. Self nducance Consider he circui shown in he Figure. When he swich is closed, he curren, and so he magneic field,
Field due to a collection of N discrete point charges: r is in the direction from
 Physcs 46 Fomula Shee Exam Coulomb s Law qq Felec = k ˆ (Fo example, f F s he elecc foce ha q exes on q, hen ˆ s a un veco n he decon fom q o q.) Elecc Feld elaed o he elecc foce by: Felec = qe (elecc
Physcs 46 Fomula Shee Exam Coulomb s Law qq Felec = k ˆ (Fo example, f F s he elecc foce ha q exes on q, hen ˆ s a un veco n he decon fom q o q.) Elecc Feld elaed o he elecc foce by: Felec = qe (elecc
- If one knows that a magnetic field has a symmetry, one may calculate the magnitude of B by use of Ampere s law: The integral of scalar product
 11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
 Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Inenaional Jounal of Science, Technology & Managemen Volume No 04, Special Issue No. 0, Mach 205 ISSN (online): 2394-537 STUDY OF THE STRESS-STRENGTH RELIABILITY AMONG THE PARAMETERS OF GENERALIZED INVERSE
Ch 30 - Sources of Magnetic Field! The Biot-Savart Law! = k m. r 2. Example 1! Example 2!
 Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
Ch 30 - Souces of Magnetic Field 1.) Example 1 Detemine the magnitude and diection of the magnetic field at the point O in the diagam. (Cuent flows fom top to bottom, adius of cuvatue.) Fo staight segments,
Monochromatic Wave over One and Two Bars
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 204, no. 6, 307-3025 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikai.com hp://dx.doi.og/0.2988/ams.204.44245 Monochomaic Wave ove One and Two Bas L.H. Wiyano Faculy of Mahemaics and Naual Sciences,
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
( ) Make-up Tests. From Last Time. Electric Field Flux. o The Electric Field Flux through a bit of area is
 Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
Mon., 3/23 Wed., 3/25 Thus., 3/26 Fi., 3/27 Mon., 3/30 Tues., 3/31 21.4-6 Using Gauss s & nto to Ampee s 21.7-9 Maxwell s, Gauss s, and Ampee s Quiz Ch 21, Lab 9 Ampee s Law (wite up) 22.1-2,10 nto to
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics. Appendix. DC Circuits Capacitors and Inductors AC Circuits Operational Amplifiers
 Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
Universiy of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Opics Appendix DC Circuis Capaciors and Inducors AC Circuis Operaional Amplifiers Circui Elemens An elecrical circui consiss of circui elemens such as
Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points]
![Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points] Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points]](/thumbs/88/115221528.jpg) Name: Toal Poins: (Las) (Firs) Muliple choice quesions [1 poins] Answer all of he following quesions. Read each quesion carefully. Fill he correc bubble on your scanron shee. Each correc answer is worh
Name: Toal Poins: (Las) (Firs) Muliple choice quesions [1 poins] Answer all of he following quesions. Read each quesion carefully. Fill he correc bubble on your scanron shee. Each correc answer is worh
The physics of induction stoves
 The physics of uction stoves This is an aticle fom my home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Contents 1. What is an uction stove...1. Including self-uctance...4 3. The contibution fom the magnetic moments...6
The physics of uction stoves This is an aticle fom my home page: www.olewitthansen.dk Contents 1. What is an uction stove...1. Including self-uctance...4 3. The contibution fom the magnetic moments...6
PHYS 1444 Lecture #5
 Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
Phys-272 Lecture 17. Motional Electromotive Force (emf) Induced Electric Fields Displacement Currents Maxwell s Equations
 Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
Phys-7 Lectue 17 Motional Electomotive Foce (emf) Induced Electic Fields Displacement Cuents Maxwell s Equations Fom Faaday's Law to Displacement Cuent AC geneato Magnetic Levitation Tain Review of Souces
EM-2. 1 Coulomb s law, electric field, potential field, superposition q. Electric field of a point charge (1)
 EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
Potential Energy. The change U in the potential energy. is defined to equal to the negative of the work. done by a conservative force
 Potential negy The change U in the potential enegy is defined to equal to the negative of the wok done by a consevative foce duing the shift fom an initial to a final state. U = U U = W F c = F c d Potential
Potential negy The change U in the potential enegy is defined to equal to the negative of the wok done by a consevative foce duing the shift fom an initial to a final state. U = U U = W F c = F c d Potential
Direct Current Circuits. February 19, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 26 1
 Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Sharif University of Technology - CEDRA By: Professor Ali Meghdari
 Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
SUMMARY GENERAL STRATEGY IMPORTANT CONCEPTS APPLICATIONS. Problem Solving. Motion Diagrams. Pictorial Representation
 The goal of Chape 1 has been o inoduce he fundamenal conceps of moion. GENERL STRTEGY Moion Diagams Help visualize moion. Povide a ool fo finding acceleaion vecos. Dos show posiions a equal ime inevals.
The goal of Chape 1 has been o inoduce he fundamenal conceps of moion. GENERL STRTEGY Moion Diagams Help visualize moion. Povide a ool fo finding acceleaion vecos. Dos show posiions a equal ime inevals.
Hall effect. Formulae :- 1) Hall coefficient RH = cm / Coulumb. 2) Magnetic induction BY 2
 Page of 6 all effec Aim :- ) To deermine he all coefficien (R ) ) To measure he unknown magneic field (B ) and o compare i wih ha measured by he Gaussmeer (B ). Apparaus :- ) Gauss meer wih probe ) Elecromagne
Page of 6 all effec Aim :- ) To deermine he all coefficien (R ) ) To measure he unknown magneic field (B ) and o compare i wih ha measured by he Gaussmeer (B ). Apparaus :- ) Gauss meer wih probe ) Elecromagne
The shortest path between two truths in the real domain passes through the complex domain. J. Hadamard
 Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Complex Analysis R.G. Halbud R.Halbud@ucl.ac.uk Depamen of Mahemaics Univesiy College London 202 The shoes pah beween wo uhs in he eal domain passes hough he complex domain. J. Hadamad Chape The fis fundamenal
Exam 3, vers Physics Spring, 2003
 1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
copper ring magnetic field
 IB PHYSICS: Magneic Fields, lecromagneic Inducion, Alernaing Curren 1. This quesion is abou elecromagneic inducion. In 1831 Michael Faraday demonsraed hree ways of inducing an elecric curren in a ring
IB PHYSICS: Magneic Fields, lecromagneic Inducion, Alernaing Curren 1. This quesion is abou elecromagneic inducion. In 1831 Michael Faraday demonsraed hree ways of inducing an elecric curren in a ring
[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u
![[ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u [ ] 0. = (2) = a q dimensional vector of observable instrumental variables that are in the information set m constituents of u](/thumbs/89/100187624.jpg) Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
Genealized Mehods of Momens he genealized mehod momens (GMM) appoach of Hansen (98) can be hough of a geneal pocedue fo esing economics and financial models. he GMM is especially appopiae fo models ha
EN221 - Fall HW # 7 Solutions
 EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
EN221 - Fall2008 - HW # 7 Soluions Pof. Vivek Shenoy 1.) Show ha he fomulae φ v ( φ + φ L)v (1) u v ( u + u L)v (2) can be pu ino he alenaive foms φ φ v v + φv na (3) u u v v + u(v n)a (4) (a) Using v
The k-filtering Applied to Wave Electric and Magnetic Field Measurements from Cluster
 The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
The -fileing pplied o Wave lecic and Magneic Field Measuemens fom Cluse Jean-Louis PINÇON and ndes TJULIN LPC-CNRS 3 av. de la Recheche Scienifique 4507 Oléans Fance jlpincon@cns-oleans.f OUTLINS The -fileing
Design Guideline for Buried Hume Pipe Subject to Coupling Forces
 Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
Design Guideline fo Buied Hume Pipe Sujec o Coupling Foces Won Pyo Hong 1), *Seongwon Hong 2), and Thomas Kang 3) 1) Depamen of Civil, nvionmenal and Plan ngineeing, Chang-Ang Univesiy, Seoul 06974, Koea
