Dynamical Economic model in a finite world Christophe Goupil 1, Eric Herbert 1, Yves D'Angelo 1, Quentin Couix 2 1
|
|
|
- Rudolf Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dynamical Economic model in a finite world Christophe Goupil 1, Eric Herbert 1, Yves D'Angelo 1, Quentin Couix 2 1 DyCoE Team, Laboratoire des Energies de Demain, LIED, UMR 8236, Université Paris Diderot 2 Université Paris Sorbonne Ecoles des Houches 10 mars 2016 christophe.goupil@univ-paris-diderot.fr
2 Including, or not, the ressources Perpetual motion et al... Glucina et al Hall et al Berg et al. 2015
3 Economics What do we learn from mechanics? What do we learn from equilibrium thermodynamics? What do we learn from out of equilibrium thermodynamics? Does economics have something to do with thermodynamics? A model where few things matter: (conservation, friction, rate )
4 Economics IS Mechanics!...? and Herman Laurent wrote to Léon Walras. (about the integrability of the model)
5 Economics ARE Thermodynamics!...?
6 Equilibrium thermodynamics: Callen approach
7 General structure
8 Thermodynamics
9 Economics
10 Thermoelastic coefficients & Elasticities Is there an Economic material?
11 Debreu: Job is done.really? So, in other words: The economics "material" is defined by the laws acting on...the economic "material The economics laws are derived from the measurements made on the economics material which is defined by the same laws that define.
12 Partial conclusion 1. Economics do not have the structure of thermodynamics. 2. There is no problem with doing local optimization until we don t claim it is GENERAL. 3. There is no fundamental equation for the economy, nor variational principle (hopefully) 4. There is no ergodicity. 5. T, P are emerging properties, are there any in economics? Commodity space GENERAL EQUILIBRIUM And.Economic systems are not equilibrium systems!
13 Out of equilibrium: Schumpeter
14 The Roegen assumption: «matter matters too» The far out of equilibrium assumption is ok, but there is no need of a fourth thermodynamics principle for matter.
15 Money temperature (Yakovenko 2009) There is no problem with such a definition, but why should we call it temperature and not simply the average value of the money carried by agents? AND! There is no emerging quantity
16 «Well-lit roads and burned bridges» (Glucina & Mayumi 2010) "The fact that there are no known exceptions to the laws of thermodynamics should be incorporated into the axiomatic foundation of economics."(underwood 1989) "Real financial markets cannot behave thermodynamically" because "financial markets are unstable, they do not approach statistical equilibrium, nor are there any available topological invariants on which to base a purely formal statistical mechanics." (Mc Caulley 2003) "If economics is to be considered as a science-based discipline, the principles of physical science, including the laws of thermodynamics, must be appropriately applied." (Wallace 2009) "We need to begin to incorporate energy and entropy thinking into economics."(kummel 2011)
17 The use of thermodynamics in Economics Conservative laws (no full substitutability) Non conservation of some physical quantities (utility...) Difference between extensive and intensive physical quantities Intensive physical quantities are the potentials from which we can derive forces Intensive physical quantities are the potentials that give a possible measurement of the quality There is no economic entropy but we can consider quantity and quality approach (general exergy) Give up the full thermodynamic paradigm (Integrability, Equation of state...) Time does matter BUT, there is no variational principle in out-of-equilibrium systems
18 Time does matter: a mechanical description (Odum & Pinkerton 1955) (Hall 1994) Efficiency is not restricted to pure thermodynamic description.
19 Odum-Pinkerton, Yvon, Chambadal, Novikov, Curzon & Ahlborn T hot Work Finite Time Thermodynamics FTT T hot Power Endoreversible T cold T cold C W 1 Q in T T cold hot P P max η CA η Carnot η CA W Q in 1 T T cold hot J. Yvon, The saclay Reactor: Two Years of Experience in the Use of a Compresed gas as a Heat Transfer Agent, Proceedings of the International Conference on the Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy (1955) P. Chambadal Les centrales nucléaires. Armand Colin, Paris, France, , (1957) I.I. Novikov, Efficiency of an Atomic Power Generation Installation, Atomic Energy 3 (1957) F.L. Curzon & B. Ahlborn, Efficiency of a Carnot Engine at Maximum Power Output, Am. J. Phys. 43 (1975) For a review, see Ouerdane et al.., Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 224, (2015) The position of the point on the curve is defined by the intensity parameter which governs the output.
20 Efficiency or Power? Irreversibilities included Friction Leak: natural degradation Low friction Source P R High friction DP P PH Production F PH Output Carnot P PL F PH «More is not always better» P S Sink Goupil et al. 2012
21 Efficiency or power : (small DP change) friction leak friction + leak restricted access to ressources friction + leak+ restricted access to ressources
22 Hall et al The Lego brick
23 The Lego brick description Internal parameters: Total ressource X T Frictions: R Coupling terms: a Natural recycling: F NR M=R in /R load Inputs: demands Production (Leontief PC) Recycling (Leontief PR) Outputs: Prod output: W PCout Recycling flux Safe: M>>1 2 Max Eff: M=(1+Z) 0.5 Max Prod: M=1 3 Unsafe: M<1 4 Healt parameter: M
24 Complete system
25 Complete system (small DP change) M 2 M 1 K
26 Smell test
27 Smell test: recycling increased
28 Conclusions 1. Economics do not have the structure of thermodynamics. 2. There is no economic entropy but quantity and quality approaches are possible 3. There is no fundamental equation for economy (hopefully) 4. There is no ergodicity. 5. Economic system are not equilibrium systems. There is no problem with doing local optimization until we don t claim it is GENERAL. 1. Conservative laws (non full substitutable) 2. Non conservation of some physical quantities (utility...) 3. Difference between extensive and intensive physical quantities 4. Intensive physical quantities are the potentials from which we can derive forces 5. Give up the full thermodynamic paradigm (Integrability, Equation of state...) 6. Time does matter BUT, there is no variational principle in out of equilibrium systems
29 References Walras 1909: Walras Léon Économique et Mécanique, Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise de Sciences Naturelles Vol. 45, p Soddy 1911: Soddy, Frederick. (1911). Matter and Energy (pgs ). H. Holt and Co. Soddy 1920: Soddy, Frederick. (1920). Science and Life, New York: Dutton. Soddy 1921: Soddy, Frederick. (1921). "Cartesian Economics: the Bearing of Physical Science upon Start Stewardship. Wilson 1938: Wilson, Edwin. (1938). "Letter to Paul Samuelson", Dec 30. Gibbs 1876: Willard Gibbs, (1876): "Internal Stability of Homogeneous Fluids as indicated by Fundamental Equations Samuelson 1947: Samuelson P. A. (1947), Foundation of Economic Analysis (Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press) Samuelson 1960: Samuelson, Paul A. (1960). "Structure of a minimum equilibrium system Debreu 1984: G. Debreu, Théorie de la valeur. Une analyse axiomatique de l'équilibre économique, Paris, Dunod, 1984 Schumpeter 1939: Business Cycles: A Theoretical, Historical and Statistical Analysis of the Capitalist Process, 1939 Yakovenko 2009: Victor M. Yakovenko and J. Barkley Rosser, Jour. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, Roegen 1971: Georgescu-Roegen, Nicholas. (1971). The Entropy Law and the Economic Process. Cambridge, Massachusetts. Ayres 1999: Robert Ayres, The second law, the fourth law, recycling and limits to growth, Ecological Economics, vol. 29, n 3, p Underwood 1989: Underwood, D. A. and King, P. G. (1989). "On the Ideological Found. of Environ. Policy", Ecological Economics 1: 324 Mc Cauley 2003: McCauley, Joseph L. (2003). "Thermo. Analogies in Eco. and Finance " Physica A, 329 (2003): Wallace 2009: Wallace, Thomas P. (2009). the Dynamics of Decaying Civilizations from Ancient Greece to America (pg. 31). AuthorHouse. Kummel 2011: Kummel, Reiner. (2011). The Second Law of Economics: Energy, Entropy, and the Origins of Wealth. Lotka 1922: A.J.Lotka (1922) 'Contribution to the energetics of evolution'. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 8. Odum 1955: H.T.Odum and R.C.Pinkerton (1955) 'Time's speed regulator., Am. Sci., 43 pp
30 Out of equilibrium thermodynamics references H. Ouerdane, Y. Apertet, C. Goupil, and Ph. Lecoeur, Continuity and boundary conditions in thermodynamics: From Carnot s efficiency to efficiencies at maximum power,eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 224, (2015) H. Ouerdane, A. A. Varlamov, A. V. Kavokin, C. Goupil, and C. B. Vining, Enhanced thermoelectric coupling near electronic phase transition: the rôle of fluctuation Cooper pairs, Physical Review B 91, (R) (2015) Y. Apertet, H. Ouerdane, C. Goupil, and Ph. Lecoeur, Influence of thermal environment on optimal working conditions of thermoelectric generators, J. Appl. Phys. 116, (2014) Y. Apertet, H. Ouerdane, C. Goupil, and Ph. Lecoeur, On the distinction between maximum power and maximum efficiency working conditions for thermoelectric generators, Journal of Applied Physics 116, (2014) Y. Apertet, H. Ouerdane, C. Goupil, and Ph. Lecoeur, Efficiency at maximum power of thermally coupled heat engines, Physical Review E vol. 85, (2012) Y. Apertet, H. Ouerdane, C. Goupil, and Ph. Lecoeur, Irreversibilities and efficiency at maximum power of heat engines: The illustrative case of a thermoelectric generator, Physical Review E vol. 85, (2012) Y. Apertet, H. Ouerdane, C. Goupil, and Ph. Lecoeur, Thermoelectric internal current loops inside inhomogeneous systems, Physical Review B vol. 85, (2012). Y. Apertet, H. Ouerdane, O. Glavatskaya, C. Goupil and Ph. Lecoeur, Optimal working conditions for thermoelectric generators with realistic thermal coupling, Europhysics Letters vol. 97, (2012)
31 Utility: Locally ok but is global optimization possible? U t The integrability question
32 Neoclassical Economy According to the feasibility study, it is feasible, but, According to the idiotability studies it is absolutely idiot.
What Thermodynamics can teach us about Economy : theory and practice
 What Thermodynamics can teach us about Economy : theory and practice Christophe Goupil, Éric Herbert, Yves D'Angelo, Aurélie-Louis Napoléon, Gael Giraud École des Houches Science & Énergie mars 2018 eric.herbert@univ-paris-diderot.fr
What Thermodynamics can teach us about Economy : theory and practice Christophe Goupil, Éric Herbert, Yves D'Angelo, Aurélie-Louis Napoléon, Gael Giraud École des Houches Science & Énergie mars 2018 eric.herbert@univ-paris-diderot.fr
Ecole Thématique du CNRS en Thermoélectricité Approche Thermodynamique de la Thermoélectricité
 Ecole Thématique du CNRS en Thermoélectricité Approche Thermodynamique de la Thermoélectricité Christophe Goupil Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire des Energies de Demain, LIED Université Paris Diderot Part
Ecole Thématique du CNRS en Thermoélectricité Approche Thermodynamique de la Thermoélectricité Christophe Goupil Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire des Energies de Demain, LIED Université Paris Diderot Part
Efficiency at maximum power of thermally coupled heat engines
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 85, 041144 (2012) Efficiency at maximum power of thermally coupled heat engines Y. Apertet, 1,* H. Ouerdane, 2 C. Goupil, 3 and Ph. Lecoeur 1 1 Institut d Electronique Fondamentale, Université
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 85, 041144 (2012) Efficiency at maximum power of thermally coupled heat engines Y. Apertet, 1,* H. Ouerdane, 2 C. Goupil, 3 and Ph. Lecoeur 1 1 Institut d Electronique Fondamentale, Université
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF SOLAR DRIVEN HEAT ENGINE WITH INTERNAL IRREVERSIBILITIES UNDER MAXIMUM POWER AND POWER DENSITY CONDITION
 VO.1, NO.3, OCTOBER 2006 ISSN 1819-6608 PERFORMANCE ANASIS OF SOAR DRIVEN EAT ENGINE WIT INTERNA IRREVERSIBIITIES UNDER MAIMUM POWER AND POWER DENSIT CONDITION A. Biswas, K. M. Pandey and R. Deb Department
VO.1, NO.3, OCTOBER 2006 ISSN 1819-6608 PERFORMANCE ANASIS OF SOAR DRIVEN EAT ENGINE WIT INTERNA IRREVERSIBIITIES UNDER MAIMUM POWER AND POWER DENSIT CONDITION A. Biswas, K. M. Pandey and R. Deb Department
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 88, (2013)
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 88, 037 03) From local force-flux relationships to internal dissipations and their impact on heat engine performance: The illustrative case of a thermoelectric generator Y. Apertet,,*
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 88, 037 03) From local force-flux relationships to internal dissipations and their impact on heat engine performance: The illustrative case of a thermoelectric generator Y. Apertet,,*
Thermo-economics of an irreversible solar driven heat engine
 Advanced Computational Methods in eat Transfer I 2 Thermo-economics of an irreversible solar driven heat engine K. M. Pandey & R. Deb Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology,
Advanced Computational Methods in eat Transfer I 2 Thermo-economics of an irreversible solar driven heat engine K. M. Pandey & R. Deb Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology,
Thermal energy harvesting: thermomagnetic versus thermoelectric generator
 Thermal energy harvesting: thermomagnetic versus thermoelectric generator Morgan Almanza, Alexandre Pasko, A. Bartok, Frédéric Mazaleyrat, Martino Lobue To cite this version: Morgan Almanza, Alexandre
Thermal energy harvesting: thermomagnetic versus thermoelectric generator Morgan Almanza, Alexandre Pasko, A. Bartok, Frédéric Mazaleyrat, Martino Lobue To cite this version: Morgan Almanza, Alexandre
Introduction to Stochastic Thermodynamics: Application to Thermo- and Photo-electricity in small devices
 Université Libre de Bruxelles Center for Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems Introduction to Stochastic Thermodynamics: Application to Thermo- and Photo-electricity in small devices Massimiliano Esposito
Université Libre de Bruxelles Center for Nonlinear Phenomena and Complex Systems Introduction to Stochastic Thermodynamics: Application to Thermo- and Photo-electricity in small devices Massimiliano Esposito
Notes on Thermodynamics of Thermoelectricity - Collège de France - Spring 2013
 Notes on hermodynamics of hermoelectricity - Collège de France - Spring 2013 Antoine Georges (Dated: March 26, 2013) I. BASIC RANSPOR EQUAIONS General references on this section: books by Ashcroft-Mermin,
Notes on hermodynamics of hermoelectricity - Collège de France - Spring 2013 Antoine Georges (Dated: March 26, 2013) I. BASIC RANSPOR EQUAIONS General references on this section: books by Ashcroft-Mermin,
SUSTAINABLE EFFICIENCY OF FAR-FROM-EQUILIBRIUM SYSTEMS
 Interdisciplinary Description of Complex Systems 0() 57-65 0 SUSAINABLE EFFICIENCY OF FAR-FROM-EQUILIBRIUM SYSEMS Michel Moreau * Bernard Gaveau and Leonard S. Schulman 3 Laboratory for heoretical and
Interdisciplinary Description of Complex Systems 0() 57-65 0 SUSAINABLE EFFICIENCY OF FAR-FROM-EQUILIBRIUM SYSEMS Michel Moreau * Bernard Gaveau and Leonard S. Schulman 3 Laboratory for heoretical and
Quantifying Dissipation
 Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-915, Vol 2 (27) DOI: 11685/CSC6171 1 Quantifying Dissipation Karl Heinz Hoffmann Institut für Physik Technische Universität Chemnitz D-917 Chemnitz Germany Reversible
Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-915, Vol 2 (27) DOI: 11685/CSC6171 1 Quantifying Dissipation Karl Heinz Hoffmann Institut für Physik Technische Universität Chemnitz D-917 Chemnitz Germany Reversible
Received: 4 December 2005 / Accepted: 30 January 2006 / Published: 31 January 2006
 Entropy 2006, 8[1], 18-24 Entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.org/entropy/ Full paper Utility Function from Maximum Entropy Principle Amir H. Darooneh Sufi Institute, P.O.Box 45195-1547, Zanjan, Iran and Department
Entropy 2006, 8[1], 18-24 Entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.org/entropy/ Full paper Utility Function from Maximum Entropy Principle Amir H. Darooneh Sufi Institute, P.O.Box 45195-1547, Zanjan, Iran and Department
Macroeconomic models with physical and monetary dimension based on constrained dynamics
 Macroeconomic models with physical and monetary dimension based on constrained dynamics Oliver Richters Carl von Ossietzky University of Oldenburg with Jonathan Barth, Erhard Glötzl, Florentin Glötzl &
Macroeconomic models with physical and monetary dimension based on constrained dynamics Oliver Richters Carl von Ossietzky University of Oldenburg with Jonathan Barth, Erhard Glötzl, Florentin Glötzl &
Energy management at micro scales
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Energy management at micro scales Luca Gammaitoni ICT- Energy Training Day, Bristol 14 Sept. 2015 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content IntroducCon to the nocon of energy. Laws of
Corso di Laurea in FISICA Energy management at micro scales Luca Gammaitoni ICT- Energy Training Day, Bristol 14 Sept. 2015 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content IntroducCon to the nocon of energy. Laws of
Application of Finite-time Thermodynamics for Evaluation Method of Heat Engines
 Application of Finite-time Thermodynamics for Evaluation Method of Heat Engines IV International Seminar on ORC Power Systems, ORC2017 13-15 September 2017, Milano, Italy Takeshi Yasunaga and Yasuyuki
Application of Finite-time Thermodynamics for Evaluation Method of Heat Engines IV International Seminar on ORC Power Systems, ORC2017 13-15 September 2017, Milano, Italy Takeshi Yasunaga and Yasuyuki
Econoengineering and Economic Behavior: Particle, Atom, Molecule, or Agent Models?
 Econoengineering and Economic Behavior: Particle, Atom, Molecule, or Agent Models? Libb Thims 29 Jan 2013 University of Pitesti Econophysics and Sociophysics Workshop / Exploratory Domains of Econophysics
Econoengineering and Economic Behavior: Particle, Atom, Molecule, or Agent Models? Libb Thims 29 Jan 2013 University of Pitesti Econophysics and Sociophysics Workshop / Exploratory Domains of Econophysics
Quantum. Thermodynamic. Processes. Energy and Information Flow at the Nanoscale. Gunter Mahler. Pan Stanford J [f I Publishing
 Quantum Thermodynamic Processes Energy and Information Flow at the Nanoscale Gunter Mahler Pan Stanford J [f I Publishing Preface Acknowledgments xiii xv 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Effective Theories 2 1.2 Partitions
Quantum Thermodynamic Processes Energy and Information Flow at the Nanoscale Gunter Mahler Pan Stanford J [f I Publishing Preface Acknowledgments xiii xv 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Effective Theories 2 1.2 Partitions
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Nov 2015 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Nov 2015](/thumbs/86/93649485.jpg) Retainability of canonical distributions for a Brownian particle controlled by a time-dependent harmonic potential arxiv:1511.01993v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Nov 015 Geng Li and Z. C. Tu Department of Physics,
Retainability of canonical distributions for a Brownian particle controlled by a time-dependent harmonic potential arxiv:1511.01993v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 6 Nov 015 Geng Li and Z. C. Tu Department of Physics,
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
Thermodynamics for small devices: From fluctuation relations to stochastic efficiencies. Massimiliano Esposito
 Thermodynamics for small devices: From fluctuation relations to stochastic efficiencies Massimiliano Esposito Beijing, August 15, 2016 Introduction Thermodynamics in the 19th century: Thermodynamics in
Thermodynamics for small devices: From fluctuation relations to stochastic efficiencies Massimiliano Esposito Beijing, August 15, 2016 Introduction Thermodynamics in the 19th century: Thermodynamics in
A Brief Review of Econophysics
 J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.2 (3A), 286-291 (2012) A Brief Review of Econophysics B. G. SHARMA Department of Physics and Computer Science, Govt. Nagarjuna P.G. College of Science Raipur, C. G., INDIA.
J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.2 (3A), 286-291 (2012) A Brief Review of Econophysics B. G. SHARMA Department of Physics and Computer Science, Govt. Nagarjuna P.G. College of Science Raipur, C. G., INDIA.
Bounds on thermal efficiency from inference
 Bounds on thermal efficiency from inference Ramandeep S. Johal, Renuka Rai and Günter Mahler Department of Physical Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Mohali, Sector 81, S.A.S.
Bounds on thermal efficiency from inference Ramandeep S. Johal, Renuka Rai and Günter Mahler Department of Physical Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Mohali, Sector 81, S.A.S.
AC : MAPPING THE FOREST OF DATA IN THERMODYNAM- ICS
 AC 2011-234: MAPPING THE FOREST OF DATA IN THERMODYNAM- ICS Yumin Zhang, Southeast Missouri State University Yumin Zhang Assistant Professor Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Southeast Missouri
AC 2011-234: MAPPING THE FOREST OF DATA IN THERMODYNAM- ICS Yumin Zhang, Southeast Missouri State University Yumin Zhang Assistant Professor Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Southeast Missouri
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Jul 2012 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Jul 2012](/thumbs/92/110749172.jpg) arxiv:1204.0737v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Jul 2012 Internal convection in thermoelectric generator models Y Apertet 1, H Ouerdane 2, C Goupil 3,4 and Ph Lecœur 1 1 Institut d Electronique Fondamentale, Université
arxiv:1204.0737v2 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 2 Jul 2012 Internal convection in thermoelectric generator models Y Apertet 1, H Ouerdane 2, C Goupil 3,4 and Ph Lecœur 1 1 Institut d Electronique Fondamentale, Université
12 The Laws of Thermodynamics
 June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
Chap. 3 The Second Law. Spontaneous change
 Chap. 3 The Second Law Spontaneous change Some things happen naturally; some things don t. the spontaneous direction of change, the direction of change that does not require work to be done to bring it
Chap. 3 The Second Law Spontaneous change Some things happen naturally; some things don t. the spontaneous direction of change, the direction of change that does not require work to be done to bring it
Lagrange Principle and the Distribution of Wealth
 Lagrange Principle and the Distribution of Wealth J. Mimkes, G. Willis*, Physics Department, University of Paderborn, 3396 Paderborn, Germany mimkes@zitmail.uni-paderborn.de, *South Elmsall, W. Yorkshire,
Lagrange Principle and the Distribution of Wealth J. Mimkes, G. Willis*, Physics Department, University of Paderborn, 3396 Paderborn, Germany mimkes@zitmail.uni-paderborn.de, *South Elmsall, W. Yorkshire,
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
On Clean Cooling Systems for Wind Turbine Nacelle operating in Hot Climate
 International Conférence en Clean Cooling Technologiesin the ME NA Regions ICT3_MENA 201 Bou Smail, W. Tipaza, 5-6 October 2015 On Clean Cooling Systems for Wind Turbine Nacelle operating in Hot Climate
International Conférence en Clean Cooling Technologiesin the ME NA Regions ICT3_MENA 201 Bou Smail, W. Tipaza, 5-6 October 2015 On Clean Cooling Systems for Wind Turbine Nacelle operating in Hot Climate
Introduction to a few basic concepts in thermoelectricity
 Introduction to a few basic concepts in thermoelectricity Giuliano Benenti Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems Univ. Insubria, Como, Italy 1 Irreversible thermodynamic Irreversible thermodynamics
Introduction to a few basic concepts in thermoelectricity Giuliano Benenti Center for Nonlinear and Complex Systems Univ. Insubria, Como, Italy 1 Irreversible thermodynamic Irreversible thermodynamics
ECOLOGICAL ECONOMICS. (Year 3)
 ECOLOGICAL ECONOMICS (Year 3) Aims of the Course This course aims to give students an insight into the new and rapidly developing subject of Ecological Economics. It is particularly suited to those who
ECOLOGICAL ECONOMICS (Year 3) Aims of the Course This course aims to give students an insight into the new and rapidly developing subject of Ecological Economics. It is particularly suited to those who
Affiliation: The Australian National University, Canberra, Australia. Keywords: Economics, social science, interdisciplinarity, policy, sustainability
 Ecological Economics David I. Stern Crawford School of Economics and Government, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia. E-mail: david.stern@anu.edu.au. Phone: +61-2-6125-0176.
Ecological Economics David I. Stern Crawford School of Economics and Government, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia. E-mail: david.stern@anu.edu.au. Phone: +61-2-6125-0176.
On Economics and Energy
 Les Houches, 5. 9. 3.2018 On Economics and Energy Jürgen Mimkes, Physics Department Paderborn University, Germany Content Future Model Differential Forms and Line Integrals Accounting The Laws of Economics
Les Houches, 5. 9. 3.2018 On Economics and Energy Jürgen Mimkes, Physics Department Paderborn University, Germany Content Future Model Differential Forms and Line Integrals Accounting The Laws of Economics
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2005](/thumbs/88/114668987.jpg) Thermoeconomic analysis of an irreversible Stirling heat pump cycle arxiv:physics/0512182v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2005 Umberto Lucia I.T.I.S. A. Volta, Spalto Marengo 42, 15100 Alessandria, Italy Gianpiero
Thermoeconomic analysis of an irreversible Stirling heat pump cycle arxiv:physics/0512182v1 [physics.class-ph] 20 Dec 2005 Umberto Lucia I.T.I.S. A. Volta, Spalto Marengo 42, 15100 Alessandria, Italy Gianpiero
The efficiency at maximum power output of endoreversible engines under combined heat transfer modes
 The efficiency at maximum power output of endoreversible engines under combined heat transfer modes F. MOUKALLED, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Mechanical Engineering Department, American University
The efficiency at maximum power output of endoreversible engines under combined heat transfer modes F. MOUKALLED, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Mechanical Engineering Department, American University
Optimal quantum driving of a thermal machine
 Optimal quantum driving of a thermal machine Andrea Mari Vasco Cavina Vittorio Giovannetti Alberto Carlini Workshop on Quantum Science and Quantum Technologies ICTP, Trieste, 12-09-2017 Outline 1. Slow
Optimal quantum driving of a thermal machine Andrea Mari Vasco Cavina Vittorio Giovannetti Alberto Carlini Workshop on Quantum Science and Quantum Technologies ICTP, Trieste, 12-09-2017 Outline 1. Slow
Core equivalence and welfare properties without divisible goods
 Core equivalence and welfare properties without divisible goods Michael Florig Jorge Rivera Cayupi First version November 2001, this version May 2005 Abstract We study an economy where all goods entering
Core equivalence and welfare properties without divisible goods Michael Florig Jorge Rivera Cayupi First version November 2001, this version May 2005 Abstract We study an economy where all goods entering
Distributive Social Justice:
 Distributive Social Justice: Insights from a Doubly-Bounded Capital Exchange Model By: G.H. Boyle 20 th March ACS 2018 Screen shot from EiLab 1.40 at OpenABM A01 Taxonomy of Concerns 1. Sustainable Society
Distributive Social Justice: Insights from a Doubly-Bounded Capital Exchange Model By: G.H. Boyle 20 th March ACS 2018 Screen shot from EiLab 1.40 at OpenABM A01 Taxonomy of Concerns 1. Sustainable Society
Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them.
 What is market design? Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them. This requires different tools and ideas than neoclassical economics, which
What is market design? Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them. This requires different tools and ideas than neoclassical economics, which
FINITE TIME THERMODYNAMIC EVALUATION OF IRREVERSIBLE ERICSSON AND STIRLING HEAT PUMP CYCLES
 IV Minsk International Seminar eat Pipes, eat Pumps, Refrigerators Minsk, Belarus, September 47, 2000 FINIE IME ERMODYNAMIC EVAUAION OF IRREVERSIBE ERICSSON AND SIRING EA PUMP CYCES S. C. Kaushik, S. Kumar
IV Minsk International Seminar eat Pipes, eat Pumps, Refrigerators Minsk, Belarus, September 47, 2000 FINIE IME ERMODYNAMIC EVAUAION OF IRREVERSIBE ERICSSON AND SIRING EA PUMP CYCES S. C. Kaushik, S. Kumar
Mathematical models in economy. Short descriptions
 Chapter 1 Mathematical models in economy. Short descriptions 1.1 Arrow-Debreu model of an economy via Walras equilibrium problem. Let us consider first the so-called Arrow-Debreu model. The presentation
Chapter 1 Mathematical models in economy. Short descriptions 1.1 Arrow-Debreu model of an economy via Walras equilibrium problem. Let us consider first the so-called Arrow-Debreu model. The presentation
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, and Wealth
 Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, and Wealth Victor M. Yakovenko Adrian A. Dragulescu and A. Christian Silva Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://www2.physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics.html
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, and Wealth Victor M. Yakovenko Adrian A. Dragulescu and A. Christian Silva Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://www2.physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics.html
Thermodynamic Modeling and Performance Analysis of an Atkinson cycle under Efficient Power Density Condition
 International Journal of Thermal Technologies E-ISSN 2277 4114 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijtt/ Research Article Thermodynamic Modeling and Performance
International Journal of Thermal Technologies E-ISSN 2277 4114 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijtt/ Research Article Thermodynamic Modeling and Performance
Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
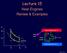 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Halesworth U3A Science Group
 Halesworth U3A Science Group Thermodynamics Or Why Things are How They Are Or Why You Can t Get Something For Nothing Ken Derham Includes quotations from publicly available internet sources Halesworth
Halesworth U3A Science Group Thermodynamics Or Why Things are How They Are Or Why You Can t Get Something For Nothing Ken Derham Includes quotations from publicly available internet sources Halesworth
Received: 16 December 2002 / Accepted: 18 June 2003 / Published: 31 December 2003
 Entropy 2003, 5, 377-390 377 Entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.org/entropy/ Full Paper Ecological Optimization and Parametric Study of an Irreversible Regenerative Modified Brayton Cycle with Isothermal
Entropy 2003, 5, 377-390 377 Entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.org/entropy/ Full Paper Ecological Optimization and Parametric Study of an Irreversible Regenerative Modified Brayton Cycle with Isothermal
Efficiency at Maximum Power in Weak Dissipation Regimes
 Efficiency at Maximum Power in Weak Dissipation Regimes R. Kawai University of Alabama at Birmingham M. Esposito (Brussels) C. Van den Broeck (Hasselt) Delmenhorst, Germany (October 10-13, 2010) Contents
Efficiency at Maximum Power in Weak Dissipation Regimes R. Kawai University of Alabama at Birmingham M. Esposito (Brussels) C. Van den Broeck (Hasselt) Delmenhorst, Germany (October 10-13, 2010) Contents
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VII: Equilibrium in a Competitive Market
 Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VII: Equilibrium in a Competitive Market Kai Hao Yang 10/31/2017 1 Partial Equilibrium in a Competitive Market In the previous lecture, e derived the aggregate
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VII: Equilibrium in a Competitive Market Kai Hao Yang 10/31/2017 1 Partial Equilibrium in a Competitive Market In the previous lecture, e derived the aggregate
Trade with differences in technologies
 4D INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF IT AND COMMERCE ISSN-2319-104X @4dcrossconnect.com.Inc2013 www.4dinternationaljournal.com Volume3,Issue-2-2013 Trade with differences in technologies Abstract Ramarcha Kumar
4D INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF IT AND COMMERCE ISSN-2319-104X @4dcrossconnect.com.Inc2013 www.4dinternationaljournal.com Volume3,Issue-2-2013 Trade with differences in technologies Abstract Ramarcha Kumar
Question 1. (p p) (x(p, w ) x(p, w)) 0. with strict inequality if x(p, w) x(p, w ).
 University of California, Davis Date: August 24, 2017 Department of Economics Time: 5 hours Microeconomics Reading Time: 20 minutes PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION FOR THE Ph.D. DEGREE Please answer any three
University of California, Davis Date: August 24, 2017 Department of Economics Time: 5 hours Microeconomics Reading Time: 20 minutes PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION FOR THE Ph.D. DEGREE Please answer any three
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. However, the first law cannot explain certain facts about thermal
Local Stability Analysis of a Thermo-Economic Model of a Chambadal-Novikov-Curzon-Ahlborn Heat Engine
 Entropy 011, 13, 1584-1594; doi:10.3390/e13091584 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Local Stability Analysis of a Thermo-Economic Model of a Chambadal-Novikov-Curzon-Ahlborn
Entropy 011, 13, 1584-1594; doi:10.3390/e13091584 OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 1099-4300 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Article Local Stability Analysis of a Thermo-Economic Model of a Chambadal-Novikov-Curzon-Ahlborn
Uncertainty Per Krusell & D. Krueger Lecture Notes Chapter 6
 1 Uncertainty Per Krusell & D. Krueger Lecture Notes Chapter 6 1 A Two-Period Example Suppose the economy lasts only two periods, t =0, 1. The uncertainty arises in the income (wage) of period 1. Not that
1 Uncertainty Per Krusell & D. Krueger Lecture Notes Chapter 6 1 A Two-Period Example Suppose the economy lasts only two periods, t =0, 1. The uncertainty arises in the income (wage) of period 1. Not that
Gechstudentszone.wordpress.com. Chapter 6. Vittal.K
 Chapter 6 Vittal.K Leads Up To Second Law Of Thermodynamics Heat source T 1 Q +ve w possible. It is now clear that we can t construct a heat engine with just one +ve heat interaction. The above engine
Chapter 6 Vittal.K Leads Up To Second Law Of Thermodynamics Heat source T 1 Q +ve w possible. It is now clear that we can t construct a heat engine with just one +ve heat interaction. The above engine
arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 29 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 29 Jan 2019 arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 29 Jan 2019](/thumbs/96/127553874.jpg) arxiv:1708.03254v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 29 Jan 2019 Thermodynamics of metabolic energy conversion under muscle load Christophe Goupil Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire des Energies de Demain (LIED), CNRS
arxiv:1708.03254v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 29 Jan 2019 Thermodynamics of metabolic energy conversion under muscle load Christophe Goupil Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire des Energies de Demain (LIED), CNRS
Computational procedure for a time-dependent Walrasian price equilibrium problem
 Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-9015, Vol. 2 2007 DOI: 10.1685/CSC06159 Computational procedure for a time-dependent Walrasian price equilibrium problem M. B. DONATO 1 and M. MILASI 2 Department
Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-9015, Vol. 2 2007 DOI: 10.1685/CSC06159 Computational procedure for a time-dependent Walrasian price equilibrium problem M. B. DONATO 1 and M. MILASI 2 Department
International Journal of Physics Research and Applications. Tsirlin AM* and Sukin IA. Abstract. Introduction. Review Article
 Open Access International Journal of Physics Research and Applications Review Article Finite-time thermodynamics: Realizability domains of thermodynamic systems and P Salamon s problem of efficiency corresponding
Open Access International Journal of Physics Research and Applications Review Article Finite-time thermodynamics: Realizability domains of thermodynamic systems and P Salamon s problem of efficiency corresponding
DOES MINIMUM ENTROPY GENERATION RATE CORRESPOND TO MAXIMUM POWER OR OTHER OBJECTIVES?
 th Joint European hermodynamics onference Brescia, July -5, 3 DOES MINIMUM ENROPY GENERAION RAE ORRESPOND O MAXIMUM POWER OR OER OBJEIVES? FEID Michel Professeur, Université de orraine EMA, avenue de la
th Joint European hermodynamics onference Brescia, July -5, 3 DOES MINIMUM ENROPY GENERAION RAE ORRESPOND O MAXIMUM POWER OR OER OBJEIVES? FEID Michel Professeur, Université de orraine EMA, avenue de la
Efficiency of Inefficient Endoreversible Thermal Machines
 DOI 10.1007/s13538-015-0396-x STATISTICAL Efficiency of Inefficient Endoreversible Thermal Machines José P. Palao 1 Luis A. Correa 2 Gerardo Adesso 3 Daniel Alonso 1 Received: 30 July 2015 Sociedade Brasileira
DOI 10.1007/s13538-015-0396-x STATISTICAL Efficiency of Inefficient Endoreversible Thermal Machines José P. Palao 1 Luis A. Correa 2 Gerardo Adesso 3 Daniel Alonso 1 Received: 30 July 2015 Sociedade Brasileira
Energy, Exergy and Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics, Maximum power, Hierarchies, and Material cycles
 Energy, Exergy and Thermodynamics Thermodynamics, Maximum power, Hierarchies, and Material cycles Energy The joule is named after James Prescott Joule. As with all SI units whose names are derived from
Energy, Exergy and Thermodynamics Thermodynamics, Maximum power, Hierarchies, and Material cycles Energy The joule is named after James Prescott Joule. As with all SI units whose names are derived from
1. Second Law of Thermodynamics
 1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
1. Second Law of hermodynamics he first law describes how the state of a system changes in response to work it performs and heat absorbed. he second law deals with direction of thermodynamic processes
OPTIMUM COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE OF IRREVERSIBLE CARNOT MAGNETIC REFRIGERATOR
 OPTIMUM COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE OF IRREVERSIBLE CARNOT MAGNETIC REFRIGERATOR Aaditya Mishra 1, Govind Maheshwari 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of engineering & Technology, Devi
OPTIMUM COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE OF IRREVERSIBLE CARNOT MAGNETIC REFRIGERATOR Aaditya Mishra 1, Govind Maheshwari 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Institute of engineering & Technology, Devi
On entropy generation in thermoelectric devices
 Energy Conversion & Management 41 (2000) 891±914 www.elsevier.com/locate/enconman On entropy generation in thermoelectric devices R.Y. Nuwayhid a, *, F. Moukalled a, N. Noueihed b a Department of Mechanical
Energy Conversion & Management 41 (2000) 891±914 www.elsevier.com/locate/enconman On entropy generation in thermoelectric devices R.Y. Nuwayhid a, *, F. Moukalled a, N. Noueihed b a Department of Mechanical
arxiv: v1 [physics.app-ph] 16 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [physics.app-ph] 16 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [physics.app-ph] 16 Jan 2018](/thumbs/74/70063089.jpg) Maximization of the thermoelectric cooling of graded Peltier by analytical heat equation resolution. arxiv:181.5175v1 [physics.app-ph] 16 Jan 218 E. Thiébaut 1, C. Goupil 2, F. Pesty 1, Y. D Angelo 3,
Maximization of the thermoelectric cooling of graded Peltier by analytical heat equation resolution. arxiv:181.5175v1 [physics.app-ph] 16 Jan 218 E. Thiébaut 1, C. Goupil 2, F. Pesty 1, Y. D Angelo 3,
Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics
 Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics Contributions of Thomas Sargent and Christopher Sims, Nobel Laureates in Economics 2011. 1 1. Personal Background Thomas J. Sargent: PhD Harvard University
Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics Contributions of Thomas Sargent and Christopher Sims, Nobel Laureates in Economics 2011. 1 1. Personal Background Thomas J. Sargent: PhD Harvard University
10.2 PROCESSES 10.3 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMO/ENTROPY Student Notes
 10.2 PROCESSES 10.3 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMO/ENTROPY Student Notes I. THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS A. SYSTEMS AND SURROUNDING B. PV DIAGRAMS AND WORK DONE V -1 Source: Physics for the IB Diploma Study
10.2 PROCESSES 10.3 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMO/ENTROPY Student Notes I. THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS A. SYSTEMS AND SURROUNDING B. PV DIAGRAMS AND WORK DONE V -1 Source: Physics for the IB Diploma Study
Scarf Instability and Production: A Simulation
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Scarf Instability and Production: A Simulation Fukiharu, T., K.Imamura Faculty of Economics, Hiroshima
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Scarf Instability and Production: A Simulation Fukiharu, T., K.Imamura Faculty of Economics, Hiroshima
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/23 Housekeeping. Class organization. Website with notes and papers as no "Mas-Collel" in macro
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/23 Housekeeping. Class organization. Website with notes and papers as no "Mas-Collel" in macro
STUDY OF HANOI AND HOCHIMINH STOCK EXCHANGE BY ECONOPHYSICS METHODS
 Communications in Physics, Vol. 24, No. 3S2 (2014), pp. 151-156 DOI:10.15625/0868-3166/24/3S2/5011 STUDY OF HANOI AND HOCHIMINH STOCK EXCHANGE BY ECONOPHYSICS METHODS CHU THUY ANH, DAO HONG LIEN, NGUYEN
Communications in Physics, Vol. 24, No. 3S2 (2014), pp. 151-156 DOI:10.15625/0868-3166/24/3S2/5011 STUDY OF HANOI AND HOCHIMINH STOCK EXCHANGE BY ECONOPHYSICS METHODS CHU THUY ANH, DAO HONG LIEN, NGUYEN
Advanced Microeconomics
 Advanced Microeconomics Partial and General Equilibrium Giorgio Fagiolo giorgio.fagiolo@sssup.it http://www.lem.sssup.it/fagiolo/welcome.html LEM, Sant Anna School of Advanced Studies, Pisa (Italy) Part
Advanced Microeconomics Partial and General Equilibrium Giorgio Fagiolo giorgio.fagiolo@sssup.it http://www.lem.sssup.it/fagiolo/welcome.html LEM, Sant Anna School of Advanced Studies, Pisa (Italy) Part
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption
 Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption Victor M. Yakovenko Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA! http://physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics/
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption Victor M. Yakovenko Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA! http://physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics/
, an adiabatic expansion machine, an isothermal compression machine at T L
 The Direct Method from Thermodynamics with Finite Speed used for Performance Computation of quasi-carnot Irreversible Cycles IEvaluation of coefficient of performance and power for refrigeration machines
The Direct Method from Thermodynamics with Finite Speed used for Performance Computation of quasi-carnot Irreversible Cycles IEvaluation of coefficient of performance and power for refrigeration machines
Discussion Papers In Economics And Business
 Discussion Papers In Economics And Business An Axiomatic Characterization of the Price-Money Message Mechanism Ken Urai Hiromi Murakami Discussion Paper 15-31-Rev. Graduate School of Economics and Osaka
Discussion Papers In Economics And Business An Axiomatic Characterization of the Price-Money Message Mechanism Ken Urai Hiromi Murakami Discussion Paper 15-31-Rev. Graduate School of Economics and Osaka
Finite-Time Thermodynamics of Port-Hamiltonian Systems
 Finite-Time Thermodynamics of Port-Hamiltonian Systems Henrik Sandberg Automatic Control Lab, ACCESS Linnaeus Centre, KTH (Currently on sabbatical leave at LIDS, MIT) Jean-Charles Delvenne CORE, UC Louvain
Finite-Time Thermodynamics of Port-Hamiltonian Systems Henrik Sandberg Automatic Control Lab, ACCESS Linnaeus Centre, KTH (Currently on sabbatical leave at LIDS, MIT) Jean-Charles Delvenne CORE, UC Louvain
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Physics 207 Lecture 27. Lecture 26. Chapters 18, entropy and second law of thermodynamics Chapter 19, heat engines and refrigerators
 Goals: Lecture 26 Chapters 18, entropy and second law of thermodynamics Chapter 19, heat engines and refrigerators Reading assignment for Wednesday: Chapter 20. Physics 207: Lecture 27, Pg 1 Entropy A
Goals: Lecture 26 Chapters 18, entropy and second law of thermodynamics Chapter 19, heat engines and refrigerators Reading assignment for Wednesday: Chapter 20. Physics 207: Lecture 27, Pg 1 Entropy A
arxiv: v3 [quant-ph] 24 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v3 [quant-ph] 24 Nov 2014 arxiv: v3 [quant-ph] 24 Nov 2014](/thumbs/80/80813311.jpg) Optimal Performance of Endoreversible Quantum Refrigerators arxiv:108073v3 quant-ph] Nov 01 Luis A Correa, 1,, José P Palao,, 3 Gerardo Adesso, 1 and Daniel Alonso, 3 1 School of Mathematical Sciences,
Optimal Performance of Endoreversible Quantum Refrigerators arxiv:108073v3 quant-ph] Nov 01 Luis A Correa, 1,, José P Palao,, 3 Gerardo Adesso, 1 and Daniel Alonso, 3 1 School of Mathematical Sciences,
8.044 Lecture Notes Chapter 5: Thermodynamcs, Part 2
 8.044 Lecture Notes Chapter 5: hermodynamcs, Part 2 Lecturer: McGreevy 5.1 Entropy is a state function............................ 5-2 5.2 Efficiency of heat engines............................. 5-6 5.3
8.044 Lecture Notes Chapter 5: hermodynamcs, Part 2 Lecturer: McGreevy 5.1 Entropy is a state function............................ 5-2 5.2 Efficiency of heat engines............................. 5-6 5.3
THERMODYNAMICS THERMOSTATISTICS AND AN INTRODUCTION TO SECOND EDITION. University of Pennsylvania
 THERMODYNAMICS AND AN INTRODUCTION TO THERMOSTATISTICS SECOND EDITION HERBERT B. University of Pennsylvania CALLEN JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CONTENTS PART I GENERAL
THERMODYNAMICS AND AN INTRODUCTION TO THERMOSTATISTICS SECOND EDITION HERBERT B. University of Pennsylvania CALLEN JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CONTENTS PART I GENERAL
DRIVING FORCE IN SIMULATION OF PHASE TRANSITION FRONT PROPAGATION
 Chapter 1 DRIVING FORCE IN SIMULATION OF PHASE TRANSITION FRONT PROPAGATION A. Berezovski Institute of Cybernetics at Tallinn Technical University, Centre for Nonlinear Studies, Akadeemia tee 21, 12618
Chapter 1 DRIVING FORCE IN SIMULATION OF PHASE TRANSITION FRONT PROPAGATION A. Berezovski Institute of Cybernetics at Tallinn Technical University, Centre for Nonlinear Studies, Akadeemia tee 21, 12618
Vol. 119 (2011) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6
 Vol. 119 011) ACA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 Endoreversible Modeling and Optimization of a Multistage Heat Engine System with a Generalized Heat ransfer Law via Hamilton Jacobi Bellman Equations and Dynamic
Vol. 119 011) ACA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 6 Endoreversible Modeling and Optimization of a Multistage Heat Engine System with a Generalized Heat ransfer Law via Hamilton Jacobi Bellman Equations and Dynamic
Newtonian and Lagrangian Mechanics of a Production System
 Newtonian and Lagrangian Mechanics of a Production System Matti Estola 1 University of Eastern Finland, Department of Health and Social Management, P.O. Box 111, 80101 Joensuu Campus, Tel.: +358 50 4422068,
Newtonian and Lagrangian Mechanics of a Production System Matti Estola 1 University of Eastern Finland, Department of Health and Social Management, P.O. Box 111, 80101 Joensuu Campus, Tel.: +358 50 4422068,
Indeterminacy and Sunspots in Macroeconomics
 Indeterminacy and Sunspots in Macroeconomics Wednesday September 6 th : Lecture 5 Gerzensee, September 2017 Roger E. A. Farmer Warwick University and NIESR Topics for Lecture 5 Sunspots (Cass-Shell paper)
Indeterminacy and Sunspots in Macroeconomics Wednesday September 6 th : Lecture 5 Gerzensee, September 2017 Roger E. A. Farmer Warwick University and NIESR Topics for Lecture 5 Sunspots (Cass-Shell paper)
3.20 Exam 1 Fall 2003 SOLUTIONS
 3.0 Exam 1 Fall 003 SOLUIONS Question 1 You need to decide whether to work at constant volume or constant pressure. Since F is given, a natural choice is constant volume. Option 1: At constant and V :
3.0 Exam 1 Fall 003 SOLUIONS Question 1 You need to decide whether to work at constant volume or constant pressure. Since F is given, a natural choice is constant volume. Option 1: At constant and V :
OPTIMIZATION OF AN IRREVERSIBLE OTTO AND DIESEL CYCLES BASED ON ECOLOGICAL FUNCTION. Paraná Federal Institute, Jacarezinho, Paraná, Brasil.
 OPIMIZAION OF AN IRREVERSIBE OO AND DIESE CYCES BASED ON ECOOGICA FUNCION André. S. MOSCAO *, Santiago D. R. OIVEIRA, Vicente. SCAON, Alcides PADIA * Paraná Federal Institute, Jacarezinho, Paraná, Brasil.
OPIMIZAION OF AN IRREVERSIBE OO AND DIESE CYCES BASED ON ECOOGICA FUNCION André. S. MOSCAO *, Santiago D. R. OIVEIRA, Vicente. SCAON, Alcides PADIA * Paraná Federal Institute, Jacarezinho, Paraná, Brasil.
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption
 Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption Victor M. Yakovenko Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics/
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption Victor M. Yakovenko Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics/
The Ramsey Model. (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 2013)
 The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
Price Index Basics* (pg. 146 of Foundations of Economic Analysis)
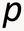 Price Index Basics* The fundamental problem upon which all the analysis rests is that of determining merely from price and quantity data which of two situations is higher up on an individual s preference
Price Index Basics* The fundamental problem upon which all the analysis rests is that of determining merely from price and quantity data which of two situations is higher up on an individual s preference
Physics 1501 Lecture 37
 Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Physics 1501: Lecture 37 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Midterm 2 in class Wednesday Friday: review session bring your questions Todays topics Chap.18: Heat and Work»
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption
 Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption Victor M. Yakovenko Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics/
Statistical Mechanics of Money, Income, Debt, and Energy Consumption Victor M. Yakovenko Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, USA http://physics.umd.edu/~yakovenk/econophysics/
Lecture 12 The Spatial Price Equilibrium Problem
 Lecture 12 The Spatial Price Equilibrium Problem Dr. Anna Nagurney John F. Smith Memorial Professor Isenberg School of Management University of Massachusetts Amherst, Massachusetts 01003 c 2009 Parallel
Lecture 12 The Spatial Price Equilibrium Problem Dr. Anna Nagurney John F. Smith Memorial Professor Isenberg School of Management University of Massachusetts Amherst, Massachusetts 01003 c 2009 Parallel
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Jul 2006
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Jul 2006 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Jul 2006](/thumbs/71/66037374.jpg) Geometry of Financial Markets Towards Information Theory Model of Markets Edward W. Piotrowski arxiv:physics/0607236v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Jul 2006 Institute of Mathematics, University of Bia lystok Lipowa
Geometry of Financial Markets Towards Information Theory Model of Markets Edward W. Piotrowski arxiv:physics/0607236v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Jul 2006 Institute of Mathematics, University of Bia lystok Lipowa
Laws of Thermodynamics
 Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
Laws of Thermodynamics The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - The first lawof thermodynamics, also called conservation of energy. We can use this knowledge to determine the amount of energy in a system, the
Performance Optimization of Generalized Irreversible Refrigerator Based on a New Ecological Criterion
 Entropy 213, 15, 5277-5291; doi:1.339/e15125277 Article OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 199-43 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Performance Optimization of Generalized Irreversible Refrigerator Based on a New Ecological
Entropy 213, 15, 5277-5291; doi:1.339/e15125277 Article OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 199-43 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Performance Optimization of Generalized Irreversible Refrigerator Based on a New Ecological
Lecture Notes Set 4c: Heat engines and the Carnot cycle
 ecture Notes Set 4c: eat engines and the Carnot cycle Introduction to heat engines In the following sections the fundamental operating principles of the ideal heat engine, the Carnot engine, will be discussed.
ecture Notes Set 4c: eat engines and the Carnot cycle Introduction to heat engines In the following sections the fundamental operating principles of the ideal heat engine, the Carnot engine, will be discussed.
The Core of a coalitional exchange economy
 The Core of a coalitional exchange economy Elena L. Del Mercato To cite this version: Elena L. Del Mercato. The Core of a coalitional exchange economy. Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques 2006.47
The Core of a coalitional exchange economy Elena L. Del Mercato To cite this version: Elena L. Del Mercato. The Core of a coalitional exchange economy. Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques 2006.47
Govind Maheshwari *, Roshan Raman
 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF AN ATKINSON CYCLE UNDER EFFICIENT POWER DENSITY CONDITION Govind Maheshwari *, Roshan Raman Associate
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF AN ATKINSON CYCLE UNDER EFFICIENT POWER DENSITY CONDITION Govind Maheshwari *, Roshan Raman Associate
ΔU = Q W. Tue Dec 1. Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM WALTER 145. Thermodynamics 1st Law. 2 nd Law. Heat Engines and Refrigerators
 Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
Lecture 1: Introduction to IO Tom Holden
 Lecture 1: Introduction to IO Tom Holden http://io.tholden.org/ Email: t.holden@surrey.ac.uk Standard office hours: Thursday, 12-1PM + 3-4PM, 29AD00 However, during term: CLASSES will be run in the first
Lecture 1: Introduction to IO Tom Holden http://io.tholden.org/ Email: t.holden@surrey.ac.uk Standard office hours: Thursday, 12-1PM + 3-4PM, 29AD00 However, during term: CLASSES will be run in the first
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
