Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 12-1 Introduction to Sequences
|
|
|
- Denis George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 12-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Finding Terms of a Sequence by Using a Recursive Formula Find the first five terms of each sequence. A. a n a n1 1, where n 2 and a 1 1 a 1 1 The first term is given. a 2 1 Substitute a 1 1 into the rule a n a n1 1 to find a 2. a 3 1 Repeat to find a 3. a 1 Repeat to find the next term. a 5 4 Repeat to find the fifth term. B. a n 3 a n1 1, where n 2 and a 1 1 a 1 1 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 12-1 Introduction to Sequences Vocabulary sequence infinite sequence finite sequence The first term is given. a 2 3(1) 1 Substitute a 1 1 into the rule a n 3 a n1 1 to find a 2. a 3 3( ) 1 Repeat to find a 3. a 3( ) 1 Repeat to find the next term. a 5 3(14) Repeat to find the fifth term. Finding Terms of a Sequence by Using the Explicit Formula Find the first three terms of each sequence. A. a n 2n 1, where n 1 a Let n 1. Substitute this value into the formula a n 2n 1 to find a 1. a 2 2( ) 1 Let n 2. Substitute this value into the formula a n 2n 1 to find a 2. a 3 2( ) 1 Let n 3. Substitute this value into the formula a n 2n 1 to find a 3. B. a n 3 n n, where n 1 a Let n 1. Substitute this value into the formula to find a 1. Repeat to find the remaining terms: a ; a Holt Algebra 2
2 Ready To Go On? Problem Solving Intervention 12-1 Introduction to Sequences A recursive formula is a rule to describe a sequence where one or more previous terms are used to generate the next term. Grace has an action figure from a popular science fiction movie still in its original packaging. It is currently worth $75. Action figures from this movie typically increase in value by about 7% a year. a. Write a recursive rule predicting the value of the figure each year. b. Use the recursive formula to predict the value of the figure in 10 years. Understand the Problem 1. What is the initial value of the figure? 2. Will the value of the figure increase or decrease? 3. By how much will the value increase each year? Make a Plan 4. What do you need to determine? 5. Let a n represent the value of the figure in year n. What symbol represents the value in the previous year? 6. By how much did the value of the figure increase in year n 1? 7. Write a recursive rule to model the value of the figure. Solve 8. Use the recursive rule to predict the value of the figure in 10 years. Look Back 9. You can check your solution by using an explicit formula. The explicit rule for this pattern is the same as the formula for compound interest. a n a 0 (1 r ) t 75(1 ) Does your answer check? 192 Holt Algebra 2
3 Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 12-2 and the Multilingual Glossary. Using Summation Notation Write this series using summation notation Find a rule for the k th term of the sequence. Look at the numerators: Each numerator is. Look at the denominators: Each denominator is the base to a power of 0, 1, 2, 3, and. Write the rule for the sequence: a k 5 Write the notation for the first five terms: k0 5 k Evaluating a Series The value of can be approximated by a partial sum of an infinite series. (1) k Expand the series 4 and evaluate. 2k 1 k0 Write out the first five terms Simplify each term Simplify. Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 12-2 Series and Summation Notation Vocabulary series summation notation infinite series Holt Algebra 2
4 Ready To Go On? Problem Solving Intervention 12-2 Series and Summation Notation A series can be represented by summation notation, indicated by, and then evaluated to find the sum of the series. A hot air balloon rises 30 m in the first minute. In each minute thereafter, the balloon rises 70% as far as it did the previous minute. How far does the balloon rise in 5 minutes? Understand the Problem 1. What is the initial height? 2. What is the height gain during the second minute? 3. What is the total height after the second minute? 4. What is the height gain during the third minute? 5. What is the total height after the third minute? Make a Plan 6. Write a rule that represents the height gain during the k th minute. 7. Write a summation that represents the total height after n minutes Solve 8. Use the summation to calculate the total height of the balloon after 5 minutes. Look Back 9. You can check your solution by using the formula for the sum of an infinite geometric series. For this series, r 0.70, which is less than, so it is a a 1 convergent series. The sum is: S n 1 r Since the result in Exercise 8 is less than the sum of the series, is your answer reasonable? 194 Holt Algebra 2
5 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 12-3 Arithmetic Sequences and Series Find this vocabulary word in Lesson 12-3 and the Multilingual Glossary. Identifying Arithmetic Sequences Determine whether the sequence, 5, 9, 13, 17,..., is arithmetic. If so, determine the common difference and the next term. Find the difference of the first two terms: 9 4 Find the difference of the next two terms: 13 Find the difference of the next two terms: Is the difference constant? Find the next term: 17 ; If so, what is the common difference? Vocabulary arithmetic series Finding the n th Term Given an Arithmetic Sequence Find the ninth term of the sequence: 7, 4, 9 2 2, 5, The formula for the n th term in a sequence is a n a 1 (n 1)d, where a 1 is the first term. What is a 1? What is n? Find the common difference: 7 2 Substitute d ; a 1 7 ; and n into the formula and solve. a (8) Finding the Sum of an Arithmetic Sequence Find the sum of the first 10 terms of the sequence: 7, 4, 9, 5, First find the 10th term of the sequence. What is a 1? What is n? What is the common difference: 7 2 Substitute known values into the formula to find the 10 th term: a ( 1) 1 2 The formula for the sum of the first n terms in an arithmetic sequence is S n n a 1 a n 2. Find S 10 : S n n a 1 a n Holt Algebra 2
6 Ready To Go On? Problem Solving Intervention 12-3 Arithmetic Sequences and Series Thanh has a college fund of $1200. He withdraws $10 from this fund the first week of college and increases the withdrawal amount by $10 each week as his expenses increase. If Thanh then withdraws $150 from his account and his statement shows an account balance of $0, how many weeks have passed? Understand the Problem 1. Is this an arithmetic series? Explain. 2. What is the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series? 3. What is the unknown in this problem? Make a Plan 4. What is the first term in the series? 5. What is the arithmetic difference? 6. What is the last term in the series? 7. Solve the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series for n. Solve 8. Substitute the known values into the formula and solve for n. 2 S n n a 1 a 2 n 9. How many weeks have passed for Thanh to now have an account balance of $0? Look Back 10. Use another method to check your solution: Write out the first 15 terms of the series, then find the sum of all 15 terms. 11. Is your solution the same using both methods: the series formula in Exercise 8 and adding up the terms of the series in Exercise 11? 196 Holt Algebra 2
7 Ready To Go On? Quiz 12-1 Introduction to Sequences Find the first five terms of each sequence. 1. a n (2 ) n 2. a n n 5 3. a n n n 1 4. a n a n1 1, a A piece of paper is 0.03 mm thick. It is torn in two equal pieces and stacked. The stack is torn in two and stacked again. The process is repeated 5 times. How thick is the pile? Write an explicit rule for the n th term of each sequence. 6. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, , 6, 13, 22, 33, 8. 4, 1, 4, 11, 20, , 4 25, 5 36, 6 49, Series and Summation Notation Write the following sums using summation notation Holt Algebra 2
8 Expand and evaluate each series n1 Ready To Go On? Quiz continued n 2n n3 1 2 n 14. Bowling pins are set up so that the first row has one pin and each subsequent row has one more pin than the previous. There are four rows. Use summation notion to write an expression for the number of bowling pins. Evaluate the expression Arithmetic Sequences and Series Find the eighth term of each arithmetic sequence , 21.5, 30, 38.5, 47, , 7, 19, 31,... Find the missing terms in each arithmetic sequence , 6,,,, 14, 19, , 18, 27,,, 54, 63,... Find the indicated sum for each series , 9, 13, 17, (5n 2) S Honus loves to collect baseball cards. His younger brother Ty decides to give him baseball cards for his birthday. As a surprise, Ty plans to give Honus only two cards today, but then give four cards tomorrow, six cards the day after, and continue the sequence for one week. What is the total number of cards Ty gives to Honus? n1 198 Holt Algebra 2
9 Ready To Go On? Enrichment Physics and Sequences It is easy to make a simple device that will demonstrate Galileo s rule for falling objects. If small weights are tied to a cord so that the distances between the weights has the following pattern, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, then when the string is dropped, the time interval between when the weights hit the ground will be the same for all weights. To see why, complete this table. Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Weight Number Distance to Next Weight Total Distance 1 1 unit 1 unit 2 3 units 4 units 3 5 units 4 7 units 5 9 units Use the table to answer each question. 1. Are the numbers in Column 2 an arithmetic series? If so, calculate d. 2. Are the numbers in Column 3 an arithmetic series? If so, calculate d. 3. Write an explicit rule for the numbers in Column Write an explicit rule for the numbers in Column The formula for distance traveled as a function of time, according to Galileo (using modern notation), is d 1 2 a t 2, where a is a constant quantity called acceleration and t is time. In the table, which column of numbers represents time? 199 Holt Algebra 2
10 12B Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 12-4 Geometric Sequences and Series Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 12-4 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary geometric sequence geometric series geometric means Identifying Geometric Sequences Determine if each sequence is arithmetic or geometric. If it is arithmetic, find the common difference. If it is geometric, find the common ratio. A. 7, 3, 1, 5, 9, 13, , 9 Find the difference between two pairs of successive terms. 5 9, Find the ratio of two pairs of successive terms. Is the sequence arithmetic or geometric? Is there a common difference or common ratio? What is it? B. 1 3, 1 12, 1 48, , Find the difference between two pairs of successive terms. 1 1, Find the ratio of two pairs of successive terms. Is the sequence arithmetic or geometric? Is there a common difference or common ratio? What is it? Finding the n th term Given a Geometric Sequence Find the 8th term of a geometric sequence if a 1 16 and r 0.5. a n a 1 r n1 Write the formula for geometric sequence. a n (0.5) Substitute known values and evaluate. 1 The 8 th term in the sequence is Holt Algebra 2
11 12B Ready To Go On? Problem Solving Intervention 12-4 Geometric Sequences and Series Each term in a geometric sequence is the product of the previous term and the common ratio. Carlos planted three tomato plants. He exposed the plants to artificial light for 12 hours per day and measured their height each week. His measurements showed that the plants increased in height by an average of 8% per week. The average initial height of the three plants was 22 cm. Predict the average height of the plants at the end of 10 weeks. Understand the Problem 1. Does the measured height of the plants form a geometric series? Explain. 2. What formula gives the n th term of a geometric sequence? 3. What is the first term of the sequence? 4. What is the second term of the sequence? 5. What is the common ratio? Make a Plan 6. In the expression for the n th term of a geometric sequence, what are the known values? 7. In the expression for the n th term of a geometric sequence, what is the unknown value? Solve 8. Substitute the appropriate values into the geometric sequence formula. 9. Evaluate the formula. 10. What is the average height of the plants after 10 weeks? Look Back 11. Use estimation to determine if your answer is reasonable. 8% can be rounded up to 10%. What is 10% of 22 cm? Multiply this value by 10. Add this value to 22. Does your answer in Exercise 10 make sense? 201 Holt Algebra 2
12 12B Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 12-5 Mathematical Induction and Infinite Geometric Series Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 12-5 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary infinite geometric series converge limit Finding the Sums of Infinite Geometric Series Determine if the following infinite series converges. If so, find its sum For an infinite geometric series, if r 1, the series. If r, the series does not converge and does not have a sum. Calculate the ratio between successive terms: r , r 1 5 Since r 1, the series. Calculate the sum of the series: S a 1 1 r Writing Repeating Decimals as Fractions Write as a fraction in simplest form. Repeating decimals are numbers. Infinite geometric series can be used to convert a repeating decimal to a fraction Write the repeating decimal as an infinite series Calculate the common ratio. a 1 Identify the first term. a 1 S 1 1 Write the formula. Substitute known values and evaluate. So, Holt Algebra 2
13 12B Ready To Go On? Problem Solving Intervention 12-5 Mathematical Induction and Infinite Geometric Series You can find the sum of an infinite geometric series, if it converges. Bacteria reproduce by fission results in one cell dividing into two cells. One particular species of bacteria reproduces about once every hour. A researcher swabs a plate of growth medium leaving 100 bacteria. Assuming inexhaustible space and unlimited food, how many bacteria would there be in 12 hours? Understand the Problem 1. Is this a geometric series? Explain how you know. 2. What is the common ratio? 3. What is the first term? 4. What is the formula for a partial sum of an infinite series? Make a Plan 5. In the formula for the partial sum of an infinite series, what are the known values? 6. In the formula for the partial sum of an infinite series, what is the unknown value? Solve 7. Substitute the known values into the formula and evaluate. S n a 1 1 r n 1 r How many bacteria were there in 12 hours? Look Back 9. Graph the function y 1 2 on your graphing calculator. 1 Does your graph support your answer to Exercise 8? 203 Holt Algebra 2
14 12B Ready To Go On? Quiz 12-4 Geometric Sequences and Series Write the first six terms of each sequence , 135, 675, 3375, , 1 3, 1 9, 1 27,... Find the 10th term of each sequence. 3. 2, 1, 1 2, 1 4, , 2, 2 2, 4, a , r 2 6. a 4 4, r 2 7. A piece of paper is 0.03 mm thick. It is torn in two equal pieces and stacked. The stack is torn in again into two equal pieces and stacked again, so it has four pieces of paper. This process is repeated many times, with the number of sheets of paper doubling each time. Write a formula for the height of the paper stack after n times. Assuming it is possible, calculate the height of the stack after 11 tears. Find the geometric mean of each pair of numbers and and 64 4 Find the geometric means to complete each sequence ,,, 27, ,,, 54, Holt Algebra 2
15 12B Ready To Go On? Quiz continued Find the indicated sums. 12. S 6 for S 8 for Mathematical Induction and Infinite Geometric Series Determine if the series converges. If it does, find the sum k1 1 9 k k k1 19. k1 4(3 ) k1 20. Prove by mathematical induction that the n th partial sum of the series (2n 1) is equal to n Holt Algebra 2
16 12B Ready To Go On? Enrichment Mathematical Induction Mathematical Induction is a powerful means of proving many mathematical conjectures. Graph the two functions f (x ) x 2 and g(x) 2 x on the same axes. 1. What is the relationship between f (x ) and g(x ) for large values of x? Mathematical Induction can be used to prove the conjecture in Exercise 1 for integers. Let the variable be n, where n 4 and can have only integer values. 2. Rewrite this conjecture using the new variable. 3. Prove the conjecture for the first case. 4. Assume the statement is true for for n k and show that it is true for n k 1. Alternating Series Does the series have a sum? To find out, calculate the first few partial sums. S1 S2 S3 S4 It is clear that these terms do not converge to a limit, so this series does not have a sum. To further test the idea, apply the rule for the sum of a convergent series, a 1 S 1 r 1 (1) 1. This answer makes no sense. Many alternating series do converge. 5. Suggest an example of an alternating series that converges. 206 Holt Algebra 2
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Integer Exponents
 7A Evaluating Expressions with Zero and Negative Exponents Zero Exponent: Any nonzero number raised to the zero power is. 4 0 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Integer Exponents Negative Exponent:
7A Evaluating Expressions with Zero and Negative Exponents Zero Exponent: Any nonzero number raised to the zero power is. 4 0 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Integer Exponents Negative Exponent:
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. arithmetic sequence. explicit formula. finite sequence. geometric mean. geometric sequence
 CHAPTER 2 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 2. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. arithmetic Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 2 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 2. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. arithmetic Term Page Definition
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Equations by Adding or Subtracting
 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Equations by Adding or Subtracting Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 2-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary equation solution of an equation Solve
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Equations by Adding or Subtracting Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 2-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary equation solution of an equation Solve
P.1 Prerequisite skills Basic Algebra Skills
 P.1 Prerequisite skills Basic Algebra Skills Topics: Evaluate an algebraic expression for given values of variables Combine like terms/simplify algebraic expressions Solve equations for a specified variable
P.1 Prerequisite skills Basic Algebra Skills Topics: Evaluate an algebraic expression for given values of variables Combine like terms/simplify algebraic expressions Solve equations for a specified variable
UNIT 1: INTEGERS WEEK 4: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 1: INTEGERS WEEK 4: Student Packet 4.1 Integers: Multiplication and Division 1 Explore integer multiplication using a marker model. Develop sign rules for integer multiplication and
Name Period Date UNIT 1: INTEGERS WEEK 4: Student Packet 4.1 Integers: Multiplication and Division 1 Explore integer multiplication using a marker model. Develop sign rules for integer multiplication and
S.3 Geometric Sequences and Series
 68 section S S. Geometric In the previous section, we studied sequences where each term was obtained by adding a constant number to the previous term. In this section, we will take interest in sequences
68 section S S. Geometric In the previous section, we studied sequences where each term was obtained by adding a constant number to the previous term. In this section, we will take interest in sequences
Use ordered pairs to locate points, to organize data,
 Eighth Grade Math Scope and Sequence Lesson Title Lesson Objective(s) TEKS First Six Weeks Problem Solving Use problem solving strategies including making a plan and choosing an appropriate method of 8.1B;
Eighth Grade Math Scope and Sequence Lesson Title Lesson Objective(s) TEKS First Six Weeks Problem Solving Use problem solving strategies including making a plan and choosing an appropriate method of 8.1B;
Sequences and Series. College Algebra
 Sequences and Series College Algebra Sequences A sequence is a function whose domain is the set of positive integers. A finite sequence is a sequence whose domain consists of only the first n positive
Sequences and Series College Algebra Sequences A sequence is a function whose domain is the set of positive integers. A finite sequence is a sequence whose domain consists of only the first n positive
A sequence is an ordered list of numbers. Each number in a sequence is called a term. a 1, a 2, a 3,..., a n
 Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Sequences and Series Lesson 1 I can identify a pattern found in a sequence. I can use a formula to find the nth term of a sequence. I can write a recursive formula for a sequence.
Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Sequences and Series Lesson 1 I can identify a pattern found in a sequence. I can use a formula to find the nth term of a sequence. I can write a recursive formula for a sequence.
TransMath Third Edition Correlated to the South Carolina High School Credential Courses: Essentials of Math I, II, and III
 TransMath Third Edition Correlated to the South Carolina High School Credential Courses: Essentials of Math I, II, and III TransMath correlated to the South Carolina High School Credential Courses: Essentials
TransMath Third Edition Correlated to the South Carolina High School Credential Courses: Essentials of Math I, II, and III TransMath correlated to the South Carolina High School Credential Courses: Essentials
Sequences A sequence is a function, where the domain is a set of consecutive positive integers beginning with 1.
 1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 8: Sequences, Series, and Combinatorics Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences A sequence
1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 8: Sequences, Series, and Combinatorics Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences A sequence
Name: Date: Block: Exponents/Logs and Sequences and Series TEST STUDY GUIDE
 Algebra STUDY GUIDE AII.6, AII.7, AII. Exponents/Logs, Sequences and Series Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Test covers: Exponents/Logs and Sequences and Series TEST STUDY GUIDE Sketch graphs of exponential
Algebra STUDY GUIDE AII.6, AII.7, AII. Exponents/Logs, Sequences and Series Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Test covers: Exponents/Logs and Sequences and Series TEST STUDY GUIDE Sketch graphs of exponential
Unit 5: Proportions and Lines. Activities: Resources:
 Timeline: 2 nd nine weeks Vocabulary: Slope Formula, Rate of Change, Y Intercept, Slope intercept form, Vertical, Horizontal Linear Function Slope Slope of a Line Unit 5: Proportions and Lines New State
Timeline: 2 nd nine weeks Vocabulary: Slope Formula, Rate of Change, Y Intercept, Slope intercept form, Vertical, Horizontal Linear Function Slope Slope of a Line Unit 5: Proportions and Lines New State
Regina Algebra 1 and A
 Regina Algebra 1 and A Summer Math Review In the following pages, you will find review materials that will prepare you for next year s math course. Please take the exercises seriously as this will allow
Regina Algebra 1 and A Summer Math Review In the following pages, you will find review materials that will prepare you for next year s math course. Please take the exercises seriously as this will allow
Name Class Date. Geometric Sequences and Series Going Deeper. Writing Rules for a Geometric Sequence
 Name Class Date 5-3 Geometric Sequences and Series Going Deeper Essential question: How can you write a rule for a geometric sequence and find the sum of a finite geometric series? In a geometric sequence,
Name Class Date 5-3 Geometric Sequences and Series Going Deeper Essential question: How can you write a rule for a geometric sequence and find the sum of a finite geometric series? In a geometric sequence,
Controlling the Population
 Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Vocabulary Match each definition with its corresponding term. 1. polynomial a. a polynomial with only 1
Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Vocabulary Match each definition with its corresponding term. 1. polynomial a. a polynomial with only 1
Algebra 2 Math Curriculum Pacing Guide (Revised 2017) Amherst County Public Schools. Suggested Sequence of Instruction and Pacing
 Algebra 2 Math Curriculum Pacing Guide (Revised 2017) Amherst County Public Schools Suggested Sequence of Instruction and Pacing 1st 9-weeks Unit 1 - Solving Equations and Inequalities (including absolute
Algebra 2 Math Curriculum Pacing Guide (Revised 2017) Amherst County Public Schools Suggested Sequence of Instruction and Pacing 1st 9-weeks Unit 1 - Solving Equations and Inequalities (including absolute
Ron Paul Curriculum Mathematics 8 Lesson List
 Ron Paul Curriculum Mathematics 8 Lesson List 1 Introduction 2 Algebraic Addition 3 Algebraic Subtraction 4 Algebraic Multiplication 5 Week 1 Review 6 Algebraic Division 7 Powers and Exponents 8 Order
Ron Paul Curriculum Mathematics 8 Lesson List 1 Introduction 2 Algebraic Addition 3 Algebraic Subtraction 4 Algebraic Multiplication 5 Week 1 Review 6 Algebraic Division 7 Powers and Exponents 8 Order
Convert the equation to the standard form for an ellipse by completing the square on x and y. 3) 16x y 2-32x - 150y = 0 3)
 Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x 6 + y = 1 1) foci: ( 15, 0) and (- 15, 0) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. ) (x + )
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x 6 + y = 1 1) foci: ( 15, 0) and (- 15, 0) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. ) (x + )
6-5 Study Guide and Intervention
 6-5 Study Guide and Intervention Simplify Radicals Product Property of Radicals For any real numbers a and b, and any integer n > 1: 1. if n is even and a and b are both nonnegative, then n ab n a n b.
6-5 Study Guide and Intervention Simplify Radicals Product Property of Radicals For any real numbers a and b, and any integer n > 1: 1. if n is even and a and b are both nonnegative, then n ab n a n b.
Algebra 2 (3) Apex - Semester 1 Part A
 Algebra 2 (3) Apex - Semester 1 Part A Name Algebra I Literacy Advantage Unit 1 : The Need to Read Lesson 1.1 : Reading and Vocabulary Activity 1.1.1 : Study - Active Reading Learn skills and strategies
Algebra 2 (3) Apex - Semester 1 Part A Name Algebra I Literacy Advantage Unit 1 : The Need to Read Lesson 1.1 : Reading and Vocabulary Activity 1.1.1 : Study - Active Reading Learn skills and strategies
Ch 9/10/11/12 Exam Review
 Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
Mathematics. Standards Plus. Grade COMMON CORE INTERVENTION SAMPLER
 Mathematics Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Grade 7 SAMPLER Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Available for Grades 1-8 Language Arts and Math Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Mathematics
Mathematics Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Grade 7 SAMPLER Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Available for Grades 1-8 Language Arts and Math Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Mathematics
6-2. Absolute Value, Square Roots, and Quadratic Equations. Vocabulary. Lesson. Example 1 Solve for x: x - 4 = 8.1. Mental Math
 Chapter 6 Lesson 6-2 Absolute Value, Square Roots, and Quadratic Equations BIG IDEA Geometrically, the absolute value of a number is its distance on a number line from 0. Algebraically, the absolute value
Chapter 6 Lesson 6-2 Absolute Value, Square Roots, and Quadratic Equations BIG IDEA Geometrically, the absolute value of a number is its distance on a number line from 0. Algebraically, the absolute value
Function Operations and Composition of Functions. Unit 1 Lesson 6
 Function Operations and Composition of Functions Unit 1 Lesson 6 Students will be able to: Combine standard function types using arithmetic operations Compose functions Key Vocabulary: Function operation
Function Operations and Composition of Functions Unit 1 Lesson 6 Students will be able to: Combine standard function types using arithmetic operations Compose functions Key Vocabulary: Function operation
Algebra II Chapter 5: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Part 1
 Algebra II Chapter 5: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Part 1 Chapter 5 Lesson 1 Use Properties of Exponents Vocabulary Learn these! Love these! Know these! 1 Example 1: Evaluate Numerical Expressions
Algebra II Chapter 5: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Part 1 Chapter 5 Lesson 1 Use Properties of Exponents Vocabulary Learn these! Love these! Know these! 1 Example 1: Evaluate Numerical Expressions
MA 180 Lecture. Chapter 0. College Algebra and Calculus by Larson/Hodgkins. Fundamental Concepts of Algebra
 0.) Real Numbers: Order and Absolute Value Definitions: Set: is a collection of objections in mathematics Real Numbers: set of numbers used in arithmetic MA 80 Lecture Chapter 0 College Algebra and Calculus
0.) Real Numbers: Order and Absolute Value Definitions: Set: is a collection of objections in mathematics Real Numbers: set of numbers used in arithmetic MA 80 Lecture Chapter 0 College Algebra and Calculus
Functions in Tables 2.0
 Ns Activate Prior Knowledge Function Table Game Topic: Functions Functions in Tables 2.0 Date: Objectives: SWBAT (Identify patterns in Tables) Main Ideas: Assignment: What is a relation? What is a function?
Ns Activate Prior Knowledge Function Table Game Topic: Functions Functions in Tables 2.0 Date: Objectives: SWBAT (Identify patterns in Tables) Main Ideas: Assignment: What is a relation? What is a function?
Using Fact Family Triangles to Solve 1-Step Equations
 Using Fact Family Triangles to Solve 1-Step Equations Strategies for Solving Two Step Equations Solving Two Step Equations using Fact Family Triangles Solving Two Step Equations using Inverse Operations
Using Fact Family Triangles to Solve 1-Step Equations Strategies for Solving Two Step Equations Solving Two Step Equations using Fact Family Triangles Solving Two Step Equations using Inverse Operations
Name Period Date DRAFT
 Name Period Date Equations and Inequalities Student Packet 4: Inequalities EQ4.1 EQ4.2 EQ4.3 Linear Inequalities in One Variable Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers. Write expressions, equations,
Name Period Date Equations and Inequalities Student Packet 4: Inequalities EQ4.1 EQ4.2 EQ4.3 Linear Inequalities in One Variable Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers. Write expressions, equations,
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Name: Linear and Exponential Functions 4.1H
 TE-18 Name: Linear and Exponential Functions 4.1H Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Recognizing arithmetic and geometric sequences Predict the next 2 terms in the sequence. State whether the sequence is arithmetic,
TE-18 Name: Linear and Exponential Functions 4.1H Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Recognizing arithmetic and geometric sequences Predict the next 2 terms in the sequence. State whether the sequence is arithmetic,
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 10.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Higher Order Polynomials and Factoring Roots of Polynomial Equations Problem Set Solve each polynomial equation using factoring. Then check your solution(s).
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Higher Order Polynomials and Factoring Roots of Polynomial Equations Problem Set Solve each polynomial equation using factoring. Then check your solution(s).
? Describe the nth term of the series and the value of S n. . Step 6 Will the original square ever be entirely shaded? Explain why or why not.
 Lesson 13-2 Geometric Series Vocabulary geometric series BIG IDEA There are several ways to fi nd the sum of the successive terms of a fi nite geometric sequence Activity Step 1 Draw a large square on
Lesson 13-2 Geometric Series Vocabulary geometric series BIG IDEA There are several ways to fi nd the sum of the successive terms of a fi nite geometric sequence Activity Step 1 Draw a large square on
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 6 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers*, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples*
6 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers*, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples*
Chapter 11 Resource Masters
 Chapter Resource Masters Consumable Workbooks Many of the worksheets contained in the Chapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks. Study Guide and Intervention Workbook 0-07-8809-X
Chapter Resource Masters Consumable Workbooks Many of the worksheets contained in the Chapter Resource Masters booklets are available as consumable workbooks. Study Guide and Intervention Workbook 0-07-8809-X
Equations Involving a Variable Expression in the Denominator
 Equations Involving a Variable Expression in the Denominator Classwork Opening Exercise Nolan says that he checks the answer to a division problem by performing multiplication. For example, he says that
Equations Involving a Variable Expression in the Denominator Classwork Opening Exercise Nolan says that he checks the answer to a division problem by performing multiplication. For example, he says that
A video College Algebra course & 6 Enrichment videos
 A video College Algebra course & 6 Enrichment videos Recorded at the University of Missouri Kansas City in 1998. All times are approximate. About 43 hours total. Available on YouTube at http://www.youtube.com/user/umkc
A video College Algebra course & 6 Enrichment videos Recorded at the University of Missouri Kansas City in 1998. All times are approximate. About 43 hours total. Available on YouTube at http://www.youtube.com/user/umkc
11.4 Partial Sums of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
 Section.4 Partial Sums of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 653 Integrated Review SEQUENCES AND SERIES Write the first five terms of each sequence, whose general term is given. 7. a n = n - 3 2. a n =
Section.4 Partial Sums of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 653 Integrated Review SEQUENCES AND SERIES Write the first five terms of each sequence, whose general term is given. 7. a n = n - 3 2. a n =
Name Period Date. Use mathematical reasoning to create polynomial expressions that generalize patterns. Practice polynomial arithmetic.
 Name Period Date POLYNOMIALS Student Packet 4: Polynomial Arithmetic Applications POLY4.1 Hundred Chart Patterns Gather empirical data to form conjectures about number patterns. Write algebraic expressions.
Name Period Date POLYNOMIALS Student Packet 4: Polynomial Arithmetic Applications POLY4.1 Hundred Chart Patterns Gather empirical data to form conjectures about number patterns. Write algebraic expressions.
Chapter 5: Sequences, Mathematic Induction, and Recursion
 Chapter 5: Sequences, Mathematic Induction, and Recursion Hao Zheng Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Florida Tampa, FL 33620 Email: zheng@cse.usf.edu Phone: (813)974-4757
Chapter 5: Sequences, Mathematic Induction, and Recursion Hao Zheng Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Florida Tampa, FL 33620 Email: zheng@cse.usf.edu Phone: (813)974-4757
Complete Week 18 Package
 Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SEQUENCES & SERIES. Arithmetic sequences LESSON
 LESSON SEQUENCES & SERIES In mathematics you have already had some experience of working with number sequences and number patterns. In grade 11 you learnt about quadratic or second difference sequences.
LESSON SEQUENCES & SERIES In mathematics you have already had some experience of working with number sequences and number patterns. In grade 11 you learnt about quadratic or second difference sequences.
Proportional Relationships
 11/2/2015 National Go Math Middle School, Grade 8 Proportional Relationships MODULE LESSON 3.1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Representing Proportional Relationships How can you use proportional relationships to solve
11/2/2015 National Go Math Middle School, Grade 8 Proportional Relationships MODULE LESSON 3.1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Representing Proportional Relationships How can you use proportional relationships to solve
Unit 4: Inequalities. Inequality Symbols. Algebraic Inequality. Compound Inequality. Interval Notation
 Section 4.1: Linear Inequalities Section 4.2: Solving Linear Inequalities Section 4.3: Solving Inequalities Applications Section 4.4: Compound Inequalities Section 4.5: Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
Section 4.1: Linear Inequalities Section 4.2: Solving Linear Inequalities Section 4.3: Solving Inequalities Applications Section 4.4: Compound Inequalities Section 4.5: Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
Semester Review Packet
 MATH 110: College Algebra Instructor: Reyes Semester Review Packet Remarks: This semester we have made a very detailed study of four classes of functions: Polynomial functions Linear Quadratic Higher degree
MATH 110: College Algebra Instructor: Reyes Semester Review Packet Remarks: This semester we have made a very detailed study of four classes of functions: Polynomial functions Linear Quadratic Higher degree
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES. Solving Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
 UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
Unit 3 Vocabulary. An algebraic expression that can contains. variables, numbers and operators (like +, An equation is a math sentence stating
 Hart Interactive Math Algebra 1 MODULE 2 An algebraic expression that can contains 1 Algebraic Expression variables, numbers and operators (like +,, x and ). 1 Equation An equation is a math sentence stating
Hart Interactive Math Algebra 1 MODULE 2 An algebraic expression that can contains 1 Algebraic Expression variables, numbers and operators (like +,, x and ). 1 Equation An equation is a math sentence stating
Miller Objectives Alignment Math
 Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
Section 1.1 Task List
 Summer 017 Math 143 Section 1.1 7 Section 1.1 Task List Section 1.1 Linear Equations Work through Section 1.1 TTK Work through Objective 1 then do problems #1-3 Work through Objective then do problems
Summer 017 Math 143 Section 1.1 7 Section 1.1 Task List Section 1.1 Linear Equations Work through Section 1.1 TTK Work through Objective 1 then do problems #1-3 Work through Objective then do problems
Lesson 18: Equations Involving a Variable Expression in the Denominator
 : Equations Involving a Variable Expression in the Denominator Student Outcomes Students interpret equations like 3 as two equations 3 and 0 joined by and. Students find the solution set for this new system
: Equations Involving a Variable Expression in the Denominator Student Outcomes Students interpret equations like 3 as two equations 3 and 0 joined by and. Students find the solution set for this new system
1-4 Powers and Exponents
 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(2) 4 2. ( 2)( 2) 4 3. ( 2)( 2)( 2) 8 4. 3(3)(3) 5. 27 4 9 Objective Evaluate expressions containing exponents. power base exponent Vocabulary
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Simplify. 1. 2(2) 4 2. ( 2)( 2) 4 3. ( 2)( 2)( 2) 8 4. 3(3)(3) 5. 27 4 9 Objective Evaluate expressions containing exponents. power base exponent Vocabulary
Vocabulary. The Geometric Mean. Lesson 8-4 Radical Notation for nth Roots. Definition of n x when x 0. Mental Math
 Lesson 8-4 Lesson 8-4 Radical Notation for nth Roots Vocabulary radical sign, O n x when x 0 geometric mean BIG IDEA For any integer n, the largest real nth root of x can be represented either by x 1 n
Lesson 8-4 Lesson 8-4 Radical Notation for nth Roots Vocabulary radical sign, O n x when x 0 geometric mean BIG IDEA For any integer n, the largest real nth root of x can be represented either by x 1 n
Modeling with Exponential Functions
 CHAPTER Modeling with Exponential Functions A nautilus is a sea creature that lives in a shell. The cross-section of a nautilus s shell, with its spiral of ever-smaller chambers, is a natural example of
CHAPTER Modeling with Exponential Functions A nautilus is a sea creature that lives in a shell. The cross-section of a nautilus s shell, with its spiral of ever-smaller chambers, is a natural example of
Essentials of Mathematics Lesson Objectives
 Essentials of Mathematics Lesson Unit 1: NUMBER SENSE Reviewing Rational Numbers Practice adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. Practice evaluating exponents.
Essentials of Mathematics Lesson Unit 1: NUMBER SENSE Reviewing Rational Numbers Practice adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. Practice evaluating exponents.
Arizona Mathematics Standards Articulated by Grade Level (2008) for College Work Readiness (Grades 11 and 12)
 Strand 1: Number and Operations Concept 1: Number Sense Understand and apply numbers, ways of representing numbers, and the relationships among numbers and different number systems. College Work Readiness
Strand 1: Number and Operations Concept 1: Number Sense Understand and apply numbers, ways of representing numbers, and the relationships among numbers and different number systems. College Work Readiness
Algebra I Chapter 6: Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities
 Algebra I Chapter 6: Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities Jun 10 9:21 AM Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Solve Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction Vocabulary Words to Review: Inequality Solution of an Inequality
Algebra I Chapter 6: Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities Jun 10 9:21 AM Chapter 6 Lesson 1 Solve Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction Vocabulary Words to Review: Inequality Solution of an Inequality
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 1 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Add or subtract. 1. 1 + ( 3) 2. 0 + ( 12) 3. 5 ( 2) 4. 4 7 5. Find two pairs of integers whose sum is 6. 6. In a city, the record monthly high temperature
Name Date Chapter 1 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Add or subtract. 1. 1 + ( 3) 2. 0 + ( 12) 3. 5 ( 2) 4. 4 7 5. Find two pairs of integers whose sum is 6. 6. In a city, the record monthly high temperature
Algebra 2 - Semester 2 - Final Exam Review
 Algebra 2 - Semester 2 - Final Exam Review Your final exam will be 60 multiple choice questions coving the following content. This review is intended to show examples of problems you may see on the final.
Algebra 2 - Semester 2 - Final Exam Review Your final exam will be 60 multiple choice questions coving the following content. This review is intended to show examples of problems you may see on the final.
Spring 2018 Math Week Week 1 Task List
 Spring 2018 Math 143 - Week 1 25 Week 1 Task List This week we will cover Sections 1.1 1.4 in your e-book. Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook.
Spring 2018 Math 143 - Week 1 25 Week 1 Task List This week we will cover Sections 1.1 1.4 in your e-book. Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook.
3. Infinite Series. The Sum of a Series. A series is an infinite sum of numbers:
 3. Infinite Series A series is an infinite sum of numbers: The individual numbers are called the terms of the series. In the above series, the first term is, the second term is, and so on. The th term
3. Infinite Series A series is an infinite sum of numbers: The individual numbers are called the terms of the series. In the above series, the first term is, the second term is, and so on. The th term
Solving and Graphing Polynomials
 UNIT 9 Solving and Graphing Polynomials You can see laminar and turbulent fl ow in a fountain. Copyright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced in whole or in part, including
UNIT 9 Solving and Graphing Polynomials You can see laminar and turbulent fl ow in a fountain. Copyright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material may not be reproduced in whole or in part, including
Mathematics Precalculus: Academic Unit 1: Polynomial and Transcendental Functions
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Functions can be used as models for real-life problems. Functions can be graphed, evaluated, transformed, analyzed, manipulated and combined using algebraic & graphical
Understandings Questions Knowledge Functions can be used as models for real-life problems. Functions can be graphed, evaluated, transformed, analyzed, manipulated and combined using algebraic & graphical
Work with a partner. How can you show that ( 1)( 1) = 1?
 . Multiplying and Dividing Rational Numbers numbers positive? Why is the product of two negative rational In Section., you used a table to see that the product of two negative integers is a positive integer.
. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Numbers numbers positive? Why is the product of two negative rational In Section., you used a table to see that the product of two negative integers is a positive integer.
Looking Ahead to Chapter 4
 Looking Ahead to Chapter Focus In Chapter, you will learn about functions and function notation, and you will find the domain and range of a function. You will also learn about real numbers and their properties,
Looking Ahead to Chapter Focus In Chapter, you will learn about functions and function notation, and you will find the domain and range of a function. You will also learn about real numbers and their properties,
Sequences. 1. Number sequences. 2. Arithmetic sequences. Consider the illustrated pattern of circles:
 Sequences 1. Number sequences Consider the illustrated pattern of circles: The first layer has just one blue ball. The second layer has three pink balls. The third layer has five black balls. The fourth
Sequences 1. Number sequences Consider the illustrated pattern of circles: The first layer has just one blue ball. The second layer has three pink balls. The third layer has five black balls. The fourth
PRECALCULUS GROUP FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Approximate the following 1-3 using: logb 2 0.6, logb 5 0.7, 2. log. 2. log b
 PRECALCULUS GROUP FINAL FIRST SEMESTER 008 Approimate the following 1-3 using: log 0.6, log 5 0.7, and log 7 0. 9 1. log = log log 5 =... 5. log 10 3. log 7 4. Find all zeros algeraically ( any comple
PRECALCULUS GROUP FINAL FIRST SEMESTER 008 Approimate the following 1-3 using: log 0.6, log 5 0.7, and log 7 0. 9 1. log = log log 5 =... 5. log 10 3. log 7 4. Find all zeros algeraically ( any comple
Centerville High School Curriculum Mapping Algebra II 1 st Nine Weeks
 Centerville High School Curriculum Mapping Algebra II 1 st Nine Weeks Chapter/ Lesson Common Core Standard(s) 1-1 SMP1 1. How do you use a number line to graph and order real numbers? 2. How do you identify
Centerville High School Curriculum Mapping Algebra II 1 st Nine Weeks Chapter/ Lesson Common Core Standard(s) 1-1 SMP1 1. How do you use a number line to graph and order real numbers? 2. How do you identify
Sequences and series UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 3 Sequences and series 3.1 Kick off with CAS 3. Describing sequences 3.3 Arithmetic sequences 3.4 Arithmetic series 3.5 Geometric sequences 3.6 Geometric series 3.7 Applications of sequences and series
3 Sequences and series 3.1 Kick off with CAS 3. Describing sequences 3.3 Arithmetic sequences 3.4 Arithmetic series 3.5 Geometric sequences 3.6 Geometric series 3.7 Applications of sequences and series
Why? + 1:32 + 1:32 + 1:32 + 1:32. d = 2 d = -4
 Then You indentified linear functions. (Lesson 3-1) Now Arithmetic Sequences as Linear Functions 1Recognize arithmetic sequences. 2Relate arithmetic sequences to linear functions. Why? During a 2000-meter
Then You indentified linear functions. (Lesson 3-1) Now Arithmetic Sequences as Linear Functions 1Recognize arithmetic sequences. 2Relate arithmetic sequences to linear functions. Why? During a 2000-meter
a. If the vehicle loses 12% of its value annually, it keeps 100% - 12% =? % of its value. Because each year s value is a constant multiple of
 Lesson 9-2 Lesson 9-2 Exponential Decay Vocabulary exponential decay depreciation half-life BIG IDEA When the constant growth factor in a situation is between 0 and 1, exponential decay occurs. In each
Lesson 9-2 Lesson 9-2 Exponential Decay Vocabulary exponential decay depreciation half-life BIG IDEA When the constant growth factor in a situation is between 0 and 1, exponential decay occurs. In each
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Algebra 2
 4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS 253
 LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS 5 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Properties of Exponents Definition of exponent, power, and base b. Multiplication Property c. Division Property
LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS LESSON 6.1 EXPONENTS 5 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Properties of Exponents Definition of exponent, power, and base b. Multiplication Property c. Division Property
1 ** The performance objectives highlighted in italics have been identified as core to an Algebra II course.
 Strand One: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and skills from the pervious grade levels. The standards are designed so that new learning builds on preceding
Strand One: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and skills from the pervious grade levels. The standards are designed so that new learning builds on preceding
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures
 Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 2-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary inductive reasoning conjecture
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 2-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary inductive reasoning conjecture
Lesson 11: The Special Role of Zero in Factoring
 Lesson 11: The Special Role of Zero in Factoring Student Outcomes Students find solutions to polynomial equations where the polynomial expression is not factored into linear factors. Students construct
Lesson 11: The Special Role of Zero in Factoring Student Outcomes Students find solutions to polynomial equations where the polynomial expression is not factored into linear factors. Students construct
Exponents and Polynomials. (5) Page 459 #15 43 Second Column; Page 466 #6 30 Fourth Column
 Algebra Name: Date: Period: # Exponents and Polynomials (1) Page 453 #22 59 Left (2) Page 453 #25 62 Right (3) Page 459 #5 29 Odd (4) Page 459 #14 42 First Column; Page 466 #3 27 First Column (5) Page
Algebra Name: Date: Period: # Exponents and Polynomials (1) Page 453 #22 59 Left (2) Page 453 #25 62 Right (3) Page 459 #5 29 Odd (4) Page 459 #14 42 First Column; Page 466 #3 27 First Column (5) Page
Comparison of Virginia s College and Career Ready Mathematics Performance Expectations with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 Comparison of Virginia s College and Career Ready Mathematics Performance Expectations with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics February 17, 2010 1 Number and Quantity The Real Number System
Comparison of Virginia s College and Career Ready Mathematics Performance Expectations with the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics February 17, 2010 1 Number and Quantity The Real Number System
Course Readiness and Skills Review Handbook (83 topics) Course Readiness (21 topics) Course Name: Algebra Course Code: UY6JA-RATXM
 Course Name: Algebra 1 2014-15 Course Code: UY6JA-RATXM ALEKS Course: Algebra 1A Instructor: Ms. Dalton Course Dates: Begin: 11/18/2014 End: 06/18/2015 Course Content: 335 Topics (334 goal + 1 prerequisite)
Course Name: Algebra 1 2014-15 Course Code: UY6JA-RATXM ALEKS Course: Algebra 1A Instructor: Ms. Dalton Course Dates: Begin: 11/18/2014 End: 06/18/2015 Course Content: 335 Topics (334 goal + 1 prerequisite)
Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review
 Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review Know all vocabulary, pay attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various types of directions in each of the sections of the textbook. Practice
Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review Know all vocabulary, pay attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various types of directions in each of the sections of the textbook. Practice
Mathematics Curricular Guide SEVENTH GRADE SCHOOL YEAR
 Mathematics Curricular Guide SEVENTH GRADE 2013-2014 SCHOOL YEAR MATHEMATICS SCOPE & SEQUENCE Unit Title Dates Page 1. Ratios and Proportion... IBD... 4 2. Rational Numbers & Prime Factorization... IBD...
Mathematics Curricular Guide SEVENTH GRADE 2013-2014 SCHOOL YEAR MATHEMATICS SCOPE & SEQUENCE Unit Title Dates Page 1. Ratios and Proportion... IBD... 4 2. Rational Numbers & Prime Factorization... IBD...
Developed in Consultation with Virginia Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Virginia Educators Table of Contents Virginia Standards of Learning Correlation Chart.............. 6 Chapter 1 Expressions and Operations.................... Lesson 1 Square
Developed in Consultation with Virginia Educators Table of Contents Virginia Standards of Learning Correlation Chart.............. 6 Chapter 1 Expressions and Operations.................... Lesson 1 Square
Sample: Do Not Reproduce EE6 STUDENT PACKET. EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Student Packet 6: Solving Equations 2. Name Period Date
 Name Period Date EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Student Packet 6: EE6.1 Cups and Counters 3 Use a visual model to solve multi-step algebraic equations. Solve equations that require working with variables that
Name Period Date EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Student Packet 6: EE6.1 Cups and Counters 3 Use a visual model to solve multi-step algebraic equations. Solve equations that require working with variables that
Lesson 7: Literal Equations, Inequalities, and Absolute Value
 , and Absolute Value In this lesson, we first look at literal equations, which are equations that have more than one variable. Many of the formulas we use in everyday life are literal equations. We then
, and Absolute Value In this lesson, we first look at literal equations, which are equations that have more than one variable. Many of the formulas we use in everyday life are literal equations. We then
Trinity Christian School Curriculum Guide
 Course Title: Calculus Grade Taught: Twelfth Grade Credits: 1 credit Trinity Christian School Curriculum Guide A. Course Goals: 1. To provide students with a familiarity with the properties of linear,
Course Title: Calculus Grade Taught: Twelfth Grade Credits: 1 credit Trinity Christian School Curriculum Guide A. Course Goals: 1. To provide students with a familiarity with the properties of linear,
ALGEBRA I SEMESTER EXAMS PRACTICE MATERIALS SEMESTER Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm. A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = cm 2. 6.
 1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
How can you solve a multistep. How can you solve an absolute value equation? How can you solve and absolute value. inequality?
 WDHS Curriculum Map Course: Algebra 1 June 2015 Time Interval/ Content Standards/ Strands Essential Questions Skills Assessment Unit 1 Transfer Goal: Recognize and solve practical or theoretical problems
WDHS Curriculum Map Course: Algebra 1 June 2015 Time Interval/ Content Standards/ Strands Essential Questions Skills Assessment Unit 1 Transfer Goal: Recognize and solve practical or theoretical problems
Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review
 Class: Date: Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review Short Answer. Evaluate the series 5n. 8 n =. Evaluate the series (n + ). n = What is the sum of the finite arithmetic series?. 9+ + 5+ 8+ + + 59. 6 + 9
Class: Date: Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review Short Answer. Evaluate the series 5n. 8 n =. Evaluate the series (n + ). n = What is the sum of the finite arithmetic series?. 9+ + 5+ 8+ + + 59. 6 + 9
The given pattern continues. Write down the nth term of the sequence {an} suggested by the pattern. 3) 4, 10, 16, 22, 28,... 3)
 M60(Precalculus) Evaluate the factorial expression. 9! ) 7!! ch practice test ) Write out the first five terms of the sequence. ) {sn} = (-)n - n + n - ) The given pattern continues. Write down the nth
M60(Precalculus) Evaluate the factorial expression. 9! ) 7!! ch practice test ) Write out the first five terms of the sequence. ) {sn} = (-)n - n + n - ) The given pattern continues. Write down the nth
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM
 COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 8 4 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. When you square five times a number you get
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 8 4 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols Write each of the following statements using symbolic language. 1. When you square five times a number you get
GTPS Curriculum 6 th Grade Math. Topic: Topic 1- Numeration
 9 days / September Compute fluently with multi-digit numbers and find common factors and multiples. 6.NS.3 Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm
9 days / September Compute fluently with multi-digit numbers and find common factors and multiples. 6.NS.3 Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 6-1 Polynomials
 6A Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 6- Polnomials Find these vocabular words in Lesson 6- and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular monomial polnomial degree of a monomial degree of a polnomial leading
6A Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 6- Polnomials Find these vocabular words in Lesson 6- and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular monomial polnomial degree of a monomial degree of a polnomial leading
3.4 Solve Equations with Variables
 3.4 Solve Equations with Variables on Both Sides Goal p Solve equations with variables on both sides. Your Notes VOCABULARY Identity Example 1 Solve 15 1 4a 5 9a 2 5. Solve an equation with variables on
3.4 Solve Equations with Variables on Both Sides Goal p Solve equations with variables on both sides. Your Notes VOCABULARY Identity Example 1 Solve 15 1 4a 5 9a 2 5. Solve an equation with variables on
Continuing Quadratic/Polynomial Real-World Problems
 Algebra 1, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Continuing Quadratic/Polynomial Real-World Problems Overview Number of instructional days: 15 (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Content to be learned Understand closed operations.
Algebra 1, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Continuing Quadratic/Polynomial Real-World Problems Overview Number of instructional days: 15 (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Content to be learned Understand closed operations.
ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER ONE NOTES SECTION 1-1 REAL NUMBERS Objectives: Classify and order real numbers A is a collection of items called.
 ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER ONE NOTES SECTION 1-1 REAL NUMBERS Objectives: Classify and order real numbers A is a collection of items called. A is a set whose elements belong to another set. The, denoted, is a set
ALGEBRA 2 CHAPTER ONE NOTES SECTION 1-1 REAL NUMBERS Objectives: Classify and order real numbers A is a collection of items called. A is a set whose elements belong to another set. The, denoted, is a set
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
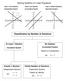 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
More Vocabulary for Expressions
 More Vocabulary for Expressions Since algebraic expressions come in several different forms, there are special words used to help describe these expressions. For example, if the expression can be written
More Vocabulary for Expressions Since algebraic expressions come in several different forms, there are special words used to help describe these expressions. For example, if the expression can be written
Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series
 23 a4, 2A2A; P4A, P4B TEKS Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series Before You studied arithmetic sequences and series Now You will study geometric sequences and series Why? So you can solve problems about
23 a4, 2A2A; P4A, P4B TEKS Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series Before You studied arithmetic sequences and series Now You will study geometric sequences and series Why? So you can solve problems about
Overview (90 Days) Properties of Equality Properties of Inequality Solve Linear Function
 Pre- Requisites Skills: Overview (90 Days) Students need to know the meanings of exponents (2 4 = 2 2 2 2) Students need to know how to graph a simple inequality on a number line (i.e. x > 4) Students
Pre- Requisites Skills: Overview (90 Days) Students need to know the meanings of exponents (2 4 = 2 2 2 2) Students need to know how to graph a simple inequality on a number line (i.e. x > 4) Students
