S.3 Geometric Sequences and Series
|
|
|
- Damian Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
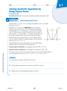
1 68 section S S. Geometric In the previous section, we studied sequences where each term was obtained by adding a constant number to the previous term. In this section, we will take interest in sequences where each term is obtained by multiplying the previous term by a constant number. Such sequences are called geometric. For example, the sequence, 2,, 8, is geometric because each term is multiplied by 2 to obtain the next term. Equivallently, the ratios between consecutive terms of this sequence are always 2. Definition 2. A sequence {aa nn } is called geometric if the quotient rr = aa nn+ aa nn the sequence is constantly the same. The general term of a geometric sequence is given by the formula aa nn = aa rr nn The quotient rr is referred to as the common ratio of the sequence. of any consecutive terms of Similarly as in the previous section, we can be visualize geometric sequences by plotting their values in a system of coordinates. For instance, Figure presents the graph of the sequence,2,, 8,. The common ratio of 2 causes each cosecutive point of the graph to be plotted twice as high as the previous one, and the slope between the nn-th and (nn + )-st point to be exactly equal to the value of aa nn. Generally, the slope between the nn-th and (nn + )-st point of any geometric sequence is proportional to the value of aa nn. This property characterises exponential functions. Hence, geometric sequences are exponential in nature. To develop the formula for the general term, we observe the pattern so aa = aa aa 22 = aa rr aa = aa rr 22 aa = aa rr aa nn = aa rr nn This is the general term of a geometric sequence aa nn 9 aa aa aa aa rr = 2 rr = 2 rr = 2 22 Figure nn Particularly, the general term of the sequence, 2,, 8, is equal to aa nn = 22 nn, because aa = and rr = 2 (the ratios of consecutive terms are constantly equal to 2). Note: To find the common ratio of a geometric sequence, divide any of its terms by the preceeding term. Identifying Geometric Sequences and Writing Their General Terms Determine whether the given sequence {aa nn } is geometric. If it is, then write a formula for the general term of the sequence. a.,,,, b.,,,,
2 section S 69 a. After calculating ratios of terms by their peceding terms, we notice that they are always equal to 2. Indeed, aa 2 = aa = 2, aa aa 2 = 8 =, and so on. Therefore, the given 2 sequence is geometric with aa = and the common ratio rr =. 2 2 To find its general term, we follow the formula aa nn = aa rr nn. This gives us aa nn = 2 2 nn = ( )nn 22 nn. b. Here, the ratios of terms by their peceding terms, aa 2 aa = the same. So the sequence is not geometric. 6 = and aa = 2 aa 2 9 = 2, are not 6 Finding Terms of a Gometric Sequence Given the information, write out the first five terms of the geometric sequence {aa nn }. Then, find the 8-th term aa 8. a. aa nn = 5( 2) nn b. aa =, rr = 2 a. To find the first five terms of this sequence, we evaluate aa nn for nn =,2,,,5. aa = 5( 2) 00 = 5 aa 22 = 5( 2) = 0 aa = 5( 2) 22 = 20 aa = 5( 2) = 0 aa 55 = 5( 2) = 80 So, the first five terms are 55,, 2222,, and The 8-th term equals aa 88 = 5( 2) 77 = b. To find the first five terms of a geometric sequence with aa =, rr = 22, we substitute these values into the general term formula aa nn = aa rr nn = 22 nn, and then evaluate it for nn =,2,,,5. This gives us aa = 2 00 = aa 22 = 2 = 2 aa = 2 22 = aa = 2 = 8 9 aa 55 = 2 = 6 27 Geometric
3 70 section S So, the first five terms are, 22,, 88, and The 8-th term equals aa 88 = 2 77 = Finding the Number of Terms in a Finite Geometric Sequence Determine the number of terms in the geometric sequence,,9, 27,,729. Since the common ratio rr of this sequence is and the first term aa =, then the nn-th term aa nn = ( ) nn. Since the last term is 729, we can set up the equation which can be written as aa nn = ( ) nn = 729, ( ) nn = ( ) 6 This equation holds if nn = 6, which gives us nn = 7. So, there are 7 terms in the given sequence. Finding Missing Terms of a Geometric Sequence Given the information, determine the values of the indicated terms of a geometric sequence. a. aa = 5 and aa 6 = 5; find aa and aa 8 b. aa = 200 and aa 5 = 50; find aa if aa > 0 a. As before, let rr be the common ratio of the given sequence. Using the general term formula aa nn = aa rr nn for nn = 6 and nn =, we can set up a system of two equations in two variables, rr and aa : 5 = aa rr 5 5 = aa rr 2 To solve this system, let s divide the two equations side by side, obtaining which gives us 27 = rr, rr =. Substituting this value to equation (2), we have 5 = aa ( ) 2, which gives us aa =
4 section S 7 To find value aa 8, we substitute aa = 5, rr =, and nn = 8 to the formula aa 2 nn = aa rr nn. This gives us aa 88 = 5 9 ( )7 =. b. Let rr be the common ratio of the given sequence. Since aa 5 = aa rr and aa = aa rr, then aa 5 = aa rr 2. Hence, rr 2 = aa 5. Therefore, aa rr = ± aa 5 aa = ± = ± = ± 2. () (2) Since aa, aa > 0 and aa = aa rr, we choose the positive rr-value. So we have aa = aa rr = 200 =. 2 Remark: A geometric mean of two quantities aa and bb is defined as aaaa. Notice that aa = 00 = = aa aa 55, so aa is indeed the geometric mean of aa and aa 55. Generally, for any nn >, we have 2 aa nn = aa nn rr = aa nn rr 2 = aa nn aa nn rr 2 = aa nn aa nn+, so every term (except for the first one) of a geometric sequence is the geometric mean of its adjacent terms. Partial Sums Similarly as with arithmetic sequences, we might be interested in evaluating the sum of the first nn terms of a geometric sequence. To find partial sum SS nn of the first nn terms of a geometric sequence, we line up formulas for SS nn and rrrr nn as shown below and then add the resulting equations side by side. SS nn = aa + aa rr + aa rr aa rr nn rrss nn = aa rr aa rr 22 aa rr nn aa rr nn the terms of inside columns add to zero, so they cancel each other out So, we obtain ( rr)ss nn = aa aa rr nn, which gives us as long as rr. SS nn = aa ( rr nn ), rr () Geometric
5 72 section S Observe that If rr <, then the value of rr nn gets closer and closer to zero for larger and larger n (we write: rr nn 0 for nn ). This means that the sum of all infinitely many terms of such a sequence exists and is equal to SS = aa rr () If rr >, then the value of rr nn grows without bound for larger and larger n. Therefore, the sum SS of all terms of such a sequence does not have a finite value. We say that such a sum does not exist. If rr =, then the sum SS becomes aa + aa + aa +, or aa aa + aa. Neither of these sums has a finite value, unless aa = 0. Hence overall, if rr, then the sum SS of a nonzero geometric sequence does not exist. Finding a Partial Sum of a Geometric Sequence a. Find SS 6, for the geometric sequence with aa = 0.5 and rr = 0.. b. Evaluate the sum a. Using formula () for nn = 6, aa = 0.5 and rr = 0., we calculate SS 66 = 0.5( 0.6 ) 0. = = b. First, we observe that the given series is geometric with aa = and rr =. Equating the formula for the general term to the last term of the sum aa rr nn = nn = 9 = 9 and comparing the exponents, nn = 9 allows us to find the number of terms nn =. Now, we are ready to calculate the sum of the given series 0 SS =
6 section S 7 Evaluating Infinite Geometric Series Decide wether or not the overall sum SS of each geometric series exists and if it does, evaluate it. a b. 2 8 ii=0 2 ii a. Since the common ratio of this series is rr = 9 2 = = >, then the sum SS 2 2 does not exist. b. This time, rr = 2 <, so the sum SS exists and can be calculated by following the formula (). Using aa = and rr = 2, we have So, ii=0 2 ii = 99. SS = 2 = = 99 Using Geometric in Application Problems When dropped from a certain height, a ball rebounds of the original height. mm a. How high will the ball rebound after the fourth bounce if it was dropped from a height of meters? Round the answer to the nearest centimeter. b. Find a formula for the rebound height of the ball after its nn-th bounce. c. Assuming that the ball bounce forever, what is the total vertical distance traveled by the ball? a. Let h nn represents the ball s rebound height after the nn-th bounce, where nn N. Since the ball rebounds of the previous height, we have h = h 22 = h 22 = h = h 2 = h = h =.99 mm 9999 cccc After the fourth bounce, the ball will rebound approximately 95 centimeters. b. Notice that the formulas developed in solution to Example a follow the pattern Geometric
7 7 section S h nn = nn So this is the formula for the rebound height of the ball after its nn-th bounce. c. Let h 0 = represents the vertical distance before the first bounce. To find the total verical distance DD traveled by the ball, we add the vertical distance h 0 before the first bounce, and twice the vertical distances h nn after each bounce. So we have DD = h 0 + h nn = + nn Applying the formula aa rr nn= nn= for the infinite sum of a geometric series, we calculate 9 DD = + = + 9 = + 9 = + 9 = mm Thus, the total vertical distance traveled by the ball is 2 meters. S. Exercises Vocabulary Check Fill in each blank with appropriate formula, one of the suggested words, or with the most appropriate term or phrase from the given list: consecutive, geometric mean, ratio.. A geometric sequence is a sequence in which there is a constant between consecutive terms. 2. The sequence, 2, 6, 2, iiii / iiii nnnnnn the same. geometric because the ratio between terms is not. The general term of a geometric sequence is given by the formula aa nn =.. If the absolute value of the common ratio of a geometric sequence is than, then the llllllll / mmmmmmmm sum of the associated geometric series exists and it is equal to SS =. 5. The expression aaaa is called the of aa and bb. Concept Check True or False? 6. The sequence,,,, is a geometric sequence The common ratio for 0.05, , , is The series ( 2 ii ) 7 ii= is a geometric series.
8 section S The nn-th partial sum SS nn of any finite geometric series exists and it can be evaluated by using the formula SS nn = aa ( rrnn ). rr Concept Check Identify whether or not the given sequence is geometric. If it is, write a formula for its n-th term. 0. 0,, 9, 27,., 5, 25,25, 2. 9,,,,., 2,,,.,,,, , 0.09, 0.009,0.0009, 6. 8, 27, 9,, 7., 2,, 8, 8., 5, 25, 6 25, Concept Check Given the information, write out the first four terms of the geometyric sequence {aa nn }. Then, find the 8-th term aa aa nn = 2 nn 20. aa nn = ( 2) nn 2. aa = 6, rr = 22. aa = 5, rr = 2. aa =, aa 2 = 6 2. aa = 00, aa 2 = 0 Concept Check Find the number of terms in each geometric sequence. 25., 2,,, , 0, 5,, , 2,,, 2 28.,,,, , 2, 2,, , 2, 6,, 2 Given the information, find the indicated term of each geometric sequence.. aa 2 = 0, rr = 0.; aa 5 2. aa =, aa = 8; aa 0. 2, 2, 2, 2, ; aa 50., 2,, ; aa 2 5. aa = 6, aa = 2 9 ; aa 8 6. aa = 9, aa 6 = 27; aa 9 7. aa = 2, aa 7 = 2 ; aa if aa > 0 8. aa 5 = 8, aa 8 = 8 ; aa 0 Given the geometric sequence, evaluate the indicated partial sum. Round your answer to three decimal places, if needed. 9. aa nn = 5 2 nn ; SS 6 0. aa nn = 2 nn ; SS 0. 2, 6, 8, ; SS ,, 2, ; SS ii= 2(.05) ii 6. 0 (2) ii ii= Geometric
9 76 section S Decide wether or not the infinite sum SS of each geometric series exists and if it does, evaluate it ii= (0.6) ii ii= 5 (.)ii 5. 2 ii= ii 5. 2 ii= ii Analytic Skills Solve each problem. 55. A company is offering a job with a salary of $0,000 for the first year and a 5% raise each year after that. If that 5% raise continues every year, find the amount of money you would earn in the 0 th year of your career. 56. Suppose you go to work for a company that pays one penny on the first day, 2 cents on the second day, cents on the third day and so on. If the daily wage keeps doubling, what will your wage be on the 0 th day? What will your total income be for working 0 days? 57. Suppose a deposit of $2000 is made at the beginning of each year for 5 years into an account paying 2% compounded annually. What is the amount in the account at the end of the forty-fifth year? 58. A father opened a savings account for his daughter on her first birthday, depositing $000. Each year on her birthday he deposits another $000, making the last deposit on her 2st birthday. If the account pays.% interest compounded annually, how much is in the account at the end of the day on the daughter s 2st birthday? 59. A ball is dropped from a height of 2 m and bounces 90% of its original height on each bounce. a. How high off the floor is the ball at the top of the eighth bounce? b. Asuming that the ball moves only vertically, how far has it traveled when it hits the ground for the eighth time? 60. Suppose that a ball always rebounds 2 of the distance from which it falls. If this ball is dropped from a height of 9 ft, then approximately how far does it travel before coming to rest? Assime that the ball moves only vertically. 6. Suppose the midpoints of a unit square ss (with the length of each side equal to one) are connected to form another square, ss 2, as in the accompanying figure. Suppose we continue indefinitely the process of creating a new square, ss nn+, by connecting the midpoints of the previous square, ss nn. Calculate the sum of the areas of the infinite sequence of squares {ss nn }.
S.2 Arithmetic Sequences and Series
 459 S. Arithmetic Sequences and Series Some sequences consist of random values while other sequences follow a certain pattern that is used to arrive at the sequence's terms. In this section, we will take
459 S. Arithmetic Sequences and Series Some sequences consist of random values while other sequences follow a certain pattern that is used to arrive at the sequence's terms. In this section, we will take
11.4 Partial Sums of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
 Section.4 Partial Sums of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 653 Integrated Review SEQUENCES AND SERIES Write the first five terms of each sequence, whose general term is given. 7. a n = n - 3 2. a n =
Section.4 Partial Sums of Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences 653 Integrated Review SEQUENCES AND SERIES Write the first five terms of each sequence, whose general term is given. 7. a n = n - 3 2. a n =
Systems of Linear Equations
 Systems of Linear Equations As stated in Section G, Definition., a linear equation in two variables is an equation of the form AAAA + BBBB = CC, where AA and BB are not both zero. Such an equation has
Systems of Linear Equations As stated in Section G, Definition., a linear equation in two variables is an equation of the form AAAA + BBBB = CC, where AA and BB are not both zero. Such an equation has
Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
 Name Date lass Equations and Inequalities in One Variable. Which of the following is ( r ) 5 + + s evaluated for r = 8 and s =? A 3 B 50 58. Solve 3x 9= for x. A B 7 3. What is the best first step for
Name Date lass Equations and Inequalities in One Variable. Which of the following is ( r ) 5 + + s evaluated for r = 8 and s =? A 3 B 50 58. Solve 3x 9= for x. A B 7 3. What is the best first step for
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. arithmetic sequence. explicit formula. finite sequence. geometric mean. geometric sequence
 CHAPTER 2 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 2. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. arithmetic Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 2 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 2. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. arithmetic Term Page Definition
Name Class Date. Geometric Sequences and Series Going Deeper. Writing Rules for a Geometric Sequence
 Name Class Date 5-3 Geometric Sequences and Series Going Deeper Essential question: How can you write a rule for a geometric sequence and find the sum of a finite geometric series? In a geometric sequence,
Name Class Date 5-3 Geometric Sequences and Series Going Deeper Essential question: How can you write a rule for a geometric sequence and find the sum of a finite geometric series? In a geometric sequence,
? Describe the nth term of the series and the value of S n. . Step 6 Will the original square ever be entirely shaded? Explain why or why not.
 Lesson 13-2 Geometric Series Vocabulary geometric series BIG IDEA There are several ways to fi nd the sum of the successive terms of a fi nite geometric sequence Activity Step 1 Draw a large square on
Lesson 13-2 Geometric Series Vocabulary geometric series BIG IDEA There are several ways to fi nd the sum of the successive terms of a fi nite geometric sequence Activity Step 1 Draw a large square on
L E S S O N M A S T E R. Name. Vocabulary. 1. In the expression b n, b is called the?.
 Vocabulary 7- See pages 7-7 for objectives.. In the epression b n, b is called the?.. The identity function f has the equation f()?.. If g(), is g an eample of a power function? Why or why not?. In a game
Vocabulary 7- See pages 7-7 for objectives.. In the epression b n, b is called the?.. The identity function f has the equation f()?.. If g(), is g an eample of a power function? Why or why not?. In a game
8.1 Multiplication Properties of Exponents Objectives 1. Use properties of exponents to multiply exponential expressions.
 8.1 Multiplication Properties of Exponents Objectives 1. Use properties of exponents to multiply exponential expressions. 2. Use powers to model real life problems. Multiplication Properties of Exponents
8.1 Multiplication Properties of Exponents Objectives 1. Use properties of exponents to multiply exponential expressions. 2. Use powers to model real life problems. Multiplication Properties of Exponents
G.3 Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 section G 2 G. Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables Forms of Linear Equations Linear equations in two variables can take different forms. Some forms are easier to use for graphing, while others are
section G 2 G. Forms of Linear Equations in Two Variables Forms of Linear Equations Linear equations in two variables can take different forms. Some forms are easier to use for graphing, while others are
Rational Expressions and Functions
 1 Rational Expressions and Functions In the previous two chapters we discussed algebraic expressions, equations, and functions related to polynomials. In this chapter, we will examine a broader category
1 Rational Expressions and Functions In the previous two chapters we discussed algebraic expressions, equations, and functions related to polynomials. In this chapter, we will examine a broader category
Algebra 2, Spring Semester Review
 Class: Date: Algebra, Spring Semester Review 1. (1 point) Graph the relation and its inverse. Use open circles to graph the points of the inverse. x 0 4 9 10 y 3 7 1 a. c. b. d. 1 . (1 point) Is relation
Class: Date: Algebra, Spring Semester Review 1. (1 point) Graph the relation and its inverse. Use open circles to graph the points of the inverse. x 0 4 9 10 y 3 7 1 a. c. b. d. 1 . (1 point) Is relation
Sequences A sequence is a function, where the domain is a set of consecutive positive integers beginning with 1.
 1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 8: Sequences, Series, and Combinatorics Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences A sequence
1 CA-Fall 2011-Jordan College Algebra, 4 th edition, Beecher/Penna/Bittinger, Pearson/Addison Wesley, 2012 Chapter 8: Sequences, Series, and Combinatorics Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences A sequence
ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS
 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS 93 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS 5 5.1 Introduction You must have observed that in nature, many things follow a certain pattern, such as the petals of a sunflower, the holes of a honeycomb,
ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS 93 ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS 5 5.1 Introduction You must have observed that in nature, many things follow a certain pattern, such as the petals of a sunflower, the holes of a honeycomb,
Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series
 23 a4, 2A2A; P4A, P4B TEKS Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series Before You studied arithmetic sequences and series Now You will study geometric sequences and series Why? So you can solve problems about
23 a4, 2A2A; P4A, P4B TEKS Analyze Geometric Sequences and Series Before You studied arithmetic sequences and series Now You will study geometric sequences and series Why? So you can solve problems about
Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review
 Class: Date: Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review Short Answer. Evaluate the series 5n. 8 n =. Evaluate the series (n + ). n = What is the sum of the finite arithmetic series?. 9+ + 5+ 8+ + + 59. 6 + 9
Class: Date: Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review Short Answer. Evaluate the series 5n. 8 n =. Evaluate the series (n + ). n = What is the sum of the finite arithmetic series?. 9+ + 5+ 8+ + + 59. 6 + 9
2.5 Powerful Tens. Table Puzzles. A Practice Understanding Task. 1. Use the tables to find the missing values of x:
 2.5 Powerful Tens A Practice Understanding Task Table Puzzles 1. Use the tables to find the missing values of x: CC BY Eli Christman https://flic.kr/p/avcdhc a. b. x! = #$ % 1-2 100 1 10 50 100 3 1000
2.5 Powerful Tens A Practice Understanding Task Table Puzzles 1. Use the tables to find the missing values of x: CC BY Eli Christman https://flic.kr/p/avcdhc a. b. x! = #$ % 1-2 100 1 10 50 100 3 1000
F.4 Solving Polynomial Equations and Applications of Factoring
 section F4 243 F.4 Zero-Product Property Many application problems involve solving polynomial equations. In Chapter L, we studied methods for solving linear, or first-degree, equations. Solving higher
section F4 243 F.4 Zero-Product Property Many application problems involve solving polynomial equations. In Chapter L, we studied methods for solving linear, or first-degree, equations. Solving higher
Sequences and Series
 UNIT 11 Sequences and Series An integrated circuit can hold millions of microscopic components called transistors. How many transistors can fit in a chip on the tip of your finger? Moore s law predicts
UNIT 11 Sequences and Series An integrated circuit can hold millions of microscopic components called transistors. How many transistors can fit in a chip on the tip of your finger? Moore s law predicts
MAT Intermediate Algebra - Final Exam Review Textbook: Beginning & Intermediate Algebra, 5th Ed., by Martin-Gay
 MAT0 - Intermediate Algebra - Final Eam Review Tetbook: Beginning & Intermediate Algebra, 5th Ed., by Martin-Gay Section 2. Solve the equation. ) 9 - ( - ) = 2 Section 2.8 Solve the inequality. Graph the
MAT0 - Intermediate Algebra - Final Eam Review Tetbook: Beginning & Intermediate Algebra, 5th Ed., by Martin-Gay Section 2. Solve the equation. ) 9 - ( - ) = 2 Section 2.8 Solve the inequality. Graph the
1.4 Properties of Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions
 0 CHAPTER Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions.4 Properties of Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions S Use Operation and Order Symbols to Write Mathematical Sentences. 2 Identify Identity Numbers and
0 CHAPTER Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions.4 Properties of Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions S Use Operation and Order Symbols to Write Mathematical Sentences. 2 Identify Identity Numbers and
Chapter 4.1 Introduction to Relations
 Chapter 4.1 Introduction to Relations The example at the top of page 94 describes a boy playing a computer game. In the game he has to get 3 or more shapes of the same color to be adjacent to each other.
Chapter 4.1 Introduction to Relations The example at the top of page 94 describes a boy playing a computer game. In the game he has to get 3 or more shapes of the same color to be adjacent to each other.
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables
 In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
In this lesson we begin our study of algebra by introducing the concept of a variable as an unknown or varying quantity in an algebraic expression. We then take a closer look at algebraic expressions to
Definition: A sequence is a function from a subset of the integers (usually either the set
 Math 3336 Section 2.4 Sequences and Summations Sequences Geometric Progression Arithmetic Progression Recurrence Relation Fibonacci Sequence Summations Definition: A sequence is a function from a subset
Math 3336 Section 2.4 Sequences and Summations Sequences Geometric Progression Arithmetic Progression Recurrence Relation Fibonacci Sequence Summations Definition: A sequence is a function from a subset
Some examples of radical equations are. Unfortunately, the reverse implication does not hold for even numbers nn. We cannot
 40 RD.5 Radical Equations In this section, we discuss techniques for solving radical equations. These are equations containing at least one radical expression with a variable, such as xx 2 = xx, or a variable
40 RD.5 Radical Equations In this section, we discuss techniques for solving radical equations. These are equations containing at least one radical expression with a variable, such as xx 2 = xx, or a variable
Radicals and Radical Functions
 0 Radicals and Radical Functions So far we have discussed polynomial and rational expressions and functions. In this chapter, we study algebraic expressions that contain radicals. For example, + 2,, or.
0 Radicals and Radical Functions So far we have discussed polynomial and rational expressions and functions. In this chapter, we study algebraic expressions that contain radicals. For example, + 2,, or.
Rational Expressions and Functions
 Rational Expressions and Functions In the previous two chapters we discussed algebraic expressions, equations, and functions related to polynomials. In this chapter, we will examine a broader category
Rational Expressions and Functions In the previous two chapters we discussed algebraic expressions, equations, and functions related to polynomials. In this chapter, we will examine a broader category
Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review
 Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review Know all vocabulary, pay attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various types of directions in each of the sections of the textbook. Practice
Algebra 1 Enriched- Midterm Review Know all vocabulary, pay attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various types of directions in each of the sections of the textbook. Practice
Section 2: Equations and Inequalities
 Topic 1: Equations: True or False?... 29 Topic 2: Identifying Properties When Solving Equations... 31 Topic 3: Solving Equations... 34 Topic 4: Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Property... 36 Topic
Topic 1: Equations: True or False?... 29 Topic 2: Identifying Properties When Solving Equations... 31 Topic 3: Solving Equations... 34 Topic 4: Solving Equations Using the Zero Product Property... 36 Topic
Content Standard Geometric Series. What number 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 9-5 Content Standard Geometric Series A.SSE.4 Derive the formula for the sum of a geometric series (when the common ratio is not 1), and use the formula to solve problems. Objective To define geometric
9-5 Content Standard Geometric Series A.SSE.4 Derive the formula for the sum of a geometric series (when the common ratio is not 1), and use the formula to solve problems. Objective To define geometric
Convert the equation to the standard form for an ellipse by completing the square on x and y. 3) 16x y 2-32x - 150y = 0 3)
 Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x 6 + y = 1 1) foci: ( 15, 0) and (- 15, 0) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. ) (x + )
Math 370 Exam 5 Review Name Graph the ellipse and locate the foci. 1) x 6 + y = 1 1) foci: ( 15, 0) and (- 15, 0) Objective: (9.1) Graph Ellipses Not Centered at the Origin Graph the ellipse. ) (x + )
Algebra 2, Spring Semester Review 2013
 Class: Date: Algebra, Spring Semester Review 01 1. (1 point) Find the annual percent increase or decrease that y = 0.5(.) x models. 0% increase 0% decrease 10% increase d. 5% decrease. (1 point) An initial
Class: Date: Algebra, Spring Semester Review 01 1. (1 point) Find the annual percent increase or decrease that y = 0.5(.) x models. 0% increase 0% decrease 10% increase d. 5% decrease. (1 point) An initial
Review of Operations on the Set of Real Numbers
 1 Review of Operations on the Set of Real Numbers Before we start our journey through algebra, let us review the structure of the real number system, properties of four operations, order of operations,
1 Review of Operations on the Set of Real Numbers Before we start our journey through algebra, let us review the structure of the real number system, properties of four operations, order of operations,
MATH 153 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM
 NAME: Solutions MATH 53 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 2, 2005. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 questions. 3. Write your name on
NAME: Solutions MATH 53 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 2, 2005. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 questions. 3. Write your name on
My Math Plan Assessment #3 Study Guide
 My Math Plan Assessment # Study Guide 1. Identify the vertex of the parabola with the given equation. f(x) = (x 5) 2 7 2. Find the value of the function. Find f( 6) for f(x) = 2x + 11. Graph the linear
My Math Plan Assessment # Study Guide 1. Identify the vertex of the parabola with the given equation. f(x) = (x 5) 2 7 2. Find the value of the function. Find f( 6) for f(x) = 2x + 11. Graph the linear
Solutions Key Exponential and Radical Functions
 CHAPTER 11 Solutions Key Exponential and Radical Functions xzare YOU READY, PAGE 76 1. B; like terms: terms that contain the same variable raised to the same power. F; square root: one of two equal factors
CHAPTER 11 Solutions Key Exponential and Radical Functions xzare YOU READY, PAGE 76 1. B; like terms: terms that contain the same variable raised to the same power. F; square root: one of two equal factors
Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Algebra Lecture notes Math 1010
 Section 1.1: The Real Number System Definition of set and subset A set is a collection of objects and its objects are called members. If all the members of a set A are also members of a set B, then A is
Section 1.1: The Real Number System Definition of set and subset A set is a collection of objects and its objects are called members. If all the members of a set A are also members of a set B, then A is
PREPARED BY: J. LLOYD HARRIS 07/17
 PREPARED BY: J. LLOYD HARRIS 07/17 Table of Contents Introduction Page 1 Section 1.2 Pages 2-11 Section 1.3 Pages 12-29 Section 1.4 Pages 30-42 Section 1.5 Pages 43-50 Section 1.6 Pages 51-58 Section 1.7
PREPARED BY: J. LLOYD HARRIS 07/17 Table of Contents Introduction Page 1 Section 1.2 Pages 2-11 Section 1.3 Pages 12-29 Section 1.4 Pages 30-42 Section 1.5 Pages 43-50 Section 1.6 Pages 51-58 Section 1.7
1.2 Algebraic Expressions and Sets of Numbers
 Section. Algebraic Expressions and Sets of Numbers 7. Algebraic Expressions and Sets of Numbers S Identify and Evaluate Algebraic Expressions. Identify Natural Numbers, Whole Numbers, Integers, and Rational
Section. Algebraic Expressions and Sets of Numbers 7. Algebraic Expressions and Sets of Numbers S Identify and Evaluate Algebraic Expressions. Identify Natural Numbers, Whole Numbers, Integers, and Rational
ABE Math Review Package
 P a g e ABE Math Review Package This material is intended as a review of skills you once learned and wish to review before your assessment. Before studying Algebra, you should be familiar with all of the
P a g e ABE Math Review Package This material is intended as a review of skills you once learned and wish to review before your assessment. Before studying Algebra, you should be familiar with all of the
Lesson 1: Successive Differences in Polynomials
 Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Successive Differences in Polynomials Classwork Opening Exercise John noticed patterns in the arrangement of numbers in the table below. 2.4 3.4 4.4 5.4 6.4 5.76 11.56 19.36 29.16 40.96
Lesson 1 Lesson 1: Successive Differences in Polynomials Classwork Opening Exercise John noticed patterns in the arrangement of numbers in the table below. 2.4 3.4 4.4 5.4 6.4 5.76 11.56 19.36 29.16 40.96
Rational Equations and Graphs
 RT.5 Rational Equations and Graphs Rational Equations In previous sections of this chapter, we worked with rational expressions. If two rational expressions are equated, a rational equation arises. Such
RT.5 Rational Equations and Graphs Rational Equations In previous sections of this chapter, we worked with rational expressions. If two rational expressions are equated, a rational equation arises. Such
Fall IM I Exam B
 Fall 2011-2012 IM I Exam B Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following equations is linear? a. y = 2x - 3 c. 2. What is the
Fall 2011-2012 IM I Exam B Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following equations is linear? a. y = 2x - 3 c. 2. What is the
SEQUENCES & SERIES. Arithmetic sequences LESSON
 LESSON SEQUENCES & SERIES In mathematics you have already had some experience of working with number sequences and number patterns. In grade 11 you learnt about quadratic or second difference sequences.
LESSON SEQUENCES & SERIES In mathematics you have already had some experience of working with number sequences and number patterns. In grade 11 you learnt about quadratic or second difference sequences.
Unit 1 Foundations of Algebra
 1 Unit 1 Foundations of Algebra Real Number System 2 A. Real Number System 1. Counting Numbers (Natural Numbers) {1,2,3,4, } 2. Whole Numbers { 0,1,2,3,4, } 3. Integers - Negative and Positive Whole Numbers
1 Unit 1 Foundations of Algebra Real Number System 2 A. Real Number System 1. Counting Numbers (Natural Numbers) {1,2,3,4, } 2. Whole Numbers { 0,1,2,3,4, } 3. Integers - Negative and Positive Whole Numbers
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 2.1. SERIES 1 (Elementary progressions and series) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER.1 SERIES 1 (Elementary progressions and series) by A.J.Hobson.1.1 Arithmetic progressions.1. Arithmetic series.1.3 Geometric progressions.1.4 Geometric series.1.5 More general
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER.1 SERIES 1 (Elementary progressions and series) by A.J.Hobson.1.1 Arithmetic progressions.1. Arithmetic series.1.3 Geometric progressions.1.4 Geometric series.1.5 More general
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3
 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 Evaluate the epression. ) a) 73 (-4)2-44 d) 4-3 e) (-)0 f) -90 g) 23 2-4 h) (-2)4 80 i) (-2)5 (-2)-7 j) 5-6 k) 3-2 l) 5-2 Simplify the epression. Write your answer
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST 3 Evaluate the epression. ) a) 73 (-4)2-44 d) 4-3 e) (-)0 f) -90 g) 23 2-4 h) (-2)4 80 i) (-2)5 (-2)-7 j) 5-6 k) 3-2 l) 5-2 Simplify the epression. Write your answer
or the number of bacteria in a colony after each hour, if the colony starts with one bacteria and each bacteria divides into two every hour
 448 Sequences and Series In everyday life, we can observe sequences or series of events in many contexts. For instance, we line up to enter a store in a sequence, we make a sequence of mortgage payments,
448 Sequences and Series In everyday life, we can observe sequences or series of events in many contexts. For instance, we line up to enter a store in a sequence, we make a sequence of mortgage payments,
My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide
 My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4 2. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x 2 + 9x + 1 = 17. Multiply and simplify
My Math Plan Assessment #2 Study Guide 1. Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the linear equation. 8x y = 4 2. Use factoring to solve the quadratic equation. x 2 + 9x + 1 = 17. Multiply and simplify
8.1 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Products. Learning Outcome To use properties of exponents involving products
 8.1 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Products Learning Outcome To use properties of exponents involving products Product of Powers Property Let a be a real number, and let m and n be positive integers.
8.1 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Products Learning Outcome To use properties of exponents involving products Product of Powers Property Let a be a real number, and let m and n be positive integers.
P.3 Division of Polynomials
 00 section P3 P.3 Division of Polynomials In this section we will discuss dividing polynomials. The result of division of polynomials is not always a polynomial. For example, xx + 1 divided by xx becomes
00 section P3 P.3 Division of Polynomials In this section we will discuss dividing polynomials. The result of division of polynomials is not always a polynomial. For example, xx + 1 divided by xx becomes
R.3 Properties and Order of Operations on Real Numbers
 1 R.3 Properties and Order of Operations on Real Numbers In algebra, we are often in need of changing an expression to a different but equivalent form. This can be observed when simplifying expressions
1 R.3 Properties and Order of Operations on Real Numbers In algebra, we are often in need of changing an expression to a different but equivalent form. This can be observed when simplifying expressions
Name Class Date. Solving Quadratic Equations by Using Square Roots Going Deeper
 Name Class Date 8-7 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using Square Roots Going Deeper Essential question: How can you solve a quadratic equation using square roots? 1 PREP FOR A-REI.2.4b ENGAGE Understanding
Name Class Date 8-7 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using Square Roots Going Deeper Essential question: How can you solve a quadratic equation using square roots? 1 PREP FOR A-REI.2.4b ENGAGE Understanding
Sequences, Series, and Probability
 Sequences, Series, and Probability 9. Sequences and Series 9. Arithmetic Sequences and Partial Sums 9.3 Geometric Sequences and Series 9.4 Mathematical Induction 9.5 The Binomial Theorem 9.6 Counting Principles
Sequences, Series, and Probability 9. Sequences and Series 9. Arithmetic Sequences and Partial Sums 9.3 Geometric Sequences and Series 9.4 Mathematical Induction 9.5 The Binomial Theorem 9.6 Counting Principles
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 12-1 Introduction to Sequences
 Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 12-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Finding Terms of a Sequence by Using a Recursive Formula Find the first five terms of each sequence. A. a n a n1 1, where n 2 and
Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 12-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Finding Terms of a Sequence by Using a Recursive Formula Find the first five terms of each sequence. A. a n a n1 1, where n 2 and
Principles of Math 12 - Geometric Series Practice Exam 1
 Principles of Math 2 - Geometric Series Practice Exam www.math2.com Principles of Math 2 - Geometric Series Practice Exam Use this sheet to record your answers. 0. 8. 26. NR ). 9. 27. 2. 2. 20. 28. 3.
Principles of Math 2 - Geometric Series Practice Exam www.math2.com Principles of Math 2 - Geometric Series Practice Exam Use this sheet to record your answers. 0. 8. 26. NR ). 9. 27. 2. 2. 20. 28. 3.
Pre-Calc 2nd Semester Review Packet - #2
 Pre-Calc 2nd Semester Review Packet - #2 Use the graph to determine the function's domain and range. 1) 2) Find the domain of the rational function. 3) h(x) = x + 8 x2-36 A) {x x -6, x 6, x -8} B) all
Pre-Calc 2nd Semester Review Packet - #2 Use the graph to determine the function's domain and range. 1) 2) Find the domain of the rational function. 3) h(x) = x + 8 x2-36 A) {x x -6, x 6, x -8} B) all
55 th AMC 12 A
 th AMC 1 A 1. Alicia earns $0 per hour, of which 1.4% is deducted to pay local taxes. How many cents per hour of Alicia s wages are used to pay local taxes? (A) 0.009 (B) 0.09 (C) 0.9 (D).9 (E) 9. On the
th AMC 1 A 1. Alicia earns $0 per hour, of which 1.4% is deducted to pay local taxes. How many cents per hour of Alicia s wages are used to pay local taxes? (A) 0.009 (B) 0.09 (C) 0.9 (D).9 (E) 9. On the
Intermediate Algebra Semester Summary Exercises. 1 Ah C. b = h
 . Solve: 3x + 8 = 3 + 8x + 3x A. x = B. x = 4 C. x = 8 8 D. x =. Solve: w 3 w 5 6 8 A. w = 4 B. w = C. w = 4 D. w = 60 3. Solve: 3(x ) + 4 = 4(x + ) A. x = 7 B. x = 5 C. x = D. x = 4. The perimeter of
. Solve: 3x + 8 = 3 + 8x + 3x A. x = B. x = 4 C. x = 8 8 D. x =. Solve: w 3 w 5 6 8 A. w = 4 B. w = C. w = 4 D. w = 60 3. Solve: 3(x ) + 4 = 4(x + ) A. x = 7 B. x = 5 C. x = D. x = 4. The perimeter of
L.4 Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation
 L. Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation 1 Mathematical inequalities are often used in everyday life situations. We observe speed limits on highways, minimum payments on credit card bills, maximum
L. Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation 1 Mathematical inequalities are often used in everyday life situations. We observe speed limits on highways, minimum payments on credit card bills, maximum
9.7 Common Logarithms, Natural Logarithms, and Change of Base
 580 CHAPTER 9 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Graph each function. 6. y = a x 2 b 7. y = 2 x + 8. y = log x 9. y = log / x Solve. 20. 2 x = 8 2. 9 = x -5 22. 4 x - = 8 x +2 2. 25 x = 25 x - 24. log
580 CHAPTER 9 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Graph each function. 6. y = a x 2 b 7. y = 2 x + 8. y = log x 9. y = log / x Solve. 20. 2 x = 8 2. 9 = x -5 22. 4 x - = 8 x +2 2. 25 x = 25 x - 24. log
1 Chapter 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models
 1 Chapter 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models 1.1 Introduction to Graphing 1.1.1 Know how to graph an equation Eample 1. Create a table of values and graph the equation y = 1. f() 6 1 0 1 f() 3 0 1 0 3 4
1 Chapter 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models 1.1 Introduction to Graphing 1.1.1 Know how to graph an equation Eample 1. Create a table of values and graph the equation y = 1. f() 6 1 0 1 f() 3 0 1 0 3 4
ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS
 ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS Chapter 2 2-1 Writing Equations 2-2 Solving One Step Equations 2-3 Solving Multi-Step Equations 2-4 Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side 2-5 Solving Equations Involving
ALGEBRA 1 FINAL EXAM TOPICS Chapter 2 2-1 Writing Equations 2-2 Solving One Step Equations 2-3 Solving Multi-Step Equations 2-4 Solving Equations with the Variable on Each Side 2-5 Solving Equations Involving
... a a a a. n times. 5 squared 2 raised to fourth power 10 cubed (5) 2 = 5 5 = 25 (2) 4 = 2222 = 16 (10) 3 = (10)(10)(10) = 1000
 272 Section 4.1 Exponents & Logarithms Exponential notation serves as a shorthand notation for products formed by repeated multiplication of the same number. For instance, the product of ten times ten
272 Section 4.1 Exponents & Logarithms Exponential notation serves as a shorthand notation for products formed by repeated multiplication of the same number. For instance, the product of ten times ten
A monomial or sum of monomials
 Polynomial: A monomial or sum of monomials Polynomial in x is an expression of the form a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 +. a 1 x 1 + a 0 where n is a positive integer and a n 0 Example: 6x 3 + 2x 8x
Polynomial: A monomial or sum of monomials Polynomial in x is an expression of the form a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 +. a 1 x 1 + a 0 where n is a positive integer and a n 0 Example: 6x 3 + 2x 8x
The given pattern continues. Write down the nth term of the sequence {an} suggested by the pattern. 3) 4, 10, 16, 22, 28,... 3)
 M60(Precalculus) Evaluate the factorial expression. 9! ) 7!! ch practice test ) Write out the first five terms of the sequence. ) {sn} = (-)n - n + n - ) The given pattern continues. Write down the nth
M60(Precalculus) Evaluate the factorial expression. 9! ) 7!! ch practice test ) Write out the first five terms of the sequence. ) {sn} = (-)n - n + n - ) The given pattern continues. Write down the nth
F.1 Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping
 section F1 214 is the reverse process of multiplication. polynomials in algebra has similar role as factoring numbers in arithmetic. Any number can be expressed as a product of prime numbers. For example,
section F1 214 is the reverse process of multiplication. polynomials in algebra has similar role as factoring numbers in arithmetic. Any number can be expressed as a product of prime numbers. For example,
MA Practice Questions for the Final Exam 07/10 .! 2! 7. 18! 7.! 30! 12 " 2! 3. A x y B x y C x xy x y D.! 2x! 5 y E.
 MA 00 Practice Questions for the Final Eam 07/0 ) Simplify:! y " [! (y " )].!! 7. 8! 7.! 0! "! A y B y C y y D.!! y E. None of these ) Which number is irrational? A.! B..4848... C. 7 D.. E.! ) The slope
MA 00 Practice Questions for the Final Eam 07/0 ) Simplify:! y " [! (y " )].!! 7. 8! 7.! 0! "! A y B y C y y D.!! y E. None of these ) Which number is irrational? A.! B..4848... C. 7 D.. E.! ) The slope
Unit 6: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Unit 6: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 Exponential Functions p. 55-56 2 Applications p. 57-58 3 Derivatives of Exponential Functions 4 Derivatives of Exponential Functions
Unit 6: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions DAY TOPIC ASSIGNMENT 1 Exponential Functions p. 55-56 2 Applications p. 57-58 3 Derivatives of Exponential Functions 4 Derivatives of Exponential Functions
Complete Week 18 Package
 Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Complete Week 18 Package Jeanette Stein Table of Contents Unit 4 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 86 Bellringer --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SY14-15 Algebra Exit Exam - PRACTICE Version
 Student Name: Directions: Solve each problem. You have a total of 90 minutes. Choose the best answer and fill in your answer document accordingly. For questions requiring a written response, write your
Student Name: Directions: Solve each problem. You have a total of 90 minutes. Choose the best answer and fill in your answer document accordingly. For questions requiring a written response, write your
Name Date Class , 100, 1000, 10,000, common ratio:
 Name Date Class 11-1 Practice A Geometric Sequences Find the common ratio of each geometric sequence. Then find the next three terms in each geometric sequence. 1. 1, 4, 16, 64, 2. 10, 100, 1000, 10,000,
Name Date Class 11-1 Practice A Geometric Sequences Find the common ratio of each geometric sequence. Then find the next three terms in each geometric sequence. 1. 1, 4, 16, 64, 2. 10, 100, 1000, 10,000,
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 1332 Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the cardinal number for the set. 1) {10, 12, 14,..., 68} 1) Are the sets
Math 1332 Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Find the cardinal number for the set. 1) {10, 12, 14,..., 68} 1) Are the sets
QUESTIONS 1-46 REVIEW THE OBJECTIVES OF CHAPTER 2.
 MAT 101 Course Review Questions Valid for Fall 2014, Spring 2015 and Summer 2015 MIDTERM EXAM FINAL EXAM Questions 1-86 are covered on the Midterm. There are 25 questions on the midterm, all multiple choice,
MAT 101 Course Review Questions Valid for Fall 2014, Spring 2015 and Summer 2015 MIDTERM EXAM FINAL EXAM Questions 1-86 are covered on the Midterm. There are 25 questions on the midterm, all multiple choice,
MAT 135. In Class Assignments
 MAT 15 In Class Assignments 1 Chapter 1 1. Simplify each expression: a) 5 b) (5 ) c) 4 d )0 6 4. a)factor 4,56 into the product of prime factors b) Reduce 4,56 5,148 to lowest terms.. Translate each statement
MAT 15 In Class Assignments 1 Chapter 1 1. Simplify each expression: a) 5 b) (5 ) c) 4 d )0 6 4. a)factor 4,56 into the product of prime factors b) Reduce 4,56 5,148 to lowest terms.. Translate each statement
Alpha Sequences and Series FAMAT State Convention 2017
 Alpha Sequences and Series FAMAT State Convention 017 For all questions, E NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. 1. We say that a number is arithmetically sequenced if the digits, in order,
Alpha Sequences and Series FAMAT State Convention 017 For all questions, E NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. 1. We say that a number is arithmetically sequenced if the digits, in order,
(MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R)
 College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
MATH 080 Final-Exam Review
 MATH 080 Final-Exam Review Can you simplify an expression using the order of operations? 1) Simplify 32(11-8) - 18 3 2-3 2) Simplify 5-3 3-3 6 + 3 A) 5 9 B) 19 9 C) - 25 9 D) 25 9 Can you evaluate an algebraic
MATH 080 Final-Exam Review Can you simplify an expression using the order of operations? 1) Simplify 32(11-8) - 18 3 2-3 2) Simplify 5-3 3-3 6 + 3 A) 5 9 B) 19 9 C) - 25 9 D) 25 9 Can you evaluate an algebraic
Algebra I EOC Review (Part 3)
 1. Statement Reason 1. 2.5(6.25x + 0.5) = 11 1. Given 2. 15.625x + 1.25 = 11 2. Distribution Property 3. 15.625x = 9.75 3. Subtraction Property of Equality 4. x = 0.624 4. Division Property of Equality
1. Statement Reason 1. 2.5(6.25x + 0.5) = 11 1. Given 2. 15.625x + 1.25 = 11 2. Distribution Property 3. 15.625x = 9.75 3. Subtraction Property of Equality 4. x = 0.624 4. Division Property of Equality
L.6 Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
 L.6 Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities 1 The concept of absolute value (also called numerical value) was introduced in Section R. Recall that when using geometrical visualisation of real numbers
L.6 Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities 1 The concept of absolute value (also called numerical value) was introduced in Section R. Recall that when using geometrical visualisation of real numbers
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Equations by Adding or Subtracting
 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Equations by Adding or Subtracting Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 2-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary equation solution of an equation Solve
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Equations by Adding or Subtracting Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 2-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary equation solution of an equation Solve
Recurrence Relations
 Recurrence Relations Recurrence Relations Reading (Epp s textbook) 5.6 5.8 1 Recurrence Relations A recurrence relation for a sequence aa 0, aa 1, aa 2, ({a n }) is a formula that relates each term a k
Recurrence Relations Recurrence Relations Reading (Epp s textbook) 5.6 5.8 1 Recurrence Relations A recurrence relation for a sequence aa 0, aa 1, aa 2, ({a n }) is a formula that relates each term a k
Test: Chapter 8 Number patterns and recursion
 Student name: Multiple-choice questions (12 marks) 1 In the sequence 6, 13, 20, 27, the value of the common difference, d, is: A 21 B 7 C 7 D 21 E 34 2 Th e thirteenth term, t 13, in the sequence 63, 56,
Student name: Multiple-choice questions (12 marks) 1 In the sequence 6, 13, 20, 27, the value of the common difference, d, is: A 21 B 7 C 7 D 21 E 34 2 Th e thirteenth term, t 13, in the sequence 63, 56,
The units on the average rate of change in this situation are. change, and we would expect the graph to be. ab where a 0 and b 0.
 Lesson 9: Exponential Functions Outline Objectives: I can analyze and interpret the behavior of exponential functions. I can solve exponential equations analytically and graphically. I can determine the
Lesson 9: Exponential Functions Outline Objectives: I can analyze and interpret the behavior of exponential functions. I can solve exponential equations analytically and graphically. I can determine the
11) 12) ) ) ) )
 Math 155 Course Review Questions 1-38 can be used as a study plan for the midterm. All questions should be studied for the final exam. Use the order of operations to find the value of the expression. 1)
Math 155 Course Review Questions 1-38 can be used as a study plan for the midterm. All questions should be studied for the final exam. Use the order of operations to find the value of the expression. 1)
10-1 Sequences as Functions. Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic. Write yes or no. 1. 8, 2, 12, 22
 Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic. Write yes or no. 1. 8, 2, 12, 22 Subtract each term from the term directly after it. The common difference is 10. 3. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 Subtract each term from
Determine whether each sequence is arithmetic. Write yes or no. 1. 8, 2, 12, 22 Subtract each term from the term directly after it. The common difference is 10. 3. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 Subtract each term from
Properties of Radicals
 9. Properties of Radicals Essential Question How can you multiply and divide square roots? Operations with Square Roots Work with a partner. For each operation with square roots, compare the results obtained
9. Properties of Radicals Essential Question How can you multiply and divide square roots? Operations with Square Roots Work with a partner. For each operation with square roots, compare the results obtained
Name: Class: Date: ID: A. c. the quotient of z and 28 z divided by 28 b. z subtracted from 28 z less than 28
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Review for Final Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Give two ways to write the algebraic expression z 28 in words.
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Review for Final Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Give two ways to write the algebraic expression z 28 in words.
2018 Pre-Cal Spring Semester Review Name: Per:
 08 Pre-Cal Spring Semester Review Name: Per: For # 4, find the domain of each function. USE INTERVAL NOTATION!!. 4 f ( ) 5. f ( ) 6 5. f( ) 5 4. f( ) 4 For #5-6, find the domain and range of each graph.
08 Pre-Cal Spring Semester Review Name: Per: For # 4, find the domain of each function. USE INTERVAL NOTATION!!. 4 f ( ) 5. f ( ) 6 5. f( ) 5 4. f( ) 4 For #5-6, find the domain and range of each graph.
Independent Study Project: Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Name: Date: Period: Independent Study Project: Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Part I: Read each section taken from the Algebra & Trigonometry (Blitzer 2014) textbook. Fill in the blanks
Name: Date: Period: Independent Study Project: Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Part I: Read each section taken from the Algebra & Trigonometry (Blitzer 2014) textbook. Fill in the blanks
Geometric Sequences and Series
 12-2 OBJECTIVES Find the nth term and geometric means of a geometric sequence. Find the sum of n terms of a geometric series. Geometric Sequences and Series ACCOUNTING Bertha Blackwell is an accountant
12-2 OBJECTIVES Find the nth term and geometric means of a geometric sequence. Find the sum of n terms of a geometric series. Geometric Sequences and Series ACCOUNTING Bertha Blackwell is an accountant
Lesson 2 Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Lesson 2 Skills Practice 1. Evaluate the following expressions for the given values. Show all of your work. Use your graphing calculator to check your answers. a. b. c. d. e. f. ( ) ( ) 2.
Name: Date: Lesson 2 Skills Practice 1. Evaluate the following expressions for the given values. Show all of your work. Use your graphing calculator to check your answers. a. b. c. d. e. f. ( ) ( ) 2.
Algebra 2 - Midterm Exam Review
 Class: Date: Algebra 2 - Midterm Exam Review The Algebra 2 Midterm Exam must be taken by ALL Algebra 2 students. An exemption pass may be used to exempt the score for the Algebra 2 Midterm Exam. It should
Class: Date: Algebra 2 - Midterm Exam Review The Algebra 2 Midterm Exam must be taken by ALL Algebra 2 students. An exemption pass may be used to exempt the score for the Algebra 2 Midterm Exam. It should
Radicals and Radical Functions
 0 Radicals and Radical Functions So far we have discussed polynomial and rational expressions and functions. In this chapter, we study algebraic expressions that contain radicals. For example, + 2, xx,
0 Radicals and Radical Functions So far we have discussed polynomial and rational expressions and functions. In this chapter, we study algebraic expressions that contain radicals. For example, + 2, xx,
REVIEW SHEETS ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA MATH 65
 REVIEW SHEETS ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA MATH 65 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts which are taught in the specified math course. The sheets
REVIEW SHEETS ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA MATH 65 A Summary of Concepts Needed to be Successful in Mathematics The following sheets list the key concepts which are taught in the specified math course. The sheets
Determine whether the given lengths can be side lengths of a right triangle. 1. 6, 7, , 15, , 4, 5
 Algebra Test Review Name Instructor Hr/Blk Determine whether the given lengths can be side lengths of a right triangle. 1., 7, 8. 17, 1, 8.,, For the values given, a and b are legs of a right triangle.
Algebra Test Review Name Instructor Hr/Blk Determine whether the given lengths can be side lengths of a right triangle. 1., 7, 8. 17, 1, 8.,, For the values given, a and b are legs of a right triangle.
Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test.
 Elementary Algebra problems you can use for practice. Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test. Use these problems to help you get up to speed. Perform the indicated operation.
Elementary Algebra problems you can use for practice. Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test. Use these problems to help you get up to speed. Perform the indicated operation.
Using the Laws of Exponents to Simplify Rational Exponents
 6. Explain Radicals and Rational Exponents - Notes Main Ideas/ Questions Essential Question: How do you simplify expressions with rational exponents? Notes/Examples What You Will Learn Evaluate and simplify
6. Explain Radicals and Rational Exponents - Notes Main Ideas/ Questions Essential Question: How do you simplify expressions with rational exponents? Notes/Examples What You Will Learn Evaluate and simplify
Lesson 26: Problem Set Sample Solutions
 Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems and 2 provide students with more practice converting arithmetic and geometric sequences between explicit and recursive forms. Fluency with geometric sequences is required
Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems and 2 provide students with more practice converting arithmetic and geometric sequences between explicit and recursive forms. Fluency with geometric sequences is required
loose-leaf paper Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Algebra 2 Trig Midterm Exam Review 2014 loose-leaf paper Do all work in a neat and organzied manner on Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Class: Date: Algebra 2 Trig Midterm Exam Review 2014 loose-leaf paper Do all work in a neat and organzied manner on Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
