Coupled CFD-STH analysis of liquid metal flows: STAR-CCM+ - RELAP5
|
|
|
- Georgina Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STAR Global Conference 2017 Berlin Mar 6-8, 2017 Coupled CFD-STH analysis of liquid metal flows: STAR-CCM+ - RELAP5 Marti Jeltsov, Kaspar Kööp, Pavel Kudinov Division of Nuclear Power Safety KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden 1
2 Outline Physical phenomena of interest In LFRs In TALL-3D experiment Coupling methodology Code qualification methodology Results Standalone Star-CCM+ Coupled Star-CCM+ - Relap5 Conclusions 2
3 Thermal-hydraulic phenomena in LFRs The use of numerical modeling and simulation (M&S) in the design and safety analysis of nuclear reactor systems is increasing. Commonly, 0D/1D System- Thermal Hydraulics (STH) codes have been used in the design, safety analysis and licensing of LWRs. Pool-type LFRs are characterized by multidimensional flows with large fraction of natural circulation (sensitive to small changes in the system). Numerical tools used for LFR analysis need to be validated for these specific phenomena. Single phase phenomena Free shear Wall shear Thermal mixing Thermal stratification Jet impingement of a surface Thermal inertia of structures Natural circulation Multi-phase phenomena Bubble/particle transport Boiling Sloshing Melting/solidification Model type Turbulence model Turbulence model, wall functions Momentum convection, bulk turbulence Thermal diffusion, buoyancy models Turbulence model (production) Conjugate heat transfer Integrally all model Model type Interfacial momentum transfer (drag) and buoyancy Irrelevant ALE, Eulerian+interphase tracking (e.g. VoF, Level Set) MYRRHA ALFRED ELFR 3
4 TALL-3D loop design The facility loop is comprised of 3 sections: main heater leg (left/red) 3D test section leg (center/green) heat exchanger leg (right/blue) Essential components Main heater Straight run 3D Test section Heat exchanger (secondary loop is not shown) Secondary loop utilizes Dowtherm HT fluid as coolant and uses a fan as a secondary heat exchanger Electric Permanent Magnet (EPM) pump 3 Ball valves (one per each section) for fine tuning of flow rate 6 expansion compensators Oxygen sensor Expansion tank Instrumentation includes Thermocouples ~330 TCs (154 in the test section) Differential pressure measurement system 5 DP groups (each contains one pressure transducer and several control valves), 11 measurement points total 15 differential pressures around the loop can be measured Flow meters: Two Carioles flow meters on the primary loop One transit time ultrasonic flow meter on the secondary loop Dimensions: Total height 6980 mm; loop height 5800 mm, width 1480 mm Pipe ID OD
5 TALL-3D test section Designed to pronounce transient 3D effects in the system The dimensions are selected such that at high flow rate (forced convection) the jet mixes the pool and at low flow rate thermal stratification develops (natural circulation) 5
6 TALL-3D test section: Flow regimes Full mixing at m ሶ > 1.0 kg/s jet penetrates the stratified layer and mixes the pool Partial mixing at mሶ 0.7 kg/s jet penetrates the stratified layer in the middle of the pool, but has not enough momentum to penetrate the buoyant wall jet at the heated wall Thermal stratification at m ሶ < 0.3 kg/s jet is too weak to break the stratified layer 6
7 TH phenomena in TALL-3D Phenomenon Description Regime Experiments Thermal mixing and stratification in the test section are governed by the jet dynamics. A necessary condition for CFD validation, Re, Ri N01, F01, T01 Free jet flow then, is that the codes accurately simulate free jets in a pool-like geometry in steady state conditions, both in forced and in natural circulation. Measurements: Temperature measurements on the inner circular plate are the validation data for this phenomenon. Jet impingement on a surface It is a key factor to produce the recirculation patterns inside the test section. The design simulations show that the jet will not reach the disk in natural circulation conditions therefore this validation can only be performed against steady state, forced circulation experiments. Measurements: Minimum mass flow rate for the jet to reach the disk measured by a Coriolis FM is used in validation metric. Re F01, T01 Jet induced circulation in the pool Thermal stratification Mixing Thermal inertia of the structure Thermal conduction through the plate Turbulence Circulation in the pool is produced by the diversion of the inlet jet due to the circular inner plate. Validation data can be therefore obtained in forced or fast natural circulation experiments. Measurements: As the circulation drives mixing, validation data for this phenomenon is the temperature field in the test section. The codes capability to capture transient development of stratification after switching on the heater can be assessed against temperature data obtained in forced (at small flow rates to prevent jet reaching the plate to enhance mixing) or natural circulation thermal transients in the loop. Measurements: Inner pool thermocouples. The codes capability to capture thermal mixing can be assessed against temperature data obtained in steady state forced circulation experiments. Measurements: Inner pool thermocouples. Heat transfer between LBE and heater/ambient is dependent on the thermal conductivity and capacity of the wall materials. Thermal inertia is important in transients where the temperature changes on either side of the walls, e.g. heater is switched on/off. Measurements: Temperature at the outer and inner side of the wall is measured in order to validate thermal conductivity model. Fluid temperatures below and above the circular plate can be different resulting in heat transfer through the plate. The circular plate is made of conductive material and the temperature gradient through that material is therefore a subject to validation. Measurements: Thermocouples at the bottom and top of the plate. Turbulence modeling is regarded as the one of the major contributors to uncertainty in the CFD M&S. TALL-3D provides integral data for turbulence studies. Turbulence produced in the wall boundary and jet shear layers is responsible for the flow energy loss in the test section. Measurements: Pressure loss over the test section is considered in validation metric. Re Gr, Re Re Re F01, T01 F01, N01, T01 F01, T01 T01 F01, N01, T01 F01, N01, T01 NB! In initial or final steady states belonging to transient tests, Reynolds number is between 3,600 and 58,000. Lower and higher Reynolds values occur during flow oscillations and in the dedicated test for different steady states. 7
8 HX mass flow rate MH power TS power HX mass flowrate MH power TS power Oil inlet temperature Tests performed in THINS project Initial steady state Final steady state # Name Notes kg/sec kw kw kg/sec kw kw C 1 C01 DPs measurements 2 C02 TCs offset 3 T Forced to natural circulation transient 4 T Forced to natural circulation transient 5 T Forced to natural circulation transient 6 T Forced to natural circulation transient 7 T Forced to natural circulation transient 8 T Forced to natural circulation transient 9 T Natural to natural circulation transient 10 T Natural to forced circulation transient 11 T Natural to natural circulation transient 12 T Natural to natural circulation transient 8
9 CFD+STH validation CFD validation STH validation Phenomena validation matrix Physical Phenomena FC 3DH Off Steady states FC 3DH On NC 3DH Off NC 3DH On Transients T01 T02 T03 T06 T09 T11 1. Drag in forced circulation x x x x x 2. Drag in natural circulation x x x x x x x x 3. Transient drag x x x x x x 4. Heat transfer in forced circulation 5. Heat transfer in natural circulation 6. Stability of natural circulation 7. Thermal inertia of the loop sections transient 8. Heat losses as a function of the system temperature steady state 9. Heat losses as a function of the system temperature transients x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x 1. Free jet flow x x x x x x x x x x 2. Jet impingement on a surface x x x x x 3.Jet-induced recirculation x x x x x 4.Stratification development x x x x x x 5. Mixing x x 6. Buyoant wall jet flow x x x x x x 1. Transient response of the CFD test section 2. Transient response of the loop 3. Nonlinear feedbacks and instabilities x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x 9
10 Code coupling The aim of the code coupling is to achieve required accuracy with affordable computational effort. CFD domain Codes that are coupled: CFD: Star-CCM+ STH: RELAP5/Mod3.3-LBE Coupling the transition and transformation of information between 1D and 3D codes. Controlled by a Java code. 10
11 Code coupling aspects What information is exchanged? Amount and type of coupling variables (values, profiles, sources, sinks etc.) Information that one code lacks must be provided by another Where is the information exchanged? Definition of the spatial division of system between codes Options: domain decomposition and domain overlapping Coupling boundary location must be selected such that data losses are minimized when transformed during transition (e.g. 1D 3D in fully developed flow region) When is the information exchanged? Frequency of the data exchange (i.e. coupling time-step) The rate of change of coupling variables must be captured Options: constant and automatically variable time-stepping How is the information exchanged? The exchange of information can be uni- or bi-directional Unidirectional approach can be used to zooming while bidirectional is required to analyze behavior of systems featuring feedbacks between components 11
12 Coupling in space Domain overlapping vs decomposition - Domain overlapping chosen to avoid STH solution stability issues 12
13 Exchanged variables During a coupling time-step: Inlet b.c. are provided to CFD STH temperature field and pressure drop are corrected. Virtual heater Qሶ ሶ Q calculation T outlet Works in both flow directions K loss K loss calculation Flow direction STH CFD T inlet mሶ 13
14 Coupling in time Start coupled calculation Execute STH for 1 coupling time step Execute CFD for 1 coupling time step Convergence? NO Iterate with STH until converged YES coupling time step NO End of simulation? YES coupled simulation End coupled calculation 14
15 Coupling algorithm STH and CFD solutions have to be converged at the beginning of coupled calculations Either a common steady state, or continuation of paused coupled calculation. Coupling starts with STH calculation Mass flow rate and inlet temperature are provided to CFD p n-1 n n+1 CFD calculates the same time-step using b.c. from STH CFD STH m, ሶ T in allowed ΔT out < ΔT out ΔT out > ΔT allowed out Q virtual The difference in solutions is evaluated against convergence criterion Δt STH < Δt CFD Based on the difference, correction terms are calculated Δt coupling = Δt CFD time STH calculates new solution until convergence criterion is met (or number of allowed STH iterations is reached) 15
16 Architecture Controls time marching (Δt C ), extrapolates and averages b.c., modifies CFD and STH models, executes codes, logs data. T inlet CFD T outlet ሶ Q T inlet mሶ ΔP K loss mሶ Coupling code features: Written in Java (a macro nested in Star-CCM+) OS agnostic (Windows/Linux, given that respective executables are available) Automatic creation of STH/CFD inputs Automatic switch between and calculation of steady state/transient models Logging of variables (only desired part of solutions are stored) LBE properties from Sobolev (2011) (since this is implemented in Relap5) 16
17 V&V process Goal: To develop sufficient evidences for robust decision making Successful V&V process is necessarily: Systematic and complete All uncertainty sources addressed Iterative Obtaining new data affects code inputs and models Converging: to a decision. User-independent 17
18 Base input model description 2D axisymmetric model to increase the computational efficiency (accuracy vs speed) Model geometry was defined according to the manufacturing specifications, CAD drawings and on-site measurements 2 nd order implicit solver for unsteady calculations Models for fluid Coupled Energy solver Coupled Flow (2 nd order upwind implicit integration) solver Gradients (2 nd order) Gravity Turbulence Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes k ε Realizable Two Layer All y + Wall treatment No-slip 1 fluid region (LBE) LBE fluid Stainless steel Heater Insulation Models for solids Constant density Coupled Solid Energy solver Gradients (2 nd order) 6 solid regions (steel walls, heater, 4 insulation regions) Heat losses Ambient temperature: from experiment Convection Contact resistance between the heater and pool walls Total resistance coefficient accoiunting for radiation and thermal conductivity effects. 18
19 Definition of SRQs Phenomena in TALL-3D experiment: Thermal stratification, Mixing, Laminar pipe flow, Turbulent pipe flow, Thermal inertia. Heat losses, Free jet dynamics. Proposed list of SRQs for CFD valiation: Steady state Outlet temperature Pressure drop Maximum LBE temperature IPT gradient (e.g. IPT8-IPT2) Transient Maximum temperature at the outlet Timing of outlet temperature peak Decay ratio (in coupled simulations) 19
20 Verification Mesh size Divide and conquer separate mesh study for different parts Fluid (convection, turbulence scales) Solids (diffusion scales) Wall mesh (turbulence model requirements) Grid Convergence Index (GCI) (Roache, 1994) ε GCI = F s r p 1 Time-step size Time-step is selected according to following criteria: Numerical criterion (e.g. CFL condition) Stability Accuracy Physical criterion Characteristics of unsteady phenomena (e.g. boundary conditions, flow field) Time-step convergence Converegence of finite-difference approximation of the numerical problem GCI coarser mesh <- Refinement step -> denser mesh 20
21 Sensitivity Analysis SA is a useful to identify the most important UIPs Morris MOAT method by coupling with Dakota Hundreds of CFD calculations Iterative Process 1. Define initial ranges Conservative, and Based on limited knowledge at the time. 2. Perform first SA Screening of influential/non-influential parameters is obtained 3. Revise ranges based on new evidence (e.g. additional experiments) Use calibration to reduce conservative ranges, and Some ranges may be enlarged based on new knowledge available. 4. Perform second SA 5. Compare first and second SA results 6. Iterate until ranges converge 7. Screening Discard/fix non-influential input parameters SA matrix helps to find UIPs with the largest effect (i.e. most influential) in terms of number of affected SRQs Helps to focus on only important input parameters! UIPs that affect a particular SRQ the most (normal Morris plot type info) Tells which UIPs can be calibrated using that SRQ! SRQs that are mostly affected by a particular UIP Tells which SRQ should be used to calibrate this input parameter! 21
22 Calibration Natural convection SS Integral Outlet temperature must be predicted correctly to predict SS heat losses. x3 Local Thermal conductivities in 6 insulation regions were calibrated to model the spatial distribution of heat losses In-pool TCs were used as SRQs x2 x4 x4 x5 x2 22
23 LOSS OF FLOW TRANSIENT (T0206) 23
24 Standalone CFD Mass flow rate 24
25 Standalone CFD Temperature 25
26 Standalone CFD Animation 26
27 Standalone CFD CIP temperature 27
28 Coupled CFD-STH Mass flow rate Coupled simulation predicts the mass flow rate dynamics better than standalone STH Timing of flow reversal duration and recovery is improved Oscillatory behavior is captured Residual deviation can be reduced by further calibration using experimental evidence 28
29 Coupled CFD-STH Temperature Coupled simulation improves the pool inlet and outlet temperature prediction Timing of peaks is improved Oscillatory behavior is captured STH sees no temperature oscillations due to under-resolving the complex 3D flow field 29
30 Conclusions Multi-scale flows are important in liquid metal cooled nuclear reactors STH codes are inadequate to resolve 3D flow phenomena and CFD codes are computationally demanding for large systems Coupling of CFD and STH improves the computational efficiency - desired accuracy at affordable computational costs Coupling introduces new physical models Translation of data between 1D and 3D codes Validation of coupled codes cannot be reduced to validation of standalone codes TALL-3D facility is designed and instrumented for validation of standalone and coupled thermal-hydraulic codes Pre-test analysis demonstrated the desired transition between thermal mixing and stratification in the 3D test section Coupled simulations reveal features that would not be captured with standalone STH code 30
31 Thank you! 31
DEVELOPMENT OF TALL-3D TEST MATRIX FOR APROS CODE VALIDATION
 DEVELOPMENT OF TALL-3D TEST MATRIX FOR APROS CODE VALIDATION I. Mickus, K. Kööp, M. Jeltsov, D. Grishchenko, P. Kudinov Division of Nuclear Power Safety, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Roslagstullsbacken
DEVELOPMENT OF TALL-3D TEST MATRIX FOR APROS CODE VALIDATION I. Mickus, K. Kööp, M. Jeltsov, D. Grishchenko, P. Kudinov Division of Nuclear Power Safety, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Roslagstullsbacken
HEAT TRANSFER CAPABILITY OF A THERMOSYPHON HEAT TRANSPORT DEVICE WITH EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES
 HEAT TRANSFER CAPABILITY OF A THERMOSYPHON HEAT TRANSPORT DEVICE WITH EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES B.M. Lingade a*, Elizabeth Raju b, A Borgohain a, N.K. Maheshwari a, P.K.Vijayan a a Reactor Engineering
HEAT TRANSFER CAPABILITY OF A THERMOSYPHON HEAT TRANSPORT DEVICE WITH EXPERIMENTAL AND CFD STUDIES B.M. Lingade a*, Elizabeth Raju b, A Borgohain a, N.K. Maheshwari a, P.K.Vijayan a a Reactor Engineering
CFD STUDIES IN THE PREDICTION OF THERMAL STRIPING IN AN LMFBR
 CFD STUDIES IN THE PREDICTION OF THERMAL STRIPING IN AN LMFBR K. Velusamy, K. Natesan, P. Selvaraj, P. Chellapandi, S. C. Chetal, T. Sundararajan* and S. Suyambazhahan* Nuclear Engineering Group Indira
CFD STUDIES IN THE PREDICTION OF THERMAL STRIPING IN AN LMFBR K. Velusamy, K. Natesan, P. Selvaraj, P. Chellapandi, S. C. Chetal, T. Sundararajan* and S. Suyambazhahan* Nuclear Engineering Group Indira
Analysis and interpretation of the LIVE-L6 experiment
 Analysis and interpretation of the LIVE-L6 experiment A. Palagin, A. Miassoedov, X. Gaus-Liu (KIT), M. Buck (IKE), C.T. Tran, P. Kudinov (KTH), L. Carenini (IRSN), C. Koellein, W. Luther (GRS) V. Chudanov
Analysis and interpretation of the LIVE-L6 experiment A. Palagin, A. Miassoedov, X. Gaus-Liu (KIT), M. Buck (IKE), C.T. Tran, P. Kudinov (KTH), L. Carenini (IRSN), C. Koellein, W. Luther (GRS) V. Chudanov
Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a monolithic exchanger related to high temperature and high pressure operating conditions
 Advanced Computational Methods in Heat Transfer X 25 Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a monolithic exchanger related to high temperature and high pressure operating conditions F. Selimovic & B. Sundén
Advanced Computational Methods in Heat Transfer X 25 Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a monolithic exchanger related to high temperature and high pressure operating conditions F. Selimovic & B. Sundén
Effective Momentum and Heat Flux Models for Simulation of Stratification and Mixing in a Large Pool of Water. Hua Li, Walter Villanueva, Pavel Kudinov
 NKS-266 ISBN 978-87-7893-339-3 Effective Momentum and Heat Flux Models for Simulation of Stratification and Mixing in a Large Pool of Water Hua Li, Walter Villanueva, Pavel Kudinov Division of Nuclear
NKS-266 ISBN 978-87-7893-339-3 Effective Momentum and Heat Flux Models for Simulation of Stratification and Mixing in a Large Pool of Water Hua Li, Walter Villanueva, Pavel Kudinov Division of Nuclear
Onset of Flow Instability in a Rectangular Channel Under Transversely Uniform and Non-uniform Heating
 Onset of Flow Instability in a Rectangular Channel Under Transversely Uniform and Non-uniform Heating Omar S. Al-Yahia, Taewoo Kim, Daeseong Jo School of Mechanical Engineering, Kyungpook National University
Onset of Flow Instability in a Rectangular Channel Under Transversely Uniform and Non-uniform Heating Omar S. Al-Yahia, Taewoo Kim, Daeseong Jo School of Mechanical Engineering, Kyungpook National University
CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE
 CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE In this chapter, the governing equations for the proposed numerical model with discretisation methods are presented. Spiral
CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE In this chapter, the governing equations for the proposed numerical model with discretisation methods are presented. Spiral
EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION
 EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION A. K. Kansal, P. Suryanarayana, N. K. Maheshwari Reactor Engineering Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION A. K. Kansal, P. Suryanarayana, N. K. Maheshwari Reactor Engineering Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
A concept for the integrated 3D flow, heat transfer and structural calculation of compact heat exchangers
 Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 133 A concept for the integrated 3D flow, heat transfer and structural calculation of compact heat exchangers F. Yang, K. Mohrlok, U.
Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 133 A concept for the integrated 3D flow, heat transfer and structural calculation of compact heat exchangers F. Yang, K. Mohrlok, U.
Numerical analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in 2D sinusoidal wavy channel
 Numerical analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in 2D sinusoidal wavy channel Arunanshu Chakravarty 1* 1 CTU in Prague, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Process Engineering,Technická
Numerical analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in 2D sinusoidal wavy channel Arunanshu Chakravarty 1* 1 CTU in Prague, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Process Engineering,Technická
White Paper FINAL REPORT AN EVALUATION OF THE HYDRODYNAMICS MECHANISMS WHICH DRIVE THE PERFORMANCE OF THE WESTFALL STATIC MIXER.
 White Paper FINAL REPORT AN EVALUATION OF THE HYDRODYNAMICS MECHANISMS WHICH DRIVE THE PERFORMANCE OF THE WESTFALL STATIC MIXER Prepared by: Dr. Thomas J. Gieseke NUWCDIVNPT - Code 8233 March 29, 1999
White Paper FINAL REPORT AN EVALUATION OF THE HYDRODYNAMICS MECHANISMS WHICH DRIVE THE PERFORMANCE OF THE WESTFALL STATIC MIXER Prepared by: Dr. Thomas J. Gieseke NUWCDIVNPT - Code 8233 March 29, 1999
A 2-D Test Problem for CFD Modeling Heat Transfer in Spent Fuel Transfer Cask Neutron Shields. G Zigh and J Solis U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission
 CFD4NRS2010 A 2-D Test Problem for CFD Modeling Heat Transfer in Spent Fuel Transfer Cask Neutron Shields G Zigh and J Solis U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission Abstract JA Fort Pacific Northwest National
CFD4NRS2010 A 2-D Test Problem for CFD Modeling Heat Transfer in Spent Fuel Transfer Cask Neutron Shields G Zigh and J Solis U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission Abstract JA Fort Pacific Northwest National
PVP COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) PROVIDES ALTERNATIVE TO CONVENTIONAL HEAT TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 Proceedings of the ASME 2017 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference PVP2017 July 16-20, 2017, Waikoloa, Hawaii, United States PVP2017-65856 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) PROVIDES ALTERNATIVE TO CONVENTIONAL
Proceedings of the ASME 2017 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference PVP2017 July 16-20, 2017, Waikoloa, Hawaii, United States PVP2017-65856 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) PROVIDES ALTERNATIVE TO CONVENTIONAL
Department of Engineering and System Science, National Tsing Hua University,
 3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering, Manufacturing Technology and Control (ICMEMTC 2016) The Establishment and Application of TRACE/CFD Model for Maanshan PWR Nuclear Power Plant Yu-Ting
3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering, Manufacturing Technology and Control (ICMEMTC 2016) The Establishment and Application of TRACE/CFD Model for Maanshan PWR Nuclear Power Plant Yu-Ting
Application of Grid Convergence Index Estimation for Uncertainty Quantification in V&V of Multidimensional Thermal-Hydraulic Simulation
 The ASME Verification and Validation Symposium (V&V05) May 3-5, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA Application of Grid Convergence Index Estimation for Uncertainty Quantification in V&V of Multidimensional Thermal-Hydraulic
The ASME Verification and Validation Symposium (V&V05) May 3-5, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA Application of Grid Convergence Index Estimation for Uncertainty Quantification in V&V of Multidimensional Thermal-Hydraulic
Analysis of the Cooling Design in Electrical Transformer
 Analysis of the Cooling Design in Electrical Transformer Joel de Almeida Mendes E-mail: joeldealmeidamendes@hotmail.com Abstract This work presents the application of a CFD code Fluent to simulate the
Analysis of the Cooling Design in Electrical Transformer Joel de Almeida Mendes E-mail: joeldealmeidamendes@hotmail.com Abstract This work presents the application of a CFD code Fluent to simulate the
CFD-Modeling of Turbulent Flows in a 3x3 Rod Bundle and Comparison to Experiments
 CFD-Modeling of Turbulent Flows in a 3x3 Rod Bundle and Comparison to Experiments C. Lifante 1, B. Krull 1, Th. Frank 1, R. Franz 2, U. Hampel 2 1 PBU, ANSYS Germany, Otterfing 2 Institute of Safety Research,
CFD-Modeling of Turbulent Flows in a 3x3 Rod Bundle and Comparison to Experiments C. Lifante 1, B. Krull 1, Th. Frank 1, R. Franz 2, U. Hampel 2 1 PBU, ANSYS Germany, Otterfing 2 Institute of Safety Research,
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER
 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER Mohammad Goharkhah Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sahand Unversity of Technology, Tabriz, Iran CHAPTER 5 NATURAL CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER BASIC CONCEPTS MECHANISM OF NATURAL
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER Mohammad Goharkhah Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sahand Unversity of Technology, Tabriz, Iran CHAPTER 5 NATURAL CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER BASIC CONCEPTS MECHANISM OF NATURAL
THE USE OF PB-BI EUTECTIC AS THE COOLANT OF AN ACCELERATOR DRIVEN SYSTEM. Joint research Centre of the European Commission Ispra, Italy.
 THE USE OF PB-BI EUTECTIC AS THE COOLANT OF AN ACCELERATOR DRIVEN SYSTEM Alberto Peña 1, Fernando Legarda 1, Harmut Wider 2, Johan Karlsson 2 1 University of the Basque Country Nuclear Engineering and
THE USE OF PB-BI EUTECTIC AS THE COOLANT OF AN ACCELERATOR DRIVEN SYSTEM Alberto Peña 1, Fernando Legarda 1, Harmut Wider 2, Johan Karlsson 2 1 University of the Basque Country Nuclear Engineering and
On the transient modelling of impinging jets heat transfer. A practical approach
 Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer 7 2012 Begell House, Inc. On the transient modelling of impinging jets heat transfer. A practical approach M. Bovo 1,2 and L. Davidson 1 1 Dept. of Applied Mechanics,
Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer 7 2012 Begell House, Inc. On the transient modelling of impinging jets heat transfer. A practical approach M. Bovo 1,2 and L. Davidson 1 1 Dept. of Applied Mechanics,
Model Studies on Slag-Metal Entrainment in Gas Stirred Ladles
 Model Studies on Slag-Metal Entrainment in Gas Stirred Ladles Anand Senguttuvan Supervisor Gordon A Irons 1 Approach to Simulate Slag Metal Entrainment using Computational Fluid Dynamics Introduction &
Model Studies on Slag-Metal Entrainment in Gas Stirred Ladles Anand Senguttuvan Supervisor Gordon A Irons 1 Approach to Simulate Slag Metal Entrainment using Computational Fluid Dynamics Introduction &
HIGH TEMPERATURE THERMAL HYDRAULICS MODELING
 HIGH TEMPERATURE THERMAL HYDRAULICS MODELING OF A MOLTEN SALT: APPLICATION TO A MOLTEN SALT FAST REACTOR (MSFR) P. R. Rubiolo, V. Ghetta, J. Giraud, M. Tano Retamales CNRS/IN2P3/LPSC - Grenoble Workshop
HIGH TEMPERATURE THERMAL HYDRAULICS MODELING OF A MOLTEN SALT: APPLICATION TO A MOLTEN SALT FAST REACTOR (MSFR) P. R. Rubiolo, V. Ghetta, J. Giraud, M. Tano Retamales CNRS/IN2P3/LPSC - Grenoble Workshop
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer. Week 9
 Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 9 補充! Multidimensional Effects Transient problems with heat transfer in two or three dimensions can be considered using the solutions obtained for one dimensional
Introduction to Heat and Mass Transfer Week 9 補充! Multidimensional Effects Transient problems with heat transfer in two or three dimensions can be considered using the solutions obtained for one dimensional
Boundary-Layer Theory
 Hermann Schlichting Klaus Gersten Boundary-Layer Theory With contributions from Egon Krause and Herbert Oertel Jr. Translated by Katherine Mayes 8th Revised and Enlarged Edition With 287 Figures and 22
Hermann Schlichting Klaus Gersten Boundary-Layer Theory With contributions from Egon Krause and Herbert Oertel Jr. Translated by Katherine Mayes 8th Revised and Enlarged Edition With 287 Figures and 22
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
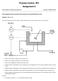 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
CFD in COMSOL Multiphysics
 CFD in COMSOL Multiphysics Mats Nigam Copyright 2016 COMSOL. Any of the images, text, and equations here may be copied and modified for your own internal use. All trademarks are the property of their respective
CFD in COMSOL Multiphysics Mats Nigam Copyright 2016 COMSOL. Any of the images, text, and equations here may be copied and modified for your own internal use. All trademarks are the property of their respective
Theoretical and Experimental Studies on Transient Heat Transfer for Forced Convection Flow of Helium Gas over a Horizontal Cylinder
 326 Theoretical and Experimental Studies on Transient Heat Transfer for Forced Convection Flow of Helium Gas over a Horizontal Cylinder Qiusheng LIU, Katsuya FUKUDA and Zheng ZHANG Forced convection transient
326 Theoretical and Experimental Studies on Transient Heat Transfer for Forced Convection Flow of Helium Gas over a Horizontal Cylinder Qiusheng LIU, Katsuya FUKUDA and Zheng ZHANG Forced convection transient
ANALYSIS OF METASTABLE REGIMES IN A PARALLEL CHANNEL SINGLE PHASE NATURAL CIRCULATION SYSTEM WITH RELAP5/ MOD 3.2
 13 th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering Beijing, China, May 16-20, 2005 ICONE13-50213 ANALYSIS OF METASTABLE REGIMES IN A PARALLEL CHANNEL SINGLE PHASE NATURAL CIRCULATION SYSTEM WITH RELAP5/
13 th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering Beijing, China, May 16-20, 2005 ICONE13-50213 ANALYSIS OF METASTABLE REGIMES IN A PARALLEL CHANNEL SINGLE PHASE NATURAL CIRCULATION SYSTEM WITH RELAP5/
Principles of Convection
 Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
1D-3D COUPLED SIMULATION OF THE FUEL INJECTION INSIDE A HIGH PERFORMANCE ENGINE FOR MOTORSPORT APPLICATION: SPRAY TARGETING AND INJECTION TIMING
 1D-3D COUPLED SIMULATION OF THE FUEL INJECTION INSIDE A HIGH PERFORMANCE ENGINE FOR MOTORSPORT APPLICATION: SPRAY TARGETING AND INJECTION TIMING M. Fiocco, D. Borghesi- Mahindra Racing S.P.A. Outline Introduction
1D-3D COUPLED SIMULATION OF THE FUEL INJECTION INSIDE A HIGH PERFORMANCE ENGINE FOR MOTORSPORT APPLICATION: SPRAY TARGETING AND INJECTION TIMING M. Fiocco, D. Borghesi- Mahindra Racing S.P.A. Outline Introduction
STAR-CCM+ and SPEED for electric machine cooling analysis
 STAR-CCM+ and SPEED for electric machine cooling analysis Dr. Markus Anders, Dr. Stefan Holst, CD-adapco Abstract: This paper shows how two well established software programs can be used to determine the
STAR-CCM+ and SPEED for electric machine cooling analysis Dr. Markus Anders, Dr. Stefan Holst, CD-adapco Abstract: This paper shows how two well established software programs can be used to determine the
Experiment 1. Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of a Metal (Brass) Bar
 Experiment 1 Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of a Metal (Brass) Bar Introduction: Thermal conductivity is a measure of the ability of a substance to conduct heat, determined by the rate of heat flow
Experiment 1 Measurement of Thermal Conductivity of a Metal (Brass) Bar Introduction: Thermal conductivity is a measure of the ability of a substance to conduct heat, determined by the rate of heat flow
Numerical modelling of direct contact condensation of steam in BWR pressure suppression pool system
 Numerical modelling of direct contact condensation of steam in BWR pressure suppression pool system Gitesh Patel, Vesa Tanskanen, Juhani Hyvärinen LUT School of Energy Systems/Nuclear Engineering, Lappeenranta
Numerical modelling of direct contact condensation of steam in BWR pressure suppression pool system Gitesh Patel, Vesa Tanskanen, Juhani Hyvärinen LUT School of Energy Systems/Nuclear Engineering, Lappeenranta
This section develops numerically and analytically the geometric optimisation of
 7 CHAPTER 7: MATHEMATICAL OPTIMISATION OF LAMINAR-FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH A VASCULARISED SOLID WITH COOLING CHANNELS 5 7.1. INTRODUCTION This section develops numerically and analytically
7 CHAPTER 7: MATHEMATICAL OPTIMISATION OF LAMINAR-FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER THROUGH A VASCULARISED SOLID WITH COOLING CHANNELS 5 7.1. INTRODUCTION This section develops numerically and analytically
Application of V&V 20 Standard to the Benchmark FDA Nozzle Model
 Application of V&V 20 Standard to the Benchmark FDA Nozzle Model Gavin A. D Souza 1, Prasanna Hariharan 2, Marc Horner 3, Dawn Bardot 4, Richard A. Malinauskas 2, Ph.D. 1 University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati,
Application of V&V 20 Standard to the Benchmark FDA Nozzle Model Gavin A. D Souza 1, Prasanna Hariharan 2, Marc Horner 3, Dawn Bardot 4, Richard A. Malinauskas 2, Ph.D. 1 University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati,
Status and Future Challenges of CFD for Liquid Metal Cooled Reactors
 Status and Future Challenges of CFD for Liquid Metal Cooled Reactors IAEA Fast Reactor Conference 2013 Paris, France 5 March 2013 Ferry Roelofs roelofs@nrg.eu V.R. Gopala K. Van Tichelen X. Cheng E. Merzari
Status and Future Challenges of CFD for Liquid Metal Cooled Reactors IAEA Fast Reactor Conference 2013 Paris, France 5 March 2013 Ferry Roelofs roelofs@nrg.eu V.R. Gopala K. Van Tichelen X. Cheng E. Merzari
CONDENSATION HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENT CORRELATION BASED ON SLIP RATIO MODEL IN A HORIZONTAL HEAT EXCHANGER
 CONDENSATION HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENT CORRELATION BASED ON SLIP RATIO MODEL IN A HORIZONTAL HEAT EXCHANGER Seok Kim, Sung Uk Ryu, Seung Tae Lee, Dong-Jin Euh, and Chul-Hwa Song Korea Atomic Energy Research
CONDENSATION HEAT TRANSFER COEFFICIENT CORRELATION BASED ON SLIP RATIO MODEL IN A HORIZONTAL HEAT EXCHANGER Seok Kim, Sung Uk Ryu, Seung Tae Lee, Dong-Jin Euh, and Chul-Hwa Song Korea Atomic Energy Research
1/54 Circulation pump, safety valve, expansion vessel
 1/54 Circulation pump, safety valve, expansion vessel pressure loss efficiency of pump secured heat output safety valve sizing expansion vessel sizing Circulation pump 2/54 similar principle as for heating
1/54 Circulation pump, safety valve, expansion vessel pressure loss efficiency of pump secured heat output safety valve sizing expansion vessel sizing Circulation pump 2/54 similar principle as for heating
Thermal Stratification and Mixing in a Large Pool Induced by Operation of Spargers, Nozzles, and Blowdown Pipes
 NKS-369 ISBN 978-87-7893-454-3 Thermal Stratification and Mixing in a Large Pool Induced by Operation of Spargers, Nozzles, and Blowdown Pipes Ignacio Gallego-Marcos, Walter Villanueva, Pavel Kudinov Division
NKS-369 ISBN 978-87-7893-454-3 Thermal Stratification and Mixing in a Large Pool Induced by Operation of Spargers, Nozzles, and Blowdown Pipes Ignacio Gallego-Marcos, Walter Villanueva, Pavel Kudinov Division
UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER
 UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER Convection is the mode of heat transfer between a surface and a fluid moving over it. The energy transfer in convection is predominately due to the bulk motion of the fluid
UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER Convection is the mode of heat transfer between a surface and a fluid moving over it. The energy transfer in convection is predominately due to the bulk motion of the fluid
Tutorial for the supercritical pressure pipe with STAR-CCM+
 Tutorial for the supercritical pressure pipe with STAR-CCM+ For performing this tutorial, it is necessary to have already studied the tutorial on the upward bend. In fact, after getting abilities with
Tutorial for the supercritical pressure pipe with STAR-CCM+ For performing this tutorial, it is necessary to have already studied the tutorial on the upward bend. In fact, after getting abilities with
Particles Removal from a Moving Tube by Blowing Systems: A CFD Analysis
 Engineering, 2013, 5, 268-276 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/eng.2013.53037 Published Online March 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Particles Removal from a Moving Tube by Blowing Systems: A CFD Analysis
Engineering, 2013, 5, 268-276 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/eng.2013.53037 Published Online March 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Particles Removal from a Moving Tube by Blowing Systems: A CFD Analysis
Tutorial for the heated pipe with constant fluid properties in STAR-CCM+
 Tutorial for the heated pipe with constant fluid properties in STAR-CCM+ For performing this tutorial, it is necessary to have already studied the tutorial on the upward bend. In fact, after getting abilities
Tutorial for the heated pipe with constant fluid properties in STAR-CCM+ For performing this tutorial, it is necessary to have already studied the tutorial on the upward bend. In fact, after getting abilities
Lectures on Applied Reactor Technology and Nuclear Power Safety. Lecture No 6
 Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 6 Title: Introduction to Thermal-Hydraulic Analysis of Nuclear Reactor Cores Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture
Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 6 Title: Introduction to Thermal-Hydraulic Analysis of Nuclear Reactor Cores Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture
TankExampleNov2016. Table of contents. Layout
 Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
Table of contents Task... 2 Calculation of heat loss of storage tanks... 3 Properties ambient air Properties of air... 7 Heat transfer outside, roof Heat transfer in flow past a plane wall... 8 Properties
Turbulent Boundary Layers & Turbulence Models. Lecture 09
 Turbulent Boundary Layers & Turbulence Models Lecture 09 The turbulent boundary layer In turbulent flow, the boundary layer is defined as the thin region on the surface of a body in which viscous effects
Turbulent Boundary Layers & Turbulence Models Lecture 09 The turbulent boundary layer In turbulent flow, the boundary layer is defined as the thin region on the surface of a body in which viscous effects
CFD as a Tool for Thermal Comfort Assessment
 CFD as a Tool for Thermal Comfort Assessment Dimitrios Koubogiannis dkoubog@teiath.gr G. Tsimperoudis, E. Karvelas Department of Energy Technology Engineering Technological Educational Institute of Athens
CFD as a Tool for Thermal Comfort Assessment Dimitrios Koubogiannis dkoubog@teiath.gr G. Tsimperoudis, E. Karvelas Department of Energy Technology Engineering Technological Educational Institute of Athens
Vertical Mantle Heat Exchangers for Solar Water Heaters
 for Solar Water Heaters Y.C., G.L. Morrison and M. Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering The University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: yens@student.unsw.edu.au Abstract
for Solar Water Heaters Y.C., G.L. Morrison and M. Behnia School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering The University of New South Wales Sydney 2052 AUSTRALIA E-mail: yens@student.unsw.edu.au Abstract
Stratification issues in the primary system. Review of available validation experiments and State-of-the-Art in modelling capabilities.
 Stratification issues in the primary system. Review of available validation experiments and State-of-the-Art in modelling capabilities. (StratRev) NKS seminar, Armémuseum, 2009-03-26 Johan Westin and Mats
Stratification issues in the primary system. Review of available validation experiments and State-of-the-Art in modelling capabilities. (StratRev) NKS seminar, Armémuseum, 2009-03-26 Johan Westin and Mats
This chapter focuses on the study of the numerical approximation of threedimensional
 6 CHAPTER 6: NUMERICAL OPTIMISATION OF CONJUGATE HEAT TRANSFER IN COOLING CHANNELS WITH DIFFERENT CROSS-SECTIONAL SHAPES 3, 4 6.1. INTRODUCTION This chapter focuses on the study of the numerical approximation
6 CHAPTER 6: NUMERICAL OPTIMISATION OF CONJUGATE HEAT TRANSFER IN COOLING CHANNELS WITH DIFFERENT CROSS-SECTIONAL SHAPES 3, 4 6.1. INTRODUCTION This chapter focuses on the study of the numerical approximation
Study on Effective Particle Diameters and Coolability of Particulate Beds Packed with Irregular Multi-size Particles
 NKS-288 ISBN 978-87-7893-363-8 Study on Effective Particle Diameters and Coolability of Particulate Beds Packed with Irregular Multi-size Particles Sachin Thakre, Weimin Ma, Pavel Kudinov, Sevostian Bechta
NKS-288 ISBN 978-87-7893-363-8 Study on Effective Particle Diameters and Coolability of Particulate Beds Packed with Irregular Multi-size Particles Sachin Thakre, Weimin Ma, Pavel Kudinov, Sevostian Bechta
Study of Forced and Free convection in Lid driven cavity problem
 MIT Study of Forced and Free convection in Lid driven cavity problem 18.086 Project report Divya Panchanathan 5-11-2014 Aim To solve the Navier-stokes momentum equations for a lid driven cavity problem
MIT Study of Forced and Free convection in Lid driven cavity problem 18.086 Project report Divya Panchanathan 5-11-2014 Aim To solve the Navier-stokes momentum equations for a lid driven cavity problem
Hideki Kamide 1. A. Ono 1, N. Kimura 1, J. Endoh 2 and O. Watanabe 2
 International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles: Safe Technologies and Sustainable Scenarios (FR13) Hideki Kamide 1 A. Ono 1, N. Kimura 1, J. Endoh 2 and O. Watanabe 2 1: Japan Atomic
International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles: Safe Technologies and Sustainable Scenarios (FR13) Hideki Kamide 1 A. Ono 1, N. Kimura 1, J. Endoh 2 and O. Watanabe 2 1: Japan Atomic
ABSTRACT I. INTRODUCTION
 2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 4 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Analysis of Compressible Effect in the Flow Metering By Orifice Plate Using Prasanna
2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 4 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Analysis of Compressible Effect in the Flow Metering By Orifice Plate Using Prasanna
Investigation of Jet Impingement on Flat Plate Using Triangular and Trapezoid Vortex Generators
 ISSN 2395-1621 Investigation of Jet Impingement on Flat Plate Using Triangular and Trapezoid Vortex Generators #1 Sonali S Nagawade, #2 Prof. S Y Bhosale, #3 Prof. N K Chougule 1 Sonalinagawade1@gmail.com
ISSN 2395-1621 Investigation of Jet Impingement on Flat Plate Using Triangular and Trapezoid Vortex Generators #1 Sonali S Nagawade, #2 Prof. S Y Bhosale, #3 Prof. N K Chougule 1 Sonalinagawade1@gmail.com
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Problems on Heat Transfer
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 150A Transport Processes Spring Semester 2017
 Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 150A Transport Processes Spring Semester 2017 Objective: Text: To introduce the basic concepts of fluid mechanics and heat transfer necessary for solution of engineering
Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 150A Transport Processes Spring Semester 2017 Objective: Text: To introduce the basic concepts of fluid mechanics and heat transfer necessary for solution of engineering
Forced Convection: Inside Pipe HANNA ILYANI ZULHAIMI
 + Forced Convection: Inside Pipe HANNA ILYANI ZULHAIMI + OUTLINE u Introduction and Dimensionless Numbers u Heat Transfer Coefficient for Laminar Flow inside a Pipe u Heat Transfer Coefficient for Turbulent
+ Forced Convection: Inside Pipe HANNA ILYANI ZULHAIMI + OUTLINE u Introduction and Dimensionless Numbers u Heat Transfer Coefficient for Laminar Flow inside a Pipe u Heat Transfer Coefficient for Turbulent
EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF R-134a FLOW CONDENSATION IN A SMOOTH TUBE
 HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF R-134a FLOW CONDENSATION IN A SMOOTH TUBE Bastos S., Fernández-Seara
HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF R-134a FLOW CONDENSATION IN A SMOOTH TUBE Bastos S., Fernández-Seara
CFX CODE APPLICATION TO THE FRENCH REACTOR FOR INHERENT BORON DILUTION SAFETY ISSUE
 CFX CODE APPLICATION TO THE FRENCH REACTOR FOR INHERENT BORON DILUTION SAFETY ISSUE Estelle Graffard, Frédéric Goux Institute for Radiological Protection and Nuclear Safety, France Abstract Inherent boron
CFX CODE APPLICATION TO THE FRENCH REACTOR FOR INHERENT BORON DILUTION SAFETY ISSUE Estelle Graffard, Frédéric Goux Institute for Radiological Protection and Nuclear Safety, France Abstract Inherent boron
Thermo-Hydraulic performance of Internal finned tube Automobile Radiator
 Thermo-Hydraulic performance of Internal finned tube Automobile Radiator Dr.Kailash Mohapatra 1, Deepiarani Swain 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Raajdhani Engineering College, Bhubaneswar, 751017,
Thermo-Hydraulic performance of Internal finned tube Automobile Radiator Dr.Kailash Mohapatra 1, Deepiarani Swain 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Raajdhani Engineering College, Bhubaneswar, 751017,
Documentation of the Solutions to the SFPE Heat Transfer Verification Cases
 Documentation of the Solutions to the SFPE Heat Transfer Verification Cases Prepared by a Task Group of the SFPE Standards Making Committee on Predicting the Thermal Performance of Fire Resistive Assemblies
Documentation of the Solutions to the SFPE Heat Transfer Verification Cases Prepared by a Task Group of the SFPE Standards Making Committee on Predicting the Thermal Performance of Fire Resistive Assemblies
CFD AND EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF SINGLE PHASE BUOYANCY DRIVEN COUNTER-CURRENT FLOW IN A PIPE
 CFD AND EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF SINGLE PHASE BUOYANCY DRIVEN COUNTER-CURRENT FLOW IN A PIPE F. Sebilleau, R. I. Issa, and S. P. Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering Imperial College London Exhibition
CFD AND EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF SINGLE PHASE BUOYANCY DRIVEN COUNTER-CURRENT FLOW IN A PIPE F. Sebilleau, R. I. Issa, and S. P. Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering Imperial College London Exhibition
PREDICTION OF MASS FLOW RATE AND PRESSURE DROP IN THE COOLANT CHANNEL OF THE TRIGA 2000 REACTOR CORE
 PREDICTION OF MASS FLOW RATE AND PRESSURE DROP IN THE COOLANT CHANNEL OF THE TRIGA 000 REACTOR CORE Efrizon Umar Center for Research and Development of Nuclear Techniques (P3TkN) ABSTRACT PREDICTION OF
PREDICTION OF MASS FLOW RATE AND PRESSURE DROP IN THE COOLANT CHANNEL OF THE TRIGA 000 REACTOR CORE Efrizon Umar Center for Research and Development of Nuclear Techniques (P3TkN) ABSTRACT PREDICTION OF
Department of Energy Science & Engineering, IIT Bombay, Mumbai, India. *Corresponding author: Tel: ,
 ICAER 2011 AN EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL INVESTIGATION OF HEAT LOSSES FROM THE CAVITY RECEIVER USED IN LINEAR FRESNEL REFLECTOR SOLAR THERMAL SYSTEM Sudhansu S. Sahoo* a, Shinu M. Varghese b, Ashwin
ICAER 2011 AN EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL INVESTIGATION OF HEAT LOSSES FROM THE CAVITY RECEIVER USED IN LINEAR FRESNEL REFLECTOR SOLAR THERMAL SYSTEM Sudhansu S. Sahoo* a, Shinu M. Varghese b, Ashwin
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Comparison between Numerical and Experimental for UVP Measurement in Double Bent Pipe with Out-of-Plane Angle
 Journal of Flow Control, Measurement & Visualization, 24, 2, 54-64 Published Online October 24 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jfcmv http://dx.doi.org/.4236/jfcmv.24.247 Comparison between Numerical
Journal of Flow Control, Measurement & Visualization, 24, 2, 54-64 Published Online October 24 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jfcmv http://dx.doi.org/.4236/jfcmv.24.247 Comparison between Numerical
USE OF CFD TO PREDICT CRITICAL HEAT FLUX IN ROD BUNDLES
 USE OF CFD TO PREDICT CRITICAL HEAT FLUX IN ROD BUNDLES Z. E. Karoutas, Y. Xu, L. David Smith, I, P. F. Joffre, Y. Sung Westinghouse Electric Company 5801 Bluff Rd, Hopkins, SC 29061 karoutze@westinghouse.com;
USE OF CFD TO PREDICT CRITICAL HEAT FLUX IN ROD BUNDLES Z. E. Karoutas, Y. Xu, L. David Smith, I, P. F. Joffre, Y. Sung Westinghouse Electric Company 5801 Bluff Rd, Hopkins, SC 29061 karoutze@westinghouse.com;
CFD SIMULATIONS OF THE SPENT FUEL POOL IN THE LOSS OF COOLANT ACCIDENT
 HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta CFD SIMULATIONS OF THE SPENT FUEL POOL IN THE LOSS OF COOLANT ACCIDENT Lin Y.T., Chiu
HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta CFD SIMULATIONS OF THE SPENT FUEL POOL IN THE LOSS OF COOLANT ACCIDENT Lin Y.T., Chiu
Comparison of two equations closure turbulence models for the prediction of heat and mass transfer in a mechanically ventilated enclosure
 Proceedings of 4 th ICCHMT May 17-0, 005, Paris-Cachan, FRANCE 381 Comparison of two equations closure turbulence models for the prediction of heat and mass transfer in a mechanically ventilated enclosure
Proceedings of 4 th ICCHMT May 17-0, 005, Paris-Cachan, FRANCE 381 Comparison of two equations closure turbulence models for the prediction of heat and mass transfer in a mechanically ventilated enclosure
Increase Productivity Using CFD Analysis
 Increase Productivity Using CFD Analysis CFD of Process Engineering Plants for Performance Estimation and Redesign Vinod Taneja Vidhitech Solutions Abhishek Jain abhishek@zeusnumerix.com +91 9819009836
Increase Productivity Using CFD Analysis CFD of Process Engineering Plants for Performance Estimation and Redesign Vinod Taneja Vidhitech Solutions Abhishek Jain abhishek@zeusnumerix.com +91 9819009836
Project #1 Internal flow with thermal convection
 Project #1 Internal flow with thermal convection MAE 494/598, Fall 2017, Project 1 (20 points) Hard copy of report is due at the start of class on the due date. The rules on collaboration will be released
Project #1 Internal flow with thermal convection MAE 494/598, Fall 2017, Project 1 (20 points) Hard copy of report is due at the start of class on the due date. The rules on collaboration will be released
VALIDATION OF TURBULENT NATURAL CONVECTION IN A SQUARE CAVITY FOR APPLICATION OF CFD MODELLING TO HEAT TRANSFER AND FLUID FLOW IN ATRIA GEOMETRIES
 VALIDATION OF TURBULENT NATURAL CONVECTION IN A SQUARE CAVITY FOR APPLICATION OF CFD MODELLING TO HEAT TRANSFER AND FLUID FLOW IN ATRIA GEOMETRIES C.A. Rundle and M.F. Lightstone Department of Mechanical
VALIDATION OF TURBULENT NATURAL CONVECTION IN A SQUARE CAVITY FOR APPLICATION OF CFD MODELLING TO HEAT TRANSFER AND FLUID FLOW IN ATRIA GEOMETRIES C.A. Rundle and M.F. Lightstone Department of Mechanical
Table of Contents. Foreword... xiii. Preface... xv
 Table of Contents Foreword.... xiii Preface... xv Chapter 1. Fundamental Equations, Dimensionless Numbers... 1 1.1. Fundamental equations... 1 1.1.1. Local equations... 1 1.1.2. Integral conservation equations...
Table of Contents Foreword.... xiii Preface... xv Chapter 1. Fundamental Equations, Dimensionless Numbers... 1 1.1. Fundamental equations... 1 1.1.1. Local equations... 1 1.1.2. Integral conservation equations...
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve
 Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics. in Marine Engineering
 Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics in Marine Engineering Objectives Understand basic CFD theory Learn how to set up and run simulations in Star CCM+ and interpret results Learn about limitations and
Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics in Marine Engineering Objectives Understand basic CFD theory Learn how to set up and run simulations in Star CCM+ and interpret results Learn about limitations and
Simulation and improvement of the ventilation of a welding workshop using a Finite volume scheme code
 1 st. Annual (National) Conference on Industrial Ventilation-IVC2010 Feb 24-25, 2010, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran IVC2010 Simulation and improvement of the ventilation of a welding workshop
1 st. Annual (National) Conference on Industrial Ventilation-IVC2010 Feb 24-25, 2010, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran, Iran IVC2010 Simulation and improvement of the ventilation of a welding workshop
CFD Simulation of Turbulent Flow Structure in Stratified Gas/Liquid Flow and Validation with Experimental Data
 SPE-174964-MS CFD Simulation of Turbulent Flow Structure in Stratified Gas/Liquid Flow and Validation with Experimental Data Ramin Dabirian, Amir Mansouri, Ram Mohan, and Ovadia Shoham, The University
SPE-174964-MS CFD Simulation of Turbulent Flow Structure in Stratified Gas/Liquid Flow and Validation with Experimental Data Ramin Dabirian, Amir Mansouri, Ram Mohan, and Ovadia Shoham, The University
Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) On Ventilation-Cooling Optimization of Electrical Machines
 Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) On Ventilation-Cooling Optimization of Electrical Machines Ryuichi Ujiie, Dr Raphael Arlitt, Hirofumi Etoh Voith Siemens Hydro Power Generation RyuichiUjiie@vs-hydrocom,
Application of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) On Ventilation-Cooling Optimization of Electrical Machines Ryuichi Ujiie, Dr Raphael Arlitt, Hirofumi Etoh Voith Siemens Hydro Power Generation RyuichiUjiie@vs-hydrocom,
Numerical and Experimental Study on the Effect of Guide Vane Insertion on the Flow Characteristics in a 90º Rectangular Elbow
 Numerical and Experimental Study on the Effect of Guide Vane Insertion on the Flow Characteristics in a 90º Rectangular Elbow Sutardi 1, Wawan A. W., Nadia, N. and Puspita, K. 1 Mechanical Engineering
Numerical and Experimental Study on the Effect of Guide Vane Insertion on the Flow Characteristics in a 90º Rectangular Elbow Sutardi 1, Wawan A. W., Nadia, N. and Puspita, K. 1 Mechanical Engineering
Piping Systems and Flow Analysis (Chapter 3)
 Piping Systems and Flow Analysis (Chapter 3) 2 Learning Outcomes (Chapter 3) Losses in Piping Systems Major losses Minor losses Pipe Networks Pipes in series Pipes in parallel Manifolds and Distribution
Piping Systems and Flow Analysis (Chapter 3) 2 Learning Outcomes (Chapter 3) Losses in Piping Systems Major losses Minor losses Pipe Networks Pipes in series Pipes in parallel Manifolds and Distribution
Prediction of Performance Characteristics of Orifice Plate Assembly for Non-Standard Conditions Using CFD
 International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-0869, Volume-3, Issue-5, May 2015 Prediction of Performance Characteristics of Orifice Plate Assembly for Non-Standard Conditions
International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-0869, Volume-3, Issue-5, May 2015 Prediction of Performance Characteristics of Orifice Plate Assembly for Non-Standard Conditions
Investigation of Flow Profile in Open Channels using CFD
 Investigation of Flow Profile in Open Channels using CFD B. K. Gandhi 1, H.K. Verma 2 and Boby Abraham 3 Abstract Accuracy of the efficiency measurement of a hydro-electric generating unit depends on the
Investigation of Flow Profile in Open Channels using CFD B. K. Gandhi 1, H.K. Verma 2 and Boby Abraham 3 Abstract Accuracy of the efficiency measurement of a hydro-electric generating unit depends on the
METHODOLOGY (3) where, x o is the heat source separation and α is the. entrainment coefficient α.
 BSO12 First Building Simulation and Optimization Conference Loughborough, UK 10-11 September 2012 MODELLING BUOYANT THERMAL PLUMES IN NATURALLY VENTILATED BUILDINGS Faisal Durrani 1, Malcolm J Cook 2,
BSO12 First Building Simulation and Optimization Conference Loughborough, UK 10-11 September 2012 MODELLING BUOYANT THERMAL PLUMES IN NATURALLY VENTILATED BUILDINGS Faisal Durrani 1, Malcolm J Cook 2,
Basic Fluid Mechanics
 Basic Fluid Mechanics Chapter 6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 4/16/2018 C6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 1 6.1 Introduction For the present chapter we will limit our study to incompressible
Basic Fluid Mechanics Chapter 6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 4/16/2018 C6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 1 6.1 Introduction For the present chapter we will limit our study to incompressible
Computation for the Backward Facing Step Test Case with an Open Source Code
 Computation for the Backward Facing Step Test Case with an Open Source Code G.B. Deng Equipe de Modélisation Numérique Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides Ecole Centrale de Nantes 1 Rue de la Noë, 44321
Computation for the Backward Facing Step Test Case with an Open Source Code G.B. Deng Equipe de Modélisation Numérique Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides Ecole Centrale de Nantes 1 Rue de la Noë, 44321
ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I. Part 8 Viscous Flow in Pipes and Ducts. Flow in Pipes and Ducts. Flow in Pipes and Ducts (cont d)
 ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Flow in Pipes and Ducts Flow in closed conduits (circular pipes and non-circular ducts) are very common. Part 8 Viscous Flow in Pipes and Ducts These presentations are prepared
ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Flow in Pipes and Ducts Flow in closed conduits (circular pipes and non-circular ducts) are very common. Part 8 Viscous Flow in Pipes and Ducts These presentations are prepared
Numerical Simulation of the MYRRHA reactor: development of the appropriate flow solver Dr. Lilla Koloszár, Philippe Planquart
 Numerical Simulation of the MYRRHA reactor: development of the appropriate flow solver Dr. Lilla Koloszár, Philippe Planquart Von Karman Institute, Ch. de Waterloo 72. B-1640, Rhode-St-Genese, Belgium,
Numerical Simulation of the MYRRHA reactor: development of the appropriate flow solver Dr. Lilla Koloszár, Philippe Planquart Von Karman Institute, Ch. de Waterloo 72. B-1640, Rhode-St-Genese, Belgium,
A Study on Hydraulic Resistance of Porous Media Approach for CANDU-6 Moderator Analysis
 Proceedings of the Korean Nuclear Society Spring Meeting Kwangju, Korea, May 2002 A Study on Hydraulic Resistance of Porous Media Approach for CANDU-6 Moderator Analysis Churl Yoon, Bo Wook Rhee, and Byung-Joo
Proceedings of the Korean Nuclear Society Spring Meeting Kwangju, Korea, May 2002 A Study on Hydraulic Resistance of Porous Media Approach for CANDU-6 Moderator Analysis Churl Yoon, Bo Wook Rhee, and Byung-Joo
CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel
 CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel *1 Hüseyin Kaya, 2 Kamil Arslan 1 Bartın University, Mechanical Engineering Department, Bartın, Turkey
CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel *1 Hüseyin Kaya, 2 Kamil Arslan 1 Bartın University, Mechanical Engineering Department, Bartın, Turkey
Experimental and Numerical Investigation of a Multi Louvered Plate Fin-and-Tube Heat Exchanger using Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Experimental and Numerical Investigation of a Multi ed Plate Fin-and-Tube Heat Exchanger using P Bharathidasan 1 K Mahadevan 2 1,2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Institute
Experimental and Numerical Investigation of a Multi ed Plate Fin-and-Tube Heat Exchanger using P Bharathidasan 1 K Mahadevan 2 1,2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Institute
Numerical Modelling of Twin-screw Pumps Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Numerical Modelling of Twin-screw Pumps Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics 6-8 th March 2017 Dr Sham Rane, Professor Ahmed Kovačević, Dr Di Yan, Professor Qian Tang, Centre for Compressor Technology,
Numerical Modelling of Twin-screw Pumps Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics 6-8 th March 2017 Dr Sham Rane, Professor Ahmed Kovačević, Dr Di Yan, Professor Qian Tang, Centre for Compressor Technology,
VALIDATION OF CFD-MODELS FOR NATURAL CONVECTION, HEAT TRANSFER AND TURBULENCE PHENOMENA. J. Stewering, B. Schramm, M. Sonnenkalb
 VALIDATION OF CFD-MODELS FOR NATURAL CONVECTION, HEAT TRANSFER AND TURBULENCE PHENOMENA J. Stewering, B. Schramm, M. Sonnenkalb Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) mbh, Schwertnergasse
VALIDATION OF CFD-MODELS FOR NATURAL CONVECTION, HEAT TRANSFER AND TURBULENCE PHENOMENA J. Stewering, B. Schramm, M. Sonnenkalb Gesellschaft für Anlagen- und Reaktorsicherheit (GRS) mbh, Schwertnergasse
Computation of turbulent natural convection with buoyancy corrected second moment closure models
 Computation of turbulent natural convection with buoyancy corrected second moment closure models S. Whang a, H. S. Park a,*, M. H. Kim a, K. Moriyama a a Division of Advanced Nuclear Engineering, POSTECH,
Computation of turbulent natural convection with buoyancy corrected second moment closure models S. Whang a, H. S. Park a,*, M. H. Kim a, K. Moriyama a a Division of Advanced Nuclear Engineering, POSTECH,
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF LAMINAR FORCED CONVECTION IN RECTANGULAR ENCLOSURES OF DIFFERENT ASPECT RATIOS
 HEFAT214 1 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 14 16 July 214 Orlando, Florida COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF LAMINAR FORCED CONVECTION IN RECTANGULAR ENCLOSURES
HEFAT214 1 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 14 16 July 214 Orlando, Florida COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF LAMINAR FORCED CONVECTION IN RECTANGULAR ENCLOSURES
Fluid Mechanics. Spring 2009
 Instructor: Dr. Yang-Cheng Shih Department of Energy and Refrigerating Air-Conditioning Engineering National Taipei University of Technology Spring 2009 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-1 General Remarks 1-2 Scope
Instructor: Dr. Yang-Cheng Shih Department of Energy and Refrigerating Air-Conditioning Engineering National Taipei University of Technology Spring 2009 Chapter 1 Introduction 1-1 General Remarks 1-2 Scope
MECHANISM BEHIND FREE /NATURAL CONVECTION
 CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER By: Prof K. M. Joshi, Assi. Professor, MED, SSAS Institute of Technology, Surat. MECHANISM BEHIND FREE /NATURAL CONVECTION The stagnate layer of fluid in immediate vicinity of
CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER By: Prof K. M. Joshi, Assi. Professor, MED, SSAS Institute of Technology, Surat. MECHANISM BEHIND FREE /NATURAL CONVECTION The stagnate layer of fluid in immediate vicinity of
CONCEPTUAL DESIGN STUDIES FOR THE LIQUID METAL SPALLATION TARGET META:LIC
 CONCEPTUAL DESIGN STUDIES FOR THE LIQUID METAL SPALLATION TARGET META:LIC J. R. Fetzer, A. G. Class, C. Fazio, S. Gordeev Institute for Nuclear and Energy Technologies () KIT University of the State of
CONCEPTUAL DESIGN STUDIES FOR THE LIQUID METAL SPALLATION TARGET META:LIC J. R. Fetzer, A. G. Class, C. Fazio, S. Gordeev Institute for Nuclear and Energy Technologies () KIT University of the State of
