Entropy Information Based Assessment of Cascade Control Loops
|
|
|
- Simon Cummings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 5 Vol I, IMECS 5, March 8 -, 5, Hong Kong Entropy Information Based Assessment of Cascade Control Loops J. Chen, Member, IAENG, J. Zhang and L. Zhang Abstract Currently, many control performance assessment methods of cascade control loops are developed based on the assumption that all the disturbances are subject to Gaussian distribution. However, in the practical condition, several disturbance sources occur in the manipulated variable or the upstream exhibits nonlinear behaviors. In this paper, a general and effective index of the performance assessment of the cascade control system subjected to the unknown disturbance distribution is proposed. Unlike the minimum variance control index, an innovative control performance index is given based on the information theory and the minimum entropy criterion. he index is informative and in agreement with the expected control knowledge. o elucidate wide applicability and effectiveness of the minimum entropy cascade control index, a simulation problem and a cascade control case of an oil refinery are applied. Index erms Cascade control; Minimum entropy; Non-Gaussian; Performance assessment I. INRODUCION Starting from the end of the 98s, a lot of statistical tools for monitoring the process performance were introduced []. hese tools formed a new field called statistical process control, which utilized statistical methods to monitor the process variability and detect the presence of disturbance. However, they cannot evaluate whether the current control action is taken in an adequate working condition. Like most of the controllers whose initial designs can meet its performance specifications, their performances can be deteriorated abruptly or gradually after long term operations. A study by Honeywell Process Solution indicated that almost 63% of all the control loops have poor performance ratings. he research on the control system performance assessment can be traced back to the 96s and 97s. Astrom (967) and DeVries and Wu (978) carried out the fundamental research [,3]. In the literature of control loop performance assessments, the minimum variance control (MVC) had been widely used as a reference bound on the achievable performance since Harris (989) proposed it [4]. he groundbreaking research has received increasing attention in the process control field. hen several research efforts have been focused on the evaluation of the control performance. his work was sponsored in part by Ministry of Science and echnology, R.O.C. (MOS 3--E MY3). J. Chen is with Department of Chemical Engineering, Chung-Yuan Christian University, Chung-Li District, aoyuan, aiwan 3, Republic of China (corresponding author to provide jason@wavenet.cycu.edu.tw). Z. Zhang and L. Zhang are with State Key Laboratory of Alternate Electrical Power System with Renewable Energy Sources, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 6, China. ISBN: ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) he performance assessment of SISO feedback control was extended to that of MIMO feedback control [5]. A generalized minimum variance as the performance assessment benchmark for the single loop control system was proposed [6]. When it comes to the performance assessment, cascade control has a significant advantage in improving the dynamic response performance and the anti-disturbance ability, but most of the research work in the past focused on applying advanced control algorithms to designing good controllers to improve cascade control quality. Sadasivarao and Chidambaram (6) applied the genetic algorithm for tuning PID controllers of cascade control systems [7]. Padhan and Majhi () proposed an improved cascade control structure with a modified Smith predictor for controlling open-loop unstable time delay processes [8]. here is not much research work on the performance assessment of cascade control in both the theories and applications. Ko and Edgar () first derived the performance assessment of the classic cascade control loops based on MVC [9]. Chen et al. (7) used the performance analysis to diagnose cascade control loop status []. So far a lot of past research on control performance assessment (CPA) assumed that the disturbances or the noises are subject to Gaussian distributions. his means that controlling the mean and the variance of the random variables was established. In fact, most industrial processes have difficulty meeting these prerequisites because of the mixture of different courses with Gaussian disturbances or other factors, resulting in misreporting the evaluation performance of the controlled process. Examples include a great variety of man-made noise sources, such as electronic devices, neon lights, relay switching noise in telephone channels and automatic ignition systems. For a system with non-gaussian noise, the lower order statistics cannot provide enough information. hat is, minimum variance is not a good benchmark for the cascade control loops with non-gaussian disturbances. In despite of this fact, the performance assessment of cascade control systems with non-gaussian noise has seldom been discussed in the open literature. o extend MVC based CPA to the cascade control system with non-gaussian disturbance, this paper presents a comprehensive minimum entropy methodology for the performance assessment of a cascade control loop. he paper is organized as follows: In Section, the conventional performance assessment for the cascade control system based on minimum variance control is reviewed. In Section 3, the cascade control performance assessment method based on minimum entropy control (MEC) criterion is proposed. In Section 4, case studies, including a simulation case and a cascade control loop from the industrial plant, are conducted IMECS 5
2 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 5 Vol I, IMECS 5, March 8 -, 5, Hong Kong to show the advantages of the proposed method. Finally, in Section 5, conclusions are made. II. CONVENIONAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMEN OF A CASCADE CONROL SYSEM a ( k ), respectively. he minimum variance in a cascade control loop can be obtained by analyzing the system model and the estimated disturbance sequences. According to the transfer functions of the system, the primary output can be further decomposed as, ysp u ( k) ( ) a ( k) a ( k) G L u k y ( k ) G Gc Gc G G L where d y ( k) Q ( q ) a ( k) S ( q ) q a ( k) feedback_invariants [ Ma( k) Ma( k)] q dd feedback_variants (3) Fig.. Cascade control system Fig. shows a discretized cascade control system with unity feedback. A cascade control loop consists of a primary loop and a secondary loop. hese loops might also be referred to as the outer loop and the inner loop, respectively. he primary loop provides the secondary loop with a setpoint, or a target, for a process related to the primary control objective. he subscript,, in this figure refers to the primary control loop while the subscript,, refers to the secondary control loop. he subscript C of the transfer function denotes the controller and the subscript L of the transfer function denotes the disturbance filters. he unmeasured stochastic disturbances in the primary loop can equivalently be added at the output of the primary loop as well as of the secondary loop. y ( k ) and y ( ) k are the process outputs of the primary loop and of the secondary loop at the sampling time k. he outputs of the two loops are y( k) Gy( k) GL a( k) () y ( k) G u ( k) G a ( k) () L y ( k ) is the deviation variable from its set point and y ( k ) is the deviation of the secondary output from its steady-state value, which is required to keep the primary output at its set point. u ( k ) and u ( ) k are the manipulated variables which are the outputs of the primary controller and of the secondary controller, respectively. a ( k ) and a ( ) k represent the disturbance in the primary loop and in the secondary loop, respectively. he process transfer function in the primary loop is G( q) G( q) q d with the time delay equal to d, and G ( ) q is the primary process model without any time delay. Similarly, for the secondary loop, G( q) G( q) q d is the process transfer function in the secondary loop with time delay equal to d and G ( ) q is the secondary process model without any time delay. he effects of all the unmeasured disturbances to the two loops are represented as disturbance filters G ( ) L q and G ( ) L q, both of which are assumed to be a rational function of the backward shift q, and they are driven by stochastic disturbances a ( k ) and R ( G G ) G G G G Q M GG GGG G G R G G GG S M GG GGG G c c c c c c c( c) c c c he MV cascade controller can be obtained by simultaneously solving M and M. he polynomials Q ( q ) and S ( ) q are feedback-invariant and depend only on the disturbance characteristics. hey can be represented by: Q Q Q q Q q Q q (4) (5) ( dd) ( dd) ( d ) S S Sq Sq S( d ) q hus, the feedback invariant term d Q ( q ) a ( k) S ( q ) q a ( k) consists of the first d d terms of the moving-average model, and used as a benchmark measure of minimum variance control. When M M, the primary output y ( k ) can achieve minimum variance. And the value of the minimum variance is ( ) var{ Qa( k) S q a ( k)} (6) d y mv dd trace Ni Nia i where N i, i,,, d d are defined as the coefficient matrices of the matrix polynomial Q( q ) S( q ) q d, and a is the variance-covariance matrix of the white noise vector a( k) a( k ). he performance index of the cascade control system is defined as: mv ( ) (7) y mv y where ( ) is the variance of the MVC output, and y mv y is the actual primary output variance of the system. Note that the performance index mv in Eq.(7) is only valid for the ISBN: ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) IMECS 5
3 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 5 Vol I, IMECS 5, March 8 -, 5, Hong Kong control process under the condition that both disturbances are subject to the Gaussian distribution. Here a simple example is used to show the weakness of the minimum variance index for a dynamic system whose disturbance does not follow the Gaussian distribution:.635 y( k) y ( k 6) a ( k).8368q.8q.355 y( k) u ( k) a ( k).948q.98q y (8) where B() is the Beta function. he indicator function I ( x) (,) ensures that only the values of x in the range (-, ) have nonzero probabilities. If the models are completely given and the two different unmeasured disturbances with non-gaussian disturbances are applied to the inner and the outer loops respectively, the output responses under the same controller parameters are shown in Fig.. For easy visual comparisons, the corresponding distributions are shown in Fig. 3, and both variances are very close to the value of 5.5. From the observations in Fig. 3, Fig. 3 is sharper and narrower than Fig. 3; it seems that Fig.3 has better control performance. However, the MVC performance assessment indexes for Fig. 7 and Fig. 7 are.87 and.739 respectively, yielding the opposite conclusions. Due to the non-gaussian disturbances, the conventional MVC performance assessment index would not provide correct information and may lead to wrong detection ime points Freq y ime points Fig.. Output responses of two different disturbances y 8 According to the engineering experience, the PI controller ( G c ) and the P controller ( G c ) in the outer loop and in the inner loop are used: G q q c Gc. Freq y Fig. 3. Output distributions of two different disturbances. a ( k ) and a ( k ) are assumed to follow the -distribution. he PDF of the -distribution can be represented by f xab x x I x Bab (, ) a b (, ) ( ) (,) ( ) ISBN: ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) (9) III. MINIMUM ENROPY BASED ASSESSMENS OF CASCADE CONROL SYSEMS A. Entropy information analysis In the information theory, entropy is a measure of uncertainty in a random variable. It is an idea inherited from thermodynamics and previously proposed by Hartley (98) IMECS 5
4 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 5 Vol I, IMECS 5, March 8 -, 5, Hong Kong as a measure of the information in a random signal []. Entropy is really a notion of self information provided by a random process about itself. Entropy has some great features. It has the property of convex, making it available to be the objective function of the optimization problem. o characterize quantitatively a finite and discrete random set X { x, x,..., x n }, Shannon (information) entropy ( H ( X ) ) can be defined. he Shannon entropy is distinguished by several unique properties [], but it is often convenient to introduce generalized Rényi entropies parametrized by a continuous parameter [3], H ( X ) ln M p i i () where each element x i X has probability p i, i,,..., n. his means that p i, i,,..., n, constructs a discrete probability distribution p p p which consists M of non negative numbers summing to unity. M pi. i Rényi entropy is a generalization of Shannon entropy. B. Minimum entropy index for cascade control loop In the real operation, the actual disturbance behavior is not known in advance. he results of the minimum variance based on the Gaussian disturbance would not be reasonable when the minimum variance index is applied to control processes with non-gaussian disturbance distribution. herefore, to assess a cascade control process with non-gaussian disturbance, a minimum entropy based performance assessment is proposed. Entropy, as a general measure of uncertainty, has more physical relevance than the lower order statistics, such as the mean and variance of the arbitrary random variables. he variance of the output can merely measure the deviated degree from the mean, but it cannot comprehensively characterize the non-gaussian disturbances. In this section, entropy, an alternative measure of uncertainty and dispersion, is used as an index to evaluate the control performance of the controller in cascade control systems. For a cascade control process shown in Eqs.() and () with the unmeasured non-gaussian disturbance a ( k ) and a ( k ), the entropy of the output y ( ) k can be written as H( y ) H( Qa S q a ( M a M a ) q ) () d dd Because the non-gaussian disturbance a ( k ) and a ( k ) are finite, stationary and mutually independent, the entropy of the output y ( ) k in Eq.() can be further decomposed into H( y ) HQa (, Maq ) HSq ( a, Maq ) d d d d d () Lemma: Given two discrete random variables X and Y, defined on a common probability space, there is and H ( X ) (3) H ( XY, ) max( H ( X), H ( Y )) (4) On the basis of Lemma, H ( Qa, M aq ) H( Qa) (3) H ( Sq a, Maq ) HSq ( a) (4) dd d dd d he lower bound of H ( y ) can be obtained, H ( y ) H( Qa ) H( S q a ) (5) d d he terms Qa and Sq a are the feedback invariant. he minimum entropy H ( y ) of cascade control can be obtained if M M, H ( y ) H( Qa ) H( S q a ) d me d HQa (, Sq a) (6) Now a new performance assessment index ( me ) can be defined for the cascade control system with the non-gaussian noises, H( y ) me H ( y ) me (7) where me is the ratio of the output of the minimum entropy ( H( y ) me ) to the current output of the minimum entropy ( H ( y ) ). IV. EXAMPLES A. Simulation of the cascade control system In this case, the cascade control process with non-gaussian disturbance is considered. a ( k ) and a ( ) k follow the same -distribution as those in Section. he minimum entropy of y based on the models is 3.9. herefore, the MEC performance index (Eq.(7)) is me.8669 and the H theoretical one is me hus, without the limitations of the assumption of the Gaussian disturbance, the MEC based performance assessment index is more favorable and trustable when it comes to the evaluation of the cascade control loops. ISBN: ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) IMECS 5
5 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 5 Vol I, IMECS 5, March 8 -, 5, Hong Kong B. Industrial cascade control loop heating steam Q FIC Qr Fig. 4. A temperature cascade control of the disturbance tower. 78 IC r ensure production running smoothly, the temperature should remain constant. And there is a regulating valve to control the heating steam flow Q. From the valve action to the temperature change, a lot of heat capacities are needed. It is better to adopt cascade control. Cascade control includes two closed-loop systems; the secondary loop is a flow control system while the primary loop is a temperature control system. he cascade control loop from refinery in a local plant in aiwan is used to test the proposed MEC method. Fig. 5 shows, measurements of the outputs for the primary loop in two different operating periods. he sampling time is second. From the normal probability analysis shown in Fig. 6, obviously, the output data cannot be exactly fitted into a straight line in the normal probability plots. hus, the underlying population of the two measurements is not exactly normal. Calculating the MVC index of the two periods, mv.946 and mv.966, apparently, these values are unreasonable. emperture ime points Probability emperture ime points Fig. 5. Outputs of the primary loop of Period and Period Oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process. he crude oil is processed and refined into more useful products, such as petroleum naphtha, gasoline, diesel fuel and so on. A multitude of separations is accomplished by distillation, but the most important and primary function in the refinery is the separation of crude oil into component fractions. o get the specific products, accurate temperature control is necessary. Hence, cascade control of temperatures is widely used in refinery. Fig. 4 shows a schematic diagram of a temperature cascade control to the distillation tower. o Probability Data Fig. 6. Normal probability plots of the output of Period and Period for the industrial cascade control loop. o assess during what period cascade control can outperform, the benchmark of the cascade control system should be set up first. he benchmark performance bounds are determined based on the process and disturbance models. Note that due to the space limit, the identification scheme for the non-gaussian disturbances will be discussed in another papers. he information theoretic delay criterion is applied to ISBN: ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) IMECS 5
6 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 5 Vol I, IMECS 5, March 8 -, 5, Hong Kong the collected data, and the delays of the primary loop and the secondary loop are 6s and s time units respectively. hen with the MEC based identification method, the ARMAX model can be obtained and the disturbance can be estimated. Fig. 7 shows the estimated disturbance distributions of Period and Period, respectively. In Period, with the estimated disturbance sequences and the model parameters, the minimum entropy of the primary loop output is found to be.39. he MEC index is me Likewise, in Period, the MEC performance assessment index is me.637. From the analysis, the cascade control system in Period performs better. Estimated Freq. Estimated Freq a a Fig. 7. Estimated disturbances of Period and Period for the industrial cascade control loop. V. CONCLUSION o continuously improve the process performance, the basic control loop must be constantly assessed. In the past, several different measures of CPA have been proposed, but the disturbance distribution is assumed to be normal. hat is, MVC performance assessment is effective in evaluating the healthy degree of the cascade control system with Gaussian disturbances, but it fails when the system has non-gaussian distribution. As the variance, a second order statistic is not sufficient to be a benchmark of the cascade control system with unknown disturbances. he contribution of this work is a reliable and general algorithm that allows one to estimate CPA for the controlled system with non-gaussian disturbance. he proposed method also works well even in the case of Gaussian disturbance. he proposed MEC based CPA is the Renyi s quadratic entropy of the output under the minimum entropy control loop. he entropy can be used to measure many other characteristics of the random disturbance, such as similarity, equality, disorder, and so on; so it is good for a performance criterion. Like MVC, when there is no set point change, the output under closed loop control can be devided into two terms, the feedback invariant entropy term and the feedback variant entropy term. he feedback invariant entropy term depends only on the disturbance characteristics rather than the function of the process model or the controller. he entropy can be used to measure many other characteristics of the random disturbance, such as similarity, equality, disorder, and so on; so it is good for a performance criterion. he proposed MEC performance is more useful in practical processes. From the analysis results of the simulation and the real plant data, the proposed MEC-based CPA method presents better generality and accuracy in practical processes. REFERENCES [] V. Venkatasubramanian, R. Rengaswamy, S. N. Kavuri and K. Yin, A review of process fault detection and diagnosis: Part III: Process history based methods, Comput. Chem. Eng. 7, pp , 3. [] K. J. Astrom, Computer control of a paper machine-an application of linear stochastic control theory, IBM Journal,, pp , 967. [3] W. DeVries and S. Wu, Evaluation of process control effectiveness and diagnosis of variation in paper basis weight via multivariate time-series analysis, IEEE rans. Autom Control, 3, pp.7-78, 978. [4]. J. Harris, Assessment of control loop performance, Can. J. Chem. Eng., 67, pp , 989. [5]. J. Harris, F. Boudreau and J. F. MacGregor, Performance assessment of multivariable feedback controllers, Automatica, 3, pp.55-58, 996. [6] M. J. Grimble, Controller performance benchmarking and tuning using generalised minimum variance control, Automatica, 38, pp.-9, [7] M. V. Sadasivarao and M. Chidambaram, PID controller tuning of cascade control systems using genetic algorithm, J. Indian Inst. Sci., 86, pp , 6. [8] D. G. Padhan and S. Majhi, Modified Smith predictor based cascade control of unstable time delay processes, ISA trans., 5, pp.95-4, [9] B. S. Ko and. F. Edgar, Performance assessment of cascade control loops, AIChE J., 46, pp.8-9,. [] J. Chen, Y. Yea and C. K. Kong, Diagnosis of cascade control loop status using performance analysis based approach, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 45, pp [] R. V. Hartley, ransmission of information, Bell Syst. ech. J., 7, pp , 98. [] A. I. Khinchin, Mathematical foundations of information theory (Vol. 434). Courier Dover Publications,957. [3] A. Rényi, On measures of entropy and information, In Fourth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, pp , 96. ISBN: ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) IMECS 5
Performance Assessment of Power Plant Main Steam Temperature Control System based on ADRC Control
 Vol. 8, No. (05), pp. 305-36 http://dx.doi.org/0.457/ijca.05.8..8 Performance Assessment of Power Plant Main Steam Temperature Control System based on ADC Control Guili Yuan, Juan Du and Tong Yu 3, Academy
Vol. 8, No. (05), pp. 305-36 http://dx.doi.org/0.457/ijca.05.8..8 Performance Assessment of Power Plant Main Steam Temperature Control System based on ADC Control Guili Yuan, Juan Du and Tong Yu 3, Academy
ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT OF THE INFLUENCE OF MEASUREMENT NOISE ON MVC BASED CONTROLLER PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT
 International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2018 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 14, Number 2, April 2018 pp. 697 716 ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT OF THE INFLUENCE OF
International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2018 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 14, Number 2, April 2018 pp. 697 716 ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT OF THE INFLUENCE OF
Algorithm for Multiple Model Adaptive Control Based on Input-Output Plant Model
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNEICS AND INFORMAION ECHNOLOGIES Volume No Sofia Algorithm for Multiple Model Adaptive Control Based on Input-Output Plant Model sonyo Slavov Department of Automatics
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNEICS AND INFORMAION ECHNOLOGIES Volume No Sofia Algorithm for Multiple Model Adaptive Control Based on Input-Output Plant Model sonyo Slavov Department of Automatics
Performance assessment of MIMO systems under partial information
 Performance assessment of MIMO systems under partial information H Xia P Majecki A Ordys M Grimble Abstract Minimum variance (MV) can characterize the most fundamental performance limitation of a system,
Performance assessment of MIMO systems under partial information H Xia P Majecki A Ordys M Grimble Abstract Minimum variance (MV) can characterize the most fundamental performance limitation of a system,
3.1 Overview 3.2 Process and control-loop interactions
 3. Multivariable 3.1 Overview 3.2 and control-loop interactions 3.2.1 Interaction analysis 3.2.2 Closed-loop stability 3.3 Decoupling control 3.3.1 Basic design principle 3.3.2 Complete decoupling 3.3.3
3. Multivariable 3.1 Overview 3.2 and control-loop interactions 3.2.1 Interaction analysis 3.2.2 Closed-loop stability 3.3 Decoupling control 3.3.1 Basic design principle 3.3.2 Complete decoupling 3.3.3
A Generalised Minimum Variance Controller for Time-Varying MIMO Linear Systems with Multiple Delays
 WSEAS RANSACIONS on SYSEMS and CONROL A Generalised Minimum Variance Controller for ime-varying MIMO Linear Systems with Multiple Delays ZHENG LI School of Electrical, Computer and elecom. Eng. University
WSEAS RANSACIONS on SYSEMS and CONROL A Generalised Minimum Variance Controller for ime-varying MIMO Linear Systems with Multiple Delays ZHENG LI School of Electrical, Computer and elecom. Eng. University
Self-tuning Control Based on Discrete Sliding Mode
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. Autom. Volume 1, Number 6, 2014, pp. 367-372 Received: July 18, 2014; Published: December 25, 2014 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation Akira Ohata 1, Akihiko
Int. J. Mech. Eng. Autom. Volume 1, Number 6, 2014, pp. 367-372 Received: July 18, 2014; Published: December 25, 2014 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation Akira Ohata 1, Akihiko
Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process
 Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process D.Angeline Vijula #, Dr.N.Devarajan * # Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Sri Ramakrishna
Design of Decentralised PI Controller using Model Reference Adaptive Control for Quadruple Tank Process D.Angeline Vijula #, Dr.N.Devarajan * # Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Sri Ramakrishna
NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve
 D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
D. SWATI et al., Nonlinear Control of ph System for Change Over Titration Curve, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 19 (4) 341 349 (2005) 341 NonlinearControlofpHSystemforChangeOverTitrationCurve D. Swati, V. S. R.
NON-LINEAR CONTROL OF OUTPUT PROBABILITY DENSITY FUNCTION FOR LINEAR ARMAX SYSTEMS
 Control 4, University of Bath, UK, September 4 ID-83 NON-LINEAR CONTROL OF OUTPUT PROBABILITY DENSITY FUNCTION FOR LINEAR ARMAX SYSTEMS H. Yue, H. Wang Control Systems Centre, University of Manchester
Control 4, University of Bath, UK, September 4 ID-83 NON-LINEAR CONTROL OF OUTPUT PROBABILITY DENSITY FUNCTION FOR LINEAR ARMAX SYSTEMS H. Yue, H. Wang Control Systems Centre, University of Manchester
Improved Identification and Control of 2-by-2 MIMO System using Relay Feedback
 CEAI, Vol.17, No.4 pp. 23-32, 2015 Printed in Romania Improved Identification and Control of 2-by-2 MIMO System using Relay Feedback D.Kalpana, T.Thyagarajan, R.Thenral Department of Instrumentation Engineering,
CEAI, Vol.17, No.4 pp. 23-32, 2015 Printed in Romania Improved Identification and Control of 2-by-2 MIMO System using Relay Feedback D.Kalpana, T.Thyagarajan, R.Thenral Department of Instrumentation Engineering,
Multirate MVC Design and Control Performance Assessment: a Data Driven Subspace Approach*
 Multirate MVC Design and Control Performance Assessment: a Data Driven Subspace Approach* Xiaorui Wang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2V4
Multirate MVC Design and Control Performance Assessment: a Data Driven Subspace Approach* Xiaorui Wang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2V4
Cramér-Rao Bounds for Estimation of Linear System Noise Covariances
 Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation (): 6- DOI: 593/jjmea Cramér-Rao Bounds for Estimation of Linear System oise Covariances Peter Matiso * Vladimír Havlena Czech echnical University in Prague
Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation (): 6- DOI: 593/jjmea Cramér-Rao Bounds for Estimation of Linear System oise Covariances Peter Matiso * Vladimír Havlena Czech echnical University in Prague
CONTROLLER PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT IN SET POINT TRACKING AND REGULATORY CONTROL
 ADCHEM 2, Pisa Italy June 14-16 th 2 CONTROLLER PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT IN SET POINT TRACKING AND REGULATORY CONTROL N.F. Thornhill *, S.L. Shah + and B. Huang + * Department of Electronic and Electrical
ADCHEM 2, Pisa Italy June 14-16 th 2 CONTROLLER PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT IN SET POINT TRACKING AND REGULATORY CONTROL N.F. Thornhill *, S.L. Shah + and B. Huang + * Department of Electronic and Electrical
DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR ph CONTROL
 DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR CONTROL Alex D. Kalafatis Liuping Wang William R. Cluett AspenTech, Toronto, Canada School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne,
DESIGN OF AN ON-LINE TITRATOR FOR NONLINEAR CONTROL Alex D. Kalafatis Liuping Wang William R. Cluett AspenTech, Toronto, Canada School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne,
APPLICATION OF ADAPTIVE CONTROLLER TO WATER HYDRAULIC SERVO CYLINDER
 APPLICAION OF ADAPIVE CONROLLER O WAER HYDRAULIC SERVO CYLINDER Hidekazu AKAHASHI*, Kazuhisa IO** and Shigeru IKEO** * Division of Science and echnology, Graduate school of SOPHIA University 7- Kioicho,
APPLICAION OF ADAPIVE CONROLLER O WAER HYDRAULIC SERVO CYLINDER Hidekazu AKAHASHI*, Kazuhisa IO** and Shigeru IKEO** * Division of Science and echnology, Graduate school of SOPHIA University 7- Kioicho,
Chapter 2 Examples of Applications for Connectivity and Causality Analysis
 Chapter 2 Examples of Applications for Connectivity and Causality Analysis Abstract Connectivity and causality have a lot of potential applications, among which we focus on analysis and design of large-scale
Chapter 2 Examples of Applications for Connectivity and Causality Analysis Abstract Connectivity and causality have a lot of potential applications, among which we focus on analysis and design of large-scale
Quis custodiet ipsos custodes?
 Quis custodiet ipsos custodes? James B. Rawlings, Megan Zagrobelny, Luo Ji Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison, WI, USA IFAC Conference on Nonlinear Model Predictive
Quis custodiet ipsos custodes? James B. Rawlings, Megan Zagrobelny, Luo Ji Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison, WI, USA IFAC Conference on Nonlinear Model Predictive
DECENTRALIZED PI CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR NON LINEAR MULTIVARIABLE SYSTEMS BASED ON IDEAL DECOUPLER
 th June 4. Vol. 64 No. 5-4 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 DECENTRALIZED PI CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR NON LINEAR MULTIVARIABLE SYSTEMS BASED ON IDEAL DECOUPLER
th June 4. Vol. 64 No. 5-4 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ISSN: 99-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISSN: 87-395 DECENTRALIZED PI CONTROLLER DESIGN FOR NON LINEAR MULTIVARIABLE SYSTEMS BASED ON IDEAL DECOUPLER
A Discrete Robust Adaptive Iterative Learning Control for a Class of Nonlinear Systems with Unknown Control Direction
 Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 16 Vol I, IMECS 16, March 16-18, 16, Hong Kong A Discrete Robust Adaptive Iterative Learning Control for a Class of
Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 16 Vol I, IMECS 16, March 16-18, 16, Hong Kong A Discrete Robust Adaptive Iterative Learning Control for a Class of
Ian G. Horn, Jeffery R. Arulandu, Christopher J. Gombas, Jeremy G. VanAntwerp, and Richard D. Braatz*
 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 996, 35, 3437-344 3437 PROCESS DESIGN AND CONTROL Improved Filter Design in Internal Model Control Ian G. Horn, Jeffery R. Arulandu, Christopher J. Gombas, Jeremy G. VanAntwerp, and
Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 996, 35, 3437-344 3437 PROCESS DESIGN AND CONTROL Improved Filter Design in Internal Model Control Ian G. Horn, Jeffery R. Arulandu, Christopher J. Gombas, Jeremy G. VanAntwerp, and
A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems
 Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems This content has been downloaded from IOPscience.
Home Search Collections Journals About Contact us My IOPscience A unified double-loop multi-scale control strategy for NMP integrating-unstable systems This content has been downloaded from IOPscience.
CONTROLLER PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT IN SET POINT TRACKING AND REGULATORY CONTROL
 This is a preprint of an article accepted for publication in International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 3, 7, 79-77 CONTROLLER PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT IN SET POINT TRACKING AND REGULATORY
This is a preprint of an article accepted for publication in International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 3, 7, 79-77 CONTROLLER PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT IN SET POINT TRACKING AND REGULATORY
inputs. The velocity form is used in the digital implementation to avoid wind-up [7]. The unified LQR scheme has been developed due to several reasons
![inputs. The velocity form is used in the digital implementation to avoid wind-up [7]. The unified LQR scheme has been developed due to several reasons inputs. The velocity form is used in the digital implementation to avoid wind-up [7]. The unified LQR scheme has been developed due to several reasons](/thumbs/86/94280335.jpg) A LQR Scheme for SCR Process in Combined-Cycle Thermal Power Plants Santo Wijaya 1 Keiko Shimizu 1 and Masashi Nakamoto 2 Abstract The paper presents a feedback control of Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR)
A LQR Scheme for SCR Process in Combined-Cycle Thermal Power Plants Santo Wijaya 1 Keiko Shimizu 1 and Masashi Nakamoto 2 Abstract The paper presents a feedback control of Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR)
ASIGNIFICANT research effort has been devoted to the. Optimal State Estimation for Stochastic Systems: An Information Theoretic Approach
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL 42, NO 6, JUNE 1997 771 Optimal State Estimation for Stochastic Systems: An Information Theoretic Approach Xiangbo Feng, Kenneth A Loparo, Senior Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL 42, NO 6, JUNE 1997 771 Optimal State Estimation for Stochastic Systems: An Information Theoretic Approach Xiangbo Feng, Kenneth A Loparo, Senior Member, IEEE,
Pass Balancing Switching Control of a Four-passes Furnace System
 Pass Balancing Switching Control of a Four-passes Furnace System Xingxuan Wang Department of Electronic Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 004, P. R. China (el: 86 656496; e-mail: wxx07@fudan.edu.cn)
Pass Balancing Switching Control of a Four-passes Furnace System Xingxuan Wang Department of Electronic Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 004, P. R. China (el: 86 656496; e-mail: wxx07@fudan.edu.cn)
Observer Based Friction Cancellation in Mechanical Systems
 2014 14th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 2014) Oct. 22 25, 2014 in KINTEX, Gyeonggi-do, Korea Observer Based Friction Cancellation in Mechanical Systems Caner Odabaş
2014 14th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS 2014) Oct. 22 25, 2014 in KINTEX, Gyeonggi-do, Korea Observer Based Friction Cancellation in Mechanical Systems Caner Odabaş
Control System Design
 ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #36 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Friday, April 4, 2003 3. Cascade Control Next we turn to an
ELEC ENG 4CL4: Control System Design Notes for Lecture #36 Dr. Ian C. Bruce Room: CRL-229 Phone ext.: 26984 Email: ibruce@mail.ece.mcmaster.ca Friday, April 4, 2003 3. Cascade Control Next we turn to an
Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance
 Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance Article (Unspecified) Kaya, İbrahim, Tan, Nusret and Atherton, Derek P. (7) Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance. Journal
Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance Article (Unspecified) Kaya, İbrahim, Tan, Nusret and Atherton, Derek P. (7) Improved cascade control structure for enhanced performance. Journal
Copyright 2002 IFAC 15th Triennial World Congress, Barcelona, Spain
 Copyright 22 IFAC 15th Triennial World Congress, Barcelona, Spain MULTIVARIABLE MPC PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT, MONITORING DIA AND GNOSIS Jochen Sch äferand Ali C ο inar 1 Chemical and Environmental Engineering
Copyright 22 IFAC 15th Triennial World Congress, Barcelona, Spain MULTIVARIABLE MPC PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT, MONITORING DIA AND GNOSIS Jochen Sch äferand Ali C ο inar 1 Chemical and Environmental Engineering
Minimum-Information-Entropy-Based Control Performance Assessment
 Entropy 13, 15, 943-959; doi:1.339/e153943 Article OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 199-43 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Minimum-Information-Entropy-Based Control Performance Assessment Qing-Wei Meng *, Fang Fang
Entropy 13, 15, 943-959; doi:1.339/e153943 Article OPEN ACCESS entropy ISSN 199-43 www.mdpi.com/journal/entropy Minimum-Information-Entropy-Based Control Performance Assessment Qing-Wei Meng *, Fang Fang
Design of Nearly Constant Velocity Track Filters for Brief Maneuvers
 4th International Conference on Information Fusion Chicago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 20 Design of Nearly Constant Velocity rack Filters for Brief Maneuvers W. Dale Blair Georgia ech Research Institute
4th International Conference on Information Fusion Chicago, Illinois, USA, July 5-8, 20 Design of Nearly Constant Velocity rack Filters for Brief Maneuvers W. Dale Blair Georgia ech Research Institute
AN EVENT-TRIGGERED TRANSMISSION POLICY FOR NETWORKED L 2 -GAIN CONTROL
 4 Journal of Marine Science and echnology, Vol. 3, No., pp. 4-9 () DOI:.69/JMS-3-3-3 AN EVEN-RIGGERED RANSMISSION POLICY FOR NEWORKED L -GAIN CONROL Jenq-Lang Wu, Yuan-Chang Chang, Xin-Hong Chen, and su-ian
4 Journal of Marine Science and echnology, Vol. 3, No., pp. 4-9 () DOI:.69/JMS-3-3-3 AN EVEN-RIGGERED RANSMISSION POLICY FOR NEWORKED L -GAIN CONROL Jenq-Lang Wu, Yuan-Chang Chang, Xin-Hong Chen, and su-ian
Optimal Polynomial Control for Discrete-Time Systems
 1 Optimal Polynomial Control for Discrete-Time Systems Prof Guy Beale Electrical and Computer Engineering Department George Mason University Fairfax, Virginia Correspondence concerning this paper should
1 Optimal Polynomial Control for Discrete-Time Systems Prof Guy Beale Electrical and Computer Engineering Department George Mason University Fairfax, Virginia Correspondence concerning this paper should
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control
 Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control 1 Cascade Control A disadvantage of conventional feedback
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies (Advanced Control) Cascade Control Time-Delay Compensation Inferential Control Selective and Override Control 1 Cascade Control A disadvantage of conventional feedback
6.435, System Identification
 SET 6 System Identification 6.435 Parametrized model structures One-step predictor Identifiability Munther A. Dahleh 1 Models of LTI Systems A complete model u = input y = output e = noise (with PDF).
SET 6 System Identification 6.435 Parametrized model structures One-step predictor Identifiability Munther A. Dahleh 1 Models of LTI Systems A complete model u = input y = output e = noise (with PDF).
System Identification for Process Control: Recent Experiences and a Personal Outlook
 System Identification for Process Control: Recent Experiences and a Personal Outlook Yucai Zhu Eindhoven University of Technology Eindhoven, The Netherlands and Tai-Ji Control Best, The Netherlands Contents
System Identification for Process Control: Recent Experiences and a Personal Outlook Yucai Zhu Eindhoven University of Technology Eindhoven, The Netherlands and Tai-Ji Control Best, The Netherlands Contents
OPTIMIZATION OF MODEL-FREE ADAPTIVE CONTROLLER USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION METHOD
 ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics - Vol. 3 - pp.37-45 Copyright c 2008 by ABCM OPTIMIZATION OF MODEL-FREE ADAPTIVE CONTROLLER USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION METHOD Leandro dos Santos Coelho Industrial
ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics - Vol. 3 - pp.37-45 Copyright c 2008 by ABCM OPTIMIZATION OF MODEL-FREE ADAPTIVE CONTROLLER USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION METHOD Leandro dos Santos Coelho Industrial
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16
 Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16 1. Cascade control 2. Time-delay compensation 3. Inferential control 4. Selective and override control 5. Nonlinear control 6. Adaptive control 1 Chapter
Enhanced Single-Loop Control Strategies Chapter 16 1. Cascade control 2. Time-delay compensation 3. Inferential control 4. Selective and override control 5. Nonlinear control 6. Adaptive control 1 Chapter
CHAPTER 6 CLOSED LOOP STUDIES
 180 CHAPTER 6 CLOSED LOOP STUDIES Improvement of closed-loop performance needs proper tuning of controller parameters that requires process model structure and the estimation of respective parameters which
180 CHAPTER 6 CLOSED LOOP STUDIES Improvement of closed-loop performance needs proper tuning of controller parameters that requires process model structure and the estimation of respective parameters which
Incorporating Feedforward Action into Self-optimizing Control Policies
 Incorporating Feedforward Action into Self-optimizing Control Policies Lia Maisarah Umar, Yi Cao and Vinay Kariwala School of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
Incorporating Feedforward Action into Self-optimizing Control Policies Lia Maisarah Umar, Yi Cao and Vinay Kariwala School of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
CONTROL SYSTEMS, ROBOTICS, AND AUTOMATION - Vol. V - Recursive Algorithms - Han-Fu Chen
 CONROL SYSEMS, ROBOICS, AND AUOMAION - Vol. V - Recursive Algorithms - Han-Fu Chen RECURSIVE ALGORIHMS Han-Fu Chen Institute of Systems Science, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy
CONROL SYSEMS, ROBOICS, AND AUOMAION - Vol. V - Recursive Algorithms - Han-Fu Chen RECURSIVE ALGORIHMS Han-Fu Chen Institute of Systems Science, Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy
Lyapunov Stability of Linear Predictor Feedback for Distributed Input Delays
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL VOL. 56 NO. 3 MARCH 2011 655 Lyapunov Stability of Linear Predictor Feedback for Distributed Input Delays Nikolaos Bekiaris-Liberis Miroslav Krstic In this case system
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL VOL. 56 NO. 3 MARCH 2011 655 Lyapunov Stability of Linear Predictor Feedback for Distributed Input Delays Nikolaos Bekiaris-Liberis Miroslav Krstic In this case system
Control of MIMO processes. 1. Introduction. Control of MIMO processes. Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes
 Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
Control of MIMO processes Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Processes Statistical Process Control Feedforward and ratio control Cascade control Split range and selective control Control
On Identification of Cascade Systems 1
 On Identification of Cascade Systems 1 Bo Wahlberg Håkan Hjalmarsson Jonas Mårtensson Automatic Control and ACCESS, School of Electrical Engineering, KTH, SE-100 44 Stockholm, Sweden. (bo.wahlberg@ee.kth.se
On Identification of Cascade Systems 1 Bo Wahlberg Håkan Hjalmarsson Jonas Mårtensson Automatic Control and ACCESS, School of Electrical Engineering, KTH, SE-100 44 Stockholm, Sweden. (bo.wahlberg@ee.kth.se
A Boiler-Turbine System Control Using A Fuzzy Auto-Regressive Moving Average (FARMA) Model
 142 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ENERGY CONVERSION, VOL. 18, NO. 1, MARCH 2003 A Boiler-Turbine System Control Using A Fuzzy Auto-Regressive Moving Average (FARMA) Model Un-Chul Moon and Kwang Y. Lee, Fellow,
142 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ENERGY CONVERSION, VOL. 18, NO. 1, MARCH 2003 A Boiler-Turbine System Control Using A Fuzzy Auto-Regressive Moving Average (FARMA) Model Un-Chul Moon and Kwang Y. Lee, Fellow,
DYNAMIC SIMULATOR-BASED APC DESIGN FOR A NAPHTHA REDISTILLATION COLUMN
 HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRY AND CHEMISTRY Vol. 45(1) pp. 17 22 (2017) hjic.mk.uni-pannon.hu DOI: 10.1515/hjic-2017-0004 DYNAMIC SIMULATOR-BASED APC DESIGN FOR A NAPHTHA REDISTILLATION COLUMN LÁSZLÓ SZABÓ,
HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRY AND CHEMISTRY Vol. 45(1) pp. 17 22 (2017) hjic.mk.uni-pannon.hu DOI: 10.1515/hjic-2017-0004 DYNAMIC SIMULATOR-BASED APC DESIGN FOR A NAPHTHA REDISTILLATION COLUMN LÁSZLÓ SZABÓ,
Model-based PID tuning for high-order processes: when to approximate
 Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 25 Seville, Spain, December 2-5, 25 ThB5. Model-based PID tuning for high-order processes: when to approximate
Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 25 Seville, Spain, December 2-5, 25 ThB5. Model-based PID tuning for high-order processes: when to approximate
Here represents the impulse (or delta) function. is an diagonal matrix of intensities, and is an diagonal matrix of intensities.
 19 KALMAN FILTER 19.1 Introduction In the previous section, we derived the linear quadratic regulator as an optimal solution for the fullstate feedback control problem. The inherent assumption was that
19 KALMAN FILTER 19.1 Introduction In the previous section, we derived the linear quadratic regulator as an optimal solution for the fullstate feedback control problem. The inherent assumption was that
Multipredictive Adaptive Control of Arc Welding Trailing Centerline Temperature
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CONTROL SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 8, NO. 1, JANUARY 2000 159 Multipredictive Adaptive Control of Arc Welding Trailing Centerline Temperature T. O. Santos, R. B. Caetano, J. M. Lemos,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CONTROL SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 8, NO. 1, JANUARY 2000 159 Multipredictive Adaptive Control of Arc Welding Trailing Centerline Temperature T. O. Santos, R. B. Caetano, J. M. Lemos,
Adaptive Robust Control
 Adaptive Robust Control Adaptive control: modifies the control law to cope with the fact that the system and environment are uncertain. Robust control: sacrifices performance by guaranteeing stability
Adaptive Robust Control Adaptive control: modifies the control law to cope with the fact that the system and environment are uncertain. Robust control: sacrifices performance by guaranteeing stability
Progress in MPC Identification: A Case Study on Totally Closed-Loop Plant Test
 Progress in MPC Identification: A Case Study on Totally Closed-Loop Plant Test Yucai Zhu Grensheuvel 10, 5685 AG Best, The Netherlands Phone +31.499.465692, fax +31.499.465693, y.zhu@taijicontrol.com Abstract:
Progress in MPC Identification: A Case Study on Totally Closed-Loop Plant Test Yucai Zhu Grensheuvel 10, 5685 AG Best, The Netherlands Phone +31.499.465692, fax +31.499.465693, y.zhu@taijicontrol.com Abstract:
LQG benchmarking for Economic Control Performance
 8 American Control Conference Westin Seattle Hotel, Seattle, Washington, USA June 11-13, 8 hc13.1 LQG benchmarking for Economic Control Performance Chao Zhao, Hongye Su, Yong Gu and Biao Huang Abstract
8 American Control Conference Westin Seattle Hotel, Seattle, Washington, USA June 11-13, 8 hc13.1 LQG benchmarking for Economic Control Performance Chao Zhao, Hongye Su, Yong Gu and Biao Huang Abstract
CHAPTER 3 TUNING METHODS OF CONTROLLER
 57 CHAPTER 3 TUNING METHODS OF CONTROLLER 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with a simple method of designing PI and PID controllers for first order plus time delay with integrator systems (FOPTDI).
57 CHAPTER 3 TUNING METHODS OF CONTROLLER 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter deals with a simple method of designing PI and PID controllers for first order plus time delay with integrator systems (FOPTDI).
Bearing fault diagnosis based on EMD-KPCA and ELM
 Bearing fault diagnosis based on EMD-KPCA and ELM Zihan Chen, Hang Yuan 2 School of Reliability and Systems Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 9, China Science and Technology on Reliability & Environmental
Bearing fault diagnosis based on EMD-KPCA and ELM Zihan Chen, Hang Yuan 2 School of Reliability and Systems Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 9, China Science and Technology on Reliability & Environmental
Process Identification for an SOPDT Model Using Rectangular Pulse Input
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(5), 586-592 (2001) SHORT COMMUNICATION Process Identification for an SOPDT Model Using Rectangular Pulse Input Don Jang, Young Han Kim* and Kyu Suk Hwang Dept. of Chem. Eng., Pusan
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 18(5), 586-592 (2001) SHORT COMMUNICATION Process Identification for an SOPDT Model Using Rectangular Pulse Input Don Jang, Young Han Kim* and Kyu Suk Hwang Dept. of Chem. Eng., Pusan
ADAPTIVE TEMPERATURE CONTROL IN CONTINUOUS STIRRED TANK REACTOR
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology (IJEET), ISSN 0976 6545(Print), ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology (IJEET), ISSN 0976 6545(Print), ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online)
ROBUSTNESS COMPARISON OF CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR A NUCLEAR POWER PLANT
 Control 004, University of Bath, UK, September 004 ROBUSTNESS COMPARISON OF CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR A NUCLEAR POWER PLANT L Ding*, A Bradshaw, C J Taylor Lancaster University, UK. * l.ding@email.com Fax: 0604
Control 004, University of Bath, UK, September 004 ROBUSTNESS COMPARISON OF CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR A NUCLEAR POWER PLANT L Ding*, A Bradshaw, C J Taylor Lancaster University, UK. * l.ding@email.com Fax: 0604
DISCRETE-TIME ADAPTIVE LQG/LTR CONTROL
 DISCRETE-TIME ADAPTIVE LQG/LTR CONTROL DARIUSZ HORLA Poznan University of Technology Inst. of Control and Inf. Eng. ul. Piotrowo 3a, 6-965 Poznan POLAND ANDRZEJ KRÓLIKOWSKI Poznan University of Technology
DISCRETE-TIME ADAPTIVE LQG/LTR CONTROL DARIUSZ HORLA Poznan University of Technology Inst. of Control and Inf. Eng. ul. Piotrowo 3a, 6-965 Poznan POLAND ANDRZEJ KRÓLIKOWSKI Poznan University of Technology
Model Predictive Controller of Boost Converter with RLE Load
 Model Predictive Controller of Boost Converter with RLE Load N. Murali K.V.Shriram S.Muthukumar Nizwa College of Vellore Institute of Nizwa College of Technology Technology University Technology Ministry
Model Predictive Controller of Boost Converter with RLE Load N. Murali K.V.Shriram S.Muthukumar Nizwa College of Vellore Institute of Nizwa College of Technology Technology University Technology Ministry
An Improved Relay Auto Tuning of PID Controllers for SOPTD Systems
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 7 WCECS 7, October 4-6, 7, San Francisco, USA An Improved Relay Auto Tuning of PID Controllers for SOPTD Systems Sathe Vivek and M.
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 7 WCECS 7, October 4-6, 7, San Francisco, USA An Improved Relay Auto Tuning of PID Controllers for SOPTD Systems Sathe Vivek and M.
Model Based Fault Detection and Diagnosis Using Structured Residual Approach in a Multi-Input Multi-Output System
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 4, No. 2, November 2007, 133-145 Model Based Fault Detection and Diagnosis Using Structured Residual Approach in a Multi-Input Multi-Output System A. Asokan
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 4, No. 2, November 2007, 133-145 Model Based Fault Detection and Diagnosis Using Structured Residual Approach in a Multi-Input Multi-Output System A. Asokan
APPLICATION OF MULTIVARIABLE PREDICTIVE CONTROL IN A DEBUTANIZER DISTILLATION COLUMN. Department of Electrical Engineering
 APPLICAION OF MULIVARIABLE PREDICIVE CONROL IN A DEBUANIZER DISILLAION COLUMN Adhemar de Barros Fontes André Laurindo Maitelli Anderson Luiz de Oliveira Cavalcanti 4 Elói Ângelo,4 Federal University of
APPLICAION OF MULIVARIABLE PREDICIVE CONROL IN A DEBUANIZER DISILLAION COLUMN Adhemar de Barros Fontes André Laurindo Maitelli Anderson Luiz de Oliveira Cavalcanti 4 Elói Ângelo,4 Federal University of
Adaptive Dual Control
 Adaptive Dual Control Björn Wittenmark Department of Automatic Control, Lund Institute of Technology Box 118, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden email: bjorn@control.lth.se Keywords: Dual control, stochastic control,
Adaptive Dual Control Björn Wittenmark Department of Automatic Control, Lund Institute of Technology Box 118, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden email: bjorn@control.lth.se Keywords: Dual control, stochastic control,
Overview of Control System Design
 Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
Overview of Control System Design General Requirements 1. Safety. It is imperative that industrial plants operate safely so as to promote the well-being of people and equipment within the plant and in
OPTIMAL CONTROL AND ESTIMATION
 OPTIMAL CONTROL AND ESTIMATION Robert F. Stengel Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION
OPTIMAL CONTROL AND ESTIMATION Robert F. Stengel Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION
CONTROL SYSTEMS, ROBOTICS, AND AUTOMATION - Vol. V - Prediction Error Methods - Torsten Söderström
 PREDICTIO ERROR METHODS Torsten Söderström Department of Systems and Control, Information Technology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden Keywords: prediction error method, optimal prediction, identifiability,
PREDICTIO ERROR METHODS Torsten Söderström Department of Systems and Control, Information Technology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden Keywords: prediction error method, optimal prediction, identifiability,
On an internal multimodel control for nonlinear multivariable systems - A comparative study
 On an internal multimodel control for nonlinear multivariable systems A comparative study Nahla Touati Karmani Dhaou Soudani Mongi Naceur Mohamed Benrejeb Abstract An internal multimodel control designed
On an internal multimodel control for nonlinear multivariable systems A comparative study Nahla Touati Karmani Dhaou Soudani Mongi Naceur Mohamed Benrejeb Abstract An internal multimodel control designed
Introduction to System Identification and Adaptive Control
 Introduction to System Identification and Adaptive Control A. Khaki Sedigh Control Systems Group Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering K. N. Toosi University of Technology May 2009 Introduction
Introduction to System Identification and Adaptive Control A. Khaki Sedigh Control Systems Group Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering K. N. Toosi University of Technology May 2009 Introduction
Model predictive control of industrial processes. Vitali Vansovitš
 Model predictive control of industrial processes Vitali Vansovitš Contents Industrial process (Iru Power Plant) Neural networ identification Process identification linear model Model predictive controller
Model predictive control of industrial processes Vitali Vansovitš Contents Industrial process (Iru Power Plant) Neural networ identification Process identification linear model Model predictive controller
STOCHASTIC INFORMATION GRADIENT ALGORITHM BASED ON MAXIMUM ENTROPY DENSITY ESTIMATION. Badong Chen, Yu Zhu, Jinchun Hu and Ming Zhang
 ICIC Express Letters ICIC International c 2009 ISSN 1881-803X Volume 3, Number 3, September 2009 pp. 1 6 STOCHASTIC INFORMATION GRADIENT ALGORITHM BASED ON MAXIMUM ENTROPY DENSITY ESTIMATION Badong Chen,
ICIC Express Letters ICIC International c 2009 ISSN 1881-803X Volume 3, Number 3, September 2009 pp. 1 6 STOCHASTIC INFORMATION GRADIENT ALGORITHM BASED ON MAXIMUM ENTROPY DENSITY ESTIMATION Badong Chen,
Computation of Stabilizing PI and PID parameters for multivariable system with time delays
 Computation of Stabilizing PI and PID parameters for multivariable system with time delays Nour El Houda Mansour, Sami Hafsi, Kaouther Laabidi Laboratoire d Analyse, Conception et Commande des Systèmes
Computation of Stabilizing PI and PID parameters for multivariable system with time delays Nour El Houda Mansour, Sami Hafsi, Kaouther Laabidi Laboratoire d Analyse, Conception et Commande des Systèmes
Iterative Controller Tuning Using Bode s Integrals
 Iterative Controller Tuning Using Bode s Integrals A. Karimi, D. Garcia and R. Longchamp Laboratoire d automatique, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 05 Lausanne, Switzerland. email: alireza.karimi@epfl.ch
Iterative Controller Tuning Using Bode s Integrals A. Karimi, D. Garcia and R. Longchamp Laboratoire d automatique, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 05 Lausanne, Switzerland. email: alireza.karimi@epfl.ch
An Adaptive LQG Combined With the MRAS Based LFFC for Motion Control Systems
 Journal of Automation Control Engineering Vol 3 No 2 April 2015 An Adaptive LQG Combined With the MRAS Based LFFC for Motion Control Systems Nguyen Duy Cuong Nguyen Van Lanh Gia Thi Dinh Electronics Faculty
Journal of Automation Control Engineering Vol 3 No 2 April 2015 An Adaptive LQG Combined With the MRAS Based LFFC for Motion Control Systems Nguyen Duy Cuong Nguyen Van Lanh Gia Thi Dinh Electronics Faculty
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Jämsä-Jounela, Sirkka-Liisa; Poikonen,
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Jämsä-Jounela, Sirkka-Liisa; Poikonen,
Design and Stability Analysis of Single-Input Fuzzy Logic Controller
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MAN, AND CYBERNETICS PART B: CYBERNETICS, VOL. 30, NO. 2, APRIL 2000 303 Design and Stability Analysis of Single-Input Fuzzy Logic Controller Byung-Jae Choi, Seong-Woo Kwak,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SYSTEMS, MAN, AND CYBERNETICS PART B: CYBERNETICS, VOL. 30, NO. 2, APRIL 2000 303 Design and Stability Analysis of Single-Input Fuzzy Logic Controller Byung-Jae Choi, Seong-Woo Kwak,
Chapter 8. Feedback Controllers. Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system.
 Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
Feedback Controllers Figure 8.1 Schematic diagram for a stirred-tank blending system. 1 Basic Control Modes Next we consider the three basic control modes starting with the simplest mode, proportional
Index Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, sensor, 383, Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709,
 Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, 83-84 sensor, 383, 772-773 Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709, 715 input conversion, 519 reasons for, 512-517 relay auto-tuning,
Accumulation, 53 Accuracy: numerical integration, 83-84 sensor, 383, 772-773 Adaptive tuning: expert system, 528 gain scheduling, 518, 529, 709, 715 input conversion, 519 reasons for, 512-517 relay auto-tuning,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 100 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 100 (015 ) 345 349 5th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, DAAAM 014 Control of Airflow
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 100 (015 ) 345 349 5th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, DAAAM 014 Control of Airflow
Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES. Professor Dae Ryook Yang
 Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University
Multi-Input Multi-output (MIMO) Processes CBE495 LECTURE III CONTROL OF MULTI INPUT MULTI OUTPUT PROCESSES Professor Dae Ryook Yang Fall 2013 Dept. of Chemical and Biological Engineering Korea University
Process Unit Control System Design
 Process Unit Control System Design 1. Introduction 2. Influence of process design 3. Control degrees of freedom 4. Selection of control system variables 5. Process safety Introduction Control system requirements»
Process Unit Control System Design 1. Introduction 2. Influence of process design 3. Control degrees of freedom 4. Selection of control system variables 5. Process safety Introduction Control system requirements»
IMC based automatic tuning method for PID controllers in a Smith predictor configuration
 Computers and Chemical Engineering 28 (2004) 281 290 IMC based automatic tuning method for PID controllers in a Smith predictor configuration Ibrahim Kaya Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
Computers and Chemical Engineering 28 (2004) 281 290 IMC based automatic tuning method for PID controllers in a Smith predictor configuration Ibrahim Kaya Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
MULTILOOP PI CONTROLLER FOR ACHIEVING SIMULTANEOUS TIME AND FREQUENCY DOMAIN SPECIFICATIONS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 1, No. 8 (215) 113-1115 School of Engineering, Taylor s University MULTILOOP PI CONTROLLER FOR ACHIEVING SIMULTANEOUS TIME AND FREQUENCY DOMAIN SPECIFICATIONS
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 1, No. 8 (215) 113-1115 School of Engineering, Taylor s University MULTILOOP PI CONTROLLER FOR ACHIEVING SIMULTANEOUS TIME AND FREQUENCY DOMAIN SPECIFICATIONS
MULTILOOP CONTROL APPLIED TO INTEGRATOR MIMO. PROCESSES. A Preliminary Study
 MULTILOOP CONTROL APPLIED TO INTEGRATOR MIMO PROCESSES. A Preliminary Study Eduardo J. Adam 1,2*, Carlos J. Valsecchi 2 1 Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico para la Industria Química (INTEC) (Universidad
MULTILOOP CONTROL APPLIED TO INTEGRATOR MIMO PROCESSES. A Preliminary Study Eduardo J. Adam 1,2*, Carlos J. Valsecchi 2 1 Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico para la Industria Química (INTEC) (Universidad
A NOVEL OPTIMAL PROBABILITY DENSITY FUNCTION TRACKING FILTER DESIGN 1
 A NOVEL OPTIMAL PROBABILITY DENSITY FUNCTION TRACKING FILTER DESIGN 1 Jinglin Zhou Hong Wang, Donghua Zhou Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, P. R. China Control Systems Centre,
A NOVEL OPTIMAL PROBABILITY DENSITY FUNCTION TRACKING FILTER DESIGN 1 Jinglin Zhou Hong Wang, Donghua Zhou Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, P. R. China Control Systems Centre,
Modeling and Control Overview
 Modeling and Control Overview D R. T A R E K A. T U T U N J I A D V A N C E D C O N T R O L S Y S T E M S M E C H A T R O N I C S E N G I N E E R I N G D E P A R T M E N T P H I L A D E L P H I A U N I
Modeling and Control Overview D R. T A R E K A. T U T U N J I A D V A N C E D C O N T R O L S Y S T E M S M E C H A T R O N I C S E N G I N E E R I N G D E P A R T M E N T P H I L A D E L P H I A U N I
Expressions for the covariance matrix of covariance data
 Expressions for the covariance matrix of covariance data Torsten Söderström Division of Systems and Control, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, P O Box 337, SE-7505 Uppsala, Sweden
Expressions for the covariance matrix of covariance data Torsten Söderström Division of Systems and Control, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University, P O Box 337, SE-7505 Uppsala, Sweden
Index. INDEX_p /15/02 3:08 PM Page 765
 INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
INDEX_p.765-770 11/15/02 3:08 PM Page 765 Index N A Adaptive control, 144 Adiabatic reactors, 465 Algorithm, control, 5 All-pass factorization, 257 All-pass, frequency response, 225 Amplitude, 216 Amplitude
A New Internal Model Control Method for MIMO Over-Actuated Systems
 Vol. 7, No., 26 A New Internal Model Control Method for MIMO Over-Actuated Systems Ahmed Dhahri University of Tuins El Manar, National Engineering School of Tunis, Laboratory of research in Automatic Control,
Vol. 7, No., 26 A New Internal Model Control Method for MIMO Over-Actuated Systems Ahmed Dhahri University of Tuins El Manar, National Engineering School of Tunis, Laboratory of research in Automatic Control,
CM 3310 Process Control, Spring Lecture 21
 CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
CM 331 Process Control, Spring 217 Instructor: Dr. om Co Lecture 21 (Back to Process Control opics ) General Control Configurations and Schemes. a) Basic Single-Input/Single-Output (SISO) Feedback Figure
Moshood Olanrewaju Advanced Filtering for Continuum and Noncontinuum States of Distillation Processes
 PhD projects in progress Fei Qi Bayesian Methods for Control Loop Diagnosis The main objective of this study is to establish a diagnosis system for control loop diagnosis, synthesizing observations of
PhD projects in progress Fei Qi Bayesian Methods for Control Loop Diagnosis The main objective of this study is to establish a diagnosis system for control loop diagnosis, synthesizing observations of
IDENTIFICATION FOR CONTROL
 IDENTIFICATION FOR CONTROL Raymond A. de Callafon, University of California San Diego, USA Paul M.J. Van den Hof, Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Keywords: Controller, Closed loop model,
IDENTIFICATION FOR CONTROL Raymond A. de Callafon, University of California San Diego, USA Paul M.J. Van den Hof, Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Keywords: Controller, Closed loop model,
Chapter 2 Review of Linear and Nonlinear Controller Designs
 Chapter 2 Review of Linear and Nonlinear Controller Designs This Chapter reviews several flight controller designs for unmanned rotorcraft. 1 Flight control systems have been proposed and tested on a wide
Chapter 2 Review of Linear and Nonlinear Controller Designs This Chapter reviews several flight controller designs for unmanned rotorcraft. 1 Flight control systems have been proposed and tested on a wide
Analysis and Synthesis of Single-Input Single-Output Control Systems
 Lino Guzzella Analysis and Synthesis of Single-Input Single-Output Control Systems l+kja» \Uja>)W2(ja»\ um Contents 1 Definitions and Problem Formulations 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Definitions 1 1.2.1 Systems
Lino Guzzella Analysis and Synthesis of Single-Input Single-Output Control Systems l+kja» \Uja>)W2(ja»\ um Contents 1 Definitions and Problem Formulations 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Definitions 1 1.2.1 Systems
Wannabe-MPC for Large Systems Based on Multiple Iterative PI Controllers
 Wannabe-MPC for Large Systems Based on Multiple Iterative PI Controllers Pasi Airikka, Mats Friman Metso Corp., Finland 17th Nordic Process Control Workshop Jan 26-27 2012 DTU Denmark Content Motivation
Wannabe-MPC for Large Systems Based on Multiple Iterative PI Controllers Pasi Airikka, Mats Friman Metso Corp., Finland 17th Nordic Process Control Workshop Jan 26-27 2012 DTU Denmark Content Motivation
Online monitoring of MPC disturbance models using closed-loop data
 Online monitoring of MPC disturbance models using closed-loop data Brian J. Odelson and James B. Rawlings Department of Chemical Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Online Optimization Based Identification
Online monitoring of MPC disturbance models using closed-loop data Brian J. Odelson and James B. Rawlings Department of Chemical Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Online Optimization Based Identification
Analyzing Control Problems and Improving Control Loop Performance
 OptiControls Inc. Houston, TX Ph: 713-459-6291 www.opticontrols.com info@opticontrols.com Analyzing Control s and Improving Control Loop Performance -by Jacques F. Smuts Page: 1 Presenter Principal Consultant
OptiControls Inc. Houston, TX Ph: 713-459-6291 www.opticontrols.com info@opticontrols.com Analyzing Control s and Improving Control Loop Performance -by Jacques F. Smuts Page: 1 Presenter Principal Consultant
Dynamic Modeling, Simulation and Control of MIMO Systems
 Dynamic Modeling, Simulation and Control of MIMO Systems M.Bharathi, C.Selvakumar HOD, Department of Electronics And Instrumentation, Bharath University Chennai 600073, India Prof & Head, St.Joseph s College
Dynamic Modeling, Simulation and Control of MIMO Systems M.Bharathi, C.Selvakumar HOD, Department of Electronics And Instrumentation, Bharath University Chennai 600073, India Prof & Head, St.Joseph s College
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6
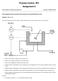 Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
Process Control, 3P4 Assignment 6 Kevin Dunn, kevin.dunn@mcmaster.ca Due date: 28 March 204 This assignment gives you practice with cascade control and feedforward control. Question [0 = 6 + 4] The outlet
PERIODIC signals are commonly experienced in industrial
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CONTROL SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 2, MARCH 2007 369 Repetitive Learning Control of Nonlinear Continuous-Time Systems Using Quasi-Sliding Mode Xiao-Dong Li, Tommy W. S. Chow,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CONTROL SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 2, MARCH 2007 369 Repetitive Learning Control of Nonlinear Continuous-Time Systems Using Quasi-Sliding Mode Xiao-Dong Li, Tommy W. S. Chow,
