An application of centre manifold theory to economics
|
|
|
- Wilfred Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An application of centre manifold theory to economics Oliver Penrose Department of Mathematics and the Maxwell Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh and Paul Hare, Department of Economics, Heriot-Watt University Conference in memory of Jack Carr, Edinburgh, May 21-22, 2018
2 Outline The Minsky moment Steve Keen s model What is a centre manifold? A centre manifold in Steve Keen s model
3 H. M. Queen Elizabeth II, visiting the London Scool of Economics, November 2008 Queen Elizabeth: Why had nobody noticed that the credit crunch was on its way? Prof. Tim Besley, FBA, London School of Economics; Bank of England Monetary Policy Committee, and Prof. Peter Hennessy, FBA, Queen Mary, University of London (27 July 2009, after about 6 months thought and consultation) : The failure to foresee the timing, extent and severity of the crisis... was principally a failure of the collective imagination of many bright people to understand the risks to the system as a whole.
4 Hyman Minsky s Financial Instability Hypothesis Firms that want to borrow money to pay for investment can manage the loan in 3 different ways: hedge financing: future profits will be enough to repay both the loan and the interest speculative financing: future profits will be enough to pay the interest but not the loan Ponzi financing: further borrowing is necessary even to pay the interest. So long as asset values (e.g. house prices) continue to increase, all is well, but eventually the growth of asset prices falters, lenders lose confidence and the edifice collapses. So long as firms are cautious and stick to hedge financing, the system seems to be stable, but as time progresses and competition intensifies, investors forget the distant past, gain confidence and work their way down the list. Eventually they get into the unstable Ponzi regime and another Minsky moment (i.e. a crash) ensues.
5 Steve Keen s model 1 Components of the model The Phillips curve Goodwin s model of investment The role of debt 1 Keen, S., A monetary Minsky model of the Great Moderation and the Great Recession J. Econ. Behav. Organ.(2011), doi: /j/jebo
6 The Phillips curve A. W. H. Phillips (1958) 2 found an empirical association, the so-called Phillips curve, between unemployment and the rate of change of wages and salaries. It is debatable whether the more recent data are consistent with a Phillips-type relationship over any long time interval, but Keen uses such a relationship in his model and for the purpose of this talk I will follow his example. 2 Phillips, A. W. H. The Relation Between Unemployment and the Rate of Change of Money Wage Rates in the United Kingdom, Economica, n.s., 25, no. 2 (1958):
7 A Phillips curve for the UK, Figure: 1. The abscissa is unemployment; the ordinate is the yearly rate of real wage growth. The blue polygon represents the observed data; the red dotted line is a linear approximation to those data. An interpretation of the negative slope is that a low value of u indicates a high demand for labour, tending to force its price, w, to increase. Whereas a high u indicates low demand for labour, so that its price is less likely to increase and may even decrease.
8 A mathematical statement of the Phillips asumption In general the Phillips assumption for real wage growth can be written where w := real wage t := time 1 dw w = Φ(u) (1) u := unemployment fraction, i.e. the fraction of labour force who are available for work but have none Φ is a (decreasing) empirical function. The dotted red line in the preceding frame represents the empirical formula Φ(u) := (u 0.05) (2)
9 The predator-prey equation system Denote the number of foxes by F, the number of rabbits by R. Then the model says df = increasing function of R, e.g. const. +R dr = decreasing function of F, e.g. const. - F The model predicts that the two population sizes will oscillate, e.g. F = const. + sin t, R = const. + cos t Figure: 2 Schematic phase diagram of a predator-prey system. The abscissa is number of foxes, the ordinate is number of rabbits
10 Goodwin s predator-prey model dw du = decreasing function of u = increasing function of w The first equation is a rewriting of the Phillips curve equation. The second equation embodies an assumption that when wages are high, the amount of unemployment tends to increase with time; but if wages are low, the amount of unemployment tends to decrease with time. The rationale for this second equation is explained in the next frame. Notation: u = unemployment w = level of real wages and salaries
11 Goodwin s proposed mechanism relating w and du/ Assumptions: no government, no foreign trade, AND All business profits are re-invested I = Π = Y wl (3) where I = total investment, Π = total business profits, Y = total production (GDP), L = number of employed workers. Investment is used to increase K, the existing stock of capital dk/ = I γk (4) where γ is the (constant) rate of depreciation Output is proportional to capital stock and to employment level Y = K/ = al (5) where is the (constant) capital-output ratio and a is labour productivity ( e αt with α constant). Available labour force grows as e βt L (1 u)e βt (6)
12 Goodwin s model, continued The equations from the previous slide are whence 1 du 1 u I = Π = Y wl (7) dk/ = I γk (8) Y = K/ = al Le αt (9) L (1 u)e βt (10) = β 1 dl L = α + β 1 K by (10) dk by (9) = α + β + γ I by (8) K = α + β + γ Y K + wl by (7) K = α + β + γ 1 + w a by (9) (11)
13 Goodwin s model : a predator-prey type system From the previous slide, the equation giving du/ in terms of w is 1 du 1 u = w a + α + β + γ 1 (12) while the Phillips eqn (1/w)dw/ = Φ(u) is (since a e αt ) equivalent to a d ( w ) = Φ(u) α (13) w a Since Φ( ) is a decreasing function, eqns (12) and (13) constitute a predator-prey type system in the two variables u and w/a. The variable w/a, which is equal to wl/y, can be interpreted as the share of GDP that is paid out in wages and salaries. This system of equations has a fixed point u 0, w 0 where Φ(u 0 ) = α, w 0 /a = 1 (α + β + γ) (14) Solutions that start near this fixed point oscillate around it with time period 2π / Φ (u 0 ) S. Keen takes = 3 years, α = 0.02/yr, β = γ = 0.01/yr whence (with Φ (u) = 0.08), u , w 0 /a 0.88, period 38 yr.
14 Steve Keen s model, which allows for debt The assumption I = Π of the Goodwin model is replaced by I /Y = Ψ(Π/Y ) (15) where Ψ( ) is an empirical function. Since I is no longer equal to the profit the shortfall is made up by borrowing: I = Π + dd (16) where D is the total amount that has already been borrowed by businesses (apparently from banks). The interest on this debt is deducted from the original formula for profit, which is amended to Π = Y wl rd (17) where r is the rate of interest charged on the loan D.
15 dd = I Π (18) I = Y Ψ(Π/Y ) (19) Π = Y wl rd (20) dk/ = I γk (21) Y = K/ = al Le αt (22) L (1 u)e βt (23) whence, using the notation z := D/Y, π := Π/Y = 1 w/a rz 1 du 1 u dz = d = α + β + γ I K as in Goodwin model = α + β + γ 1 Ψ(π) by (19) (24) ( ) I γk ( ) D Y = I Π Y D Y ( = 1 z K ) Ψ(π) π + γz (25)
16 Summary of Keen s model where 1 du 1 u 1 dw w dz = α + β + γ 1 Ψ(π) (26) = Φ(u) α (27) = ( 1 z ) Ψ(π) π + γz (28) π = 1 w a rz (29) This equation system has a fixed point (u 0, w 0, z 0 ) where Φ(u 0 ) = α (30) w 0 /a = 1 π 0 rz 0 (31) z 0 = Ψ(π 0) π 0 Ψ(π 0 ) γ (32) π 0 = (α + β + γ) (33)
17 Behaviour near the fixed point, for small r To study this model near its fixed point for small values of the interest rate r, we treat r as a new dependent variable, satisfying the equation dr/ = 0. The new system, when linearized, is 1 du 1 u 0 1 dw w 0 dr dz = α + β + γ 1 Ψ(π) = 1 Ψ (π 0 )(π π 0 ) +... (34) = Φ(u) α = Φ (u 0 )(u u 0 ) +... (35) = 0 (36) ( = 1 z ) Ψ(π) π + γz +... (37) ( = γ Ψ(π ) ( 0) (z z 0 ) + 1 z ) 0 Ψ (π 0 )(π π 0 ) +... where (since π = 1 w/a rz and r is small, i.e. r 0 = 0) π π 0 = w w 0 a rz (38)
18 Matrix form of the linearized equations Using the abbreviations Ψ 0 := Ψ(u 0 ), Ψ 0 := Ψ (u 0 ), Φ 0 := Φ(u 0 ), the linearized equation system can be written du (1 u 0 0 )Ψ 0 (1 u 0 )z 0 Ψ 0 a 0 dw dr w 0 Φ dz 0 (1 z 0/)Ψ 0 a (1 z 0 )z 0 Ψ 0 γ Ψ 0 [ ] [ ] A 0 x x0 = C b z z 0 in which A := 0 (1 u 0 ) Ψ 0 Ψ a (1 u 0 )z 0 0 w 0 Φ (39) (40) C := [ 0 ( 1 z 0 ) Ψ 0 a ( 1 z 0 ) z0 Ψ 0 ] (41) b := γ Ψ 0 / (42) x := [u w r] T (43) u u 0 w w 0 r z z 0
19 Is there a centre manifold? To simplify the equations a little, let 1 3 denote the unit 3 3 matrix and define y := z + C(b1 3 A) 1 x (44) Then it follows from the previous equations that dy/ = b(y y 0 ) (45) so that (remembering x := [u w r]) [ d x y ] = [ A 0 0 b ] [ x x0 y y 0 ] +... (46) If all the eigenvalues of A have zero real parts and b has negative real part, the system has a centre manifold 3 3 J. Carr, Applications of centre manifold theory Springer 1981.
20 Applicability of centre manifold theory The equations are d [ x y ] = [ A 0 0 b ] [ x y ] +... (47) with A := 0 (1 u 0 ) Ψ 0 Ψ a (1 u 0 )z 0 0 w 0 Φ b := γ Ψ 0 / = γ Ψ(π 0) (48) (49) Characteristic polynomial of A is λ(λ 2 (1 u 0 ) Ψ 0 a w 0Φ 0 ). Eigenvalues are zero and (since Φ 0 < 0) two purely imaginary numbers. The sign of b is the same as that of γ Ψ(π 0 ); it seems likely to be negative so long as businesses invest more than around 10% of their profits. So the conditions for a centre manifold are satisfied.
21 Figure: 3 A trajectory of Keen s model in (u, w, z) space, using γ = 0.03, Ψ(π) = 1.2π, u(0) = 0.03, w(0) = 0.85, r = 0.01, z(0) = 2
22 What centre manifold theory tells us In the linear approximation, y decays exponentially to its fixed-point value y 0, r stays constant, while the other two variables move on an elliptical orbit. Centre manifold theory enables us to generalize these statements to the non-linear case. By a centre manifold we mean a smooth invariant set in the four-dimensional state space, which at the fixed point is tangential to the linear space containing the elliptical orbits. Theorem: There exists a 3-dimensional centre manifold containing the fixed point (u 0, w 0, 0, y 0 ). The flow on the centre manifold obeys a system of 3 differential equations. Theorem: An orbit starting sufficiently close to the centre manifold will approach an orbit that lies in the centre manifold, exponentially fast In economic terms, these results tell us that the Keen model discussed here has a family of stable oscillatory solutions. To describe the unstable economic behaviour of the real world, one must either look outside this stable family, or use a different model (as Keen himself proposes later on in the paper I have cited.)
fragility M. R. Grasselli Quantitative Finance Seminar Series - Fields Institute, October 26, 2011
 Keen Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima Quantitative Finance Seminar Series - Fields Institute, October 26, 2011 Outline
Keen Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima Quantitative Finance Seminar Series - Fields Institute, October 26, 2011 Outline
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1
 Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
M. R. Grasselli. 9th World Congress of The Bachelier Finance Society New York City, July 18, 2016
 Keen Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University and The Fields Institute Joint with B. Costa Lima (Morgan Stanley) and A. Nguyen Huu (CREST) 9th World Congress of The Bachelier Finance Society New
Keen Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University and The Fields Institute Joint with B. Costa Lima (Morgan Stanley) and A. Nguyen Huu (CREST) 9th World Congress of The Bachelier Finance Society New
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
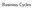 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
investment M. R. Grasselli EPOG Seminar Paris Nord, November 18, 2016
 Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint A. Nguyen Huu (Montpellier) EPOG Seminar Paris Nord, November 18, 2016 Cycles Small fraction of output (about 1% in the U.S.) but major fraction of
Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint A. Nguyen Huu (Montpellier) EPOG Seminar Paris Nord, November 18, 2016 Cycles Small fraction of output (about 1% in the U.S.) but major fraction of
Test Goodwin s Model Parameters Estimation and References
 Test Goodwin s Model Parameters Estimation and References Hao Yin, Yihui Tian August 23, 203 Introduction Goodwin s Model(967, 972) was simply a dynamical model of employment and workers shares of output.
Test Goodwin s Model Parameters Estimation and References Hao Yin, Yihui Tian August 23, 203 Introduction Goodwin s Model(967, 972) was simply a dynamical model of employment and workers shares of output.
macroeconomics M. R. Grasselli Research in Options, December 10, 2012
 of of Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima, X.-S. Wang, J. Wu Research in Options, December, 22 What is wrong with this
of of Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima, X.-S. Wang, J. Wu Research in Options, December, 22 What is wrong with this
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory
 ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
macroeconomics M. R. Grasselli University of Technology Sydney, February 21, 2013
 of of Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima, X.-S. Wang, J. Wu University of Technology Sydney, February 2, 23 What is wrong
of of Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima, X.-S. Wang, J. Wu University of Technology Sydney, February 2, 23 What is wrong
Inflation and Speculation in a Dynamic Macroeconomic Model
 J. Risk Financial Manag. 2015, 8, 285-310; doi:10.3390/jrfm8030285 OPEN ACCESS Journal of Risk and Financial Management ISSN 1911-8074 www.mdpi.com/journal/jrfm Article Inflation and Speculation in a Dynamic
J. Risk Financial Manag. 2015, 8, 285-310; doi:10.3390/jrfm8030285 OPEN ACCESS Journal of Risk and Financial Management ISSN 1911-8074 www.mdpi.com/journal/jrfm Article Inflation and Speculation in a Dynamic
Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies
 Journal of Regional Development Studies2010 131 Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies Ken-ichi ISHIYAMA 1. Introduction We have observed large increases in trade and
Journal of Regional Development Studies2010 131 Relationships between phases of business cycles in two large open economies Ken-ichi ISHIYAMA 1. Introduction We have observed large increases in trade and
M. R. Grasselli. Research Seminar, Political Economy Group Groningen, January 29, 2015
 Keen Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University and The Fields Institute Joint with B. Costa Lima (Morgan Stanley) and A. Nguyen Huu (CERMICS) Research Seminar, Political Economy Group Groningen,
Keen Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University and The Fields Institute Joint with B. Costa Lima (Morgan Stanley) and A. Nguyen Huu (CERMICS) Research Seminar, Political Economy Group Groningen,
macroeconomics M. R. Grasselli UMass - Amherst, April 29, 2013
 of of Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima, X.-S. Wang, J. Wu UMass - Amherst, April 29, 23 What is wrong with this picture?
of of Sharcnet Chair in Financial Mathematics Mathematics and Statistics - McMaster University Joint work with B. Costa Lima, X.-S. Wang, J. Wu UMass - Amherst, April 29, 23 What is wrong with this picture?
Information Bulletin 12/2008
 Information Bulletin 12/2008 Warsaw, May 2009 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at February 12, 2009. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 12/2008 Warsaw, May 2009 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at February 12, 2009. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
The Foley Liquidity / Profit-Rate Cycle Model Reconsidered
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The Foley Liquidity / Profit-Rate Cycle Model Reconsidered Helmar Nunes Moreira and Ricardo Azevedo Araujo and Peter Flaschel Department of Mathematics, University of
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The Foley Liquidity / Profit-Rate Cycle Model Reconsidered Helmar Nunes Moreira and Ricardo Azevedo Araujo and Peter Flaschel Department of Mathematics, University of
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations. Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno
 Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
Economic Growth (Continued) The Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans Model. 1 Literature. Ramsey (1928) Cass (1965) and Koopmans (1965) 2 Households (Preferences)
 III C Economic Growth (Continued) The Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans Model 1 Literature Ramsey (1928) Cass (1965) and Koopmans (1965) 2 Households (Preferences) Population growth: L(0) = 1, L(t) = e nt (n > 0 is
III C Economic Growth (Continued) The Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans Model 1 Literature Ramsey (1928) Cass (1965) and Koopmans (1965) 2 Households (Preferences) Population growth: L(0) = 1, L(t) = e nt (n > 0 is
Business Failure and Labour Market Fluctuations
 Business Failure and Labour Market Fluctuations Seong-Hoon Kim* Seongman Moon** *Centre for Dynamic Macroeconomic Analysis, St Andrews, UK **Korea Institute for International Economic Policy, Seoul, Korea
Business Failure and Labour Market Fluctuations Seong-Hoon Kim* Seongman Moon** *Centre for Dynamic Macroeconomic Analysis, St Andrews, UK **Korea Institute for International Economic Policy, Seoul, Korea
Permanent Income Hypothesis Intro to the Ramsey Model
 Consumption and Savings Permanent Income Hypothesis Intro to the Ramsey Model Lecture 10 Topics in Macroeconomics November 6, 2007 Lecture 10 1/18 Topics in Macroeconomics Consumption and Savings Outline
Consumption and Savings Permanent Income Hypothesis Intro to the Ramsey Model Lecture 10 Topics in Macroeconomics November 6, 2007 Lecture 10 1/18 Topics in Macroeconomics Consumption and Savings Outline
Final Exam. You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind.
 Professor Christiano Economics 311, Winter 2005 Final Exam IMPORTANT: read the following notes You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind. A total of 100 points is possible, with the distribution
Professor Christiano Economics 311, Winter 2005 Final Exam IMPORTANT: read the following notes You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind. A total of 100 points is possible, with the distribution
Chapter 2: Economic Theories, Data, and Graphs
 Microeconomics Canadian 15th Edition Ragan SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microeconomics-canadian-15th-editionragan-solutions-manual-2/ Microeconomics Canadian
Microeconomics Canadian 15th Edition Ragan SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microeconomics-canadian-15th-editionragan-solutions-manual-2/ Microeconomics Canadian
Lecture Notes. Applied Mathematics for Business, Economics, and the Social Sciences (4th Edition); by Frank S. Budnick
 1 Lecture Notes Applied Mathematics for Business, Economics, and the Social Sciences (4th Edition); by Frank S. Budnick 2 Chapter 2: Linear Equations Definition: Linear equations are first degree equations.
1 Lecture Notes Applied Mathematics for Business, Economics, and the Social Sciences (4th Edition); by Frank S. Budnick 2 Chapter 2: Linear Equations Definition: Linear equations are first degree equations.
Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade
 Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 147-158 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade Michiya Nozaki Gifu Keizai
Journal of Mathematics and System Science 6 (2016) 147-158 doi: 10.17265/2159-5291/2016.04.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Dynamic IS-LM model with Philips Curve and International Trade Michiya Nozaki Gifu Keizai
Persistence theory applied to Keen s model a link between mathematical biology and mathematical economics
 Persistence theory applied to Keen s model a link between mathematical biology and mathematical economics Jianhong Wu and Xiang-Sheng Wang Mprime Centre for Disease Modelling York University, Toronto Persistence
Persistence theory applied to Keen s model a link between mathematical biology and mathematical economics Jianhong Wu and Xiang-Sheng Wang Mprime Centre for Disease Modelling York University, Toronto Persistence
Information Bulletin 5/2007
 Information Bulletin /2007 Warsaw, September 2007 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at July 13, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin /2007 Warsaw, September 2007 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at July 13, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory
 2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
Information Bulletin 6/2008
 Information Bulletin 6/2008 Warsaw, October 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at August 12, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 6/2008 Warsaw, October 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at August 12, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Introduction to Macroeconomics
 Introduction to Macroeconomics Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 39 Macroeconomics is Dynamic Decisions are taken over
Introduction to Macroeconomics Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) Introduction Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 39 Macroeconomics is Dynamic Decisions are taken over
Information Bulletin 7/2007
 Information Bulletin 7/2007 Warsaw, December 2007 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at September 12, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP
Information Bulletin 7/2007 Warsaw, December 2007 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at September 12, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP
Supplementary Information: Quantifying Trading Behavior in Financial Markets Using Google Trends
 TITLE Supplementary Information: Quantifying Trading Behavior in Financial Markets Using Google Trends AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS Tobias Preis 1#*, Helen Susannah Moat 2,3#, and H. Eugene Stanley 2# 1 Warwick
TITLE Supplementary Information: Quantifying Trading Behavior in Financial Markets Using Google Trends AUTHORS AND AFFILIATIONS Tobias Preis 1#*, Helen Susannah Moat 2,3#, and H. Eugene Stanley 2# 1 Warwick
Information Bulletin 4/2008
 Information Bulletin 4/2008 Warsaw, August 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at June 17, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 4/2008 Warsaw, August 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at June 17, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 11/2011
 Information Bulletin 11/2011 Warsaw, 2012 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at January 13, 2012. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 11/2011 Warsaw, 2012 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at January 13, 2012. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Advanced Macroeconomics
 Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model
 MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 38 Beyond IS-LM We have reviewed the
MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 38 Beyond IS-LM We have reviewed the
Information Bulletin 8/2009
 Information Bulletin 8/2009 Warsaw, 2010 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at October 13, 2009. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 8/2009 Warsaw, 2010 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at October 13, 2009. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Simplifying Radical Expressions
 Simplifying Radical Expressions Product Property of Radicals For any real numbers a and b, and any integer n, n>1, 1. If n is even, then When a and b are both nonnegative. n ab n a n b 2. If n is odd,
Simplifying Radical Expressions Product Property of Radicals For any real numbers a and b, and any integer n, n>1, 1. If n is even, then When a and b are both nonnegative. n ab n a n b 2. If n is odd,
Aggregate Supply. A Nonvertical AS Curve. implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup
 A Nonvertical AS Curve nominal wage rigidity nominal price rigidity labor and goods markets implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup Case 1: Sticky W, Flexible
A Nonvertical AS Curve nominal wage rigidity nominal price rigidity labor and goods markets implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup Case 1: Sticky W, Flexible
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8
 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Information Bulletin 5/2010
 Information Bulletin /2010 Warsaw, 2010 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at July 13, 2010. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop Published
Information Bulletin /2010 Warsaw, 2010 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at July 13, 2010. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop Published
Information Bulletin 4/2007
 Information Bulletin 4/2007 Warsaw, September 2007 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at May 18, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 4/2007 Warsaw, September 2007 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at May 18, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
8 Ecosystem stability
 8 Ecosystem stability References: May [47], Strogatz [48]. In these lectures we consider models of populations, with an emphasis on the conditions for stability and instability. 8.1 Dynamics of a single
8 Ecosystem stability References: May [47], Strogatz [48]. In these lectures we consider models of populations, with an emphasis on the conditions for stability and instability. 8.1 Dynamics of a single
The macrodynamics of household debt, growth, and inequality
 The macrodynamics of household debt, growth, and inequality Gaël Giraud Matheus Grasselli April 8, 2017 Abstract How do inequality and growth evolve in the long run and why? We address this question by
The macrodynamics of household debt, growth, and inequality Gaël Giraud Matheus Grasselli April 8, 2017 Abstract How do inequality and growth evolve in the long run and why? We address this question by
Economics 232c Spring 2003 International Macroeconomics. Problem Set 3. May 15, 2003
 Economics 232c Spring 2003 International Macroeconomics Problem Set 3 May 15, 2003 Due: Thu, June 5, 2003 Instructor: Marc-Andreas Muendler E-mail: muendler@ucsd.edu 1 Trending Fundamentals in a Target
Economics 232c Spring 2003 International Macroeconomics Problem Set 3 May 15, 2003 Due: Thu, June 5, 2003 Instructor: Marc-Andreas Muendler E-mail: muendler@ucsd.edu 1 Trending Fundamentals in a Target
M. R. Grasselli. QMF, Sydney, December 16, Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint with Gaël Giraud (AFD, CNRS, ENPC)
 Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint with Gaël Giraud (AFD, CNRS, ENPC) QMF, Sydney, December 16, 2016 The book Opening salvo To put it bluntly, the discipline of economics has yet to
Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint with Gaël Giraud (AFD, CNRS, ENPC) QMF, Sydney, December 16, 2016 The book Opening salvo To put it bluntly, the discipline of economics has yet to
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam?
 The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
BEE1024 Mathematics for Economists
 BEE1024 Mathematics for Economists Dieter and Jack Rogers and Juliette Stephenson Department of Economics, University of Exeter February 1st 2007 1 Objective 2 Isoquants 3 Objective. The lecture should
BEE1024 Mathematics for Economists Dieter and Jack Rogers and Juliette Stephenson Department of Economics, University of Exeter February 1st 2007 1 Objective 2 Isoquants 3 Objective. The lecture should
Information Bulletin 9/2007
 Information Bulletin 9/2007 Warsaw, January 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at November 13, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP
Information Bulletin 9/2007 Warsaw, January 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at November 13, 2007. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP
Lecture 7. The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium. ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter Kam Yu Department of Economics Lakehead University
 Lecture 7 The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 2013 Phillips Department of Economics Lakehead University 7.1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Phillips Phillips 7.2 Market Equilibrium:
Lecture 7 The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 2013 Phillips Department of Economics Lakehead University 7.1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Phillips Phillips 7.2 Market Equilibrium:
Quantitative Evidence of Goodwin s. Non-linear Growth Cycles
 Applied athematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 29, 1409-1417 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Quantitative Evidence of Goodwin s Non-linear Growth Cycles Ibrahim assy CAD Research Bogota 1101, Colombia imassy@uniandes.edu.co
Applied athematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 29, 1409-1417 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Quantitative Evidence of Goodwin s Non-linear Growth Cycles Ibrahim assy CAD Research Bogota 1101, Colombia imassy@uniandes.edu.co
Information Bulletin 1/2008
 Information Bulletin 1/2008 Warsaw, May 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at March 13, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 1/2008 Warsaw, May 2008 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at March 13, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Employment and Income Distribution from a Classical-Keynesian point of view. Some tools to ground a normative analysis
 Employment and Income Distribution from a Classical-Keynesian point of view Some tools to ground a normative analysis Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Milano e-mail: enricobellino@unicattit Tho Global
Employment and Income Distribution from a Classical-Keynesian point of view Some tools to ground a normative analysis Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Milano e-mail: enricobellino@unicattit Tho Global
Information Bulletin 9/2011
 Information Bulletin 9/2011 Warsaw, 2011 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at November 1, 2011. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 9/2011 Warsaw, 2011 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at November 1, 2011. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I
 14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model
 Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
A suggested solution to the problem set at the re-exam in Advanced Macroeconomics. February 15, 2016
 Christian Groth A suggested solution to the problem set at the re-exam in Advanced Macroeconomics February 15, 216 (3-hours closed book exam) 1 As formulated in the course description, a score of 12 is
Christian Groth A suggested solution to the problem set at the re-exam in Advanced Macroeconomics February 15, 216 (3-hours closed book exam) 1 As formulated in the course description, a score of 12 is
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999)
 Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Information Bulletin 2/2011
 Information Bulletin 2/2011 Warsaw, 2011 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at April 13, 2011. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop Published
Information Bulletin 2/2011 Warsaw, 2011 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at April 13, 2011. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop Published
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case.
 Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV
 Keynes and the Classics Notes on the Monetary Theory of Production Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV Social production, value and distribution (436-445) The starting point is a Leontief price system:
Keynes and the Classics Notes on the Monetary Theory of Production Formelsammlung zu Wirtschaftstheorie IV Social production, value and distribution (436-445) The starting point is a Leontief price system:
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 Solutions
 Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth
 Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) D(S)GE and Growth Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 43 Macroeconomics is Dynamic
Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium and Growth Martin Ellison Nuffi eld College Michaelmas Term 2018 Martin Ellison (Nuffi eld) D(S)GE and Growth Michaelmas Term 2018 1 / 43 Macroeconomics is Dynamic
Information Bulletin 11/2010
 Information Bulletin 11/2010 Warsaw, 2011 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at January 13, 2011. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
Information Bulletin 11/2010 Warsaw, 2011 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at January 13, 2011. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP Printshop
A Growth Cycle. R. M. Goodwin. July 30, Presented at the First World Congress of the Econometric Society, held in Rome, 1965.
 A Growth Cycle R. M. Goodwin July 30, 2014 Presented at the First World Congress of the Econometric Society, held in Rome, 1965. The Model Presented here is a starkly schematized and hence quite unrealistic
A Growth Cycle R. M. Goodwin July 30, 2014 Presented at the First World Congress of the Econometric Society, held in Rome, 1965. The Model Presented here is a starkly schematized and hence quite unrealistic
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I. Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form:
 Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
The Real Business Cycle Model
 The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
Number of People Contacted
 Section 7.2 Problem Solving Using Exponential Functions (Exponential Growth and Decay) Key Words: exponential, growth, decay, critical mass Key Concepts: exponential growth, exponential decay, simple interest,
Section 7.2 Problem Solving Using Exponential Functions (Exponential Growth and Decay) Key Words: exponential, growth, decay, critical mass Key Concepts: exponential growth, exponential decay, simple interest,
Discussion of Contagious Malady? Global Dimensions of Secular Stagnation
 Discussion of Contagious Malady? Global Dimensions of Secular Stagnation Jaume Ventura CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE 18 June, 2015 Jaume Ventura (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Florence workshop 18 June, 2015
Discussion of Contagious Malady? Global Dimensions of Secular Stagnation Jaume Ventura CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE 18 June, 2015 Jaume Ventura (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Florence workshop 18 June, 2015
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions
 Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis
 Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis Yulei Luo Econ, HKU November 13, 2017 Luo, Y. (Econ, HKU) ECON2220CB: Intermediate Macro November 13, 2017 1 / 14 The
Appendix to Chapter 9: The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macro Analysis Yulei Luo Econ, HKU November 13, 2017 Luo, Y. (Econ, HKU) ECON2220CB: Intermediate Macro November 13, 2017 1 / 14 The
Economic Motion: An Economic Application of the Lotka-Volterra Predator-Prey Model. Viktor Vadasz
 Economic Motion: An Economic Application of the Lotka-Volterra Predator-Prey Model Viktor Vadasz Table of Contents. Introduction 3. Goodwin s Model 4. The Foundations of the Model 4. The Original Model
Economic Motion: An Economic Application of the Lotka-Volterra Predator-Prey Model Viktor Vadasz Table of Contents. Introduction 3. Goodwin s Model 4. The Foundations of the Model 4. The Original Model
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: Solving Models with Rational Expectations
 MA Advanced Macroeconomics: Solving Models with Rational Expectations Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 6, 2009 Karl Whelan (UCD) Models with Rational Expectations February 6, 2009 1 / 32 Moving
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: Solving Models with Rational Expectations Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 6, 2009 Karl Whelan (UCD) Models with Rational Expectations February 6, 2009 1 / 32 Moving
Employment-Centred Stabilisation Policy Propelling the Economy to Escape Velocity
 Employment-Centred Stabilisation Policy Propelling the Economy to Escape Velocity Alexander V. RYZHENKOV Economic Faculty Novosibirsk State University 2 Pirogov street Novosibirsk 630090 Russia Institute
Employment-Centred Stabilisation Policy Propelling the Economy to Escape Velocity Alexander V. RYZHENKOV Economic Faculty Novosibirsk State University 2 Pirogov street Novosibirsk 630090 Russia Institute
Solution by the Maximum Principle
 292 11. Economic Applications per capita variables so that it is formally similar to the previous model. The introduction of the per capita variables makes it possible to treat the infinite horizon version
292 11. Economic Applications per capita variables so that it is formally similar to the previous model. The introduction of the per capita variables makes it possible to treat the infinite horizon version
Solow Growth Model. Michael Bar. February 28, Introduction Some facts about modern growth Questions... 4
 Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
Discussion of Robert Hall s Paper The High Sensitivity of Economic Activity to Financial Frictions
 Discussion of Robert Hall s Paper The High Sensitivity of Economic Activity to Financial Frictions Matteo Iacoviello Federal Reserve Board March 26, 21 This is a Timely Paper and I am Sympathetic to its
Discussion of Robert Hall s Paper The High Sensitivity of Economic Activity to Financial Frictions Matteo Iacoviello Federal Reserve Board March 26, 21 This is a Timely Paper and I am Sympathetic to its
MA Macroeconomics 4. Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model
 MA Macroeconomics 4. Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 28 Part I Inflation Expectations Karl Whelan
MA Macroeconomics 4. Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 28 Part I Inflation Expectations Karl Whelan
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4
 Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Chaotic Price Dynamics, Increasing Returns & the Phillips Curve. by Graciela Chichilnisky, Columbia University Geoffrey Heal, Columbia Business School
 Chaotic Price Dynamics, Increasing Returns & the Phillips Curve by Graciela Chichilnisky, Columbia University Geoffrey Heal, Columbia Business School Yun Lin, Columbia University March 1992, Revised February
Chaotic Price Dynamics, Increasing Returns & the Phillips Curve by Graciela Chichilnisky, Columbia University Geoffrey Heal, Columbia Business School Yun Lin, Columbia University March 1992, Revised February
Problem Set 2: Sketch of Answers
 Problem Set 2: Sketch of Answers HEC Lausanne, Département d économie politique Business Cycles 2003 Prof. Aude Pommeret Ivan Jaccard April 30, 2004 Part I: Open questions 1. Explain why the consensus
Problem Set 2: Sketch of Answers HEC Lausanne, Département d économie politique Business Cycles 2003 Prof. Aude Pommeret Ivan Jaccard April 30, 2004 Part I: Open questions 1. Explain why the consensus
APPENDIX Should the Private Sector Provide Public Capital?
 APPENIX Should the Private Sector Provide Public Capital? Santanu Chatterjee epartment of Economics Terry College of Business University of eorgia Appendix A The appendix describes the optimization problem
APPENIX Should the Private Sector Provide Public Capital? Santanu Chatterjee epartment of Economics Terry College of Business University of eorgia Appendix A The appendix describes the optimization problem
Lecture 3, November 30: The Basic New Keynesian Model (Galí, Chapter 3)
 MakØk3, Fall 2 (blok 2) Business cycles and monetary stabilization policies Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen Lecture 3, November 3: The Basic New Keynesian Model (Galí, Chapter
MakØk3, Fall 2 (blok 2) Business cycles and monetary stabilization policies Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen Lecture 3, November 3: The Basic New Keynesian Model (Galí, Chapter
Warwick Business School Forecasting System. Summary. Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 2014
 Warwick Business School Forecasting System Summary Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 21 The main objective of the Warwick Business School Forecasting System is to provide competitive
Warwick Business School Forecasting System Summary Ana Galvao, Anthony Garratt and James Mitchell November, 21 The main objective of the Warwick Business School Forecasting System is to provide competitive
EC744 Lecture Notes: Economic Dynamics. Prof. Jianjun Miao
 EC744 Lecture Notes: Economic Dynamics Prof. Jianjun Miao 1 Deterministic Dynamic System State vector x t 2 R n State transition function x t = g x 0 ; t; ; x 0 = x 0 ; parameter 2 R p A parametrized dynamic
EC744 Lecture Notes: Economic Dynamics Prof. Jianjun Miao 1 Deterministic Dynamic System State vector x t 2 R n State transition function x t = g x 0 ; t; ; x 0 = x 0 ; parameter 2 R p A parametrized dynamic
Mathematics for Economics ECON MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018. Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics
 Mathematics for Economics ECON 53035 MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018 Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS LERNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this course unit
Mathematics for Economics ECON 53035 MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018 Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS LERNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this course unit
Supplementary Notes on Chapter 6 of D. Romer s Advanced Macroeconomics Textbook (4th Edition)
 Supplementary Notes on Chapter 6 of D. Romer s Advanced Macroeconomics Textbook (4th Edition) Changsheng Xu & Ming Yi School of Economics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology This version: June
Supplementary Notes on Chapter 6 of D. Romer s Advanced Macroeconomics Textbook (4th Edition) Changsheng Xu & Ming Yi School of Economics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology This version: June
Capital, Institutions and Urban Growth Systems
 Capital, Institutions and Urban Growth Systems Robert Huggins Centre for Economic Geography, School of Planning and Geography, Cardiff University Divergent Cities Conference, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
Capital, Institutions and Urban Growth Systems Robert Huggins Centre for Economic Geography, School of Planning and Geography, Cardiff University Divergent Cities Conference, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
"0". Doing the stuff on SVARs from the February 28 slides
 Monetary Policy, 7/3 2018 Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen "0". Doing the stuff on SVARs from the February 28 slides 1. Money in the utility function (start) a. The basic
Monetary Policy, 7/3 2018 Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen "0". Doing the stuff on SVARs from the February 28 slides 1. Money in the utility function (start) a. The basic
Information Bulletin 10/2008
 Information Bulletin 10/2008 Warsaw, February 2009 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at December 12, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP
Information Bulletin 10/2008 Warsaw, February 2009 Compiled from NBP materials by the Department of Statistics as at December 12, 2008. Design: Oliwka s.c. Cover photo: Corbis/Free Layout and print: NBP
IA_Core Curriculum Social Studies (2010) High School
 IA_Core Curriculum Social Studies (2010) High School Content Area 1 Behavioral sciences include, but are not limited to, the areas of sociology, anthropology and psychology. In addressing these disciplines
IA_Core Curriculum Social Studies (2010) High School Content Area 1 Behavioral sciences include, but are not limited to, the areas of sociology, anthropology and psychology. In addressing these disciplines
Unstable periodic orbits of a chaotic growth cycle model. Yoshitaka Saiki
 Unstable periodic orbits of a chaotic growth cycle model Yoshitaka Saiki Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Tokyo (with Ken-ichi Ishiyama) March 28, 26 Business cycle theory [2] Important
Unstable periodic orbits of a chaotic growth cycle model Yoshitaka Saiki Department of Mathematical Sciences University of Tokyo (with Ken-ichi Ishiyama) March 28, 26 Business cycle theory [2] Important
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Equating output per worker to GDP per capita, the growth rate of GDP per capita
 3 Homework 3 1. We have seen in class Kaldor s stylized facts of growth in developed countries. The Cobb-Douglas production function is used to replicate fact a. In this exercise, you are asked to show
3 Homework 3 1. We have seen in class Kaldor s stylized facts of growth in developed countries. The Cobb-Douglas production function is used to replicate fact a. In this exercise, you are asked to show
Scaling invariant distributions of firms exit in OECD countries
 Scaling invariant distributions of firms exit in OECD countries Corrado Di Guilmi a Mauro Gallegati a Paul Ormerod b a Department of Economics, University of Ancona, Piaz.le Martelli 8, I-62100 Ancona,
Scaling invariant distributions of firms exit in OECD countries Corrado Di Guilmi a Mauro Gallegati a Paul Ormerod b a Department of Economics, University of Ancona, Piaz.le Martelli 8, I-62100 Ancona,
T h o m a s B r e d g a a r d, P r o f e s s o r, P h. d.
 Danish flexicurity and the crisis T h o m a s B r e d g a a r d, P r o f e s s o r, P h. d. Centre for Labour Market Research at Aalborg University (CARMA), Denmark What is flexicurity? C o n t r a c t
Danish flexicurity and the crisis T h o m a s B r e d g a a r d, P r o f e s s o r, P h. d. Centre for Labour Market Research at Aalborg University (CARMA), Denmark What is flexicurity? C o n t r a c t
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium
 Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
Economics - Canadian Edition, 15e (Ragan) Chapter 2 Economic Theories, Data, and Graphs. 2.1 Positive and Normative Statements
 Economics - Canadian Edition, 15e (Ragan) Chapter 2 Economic Theories, Data, and Graphs 2.1 Positive and Normative Statements 1) Disagreements over positive statements A) cannot arise because positive
Economics - Canadian Edition, 15e (Ragan) Chapter 2 Economic Theories, Data, and Graphs 2.1 Positive and Normative Statements 1) Disagreements over positive statements A) cannot arise because positive
Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination
 Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination January 2016 Department of Economics UNC Chapel Hill Instructions: This examination consists of 3 questions. Answer all questions. If you believe a question is ambiguously
Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination January 2016 Department of Economics UNC Chapel Hill Instructions: This examination consists of 3 questions. Answer all questions. If you believe a question is ambiguously
