MA Macroeconomics 4. Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model
|
|
|
- Eugene Stokes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MA Macroeconomics 4. Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
2 Part I Inflation Expectations Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
3 Changes in Inflation Expectations Last time we considered the simplest possible example: ɛ π t = ɛ y t = 0 and πt e = π This means no shocks and the public s expectation of inflation equals the central bank s inflation target, π = π 1. This generates an outcome where π t = π 1 and y t = y t. Now consider a case where inflation expectations shift to being higher than the central bank s target rate. In this case, π e t = π > π 1 = π : After the increase in inflation expectations: The PC curve shifts upwards. Output ends up being lower than its natural rate Inflation rises. It ends up taking a value between πt e and π. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
4 Expected Inflation Equals the Inflation Target Inflation IS-MP ( PC ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
5 Expected Inflation Exceeds the Inflation Target Inflation IS-MP ( PC ( PC ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
6 Can We Learn More? The outcome here shows that inflation ends up between the public s inflation expectations and the central bank s inflation target. What determines this outcome? What determines how far from away target inflation will move when the public s inflation expectations change? How much does it depend on the monetary policy rule? How much does it depend on other aspects of the model, like the impact of real interest rates on output and the impact of output on inflation? It would be tricky to get these answers from a graph. However, using the equations underlying the model, we can fully answer all these questions. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
7 Getting a Solution for the IS-MP-PC Model Let s repeat the equations describing our two curves. The PC curve is π t = πt e + γ (y t yt ) + ɛ π t And the IS-MP curve is y t = y t α (β π 1) (π t π ) + ɛ y t Taking all the other elements of the model as given, we can view this as two linear equations in the two variables π t and y t. These equations can be solved to give solutions that describe how these two variables depend on all the other elements of the model. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
8 The IS-MP-PC Model Solution for Inflation The PC curve is π t = π e t + γ (y t y t ) + ɛ π t And the IS-MP curve tells us that y t y t = α (β π 1) (π t π ) + ɛ y t Substituting this expression for the output gap into the Phillips curve and re-arranging we get ( ) ( ) 1 αγ π t = π e (βπ 1) t + π γɛ y t + ɛ π t αγ (β π 1) 1 + αγ (β π 1) 1 + αγ (β π 1) Letting We get θ = αγ (β π 1) π t = θπ e t + (1 θ) π + θ (γɛ y t + ɛ π t ) Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
9 Interpreting the Solution for Inflation What s the meaning of our solution? π t = θπ e t + (1 θ) π + θ (γɛ y t + ɛ π t ) If β π > 1 as we ve been assuming, then 0 < θ < 1. This means that inflation lies between the central bank s inflation target and the public s expectation of inflation. We can show that θ depends negatively on α, γ and β π. This means that the central bank s inflation target plays more role in determining inflation when 1 γ increases: This parameter determines how inflation changes when output changes. 2 α increases: This parameter determines how output changes when real interest rates change. 3 β π increases: This parameter determines how the central bank responds to inflation. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
10 The IS-MP-PC Model Solution for Output The IS-MP curve tells us that output depends on how far inflation is from the central bank s target y t y t = α (β π 1) (π t π ) + ɛ y t Re-arranging the solution for inflation, we get This gives which can be simplified to π t π = θ (π e t π + ɛ π t + γɛ y t ) y t = y t θα (β π 1) (π e t π + ɛ π t + γɛ y t ) + ɛ y t y t = y t θα (β π 1) (π e t π + ɛ π t ) + (1 θαγ (β π 1)) ɛ y t Output falls short of its natural rate if inflation expectations exceed the inflation target. And the amount of the shortfall depends positively on the three factors mentioned before: α, γ and β π. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
11 How Do Inflation Expectations Change? We have seen that after the public s inflation expectations rise, the result is a fall in output below its natural rate and in increase inflation, though this increase is smaller than had been expected by the public. What happens next? How does the public s expectation of inflation change at this point? Milton Friedman s 1968 paper suggested that people gradually adapt their expectations based on past outcomes for inflation. Consider now a simple model of this idea of adaptive expectations π e t = π t 1 Under this formulation of expectations, the Phillips curve becomes π t = π t 1 + γ (y t y t ) + ɛ π t In other words, there should be a positive relationship between the change in inflation and the output gap. Alternatively, there should be a negative relationship between the change in inflation and the rate of unemployment. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
12 The Failure of the Phillips Curve 11 US Inflation and Unemployment, Inflation is the Four-Quarter Percentage Change in GDP Deflator 10 9 Unemployment Inflation Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
13 Evidence for Adaptive Inflation Expectations 11 Changes in US Inflation and Unemployment, Change in Inflation is Four-Quarter Inflation Relative to a Year Earlier Unemployment Change in Inflation Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
14 Inflation Expectations Adjusting Back Downwards Inflation IS-MP ( PC ( PC ( ) PC ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
15 Inflation and Output Adjust Back to Starting Position Inflation IS-MP ( PC ( PC ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
16 Part II Temporary Demand Shocks Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
17 A Temporary Aggregate Demand Shock (ɛ y t > 0) IS-MP2 ( Inflation IS-MP1 ( PC2 ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
18 Inflation Expectations Adjust Upwards to π 2 IS-MP3 ( PC3 ( ) Inflation IS-MP1 ( PC1 ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
19 Inflation Expectations Adjust Upwards Further to π 3 IS-MP4 ( PC4 ( ) Inflation IS-MP1 ( PC1 ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
20 Reversal of Shock Leads to Recession With High Inflation PC5 ( ) Inflation IS-MP5 ( PC1 ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
21 US Inflation-Output Loops Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
22 US Inflation-Output Loops Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
23 Part III Soft Versus Tough Central Banks Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
24 Adjustment if Inflation Expectations Don t Change IS-MP2 ( Inflation IS-MP1 ( PC ( ) Output Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
25 Implications for Central Bank Institutional Design What kind of central bank do we want? Do we want a soft central bank that limits the increase in real interest rates when inflation rises to protect the economy and which isn t too concerned about getting inflation back to target quickly? Or do we want a tough central bank that raises interest rates aggressively and is very concerned about getting inflation back to target? Suppose we wish to avoid large recessions if possible. You might imagine the soft central bank would be more likely to deliver this. However, our model says the exact opposite. Recessions are smaller and shorter and the economy less volatile when the central bank acts aggressively. The more people believe that a central bank is maintaining its low inflation target, the less likely the economy is to go through boom-bust cycles. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
26 Implications for Central Bank Institutional Design A better outcome is obtained if the central bank can commit to a low inflation, and this commitment be believed by the public. This suggests the following ways of achieving the best outcome: 1 Political Independence: Central banks that plan for the long-term and don t worry about economic performance during election years are is more likely to stick to a commitment to low inflation. 2 Conservative Central Bankers: If the central banker is known to really dislike inflation and the public believes this, the economy gets closer to the ideal low inflation outcome even without commitment. The government may choose to appoint a central banker who is more inflation-averse than they are. 3 Consequences for Bad Inflation Outcomes: If bad things happen to central bankers when inflation is high, then the public are more likely to believe they will commit to a low inflation rate. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
27 Influence of these Ideas This research has had a considerable influence on the legal structure of central banks around the world: 1 Political Independence: There has been a substantial move around the world towards making central banks more independent. Close to home, the Bank of England was made independent in 1997 and the ECB/Eurosystem is highly independent from political control. 2 Conservative Central Bankers: All around the world, central bankers talk much more now about the evils of inflation and the benefits of price stability. Mainly, this is because they believe this to be the case. But there is also a marketing element. Perhaps they can face a better macroeconomic tradeoff if the public believes the central bank s commitment to low inflation. 3 Consequences for Bad Inflation Outcomes: Many central banks now have legally imposed inflation targets and bad things happen when the inflation target is not met. For instance, the Governor of the Bank of England has to write a letter to the Chancellor explaining why the target was not met. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
28 Things to Understand From This Topic 1 What happens when inflation expectations rise above the central bank s target. 2 The IS-MP-PC solution for inflation and how to derive it. 3 The IS-MP-PC solution for output and how to derive it. 4 Adaptive expectations. 5 Evidence for the adaptive expectations version of the Phillips curve. 6 Effects of a temporary demand shock under adaptive expectations. 7 Effects of a temporary demand shock when inflation expectations don t change. 8 Implications for central bank design and practice. Karl Whelan (UCD) Analysing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn / 28
MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model
 MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 38 Beyond IS-LM We have reviewed the
MA Macroeconomics 3. Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Autumn 2014 Karl Whelan (UCD) Introducing the IS-MP-PC Model Autumn 2014 1 / 38 Beyond IS-LM We have reviewed the
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
A Dynamic Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply 1 Introduction Theoritical Backround 2 3 4 I Introduction Theoritical Backround The model emphasizes the dynamic nature of economic fluctuations.
Supplementary Notes on Chapter 6 of D. Romer s Advanced Macroeconomics Textbook (4th Edition)
 Supplementary Notes on Chapter 6 of D. Romer s Advanced Macroeconomics Textbook (4th Edition) Changsheng Xu & Ming Yi School of Economics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology This version: June
Supplementary Notes on Chapter 6 of D. Romer s Advanced Macroeconomics Textbook (4th Edition) Changsheng Xu & Ming Yi School of Economics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology This version: June
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 4. VARs With Long-Run Restrictions
 MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 4. VARs With Long-Run Restrictions Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Long-Run Restrictions Spring 2016 1 / 11 An Alternative Approach: Long-Run
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 4. VARs With Long-Run Restrictions Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Long-Run Restrictions Spring 2016 1 / 11 An Alternative Approach: Long-Run
Queen s University Department of Economics Instructor: Kevin Andrew
 Queen s University Department of Economics Instructor: Kevin Andrew Econ 320: Assignment 4 Section A (100%): Long Answer Due: April 2nd 2014 3pm All questions of Equal Value 1. Consider the following version
Queen s University Department of Economics Instructor: Kevin Andrew Econ 320: Assignment 4 Section A (100%): Long Answer Due: April 2nd 2014 3pm All questions of Equal Value 1. Consider the following version
Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model.
 Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, UiO 22 September 2009 Lecture notes on closed economy macro dynamics AD-AS model Inflation targeting regime.
Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, UiO 22 September 2009 Lecture notes on closed economy macro dynamics AD-AS model Inflation targeting regime.
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999)
 Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8
 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 8 Problem 1: a: The average unemployment rate from 1959 to 2002 is 5.9136% 5.9%. b/c: 27 out of 43 years have a strictly negative sign for the product (π t π t 1 )(u
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 10
 UNIVERSIT OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 10 THE ZERO LOWER BOUND IN THE IS-MP-IA FRAMEWORK FEBRUAR 21, 2018 I. INTRODUCTION II. THE IS-MP-IA
UNIVERSIT OF CALIFORNIA Economics 134 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS Spring 2018 Professor David Romer LECTURE 10 THE ZERO LOWER BOUND IN THE IS-MP-IA FRAMEWORK FEBRUAR 21, 2018 I. INTRODUCTION II. THE IS-MP-IA
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE
 THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 ECB Forum on Central Banking Macroeconomics of Price- and Wage-Setting June 19, 2018 Sintra, Portugal Any opinions expressed
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 ECB Forum on Central Banking Macroeconomics of Price- and Wage-Setting June 19, 2018 Sintra, Portugal Any opinions expressed
Indeterminacy and Sunspots in Macroeconomics
 Indeterminacy and Sunspots in Macroeconomics Friday September 8 th : Lecture 10 Gerzensee, September 2017 Roger E. A. Farmer Warwick University and NIESR Topics for Lecture 10 Tying together the pieces
Indeterminacy and Sunspots in Macroeconomics Friday September 8 th : Lecture 10 Gerzensee, September 2017 Roger E. A. Farmer Warwick University and NIESR Topics for Lecture 10 Tying together the pieces
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
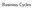 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Identifying Aggregate Liquidity Shocks with Monetary Policy Shocks: An Application using UK Data
 Identifying Aggregate Liquidity Shocks with Monetary Policy Shocks: An Application using UK Data Michael Ellington and Costas Milas Financial Services, Liquidity and Economic Activity Bank of England May
Identifying Aggregate Liquidity Shocks with Monetary Policy Shocks: An Application using UK Data Michael Ellington and Costas Milas Financial Services, Liquidity and Economic Activity Bank of England May
The Zero Lower Bound
 The Zero Lower Bound Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 7 Introduction In the standard New Keynesian model, monetary policy is often described by an interest rate rule (e.g. a Taylor rule) that
The Zero Lower Bound Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 7 Introduction In the standard New Keynesian model, monetary policy is often described by an interest rate rule (e.g. a Taylor rule) that
POLICY GAMES. u t = θ 0 θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) β t (u 2 t + ωπ 2 t ). (3)
 Eco5, Part II Spring C. Sims POLICY GAMES The policy authority believes 1. THE SAN JOSE MODEL u t = θ θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) In fact, though, u t = ū α (π t E t 1 π t ) + ξ t. () They minimize. POLICYMAKERS
Eco5, Part II Spring C. Sims POLICY GAMES The policy authority believes 1. THE SAN JOSE MODEL u t = θ θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) In fact, though, u t = ū α (π t E t 1 π t ) + ξ t. () They minimize. POLICYMAKERS
POLICY GAMES. u t = θ 0 θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) β t (u 2 t + ωπ 2 t ). (3) π t = g t 1 + ν t. (4) g t = θ 1θ 0 ω + θ 2 1. (5)
 Eco504, Part II Spring 2004 C. Sims POLICY GAMES The policy authority believes In fact, though, 1. THE SAN JOSE MODEL u t = θ 0 θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) u t = ū α (π t E t 1 π t ) + ξ t. (2) They minimize 2.
Eco504, Part II Spring 2004 C. Sims POLICY GAMES The policy authority believes In fact, though, 1. THE SAN JOSE MODEL u t = θ 0 θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) u t = ū α (π t E t 1 π t ) + ξ t. (2) They minimize 2.
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 7. The Real Business Cycle Model
 MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 7. The Real Business Cycle Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Real Business Cycles Spring 2016 1 / 38 Working Through A DSGE Model We have
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 7. The Real Business Cycle Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Real Business Cycles Spring 2016 1 / 38 Working Through A DSGE Model We have
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE
 THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 BOJ-IMES Conference Central Banking in a Changing World May 31, 2018 Tokyo, Japan Any opinions expressed here are my own
THE CASE OF THE DISAPPEARING PHILLIPS CURVE James Bullard President and CEO 2018 BOJ-IMES Conference Central Banking in a Changing World May 31, 2018 Tokyo, Japan Any opinions expressed here are my own
Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes.
 14.452. Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes. Olivier Blanchard May 12, 2007 Nr. 1 Look at three issues: Time consistency. The inflation bias. The trade-off between inflation and activity. Implementation and
14.452. Topic 9. Monetary policy. Notes. Olivier Blanchard May 12, 2007 Nr. 1 Look at three issues: Time consistency. The inflation bias. The trade-off between inflation and activity. Implementation and
Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion
 14.05 Lecture Notes Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion A large number of private agents play against a government. Government objective. The government objective is given by the following loss function:
14.05 Lecture Notes Inflation traps, and rules vs. discretion A large number of private agents play against a government. Government objective. The government objective is given by the following loss function:
F11. Lecture 7. Inflation and Unemployment M&I 6. Adaptive vs Rational Expectations. M&B 19, p. 24
 F11 Lecture 7 Inflation and Unemployment M&I 6 Adaptive vs Rational Expectations M&B 19, p. 24 Inflation and Unemployment Second of 3 motives gov t may have for ΔM/M, : 1. Inflationary Finance (Seigniorage)
F11 Lecture 7 Inflation and Unemployment M&I 6 Adaptive vs Rational Expectations M&B 19, p. 24 Inflation and Unemployment Second of 3 motives gov t may have for ΔM/M, : 1. Inflationary Finance (Seigniorage)
INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT: THE PHILLIPS CURVE. Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University
 INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT: THE PHILLIPS CURVE Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University ROADMAP INCOME EXPENDITURE LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE IS CURVE LM CURVE SHORT-RUN IS-LM MODEL AGGREGATE
INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT: THE PHILLIPS CURVE Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University ROADMAP INCOME EXPENDITURE LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE IS CURVE LM CURVE SHORT-RUN IS-LM MODEL AGGREGATE
The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap
 The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé and Martín Uribe Columbia University European Central Bank Conference on Monetary Policy Frankfurt am Main, October 29-3, 218
The Neo Fisher Effect and Exiting a Liquidity Trap Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé and Martín Uribe Columbia University European Central Bank Conference on Monetary Policy Frankfurt am Main, October 29-3, 218
Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy
 Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy Leonardo Melosi London Business School 24 May 2012 Motivation Disperse information about aggregate fundamentals Morris and Shin (2003), Sims (2003), and Woodford (2002)
Signaling Effects of Monetary Policy Leonardo Melosi London Business School 24 May 2012 Motivation Disperse information about aggregate fundamentals Morris and Shin (2003), Sims (2003), and Woodford (2002)
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 6. Solving Models with Rational Expectations
 MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 6. Solving Models with Rational Expectations Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Models with Rational Expectations Spring 2016 1 / 36 Moving Beyond
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 6. Solving Models with Rational Expectations Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Models with Rational Expectations Spring 2016 1 / 36 Moving Beyond
A Discussion of Arouba, Cuba-Borda and Schorfheide: Macroeconomic Dynamics Near the ZLB: A Tale of Two Countries"
 A Discussion of Arouba, Cuba-Borda and Schorfheide: Macroeconomic Dynamics Near the ZLB: A Tale of Two Countries" Morten O. Ravn, University College London, Centre for Macroeconomics and CEPR M.O. Ravn
A Discussion of Arouba, Cuba-Borda and Schorfheide: Macroeconomic Dynamics Near the ZLB: A Tale of Two Countries" Morten O. Ravn, University College London, Centre for Macroeconomics and CEPR M.O. Ravn
The Dornbusch overshooting model
 4330 Lecture 8 Ragnar Nymoen 12 March 2012 References I Lecture 7: Portfolio model of the FEX market extended by money. Important concepts: monetary policy regimes degree of sterilization Monetary model
4330 Lecture 8 Ragnar Nymoen 12 March 2012 References I Lecture 7: Portfolio model of the FEX market extended by money. Important concepts: monetary policy regimes degree of sterilization Monetary model
MA Advanced Econometrics: Applying Least Squares to Time Series
 MA Advanced Econometrics: Applying Least Squares to Time Series Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 15, 2011 Karl Whelan (UCD) Time Series February 15, 2011 1 / 24 Part I Time Series: Standard
MA Advanced Econometrics: Applying Least Squares to Time Series Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 15, 2011 Karl Whelan (UCD) Time Series February 15, 2011 1 / 24 Part I Time Series: Standard
Eco504, Part II Spring 2008 C. Sims POLICY GAMES
 Eco504, Part II Spring 2008 C. Sims POLICY GAMES The policy authority believes 1. THE SAN JOSE MODEL u t = θ 0 θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) In fact, though, u t = ū α (π t E t 1 π t ) + ξ t. (2) 2. POLICYMAKERS
Eco504, Part II Spring 2008 C. Sims POLICY GAMES The policy authority believes 1. THE SAN JOSE MODEL u t = θ 0 θ 1 π t + ε t. (1) In fact, though, u t = ū α (π t E t 1 π t ) + ξ t. (2) 2. POLICYMAKERS
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case.
 Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Lecture 8: Aggregate demand and supply dynamics, closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 20, 2008 1 Ch 17, 19 and 20 in IAM Since our primary concern is to
Strategic Interactions between Fiscal and Monetary Policies in a Monetary Union
 Strategic Interactions between Fiscal and Monetary Policies in a Monetary Union Reinhard Neck Doris A. Behrens Preliminary Draft, not to be quoted January 2003 Corresponding Author s Address: Reinhard
Strategic Interactions between Fiscal and Monetary Policies in a Monetary Union Reinhard Neck Doris A. Behrens Preliminary Draft, not to be quoted January 2003 Corresponding Author s Address: Reinhard
Empirical Project, part 1, ECO 672
 Empirical Project, part 1, ECO 672 Due Date: see schedule in syllabus Instruction: The empirical project has two parts. This is part 1, which is worth 15 points. You need to work independently on this
Empirical Project, part 1, ECO 672 Due Date: see schedule in syllabus Instruction: The empirical project has two parts. This is part 1, which is worth 15 points. You need to work independently on this
Deviant Behavior in Monetary Economics
 Deviant Behavior in Monetary Economics Lawrence Christiano and Yuta Takahashi July 26, 2018 Multiple Equilibria Standard NK Model Standard, New Keynesian (NK) Monetary Model: Taylor rule satisfying Taylor
Deviant Behavior in Monetary Economics Lawrence Christiano and Yuta Takahashi July 26, 2018 Multiple Equilibria Standard NK Model Standard, New Keynesian (NK) Monetary Model: Taylor rule satisfying Taylor
Introduction to Rational Expectations
 Lecture 7: Introduction to Rational Expectations Muth: Rational Expectations and the Theory of Price Movements Lucas: Econometric Policy Evaluation: A Critique BU 2008 macro lecture 7 1 A. Rational Expectations
Lecture 7: Introduction to Rational Expectations Muth: Rational Expectations and the Theory of Price Movements Lucas: Econometric Policy Evaluation: A Critique BU 2008 macro lecture 7 1 A. Rational Expectations
The transmission mechanism How the monetary-policy instrument affects the economy and the target variables
 Eco 200, part 3, Fall 2004 200L2.tex Lars Svensson 11/18/04 The transmission mechanism How the monetary-policy instrument affects the economy and the target variables Variables t =..., 1, 0, 1,... denotes
Eco 200, part 3, Fall 2004 200L2.tex Lars Svensson 11/18/04 The transmission mechanism How the monetary-policy instrument affects the economy and the target variables Variables t =..., 1, 0, 1,... denotes
General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory
 General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory Fall 2003 You have FOUR hours Solve all questions The exam has 4 parts Each part has its own sheet Please spend the following time on each part I 60 minutes
General Examination in Macroeconomic Theory Fall 2003 You have FOUR hours Solve all questions The exam has 4 parts Each part has its own sheet Please spend the following time on each part I 60 minutes
V. The Speed of adjustment of Endogenous Variables and Overshooting
 V. The Speed of adjustment of Endogenous Variables and Overshooting The second section of Chapter 11 of Dornbusch (1980) draws on Dornbusch (1976) Expectations and Exchange Rate Dynamics, Journal of Political
V. The Speed of adjustment of Endogenous Variables and Overshooting The second section of Chapter 11 of Dornbusch (1980) draws on Dornbusch (1976) Expectations and Exchange Rate Dynamics, Journal of Political
Lecture 7. The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium. ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter Kam Yu Department of Economics Lakehead University
 Lecture 7 The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 2013 Phillips Department of Economics Lakehead University 7.1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Phillips Phillips 7.2 Market Equilibrium:
Lecture 7 The Dynamics of Market Equilibrium ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 2013 Phillips Department of Economics Lakehead University 7.1 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 Phillips Phillips 7.2 Market Equilibrium:
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition
 Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 9: Macroeconomics policy, credibility, and politics Ben J. Heijdra Department of Economics & Econometrics University of Groningen 1 September
Foundations of Modern Macroeconomics Second Edition Chapter 9: Macroeconomics policy, credibility, and politics Ben J. Heijdra Department of Economics & Econometrics University of Groningen 1 September
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: Solving Models with Rational Expectations
 MA Advanced Macroeconomics: Solving Models with Rational Expectations Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 6, 2009 Karl Whelan (UCD) Models with Rational Expectations February 6, 2009 1 / 32 Moving
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: Solving Models with Rational Expectations Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 6, 2009 Karl Whelan (UCD) Models with Rational Expectations February 6, 2009 1 / 32 Moving
Lecture 9: Stabilization policy with rational expecations; Limits to stabilization policy; closed economy case.
 Lecture 9: Stabilization policy with rational expecations; Limits to stabilization policy; closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 17, 2008 1 Ch21andch22inIAM
Lecture 9: Stabilization policy with rational expecations; Limits to stabilization policy; closed economy case. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, University of Oslo October 17, 2008 1 Ch21andch22inIAM
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
What Happened to the Phillips Curve in the 1990s in Canada?
 What Happened to the Phillips Curve in the 1990s in Canada? Paul Beaudry and Matthew Doyle* Introduction There are at least two broad categories of interpretation to consider when examining observations
What Happened to the Phillips Curve in the 1990s in Canada? Paul Beaudry and Matthew Doyle* Introduction There are at least two broad categories of interpretation to consider when examining observations
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Novasbe February 2016 Francesco Franco (Novasbe) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 8 The Social Planner Solution Notice no intertemporal issues (Y t =
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco Novasbe February 2016 Francesco Franco (Novasbe) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 8 The Social Planner Solution Notice no intertemporal issues (Y t =
GDP growth and inflation forecasting performance of Asian Development Outlook
 and inflation forecasting performance of Asian Development Outlook Asian Development Outlook (ADO) has been the flagship publication of the Asian Development Bank (ADB) since 1989. Issued twice a year
and inflation forecasting performance of Asian Development Outlook Asian Development Outlook (ADO) has been the flagship publication of the Asian Development Bank (ADB) since 1989. Issued twice a year
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction
 The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
The New Keynesian Model: Introduction Vivaldo M. Mendes ISCTE Lisbon University Institute 13 November 2017 (Vivaldo M. Mendes) The New Keynesian Model: Introduction 13 November 2013 1 / 39 Summary 1 What
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
The New-Keynesian Liquidity Trap
 The New-Keynesian Liquidity Trap John H. Cochrane Univeristy of Chicago Booth School of Business, NBER, Hoover, Cato New Keynesian models: Diagnosis I Consensus NK diagnosis: Natural rate r
The New-Keynesian Liquidity Trap John H. Cochrane Univeristy of Chicago Booth School of Business, NBER, Hoover, Cato New Keynesian models: Diagnosis I Consensus NK diagnosis: Natural rate r
Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy
 Class handout Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy Giovanni Di Bartolomeo University of Teramo 1. The Phillips menu In the 190s, econometricians estimated a negative relationship
Class handout Phillips curve and the Tinbergen and Theil approach to economic policy Giovanni Di Bartolomeo University of Teramo 1. The Phillips menu In the 190s, econometricians estimated a negative relationship
APPENDIX TO RESERVE REQUIREMENTS AND OPTIMAL CHINESE STABILIZATION POLICY
 APPENDIX TO RESERVE REQUIREMENTS AND OPTIMAL CHINESE STABILIZATION POLICY CHUN CHANG ZHENG LIU MARK M. SPIEGEL JINGYI ZHANG Abstract. This appendix shows some additional details of the model and equilibrium
APPENDIX TO RESERVE REQUIREMENTS AND OPTIMAL CHINESE STABILIZATION POLICY CHUN CHANG ZHENG LIU MARK M. SPIEGEL JINGYI ZHANG Abstract. This appendix shows some additional details of the model and equilibrium
Lessons of the long quiet ELB
 Lessons of the long quiet ELB Comments on Monetary policy: Conventional and unconventional Nobel Symposium on Money and Banking John H. Cochrane Hoover Institution, Stanford University May 2018 1 / 20
Lessons of the long quiet ELB Comments on Monetary policy: Conventional and unconventional Nobel Symposium on Money and Banking John H. Cochrane Hoover Institution, Stanford University May 2018 1 / 20
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium
 Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
Two Models of Macroeconomic Equilibrium 1 The Static IS-LM Model The model equations are given as C η +γ(y T) (1) T τy (2) I α r (3) G T (4) L φy θr (5) M µ (6) Y C +I +G (7) L M (8) where η,α,,φ,θ,µ >
GCOE Discussion Paper Series
 GCOE Discussion Paper Series Global COE Program Human Behavior and Socioeconomic Dynamics Discussion Paper No.34 Inflation Inertia and Optimal Delegation of Monetary Policy Keiichi Morimoto February 2009
GCOE Discussion Paper Series Global COE Program Human Behavior and Socioeconomic Dynamics Discussion Paper No.34 Inflation Inertia and Optimal Delegation of Monetary Policy Keiichi Morimoto February 2009
Eco 200, part 3, Fall 2004 Lars Svensson 12/6/04. Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation
 Eco 00, part 3, Fall 004 00L5.tex Lars Svensson /6/04 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation The zero lower bound for interest rates (ZLB) A forward-looking aggregate-demand
Eco 00, part 3, Fall 004 00L5.tex Lars Svensson /6/04 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation The zero lower bound for interest rates (ZLB) A forward-looking aggregate-demand
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Lars Svensson 10/2/05. Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation
 Eco 00, part, Fall 005 00L5_F05.tex Lars Svensson 0//05 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation Japan: recession, low growth since early 90s, deflation in GDP deflator and
Eco 00, part, Fall 005 00L5_F05.tex Lars Svensson 0//05 Liquidity traps, the zero lower bound for interest rates, and deflation Japan: recession, low growth since early 90s, deflation in GDP deflator and
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions
 Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Modelling Czech and Slovak labour markets: A DSGE model with labour frictions Daniel Němec Faculty of Economics and Administrations Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic nemecd@econ.muni.cz ESF MU (Brno)
Expectations, Learning and Macroeconomic Policy
 Expectations, Learning and Macroeconomic Policy George W. Evans (Univ. of Oregon and Univ. of St. Andrews) Lecture 4 Liquidity traps, learning and stagnation Evans, Guse & Honkapohja (EER, 2008), Evans
Expectations, Learning and Macroeconomic Policy George W. Evans (Univ. of Oregon and Univ. of St. Andrews) Lecture 4 Liquidity traps, learning and stagnation Evans, Guse & Honkapohja (EER, 2008), Evans
GDP forecast errors Satish Ranchhod
 GDP forecast errors Satish Ranchhod Editor s note This paper looks more closely at our forecasts of growth in Gross Domestic Product (GDP). It considers two different measures of GDP, production and expenditure,
GDP forecast errors Satish Ranchhod Editor s note This paper looks more closely at our forecasts of growth in Gross Domestic Product (GDP). It considers two different measures of GDP, production and expenditure,
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam?
 The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
Monetary Policy and the Uncovered Interest Rate Parity Puzzle. David K. Backus, Chris Telmer and Stanley E. Zin
 Monetary Policy and the Uncovered Interest Rate Parity Puzzle David K. Backus, Chris Telmer and Stanley E. Zin UIP Puzzle Standard regression: s t+1 s t = α + β(i t i t) + residuals Estimates of β are
Monetary Policy and the Uncovered Interest Rate Parity Puzzle David K. Backus, Chris Telmer and Stanley E. Zin UIP Puzzle Standard regression: s t+1 s t = α + β(i t i t) + residuals Estimates of β are
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II
 ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 9 October 2018 The reference to this lecture is:
ECON 4160: Econometrics-Modelling and Systems Estimation Lecture 9: Multiple equation models II Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics University of Oslo 9 October 2018 The reference to this lecture is:
Is the Macroeconomy Locally Unstable and Why should we care?
 Is the Macroeconomy Locally Unstable and Why should we care? Paul Beaudry, Dana Galizia & Franck Portier NBER macroannual April 2016 1 / 22 Introduction In most macro-models, BC fluctuation arises as the
Is the Macroeconomy Locally Unstable and Why should we care? Paul Beaudry, Dana Galizia & Franck Portier NBER macroannual April 2016 1 / 22 Introduction In most macro-models, BC fluctuation arises as the
Are 'unbiased' forecasts really unbiased? Another look at the Fed forecasts 1
 Are 'unbiased' forecasts really unbiased? Another look at the Fed forecasts 1 Tara M. Sinclair Department of Economics George Washington University Washington DC 20052 tsinc@gwu.edu Fred Joutz Department
Are 'unbiased' forecasts really unbiased? Another look at the Fed forecasts 1 Tara M. Sinclair Department of Economics George Washington University Washington DC 20052 tsinc@gwu.edu Fred Joutz Department
Aggregate Supply. A Nonvertical AS Curve. implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup
 A Nonvertical AS Curve nominal wage rigidity nominal price rigidity labor and goods markets implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup Case 1: Sticky W, Flexible
A Nonvertical AS Curve nominal wage rigidity nominal price rigidity labor and goods markets implications for unemployment, rms pricing behavior, the real wage and the markup Case 1: Sticky W, Flexible
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor. Advanced Macroeconomic Theory
 RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
MA Advanced Econometrics: Spurious Regressions and Cointegration
 MA Advanced Econometrics: Spurious Regressions and Cointegration Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 22, 2011 Karl Whelan (UCD) Spurious Regressions and Cointegration February 22, 2011 1 / 18
MA Advanced Econometrics: Spurious Regressions and Cointegration Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD February 22, 2011 Karl Whelan (UCD) Spurious Regressions and Cointegration February 22, 2011 1 / 18
Title. Description. Remarks and examples. stata.com. stata.com. Introduction to DSGE models. intro 1 Introduction to DSGEs and dsge
 Title stata.com intro 1 Introduction to DSGEs and dsge Description Remarks and examples References Also see Description In this entry, we introduce DSGE models and the dsge command. We begin with an overview
Title stata.com intro 1 Introduction to DSGEs and dsge Description Remarks and examples References Also see Description In this entry, we introduce DSGE models and the dsge command. We begin with an overview
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES OPTIMAL TAYLOR RULES IN NEW KEYNESIAN MODELS. Christoph E. Boehm Christopher L. House
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES OPTIMAL TAYLOR RULES IN NEW KEYNESIAN MODELS Christoph E. Boehm Christopher L. House Working Paper 37 http://www.nber.org/papers/w37 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH 5 Massachusetts
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES OPTIMAL TAYLOR RULES IN NEW KEYNESIAN MODELS Christoph E. Boehm Christopher L. House Working Paper 37 http://www.nber.org/papers/w37 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH 5 Massachusetts
Changing expectations of future fed moves could be a shock!
 START HERE 10/14. The alternative shock measures are poorly correlated. (Figure 1) Doesn t this indicate that at least two of them are seriously wrong? A: see p. 24. CEE note the responses are the same.
START HERE 10/14. The alternative shock measures are poorly correlated. (Figure 1) Doesn t this indicate that at least two of them are seriously wrong? A: see p. 24. CEE note the responses are the same.
Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions
 Monetary Economics Problem Set #4 Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions This problem set is marked out of 100 points. The weight given to each part is indicated below. Please contact me asap if
Monetary Economics Problem Set #4 Monetary Economics: Problem Set #4 Solutions This problem set is marked out of 100 points. The weight given to each part is indicated below. Please contact me asap if
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model
 Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Monetary Policy in a Macro Model ECON 40364: Monetary Theory & Policy Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2017 1 / 67 Readings Mishkin Ch. 20 Mishkin Ch. 21 Mishkin Ch. 22 Mishkin Ch. 23, pg. 553-569
Searching for the Output Gap: Economic Variable or Statistical Illusion? Mark W. Longbrake* J. Huston McCulloch
 Draft Draft Searching for the Output Gap: Economic Variable or Statistical Illusion? Mark W. Longbrake* The Ohio State University J. Huston McCulloch The Ohio State University August, 2007 Abstract This
Draft Draft Searching for the Output Gap: Economic Variable or Statistical Illusion? Mark W. Longbrake* The Ohio State University J. Huston McCulloch The Ohio State University August, 2007 Abstract This
The Econometric Analysis of Mixed Frequency Data with Macro/Finance Applications
 The Econometric Analysis of Mixed Frequency Data with Macro/Finance Applications Instructor: Eric Ghysels Structure of Course It is easy to collect and store large data sets, particularly of financial
The Econometric Analysis of Mixed Frequency Data with Macro/Finance Applications Instructor: Eric Ghysels Structure of Course It is easy to collect and store large data sets, particularly of financial
Fresh perspectives on unobservable variables: Data decomposition of the Kalman smoother
 Fresh perspectives on unobservable variables: Data decomposition of the Kalman smoother AN 2013/09 Nicholas Sander December 2013 Reserve Bank of New Zealand Analytical Note series ISSN 2230 5505 Reserve
Fresh perspectives on unobservable variables: Data decomposition of the Kalman smoother AN 2013/09 Nicholas Sander December 2013 Reserve Bank of New Zealand Analytical Note series ISSN 2230 5505 Reserve
Taylor-Rule Exit Policies for the Zero Lower Bound
 Taylor-Rule Exit Policies for the Zero Lower Bound Siddhartha Chattopadhyay a and Betty C. Daniel b a Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur b University at Albany SUNY The monetary authority loses the
Taylor-Rule Exit Policies for the Zero Lower Bound Siddhartha Chattopadhyay a and Betty C. Daniel b a Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur b University at Albany SUNY The monetary authority loses the
Toulouse School of Economics, Macroeconomics II Franck Portier. Homework 1. Problem I An AD-AS Model
 Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Toulouse School of Economics, 2009-2010 Macroeconomics II Franck Portier Homework 1 Problem I An AD-AS Model Let us consider an economy with three agents (a firm, a household and a government) and four
Do Markov-Switching Models Capture Nonlinearities in the Data? Tests using Nonparametric Methods
 Do Markov-Switching Models Capture Nonlinearities in the Data? Tests using Nonparametric Methods Robert V. Breunig Centre for Economic Policy Research, Research School of Social Sciences and School of
Do Markov-Switching Models Capture Nonlinearities in the Data? Tests using Nonparametric Methods Robert V. Breunig Centre for Economic Policy Research, Research School of Social Sciences and School of
Looking for the stars
 Looking for the stars Mengheng Li 12 Irma Hindrayanto 1 1 Economic Research and Policy Division, De Nederlandsche Bank 2 Department of Econometrics, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam April 5, 2018 1 / 35 Outline
Looking for the stars Mengheng Li 12 Irma Hindrayanto 1 1 Economic Research and Policy Division, De Nederlandsche Bank 2 Department of Econometrics, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam April 5, 2018 1 / 35 Outline
A Modern Equilibrium Model. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them.
 What is market design? Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them. This requires different tools and ideas than neoclassical economics, which
What is market design? Increasingly, economists are asked not just to study or explain or interpret markets, but to design them. This requires different tools and ideas than neoclassical economics, which
Identification of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve: Problems and Consequences
 MACROECONOMIC POLICY WORKSHOP: CENTRAL BANK OF CHILE The Relevance of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve Identification of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve: Problems and Consequences James. H. Stock Harvard
MACROECONOMIC POLICY WORKSHOP: CENTRAL BANK OF CHILE The Relevance of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve Identification of the New Keynesian Phillips Curve: Problems and Consequences James. H. Stock Harvard
1.2. Structural VARs
 1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.2. Structural VARs How to identify A 0? A review: Choleski (Cholesky?) decompositions. Short-run restrictions. Inequality restrictions. Long-run restrictions. Then, examples, applications,
1. Shocks Nr. 1 1.2. Structural VARs How to identify A 0? A review: Choleski (Cholesky?) decompositions. Short-run restrictions. Inequality restrictions. Long-run restrictions. Then, examples, applications,
An Introduction to Rational Inattention
 An Introduction to Rational Inattention Lecture notes for the course Bounded Rationality and Macroeconomics December 2, 2005 1 Introduction The objective of modelling economic agents as being rationally
An Introduction to Rational Inattention Lecture notes for the course Bounded Rationality and Macroeconomics December 2, 2005 1 Introduction The objective of modelling economic agents as being rationally
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective
 Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE April 215 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment April 215 1 / 16
Monetary Policy and Unemployment: A New Keynesian Perspective Jordi Galí CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE April 215 Jordi Galí (CREI, UPF and Barcelona GSE) Monetary Policy and Unemployment April 215 1 / 16
Monetary Economics. Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one. Chris Edmond. 2nd Semester 2014
 Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
Monetary Economics Lecture 15: unemployment in the new Keynesian model, part one Chris Edmond 2nd Semester 214 1 This class Unemployment fluctuations in the new Keynesian model, part one Main reading:
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations. Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno
 Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
Financial Factors in Economic Fluctuations Lawrence Christiano Roberto Motto Massimo Rostagno Background Much progress made on constructing and estimating models that fit quarterly data well (Smets-Wouters,
The US Phillips Curve and inflation expectations: A State. Space Markov-Switching explanatory model.
 The US Phillips Curve and inflation expectations: A State Space Markov-Switching explanatory model. Guillaume Guerrero Nicolas Million February 2004 We are grateful to P.Y Hénin, for helpful ideas and
The US Phillips Curve and inflation expectations: A State Space Markov-Switching explanatory model. Guillaume Guerrero Nicolas Million February 2004 We are grateful to P.Y Hénin, for helpful ideas and
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics
 Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics Contributions of Thomas Sargent and Christopher Sims, Nobel Laureates in Economics 2011. 1 1. Personal Background Thomas J. Sargent: PhD Harvard University
Study of Causal Relationships in Macroeconomics Contributions of Thomas Sargent and Christopher Sims, Nobel Laureates in Economics 2011. 1 1. Personal Background Thomas J. Sargent: PhD Harvard University
New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks
 New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks Satya P. Das @ NIPFP Satya P. Das (@ NIPFP) New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks 1 / 20 1 Blanchard-Kiyotaki Model 2 New Keynesian Phillips Curve 3 Utility
New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks Satya P. Das @ NIPFP Satya P. Das (@ NIPFP) New Keynesian DSGE Models: Building Blocks 1 / 20 1 Blanchard-Kiyotaki Model 2 New Keynesian Phillips Curve 3 Utility
WORKING PAPER NO DO GDP FORECASTS RESPOND EFFICIENTLY TO CHANGES IN INTEREST RATES?
 WORKING PAPER NO. 16-17 DO GDP FORECASTS RESPOND EFFICIENTLY TO CHANGES IN INTEREST RATES? Dean Croushore Professor of Economics and Rigsby Fellow, University of Richmond and Visiting Scholar, Federal
WORKING PAPER NO. 16-17 DO GDP FORECASTS RESPOND EFFICIENTLY TO CHANGES IN INTEREST RATES? Dean Croushore Professor of Economics and Rigsby Fellow, University of Richmond and Visiting Scholar, Federal
Stagnation Traps. Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro
 Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Stagnation Traps Gianluca Benigno and Luca Fornaro May 2015 Research question and motivation Can insu cient aggregate demand lead to economic stagnation? This question goes back, at least, to the Great
Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory
 2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
2 Keynesian Macroeconomic Theory 2.1. The Keynesian Consumption Function 2.2. The Complete Keynesian Model 2.3. The Keynesian-Cross Model 2.4. The IS-LM Model 2.5. The Keynesian AD-AS Model 2.6. Conclusion
Final Exam. You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind.
 Professor Christiano Economics 311, Winter 2005 Final Exam IMPORTANT: read the following notes You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind. A total of 100 points is possible, with the distribution
Professor Christiano Economics 311, Winter 2005 Final Exam IMPORTANT: read the following notes You may not use calculators, notes, or aids of any kind. A total of 100 points is possible, with the distribution
Behavioural & Experimental Macroeconomics: Some Recent Findings
 Behavioural & Experimental Macroeconomics: Some Recent Findings Cars Hommes CeNDEF, University of Amsterdam MACFINROBODS Conference Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany 3-4 April 27 Cars Hommes (CeNDEF,
Behavioural & Experimental Macroeconomics: Some Recent Findings Cars Hommes CeNDEF, University of Amsterdam MACFINROBODS Conference Goethe University, Frankfurt, Germany 3-4 April 27 Cars Hommes (CeNDEF,
Macroeconomics Field Exam. August 2007
 Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Recession Aversion, Output and the Kydland-Prescott Barro-Gordon Model
 Recession Aversion, Output and the Kydland-Prescott Barro-Gordon Model by Stefan Gerlach* Hong Kong Monetary Authority Hong Kong Institute for Monetary Research University of Basel and the CEPR June 3
Recession Aversion, Output and the Kydland-Prescott Barro-Gordon Model by Stefan Gerlach* Hong Kong Monetary Authority Hong Kong Institute for Monetary Research University of Basel and the CEPR June 3
